A Compact Laboratory Spectro-Goniometer (CLabSpeG) to Assess the BRDF of Materials. Presentation, Calibration and Implementation on Fagus sylvatica L. Leaves
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (i)
- Geometric stability of the apparatus, velocity of the components, and deviation of the sensor field-of-view across the target.
- (ii)
- Stability, homogeneity, and conical illumination of the light source, consistency and repeatability of measurements, and the deviation of Spectralon from an ideal Lambertian reference panel.
- (iii)
- Water stress induced to the samples due to heat from the light source, and the irregularity of sample sizes compared to the field of view of the spectroradiometer.
2. Theoretical background
- Lr = sensor radiance (W m-2 sr-1 nm-1),
- Ei = hemispherical irradiance (W m-2 nm-1),
- λ = wavelength (nm),
- θi,φi = source zenith and azimuth angles, respectively,
- θr,φr = view zenith and azimuth angles, respectively.
- fr values range theoretically from zero to infinity.
- ρ = hemispherical reflectance of sample.
- Rref = correction factor for the non-Lambertian reflection properties of the reference panel.
- Li = incoming radiance (W m-2 sr-1 nm-1),
- R = Bidirectional Reflectance Factor,
- μ = cosθ,
- rs= the distance between the location (x,y,0) and the position of the sensor,
- θ0,φ0 and θ,φ = nominal illumination and sensor angles, respectively.
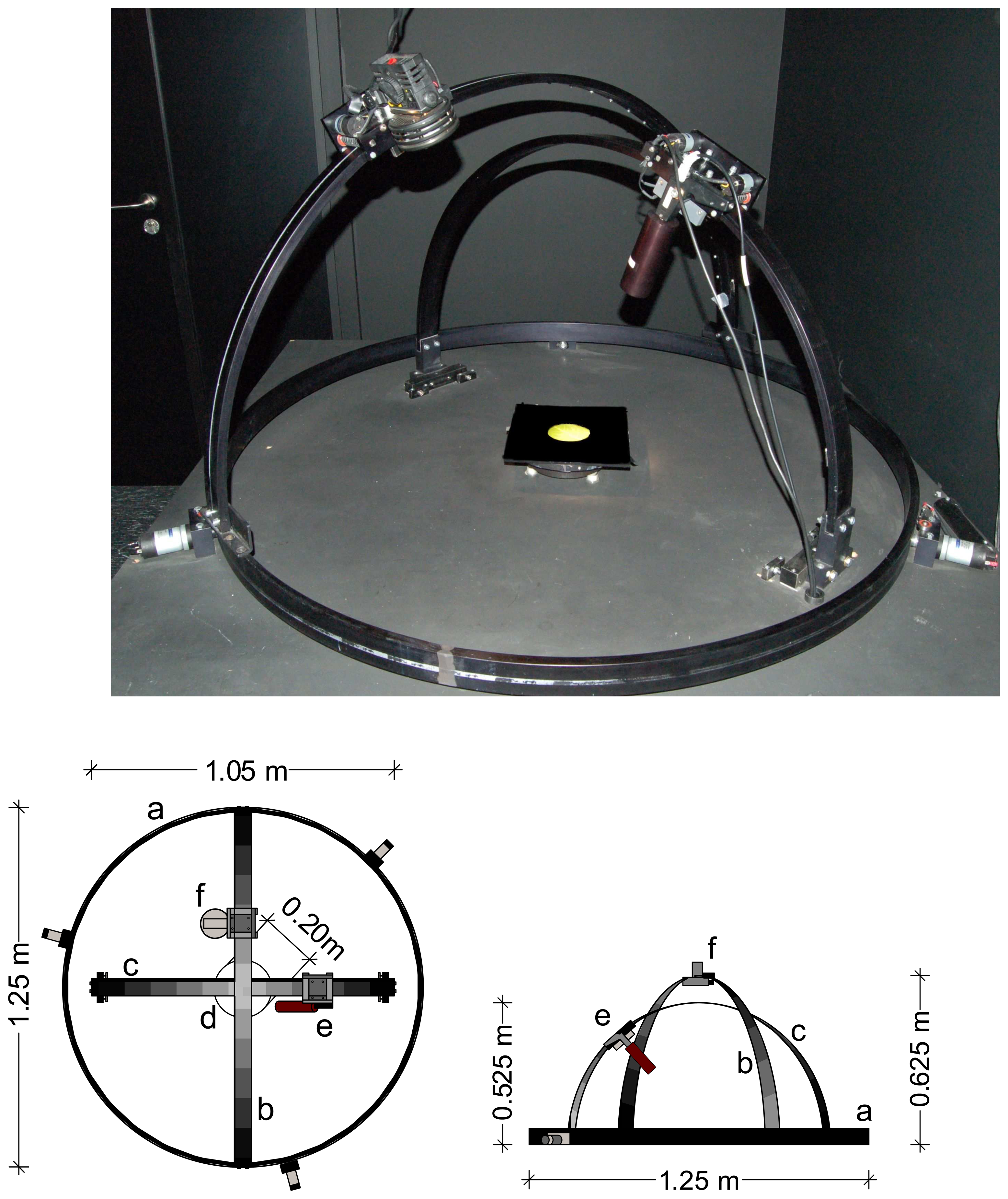
3. System Set up and Technical specifications
- A horizontal, circular black anodized aluminum rail ring of 1.25 m diameter for the azimuthal movement of the light source.
- A vertical half-circular arc (diameter = 1.25 m) mounted on the horizontal rail, supporting the zenith movement of the light source.
- A vertical stationary half-circular arc (diameter = 1.05 m) mounted inside both previous arcs on a black wooden table to support the zenith movement of the spectroradiometer.
- A rotating stainless steel horizontal plate of 0.20 m diameter, placed in the centre of the apparatus, which enables the azimuthal movement of the sample holder.
