BED-YOLO: An Enhanced YOLOv10n-Based Tomato Leaf Disease Detection Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
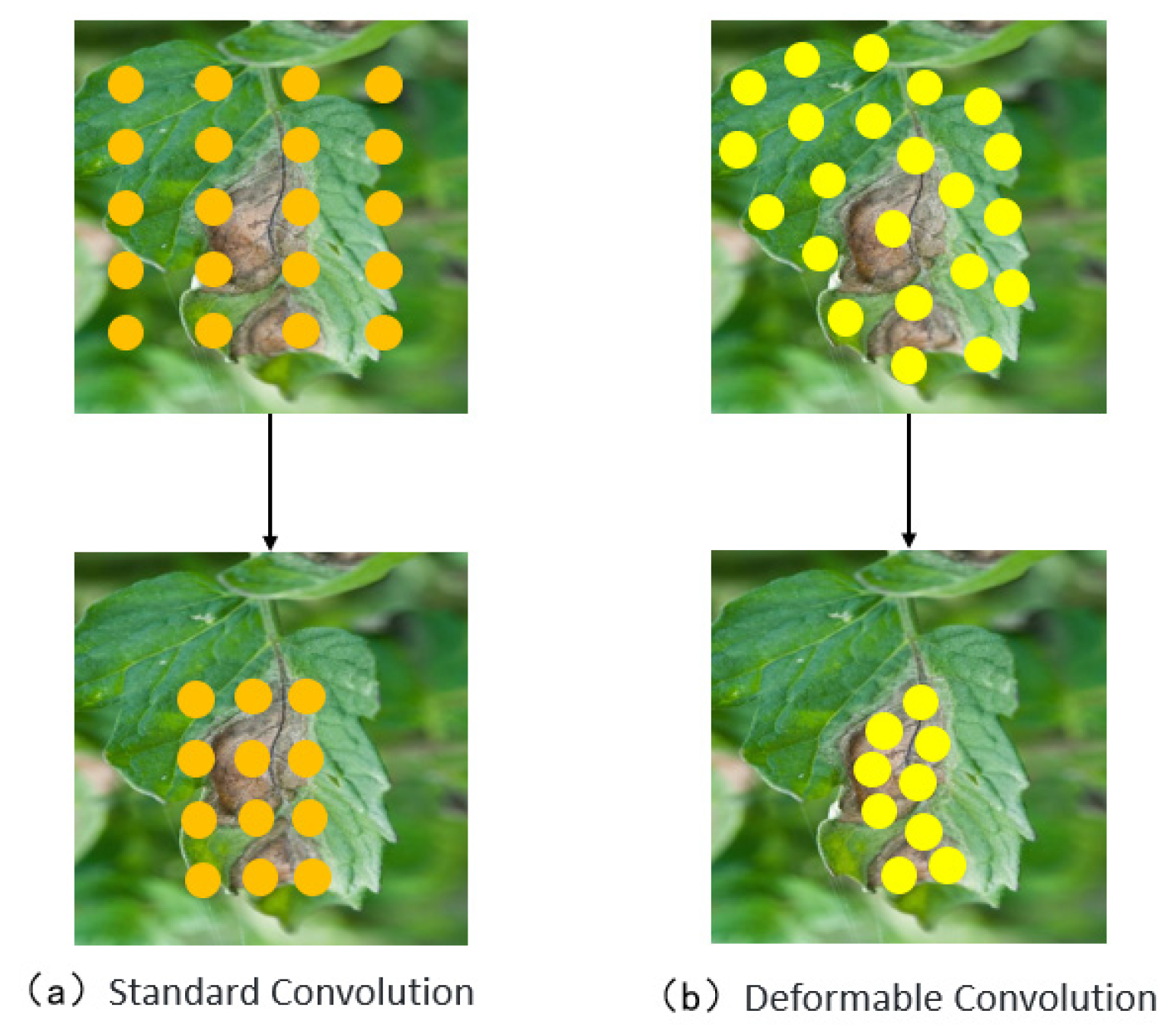
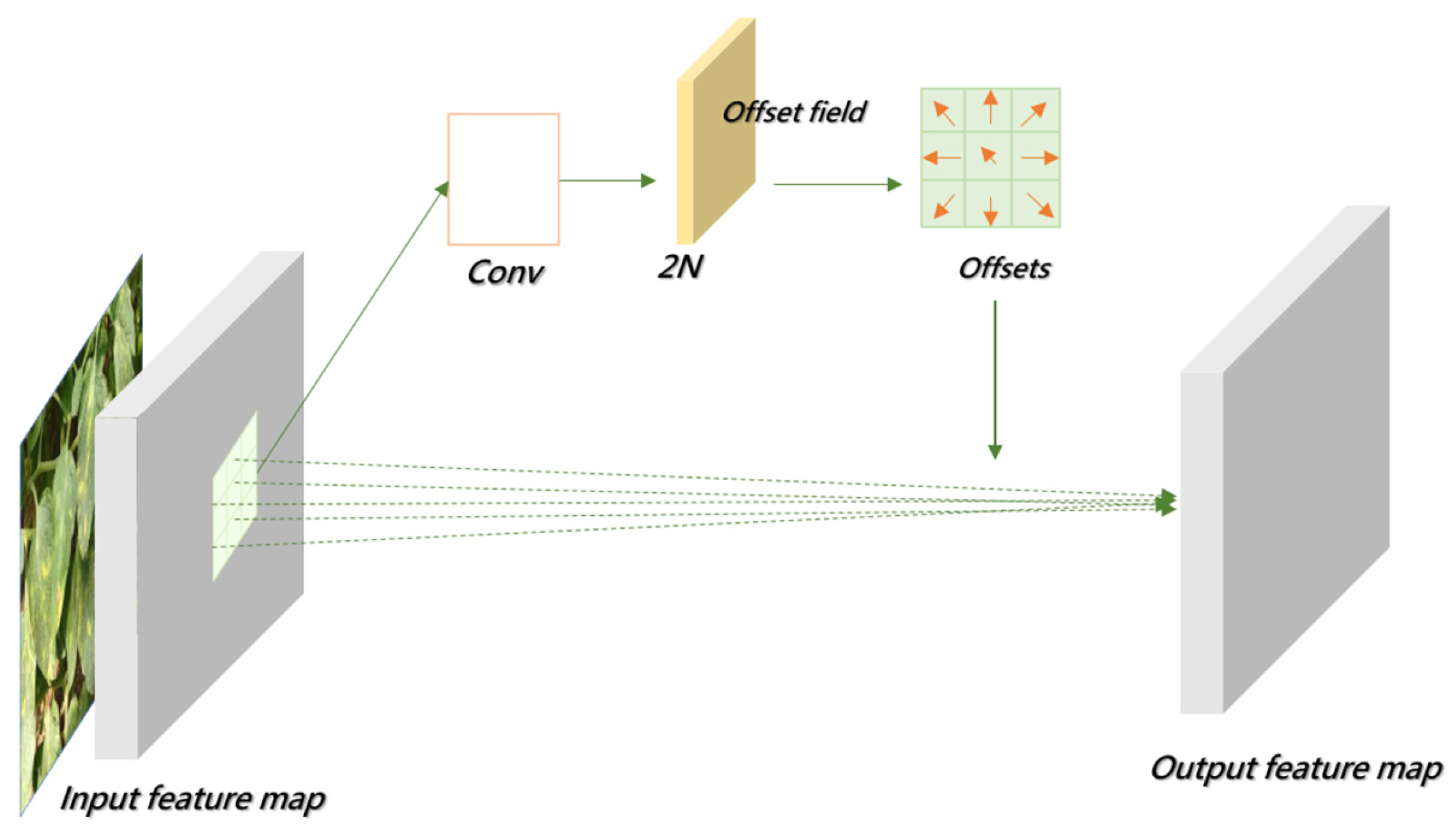
- Introducing Deformable Convolutional Networks (DCNs) into the backbone network to replace conventional convolution enhances the model’s adaptability to leaf overlap, occlusion, and morphological variations in disease regions. This improves feature extraction from diseased areas.
