1. Introduction
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), operating in swarms, are distinguished by their flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and rapid deployment capabilities. These swarms are increasingly utilized in various cooperative tasks such as detection, early warning, agricultural management, environmental protection, and disaster relief [
1,
2]. Motivated by the need for high-precision relative positional information, UAV swarms enhance the accuracy of cooperative operational tasks through sophisticated inter-UAV communication, coordination, and control [
3]. UAVs’ dynamic characteristics often cause satellite signal blockages in complex environments, leading to significant localization errors or complete loss of localization capabilities [
4,
5]. To address this, cooperative localization in UAV swarms, which utilizes relative distances between UAVs to estimate positions, has become a key research area for maximizing node resources and extending the localization range.
In recent years, cooperative methods have principally focused on acquiring specific information about swarming UAVs, such as their relative distances, to adjust the localization data derived from the Global Positioning System (GPS) [
6]. To address the previously inadequate consideration of the performance of cooperative navigation information in traditional range-based cooperative localization algorithms, a performance evaluation strategy employing Fisher information (FI) and relative entropy was introduced [
7]. This approach effectively selects contributory cooperative information for precise localization calculations. Despite these advancements, relative positioning methods continue to confront challenges in balancing accuracy with computational demands in uncharted environments. An unmanned aircraft system was specifically designed to resolve the three-dimensional relative positioning problem, incorporating a dynamic correction direct–indirect link optimization algorithm to enhance positioning accuracy while fulfilling real-time requirements [
8]. Additionally, a cooperative localization approach based on relative position estimation and optimized belief propagation was proposed [
9]. This method utilizes relative estimation to augment belief propagation, achieving an effective balance between computational load and estimation accuracy. However, in practical application scenarios, the positions of most UAVs are discontinuous or uncertain, necessitating the simultaneous resolution of relative localization and cooperative coverage issues among multiple UAVs. In [
10], a diversity threshold based on Gini purity was designed to address the particle impoverishment problem, accompanied by a fast bare-bone particle self-recovery algorithm with distance constraints. This algorithm guides anomalous particles to regions of high likelihood, significantly improving both the accuracy of localization and the scope of cooperative coverage. Moreover, while utilizing relative distance information, it is essential to consider that signal interference among UAVs can significantly degrade the performance of cooperative localization. To mitigate the detrimental effects of deceptive interference, the multi-UAV localization system was conceptualized as a natural immune biological network [
11]. UAVs equipped with visual sensors offer the capability to perceive their surroundings and estimate mutual positions and postures by comparing visual data. Despite the challenges posed by observation noise and errors, a distributed estimation architecture was constructed by integrating distance, visual data, and intermittent position information. A covariance intersection (CI) algorithm was employed in this distributed fusion scheme, which establishes both direct and indirect geometric constraints between UAVs by utilizing relative distances and co-observed features [
12]. Nonetheless, accurately distinguishing visually similar targets remains a significant challenge due to the similarity of target features and the limitations of UAV resolution ratios, ultimately causing errors in cooperative localization. To address the localization and tracking inaccuracies arising from the correlation challenges among targets with similar visual features, a globally consistent target association algorithm was developed for multi-UAV visual sensors [
13]. This algorithm employs a triangular topology sequence to utilize the relationships between targets, facilitating the distinction and association of those with similar visual features and trajectories. Additionally, to tackle the data association challenges inherent in visual measurements within a homogeneous UAV swarm, an enhanced directional union position and attitude determination (PAD) algorithm was introduced in [
14]. This algorithm mitigates localization errors stemming from the angles of visual measurement by increasing the directional weighting factor. To further enhance the performance of cooperative localization, the integration of inertial measurement units (IMUs) into the UAVs’ measurement systems has been widely adopted. IMUs provide precise measurements of UAV attitudes, thereby increasing the fault tolerance and stability of cooperative localization systems. A novel multi-UAV cooperative localization method, leveraging a density peak clustering-based range data preprocessing scheme was proposed in [
15]. It utilizes the unscented Kalman filter (UKF) to achieve efficient fusion and localization of multiple UAV ranging and IMU modules. As a result, it resolves issues related to localization accuracy and stability caused by UAV coordinate deviation and distance interference. However, IMUs are prone to error accumulation, leading to position drift and expanding localization errors. Consequently, additional information is necessary to calibrate these errors. In [
16], an indoor ultra-wideband (UWB) UAV group cooperative localization system is proposed that combines a balance filter with the inertial system to compensate for the accumulated IMU errors. Beyond these specific methods, the comprehensive utilization of various sensors and algorithms is critical for enhancing the accuracy and robustness of UAV localization. A cooperative synchronous localization and mapping (SLAM) framework based on image feature point matching was proposed in [
17]. This framework effectively utilizes the fusion of vision and IMU data for localization estimation, particularly beneficial when GPS availability is compromised. To address the discrepancies in localization information formats and parameters, a multi-source fusion UAV cooperative localization method employing Information Geometry (UCP IG) and Kullback–Leibler Divergence Minimization (KLM) was proposed in [
18]. This method transforms diverse navigation source information into an information geometric probability model, thus minimizing the impact of accidental errors. However, current multi-UAV cooperative localization methods often suffer from inadequate organization and coordination mechanisms, leading to inefficient collaboration among UAVs, significant data redundancy, and increased energy consumption.
To mitigate these challenges, a cluster networking strategy was developed, segmenting the UAV swarm into various clusters coordinated and managed by a master node in each cluster. This strategy aims to simplify communication complexity and minimize energy consumption [
19]. In [
20], a novel assisted distributed method for UAV clusters was proposed, using a new distributed computation strategy, cost function, and iterative algorithms to reduce global communication costs and address the challenge of using high-quality passive transmitters with limited resources. A distributed maximum minimization (DMM) method was proposed in [
21], deriving a tight upper bound on the objective function relative to the original objective function to expedite convergence. Additionally, a distributed estimation scheme based on Fisher’s information matrix requires only a single round of communication between the edge UAV and the center UAV, streamlining the communication process. To enhance the robustness of UAV networks, researchers proposed a cluster relative localization algorithm leveraging spatiotemporal correlation information [
22]. It formulates the localization equation and subsequently solves it using multidimensional scaling (MDS) and multiple objective particle swarm optimization (MOPSO). The above methods have achieved remarkable progress in the reduction in communication requirements and large-scale deployment; the sensitivity to ambient noise and anomalous data make them insufficiently adaptable to complex dynamic environments with poor robustness. In pursuit of further robustness, significant efforts have been made to optimize UAV cluster models. Ref. [
23] introduced a novel node localization strategy within a flying ad hoc network (FANET) by implementing a clustering routing protocol that uniformly clusters UAVs based on node positions and selects cluster heads considering intra-cluster distances and the residual energies of nodes. In [
24], a passive localization algorithm for moving targets was developed, guided by an optimization criterion. This method employs a cluster cooperative passive localization approach to construct the measurement model and enhances the particle swarm optimization algorithm through grouping and a periodic strategy. A cluster UAV localization method utilizing the K-means algorithm was proposed in [
25]. This approach utilizes user coordinates as features, positioning UAVs at the central locations of each cluster to significantly reduce user interruptions. Although the K-means-based UAV clustering and localization method performs well in reducing user interference, its localization accuracy and stability may be degraded when the topology of the UAV cluster or the energy state of the node changes. In contrast, Ref. [