4. Calibration
4.1 Geometric Calibration
4.1.1 Ground Instantaneous Field Of View
4.2 Radiometric Calibration
4.2.1 Stability and homogeneity of the light source
4.2.2 Temperature of the light source
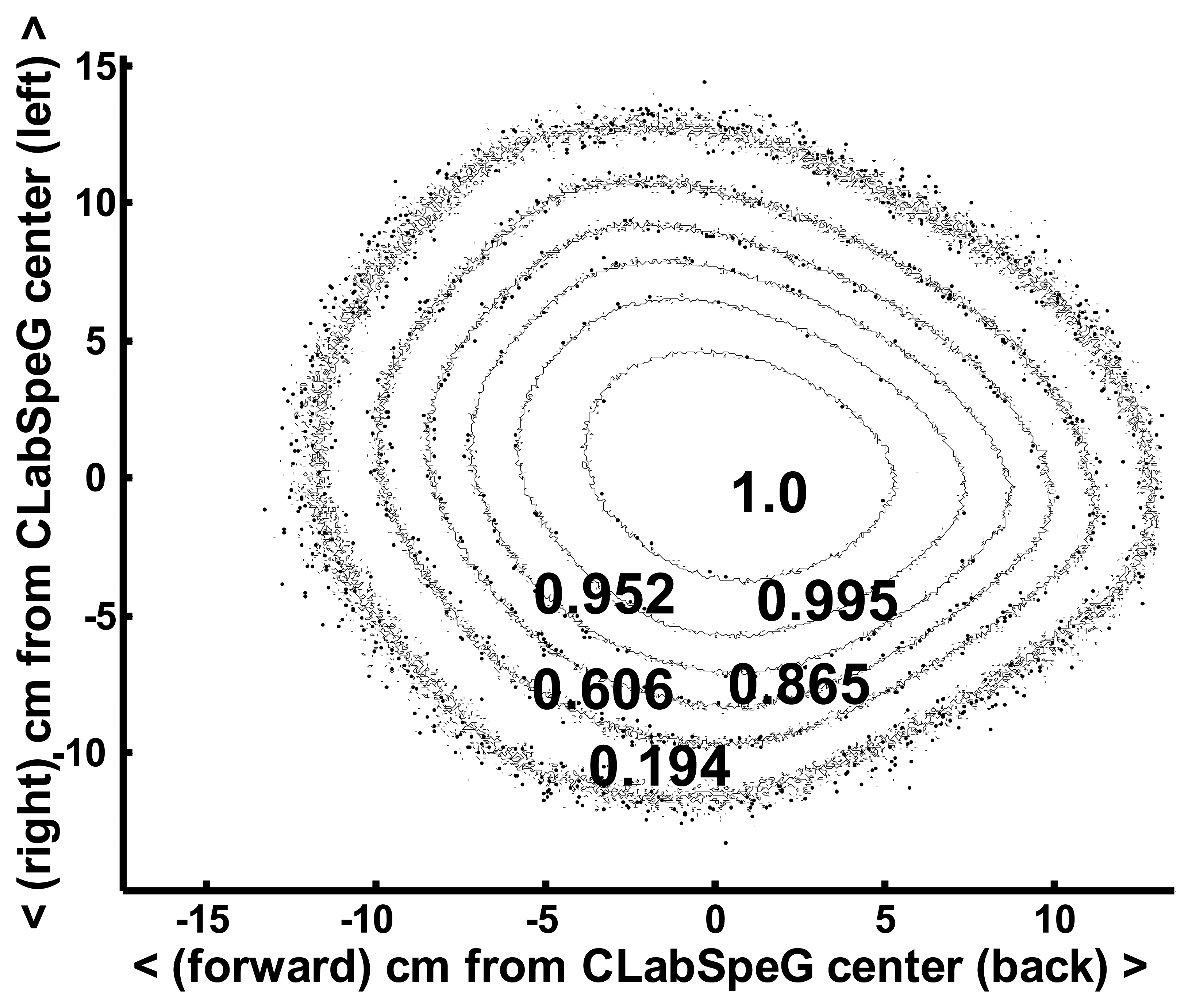
4.2.3 Reproducibility of the measurements
5. BRDF data processing
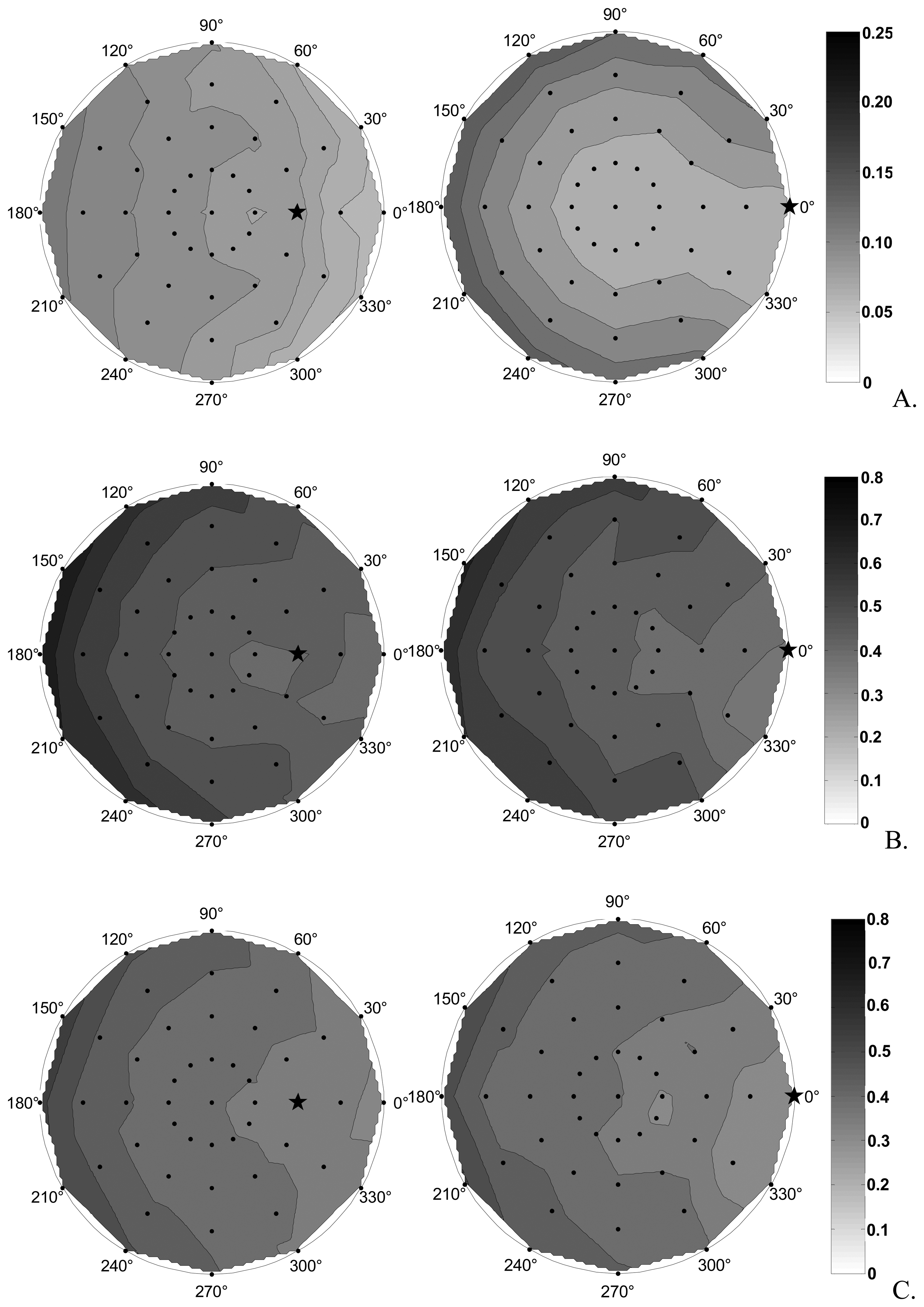
5.1 Spectralon
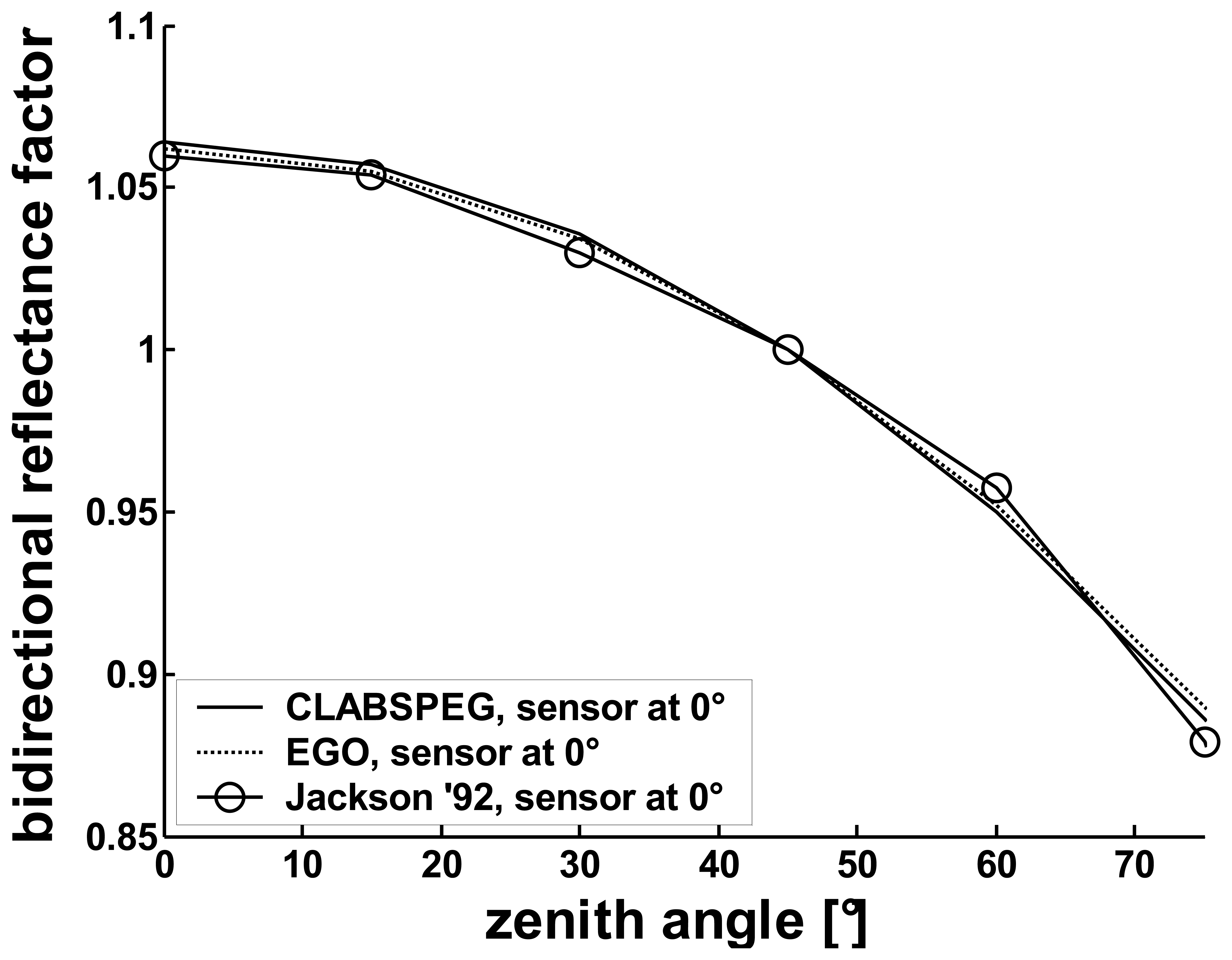
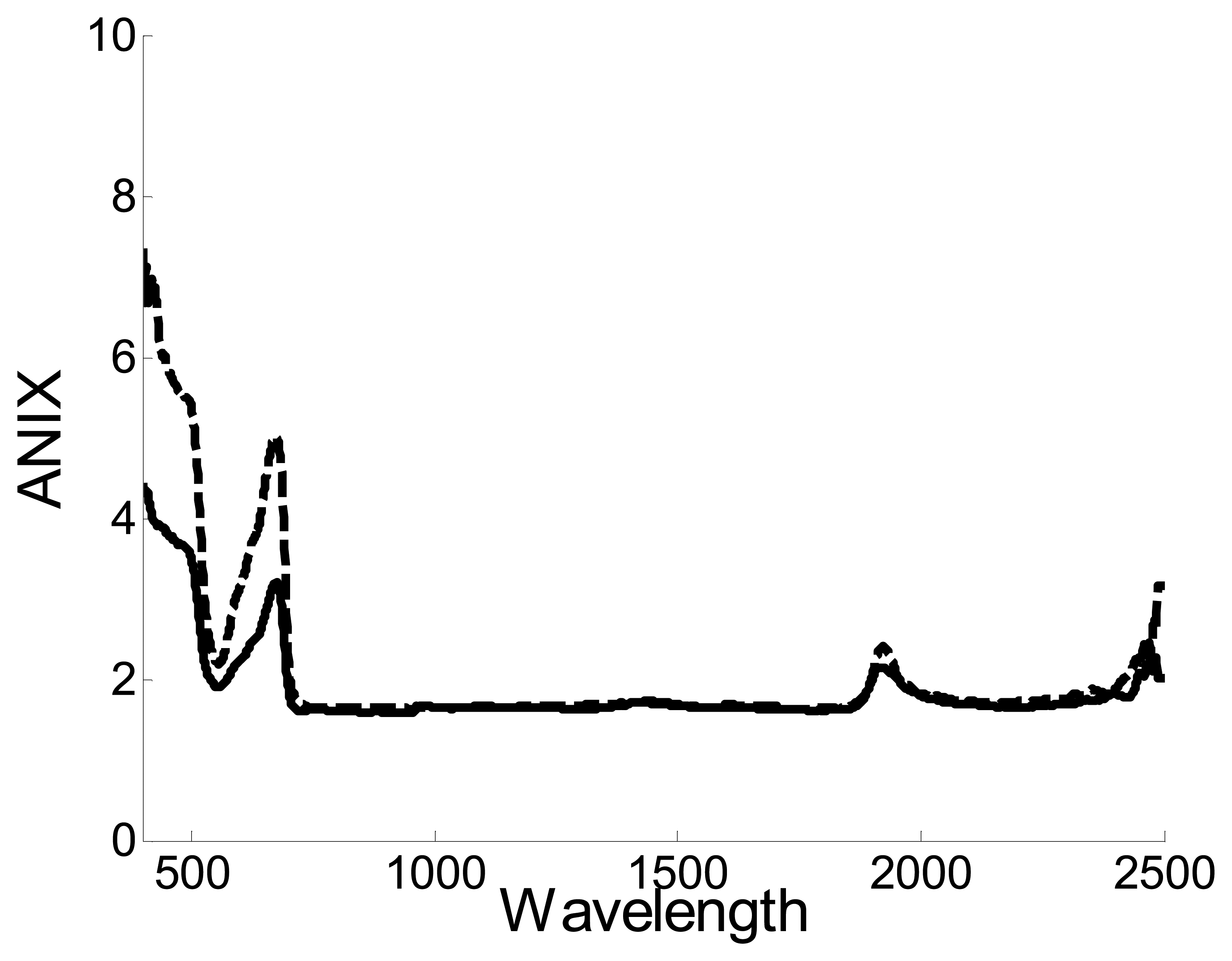
5.1.1. The Spectralon, as non-Lambertian body
5.2. Correction of the biconical effect
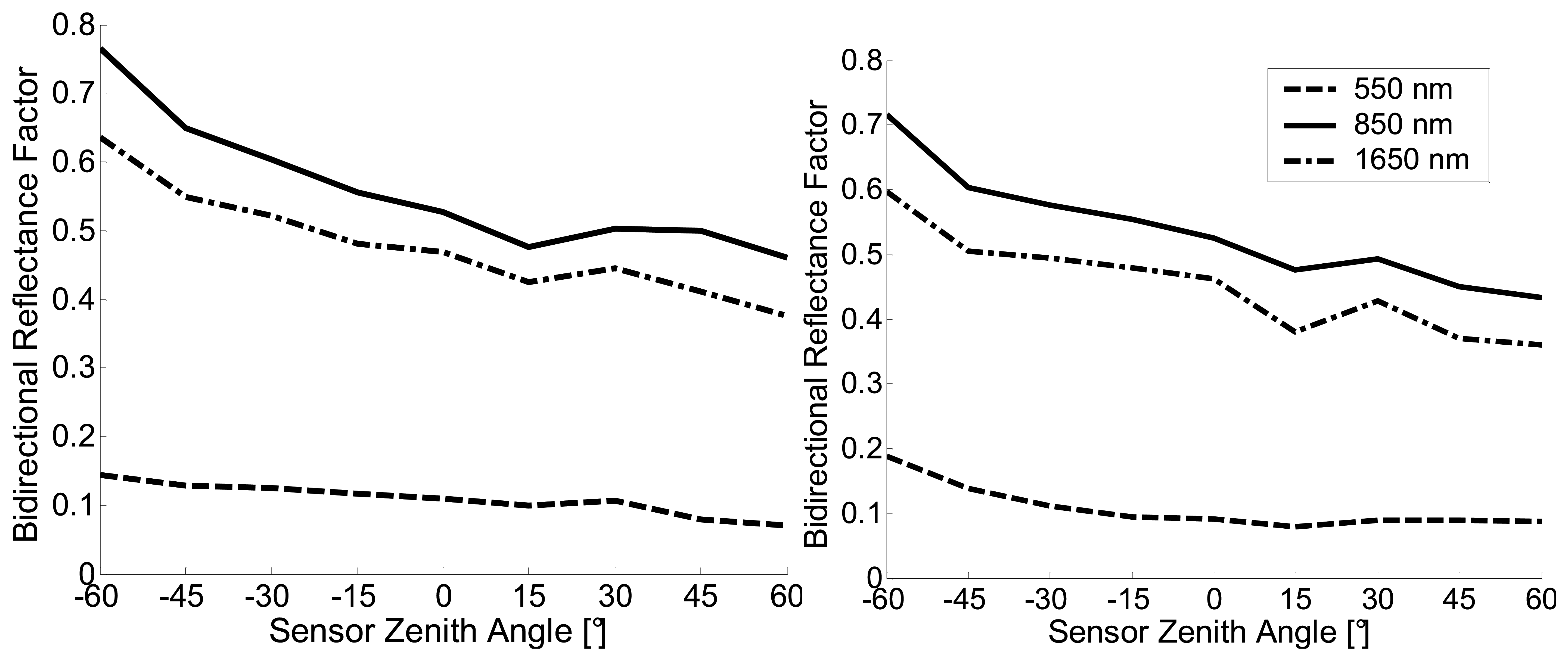
5.3 Leaves
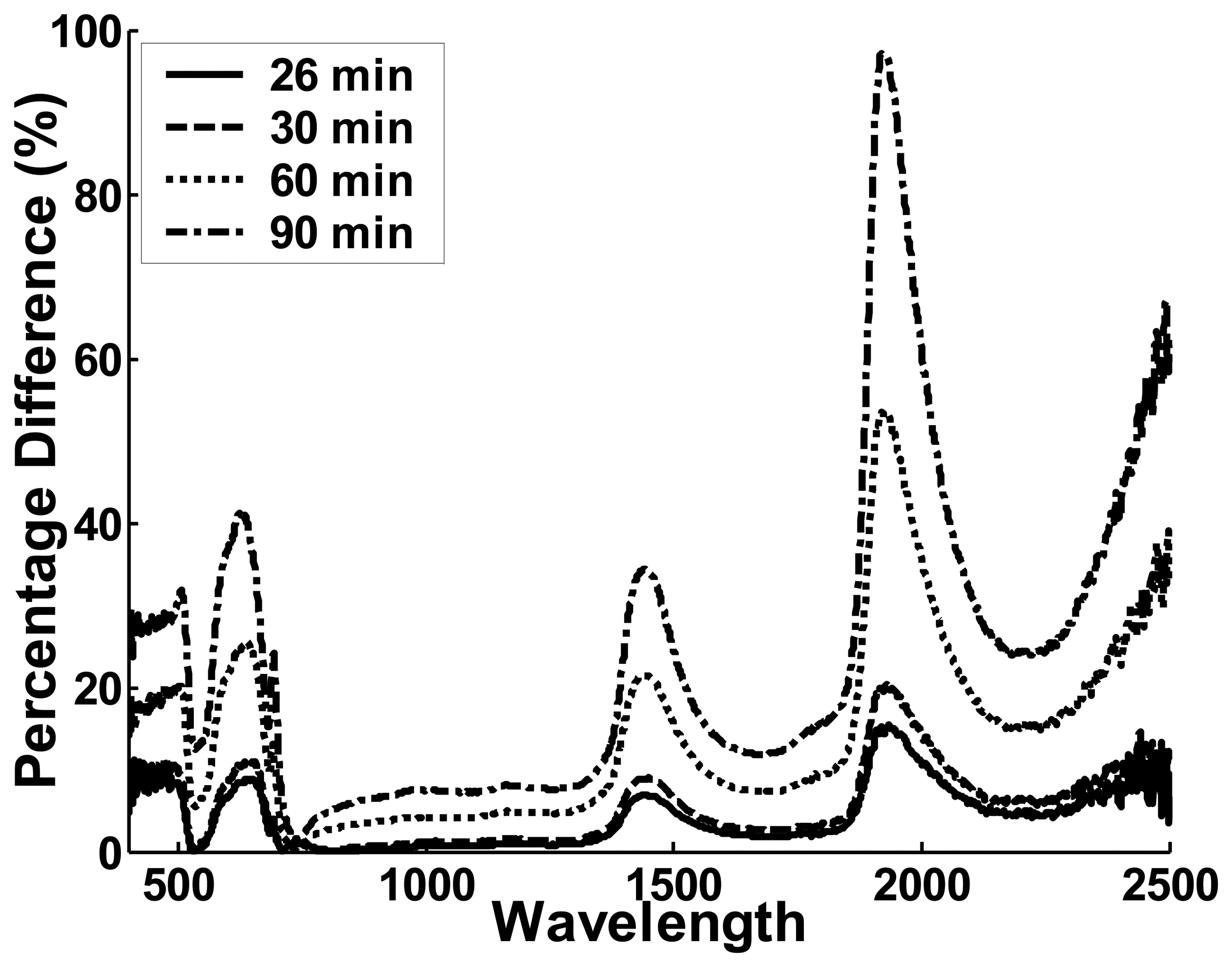
5.3.1 Leaf endurance under light source stress
5.3.2 Leaf BRF acquisition
6. Discussion and Conclusion
Acknowledgments
Appendix A.
| λ (nm) | Coeff. α0 | Coeff. α1 | Coeff. α2 | RMSE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 350 | 1.074 | -1.5904e-007 | -2.275e-005 | 1.0821 |
| 400 | 1.066 | -1.4206e-007 | -3.374e-005 | 1.0824 |
| 450 | 1.066 | -1.4290e-007 | -3.280e-005 | 1.0819 |
| 500 | 1.065 | -1.4382e-007 | -3.245e-005 | 1.0820 |
| 550 | 1.064 | -1.4460e-007 | -3.191e-005 | 1.0818 |
| 600 | 1.064 | -1.4506e-007 | -3.169e-005 | 1.0818 |
| 650 | 1.063 | -1.4572e-007 | -3.135e-005 | 1.0818 |
| 700 | 1.064 | -1.4612e-007 | -3.115e-005 | 1.0818 |
| 750 | 1.064 | -1.4658e-007 | -3.089e-005 | 1.0818 |
| 800 | 1.061 | -1.4668e-007 | -3.058e-005 | 1.0816 |
| 850 | 1.058 | -1.4662e-007 | -3.053e-005 | 1.0815 |
| 900 | 1.062 | -1.4664e-007 | -3.066e-005 | 1.0816 |
| 950 | 1.061 | -1.4782e-007 | -3.000e-005 | 1.0816 |
