A Case Study of a Hailstorm in the Shanghai Region: Leveraging Multisource Observational Data and a Novel Single-Polarization X-Band Array Weather Radar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
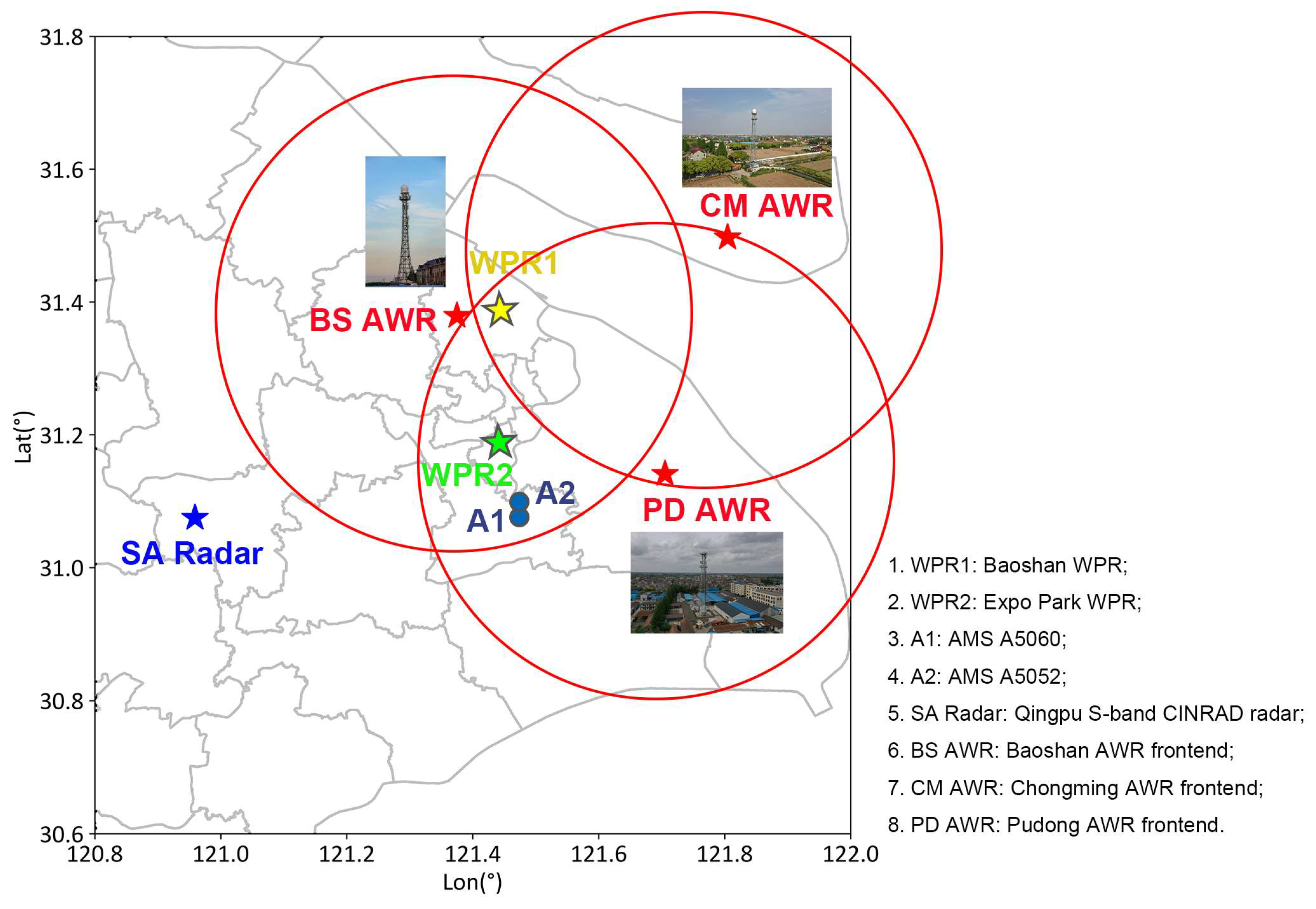
2.1. Layout of Observational Equipment for the Severe Precipitation Event Accompanied by Hail
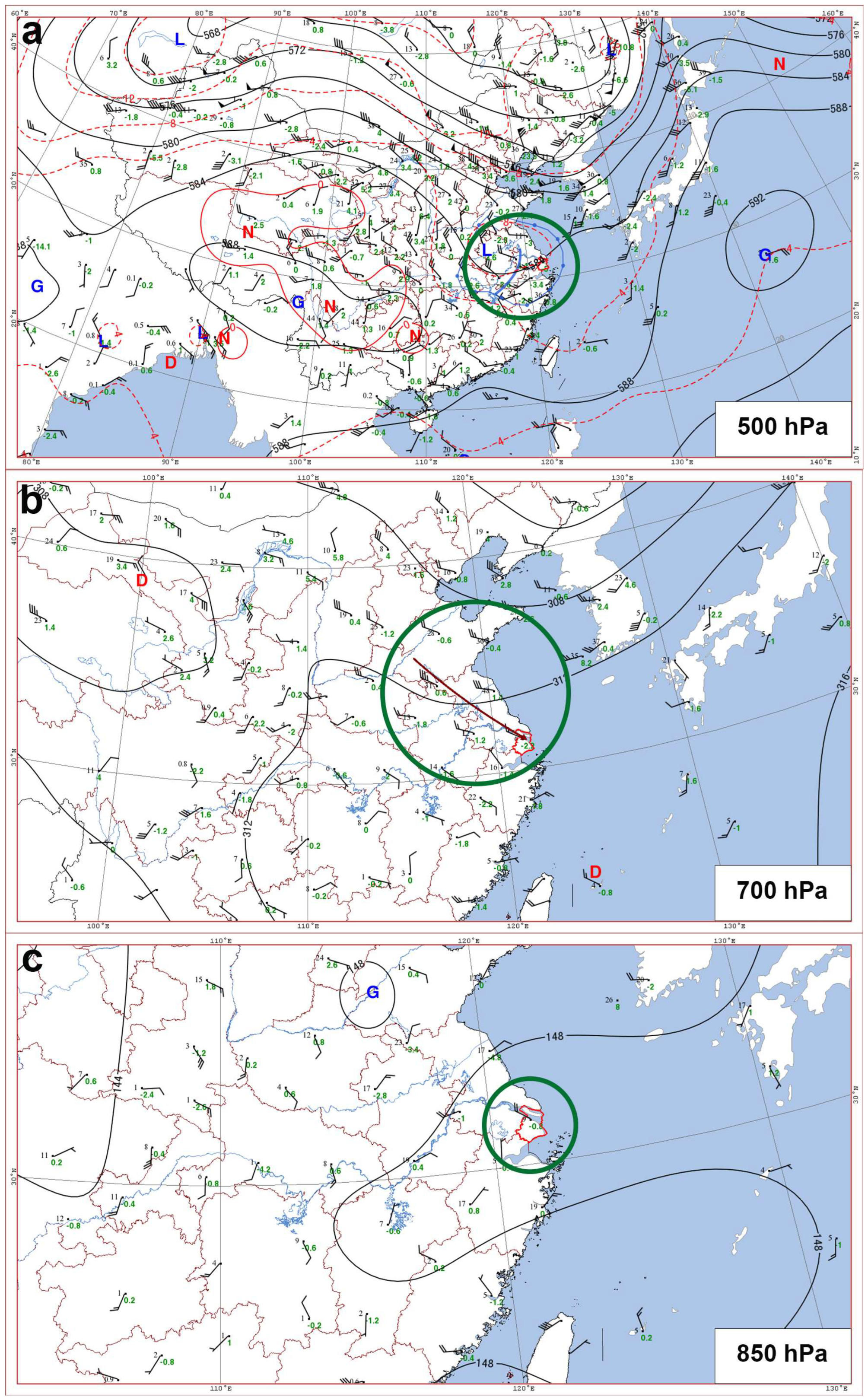
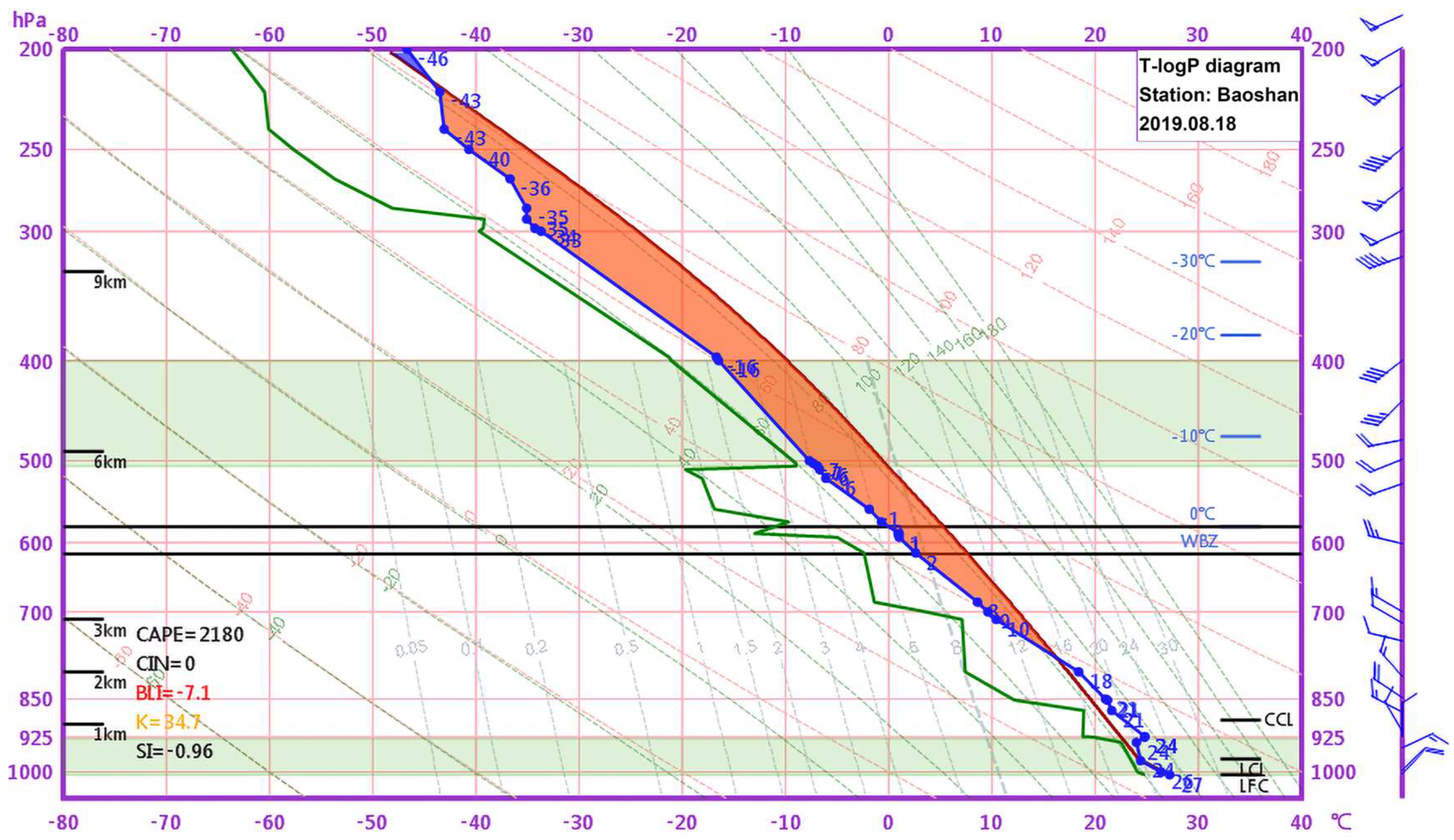
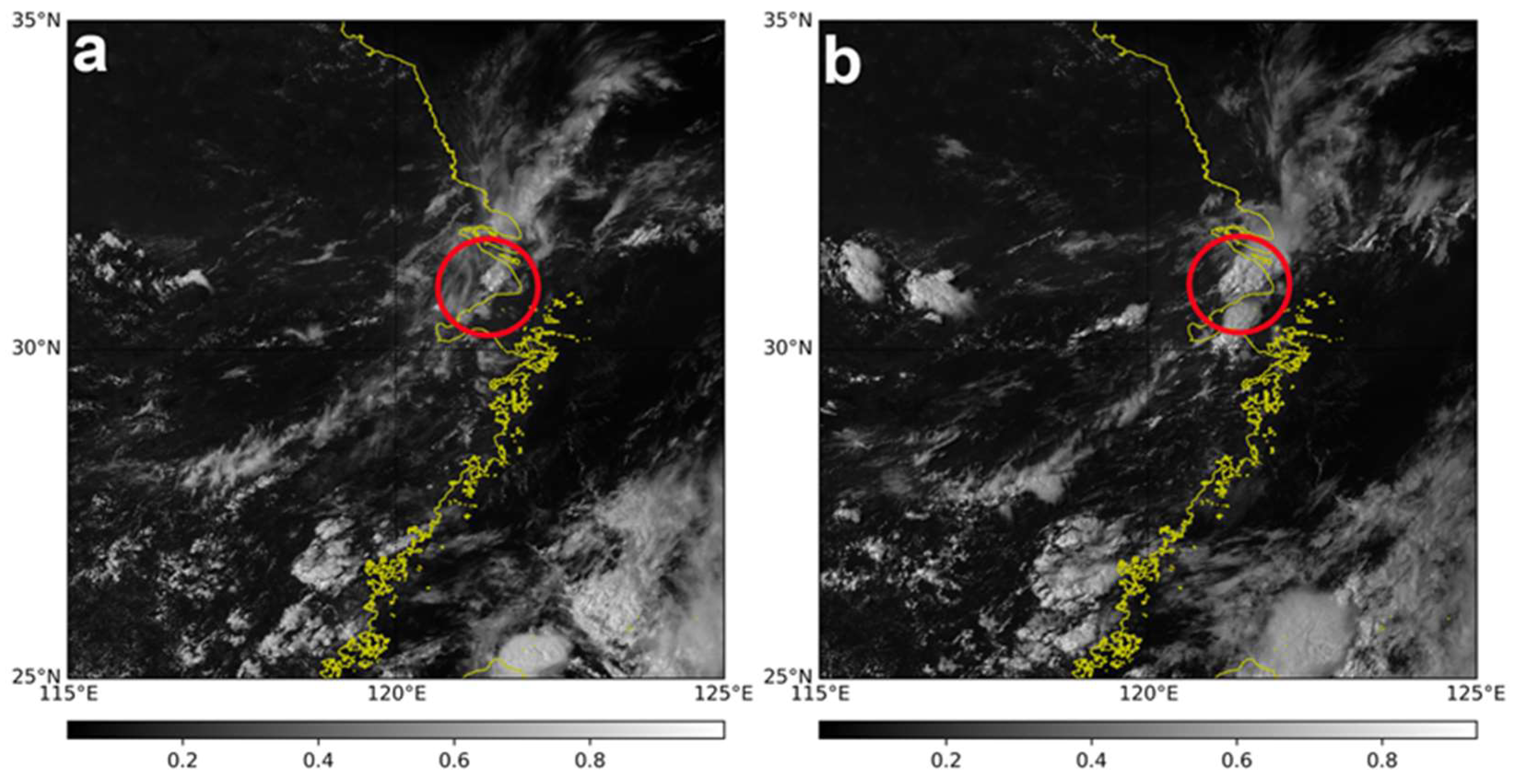
2.2. Synoptic Analysis and Meteorological Background
3. Results
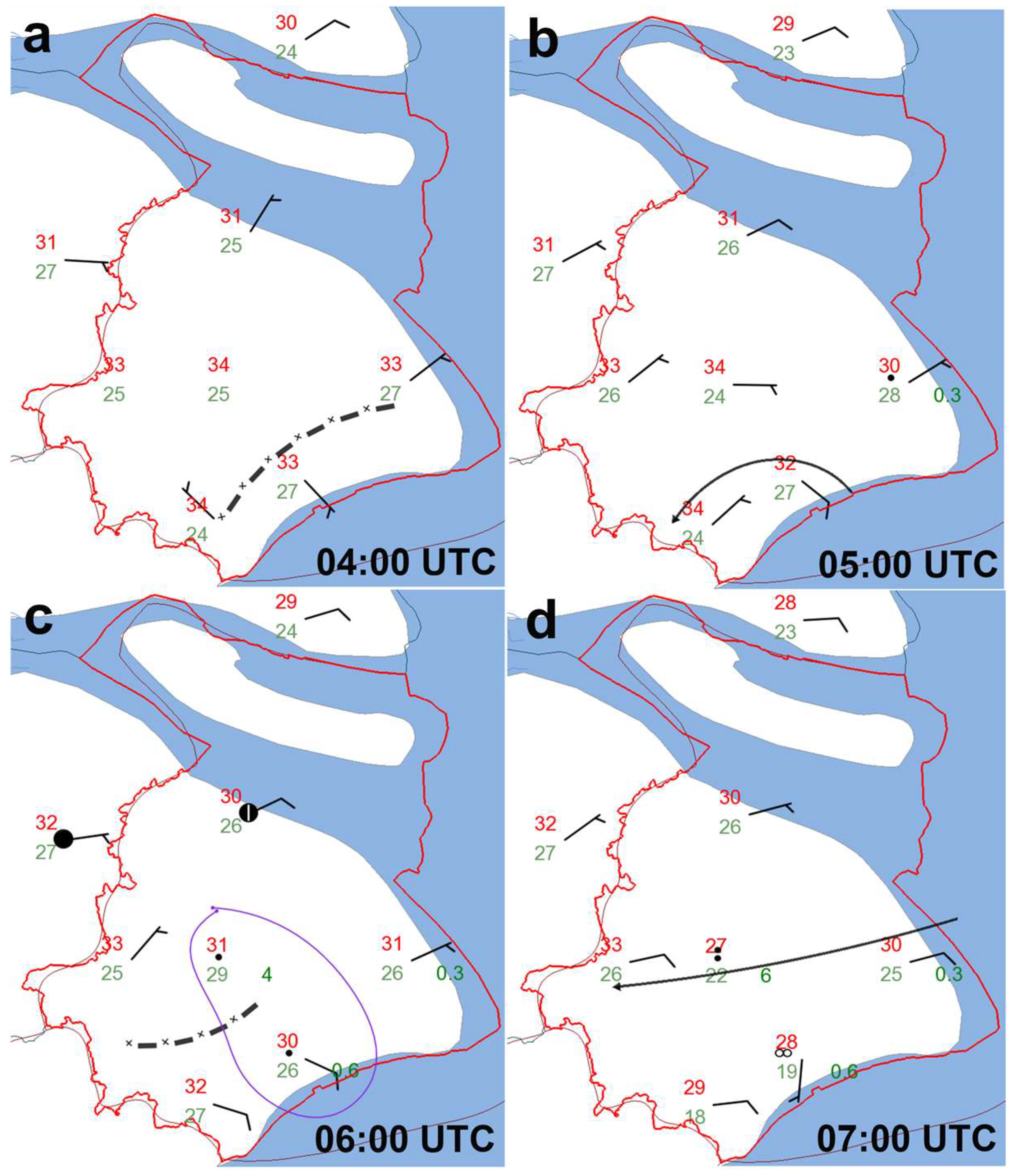
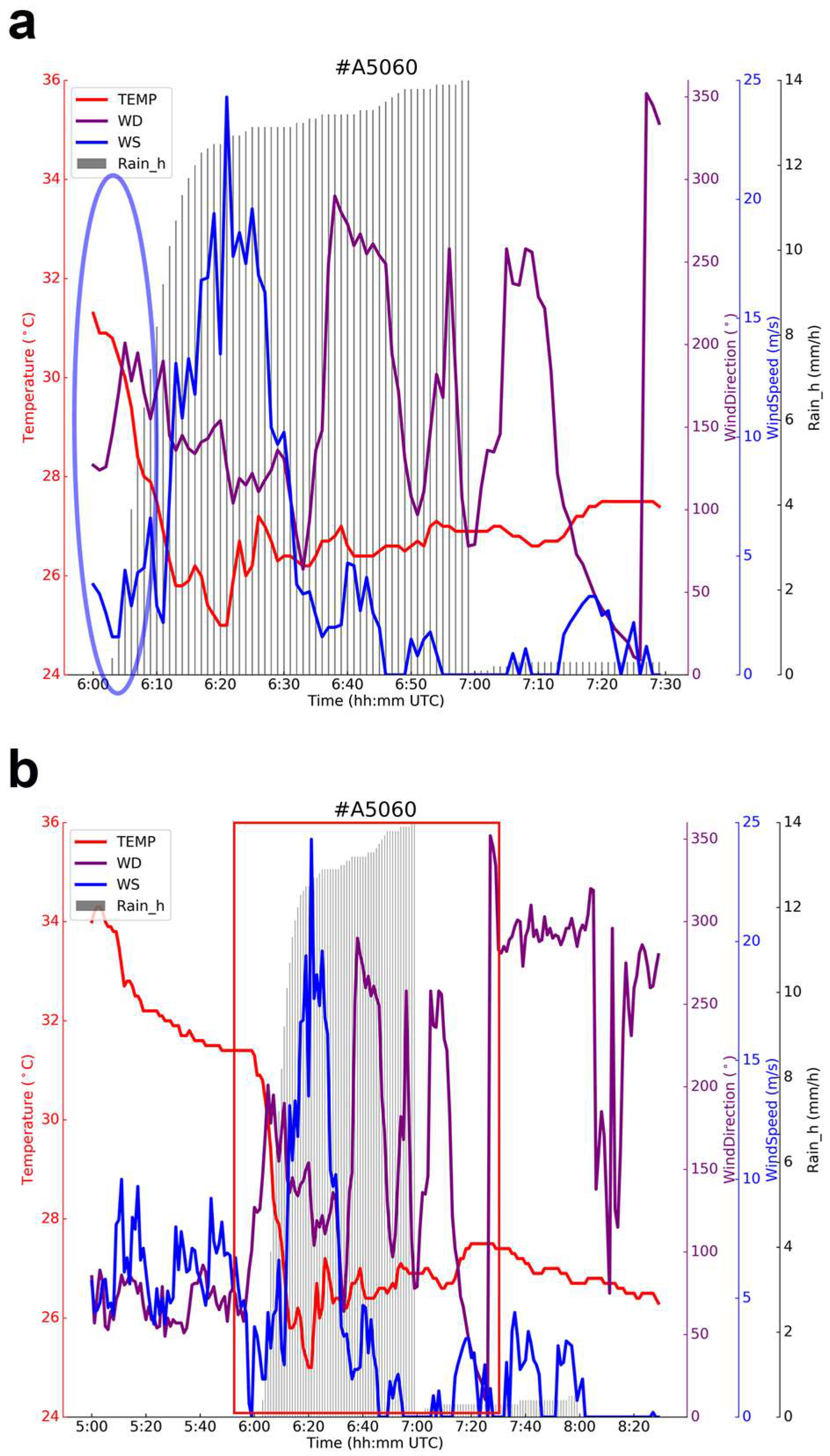
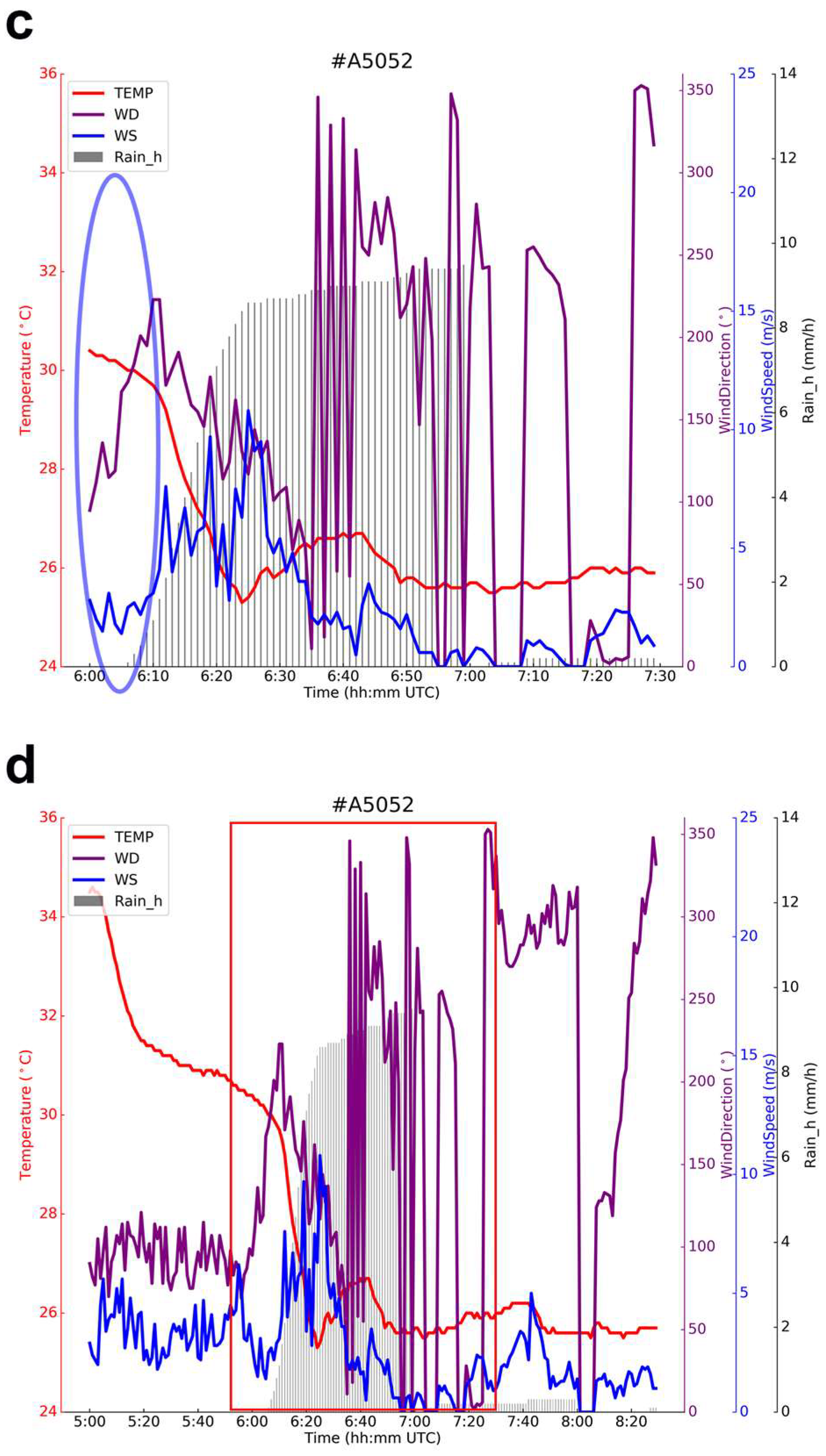
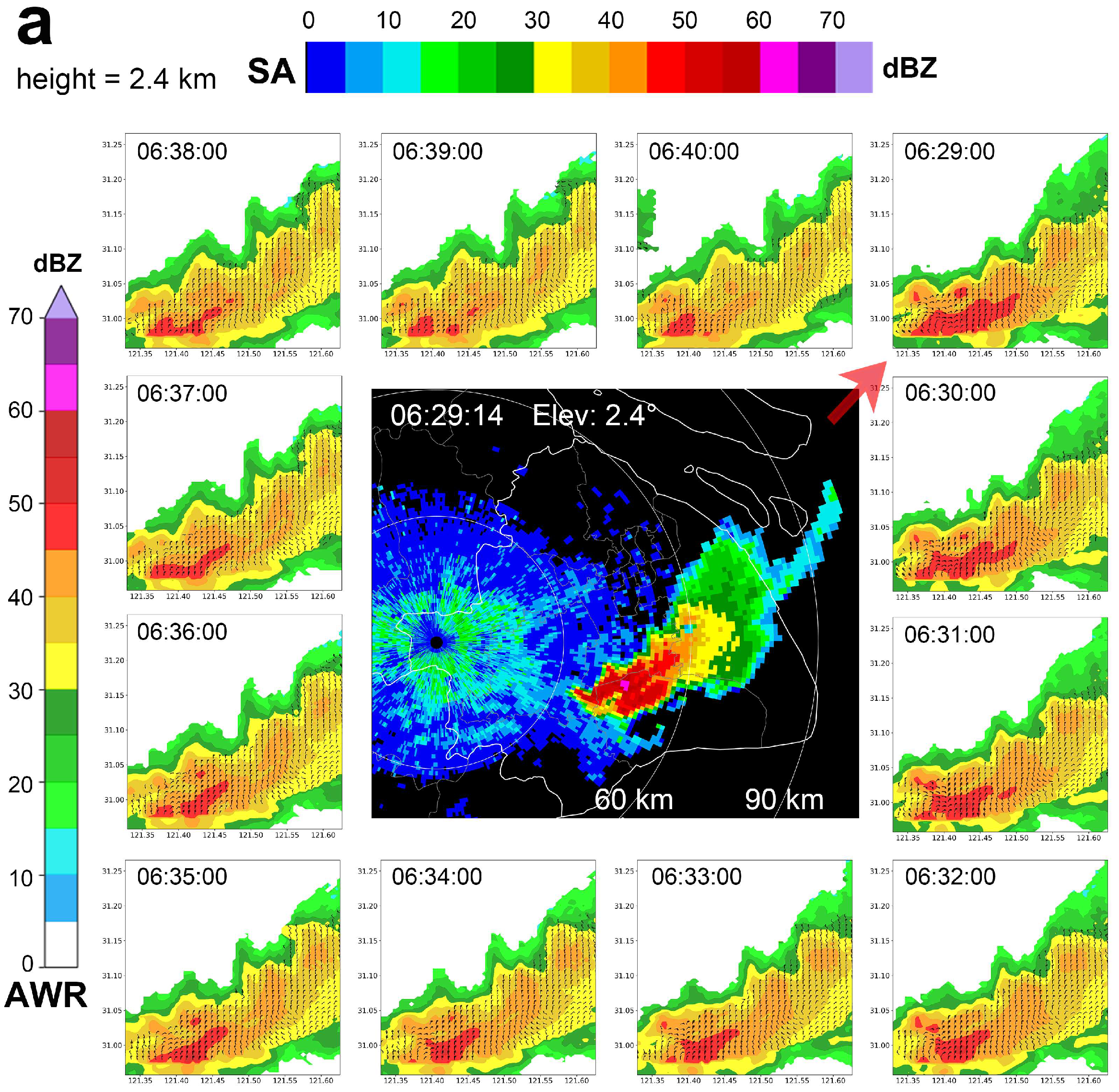
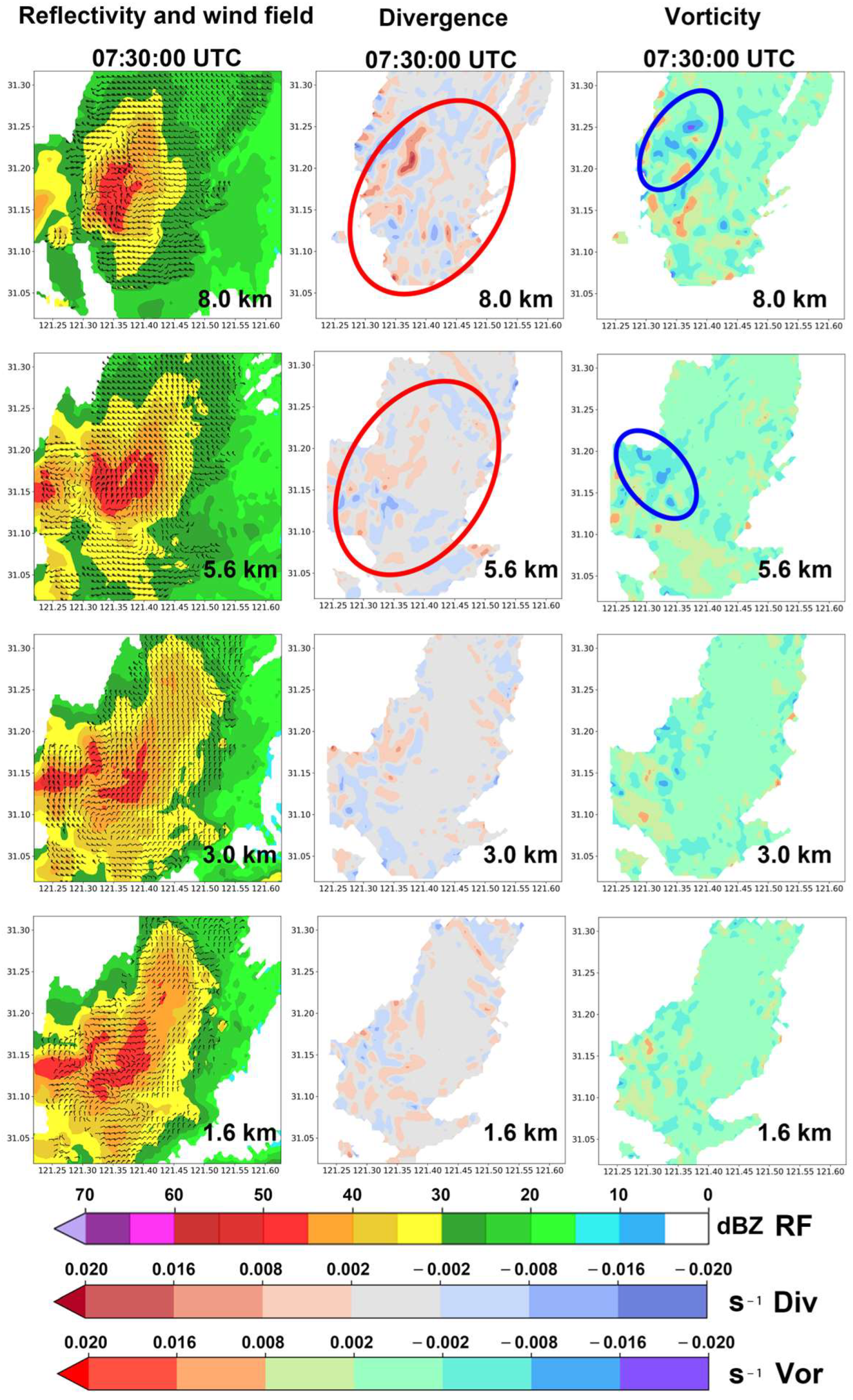
3.1. Analysis of WPR and Ground-Based AMS Data
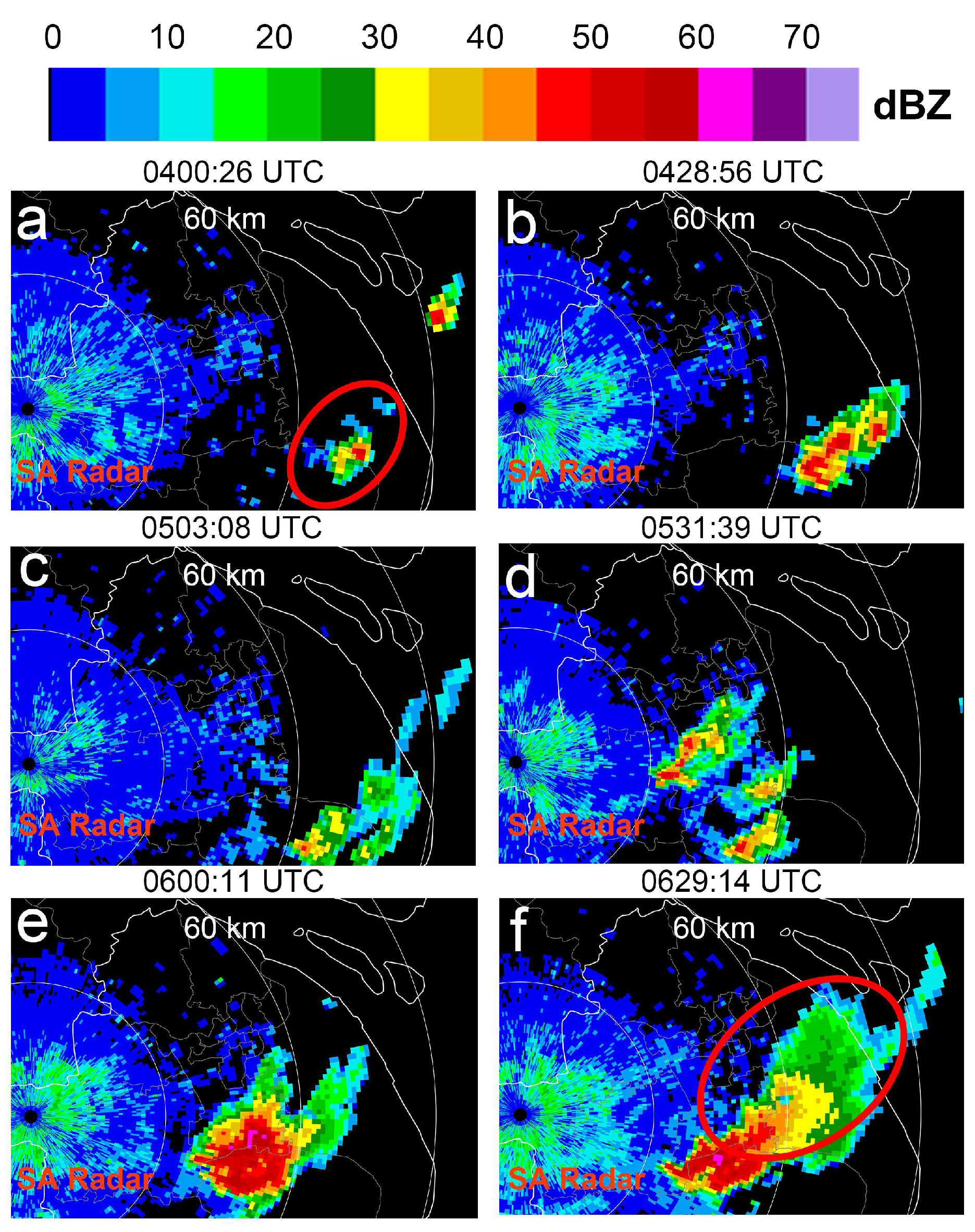
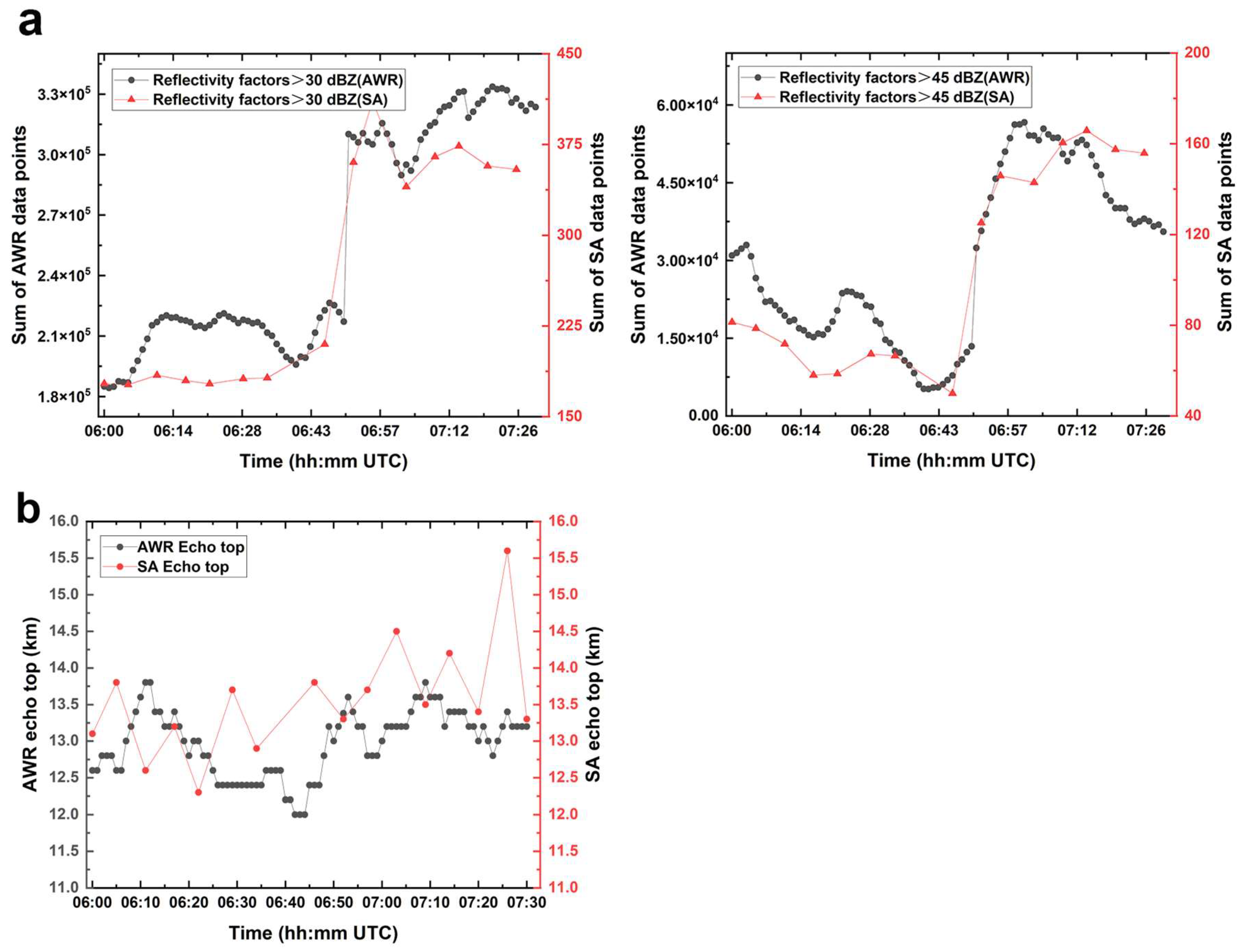
3.2. Statistical Analysis of Data from Two Weather Radars
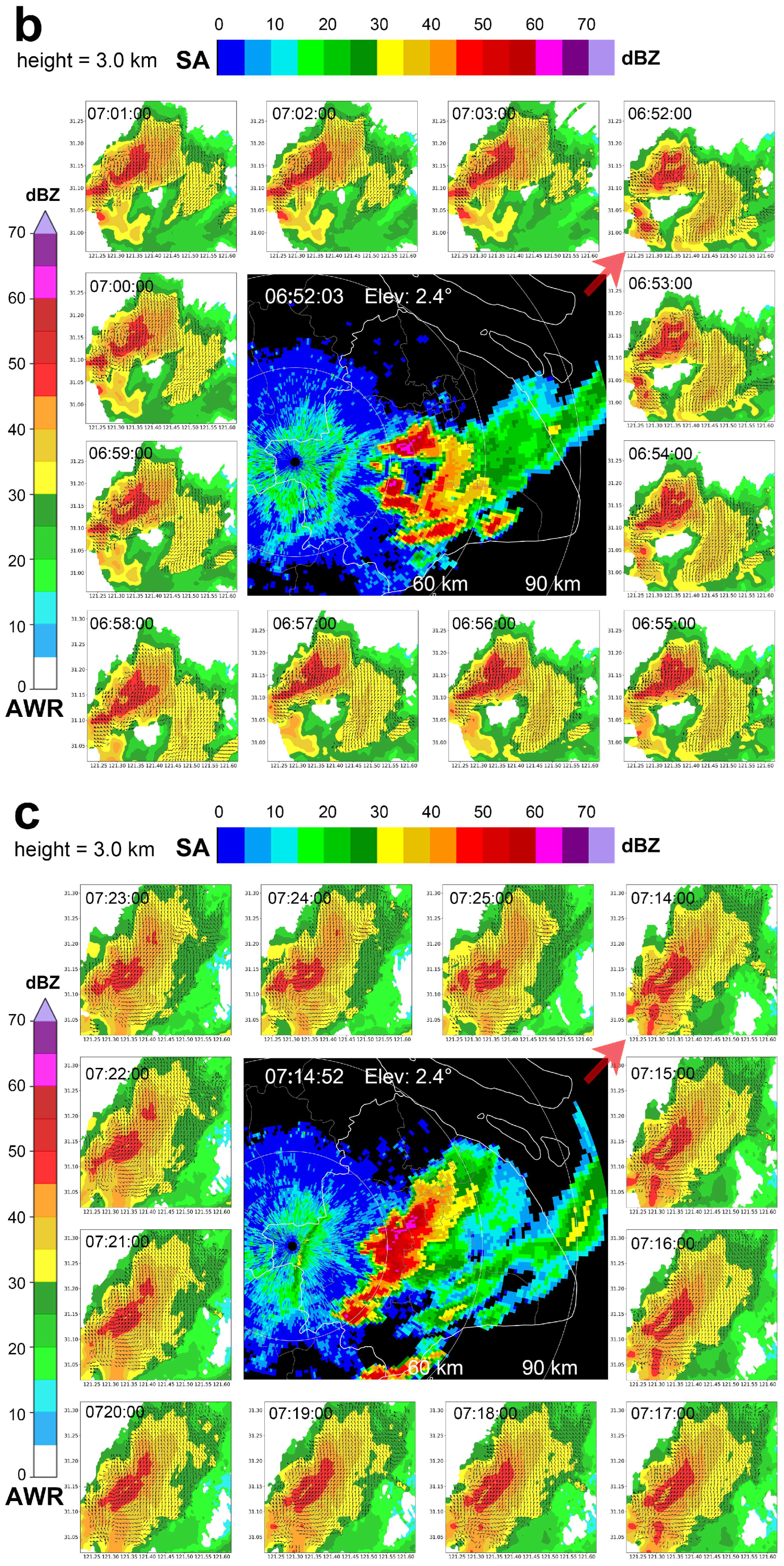
3.2.1. Classification of the Three Lifecycle Stages of the Strong Convective Precipitation Process
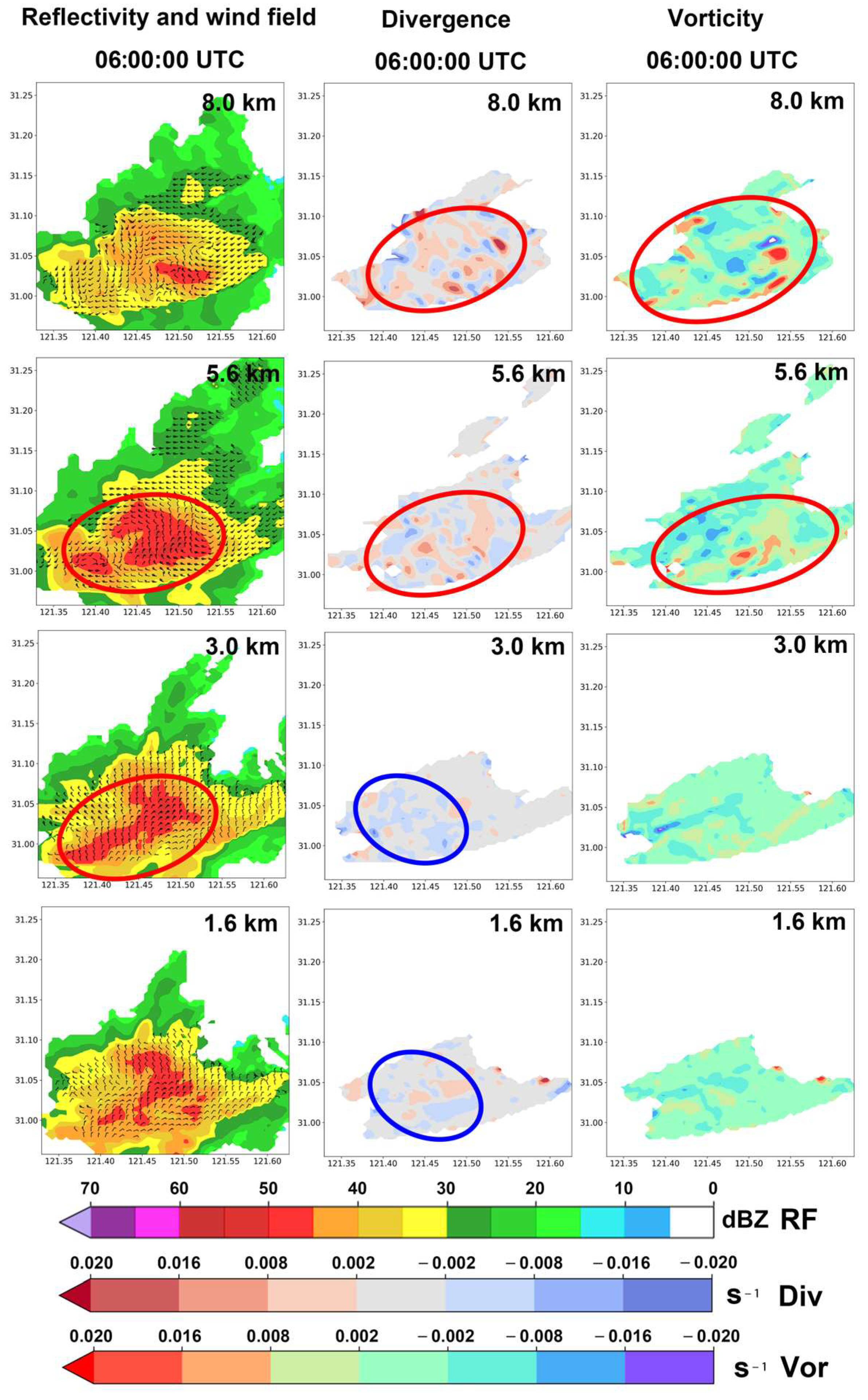
3.2.2. Analysis of the Strong Convective Precipitation Process Accompanied by Hail Using Shanghai AWR Detection Data
4. Conclusions and Discussions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PAR | Phased-array radar |
| NWRT | National Weather Radar Testbed |
| LMA | Lightning mapping array |
| PARISE | Phased-Array Radar Innovative Sensing Experiment |
| MWR-05XP | Meteorological Weather Radar 2005 X-band Phased Array |
| WSR-88D | Weather Surveillance Radar-1988 Doppler |
| S-PAR | S-band vehicle-mounted one-dimensional phased-array weather radar |
| APAR | X-band dual-polarization phased-array weather radar |
| C-PAR | C-band phased-array radar |
| AWR | Array weather radar |
| SAS | Synchronized azimuthal scanning |
| DTD | Detection data time difference |
| BS AWR | Baoshan Array Weather Radar |
| PD AWR | Pudong Array Weather Radar |
| CM AWR | Chongming Array Weather Radar |
| T-logP | Temperature–pressure logarithmic |
| CAPE | Convective available potential energy |
| CIN | Convective inhibition |
| SI | Showalter index |
