Novel Gain-Optimized Two-Step Fusion Filtering Method for Ranging-Based Localization Using Predicted Residuals
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Setting the distance measurement based on TOA as a Gaussian stochastic process, adopting the nonlinear system parametric method to derive the pseudo-linear equation with unknown multipath delay, then applying the weighted least squares (WLS) criterion and the effective analytical calculation of process parameters to obtain the approximate solution for the target primary position estimation that can approximate the CRLB based on TOA measurement estimation.
- Realizing the optimal estimation, using the new Gaussian distributed white noise statistic to whiten the observed colored noise to eliminate the adverse effect of the colored noise on the filter localization, and update the Kalman filter parameters after obtaining the new measurement model.
- Setting the correlation coupling matrix to realize the decoupling according to the independent conditions of process and observation error, to derive the filter decoupling measurement model, and then update the filter parameters.
- Because of the problem of error in noise modeling, realizing self-optimization filtering estimation using predicting residual statistics, noise covariance, and gain update, and by compensating the estimation error again to accelerate localization convergence and enhance the robustness of the system. Finally, the feasibility and effectiveness of the positioning algorithm are verified by numerical simulation experiments.
2. Related Work
3. TOA Ranging Modeling and Initial Positioning
3.1. Location Information Modeling
3.2. Positioning Algorithm Based on the Observed Pseudo-Linearized Analytical Solution
| Algorithm 1. The initial localization algorithm |
| 1: Initialization, set , calculate , , and . |
| 2: If , then select the other algorithm as an alternative. |
| 3: If , then have from Equation (10). |
