RMTSE: A Spatial-Channel Dual Attention Network for Driver Distraction Recognition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Traditional Driver Distraction Recognition Methods
2.2. Deep Learning-Based Driver Distraction Recognition Methods
3. Methodology
3.1. Overall Architecture
3.2. MaSA-SE Module
3.2.1. Manhattan Distance-Decayed Self-Attention
3.2.2. Learnable Channel Weight Recalibration Module
3.2.3. Depthwise Separable Convolution and Regularization
3.3. Transfer Learning Strategy
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset Description
4.2. Experiment Setting
4.3. Experiment Results on SFD3
4.4. Experiment Results on 100-Driver
4.5. Ablation Study
4.5.1. Ablation Study on SE-Net
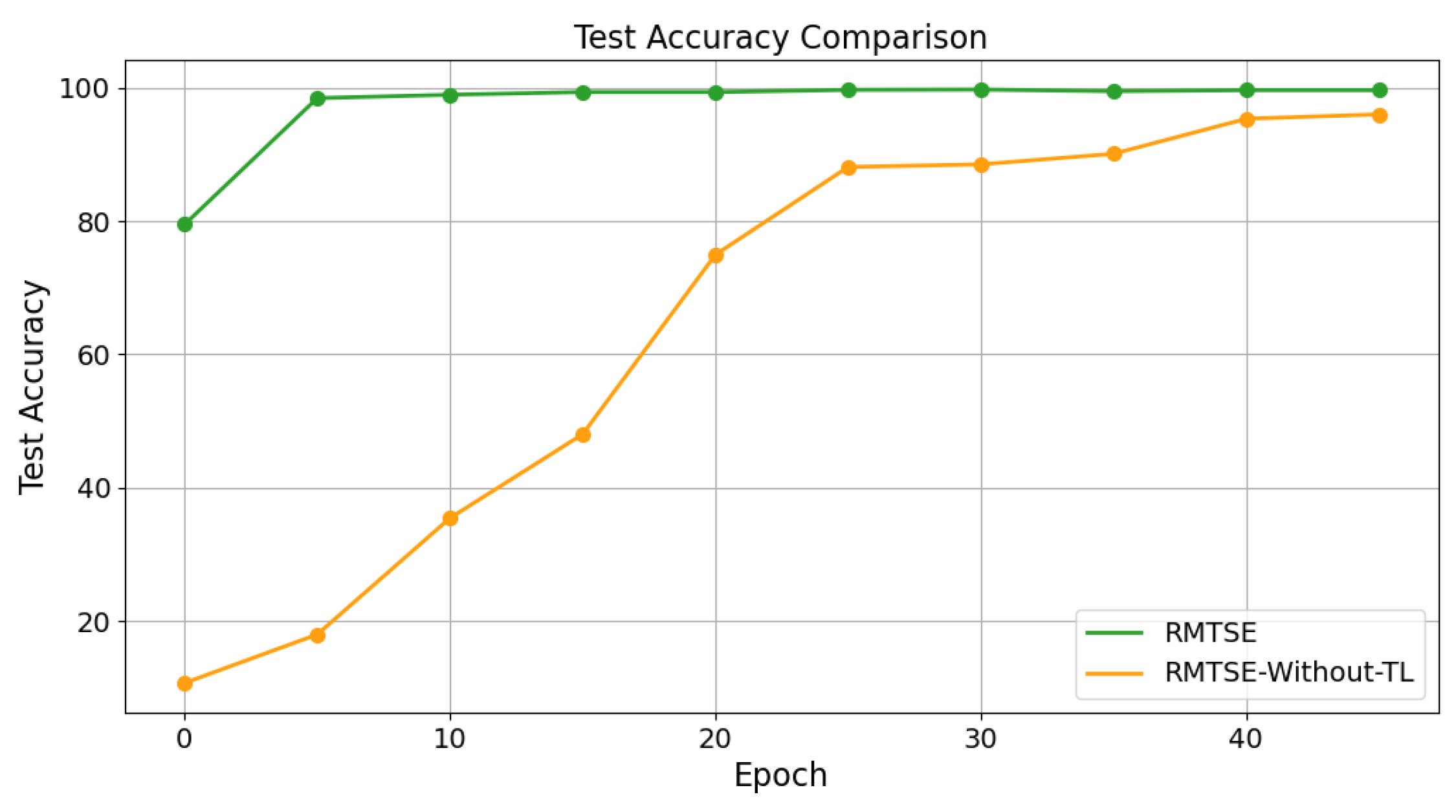
4.5.2. Ablation Study on Transfer Learning
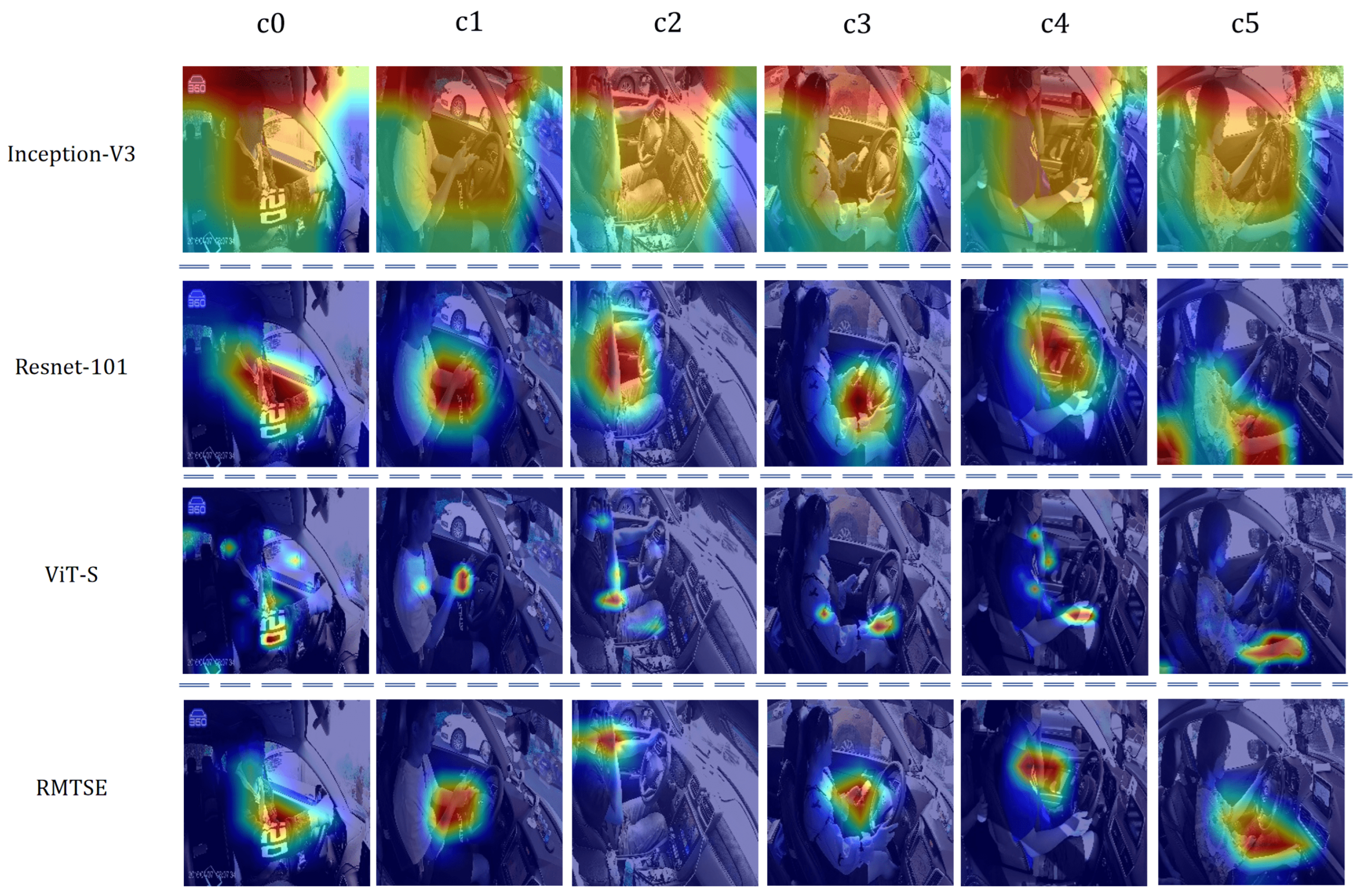
4.6. Model Visualization
5. Limitation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stavrinos, D.; Jones, J.L.; Garner, A.A.; Griffin, R.; Franklin, C.A.; Ball, D.; Welburn, S.C.; Ball, K.K.; Sisiopiku, V.P.; Fine, P.R. Impact of distracted driving on safety and traffic flow. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2013, 61, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Global Status Report on Road Safety 2023: Summary; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, D.; Tian, W.; Wang, C.; Chen, L.; Xiong, L. Driver distraction behavior recognition for autonomous driving: Approaches, datasets and challenges. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Gong, Y.; Liao, J.; Zhang, M.; Cao, L. FRNet: DCNN for real-time distracted driving detection toward embedded deployment. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 9835–9848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yao, L. Recongnition of Distracted Driving Behavior Based on Improved Bi-LSTM Model and Attention Mechanism. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 67711–67725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, H.; Verma, B. CAT-CapsNet: A convolutional and attention based capsule network to detect the driver’s distraction. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 9561–9570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Hu, Y.; Lu, X. Driver action recognition using deformable and dilated faster R-CNN with optimized region proposals. Appl. Intell. 2020, 50, 1100–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, Z. ViT-DD: Multi-task vision transformer for semi-supervised driver distraction detection. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 2–5 June 2024; pp. 417–423. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Liu, H.; Feng, X.; Chen, H. Distracted driving recognition using vision transformer for human-machine co-driving. In Proceedings of the 2021 5th CAA International Conference on Vehicular Control and Intelligence (CVCI), Tianjin, China, 29–31 October 2021; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Jain, J.J.; Busso, C. Modeling of driver behavior in real world scenarios using multiple noninvasive sensors. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2013, 15, 1213–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshadri, K.; Juefei-Xu, F.; Pal, D.K.; Savvides, M.; Thor, C.P. Driver Cell Phone Usage Detection on Strategic Highway Research Program (SHRP2) Face View Videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- SHRP2. Available online: http://www.trb.org/StrategicHighwayResearchProgram2SHRP2/Blank2.aspx (accessed on 24 February 2025).
- Alkinani, M.H.; Khan, W.Z.; Arshad, Q. Detecting human driver inattentive and aggressive driving behavior using deep learning: Recent advances, requirements and open challenges. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 105008–105030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Dang, N.; Furht, B.; Nojoumian, M. Comprehensive study of driver behavior monitoring systems using computer vision and machine learning techniques. J. Big Data 2024, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2015, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2021, Vienna, Austria, 3–7 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 9992–10002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, X.; Ke, Z.; Zhang, W.; Lau, R.W. Biformer: Vision transformer with bi-level routing attention. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 10323–10333. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Q.; Huang, H.; Chen, M.; Liu, H.; He, R. Rmt: Retentive networks meet vision transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 5641–5651. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhou, H.; Huang, J. A lightweight model combining convolutional neural network and Transformer for driver distraction recognition. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 132, 107910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koay, H.V.; Chuah, J.H.; Chow, C.O. Shifted-window hierarchical vision transformer for distracted driver detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Region 10 Symposium (TENSYMP), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 23–25 August 2021; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- SFD3. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/competitions/state-farm-distracted-driver-detection (accessed on 12 January 2025).