26] not only solves the GPS limitation problem by introducing a hierarchical heterogeneous swarm control framework based on visual information, but also improves the flexibility and robustness by dynamically managing the UAV swarm. Considering the high mobility, dynamic topology, and limited energy resources typical of UAVs in FANETs, a firefly swarm intelligence-based co-localization and automatic clustering method was developed [
27]. Furthermore, a cluster UAV localization scheme based on swarm intelligence was proposed in [
28]. This scheme employs a bounding box approach to effectively utilize the particle search space within a constrained boundary and determines distances to existing anchor nodes to estimate the target UAV nodes’ locations, improving convergence times and localization accuracy while reducing computational costs and energy consumption to extend the network’s lifetime. A novel cluster UAV framework for large-scale dense reconstruction and real-time cooperative localization was introduced in [
29]. This framework employs a two-stage joint optimization algorithm and a relative pose optimization method to achieve accurate relative localization of UAVs and mitigate scale drift. However, the adaptability of this framework to varying environments was not considered, which negatively impacts the topicality and stability of the UAV cooperative positioning. To address this issue, a real-time distributed SLAM system for cluster UAV cooperative localization was proposed in [
30]. It integrates ultra-wideband (UWB) ranging with Visual–Inertial Odometry (VIO) for self-motion estimation and utilizes consistency measurement filtering to enhance localization accuracy. However, it requires substantial bandwidth for communication among UAVs, presenting a challenge in infrastructure-less environments. An innovative clustering-based cooperative relative localization scheme for UAV swarms was presented in [
31]. Structured as a two-level framework, it includes inter-cluster and intra-cluster localization, employing the double-sided two-way ranging (DS-TWR) method and an MDS-MAP relative localization method based on matrix completion to speed up ranging and improve localization accuracy. In [
32], novel bio-inspired localization (BIL) and bio-inspired clustering (BIC) schemes were proposed for dynamic cluster UAV localization. These schemes aim to reduce localization errors and achieve high localization accuracy, yet they rely on multi-hop communication in remote areas, potentially increasing the number of hops required for data transmission from cluster members to the base station (BS). A multistage clustering-based model for UAV swarms was constructed in [
33]. This model is designed to effectively mitigate ranging packet losses and enhance localization accuracy across various network topologies. Ref. [
34] introduced a multi-drone cluster coordinated navigation approach equipped with fault detection and exclusion capabilities. This method leverages communication and mutual sensing among multiple drones within the cluster, which establishes a distributed navigation system to facilitate coordinated navigation and fault detection. In [
35], a sophisticated solution for UAV localization was proposed to address the limitations inherent in traditional Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) algorithms. The authors introduced a hybrid approach that combines the advantages of Hierarchical Particle Swarm Optimization (HPSO) and Reference Particle Swarm Optimization (RPSO). This innovation successfully mitigates the complexity and reduces the localization errors typically associated with UAV localization by overcoming the shortcomings of traditional PSO algorithms. Further advancing UAV localization techniques, Ref. [
36] established a TDOA-based passive localization method for drone clusters. This approach provides a real-time algorithmic framework that not only facilitates the localization but also the spatial optimization of drones within the cluster. By utilizing TDOA measurements, the proposed method enables real-time scheduling of UAVs within the cluster and achieves optimal localization of targets. A novel distributed cooperative 3D localization method for cluster-based UAVs, termed super-multidimensional scaling (SMDS), was proposed in [
37]. This method employs SMDS and its low-complexity variant. The Super-Multidimensional Scaling based on the Nystrom (SMDS-NyPM) algorithm surpasses other MDS-based cooperative localization algorithms. It significantly enhances the localization accuracy and robustness of GPS-dependent cluster-based UAVs. Existing algorithms for cooperative localization in UAV clusters based on cluster networking offer significant advantages, including high cooperative efficiency and reduced data redundancy. However, incorporating additional information such as angles to improve localization accuracy leads to increased algorithmic complexity. Moreover, as the tasks become more complex and the number of drones in large-scale UAVs clusters continues to grow, the computational costs at the terminal also keep rising. In response to these challenges, this paper proposes a biogeography optimization-based cluster networking and adaptive sampling-improved Nystrom super-multidimensional scaling-based (BOCN-ASNSMS) cooperative localization algorithm. This algorithm is specifically designed for multi-UAV systems and aims to minimize energy consumption and computational complexity while achieving high-precision localization. To improve energy efficiency, this paper proposes a cluster networking method based on biogeography optimization (BO) to enhances the likelihood that nodes with higher residual energy are selected as cluster heads, thereby optimizing the distribution of cluster heads across the network. Additionally, an adaptive sampling-improved Nystrom super-multidimensional scaling (ASNSMS) algorithm is introduced. This algorithm dynamically constructs the sample matrix, thereby reducing the volume of data processed and enhancing the approximation accuracy of the similarity matrix. These improvements not only reduce computational complexity but also enhance localization accuracy. Furthermore, Procrustes analysis and the least squares method are employed to achieve inter-cluster fusion and coordinate transformation within the UAV swarm. These techniques facilitate high-precision global cooperative localization of the UAV swarm. The primary contributions of this paper are summarized as follows:
1. To reduce energy consumption and localization errors associated with random selections in cluster networking, this paper proposes a biogeography optimization (BO)-based cluster networking strategy. This strategy selectively prioritizes UAV nodes with optimal residual energy and spatial distribution for the role of cluster head. It employs habitat fitness function minimization alongside a roulette wheel method to regulate the frequency of changes in cluster head roles. Additionally, when the rates of node migration into and out of the cluster head roles reach equilibrium, a mutation operation is introduced to refine the fitness function. This aims to identify the globally optimal cluster networking scheme, ensuring a uniform distribution of UAVs within the network and significantly enhancing localization accuracy.
2. A low-complexity adaptive sampling-improved Nystrom super-multidimensional scaling (ASNSMS) algorithm is designed to facilitate cooperative localization within UAV clusters. This algorithm constructs the sample matrix by selectively extracting key rows from the kernel matrix, thus avoiding extensive manipulation of the entire matrix and substantially reducing data processing requirements. By dynamically adjusting the sampling probabilities of each row based on the Frobenius norm, the algorithm intelligently identifies row vectors that significantly influence localization accuracy. This process enhances the estimation of eigenvectors and improves the accuracy of the similarity matrix approximation, further refining localization precision. Once the kernel matrix approximation is obtained, the relative coordinates of the UAV nodes are succinctly and accurately determined using the low-order truncation method, ensuring the reliability of the localization outcomes.
3. Upon determining the relative intra-cluster coordinates of the UAVs, Procrustes analysis is employed to achieve the fusion of inter-cluster coordinates. This method resolves the rotational and translational transformations required to align the coordinates of UAVs from different clusters into a unified coordinate system, thereby facilitating high-precision global localization. Furthermore, this paper leverages GPS data from anchor UAV nodes to estimate the rotation matrix and translation vectors through the least squares method to convert the relative coordinates of the UAVs into absolute coordinates, which improves the accuracy of localization.
The rest of this article is organized as follows.
Section 2 presents the system model. The proposed BO-based cluster networking and ASNSMS-based cooperative localization algorithm for multi-UAVs are given in
Section 3. The simulation is illustrated in
Section 4. Finally,
Section 5 concludes this paper.
2. System Model
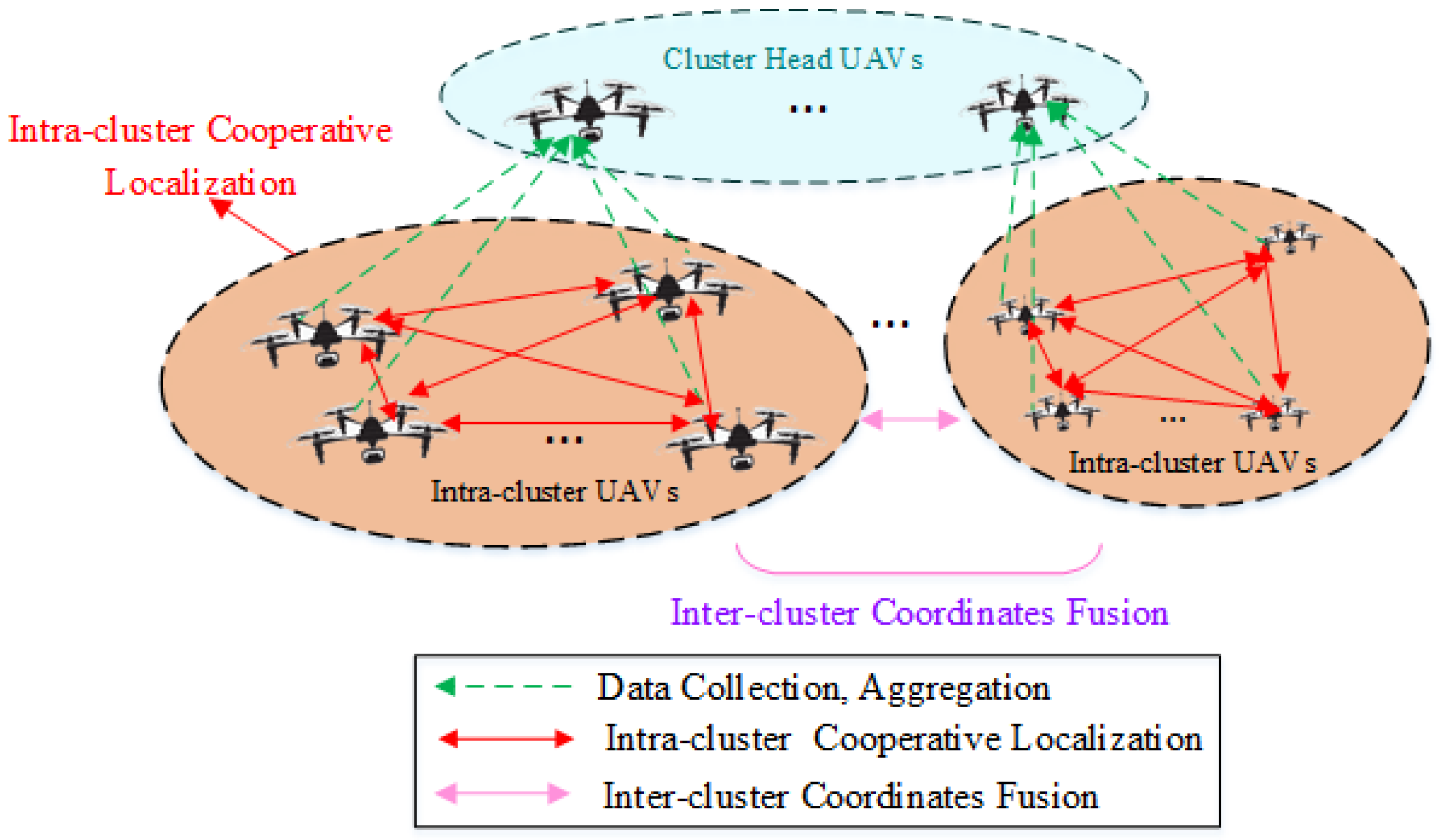
A distributed cooperative positioning model for a UAV swarm utilizing clustered network-based localization is depicted in
Figure 1. The UAV cluster is structured in a two-tier network. In the upper tier, cluster head UAVs, selected from sub-networks, are tasked with data collection, aggregation, and communication with ground facilities. In the lower tier, UAVs within each cluster gather reconnaissance data across the network coverage and manage routing for inter-node communication.
