Exploration of Advanced Applications of Triboelectric Nanogenerator-Based Self-Powered Sensors in the Era of Artificial Intelligence
Abstract
:1. Introduction
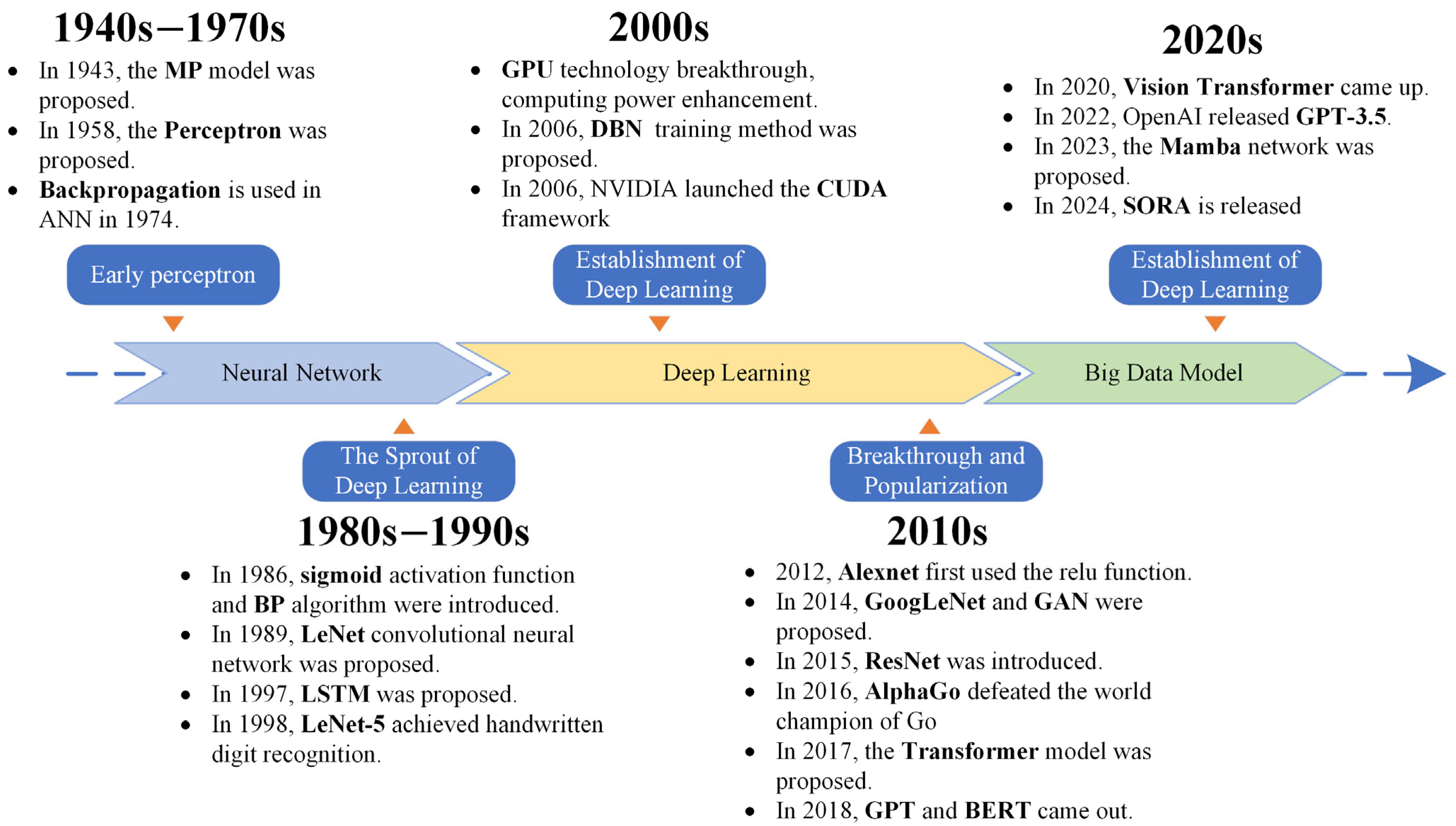
2. Overview of Deep Learning
2.1. History of Deep Learning
2.2. Comparative Analysis of Deep Learning Models
