Non-Fragile Estimation for Nonlinear Delayed Complex Networks with Random Couplings Using Binary Encoding Schemes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Problem Formulation and Preliminaries
2.1. The Mathematical Description of Network Nodes
2.2. The Adoption of BESs
2.3. The Model Establishment of Non-Fragile State Estimator
3. Main Results
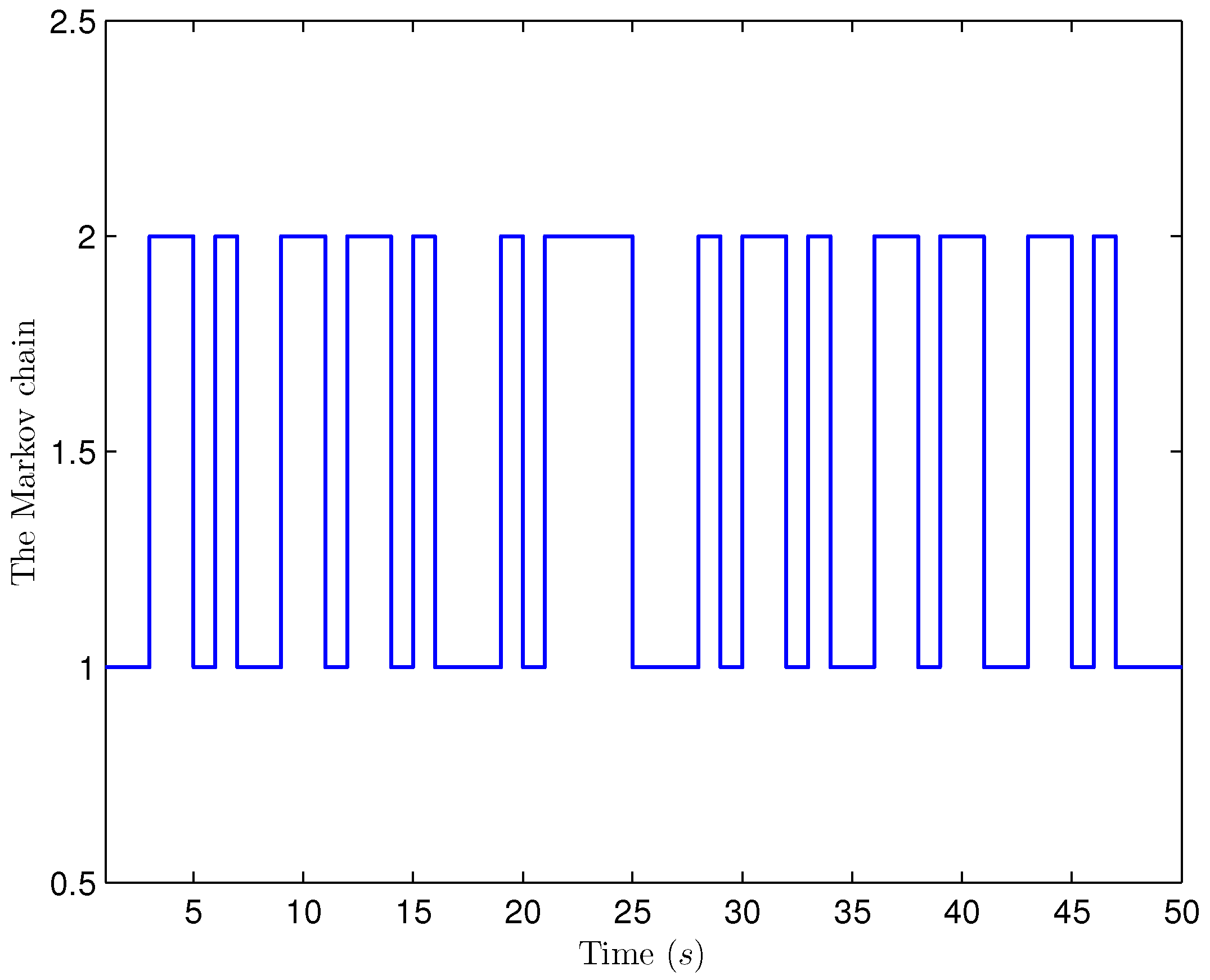
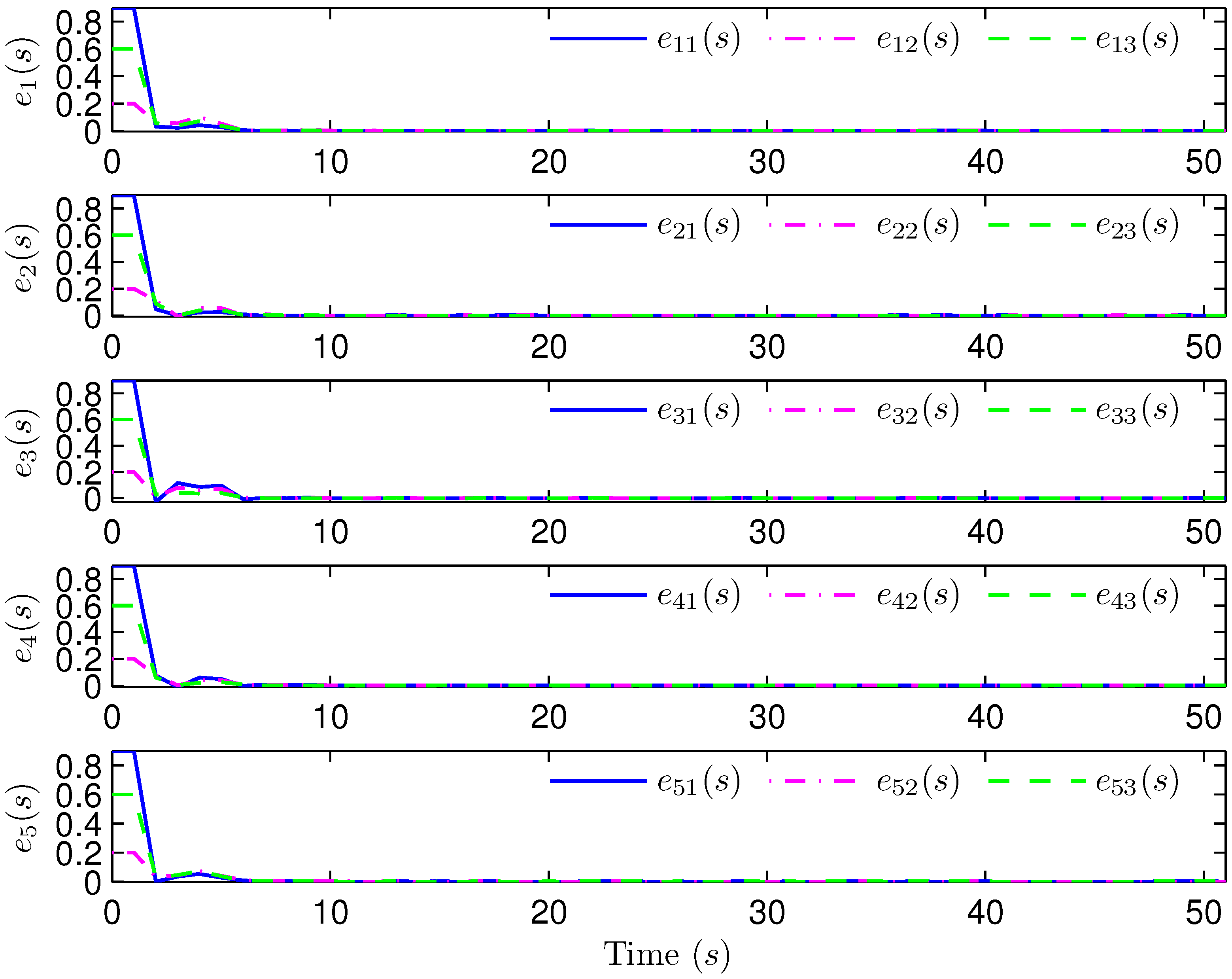
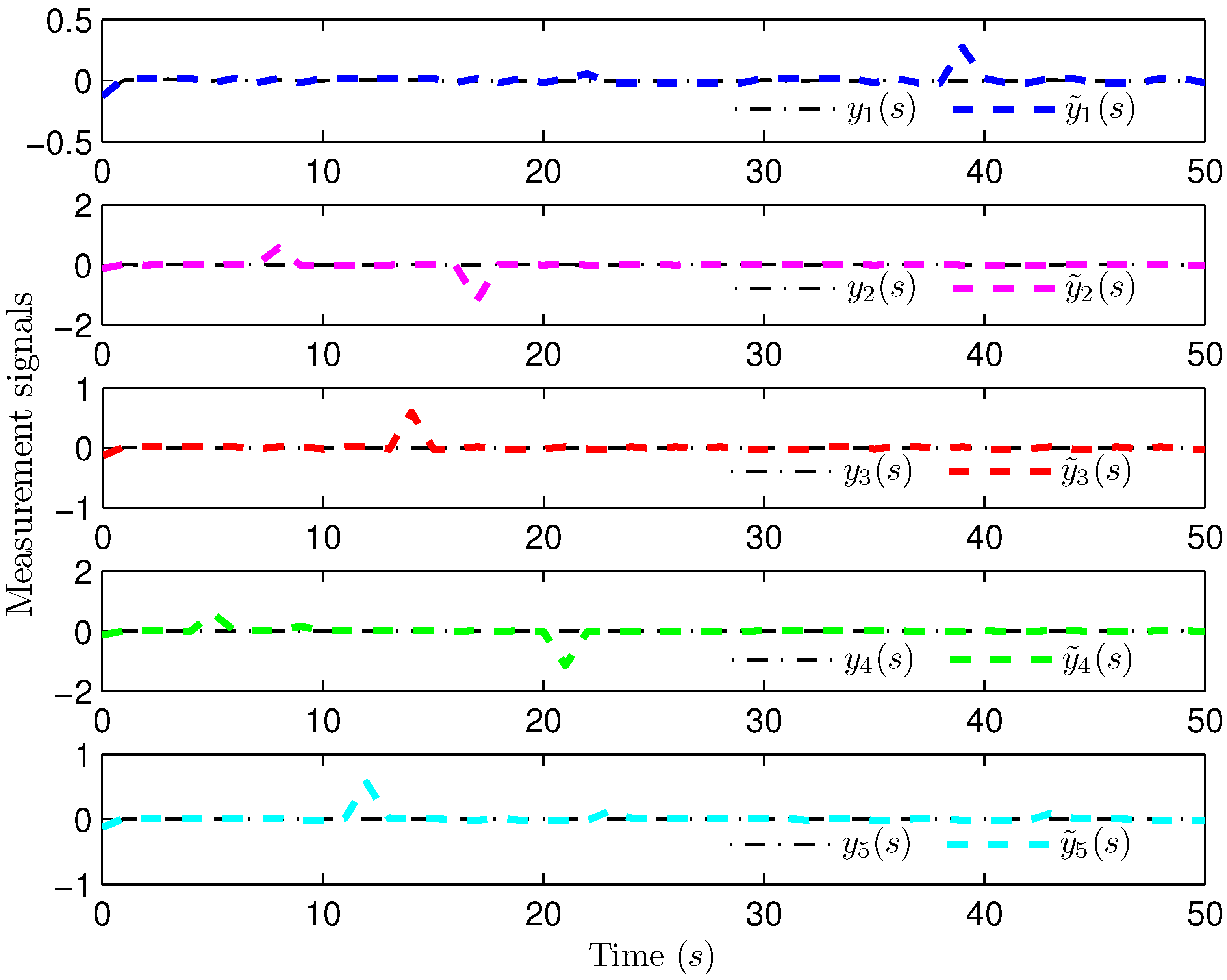
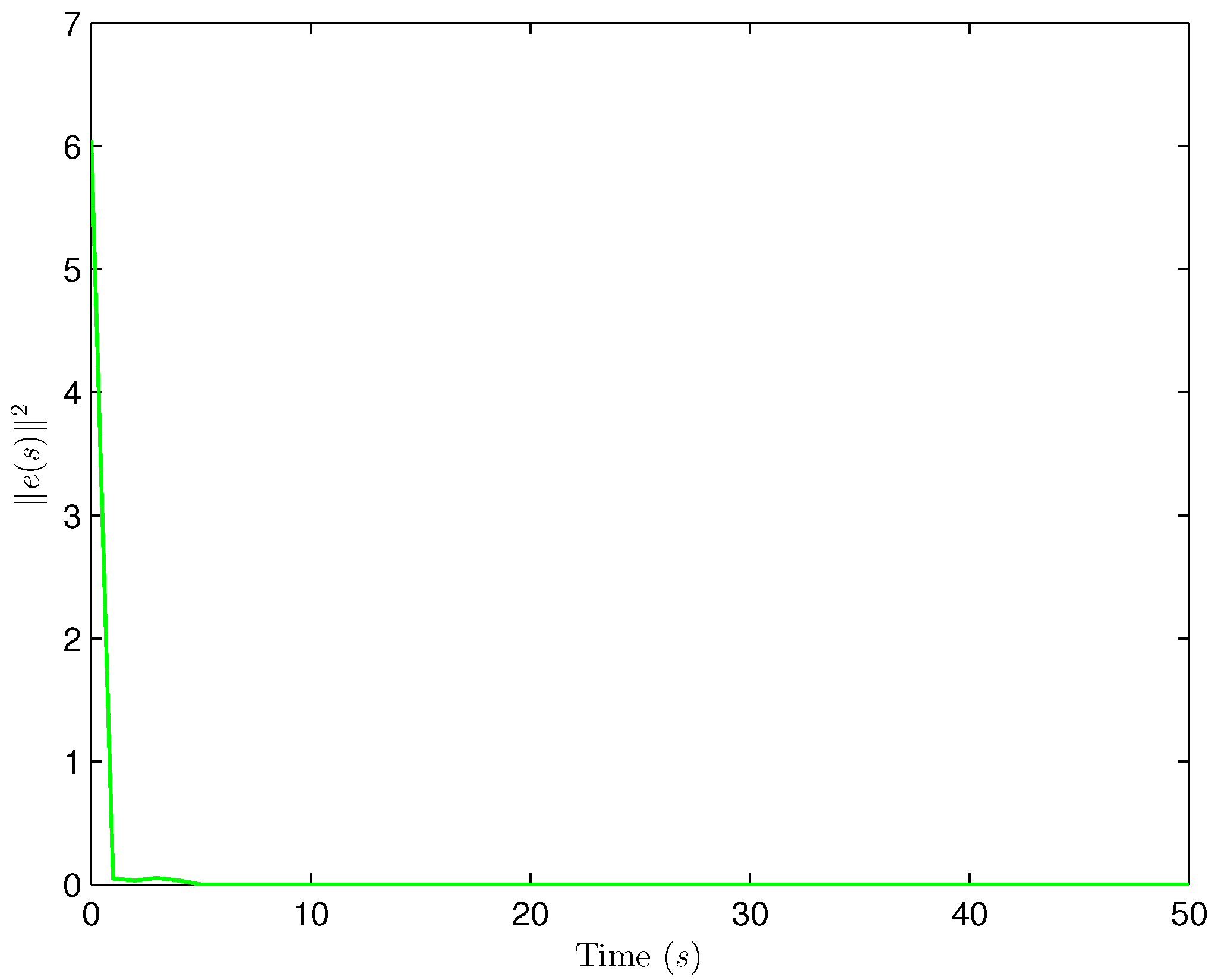
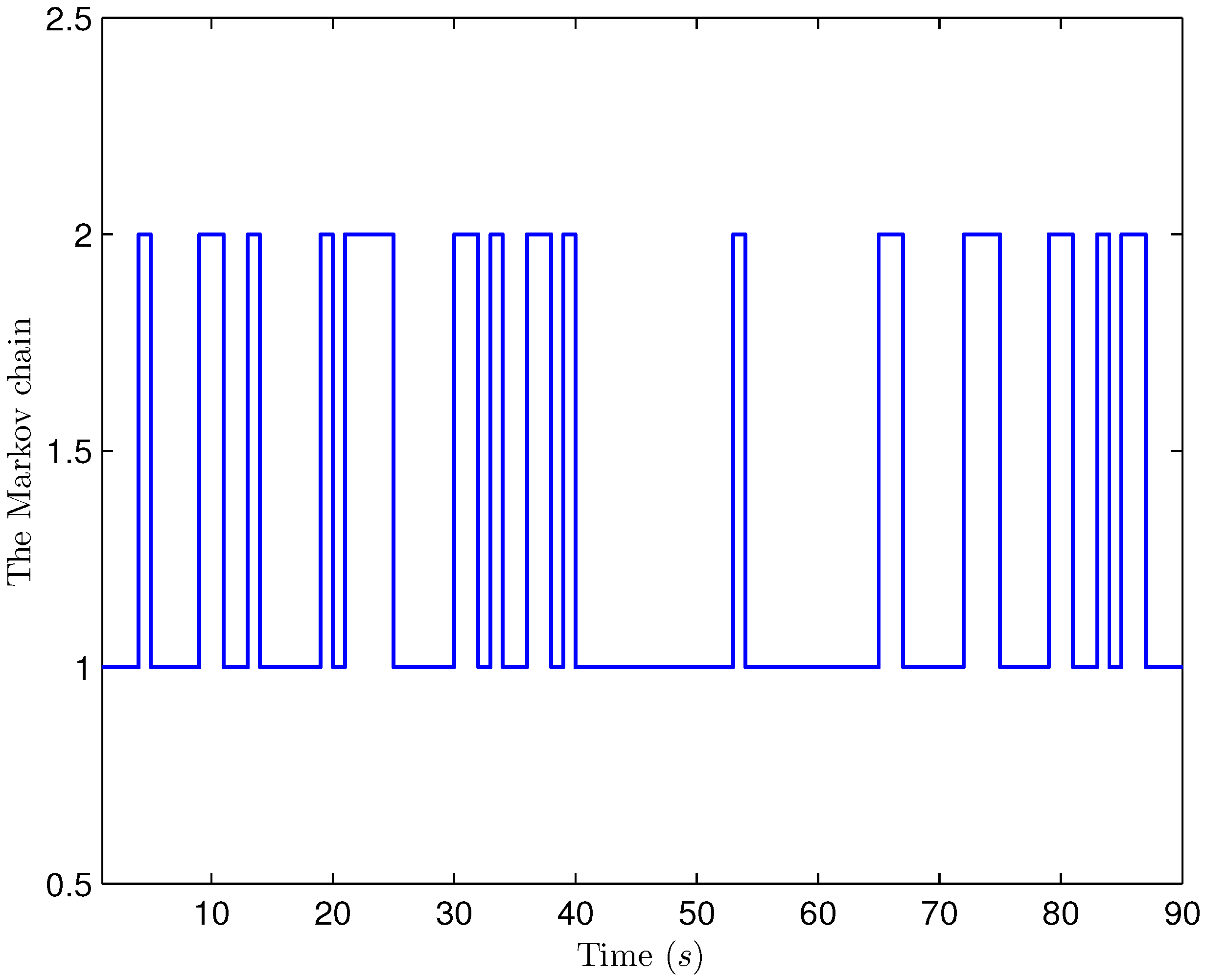
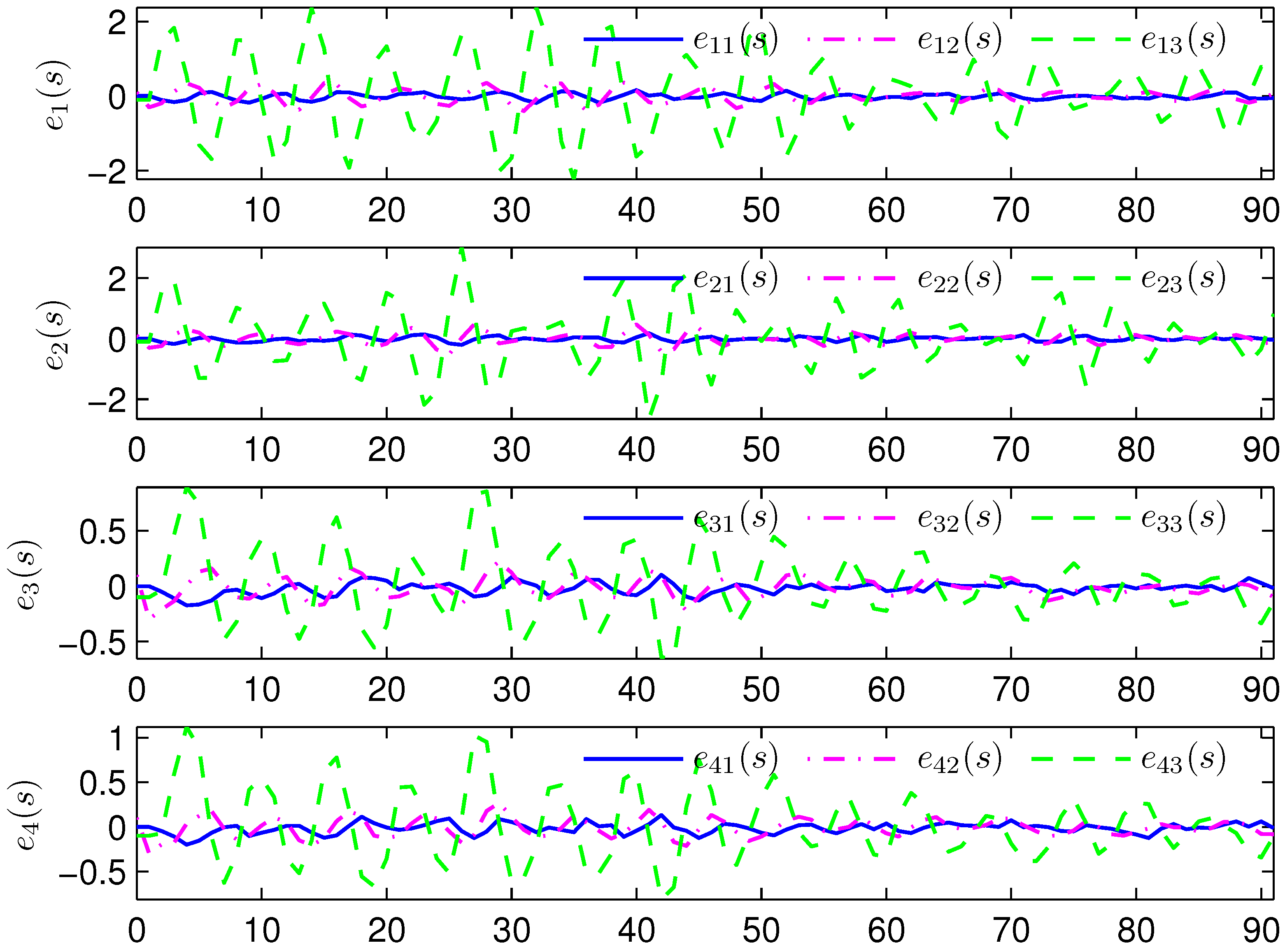
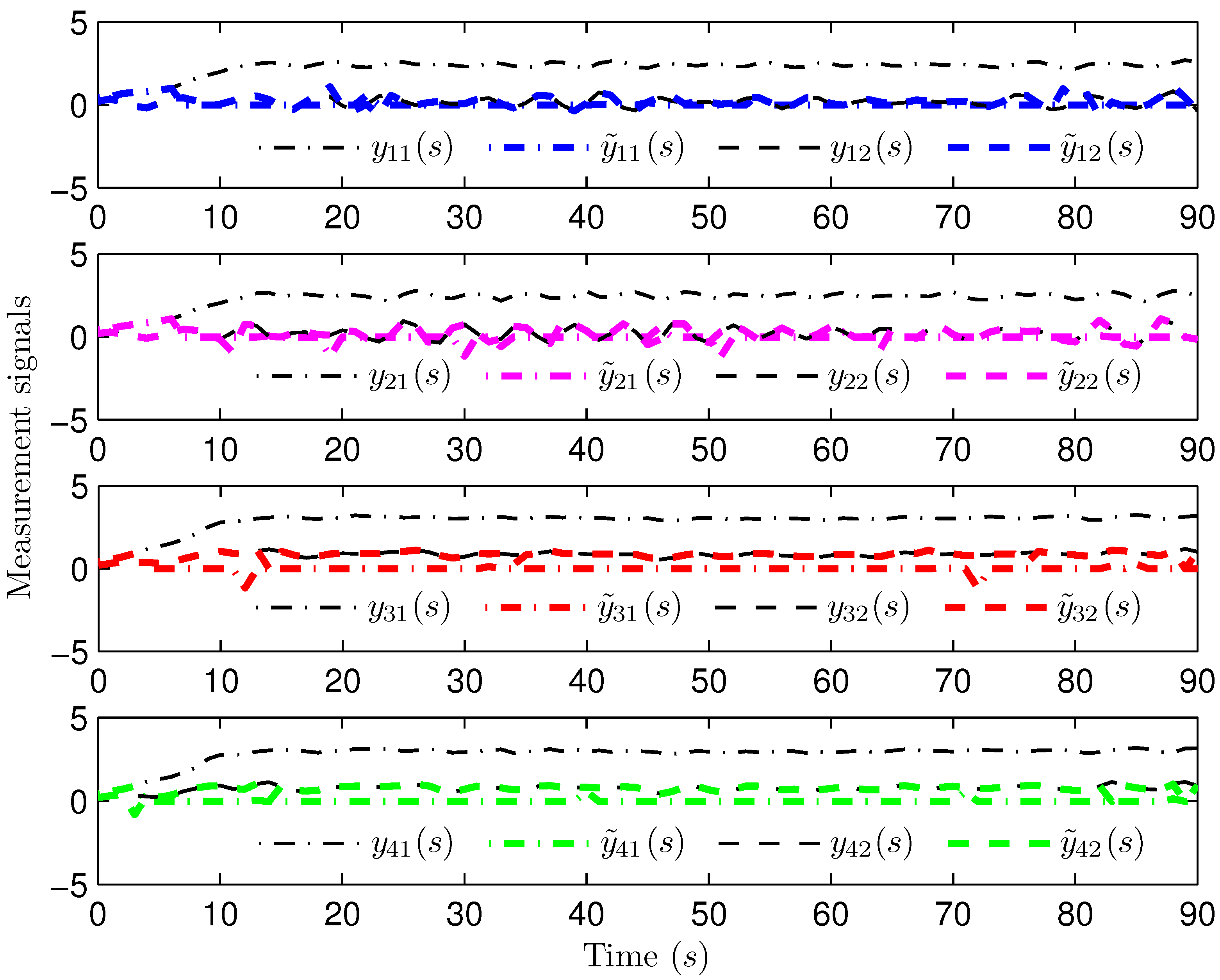
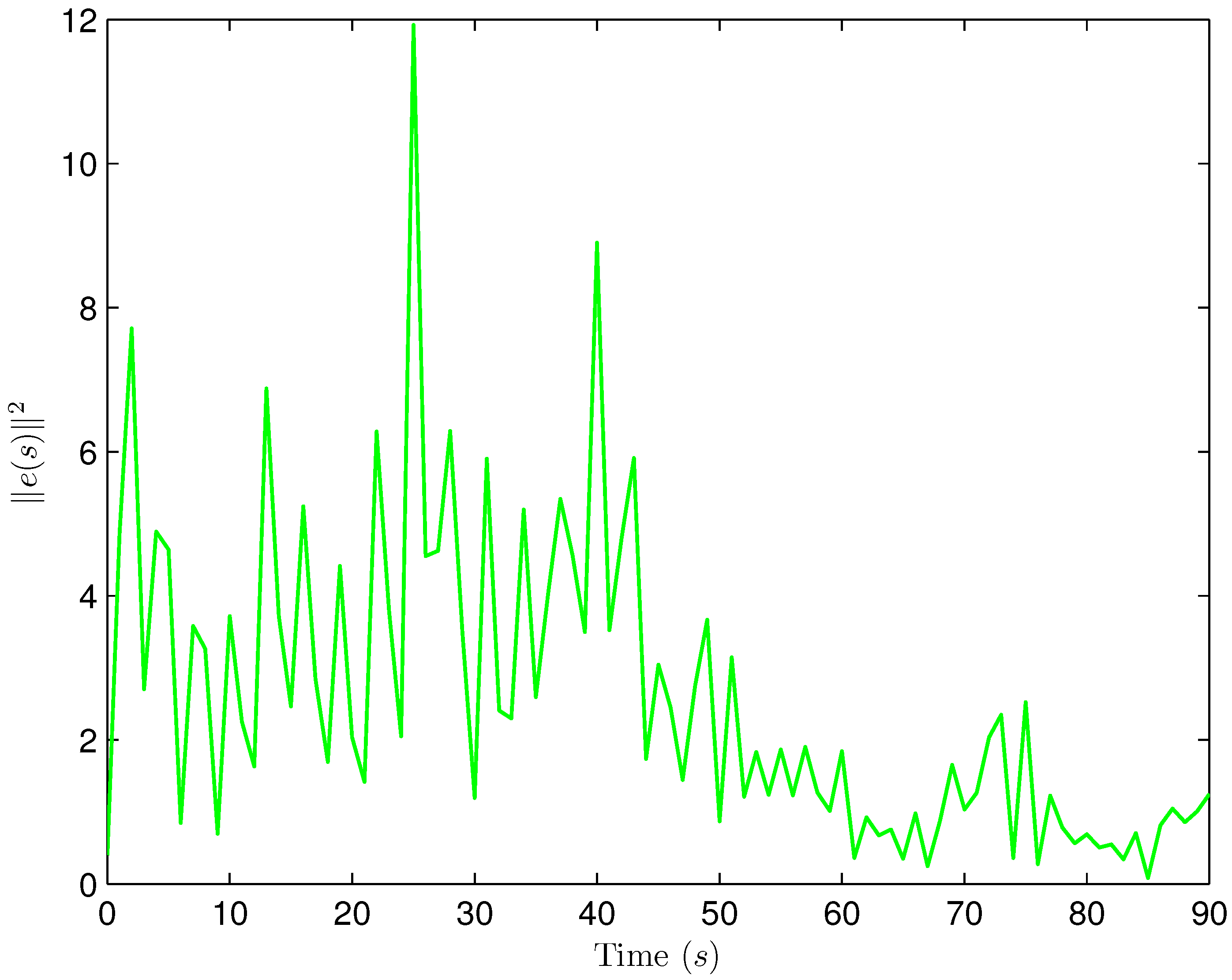
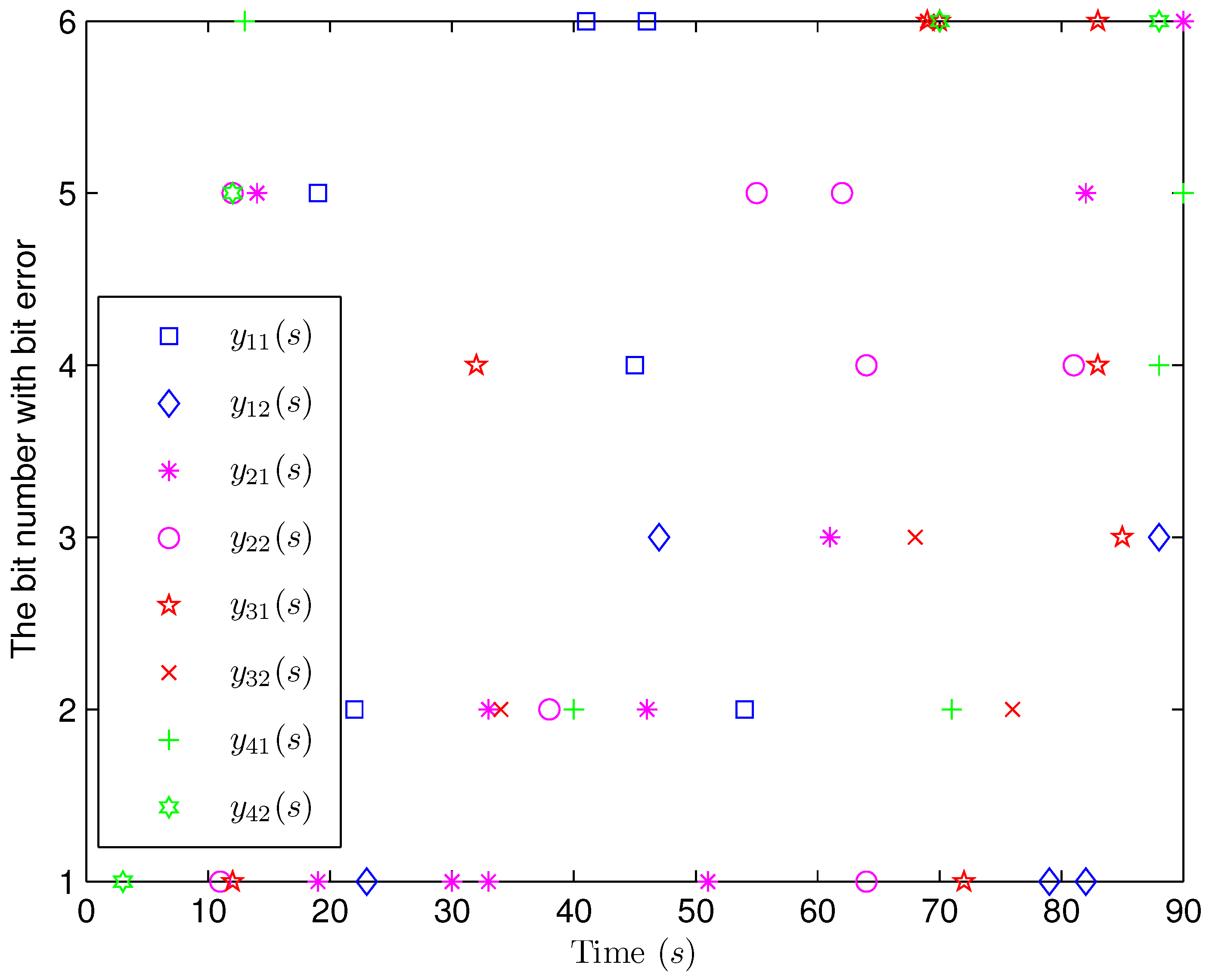
4. Simulation Examples
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNs | Complex networks. |
| SE | State estimation. |
| NCSs | Networked control systems. |
| BES | Binary encoding scheme. |
| BBS | Binary bit string. |
| BSC | Binary symmetric channel. |
| BER | Bit error rate. |
| EUB | Exponentially ultimately bounded. |
References
- Mei, Z.; Oguchi, T. A real-time identification method of network structure in complex network systems. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2023, 54, 549–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Dong, H.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y. Set-membership state estimation for multirate nonlinear complex networks under FlexRay protocols: A neural-network-based approach. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2025, 36, 4922–4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, R.; Dong, H.; Wang, C.; Chen, S.; Sun, T.; Guan, C. Imbalanced data augmentation for pipeline fault diagnosis: A multi-generator switching adversarial network. Control Eng. Pract. 2024, 144, 105839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Hu, X.; Wu, X.; He, S.; Wang, J. Generalized dissipative state estimation of singularly perturbed switched complex dynamic networks with persistent dwell-time mechanisms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Syst. 2022, 52, 1795–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ma, L.; Alsaadi, F.E. A partial-nodes-based information fusion approach to state estimation for discrete-time delayed stochastic complex networks. Inf. Fusion 2019, 49, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhou, H.; Li, Z. On the resilience of modern power systems: A complex network perspective. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 152, 111646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.