| 1000 | 1.063 | -1.4098e-007 | -2.877e-005 | 1.0780 |
| 1050 | 1.064 | -1.4174e-007 | -2.826e-005 | 1.0779 |
| 1100 | 1.060 | -1.4080e-007 | -2.852e-005 | 1.0778 |
| 1150 | 1.059 | -1.4130e-007 | -2.800e-005 | 1.0776 |
| 1200 | 1.064 | -1.4184e-007 | -2.812e-005 | 1.0778 |
| 1250 | 1.058 | -1.4096e-007 | -2.821e-005 | 1.0776 |
| 1300 | 1.050 | -1.4050e-007 | -2.745e-005 | 1.0768 |
| 1350 | 1.061 | -1.4148e-007 | -2.803e-005 | 1.0776 |
| 1400 | 1.048 | -1.3984e-007 | -2.781e-005 | 1.0769 |
| 1450 | 1.041 | -1.3966e-007 | -2.733e-005 | 1.0764 |
| 1500 | 1.043 | -1.4032e-007 | -2.704e-005 | 1.0764 |
| 1550 | 1.052 | -1.4142e-007 | -2.735e-005 | 1.0771 |
| 1600 | 1.054 | -1.4142e-007 | -2.772e-005 | 1.0774 |
| 1650 | 1.059 | -1.4224e-007 | -2.791e-005 | 1.0778 |
| 1700 | 1.064 | -1.4360e-007 | -2.775e-005 | 1.0782 |
| 1750 | 1.064 | -1.4358e-007 | -2.778e-005 | 1.0782 |
| 1800 | 1.064 | -1.5060e-007 | -2.829e-005 | 1.0811 |
| 1850 | 1.072 | -1.5006e-007 | -2.947e-005 | 1.0819 |
| 1900 | 1.073 | -1.5086e-007 | -2.936e-005 | 1.0821 |
| 1950 | 1.073 | -1.5116e-007 | -2.889e-005 | 1.0818 |
| 2000 | 1.078 | -1.5198e-007 | -2.899e-005 | 1.0822 |
| 2050 | 1.090 | -1.5324e-007 | -2.941e-005 | 1.0829 |
| 2100 | 1.098 | -1.5436e-007 | -2.981e-005 | 1.0837 |
| 2150 | 1.106 | -1.5582e-007 | -2.947e-005 | 1.0839 |
| 2200 | 1.089 | -1.5224e-007 | -2.994e-005 | 1.0830 |
| 2250 | 1.087 | -1.5258e-007 | -2.950e-005 | 1.0827 |
| 2300 | 1.098 | -1.5460e-007 | -2.920e-005 | 1.0832 |