| MICAPS | Meteorological Information Comprehensive Analysis and Processing System |
| AGRI | Advanced Geostationary Radiation Imager |
| FY-4 | Fengyun-4 |
| WPR | Wind profiler radar |
| FDA | Fine detection area |
| EDA | Enhanced detection area |
| PPT | Plan position indicator |
| ET | Echo top |
References
- Wang, D.; Pan, D.; Guo, G. Regional analysis of agro-meteorological disasters loss tendency variation from 1978 to 2016 in China. J. Catastrophol. 2018, 2018, 114–121. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Zhu, Y. Review on the observation investigation of thunderstorms. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 36, 411–422. [Google Scholar]
- Crum, T.D.; Saffle, R.E.; Wilson, J.W. An update on the NEXRAD program and future WSR-88D support to operations. Weather Forecast. 1998, 13, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Diao, X.; Huang, X. Study of CINRAD/SA products for a hail storm. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2004, 15, 579–589. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X. The advances in the nowcasting techniques on thunderstorms and severe convection. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2012, 70, 311–337. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.; Gu, H.; Liang, X.; Yu, M.; Sun, J.; Xie, Y.; Li, F.; Wu, C. A possible dynamic mechanism for rapid production of the extreme hourly rainfall in Zhengzhou city on 20 July 2021. J. Meteorol. Res. 2022, 36, 6–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istok, M.J.; Blanchard, W.M. Radar Informaiton Enhancements for the NWS Operational User. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Interactive Information and Processing Systems (IIPS) for Meteorology, Oceanography, and Hydrology, Seattle, WA, USA, 10–15 January 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Serafin, R.J.; Wilson, J.W. Operational weather radar in the United States: Progress and opportunity. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 81, 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.R.; White, A. Improvement of the WSR-88D mesocyclone algorithm. Weather Forecast. 