- Wang, J.; Li, W.; Li, F.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhong, Z.; Sebe, N. 100-driver: A large-scale, diverse dataset for distracted driver classification. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 7061–7072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, A.; Keidel, A.H. Latent body-pose guided densenet for recognizing driver’s fine-grained secondary activities. In Proceedings of the 2018 15th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS), Auckland, New Zealand, 24–30 November 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Dhakate, K.R.; Dash, R. Distracted driver detection using stacking ensemble. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Students’ Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Computer Science (SCEECS), Bhopal, India, 22–23 February 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wu, F.; Chen, D.; Wang, C. A Lightweight and Efficient Distracted Driver Detection Model Fusing Convolutional Neural Network and Vision Transformer. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
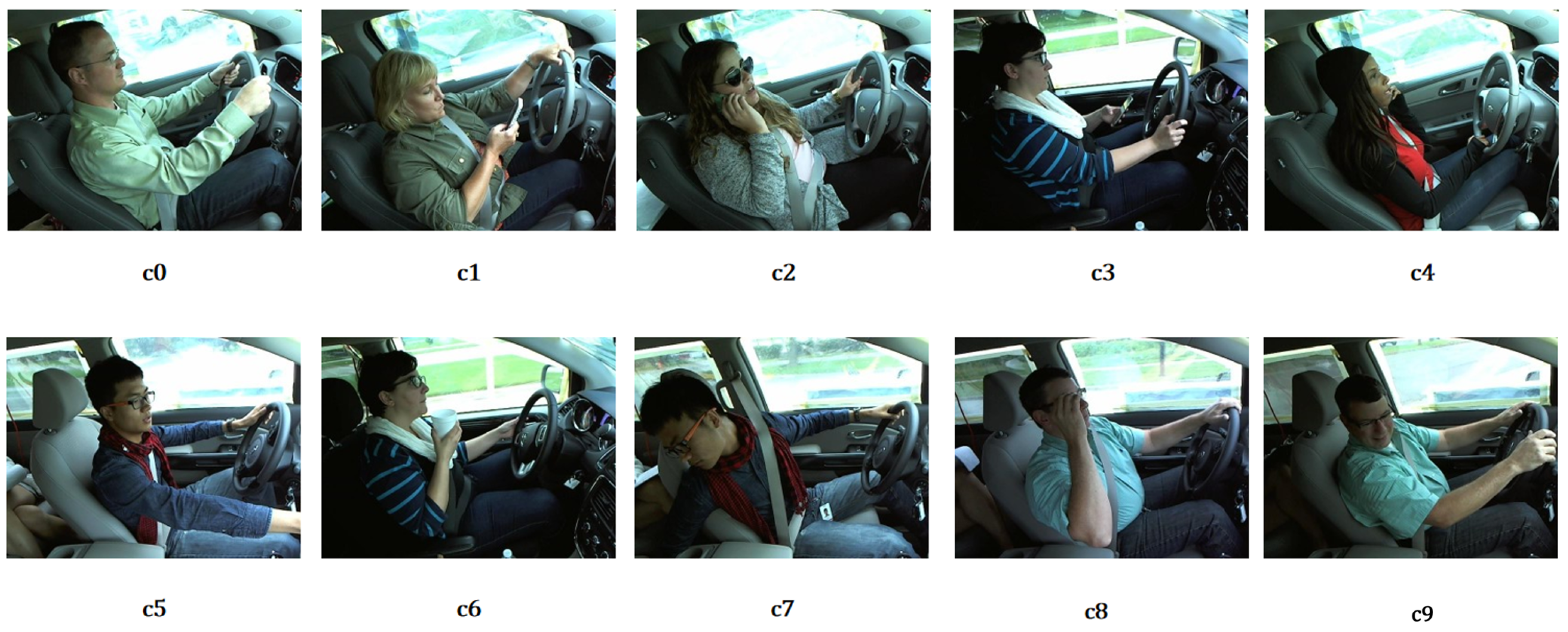
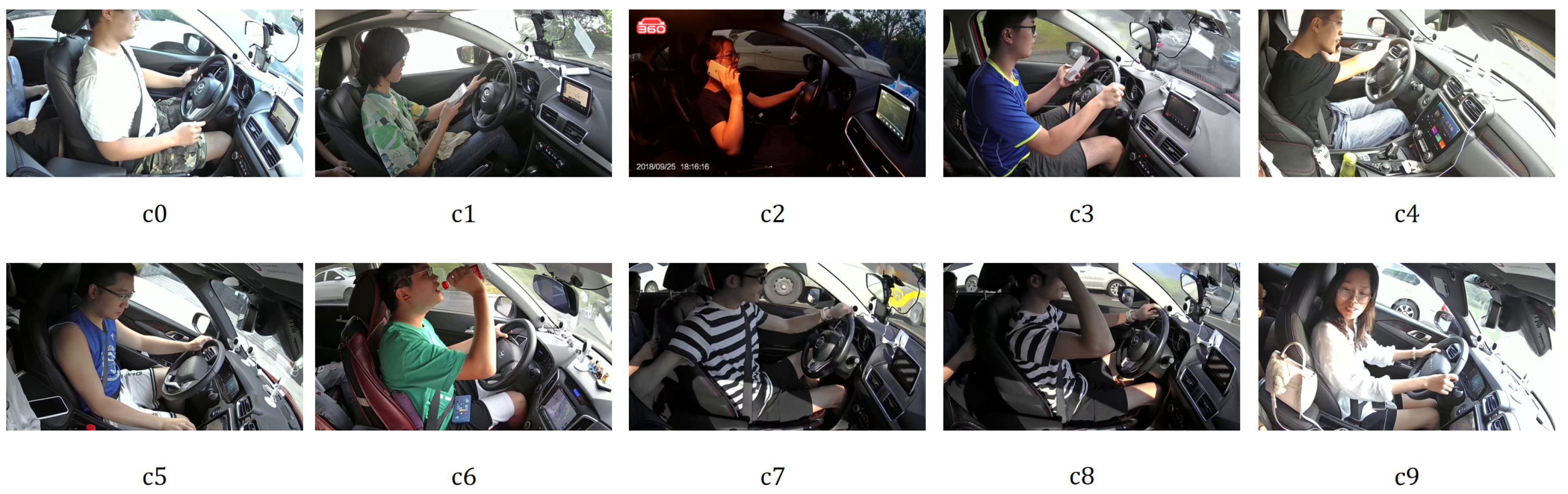








| Class Description | SFD3 | 100-Driver |
|---|---|---|
| c0: Safe driving | 2489 | 4455 |
| c1: Texting with right hand | 2267 | 3284 |
| c2: Calling with right hand | 2317 | 3400 |
| c3: Texting with left hand | 2346 | 3140 |
| c4: Calling with left hand | 2326 | 3479 |