We consider a set of
N available anchor nodes of UAVs, each equipped with GPS receivers and denoted as
within a 3D space, where
represents the GPS coordinate vector of the
ith UAV. Within a cluster comprising
M UAVs
, the coordinate matrix for each UAV is denoted as
, where
is the 3D coordinate vector of the
ith UAV node. The Euclidean distance between node
i and node
j is given by
where
represents the measurement error, and the Euclidean distance measurement is
. The Euclidean distance matrix for a UAV swarm is thus defined as follows:
where
,
(
).
The main communication link in the cooperative operations of a UAV swarm is the Line of Sight Link (LoS) link [
38], where the inter-node communication message power gain
is defined as follows:
where
denotes the unit distance channel gain. Consequently, the signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR) of the communication link between the
i-th node and the
j-th node is expressed as follows:
where
denotes the interference node set, the environment noise
is
, and
is the
k-th sub-network of the UAVs swarm.
Each node can independently and randomly transmit information to others at each time slot [
33], allowing the interference expectation
to be described as follows:
where
r is the interference rate. Thus, the SINR can be further approximated as follows:
A radio energy model characterizes the energy consumption of UAV nodes [
39], distinguishing between the free-space loss model and the multipath fading loss model based on the transmission distances
d. When
, a free-space path loss model is adopted, and the path loss is inversely proportional to the square of the distance; when
, a multipath fading path loss model is adopted, and the path loss is inversely proportional to the fourth power of the distance. Thus, the energy consumption for sending and receiving data
and
for
k bits by UVA nodes is respectively shown in (
7) and (
8),
where
is the coefficient of the free-space model circuit,
is the coefficient of the multipath loss model circuit,
is the energy consumption per unit bit of data transmission,
d expresses the distance between UAV transmitting and receiving data nodes, and the model differentiation threshold is
. In the case of
, the free-space loss model is utilized to construct
; in another case, the multipath fading loss model is used.
In addition to routine data forwarding tasks, the UAV head nodes in the cluster also undertake an in-cluster data fusion task. This not only effectively reduces the frequency of network node communication and data transmission but also minimizes the overall energy consumption of data fusion,
where
represents the unit bit data fusion energy consumption, and
is the number of ordinary UAV nodes within the cluster.
4. Simulation
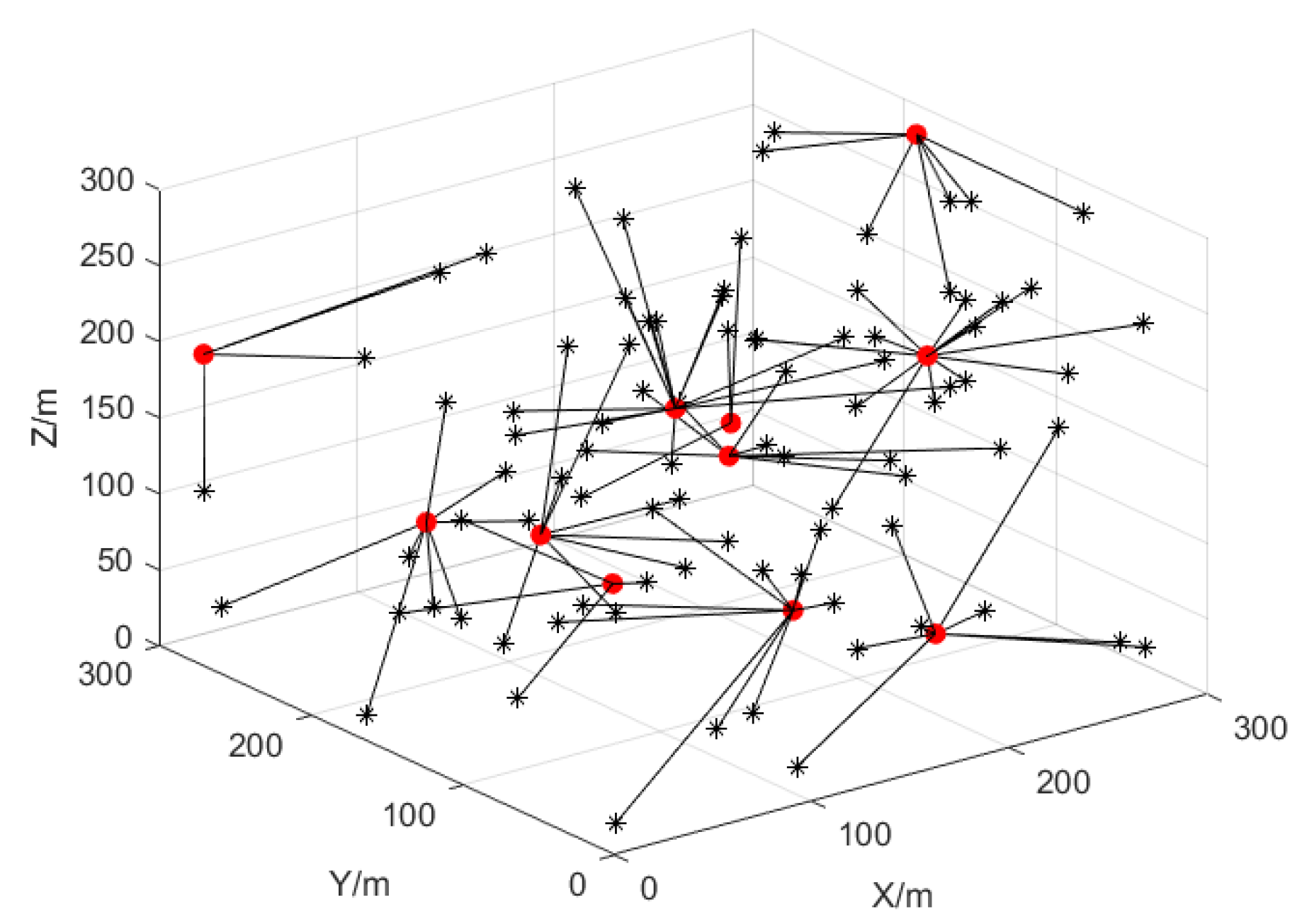
According to [
37], 100 UAVs are chosen evenly across a space of 300 × 300 × 300 m
3. The UAVs’ communication range is 60 m to ensure sufficient connectivity while avoiding signal interference. The root mean square error (RMSE) is used to quantify the positioning accuracy, which is expressed as follows:
where
is the estimated coordinate and
is the real coordinate. The UAV is made to move in a random model in the simulation, and the node positions change randomly in each round of simulation to reflect the mobility of the UAV nodes. The ranging and angular errors of the UAVs in 3D obey the Gaussian distribution, and the angle error is
and the ranging error is
. The situation where the UAV nodes enter the communication range of neighboring UAVs is depicted in
Figure 2, where the cluster head UAV node is represented by a red solid dot and the ordinary UAV nodes within the cluster are marked with a black “*”.