-A.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Zhao, Z.; Wen, X. Fixed-time event-triggered pinning synchronization of complex network via aperiodically intermittent control. Neurocomputing 2024, 614, 128818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Wang, Z.; Han, Q.; Wu, M. Finite-time H∞ state estimation for discrete time-delayed genetic regulatory networks under stochastic communication protocols. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Regul. Pap. 2018, 65, 3481–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Wu, L. Interval type-2 FNN-based quantized tracking control for hypersonic flight vehicles with prescribed performance. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Syst. 2021, 51, 1981–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.-H.; Wen, S.; Xu, M.; Shi, K.; Zhu, S.; Huang, T. PID control for output synchronization of multiple output coupled complex networks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 9, 1553–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Shen, B.; Ahn, C.K.; Li, W. Intermittent dynamic event-triggered control for synchronization of stochastic complex networks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Regul. Pap. 2021, 68, 2639–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Cao, J.; Wen, F.; Yang, X. Stability analysis of SIR model with distributed delay on complex networks. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; Li, B. Existence and global exponential stability of Weyl almost automorphic solution in finite dimensional distributions for SDINNs. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2025, 56, 561–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Tan, H. Dynamic event-triggered state estimation for discrete-time delayed switched neural networks with constrained bit rate. Syst. Sci. Control Eng. 2024, 12, 2334304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, N.; Wang, Z.; Dong, H.; Hu, J.; Liu, X. Sensor fault estimation for nonlinear complex networks with time delays under saturated innovations: A binary encoding scheme. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 9, 4171–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, G.-P.; Zhang, H. Variance-constrained recursive state estimation for time-varying complex networks with quantized measurements and uncertain inner coupling. