Determination of Diclofenac on a Dysprosium Nanowire- Modified Carbon Paste Electrode Accomplished in a Flow Injection System by Advanced Filtering
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Instrumentation
2.2. Carbon paste electrode
2.3. Materials and reagents
2.4. Stripping voltammetry
2.5. Sample preparation assay
2.6. Determination of diclofenac in human urine and plasma
3. Results and Discussion
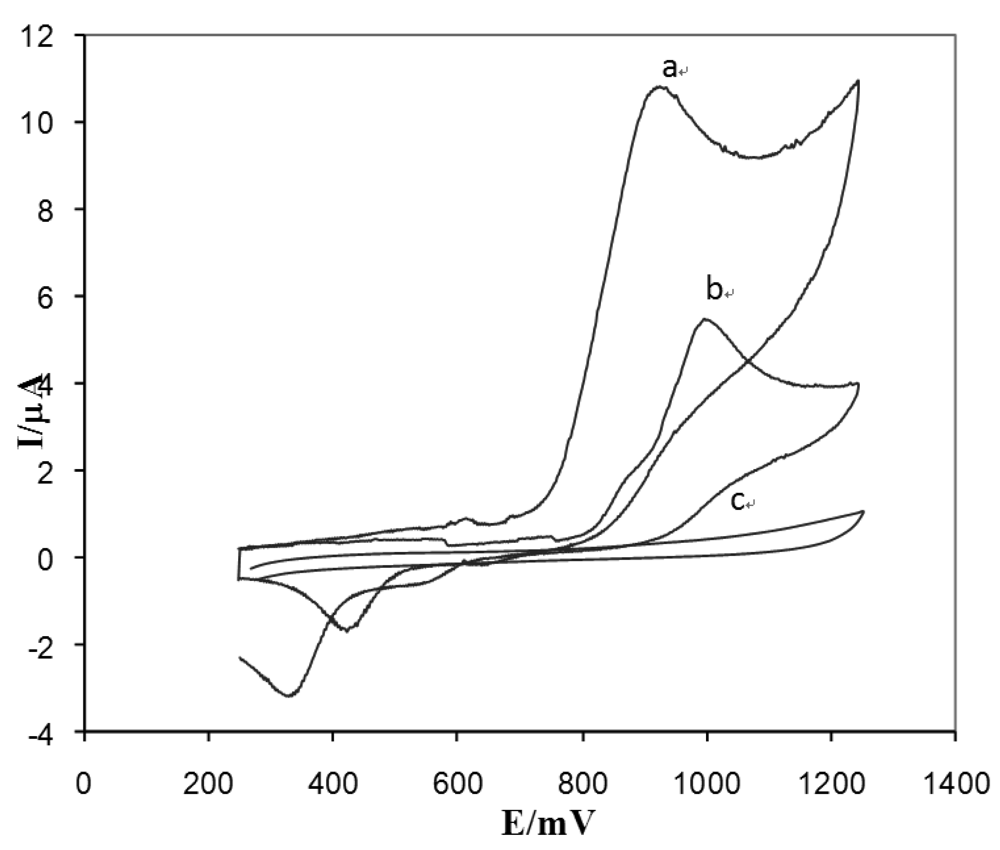
3.1. Electrochemical behavior of diclofenac by using modified DyNW/CPE
3.2. Effect of pH
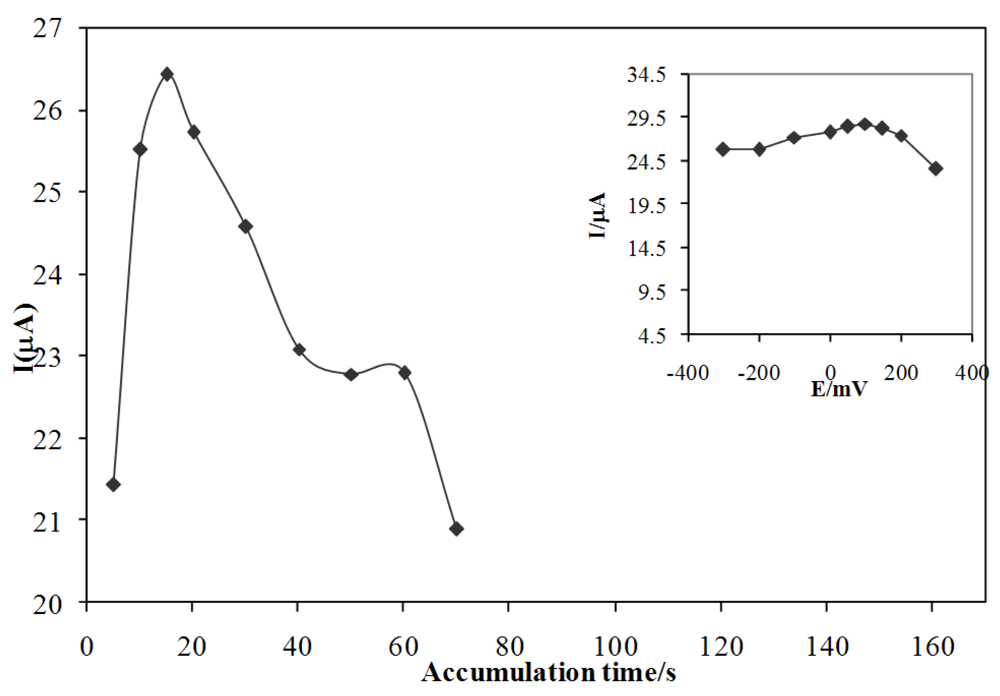
3.3. Effect of accumulation time
3.4. Effect of accumulation potential
3.5. Optimization of FFT-SW frequency and amplitude
3.6. Calibration curves
3.7. Assay of tablets
3.8. Analytical applications
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References and Notes
- Iliescu, T.; Baia, M.; Miclăus¸, V. A Raman spectroscopic study of the diclofenac sodium-beta-cyclodextrin interaction. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 22, 487–495. [Google Scholar]
- Gostick, N.; James, I.G.; Khong, T.K.; Roy, P.; Shepherd, P.R.; Miller, A.J. Controlled-release indomethacin and sustained-release diclofenac sodium in the treatment of osteoarthritis – a comparative controlled clinical-trial in general-practice. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 1990, 12, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Crowley, B.; Hamill, J.J.; Lyndon, S.; Mckellican, J.F.; Williams, P.; Miller, A.J. Controlled-release indomethacin and sustained-release diclofenac sodium in the treatment of rheumatoid-arthritis – a comparative controlled clinical-trial. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 1990, 12, 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Roskar, R.; Kmetec, V. Liquid chromatographic determination of diclofenac in human synovial fluid. J. Chromatogr. B 2003, 788, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Shamsipur, M.; Jalali, F.; Ershad, S. Preparation of a diclofenac potentiometric sensor and its application to pharmaceutical analysis and to drug recovery from biological fluids. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2005, 37, 943–947. [Google Scholar]
- Santini, A.O.; Pezza, H.R.; Pezza, L. Determination of diclofenac in pharmaceutical preparations using a potentiometric sensor immobilized in a graphite matrix. Talanta 2006, 68, 636–642. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, S.S.M.; Mahmoud, W.H.; Elmosallany, M.A.F.; Almazzooqi, M.H. Iron(II)-phthalocyanine as a novel recognition sensor for selective potentiometric determination of diclofenac and warfarin drugs. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2005, 39, 315–321. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, W.; Zhang, J. Determination of diclofenac sodium by capillary zone electrophoresis with electrochemical detection. J. Chromatogr. 2000, A868, 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- González, L.; Yuln, G.; Volonté, M.G. Determination of cyanocobalamin, betamethasone, and diclofenac sodium in pharmaceutical formulations, by high performance liquid chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1999, 20, 487–492. [Google Scholar]