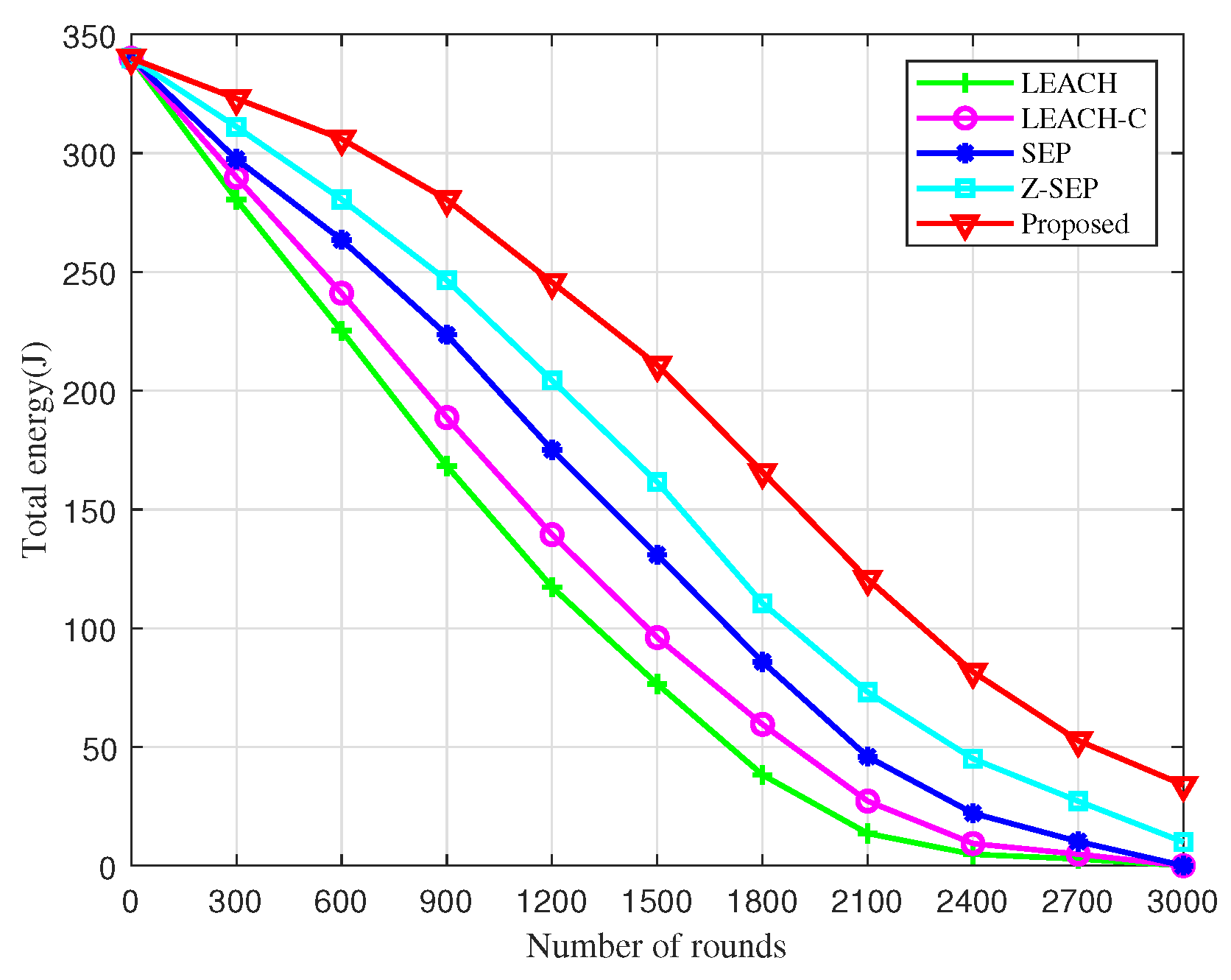
Figure 3 presents a comparison of the residual energy among five different algorithms. It is observable that the residual energy of the network diminishes as the number of simulation rounds increases, reaching 3000 rounds. Notably, the residual energy of the network utilizing the proposed algorithm is significantly higher than that of the other algorithms at the same juncture. Moreover, the total residual energy of the UAV network under the BOCN-ASNSMS-based cooperative localization algorithm is considerably greater than that of other algorithms during the same period, demonstrating its effectiveness in reducing energy consumption during sub-cluster networking and thereby prolonging the network’s operational lifetime. This enhancement is due to the BO-based cluster head election mechanism, which extends the network lifetime and reduces the energy consumption of UAV nodes through dynamic reclustering. The proposed algorithm exploits energy consumption equalization and network lifetime enhancement by introducing the intra-cluster node density and cluster head distribution to optimize the fitness function, and using move-in–move-out operations to trigger dynamic re-election. The higher the node density around the cluster head, the higher the efficiency of data fusion and forwarding, and the lower the energy consumption.
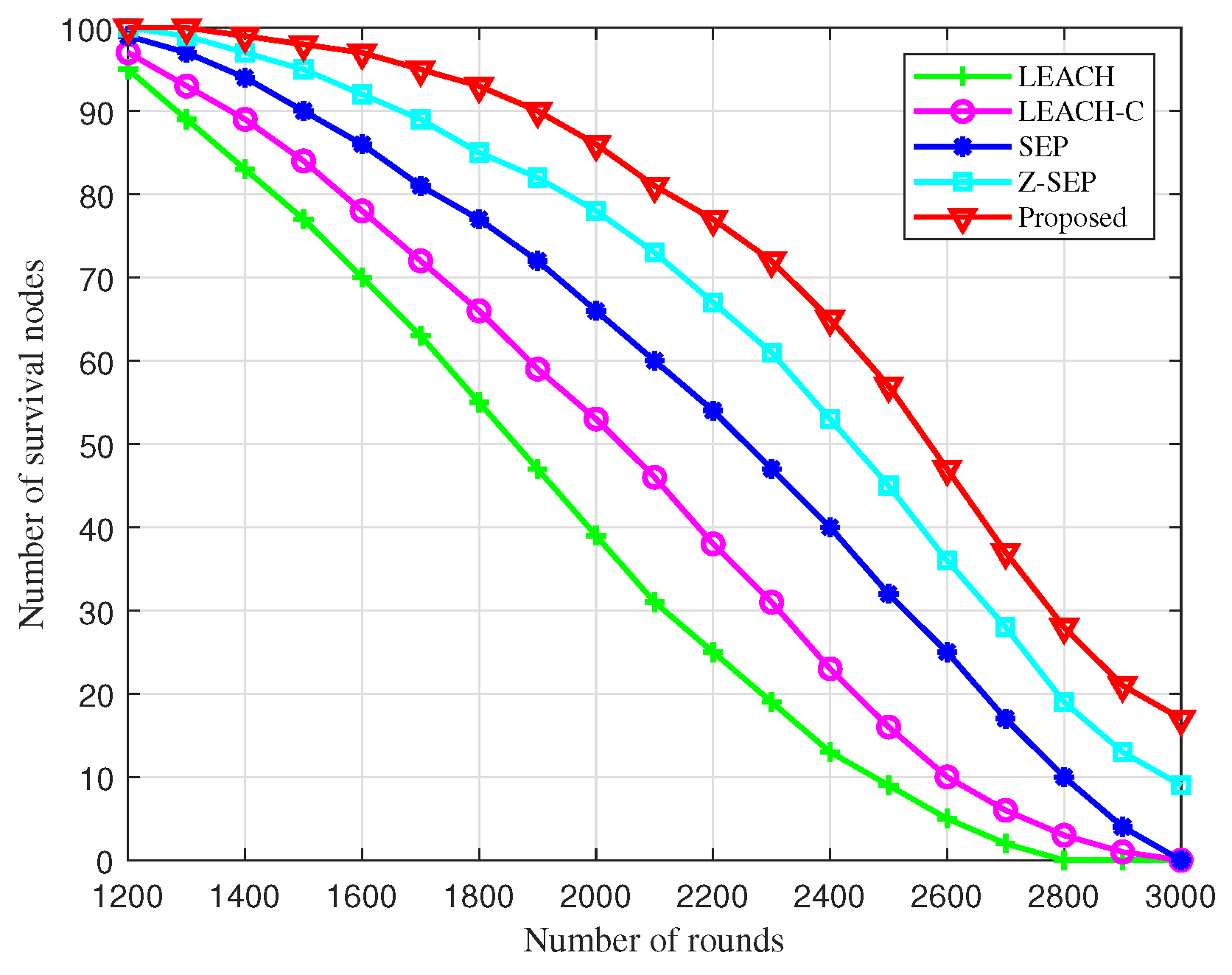
Figure 4 illustrates the comparison of surviving nodes across different algorithms during cluster networking. Under conditions of a single energy supply, nodes succumb to energy depletion as the number of rounds increases. The BOCN-ASNSMS-based cooperative localization algorithm allows the network to sustain more surviving nodes over an extended period, thus enhancing the operational quality duration of the network. At 1400 rounds, dead nodes first appear in the simulations using the proposed algorithm; comparatively, these dead nodes manifest later than in other algorithms, indicating superior performance during the network stabilization phase and effectively extending the endurance of the UAV network. This performance boost is due to the BO-based cluster networking algorithm’s strategic optimization of cluster head election, which reduces the frequency of nodes becoming cluster heads through migrate-in and migrate-out operations, ensuring effective load balancing among network nodes.