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019, 31, 1955–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Jian, Z.; Duan, H.; Wang, Z. A review: State estimation based on hybrid models of Kalman filter and neural network. Syst. Sci. Control Eng. 2023, 11, 2173682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Dong, H. Minimum-variance state and fault estimation for multirate systems with dynamical bias. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 2361–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Z.; Sheng, W.; Alsaadi, F.E.; Alsaadi, F.E. Dynamic event-triggered mechanism for H∞ non-fragile state estimation of complex networks under randomly occurring sensor saturations. Inf. Sci. 2020, 509, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Alsaadi, F.E.; Alsaadi, F.E. Recursive state estimation for stochastic complex networks under round-robin communication protocol: Handling packet disorders. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2021, 8, 2455–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, P.; Dong, H. A robust covert attack strategy for a class of uncertain cyber-physical systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2024, 69, 1983–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Sun, W. Predefined time fuzzy adaptive control of switched fractional-order nonlinear systems with input saturation. Int. J. Netw. Dyn. Intell. 2023, 2, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-A.; Shen, B.; Zou, L.; Han, Q.-L. A survey on recent advances in distributed filtering over sensor networks subject to communication constraints. Int. J. Netw. Dyn. Intell. 2023, 2, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.-J.; Tan, H.-L. An overview of filtering for sampled-data systems under communication constraints. Int. J. Netw. Dyn. Intell. 2023, 2, 100011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xiao, F.; Liu, J.; Wang, R. Distributed soft fault detection for interval type-2 fuzzy-model-based stochastic systems with wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Dong, H.; Lauria, S.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Fadzil, F.; Liu, H. Fusionformer: A novel adversarial transformer utilizing fusion attention for multivariate anomaly detection. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, X.; Sun, Y.; Dong, H.; Xu, G. First-arrival picking for out-of-distribution noisy data: A cost-effective transfer learning method with tens of samples. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhou, S.; Niu, Y.; Cao, Z.; He, S. Anti-disturbance control for hidden Markovian jump systems: Asynchronous disturbance observer approach. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2023, 68, 6982–6989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F. Complex networks: Topology, dynamics and synchronization. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2002, 12, 885–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Jia, C.; Zhou, A. Encryption-decryption-based state estimation for nonlinear complex networks subject to coupled perturbation. Syst. Sci. Control Eng. 2024, 12, 2357796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Cao, J.; Lu, J. Synchronization of Markovian coupled neural networks with nonidentical node-delays and random coupling strengths. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2011, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Guo, B.; Xiao, Y.; Bao, J. Aperiodically synchronization of multi-links delayed complex networks with semi-Markov jump and their numerical simulations to single-link robot arms. Neurocomputing 2024, 575, 127286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, G.-P. Delay compensation-based state estimation for time-varying complex networks with incomplete observations and dynamical bias. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 52, 12071–12083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, B.; Wang, Z.; Ding, D.; Shu, H. H∞ state estimation for complex networks with uncertain inner coupling and incomplete measurements. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2013, 24, 2027–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, H.; Seneviratne, C.; Xu, M. A novel statistical model for distributed estimation in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2015, 63, 3154–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, N.; Shen, D. Encoding-decoding mechanism-based finite-level quantized iterative learning control with random data dropouts. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2019, 17, 1343–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Li, J.; Dong, H.; Shen, Y. Proportional-integral-type estimator design for delayed recurrent neural networks under encoding-decoding mechanism. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2022, 53, 2729–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Wang, Z.; Shen, B.; Dong, H. Secure recursive state estimation of networked systems against eavesdropping: A partial-encryption-decryption method. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control, 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Wang, Z.; Shen, B.; Dong, H. Encryption-decryption-based state estimation with multirate measurements against eavesdroppers: A recursive minimum-variance approach. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2023, 68, 8111–8118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Wang, Z.; Shen, B.; Dong, H. Recursive state estimation in relay channels with enhanced security against eavesdropping: An Innovative encryption-decryption framework. Automatica 2025, 174, 112159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Xu, J. Control for networked control systems with remote and local controllers over unreliable communication channel. Automatica 2018, 98, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Dong, H.; Fei, W. Delay-distribution-dependent state estimation for neural networks under stochastic communication protocol with uncertain transition probabilities. Neural Netw. 2020, 130, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Ma, X.; Meng, X.; Chen, Y. Distributed fusion filtering for cyber-physical systems under Round-Robin protocol: A mixed H2/H∞ framework. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2023, 54, 1661–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yi, X.; Cheng, Y. Variance-constrained filtering fusion for nonlinear cyber-physical systems with the denial-of-service attacks and stochastic communication protocol. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2022, 9, 978–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shen, B.; Dong, H. Outlier-resistant recursive filtering for multisensor multirate networked systems under weighted try-once-discard protocol. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 51, 4897–4908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Dong, H.; Wang, Z.; Han, F. Set-membership filtering for state-saturated systems with mixed time-delays under weighted try-once-discard protocol. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2018, 66, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Chen, W.; Wu, Z.; Chen, D.; Yi, X. Design of protocol-based finite-time memory fault detection scheme with circuit system application. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2024, 54, 3110–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Wang, Z.; Dong, H.; Alsaadi, F.E.; Alharbi, K.H. A local approach to distributed H∞-consensus state estimation over sensor networks under hybrid attacks: Dynamic event-triggered scheme. IEEE Trans. Signal Inf. Process. Over Netw. 2022, 8, 556–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Yan, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, M. Fixed time cluster consensus for nonlinear multiagent systems by double dynamic event-triggered mechanisms. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2024, 55, 3322–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Hu, Z.; Caballero-Aguila, R.; Chen, C.; Fan, S.; Yi, X. Distributed resilient fusion filtering for nonlinear systems with multiple missing measurements via dynamic event-triggered mechanism. Inf. Sci. 2023, 637, 118950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ma, L.; Rui, Q.; Gao, C. A survey on privacy-preserving control and filtering of networked control systems. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2024, 55, 2269–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Dong, H.; Yi, X. Outlier-resistant observer-based control for a class of networked systems under encoding-decoding mechanism. IEEE Syst. J. 2020, 16, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Hu, J.; Chi, K.; Jia, C.; Qi, J. A variance-constrained method to encoding-decoding H∞ state estimation for memristive neural networks with energy harvesting sensor. Neurocomputing 2024, 579, 127448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Ma, L.; Zhao, C.; Liu, Q. A quantization-coding scheme with variable data rates for cyber-physical systems under DoS attacks. Syst. Sci. Control Eng. 2024, 12, 2348690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Hou, N.; Yang, F.; Bu, X.; Sun, L. Finite-horizon variance-constrained H∞ estimation for complex networks subject to dynamical bias using binary encoding schemes. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 142589–142600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Dong, H.; Jiang, C. Remote estimation for energy harvesting systems under multiplicative noises: A binary encoding scheme with probabilistic bit flips. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2022, 68, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.; Dong, H.; Huo, F.; Li, J.; Lu, X. Observer-based PID control for actuator-saturated systems under binary encoding scheme. Neurocomputing 2022, 99, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, Z.; Ding, D.; Dong, H. Consensusability of discrete-time multi-agent systems under binary encoding with bit errors. Automatica 2021, 133, 109867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Dong, H.; Chen, Y. A dynamic event-triggered approach to recursive nonfragile filtering for complex networks with sensor saturations and switching topologies. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 52, 11041–11054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Wang, Z.; Wei, G.; Liu, X. Nonfragile H∞ state estimation for recurrent neural networks with time-varying delays: On proportional-integral observer design. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 32, 3553–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Hu, X.; Li, S. Secure state estimation of memristive neural networks with dynamic self-triggered strategy subject to deception attacks. Neurocomputing 2024, 601, 128142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Peng, S.; Peng, H. Non-fragile exponential synchronisation of stochastic neural networks via aperiodic intermittent impulsive control. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2024, 55, 1021–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.; Ding, D.; Dong, H.; Alsaadi, F.E.; Hayat, T. Nonfragile H∞ fuzzy filtering with randomly occurring gain variations and channel fadings. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2015, 24, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.; Dong, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H. Non-fragile distributed fault estimation for a class of nonlinear time-varying systems over sensor networks: The finite-horizon case. IEEE Trans. Signal Inf. Process. Over Netw. 2018, 5, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.; He, X.; Ghinea, G.; Alsaadi, F.E. A resilient approach to distributed filter design for time-varying systems under stochastic nonlinearities and sensor degradation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 65, 1300–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Song, J.; Hou, N.; Dai, D.; Yang, F. Finite-horizon distributed set-membership filtering with dynamical bias and DoS attacks under binary encoding schemes. Inf. Sci. 2023, 641, 119084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, Z. Moving-horizon estimation for linear dynamic networks with binary encoding schemes. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2020, 66, 1763–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X. Global exponential stability of generalized recurrent neural networks with discrete and distributed delays. Neural Netw. 2006, 19, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Hernández, C.; Romero-Haros, N. Communicating via synchronized time-delay Chua’s circuits. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2008, 13, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, W. Event-triggered partial-nodes-based state estimation for delayed complex networks with bounded distributed delays. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2017, 49, 1088–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-Y.; Wang, Z.; Lu, R.; Xu, Y. Partial-nodes-based state estimation for complex networks with constrained bit rate. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2021, 8, 1887–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Dong, H.; Lu, G. Local design of distributed state estimators for linear discrete time-varying systems over binary sensor networks: A set-membership approach. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Syst. 2024, 54, 5641–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, J.; Yan, H.; Liu, H. Optimized distributed filtering for saturated systems with amplify-and-forward relays over sensor networks: A dynamic event-triggered approach. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 35, 17742–17753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Wang, Y.-K.; Niu, Y.; Lam, H.-K.; He, S.; Liu, H. Periodic event-triggered terminal sliding mode speed control for networked PMSM system: A GA-optimized extended state observer approach. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2022, 27, 4153–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H. Decentralized output-feedback control with asymmetric one-step delayed information. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2023, 68, 7871–7878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
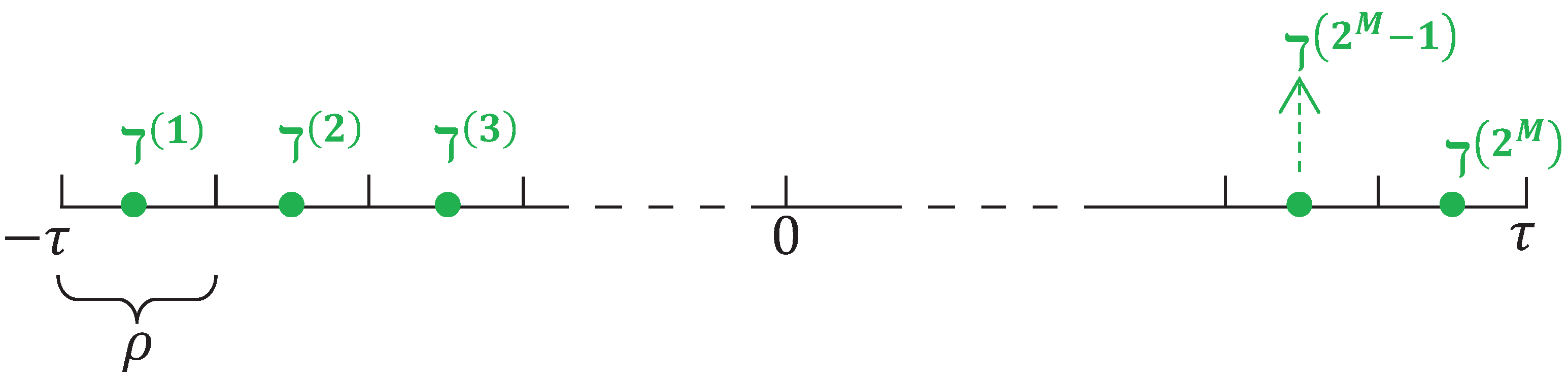



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, N.; Li, W.; Song, Y.; Chang, M.; Bu, X. Non-Fragile Estimation for Nonlinear Delayed Complex Networks with Random Couplings Using Binary Encoding Schemes. Sensors 2025, 25, 2880. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092880
Hou N, Li W, Song Y, Chang M, Bu X. Non-Fragile Estimation for Nonlinear Delayed Complex Networks with Random Couplings Using Binary Encoding Schemes. Sensors. 2025; 25(9):2880. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092880
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Nan, Weijian Li, Yanhua Song, Mengdi Chang, and Xianye Bu. 2025. "Non-Fragile Estimation for Nonlinear Delayed Complex Networks with Random Couplings Using Binary Encoding Schemes" Sensors 25, no. 9: 2880. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092880
APA StyleHou, N., Li, W., Song, Y., Chang, M., & Bu, X. (2025). Non-Fragile Estimation for Nonlinear Delayed Complex Networks with Random Couplings Using Binary Encoding Schemes. Sensors, 25(9), 2880. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092880