- Kasperek, R. Determination of diclofenac sodium and papaverine hydrochloride in tablets by hplc method. Acta Poloniae Pharm. 2008, 65, 403–408. [Google Scholar]
- Arcelloni, C.; Lanzi, R.; Pedercini, S.; Molteny, G. High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of diclofenac in human plasma after solid-phase extraction. J. Chromatogr. 2001, B763, 195–200. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Hamid, M.E.; Novotny, L.; Hamza, H.J. Determination of diclofenac sodium, flufenamic acid, indomethacin and ketoprofen by LC-APCI-MS. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2001, 24, 587–594. [Google Scholar]
- Botello, J.C.; Pérez-Caballero, G. Spectrophotometric determination of diclofenac sodium with methylene-blue. Talanta 1995, 42, 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Arancibia, J.A.; Boldrini, M.A.; Escandar, G.M. Spectrofluorimetric determination of diclofenac in the presence of alpha-cyclodextrin. Talanta 2000, 52, 261–268. [Google Scholar]
- Damiani, P.C.; Bearzotti, M.; Cabezon, M.A.; Olivieri, A.C. Spectrofluorometric determination of diclofenac in tablets and ointments. J. Pharm. Biomed. 1999, 20, 587–590. [Google Scholar]
- Carreira, L.A.; Rizk, M.; El-Shabrawy, Y.; Zakhari, N.A.; Toubar, S.S. Europium(iii) ion probe spectrofluorometric determination of diclofenac sodium. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1995, 13, 1331–1337. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.W.; Fabre, H. Practical approach for validating the tlc assay of an active ingredient in a pharmaceutical formulation. J. Liq. Chromatogr. 1994, 17, 433–445. [Google Scholar]
- Siou, A.; Pommier, F.; Godbillon, J. Determination of diclofenac in plasma and urine by capillary gas-chromatography mass-spectrometry with possible simultaneous determination of deuterium-labeled diclofenac. J. Chromatogr. 1991, 571, 87–100. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.T.; Chen, L.F.; Song, J.F. Polarographic behaviors of diclofenac sodium in the presence of dissolved oxygen and its analytical application. Anal. Biochem. 2004, 329, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- De Souza, R.L.; Tubino, M. Spectrophotometric determination of diclofenac in pharmaceutical preparations. J. Brazil Chem. Soc. 2005, 16, 1068–1073. [Google Scholar]
- Agatonovic-Kustrin, S.; Zivanovic, L.J.; Zecevic, M.; Radulovic, D. Spectrophotometric study of diclofenac-Fe(III) complex. J. Pharm. Biom. Anal. 1997, 16, 147–153. [Google Scholar]