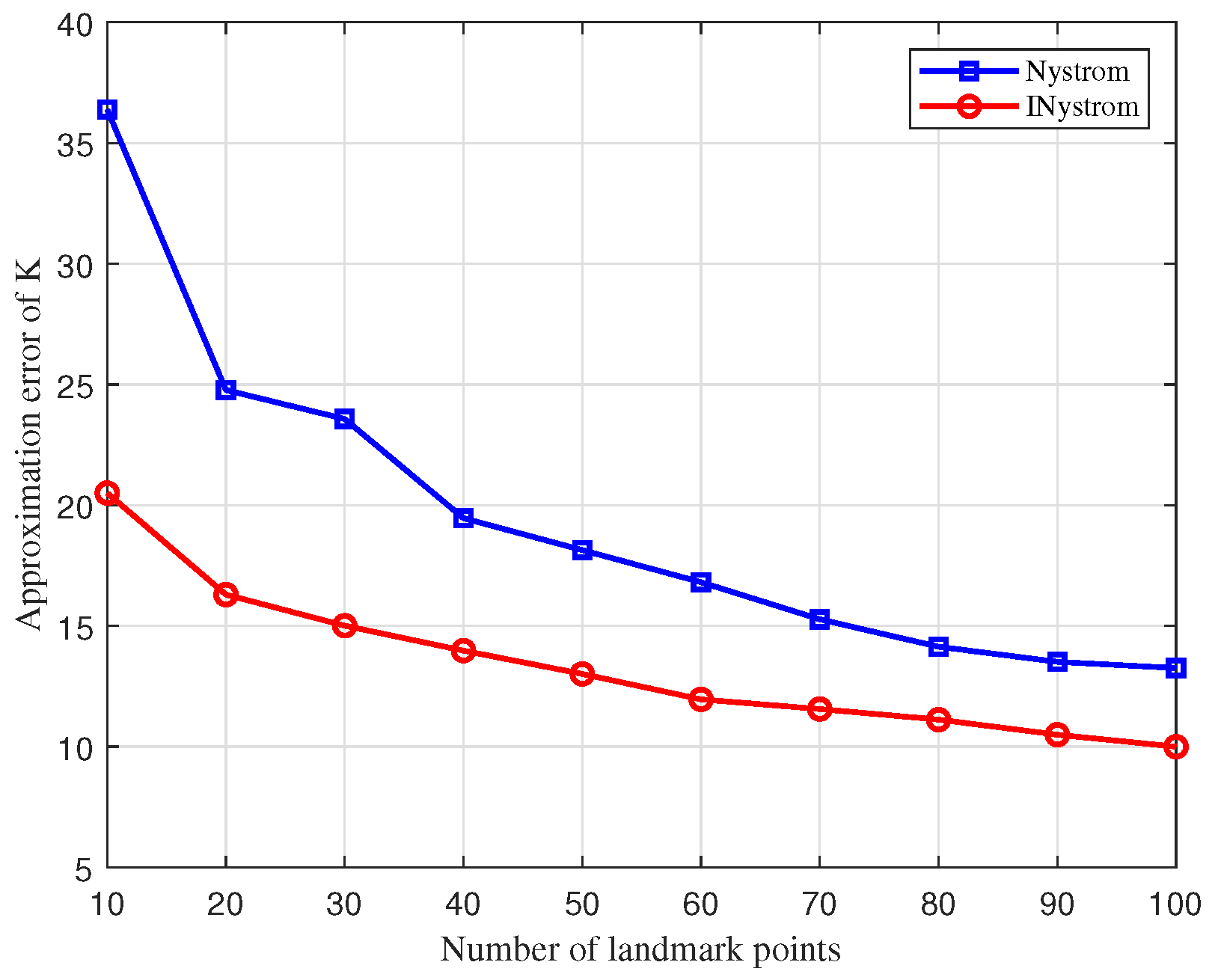
The approximation error comparison curves for the traditional Nystrom approximation algorithm and the improved Nystrom approximation algorithm (INystrom) are depicted in
Figure 5. Through low-rank approximation error experiments on coded samples with 100 marked points, the INystrom approximation algorithm displays a significantly reduced approximation error relative to the traditional Nystrom method. The INystrom algorithm enhances the construction process of the sample matrix by integrating an adaptive sampling method, which not only inherits the advantages of the adaptive algorithm but also diminishes computational complexity. By dynamically updating the probability of row vectors being selected during multiple traversals, the samples obtained are more representative and accurately depict the original dissimilarity measure matrix.
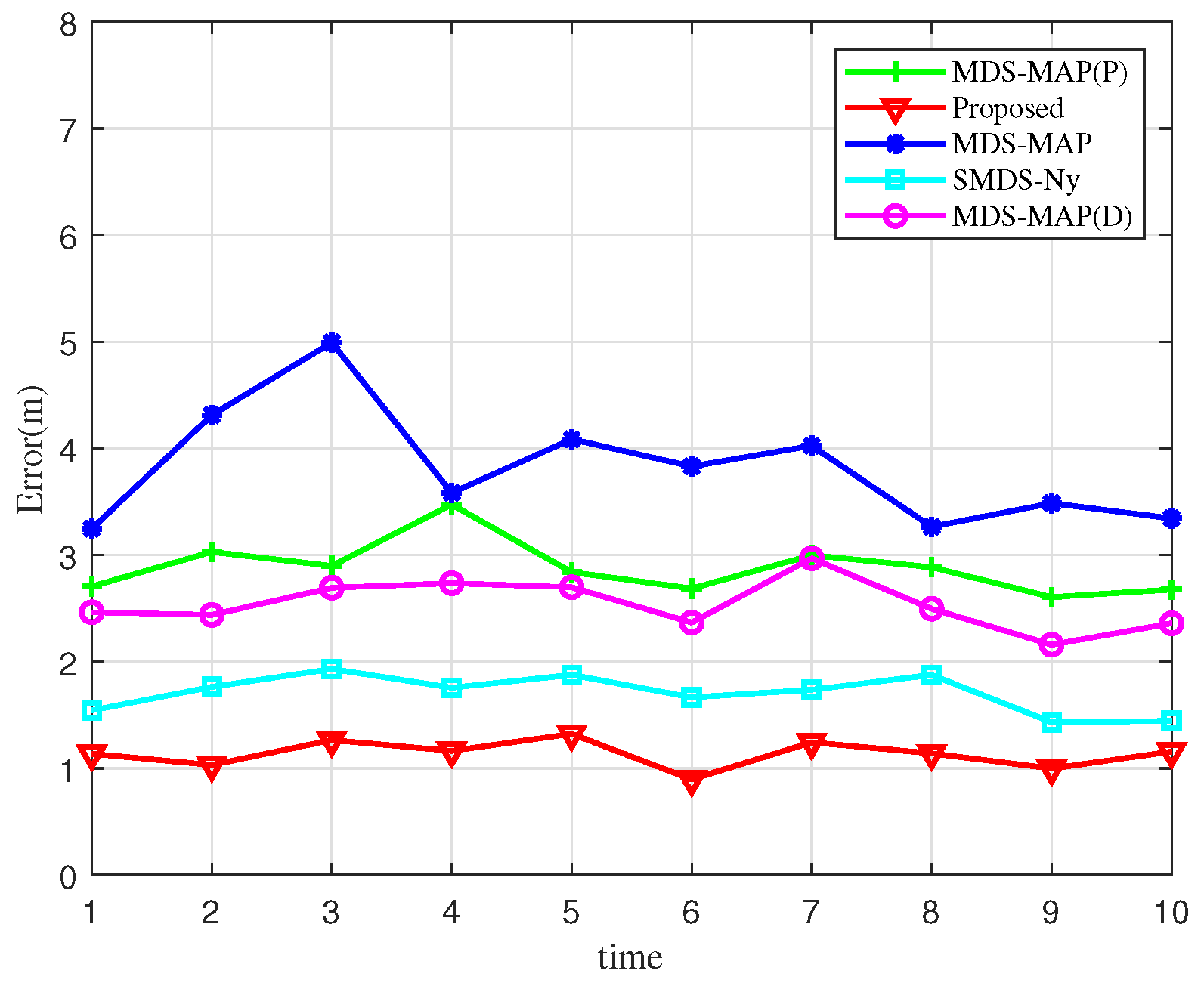
Figure 6 presents a comparison of localization errors across 10 simulation experiments. By examining the error curves of various algorithms, it becomes evident that the algorithm proposed in this study achieves the lowest localization error distribution, with notably smaller fluctuations compared to its counterparts. This demonstrates the accuracy of the BOCN-ASNSMS-based positioning algorithm, which consistently maintains the lowest error levels. The MDS-MAP algorithm, in contrast, exhibits larger fluctuations in localization error. This variability arises because the MDS-MAP algorithm substitutes actual ranging data with the shortest path computations to complete the distance matrix when direct ranging information is unavailable, effectively addressing the limitations of traditional MDS algorithms in non-fully connected networks. However, this approach introduces significant errors in estimating the distances of nodes beyond the single-hop communication range, thereby increasing overall localization errors.