| 2350 | 1.110 | -1.5624e-007 | -2.933e-005 | 1.0840 |
| 2400 | 1.116 | -1.5304e-007 | -3.266e-005 | 1.0855 |
| 2450 | 1.115 | -1.5862e-007 | -2.904e-005 | 1.0847 |
| 2500 | 1.105 | -1.5832e-007 | -2.804e-005 | 1.0840 |
References
- Privette, J.L.; Deering, D.W.; Wickland, D.E. Report on the workshop on Multiangular Remote Sensing for Env. App. NASA Technical Memorandum 113202 1997, 60. [Google Scholar]
- Nicodemus, F.E.; Richmond, J.C.; Hsia, J.J.; Ginsberg, I.W.; Limperis, T. Geometrical Considerations and Nomenclature for Reflectance, NBS Monograph; National Bureau of Standards, US Department of Commerce: Washington, D.C., 1977; p. 160. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Strahler, A.H. Geometrical - Optical Modelling of a Conifer Forest Canopy. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1985, 23(5), 705–721. [Google Scholar]
- Jacquemoud, S.; Baret, F. PROSPECT: A Model of Leaf Optical Properties Spectra. Remote Sens. Environ. 1990, 34, 75–91. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J.; Cabot, F.; Moran, M.S.; Dedieu, G. Biophysical Parameter Estimation Using multidirectional Spectral Measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 1995, 54, 71–83. [Google Scholar]
- Pinty, B.; Verstraete, M.M.; Gobron, N. The effect of soil anisotropy on the radiance field emerging from vegetation canopies. Geophysical Res. Ltrs. 1998, 25(6), 797–800. [Google Scholar]