- Matin, A.A.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Joyuban, A. A simple spectrophotometric method for determination of sodium diclofenac in pharmaceutical formulations. IL Farmac 2005, 60, 855–861. [Google Scholar]
- Sastry, C.S.P.; Prasad-Tipirneni, A.S.R.; Suryanarayana, M.V. Spectrophotometric analysis of some anthranilic acid-derivatives and their pharmaceutical preparations. Microchem. J. 1989, 39, 277–289. [Google Scholar]
- Sena, M.M.; Chaudhry, Z.F.; Collins, C.H.; Poppi, R.J. N-way PLS applied to simultaneous spectrophotometric determination of acetylsalicylic acid, paracetamol and caffeine. J. Pharm. Biom. Anal. 2004, 36, 743–749. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemi, J.; Niazi, A.; Ghobadi, S. Simultaneous spectrophotometric determination of benzyl alcohol and diclofenac in pharmaceutical formulations by chemometrics method. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2005, 52, 1049–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemi, J.; Niazi, A.; Ghobadi, S. Simultaneous spectrophotometric determination of benzyl alcohol and diclofenac in pharmaceuticals using methods based on the first derivative of the optical density ratio. Pharm. Chem. J. 2005, 39, 671–765. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, Y.C.; Coles, B.A.; Compton, G.; Marken, F. Microwave activation of electrochemical processes: square-wave voltammetric stripping detection of cadmium in the presence of the surfactant Triton X. Electroanalysis 2001, 13, 639–645. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, S.H.; Kounaves, S.P. Microwave-enhanced anodic stripping detection of lead in a river sediment sample. A mercury-free procedure employing a boron-doped diamond electrode. Electroanalysis 1998, 10, 364–368. [Google Scholar]
- Rurikova, D.; Kunakova, I. Determination of selenium in soils by cathodic stripping voltammetry after separation as gaseous selenium tetrabromide. Chem. Pap. 1999, 53, 246–250. [Google Scholar]
- Kalcher, K.; Kaufmann, J.M.; Wang, J.; Svancara, I.; Vytras, K.; Neuhold, C.; Yang, Z. Sensors based on carbon-paste in electrochemical analysis – a review with particular emphasis on the period 1990-1993. Electroanalysis 1995, 7, 5–22. [Google Scholar]
- Valentini, F.; Amine, A.; Orlandocci, S.; Terranova, M.L.; Palleschi, G. Carbon nanotube purification: Preparation and characterization of carbon nanotube paste electrodes. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 5413–5421. [Google Scholar]
- Antiochia, A.; Lavagnini, I.; Magno, F.; Valentini, F.; Palleschi, G. Single-wall carbon nanotube paste electrodes: a comparison with carbon paste, platinum and glassy carbon electrodes via cyclic voltammetric data. Electroanalysis 2004, 16, 1451–1458. [Google Scholar]
- Norouzi, P.; Shirvani-Arani, S.; Daneshgar, P.; Ganjali, M.R. Sub-second adsorptive fast Fourier transform coulometric technique as a novel method for the determination of nanomolar concentrations of sodium valproate in its pharmaceutical preparation in flowing solution systems. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar]