| c5: Operating the radio | 2312 | 2512 |
| c6: Drinking | 2325 | 2882 |
| c7: Reaching behind | 2002 | 2068 |
| c8: Adjusting hair or makeup | 1911 | 2402 |
| c9: Talking to passenger | 2129 | 2485 |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Input size | 224 × 224 |
| Epochs | 50 |
| Batch size | 64 |
| Optimizer | AdamW |
| Initial learning rate | 1 |
| MixUp () | 0.8 |
| DropPath rate | 0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, J.; Li, C.; Xie, Y.; Luo, H.; Zheng, W.; Wang, Y. RMTSE: A Spatial-Channel Dual Attention Network for Driver Distraction Recognition. Sensors 2025, 25, 2821. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092821
He J, Li C, Xie Y, Luo H, Zheng W, Wang Y. RMTSE: A Spatial-Channel Dual Attention Network for Driver Distraction Recognition. Sensors. 2025; 25(9):2821. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092821
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Junyi, Chang Li, Yang Xie, Haotian Luo, Wei Zheng, and Yiqun Wang. 2025. "RMTSE: A Spatial-Channel Dual Attention Network for Driver Distraction Recognition" Sensors 25, no. 9: 2821. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092821
APA StyleHe, J., Li, C., Xie, Y., Luo, H., Zheng, W., & Wang, Y. (2025). RMTSE: A Spatial-Channel Dual Attention Network for Driver Distraction Recognition. Sensors, 25(9), 2821. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092821