1998, 13, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotzge, J.; Droegemeier, K.; McLaughlin, D. Collaborative adaptive sensing of the atmosphere: New radar system for improving analysis and forecasting of surface weather conditions. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2006, 1948, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.E.; Cho, J.Y.N.; Herd, J.S.; Flavin, J.M.; Benner, W.E.; Torok, G.S. The next-generation multimission U.S. surveillance radar network. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 88, 1739–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meischner, P.; Hagen, M. Weather radars in Europe potential for advanced applications. Phys. Chem. Earth Part B Hydrol. Ocean. Atmos. 2000, 25, 813–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köck, K.; Leitner, T.; Randeu, W.L.; Divjak, M.; Schrelber, K.J. OPERA: Operational programme for the exchange of weather radar information. First results and outlook for the future. Phys. Chem. Earth Part B Hydrol. Ocean. Atmos. 2000, 25, 1147–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamura, S.; Chandrasekar, V.; Ushio, T.; Kim, G.; Yoshikawa, E.; Chen, H. Probabilistic attenuation correction in a networked radar environment. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 6930–6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, B.; Antonescu, B.; Sills, D.M.L.; de Lima Nascimento, E.; Hanstrum, B.; Tochimoto, E.; Chernokulsky, A.M.A.; Zhang, X.; Doswell Iii, C.A.; Brooks, H.E. A century of progress in severe convective storm research and forecasting. Meteorol. Monogr. 2019, 59, 18.11–18.41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zrnic, D.S.; Kimpel, J.F.; Forsyth, D.E.; Shapiro, A.; Crain, G.; Ferek, R.; Heimmer, J.; Benner, W.; McNellis, F.T.J.; Vogt, R.J. Agile-beam phased array radar for weather observations. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 88, 1753–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, E.; Ushio, T.; Kawasaki, Z.; Mega, T.; Yoshida, S.; Morimoto, T.; Imai, K.; Nagayama, S.i. Development and initial observation of high-resolution volume-scanning radar for meteorological application. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 3225–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, E.; Ushio, T.; Kawasaki, Z.; Yoshida, S.; Morimoto, T.; Mizutani, F.; Wada, M. MMSE beam forming on fast-scanning phased array weather radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 3077–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, N.; Ushio, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Mizutani, F.; Iwanami, K.; Yamaji, A.; Kawagoe, T.; Osada, M.; Ohta, T.; Kawasaki, M. Development of multi-parameter phased array weather radar (MP-PAWR) and early detection of torrential rainfall and tornado risk. J. Disaster Res. 2019, 14, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, H.; Suezawa, T.; Ushio, T.; Takahashi, N.; Hanado, H.; Nakagawa, K.; Osada, M.; Maesaka, T.; Iwanami, K.; Yoshimi, K.; et al. Initial observations for precipitation cores with X-band dual polarized phased array weather radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 3657–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushio, T.; Shimamura, S.; Kikuchi, H.; Mizutani, F.; Naito, K.; Watanabe, T.; Wada, M.; Takahashi, N. Osaka urban phased array radar network experiment. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 5966–5968. [Google Scholar]
- Adachi, T.; Kusunoki, K.; Yoshida, S.; Arai, K.-I.; Ushio, T. High-speed volumetric observation of a wet microburst using X-band phased array weather radar in Japan. Mon. Weather Rev. 2016, 144, 3749–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, T.; Kusunoki, K.; Yoshida, S.; Hanako, I.; Arai, K.-I.; Ushio, T. Rapid volumetric growth of misocyclone and vault-like structure in horizontal shear observed by phased array weather radar. Sola 2016, 12, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Adachi, T.; Kusunoki, K.; Hayashi, S.; Wu, T.; Ushio, T.; Yoshikawa, E. Relationship between thunderstorm electrification and storm kinetics revealed by phased array weather radar. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 3821–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.W.; Smith, T.M.; Manross, K.L.; Priegnitz, D.L.; Heinselman, P.L. Rapid sampling of severe storms by the national weather radar testbed phased array radar. Weather Forecast. 