- (2)
- To tackle the challenge of detecting small lesion targets, the model integrates the Bidirectional Feature Pyramid Network (BiFPN) with the FPN + PAN structure to optimize feature fusion. This approach strengthens the representation of disease regions at different scales and improves the detection accuracy of small lesions.
- (3)
- Incorporating the Efficient Multi-Scale Attention (EMA) mechanism into the C2f module within the neck part of the model enhances feature extraction effectiveness, allowing the model to better focus on diseased areas, reduce background noise interference, and ensure the full retention of disease features during multi-scale fusion.
2. Data Collection and Processing
Dataset Construction and Preprocessing
3. Methodology and Design
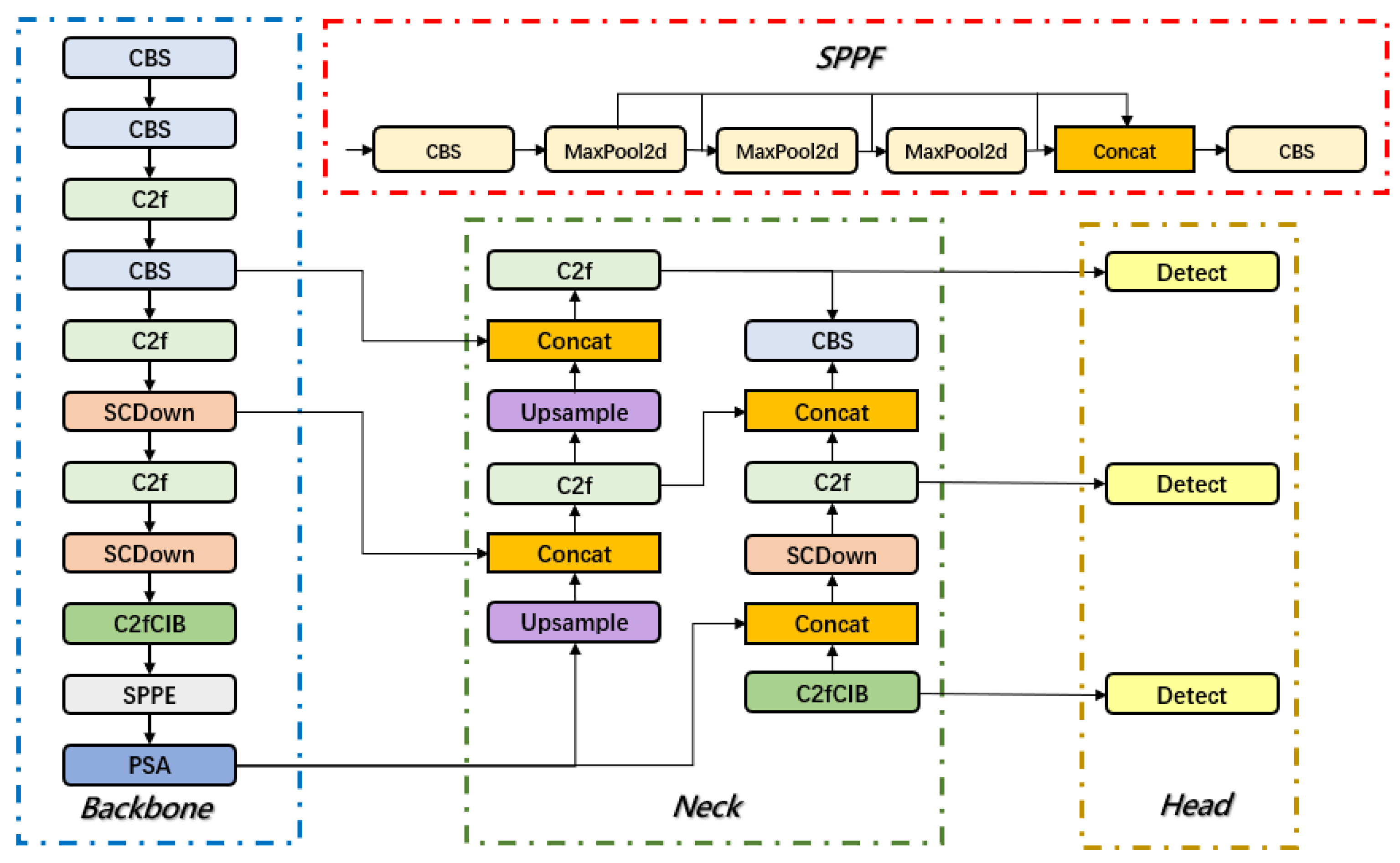
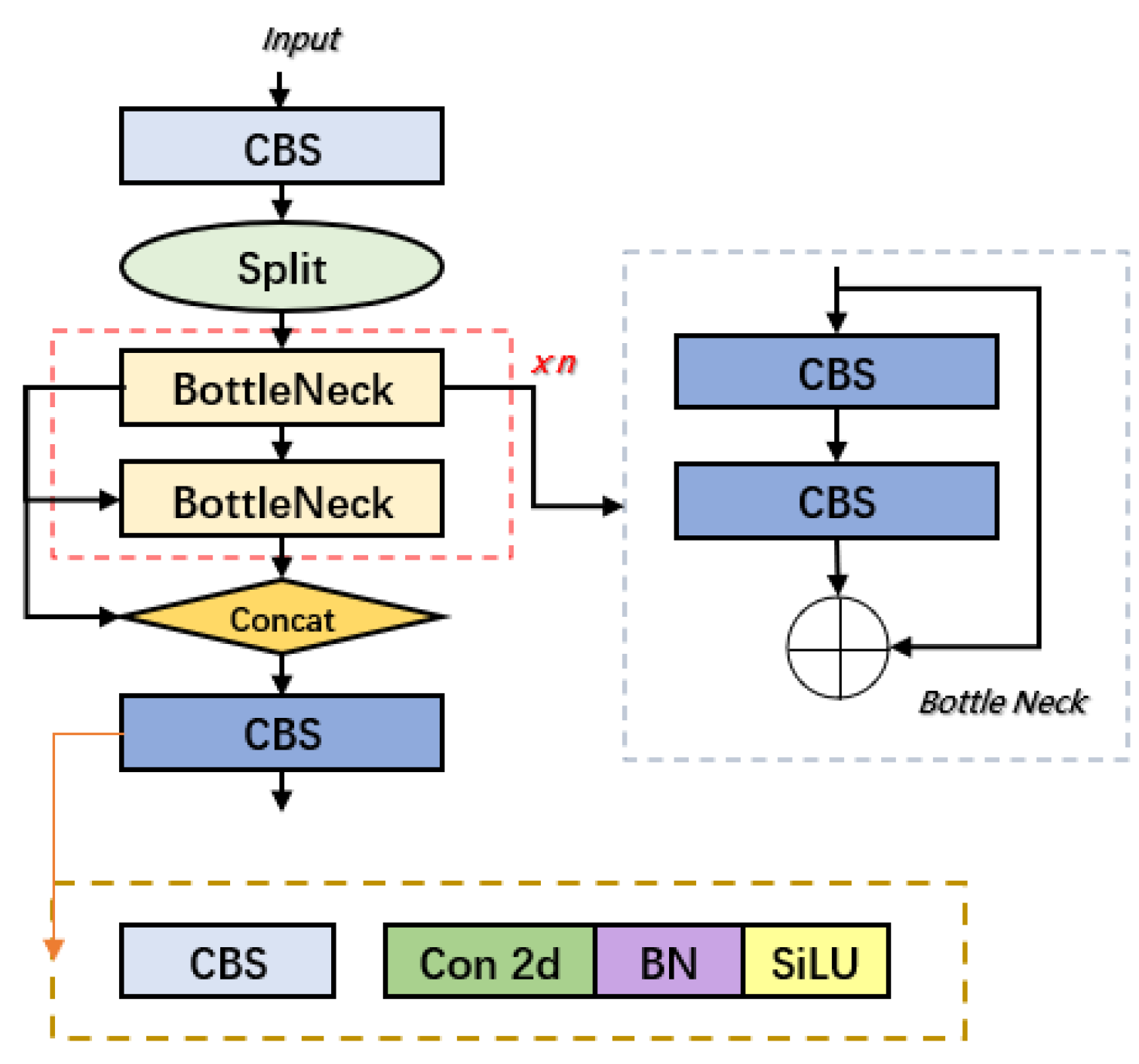
3.1. Overview of the YOLOv10 Network
3.2. Design of BED-YOLO
3.2.1. Deformable Convolution Network (DCN)
3.2.2. Multi-Scale Feature Fusion in the Neck
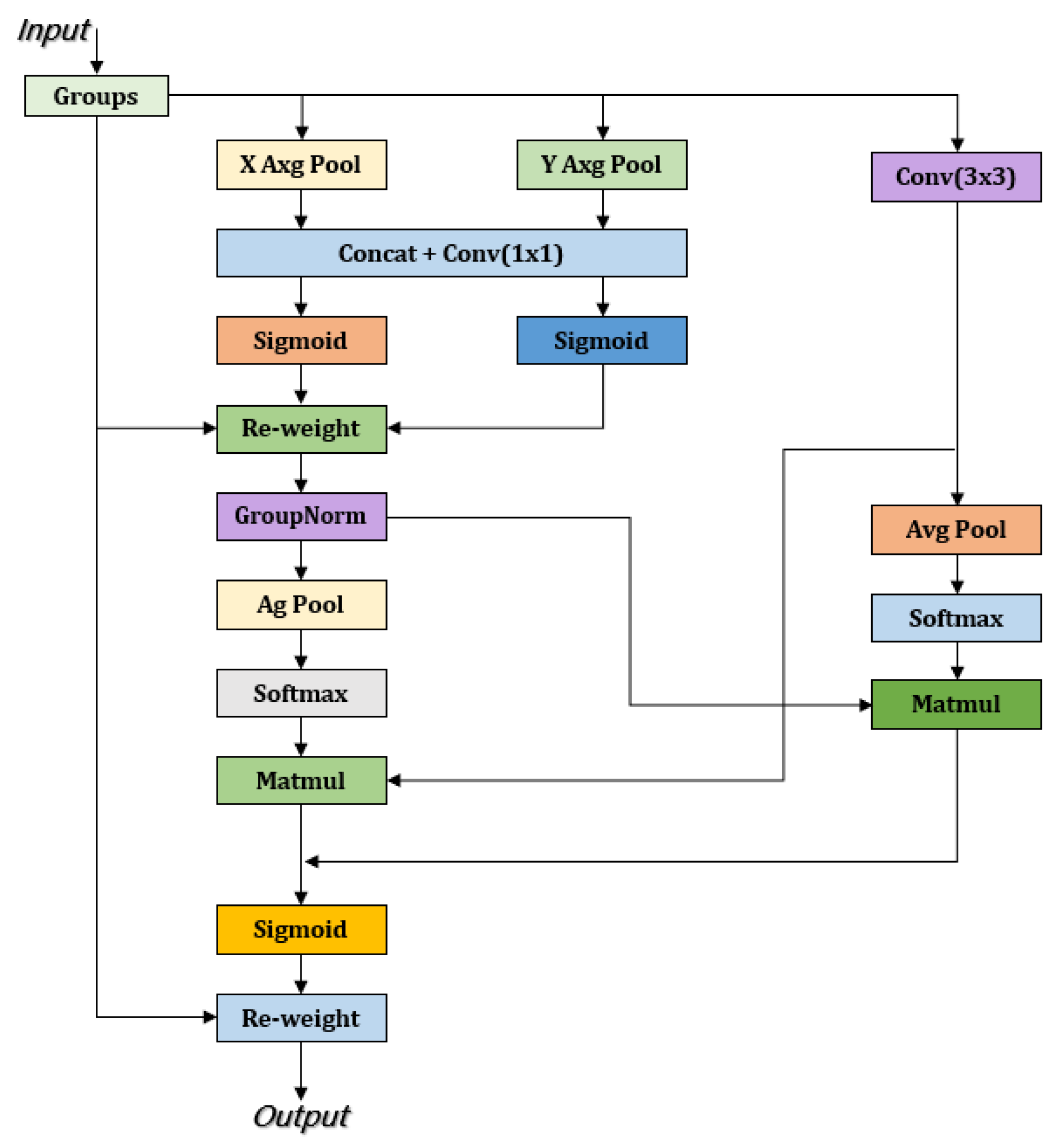
3.2.3. EMA Attention Mechanism
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
4.1. Experimental Environment
4.2. Experimental Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Performance Evaluation of the Improved Model
4.4. Ablation Study
4.5. Performance Comparison with Mainstream Models
4.6. Analysis of Tomato Leaf Disease Detection Performance
5. Conclusions
6. Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mallick, P.K. Medicinal values of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.–Solanaceae). Int. J. Appl. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 166–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natalini, A.; Acciarri, N.; Cardi, T. Breeding for nutritional and organoleptic quality in vegetable crops: The case of tomato and cauliflower. Agriculture 2021, 11, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, H.; Ichihashi, Y.; Kimura, S. Diversity of tomato leaf form provides novel insights into breeding. Breed. Sci. 2023, 73, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, E.J.; Bowyer, C.; Tsouza, A.; Chopra, M. Tomatoes: An extensive review of the associated health impacts of tomatoes and factors that can affect their cultivation. Biology 2022, 11, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, J.K.; Behera, T.K.; Rai, N.; Yerasu, S.R.; Singh, M.K.; Singh, P.M. Tomato breeding for processing in India: Current status and prospects. Veg. Sci. 2022, 49, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, A.; Rovira-Val, M.R.; Mendoza, J.M.F. Life