- Baranoski, G.V.G.; Rokne, J.G. Light Interaction with Plants, A Computer Graphics Percpective. Horwood Publishing 2004, 186. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Dorsey, J.; Yang, X.; Guo, B.; Shum, H-Y. Real-time rendering of plant leaves. ACM Transactions on Graphics 1992, 26(2), 712–719. [Google Scholar]
- Phong, B-T. Illumination for computer generated pictures. Communications of the ACM 1975, 18(6), 311–317. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, R.L.; Torrance, K.E. A reflectance model for computer graphics. Richards, W., Ullman, S., Eds.; In Image Understanding; Norwood, NJ; Ablex, 1987; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Lafortune, E.P.F.; Willems, Y.D. A theoretical framework for physically based rendering. Computer Graphics Forum 1994, 13(2), 97–107. [Google Scholar]
- Oren, M.; Nayar, K.S. Generalisation of lambert's reflectance model. Procceedings of SIGGRAPH'94. Computer Graphics Proceedings; Glassner, A., Ed.; 1994; pp. 239–246. [Google Scholar]
- Deering, D.W. Field measurements of bidirectional reflectance. In Theory and Applications of Optical Remote Sensing; Asrar, G., Ed.; Wiley: New York, 1989; pp. 14–65. [Google Scholar]
- Sandmeier, St.; Sandmeier, W.; Itten, K.I.; Schaepman, M.E.; Kellenberger, T.W. Acquisition of bidirectional reflectance data using the Swiss Field-Goniometer System (FIGOS). Proceedings of EARSeL symposium, Basel, Switzerland, Balkema, Rotterdam; 1995; pp. 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Painter, T.H.; Paden, B.; Dozier, J. Automated spectro-goniometer: A spherical robot for the field measurement of the directional reflectance of snow. Rev. of Scient. Instr. 2003, 74(12), 5179–5188. [Google Scholar]