| 4: If , then have from Equation (11). |
| 5: If , then obtain two from Equation (12). |
| 6: the uniqueness of the solution can be solved by Equation (13). |
| 7: return. |
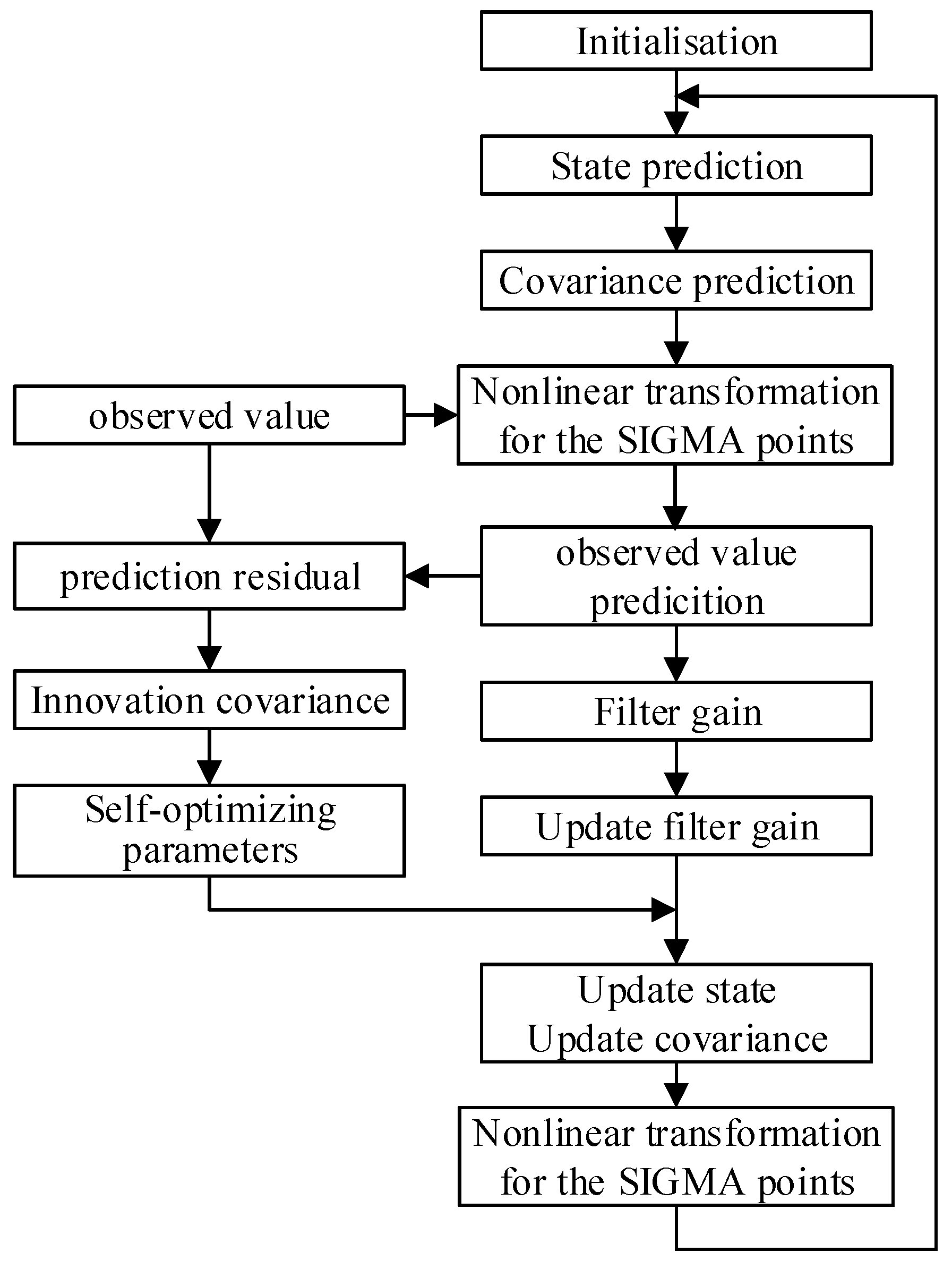
4. Self-Optimized Target Filter Localization Method with Colour Noise Observation
4.1. Filter Localization Problem Modeling and the Basic UKF Algorithm
4.1.1. Filter Localization Problem Modeling
4.1.2. The Basic UKF Algorithm
4.2. Nonlinear Filtering of the Localization System Based on the Whitening of the Colored Noise
4.2.1. Colored Noise Modeling and Whitening-Based Filtering Methods
4.2.2. Noise Decoupling Filtering Algorithm
4.2.3. A Nonlinear Filtering Process Based on a New Measurement Model of the System
4.3. Self-Optimizing Parameter Filtering Algorithm Based on Prediction Residuals
5. Positioning Performance Evaluation
6. Numerical Simulation and Analysis
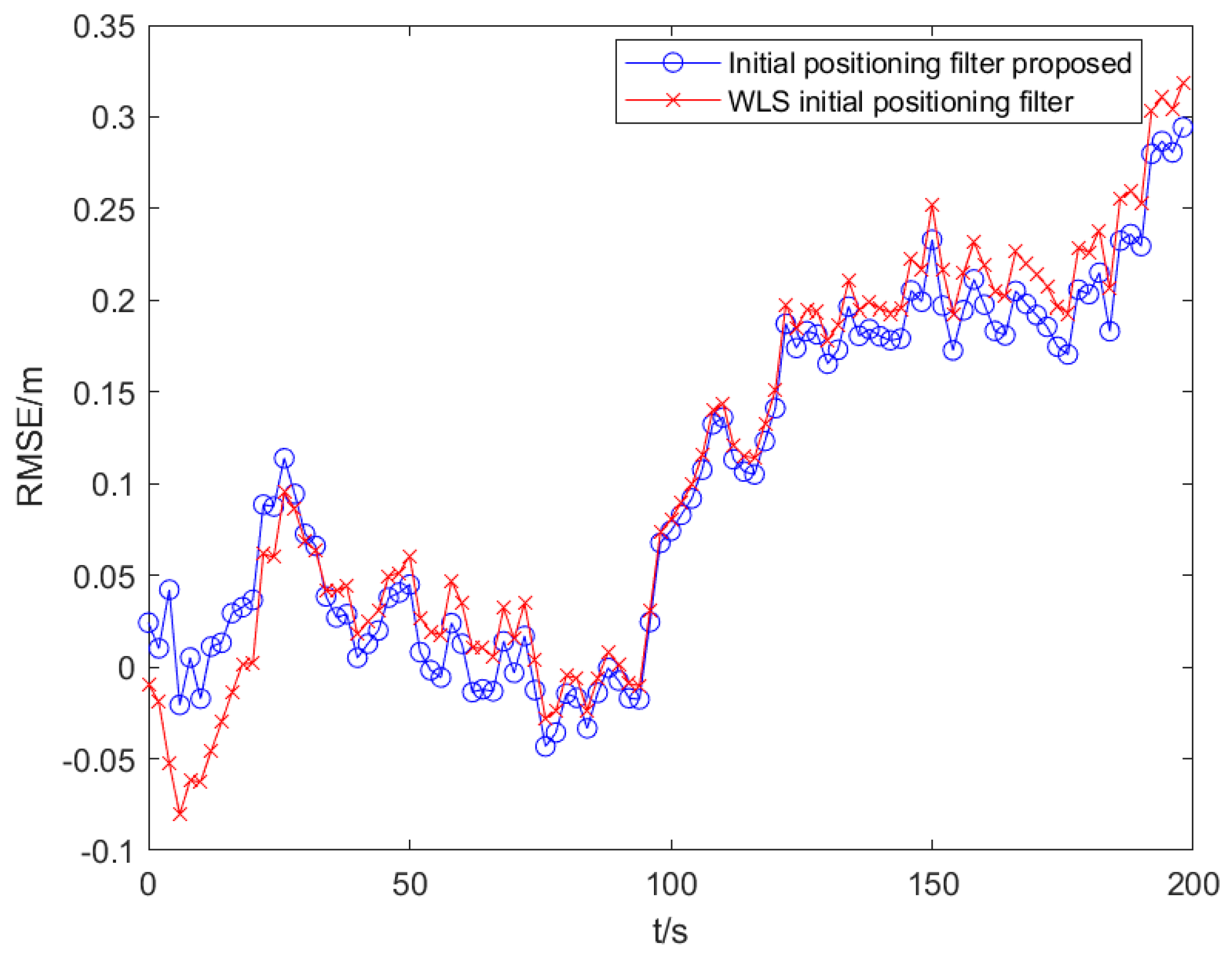
6.1. Initial Positioning Simulation
6.2. Filtering Simulation
6.2.1. Experimental Environment
6.2.2. Target Observation and Filtering Results
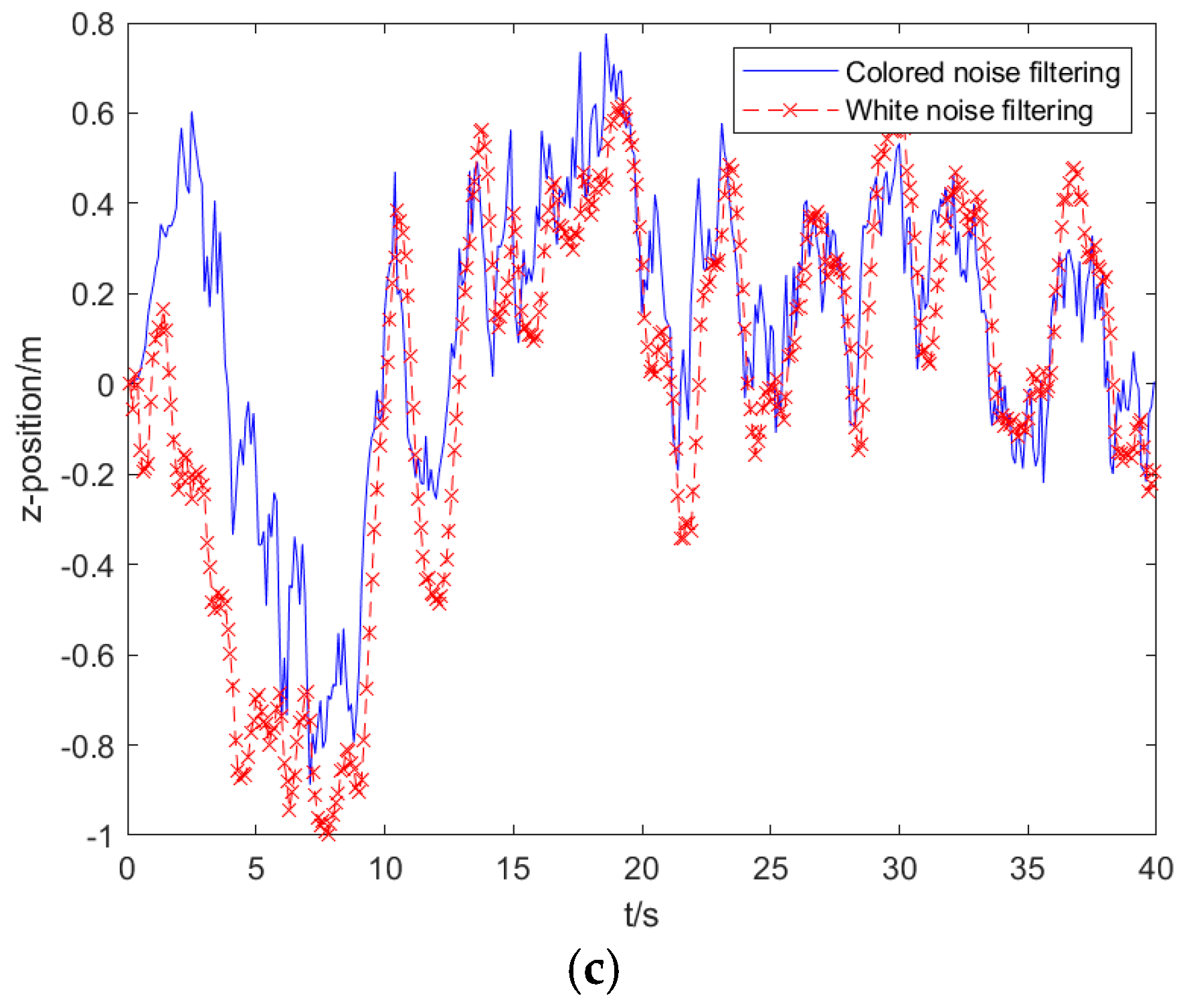
6.2.3. Comparison of Filtering Results Based on White Noise and Colored Noise
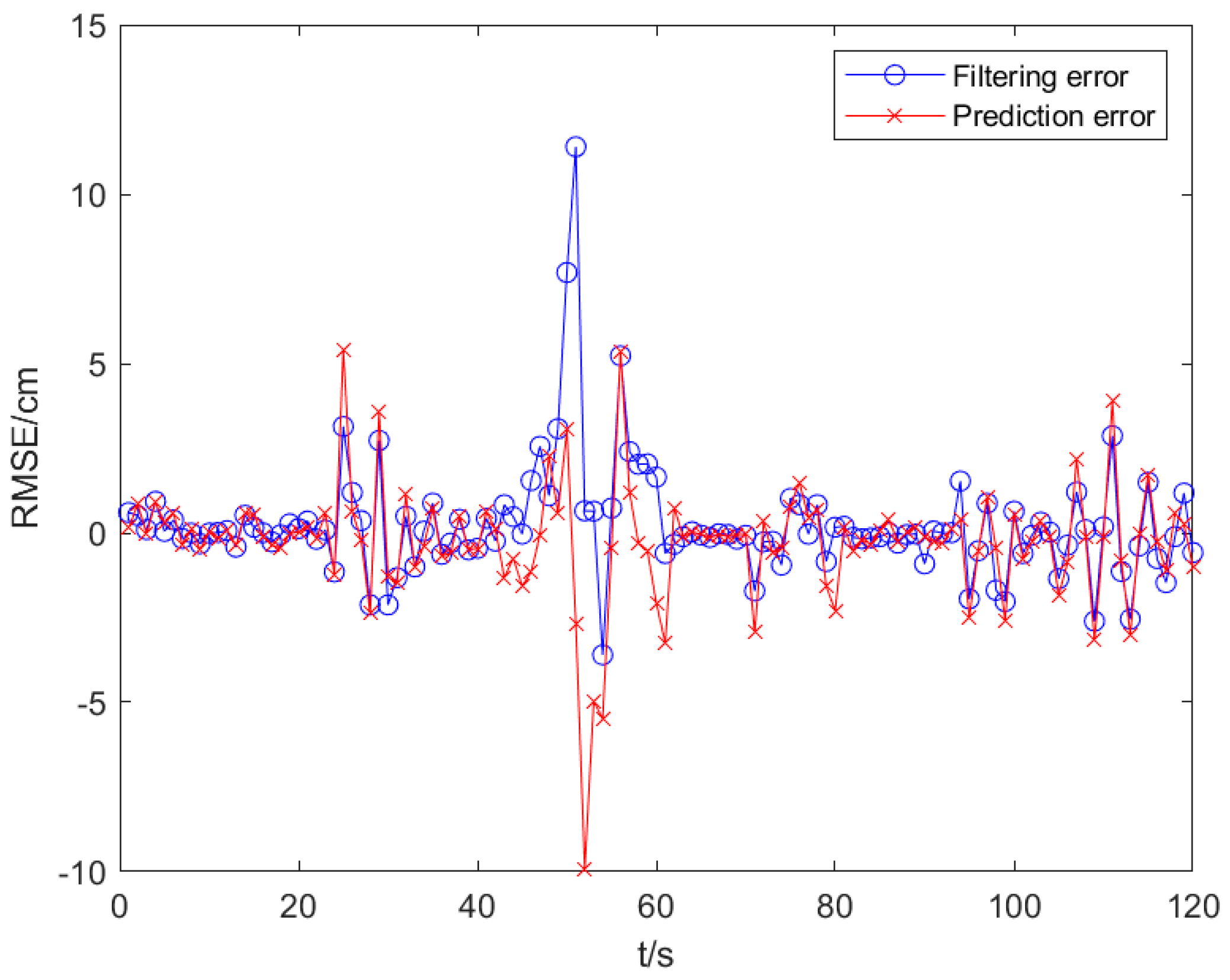
6.2.4. Prediction Error and Filtering Error
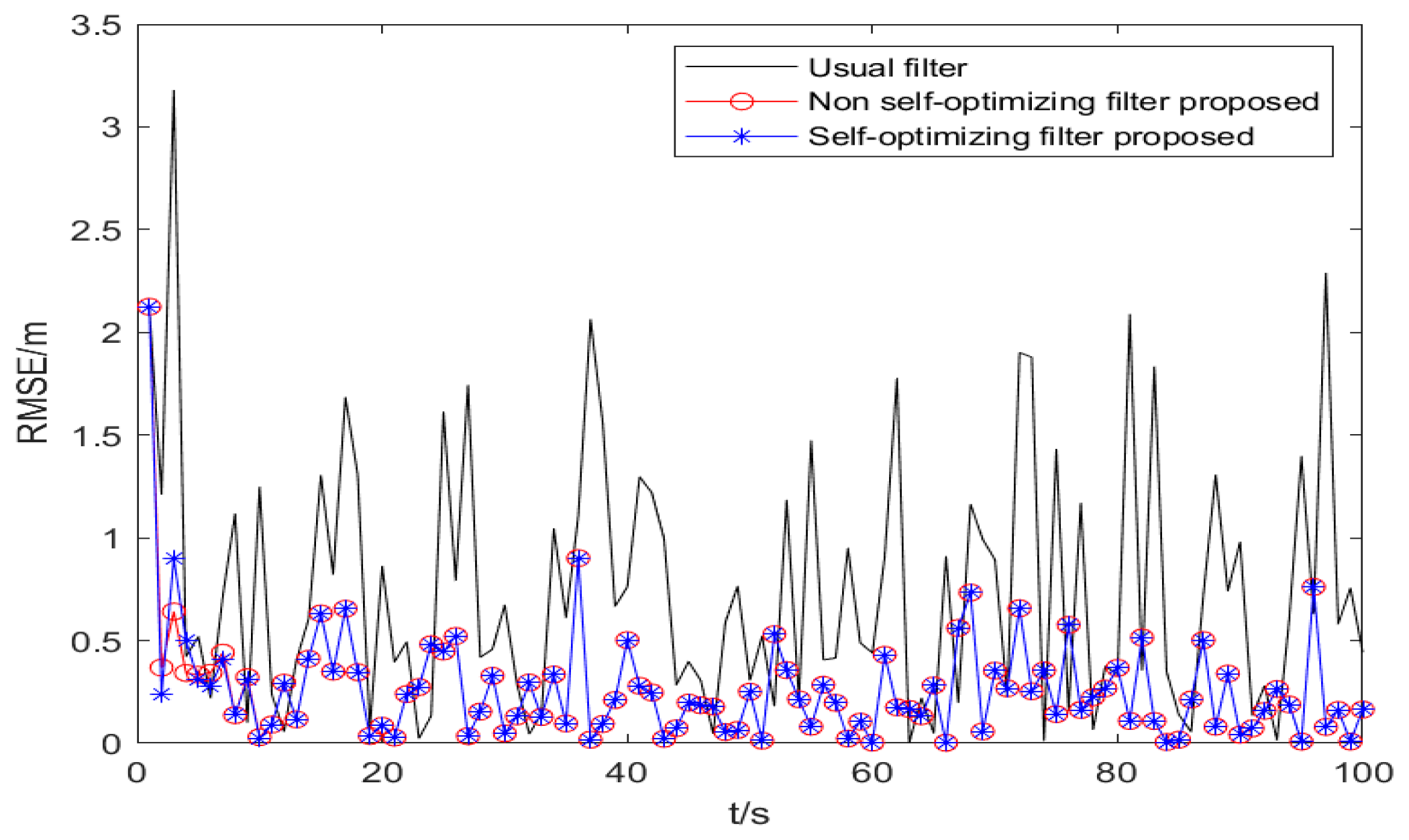
6.2.5. RMSE Error and Analysis Based on Colored Noise Processing
6.2.6. Filtering Results and Analysis Under Different Initial Positioning Conditions
6.2.7. Computation Time
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Isaia, C.; Michaelides, M.P. A review of wireless positioning techniques and technologies: From smart sensors to 6G. Signals 2023, 4, 90–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.L.D.; Eisenkraemer, G.H.; Carara, E.A.; Martins, J.B.; Monteiro, J. Mobile Localization Techniques for Wireless Sensor Networks: Survey and Recommendations. ACM Trans. Sens. Netw. 2023, 19, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruthi, S.P.; Panigrahi, T. Robust mixed source localization in WSN using swarm intelligence algorithms. Digit. Signal Process. 