Figure 7 illustrates the relationship between localization errors and the cumulative distribution function (CDF) for various unmanned aerial node localization algorithms. At a CDF value of 0.8, the localization error for the proposed algorithm is approximately 1.3 m, outperforming the SMDS-Ny algorithm and performing significantly better than the MDS-MAP algorithm, which shows the poorest performance. This analysis suggests that the localization error of 80% of nodes using the proposed algorithm is less than 1.3 m, indicating superior performance. Moreover, the slope of the curve associated with the BOCN-ASNSMS algorithm is steeper than that of other algorithms throughout the analysis, signifying smaller fluctuations and enhanced localization accuracy. This superior performance is attributed to the use of an adaptive sampling method in the Nystrom SMDS kernel matrix, which optimizes the selection of row vectors to construct the sample matrix, thereby minimizing the estimation error in the kernel matrix approximation and consequently reducing the localization error.
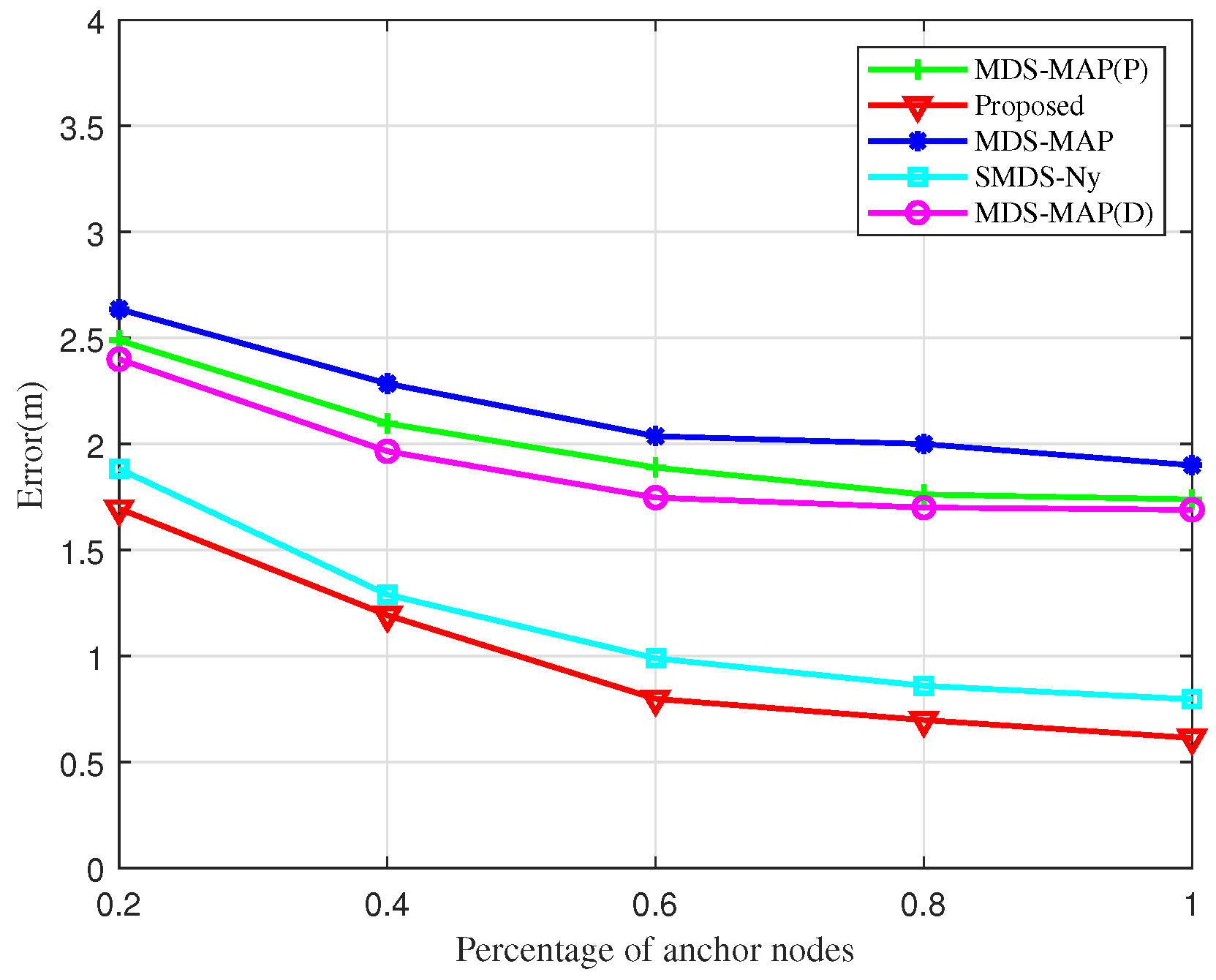
Figure 8 depicts the impact of increasing the proportion of anchor nodes on UAV node localization error within the cluster network. As the percentage of anchor nodes increases, there is a general decrease in localization error, with the BOCN-ASNSMS algorithm outperforming others under comparable conditions. The MDS-MAP algorithm records the highest error rates, whereas the proposed algorithm consistently shows the lowest. The SMDS-based algorithm, which enriches the traditional MDS approach with angular data in addition to ranging information, demonstrates significantly enhanced accuracy through the joint processing of these metrics. Furthermore, when the proportion of anchor nodes exceeds 60%, further increases in their number yield diminishing reductions in localization errors for all algorithms. This plateau effect is due to the reliance on inter-node ranging and angular data, along with anchor nodes facilitating coordinate alignment; hence, beyond a certain threshold, additional anchor nodes contribute minimally to reducing localization errors.