- Peltoniemi, I.J.; Kaasalainen, S.; Näränen, J.; Rautiainen, M.; Stenberg, P.; Smolander, H.; Smolander, S.; Voipio, P. BRDF measurement of understory vegetation in pine forests: dwarf shrubs, lichen and moss. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 94, 343–354. [Google Scholar]
- Bourgeois, C.S.; Ohmura, A.; Schroff, K.; Frei, H-J.; Calanca, P. IAC ETH Goniospectrometer: A Tool for Hyperspectral HDRF Measurements. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Techn. 2006, 23, 573–584. [Google Scholar]
- Breece, H.T.; Holmes, R.A. Bidirectional scattering characteristics of healthy green soybean and corn leaves in vivo. Applied Opt. 1971, 10, 119–127. [Google Scholar]
- Kriebel, K.T. Measured spectral bidirectional reflectance properties of vegetated surfaces. Applied Opt. 1978, 253–259. [Google Scholar]
- Brakke, T.W.; Smith, J.A.; Harnden, J. Bidirectional Scattering of Light from Tree Leaves. Remote Sens. Environ. 1989, 29, 175–183. [Google Scholar]
- Walter-Shea, E.A.; Norman, J.M.; Blad, B.L. Leaf Bidirectional Reflectance and Transmittance in Corn and Soybean. Remote Sens. Environ. 1989, 29, 161–174. [Google Scholar]
- Koechler, C.; Hosgood, B.; Andreoli, G.; Schmuck, G.; Verdebout, J.; Pegoraro, A.; Hill, J.; Mehl, W.; Roberts, D.; Smith, M. The European Optical Goniometer Facility: Technical Description and First Experiments on Spectral Unmixing. Proceedings of IGARSS'94, Pasadena, 8-12 August, 1994; pp. 2375–2377.