cycle cost analysis of tomato production in innovative urban agriculture systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 367, 133037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solankey, S.S.; Ray, P.K.; Kumari, M.; Singh, H.K.; Shamim, M.; Verma, D.K.; Jha, V.B. Tomato diseases, their impact, and management. In Biotic Stress Management in Tomato; Apple Academic Press: Palm Bay, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhu, X. Early real-time detection algorithm of tomato diseases and pests in the natural environment. Plant Methods 2021, 17, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Lu, J.; Jiang, H. Tomato leaf diseases classification based on leaf images: A comparison between classical machine learning and deep learning methods. AgriEngineering 2021, 3, 542–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, M.S.; Alsaade, F.W. Transform and deep learning algorithms for the early detection and recognition of tomato leaf disease. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhou, S.; Xing, J.; Song, J. Tomato leaf disease identification by restructured deep residual dense network. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 28822–28831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, G. Diseases detection of occlusion and overlapping tomato leaves based on deep learning. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 792244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahimi, M.; Boukhalfa, K.; Moussaoui, A. Deep learning for tomato diseases: Classification and symptoms visualization. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2017, 31, 299–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotwal, J.; Kashyap, R.; Pathan, S. Agricultural plant diseases identification: From traditional approach to deep learning. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 80, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wspanialy, P.; Moussa, M. A detection and severity estimation system for generic diseases of tomato greenhouse plants. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 178, 105701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanya, V.G.; Subeesh, A.; Kushwaha, N.L.; Vishwakarma, D.K.; Kumar, T.N.; Ritika, G.; Singh, A.N. Deep learning based computer vision approaches for smart agricultural applications. Artif. Intell. Agric. 