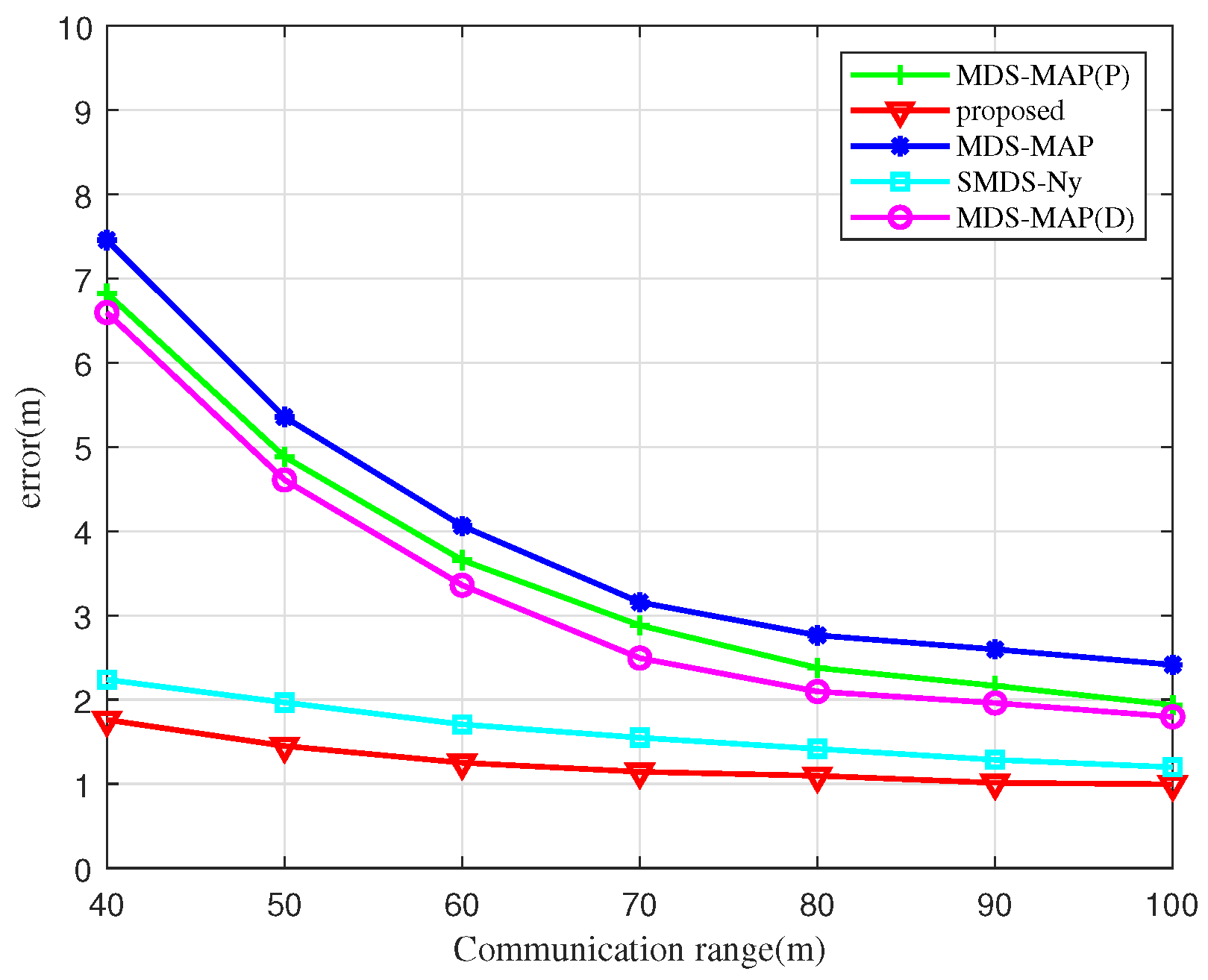
Figure 9 illustrates the impact of communication distance on UAV node localization errors using various algorithms. As shown, the localization error decreases with increasing communication distance for all algorithms examined. For communication distances under 50 m, the MDS-MAP and MDS-MAP(D) algorithms experience larger localization errors due to non-connected regions between UAV nodes. This leads to significant errors when the shortest path distance is used as a substitute for actual distance information. At a communication distance of 60 m, the localization errors of the SMDS-Ny algorithm and BOCN-ASNSMS are significantly smaller than those of the MDS-MAP and MDS-MAP(P) algorithms. This suggests that traditional MDS-based localization algorithms are notably influenced by communication distances among UAV nodes, while the SMDS-Ny algorithm and our proposed algorithm exhibit smaller errors less affected by communication distance, thanks to the integration of angle measurement data. Moreover, when the communication distance exceeds 70 m, the relationship curve between communication distance and localization error begins to plateau, indicating that further increases in communication distance lead to a more connected network, thus diminishing the influence of communication distance on the localization error of different algorithms.
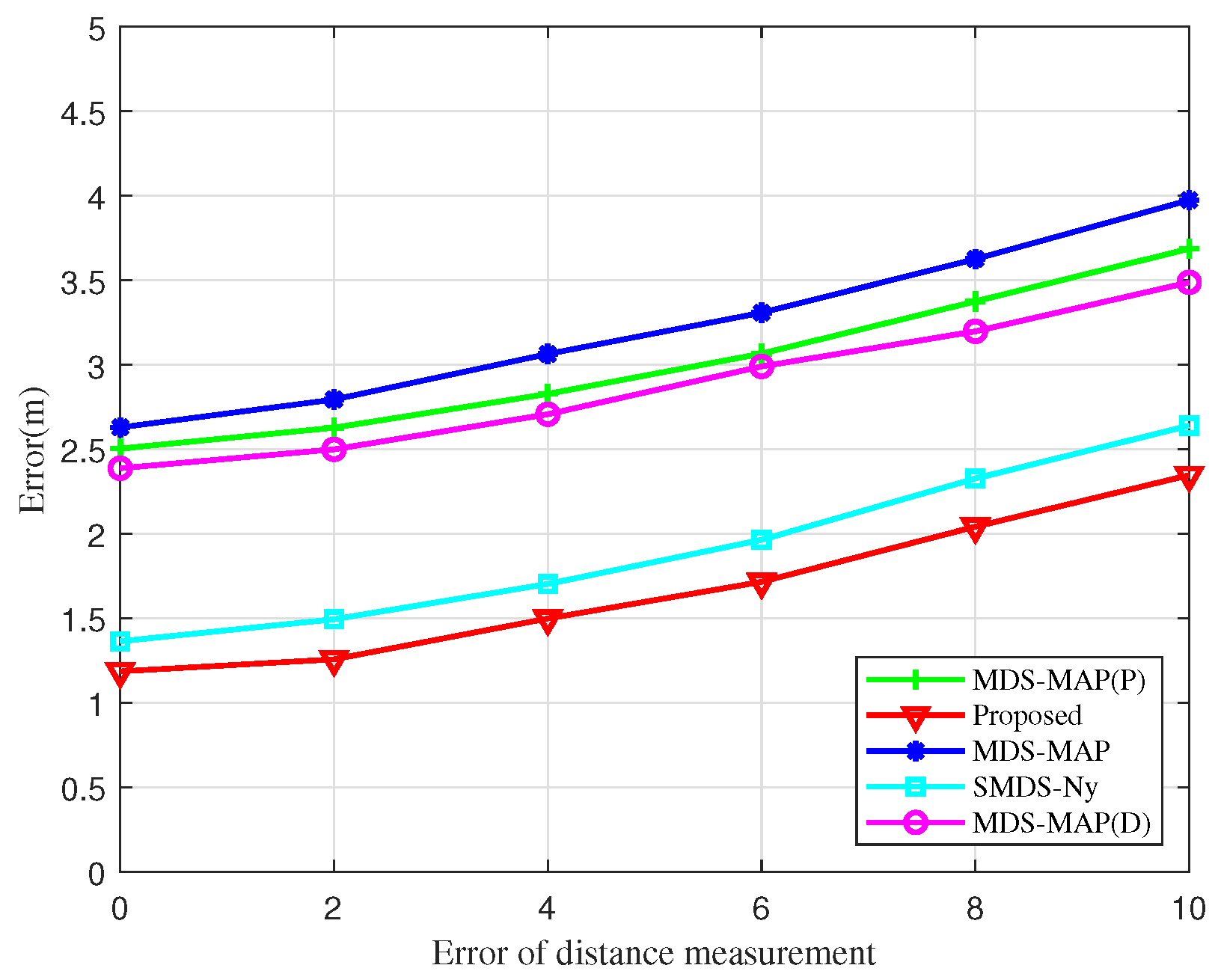
Furthermore, a simulation analysis assessing the impact of ranging errors on localization errors across various algorithms is performed in
Figure 10. The errors associated with the BOCN-ASNSMS localization algorithm are consistently lower than those of other algorithms under identical distance measurement errors. Notably, the SMDS-based localization algorithm displays a smaller error compared to the traditional MDS-based algorithm, attributed to the SMDS algorithm’s incorporation of angle measurement information alongside distance measurement. Although localization errors for each algorithm increase in direct proportion to the ranging error, the growth rate of these errors is minimal. This demonstrates that the proposed algorithms not only deliver superior localization performance but also exhibit robust resistance to the effects of ranging errors.