- Serrot, G.; Bodilis, M.; Briottet, X.; Cosnefroy, H. Presentation of a new BRDF measurement device. The European Symposium on Remote Sensing, SPIE, Euporto, Barcelona, Spain; 1998; 3493, pp. 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Schaepman, M.E.; Dangel, S. Solid laboratory calibration of a nonimaging spectroradiometer. Applied Opt. 2000, 39(21), 3753–3765. [Google Scholar]
- Bousquet, L.; Lachérade, S.; Jacquemoud, S.; Moya, I. Leaf BRDF measurements and model for speculalar and diffuse components differentiation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 201–211. [Google Scholar]
- Combes, D.; Bousquet, L.; Jacquemoud, S.; Sinoquet, H.; Varlet-Grancher, C.; Moya, I. A new spectrogoniophotometer to measure leaf spectral and directional optical properties. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönermark, M.; Geiger, B.; Röser, H.P. Reflection Properties of Vegetation and Soil with a BRDF Data base; Wissenschaft und Technik Verlag: Berlin, 2004; p. 352. [Google Scholar]
- Sandmeier, St.; Muller, Ch.; Hosgood, B.; Andreoli, G. Sensitivity Analysis and quality Assessment of Laboratory BRDF Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 64, 176–191. [Google Scholar]
- Martonchick, J.V.; Bruegge, C.J.; Strahler, A.H. A Review of Reflectance Nomenclature Used in Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing Rev. 2000, 19, 9–20. [Google Scholar]
- Schaepman-Strub, G.; Schaepman, M.E.; Painter, T.H.; Dangel, S.; Martonchik, J.V. Reflectance quantities in optical remote sensing – definitions and case studies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 103, 27–42. [Google Scholar]
- Dangel, S.; Verstraete, M.M.; Schopfer, J.; Kneubühler, M.; Schaepman, M.; Itten, K.I. Toward a Direct Comparison of Field and Laboratory Goniometer Measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43(11), 2666–2675. [Google Scholar]
- Sandmeier, St. Acquisition of Bidirectional Reflectance Factor Data with Field Goniometers. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 73, 257–269. [Google Scholar]
- Analytical Spectral Devices, Inc. (ASD) Technical guide., 3rd ed.; 1999; p. 136. [Google Scholar]
- Solheim, I.; Hosgood, B.; Andreoli, G.; Piironen, J. Calibration and Characterization of Data from the European Goniometer Facility (EGO). Joint Research Centre Report EUR 17268 EN. 1996, 169. [Google Scholar]
- Sandmeier, S.R.; Itten, K.I. A Field Goniometer System (FIGOS) for Acquisition of Hyperspectral BRDF Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37(2), 978–986. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, R.D.; Clarke, T.R.; Moran, M.S. Bidirectional Calibration Results for 11 Spectralon and 16 BaSO4 Reference Reflectance Panels. Remote Sens. Environ. 1992, 40, 231–239. [Google Scholar]
- Bruegge, C.; Chrien, N.; Haner, D. A Spectralon BRF data base for MISR calibration applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 76, 354–366. [Google Scholar]
- Sandmeier, St.; Muller, Ch.; Hosgood, B.; Andreoli, G. Physical mechanisms in hyperspectral BRDF data of grass and watercress. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 222–233. [Google Scholar]
- Schaepman, M.E. Imaging Spectroscopy in Ecology and the Carbon Cycle: Heading Towards New Frontiers. Proceedings of the EARSeL 4th workshop on Imaging Spectroscopy, Warsaw, Poland; 2005; pp. 13–37. [Google Scholar]