2008, 23, 808–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, C.; Salazar, J.L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Kelly, R.; Meier, J.; McCord, M.; Schmidt, D.; Byrd, A.D.; Bhowmik, L.M.; et al. Cylindrical polarimetric phased array radar: Beamforming and calibration for weather applications. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 2827–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Doviak, R.J.; Zrnić, D.S.; Palmer, R.; Lei, L.; Al-Rashid, Y. Polarimetric phased-array radar for weather measurement: A planar or cylindrical configuration? J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2011, 28, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluestein, H.B.; French, M.M.; PopStefanija, I.; Bluth, R.T.; Knorr, J.B. A mobile, phased-array doppler radar for the study of severe convective storms. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 579–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggerstaff, M.I.; Yu, T.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cheong, B.-L.; Yeary, M.; Bodine, D.; Meier, J.; Kelley, R.; Palmer, R.; Isom, B. The atmospheric imaging radar: Simultaneous volumetric observations using a phased array weather radar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 655–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, F. Development of active phased array weather radar. In Proceedings of the 35th Conference on Radar Meteorology, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 26–30 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Doviak, R.J.; Lei, L.; Zhang, G.; Meier, J.; Curtis, C. Comparing theory and measurements of cross-polar fields of a phased-array weather radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 1002–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emersic, C.; Heinselman, P.L.; MacGorman, D.R.; Bruning, E.C. Lightning activity in a hail-producing storm observed with phased-array radar. Mon. Weather Rev. 2011, 139, 1809–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, K.A.; Heinselman, P.L.; Kingfield, D.M.; Thomas, R.P. Impacts of phased-array radar data on forecaster performance during severe hail and wind events. Weather Forecast. 