2022, 6, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.; Santos, F.N.; Oliveira, P.M.; Shinde, P. Deep learning applications in agriculture: A short review. In Robot 2019: Fourth Iberian Robotics Conference: Advances in Robotics; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 1, pp. 139–151. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, C.; Kim, D.K.; Jeong, D. A survey of deep learning in agriculture: Techniques and their applications. J. Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 16, 1015–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Bal, F.; Kayaalp, F. Review of machine learning and deep learning models in agriculture. Int. Adv. Res. Eng. J. 2021, 5, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, S.; Li, M.; Liu, H.; Qiao, L.; Zhang, Y. Research progress of image sensing and deep learning in agriculture. Nongye Jixie Xuebao/Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2020, 51, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Hoang, T.D.; Pham, M.T.; Vu, T.T.; Nguyen, T.H.; Huynh, Q.T.; Jo, J. Monitoring agriculture areas with satellite images and deep learning. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 95, 106565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butera, L.; Ferrante, A.; Jermini, M.; Prevostini, M.; Alippi, C. Precise agriculture: Effective deep learning strategies to detect pest insects. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2021, 9, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koul, S. Machine learning and deep learning in agriculture. In Smart Agriculture: Emerging Pedagogies of Deep Learning, Machine Learning and Internet of Things; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Gong, C.; Chen, Y.; Yu, H. Applications of deep learning for dense scenes analysis in agriculture: A review. Sensors 2020, 20, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Ma, Y.; Liu, B.; He, J.; Li, S.; Wang, H. A deep-learning-based real-time detector for grape leaf diseases using improved convolutional neural networks. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wosner, O.; Farjon, G.; Bar-Hillel, A. Object detection in agricultural contexts: A multiple resolution benchmark and comparison to human. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 189, 106404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badgujar, C.M.; Poulose, A.; Gan, H. Agricultural object detection with You Only Look Once (YOLO) Algorithm: A bibliometric and systematic literature review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 223, 109090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbyshire, M.; Salazar-Gomez, A.; Gao, J.; Sklar, E.I.; Parsons, S. Towards practical object detection for weed spraying in precision agriculture. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1183277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohan, M.; Sai Ram, T.; Rami Reddy, C.V. A review on YOLOv8 and its advancements. In International Conference on Data Intelligence and Cognitive Informatics; Springer: Singapore, 2024; pp. 529–545. [Google Scholar]
- Alif, M.A.R.; Hussain, M. YOLOv1 to YOLOv10: A comprehensive review of YOLO variants and their application in the agricultural domain. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.10139. [Google Scholar]
- Lippi, M.; Bonucci, N.; Carpio, R.F.; Contarini, M.; Speranza, S.; Gasparri, A. A yolo-based pest detection system for precision agriculture. In Proceedings of the 2021 29th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation (MED), Online, 22–25 June 2021; pp. 342–347. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, X. Agricultural greenhouses detection in high-resolution satellite images based on convolutional neural networks: Comparison of faster R-CNN, YOLO v3 and SSD. Sensors 2020, 20, 4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rane, N. YOLO and Faster R-CNN Object Detection for Smart Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0: Applications, Challenges, and Opportunities. 2023. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4624206 (accessed on 12 July 2024.).
- Lv, M.; Su, W.H. YOLOV5-CBAM-C3TR: An optimized model based on transformer module and attention mechanism for apple leaf disease detection. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 14, 1323301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Yao, J.; Teng, G. Corn leaf spot disease recognition based on improved YOLOv8. Agriculture 2024, 14, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhai, Y.; Xia, Y. Tomato leaf disease identification method based on improved YOLOX. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, J. An efficient deep learning model for tomato disease detection. Plant Methods 2024, 20, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abulizi, A.; Ye, J.; Abudukelimu, H.; Guo, W. DM-YOLO: Improved YOLOv9 model for tomato leaf disease detection. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 15, 1473928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, X. Plant diseases and pests detection based on deep learning: A review. Plant Methods 2021, 17, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoaib, M.; Shah, B.; Ei-Sappagh, S.; Ali, A.; Ullah, A.; Alenezi, F.; Gechev, T.; Hussain, T.; Ali, F. An advanced deep learning models-based plant disease detection: A review of recent research. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1158933. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Kumar, V.; Longchamps, L. Comparative performance of YOLOv8, YOLOv9, YOLOv10, YOLOv11 and Faster R-CNN models for detection of multiple weed species. Smart Agric. Technol. 2024, 9, 100648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanam, R.; Hussain, M. Yolov11: An overview of the key architectural enhancements. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.17725. [Google Scholar]
- Xuemeng, J.I.N.; Xiyin, L.I.A.N.G.; Pengfei, D.E.N.G. Lightweight Daylily Grading and Detection Model Based on Improved YOLOv10. Smart Agric. 2024, 6, 108. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Han, J. Yolov10: Real-time end-to-end object detection. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 107984–108011. [Google Scholar]
- Sapkota, R.; Qureshi, R.; Calero, M.F.; Badjugar, C.; Nepal, U.; Poulose, A.; Zeno, P.; Vaddevolu, U.P.; Yan, H.; Karkee, M. YOLOv10 to its genesis: A decadal and comprehensive review of the you only look once (YOLO) series. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.19407. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv1 to YOLOv10: The fastest and most accurate real-time object detection systems. APSIPA Trans. Signal Inf. Process. 2024, 13, e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltık, A.O.; Allmendinger, A.; Stein, A. Comparative analysis of yolov9, yolov10 and rt-detr for real-time weed detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.13490. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Liang, Z.; Huang, H.; Liang, A.; Sun, H.; Zhao, Y. Research and Application of YOLOv10 Algorithm Based on Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Engineering, Wuhu, China, 8–10 November 2024; pp. 535–540. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M. Yolov5, yolov8 and yolov10: The go-to detectors for real-time vision. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.02988. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Jia, H.; Jiang, S.; Xu, F.; Tang, H.; Xiang, C.; Wang, G.; Zheng, H.; Chen, L. Multi-Scale Crack Detection and Quantification of Concrete Bridges Based on Aerial Photography and Improved Object Detection Network. Buildings 2025, 15, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Qi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. Deformable convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 764–773. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, D.; He, S.; Zhang, G.; Luo, M.; Guo, H.; Zhan, J.; Huang, Z. Efficient multi-scale attention module with cross-spatial learning. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023—2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 4–10 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]













| Name | Environmental Parameters |
|---|---|
| Operating System | Windows10 |
| GPU | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4060 |
| CPU | IntelCorei5-12400F |
| Python | 3.11 |
| Pytorch | 2.0.0 |
| CUDA | 11.8 |
| DCN | BiFPN | EMA | P (%) | R (%) | mAP | Params/M | Flops/G | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 85.1 | 86.3 | 87.4 | 2.3 | 6.7 | |||
| B | √ | 86.2 | 87.5 | 89.1 | 2.8 | 7.9 | ||
| C | √ | 85.6 | 86.9 | 88.3 | 2.6 | 7.4 | ||
| D | √ | 85.7 | 87.0 | 88.6 | 2.5 | 7.2 | ||
| E | √ | √ | 86.6 | 88.1 | 90.4 | 3.4 | 9.2 | |
| F | √ | √ | 86.8 | 88.4 | 90.7 | 3.1 | 8.7 | |
| G | √ | √ | √ | 87.2 | 89.1 | 91.3 | 3.7 | 9.8 |
| P (%) | R (%) | mAP | Params/M | Flops/G | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster R-CNN | 60.2 | 62.3 | 65.4 | 137.0 | 370 |
| YOLOv5n | 81.4 | 78.3 | 83.7 | 2.5 | 7.1 |
| YOLOv7-tiny | 82.7 | 83.1 | 84.4 | 6.3 | 13.2 |
| YOLOv8n | 84.1 | 82.9 | 86.9 | 3.0 | 8.1 |
| YOLOv9t | 83.8 | 80.5 | 86.1 | 1.9 | 7.6 |
| YOLOv10n | 85.1 | 86.2 | 87.4 | 2.7 | 8.2 |
| YOLOv11n | 83.5 | 82.3 | 86.6 | 2.6 | 6.3 |
| BED-YOLO | 87.2 | 89.1 | 91.3 | 3.7 | 9.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Yan, N.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, X. BED-YOLO: An Enhanced YOLOv10n-Based Tomato Leaf Disease Detection Algorithm. Sensors 2025, 25, 2882. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092882
Wang Q, Yan N, Qin Y, Zhang X, Li X. BED-YOLO: An Enhanced YOLOv10n-Based Tomato Leaf Disease Detection Algorithm. Sensors. 2025; 25(9):2882. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092882
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qing, Ning Yan, Yasen Qin, Xuedong Zhang, and Xu Li. 2025. "BED-YOLO: An Enhanced YOLOv10n-Based Tomato Leaf Disease Detection Algorithm" Sensors 25, no. 9: 2882. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092882
APA StyleWang, Q., Yan, N., Qin, Y., Zhang, X., & Li, X. (2025). BED-YOLO: An Enhanced YOLOv10n-Based Tomato Leaf Disease Detection Algorithm. Sensors, 25(9), 2882. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092882