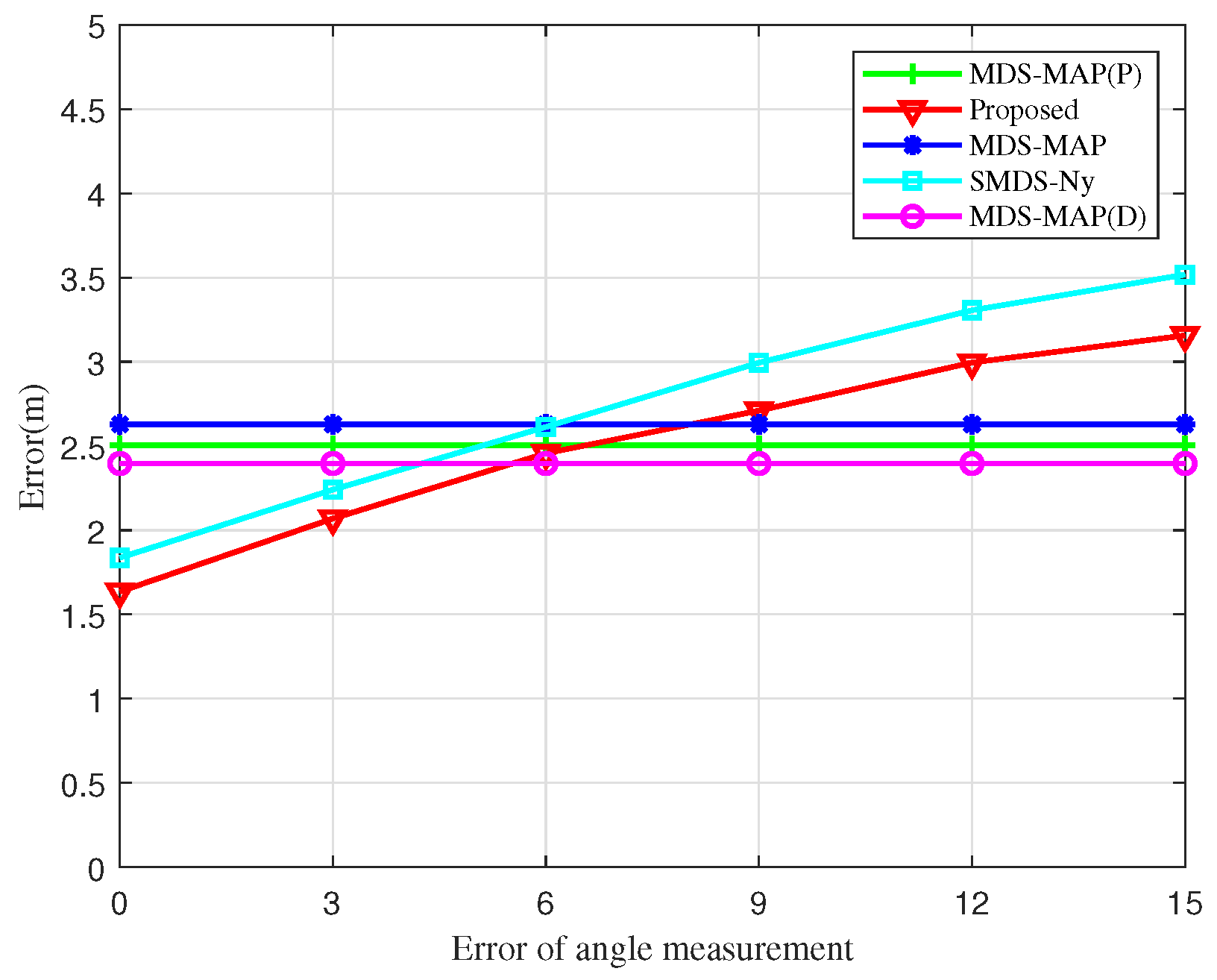
Figure 11 explores the influence of angular measurement error on the localization error of UAV nodes. As the angular measurement error increases, both the SMDS-Ny and the BOCN-ASNSMS algorithms show an increase in localization errors. However, under identical angular measurement conditions, the BOCN-ASNSMS algorithm consistently achieves a smaller localization error compared to the SMDS-Ny algorithm. This performance enhancement is due to the proposed algorithm’s use of an adaptive sampling method to construct the matrix, which more accurately represents the information of the original kernel matrix, thus further reducing localization errors. The MDS-MAP, MDS-MAP(D), and MDS-MAP(P) algorithms rely solely on inter-node distance measurements to construct the matrix and therefore do not exhibit changes in localization error with increasing angular measurement error. Additionally, the BOCN-ASNSMS algorithm demonstrates a slower increase in localization error compared to the SMDS-Ny algorithm at later stages. This is because the proposed algorithm first performs cluster-based processing on the network, which mitigates the impact of angular measurement errors on localization errors compared to centralized localization algorithms.
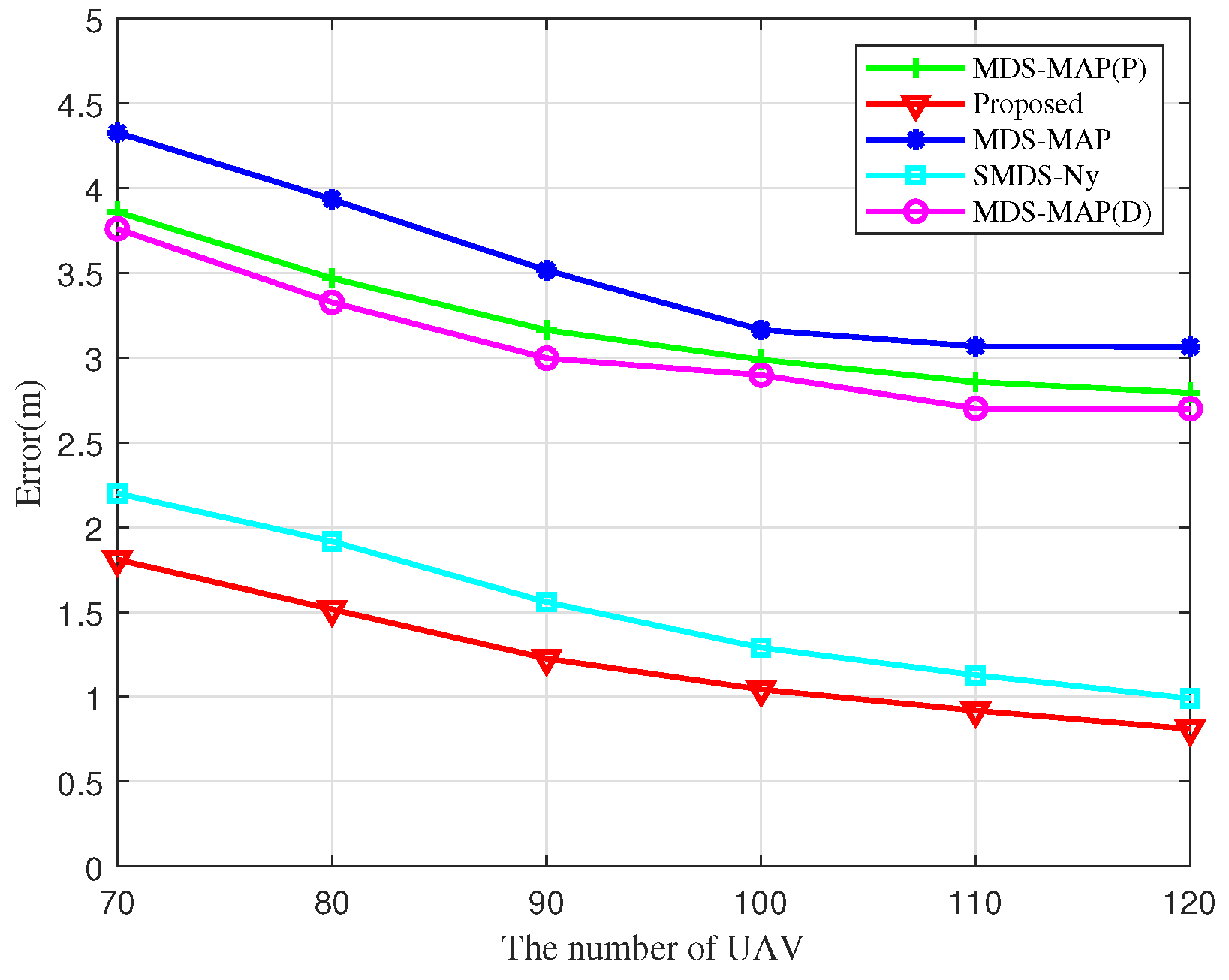
Figure 12 reveals the effect of the number of UAV nodes on localization errors. The localization errors of the different algorithms decrease monotonically with an increase in the number of UAV nodes, and the proposed algorithm consistently exhibits the lowest localization error compared to other algorithms. This improvement is attributed to the expectation value in a fully connected network. As the number of links within the UAV cluster increases in proportion to the number of UAV nodes, observed distance and angle measurements are continuously supplemented and refined, improving the quality of the entire heterodyne measurement kernel matrix and reducing the localization error of the algorithm. Overall, this analysis demonstrates that the BOCN-ASNSMS algorithm outperforms other algorithms in terms of localization performance.