2020, 98, 102651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Xue, M.; Bi, Y. An indoor robust localization algorithm based on data association technique. Sensors 2020, 20, 6598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Zhang, S.; Guo, H.; Zhao, F.; Li, N.; He, M.; Li, Z.; Ma, R.; Wang, K.; Tao, W.-Q. A parametric optimization framework for fin-and-tube heat exchangers based on response surface methodology and artificial intelligence. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 253, 123775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Zhang, S.; Jin, P.; Li, N.; Yang, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, K.; Hao, X.; Zhao, F. An intelligent plate fin-and-tube heat exchanger design system through integration of CFD, NSGA-II, ANN and TOPSIS. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 233, 120926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Zhang, S.; Li, N.; Zhao, F.; Hao, X.; He, M.; Li, Z.; Ma, R.; Wang, K.; Tao, W.-Q. A fast design tool for compact heat exchangers tube geometry to enhance thermohydraulic performance using various AI models. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 271, 126635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, S.; Peng, T.; Jiang, W.; Ji, J.; Hao, X. An Integrated Framework Based on an Improved Gaussian Process Regression and Decomposition Technique for Hourly Solar Radiation Forecasting. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Zhang, S.; Peng, T.; Zhou, J.; Sun, X. A Composite Uncertainty Forecasting Model for Unstable Time Series: Application of Wind Speed and Streamflow Forecasting. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 209251–209266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coluccia, A.; Fascista, A. A review of advanced localization techniques for crowdsensing wireless sensor networks. Sensors 2019, 19, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafari, F.; Gkelias, A.; Leung, K.K. A survey of indoor localization systems and technologies. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2019, 21, 2568–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molaei, A.M.; Ramezani-Varkani, A.; Soheilifar, M.R. A pure cumulant-based method with low computational complexity for classification and localization of multiple near and far field sources using a symmetric array. Prog. Electromagn. Res. C 2019, 96, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Qi, X.; Wei, Q.; Liu, L. TOA NLOS mitigation cooperative localisation algorithm based on topological unit. IET Signal Process. 2020, 14, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Zhao, S.; Cui, X.; Lu, M.; Jia, M. Anchor self-localization algorithm based on UWB ranging and inertial measurements. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2019, 24, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Shen, Y. Joint spatiotemporal multipath mitigation in large-scale array localization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 67, 783–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garraffa, G.; Sferlazza, A.; D’Ippolito, F.; Alonge, F. Localization Based on Parallel Robots Kinematics As an Alternative to Trilateration. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Wang, C.; He, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Xia, X.G. Kalman-Filter-Based Integration of IMU and UWB for High-Accuracy Indoor Positioning and Navigation. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 3133–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S. Optimal sensor placement for target localization using hybrid RSS, AOA and TOA measurements. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 24, 1966–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katwe, M.; Ghare, P.; Sharma, P.K.; Kothari, A. NLOS error mitigation in hybrid RSS-TOA-based localization through semi-definite relaxation. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 24, 2761–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petukhov, N.; Chugunov, A.; Zamolodchikov, V.; Tsaregorodtsev, D.; Korogodin, I. Synthesis and experimental accuracy assessment of Kalman filter algorithm for UWB ToA local positioning system. In Proceedings of the 2021 3rd International Youth Conference on Radio Electronics, Electrical and Power Engineering (REEPE), Moscow, Russia, 1 April 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, K.; Chen, B. Converted state equation Kalman filter for nonlinear maneuvering target tracking. Signal Process. 2023, 202, 108741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Qiao, S.; Wang, G.; Chen, S.; Zhang, H. A modified adaptive Kalman filtering method for maneuvering target tracking of unmanned surface vehicles. Ocean Eng. 2022, 266, 112890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.D.; Kim, L.W.; Lee, H.K. A tightly-coupled compressed-state constraint Kalman Filter for integrated visual-inertial-Global Navigation Satellite System navigation in GNSS-Degraded environments. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2022, 16, 1344–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, W.; Li, K. Simulation experiment and analysis of GNSS/INS/LEO/5G integrated navigation based on federated filtering algorithm. Sensors 2022, 22, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ma, Z.; Chen, X. Generalized dynamic fuzzy NN model based on multiple fading factors SCKF and its application in integrated navigation. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 21, 3680–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Fang, Y. Vehicle state estimation for INS/GPS aided by sensors fusion and SCKF-based algorithm. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 150, 107315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, T. A novel method for AI-assisted INS/GNSS navigation system based on CNN-GRU and CKF during GNSS outage. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeyatdoost, N.; Bongards, M.; Bäck, T.; Wolf, C. Robust state estimation of the anaerobic digestion process for municipal organic waste using an unscented Kalman filter. J. Process Control 2023, 121, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Fu, X.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y. Unscented Kalman filter of graph signals. Automatica 2023, 148, 110796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaveni, B.V.; Reddy, K.S.; Reddy, P.R. Indoor tracking by adding IMU and UWB using Unscented Kalman filter. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2022, 123, 3575–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Gao, H.; You, J. In-flight alignment of integrated SINS/GPS/Polarization/Geomagnetic navigation system based on federal UKF. Sensors 2022, 22, 5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Zhao, P.; Wei, D.; Wang, Y. A robust indoor localization algorithm based on polynomial fitting and Gaussian mixed model. China Commun. 2023, 20, 179–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; So, H.C. TOA-based localization with NLOS mitigation via robust multidimensional similarity analysis. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2019, 26, 1334–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, F.; Etzlinger, B.; Liu, Z.; Hlawatsch, F.; Win, M.Z. A scalable algorithm for network localization and synchronization. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 4714–4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, S.; Huang, D. A TOA-based localization algorithm with simultaneous NLOS mitigation and synchronization error elimination. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2019, 3, 6000504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Ban, H.; Luo, X.; Zhao, H.; Guan, X. Joint localization and tracking design for AUV with asynchronous clocks and state disturbances. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 4707–4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Chen, Z.; Hu, X.; Li, X. Multi-source localization using time of arrival self-clustering method in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 82110–82121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, G.; Wu, X. Cooperative multiple target nodes localization using TOA in mixed LOS/NLOS environments. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 20, 1473–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, D.; Liu, R.-r.; Yin, J.-x.; Wu, Y. Structural total least squares algorithm for locating multiple disjoint sources based on AOA/TOA/FOA in the presence of system error. Front. Inf. Technol. Electron. Eng. 2018, 19, 917–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Peng, Y.; Li, H.; Xia, Y.; Zheng, W.X. Frequency domain joint-normalized stochastic gradient projection-based algorithm for widely linear quaternion-valued adaptive filtering. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2023, 71, 3898–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, B.; Jiang, Y. Enhanced fault detection and exclusion based on Kalman filter with colored measurement noise and application to RTK. Gps Solut. 2021, 25, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Dong, Y.; Li, Y.; He, W. Robust extended state estimation for nonlinear complex networks with colored noise. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part I J. Syst. Control Eng. 2023, 237, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-J.; Dou, C.-H.; Shen, F.; Sun, Q.-Y. Vehicle state estimation based on unscented Kalman filtering and a genetic-particle swarm algorithm. J. Inst. Eng. 2021, 102, 447–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Shen, Y.; Su, X.; Esposito, C.; Choi, C. A localization based on unscented Kalman filter and particle filter localization algorithms. IEEE Access 2019, 8, 2233–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