- Gilabert, M.A.; Garcia-Haro, F.J.; Melia, J. A mixture modelling approach to estimate vegetation parameters for heterogeneous canopies in remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 72, 328–345. [Google Scholar]
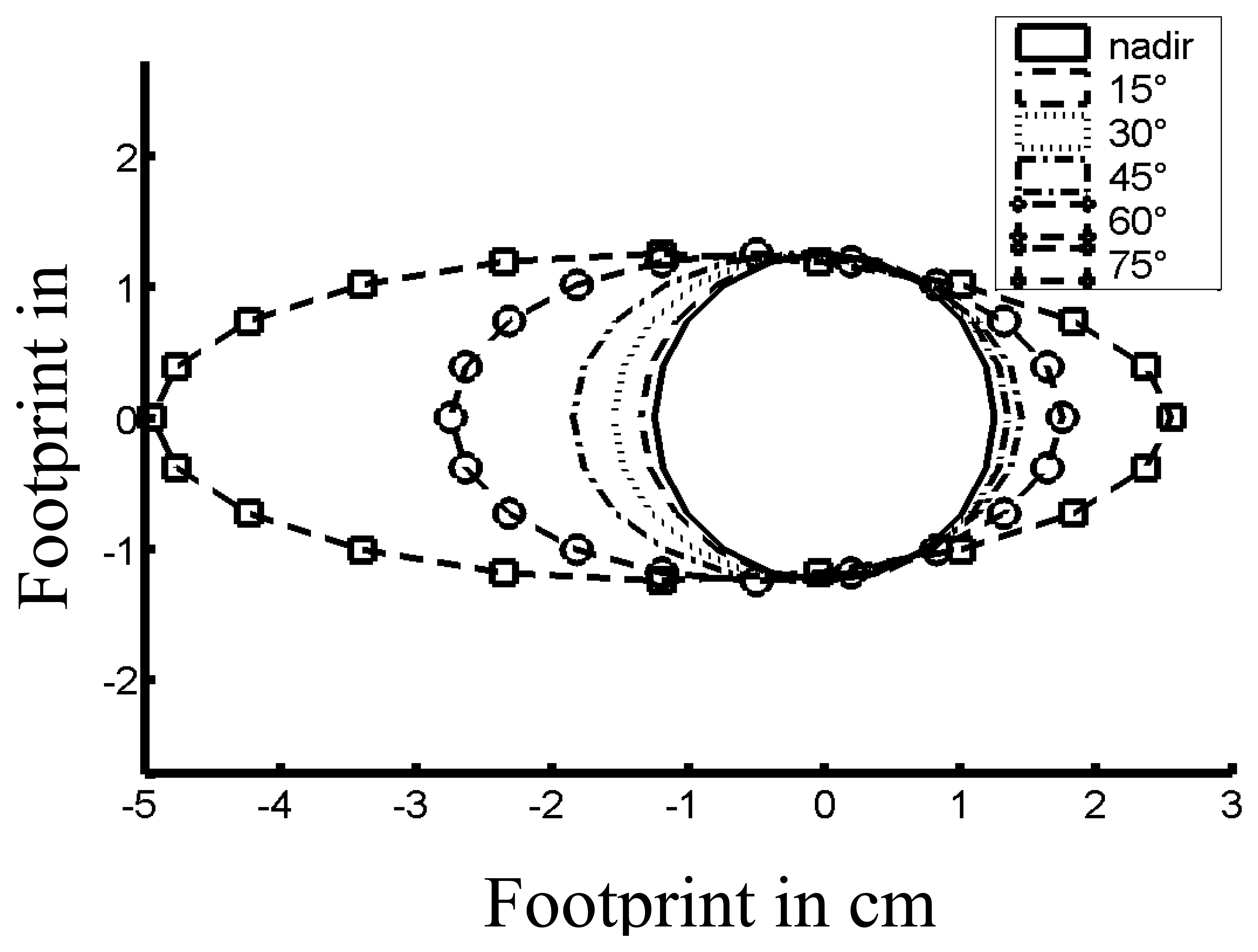
| SENSOR Zenith | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LIGHT SOURCE Zenith | 0° | 15° | 30° | 45° | 60° | 75° |
| 15° | 3.94 ± 1.73 | 5.84 ± 4.85 | 3.79 ± 2.84 | 5.98 ± 5.06 | 5.44 ± 3.63 | 11.64 ± 8.80 |
| 30° | 17.68 ± 3.40 | 12.91 ± 5.86 | 16.04 ± 7.26 | 10.23 ± 5.03 | 10.36 ± 5.84 | 12.76 ± 8.31 |
| 45° | 37.84 ± 4.28 | 33.59 ± 7.20 | 34.83 ± 5.45 | 27.56 ± 9.88 | 27.40 ± 8.52 | 18.57 ± 12.77 |
| 60° | 64.38 ± 2.98 | 61.18 ± 4.96 | 61.79 ± 4.04 | 56.36 ± 5.85 | 53.42 ± 7.37 | 30.83 ± 20.50 |
| 75° | 83.25 ± 1.21 | 82.04 ±1.84 | 81.64 ± 1.43 | 79.03 ± 2.51 | 75.02 ± 4.18 | 51.29 ± 25.52 |
| Light Azimuth | Light (L) over sensor (S) Zenith positions |
|---|---|
| 0° | 0°L/0°S |
| 30° | 0°L/0°S |
| 60° | 15°L/75°S, -15°L/60°S, 15°L/45°S, -15°L/30°S, -15°L/15°S, and 0°L/0°S |
| 90° | -75°L/75°S, -60°L/60°S, -45°L/45°S, -30°L/30°S, -15°L/15°S, and 0°L/0°S |
| 120° | 15°L/60°S, -15°L/45°S, 15°L/30°S, -15°L/15°S, and 0°L/0°S |
| 150° | 0°L/45°S, 0°L/30°S, 0°L/15°S, and 0°L/0°S |
| Wavelength (nm) | 450 | 500 | 550 | 600 | 650 | 700 | 750 | 800 | 850 | 900 | 950 | 1000 |
| Difference (%) | 1.69 | 1.44 | 0.95 | 0.75 | 0.51 | 0.21 | 0.53 | 1.06 | 1.54 | 1.39 | 1.92 | 3.23 |
| Wavelength (nm) and Light Source Zenith (°) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STD (%) | 550 (30°) | 550 (60°) | 850 (30°) | 850 (60°) | 1650 (30°) | 1650 (60°) |
| MIN | 5.39 | 2.9 | 3.87 | 4.21 | 2.78 | 3.75 |
| MAX | 17.38 | 17.73 | 10.36 | 10.11 | 8.30 | 9.49 |
© 2007 by MDPI ( http://www.mdpi.org). Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.
Share and Cite
Biliouris, D.; Verstraeten, W.W.; Dutré, P.; Van Aardt, J.A.N.; Muys, B.; Coppin, P. A Compact Laboratory Spectro-Goniometer (CLabSpeG) to Assess the BRDF of Materials. Presentation, Calibration and Implementation on Fagus sylvatica L. Leaves. Sensors 2007, 7, 1846-1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/s7091846
Biliouris D, Verstraeten WW, Dutré P, Van Aardt JAN, Muys B, Coppin P. A Compact Laboratory Spectro-Goniometer (CLabSpeG) to Assess the BRDF of Materials. Presentation, Calibration and Implementation on Fagus sylvatica L. Leaves. Sensors. 2007; 7(9):1846-1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/s7091846
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiliouris, Dimitrios, Willem W. Verstraeten, Phillip Dutré, Jan A.N. Van Aardt, Bart Muys, and Pol Coppin. 2007. "A Compact Laboratory Spectro-Goniometer (CLabSpeG) to Assess the BRDF of Materials. Presentation, Calibration and Implementation on Fagus sylvatica L. Leaves" Sensors 7, no. 9: 1846-1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/s7091846
APA StyleBiliouris, D., Verstraeten, W. W., Dutré, P., Van Aardt, J. A. N., Muys, B., & Coppin, P. (2007). A Compact Laboratory Spectro-Goniometer (CLabSpeG) to Assess the BRDF of Materials. Presentation, Calibration and Implementation on Fagus sylvatica L. Leaves. Sensors, 7(9), 1846-1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/s7091846