2015, 30, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, K.A.; Heinselman, P.L. A qualitative analysis of NWS forecasters’ use of phased-array radar data during severe hail and wind events. Weather Forecast. 2016, 31, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Liu, L. Comparison of the observation capability of an X-band phased-array radar with an X-band Doppler radar and S-band operational radar. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 31, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, T. Analysis of the characteristics of X-band dual-polarization and phased-array weather radar during a hail weather process in early spring. Adv. Geosci. 2021, 11, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, L. A simulation and analysis of the observation errors of cloud intensity and structure with the S-band phased array radar and the CINRAD/SA. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2011, 69, 729–735. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, F.; Liu, L. Study on attenuation correction for the reflectivity of X-band dual-polarization phased-array weather radar based on a network with S-band weather radar. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Liu, L.; Liu, X.; Li, G.; Chen, C. Advances in Chinese dual-polarization and phased-array weather radars: Observational analysis of a supercell in southern China. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2018, 35, 1785–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Fu, P.; Hu, D.; Bao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Huang, H. The Guangzhou phased-array radar networking scheme setup and observation test. Meteorol. Mon. 2020, 46, 823–836. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, L.; Hu, D.; Chen, S.; Zhang, H.; Tian, C.; Zhang, A. Study on attenuation correction algorithm of X-band dual-polarization phased array radar. Meteorol. Mon. 2021, 47, 703–716. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, X.; Liu, X.; Lu, J.; Gen, L.; Huang, H.; Zhen, G. Severe convection weather monitoring by phased array radar at Beijing Daxing International Airport. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2022, 33, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Chen, H.; Wang, G.; Zhen, X.; Xu, X.; Li, S. Array weather radar design and initial implementation. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2019, 30, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, S.; Yang, L.; Zhen, X.; Qiao, D. Wind field verification for array weather radar at Changsha airport. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2020, 31, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, S.; Yang, L.; Zhen, X.; Qiao, D. Sensitivity analysis on data time difference for wind fields synthesis of array weather radar. Sci. Online Lett. Atmos. 2020, 16, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Ma, S.; Yang, L.; Zhen, X. Ground clutter detection algorithm for array weather Radar at Changsha airport. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2020, 31, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, X.; Ma, S.; Chen, H.; Wang, G.; Xu, X.; Li, S. A new X-band weather radar system with distributed phased-array front-ends: Development and preliminary observation results. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 39, 386–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushio, T.; Kim, D.-K.; Baron, P.; Wada, Y.; Mega, T.; Mizutani, F.; Wada, M.; Yoshikawa, E.; Satoh, S.; Hanado, H. Recent progress on the phased array weather radar at X band. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf22), New York, NY, USA, 21–25 March 2022; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, A.; Mewes, J.J. New formulations of dual-Doppler wind analysis. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1999, 16, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, A.; Potvin, C.K.; Gao, J. Use of a vertical vorticity equation in variational dual-Doppler wind analysis. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 2089–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potvin, C.K.; Shapiro, A.; Xue, M. Impact of a vertical vorticity constraint in variational dual-Doppler wind analysis: Tests with real and simulated supercell data. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2012, 29, 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Array Weather Radar (AWR) | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Technology | Distributed and active phased array One-dimensional, Doppler, single-polarized |
| Frequency | 9.3–9.5 GHz |
| Volume scan update time | 30 s |
| Each frontend scanning mode | Mechanical scan horizontally and electronic scan vertically |
| Maximum detection range of one radar | ~44 km |
| Grid size of outputs | 0.1 km × 0.1 km × 0.1 km |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhen, X.; Chen, H.; Shi, H.; Fan, X.; Chen, H.; Fu, J.; Wei, W.; Ma, S.; Yang, L.; He, J. A Case Study of a Hailstorm in the Shanghai Region: Leveraging Multisource Observational Data and a Novel Single-Polarization X-Band Array Weather Radar. Sensors 2025, 25, 2870. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092870
Zhen X, Chen H, Shi H, Fan X, Chen H, Fu J, Wei W, Ma S, Yang L, He J. A Case Study of a Hailstorm in the Shanghai Region: Leveraging Multisource Observational Data and a Novel Single-Polarization X-Band Array Weather Radar. Sensors. 2025; 25(9):2870. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092870
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhen, Xiaoqiong, Hongbin Chen, Hongrong Shi, Xuehua Fan, Haojun Chen, Jie Fu, Wanyi Wei, Shuqing Ma, Ling Yang, and Jianxin He. 2025. "A Case Study of a Hailstorm in the Shanghai Region: Leveraging Multisource Observational Data and a Novel Single-Polarization X-Band Array Weather Radar" Sensors 25, no. 9: 2870. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092870
APA StyleZhen, X., Chen, H., Shi, H., Fan, X., Chen, H., Fu, J., Wei, W., Ma, S., Yang, L., & He, J. (2025). A Case Study of a Hailstorm in the Shanghai Region: Leveraging Multisource Observational Data and a Novel Single-Polarization X-Band Array Weather Radar. Sensors, 25(9), 2870. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092870