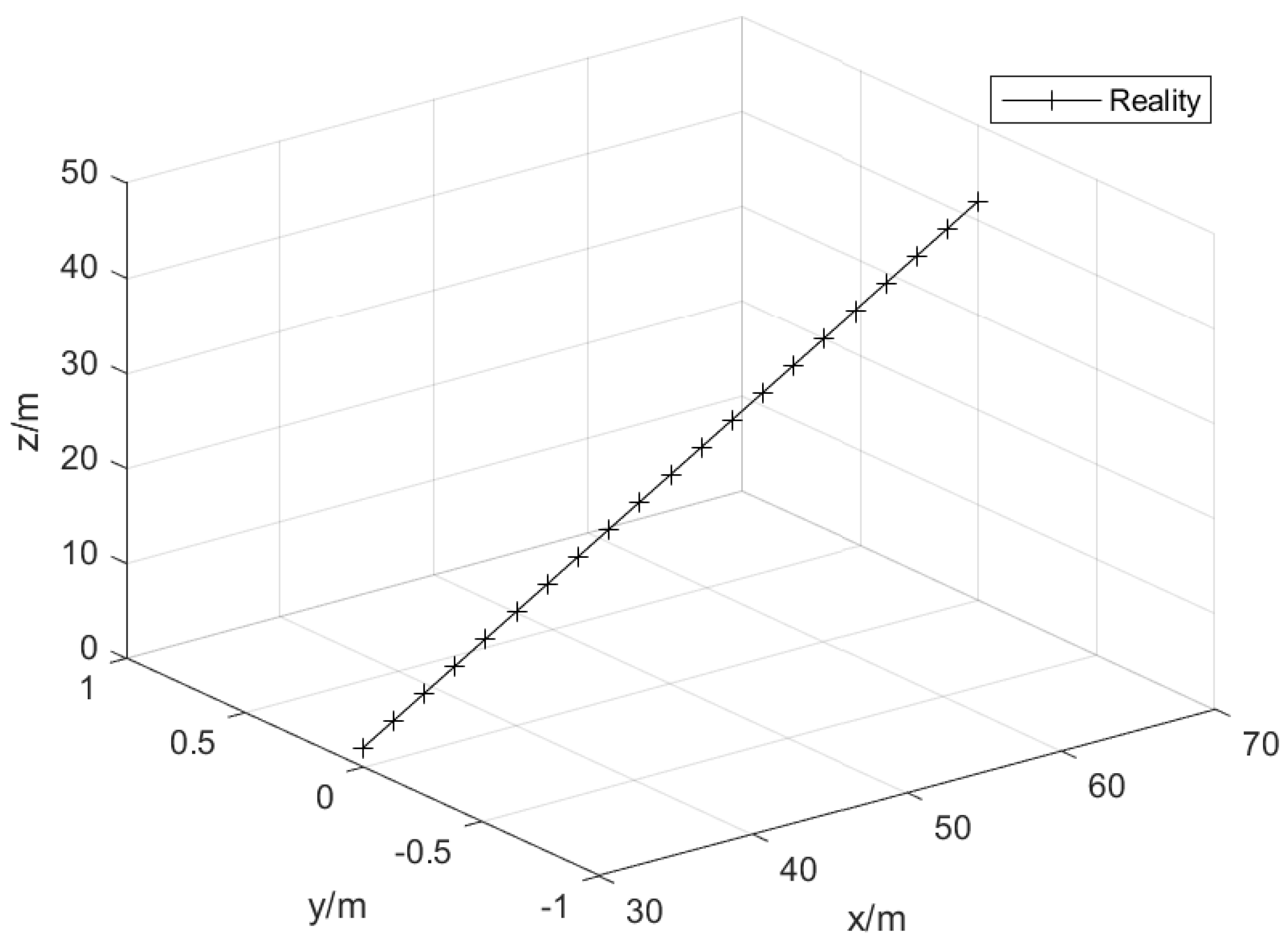



| Coordinates | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | −300 | 0 | 300 | −300 | 0 | 300 | −300 | 0 | 300 |
| y | 300 | 300 | 300 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −300 | −300 | −300 |
| z | −300 | −300 | 300 | 300 | 0 | 0 | 300 | 0 | −300 |
| Performance of Error (m) | Gaussian White Noise | Processed Colored Noise | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X-Axis | Y-Axis | Z-Axis | X-Axis | Y-Axis | Z-Axis | |
| Mean | −0.3857 | 0.2352 | −0.6384 | −0.2367 | −0.0153 | −0.4231 |
| Standard deviation | 0.6652 | 0.6256 | 0.6132 | 0.4428 | 0.4432 | 0.4284 |
| Algorithm | WLS Initial Positioning Filter | Initial Positioning Filter Proposed |
|---|---|---|
| Time (ms) | 10.78 | 11.85 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, B.; Zhang, X.; Sun, N.; Ni, H. Novel Gain-Optimized Two-Step Fusion Filtering Method for Ranging-Based Localization Using Predicted Residuals. Sensors 2025, 25, 2883. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092883
Chang B, Zhang X, Sun N, Ni H. Novel Gain-Optimized Two-Step Fusion Filtering Method for Ranging-Based Localization Using Predicted Residuals. Sensors. 2025; 25(9):2883. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092883
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Bo, Xinrong Zhang, Na Sun, and Hao Ni. 2025. "Novel Gain-Optimized Two-Step Fusion Filtering Method for Ranging-Based Localization Using Predicted Residuals" Sensors 25, no. 9: 2883. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092883
APA StyleChang, B., Zhang, X., Sun, N., & Ni, H. (2025). Novel Gain-Optimized Two-Step Fusion Filtering Method for Ranging-Based Localization Using Predicted Residuals. Sensors, 25(9), 2883. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092883