- Norouzi, P.; Ganjali, M.R.; Daneshgar, P.; Alizadeh, T.; Mohammadi, A. Development of fast Fourier transformation continuous cyclic voltammetry as a highly sensitive detection system for ultra trace monitoring of penicillin V. Anal. Biochem. 2007, 360, 175–181. [Google Scholar]
- Radi, A.; El Ries, M.A.; El-Anwar, F.; El-Sherif, Z. Electrochemical oxidation of meloxicam and its determination in tablet dosage form. Anal. Lett. 2001, 34, 739–748. [Google Scholar]
- Zare, H.R.; Namazian, M.; Nasirizadeh, N. Electrochemical behavior of quercetin: Experimental and theoretical studies. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2005, 584, 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Norouzi, P.; Ganjali, M.R.; Zare, M.; Mohammadi, A. Nano-level detection of naltrexone hydrochloride in its pharmaceutical preparation at Au microelectrode in flowing solutions by fast Fourier transforms continuous cyclic voltammetry as a novel detector. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 96, 2009–2017. [Google Scholar]
- Norouzi, P.; Ganjali, M.R.; Daneshgar, P. Development a new method for the determination of paromomycin in trace amounts by fast Fourier continuous cyclic voltammetry at an Au microelectrode in a flowing system. Sens. Actuat. B 2007, 123, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar]
- Nabi Bidhendi, G.; Norouzi, P.; Daneshgar, P.; Ganjali, M.R. A sub-second fast Fourier transform-adsorptive voltammetric technique for the nano-level determination of guthion at a gold microelectrode in flowing solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 143, 264–270. [Google Scholar]
- Norouzi, P.; Ganjali, M.R.; Alizadeh, T.; Daneshgar, P. Fast Fourier continuous cyclic voltammetry at gold ultramicroelectrode in flowing solution for determination of ultra trace amounts of penicillin G. Electroanalysis 2006, 18, 947–954. [Google Scholar]
- Norouzi, P.; Ganjali, M.R.; Daneshgar, P.; Dinarvand, P.; Moosavi-Movahedi, A.A.; Saboury, A.A. Development of fast Fourier transform continuous cyclic voltammetry at Au microelectrode in flowing solutions as a novel method for sub-nanomolar monitoring of lidocaine in injection and biological fluids. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2007, 590, 74–80. [Google Scholar]
- Baranski, A.; Szulborska, A. Fourier-transform square-wave voltammetry. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1994, 373, 157–165. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.D. Preparation and optical properties of one dimensional nano hydroxides and oxides. Chem. Eur. J. 2003, 9, 5627–5635. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Sun, X.M.; Li, Y.D. Rare earth compound nanotubes. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1442–1445. [Google Scholar]
- Norouzi, P.; Ganjali, M.R.; Larijani, B.; Karamdoust, S. A fast stripping continuous cyclic voltammetry method for determination of ultra trace amounts of nalidixic acid. Croatica Chim. Acta. 2008, 81, 423–430. [Google Scholar]
- Daneshgar, P.; Norouzi, P.; Ganjali, M.R.; Ordikhani-Seyedlar, A.; Eshraghi, H. A dysprosium nanowire modified carbon paste electrode for determination of levodopa using fast Fourier transformation square-wave voltammetry method. Colloids Surf. B 2009, 68, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Daneshgar, P.; Norouzi, P.; Ganjali, M.R.; Dousty, F. A dysprosium nanowire modified carbon paste electrode for determination of nanomplar level of diphenhydramin by continuous square wave voltammetry in flow injection system. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2009, 4, 444–457. [Google Scholar]
- Ganjali, M.R.; Norouzi, P.; Ghorbani, M.; Sepehri, A. Fourier transform cyclic voltammetric technique for monitoring ultratrace amounts of salbutamol at gold ultra microelectrode in flowing solutions. Talanta 2005, 66, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, J.C.; Miller, J.N. Statistics for Analytical Chemistry; Ellis Horwood: Chichester, UK, 1984; Volume 22, pp. 82–86. [Google Scholar]







| Added (ng/mL) | Interpolated concentration | R.S.D (%) | R.E. (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 (plasma) | 5.1 ± 0.4 | 1.2 | 1.1 |
| 5(urine) | 4.8 ± 0.1 | 1.15 | 0.98 |
| Method | Detection limit | Ref. No. |
|---|---|---|
| Potentiometry | 3 × 10−6 M | 7 |
| HPLC-MS | 0.5 ng mL−1 | 12 |
| Spectrophotometry | 0.37 μg/mL | 21 |
| GC | 100 pg/mL | 18 |
| FFTSWV | 2.0 × 10−9 M | This work |
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Daneshgar, P.; Norouzi, P.; Ganjali, M.R.; Dinarvand, R.; Moosavi-Movahedi, A.A. Determination of Diclofenac on a Dysprosium Nanowire- Modified Carbon Paste Electrode Accomplished in a Flow Injection System by Advanced Filtering. Sensors 2009, 9, 7903-7918. https://doi.org/10.3390/s91007903
Daneshgar P, Norouzi P, Ganjali MR, Dinarvand R, Moosavi-Movahedi AA. Determination of Diclofenac on a Dysprosium Nanowire- Modified Carbon Paste Electrode Accomplished in a Flow Injection System by Advanced Filtering. Sensors. 2009; 9(10):7903-7918. https://doi.org/10.3390/s91007903
Chicago/Turabian StyleDaneshgar, Parandis, Parviz Norouzi, Mohammad Reza Ganjali, Rasoul Dinarvand, and Ali Akbar Moosavi-Movahedi. 2009. "Determination of Diclofenac on a Dysprosium Nanowire- Modified Carbon Paste Electrode Accomplished in a Flow Injection System by Advanced Filtering" Sensors 9, no. 10: 7903-7918. https://doi.org/10.3390/s91007903
APA StyleDaneshgar, P., Norouzi, P., Ganjali, M. R., Dinarvand, R., & Moosavi-Movahedi, A. A. (2009). Determination of Diclofenac on a Dysprosium Nanowire- Modified Carbon Paste Electrode Accomplished in a Flow Injection System by Advanced Filtering. Sensors, 9(10), 7903-7918. https://doi.org/10.3390/s91007903