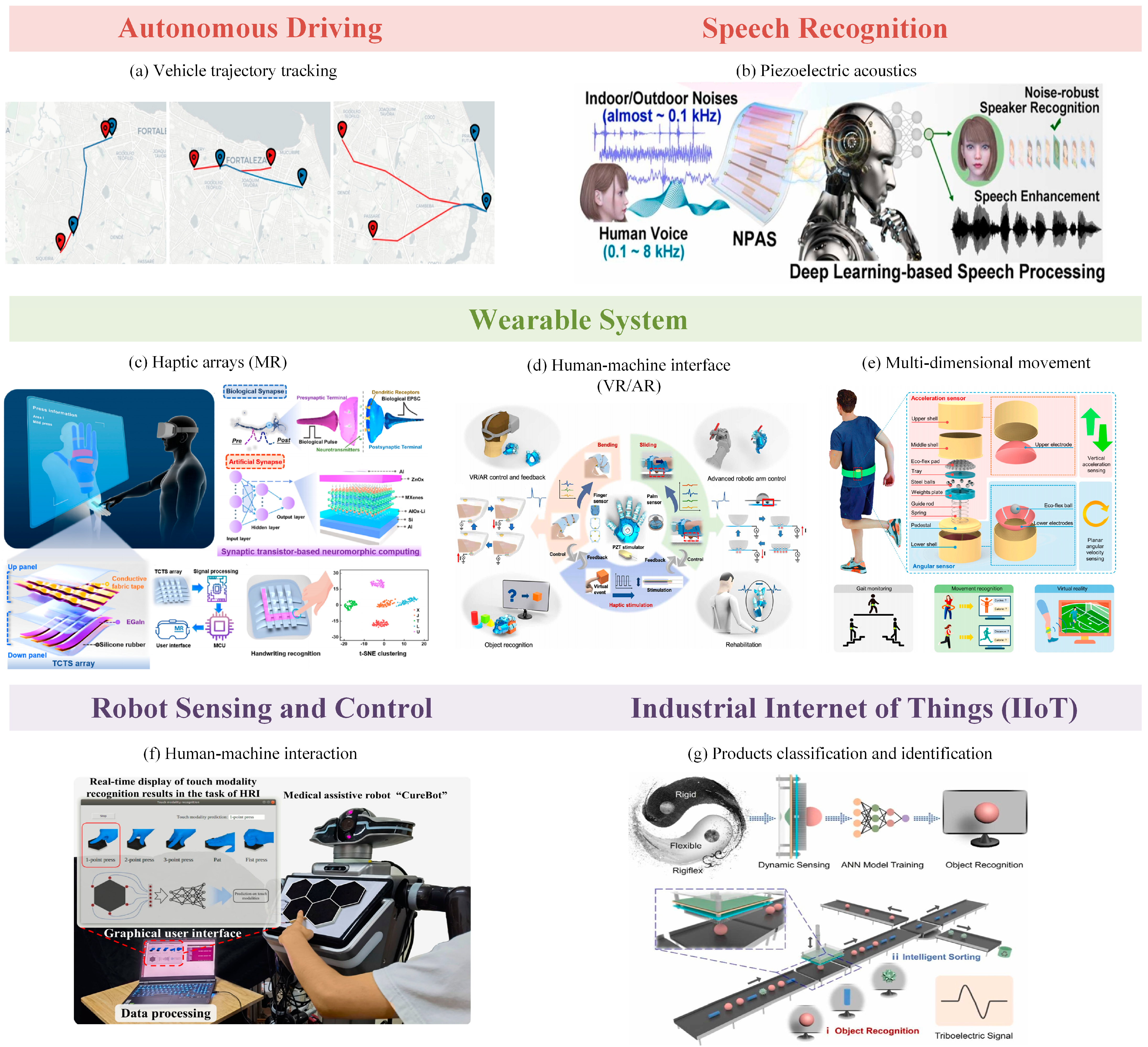
3. Sensor Applications Combined with Neural Networks
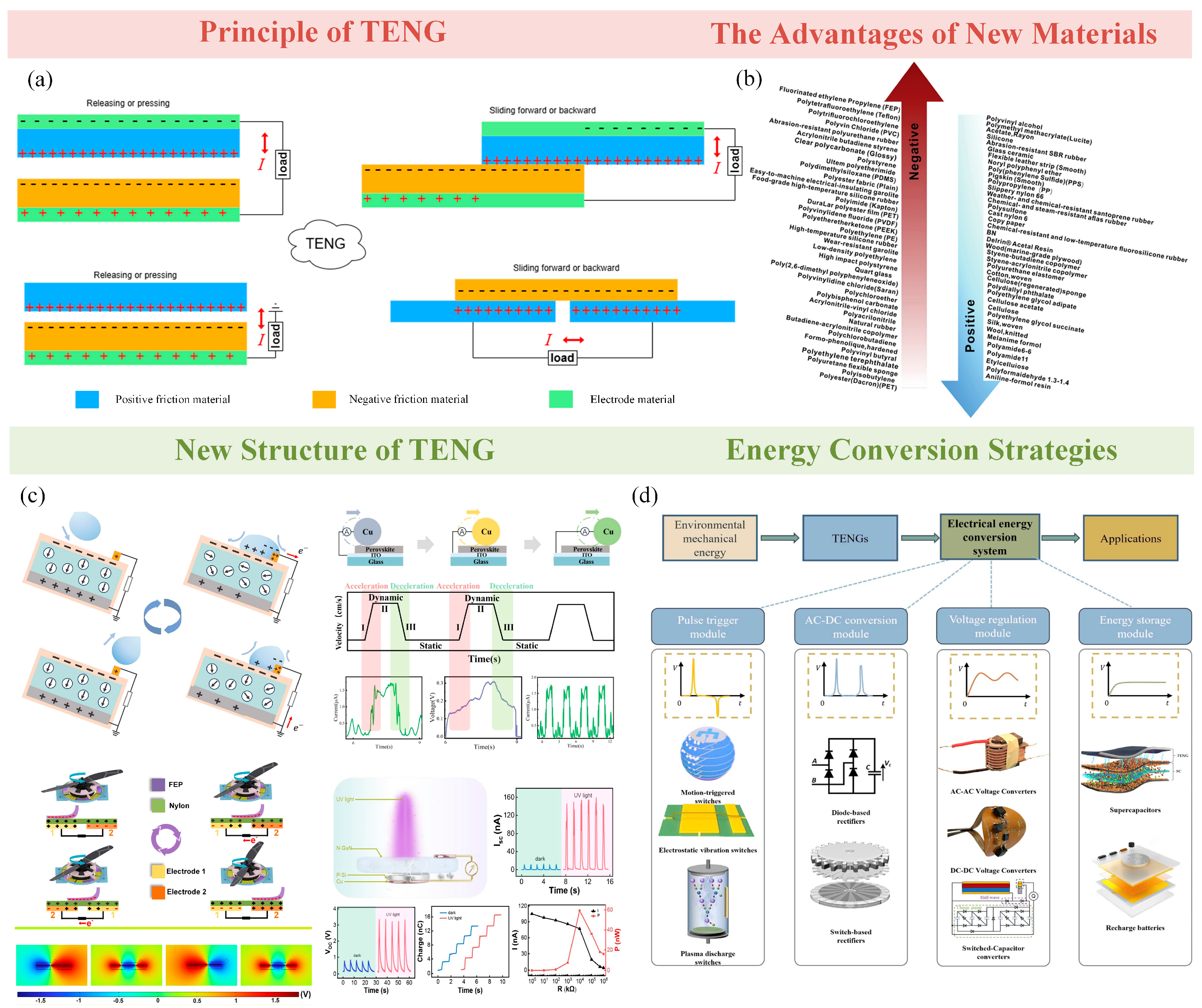
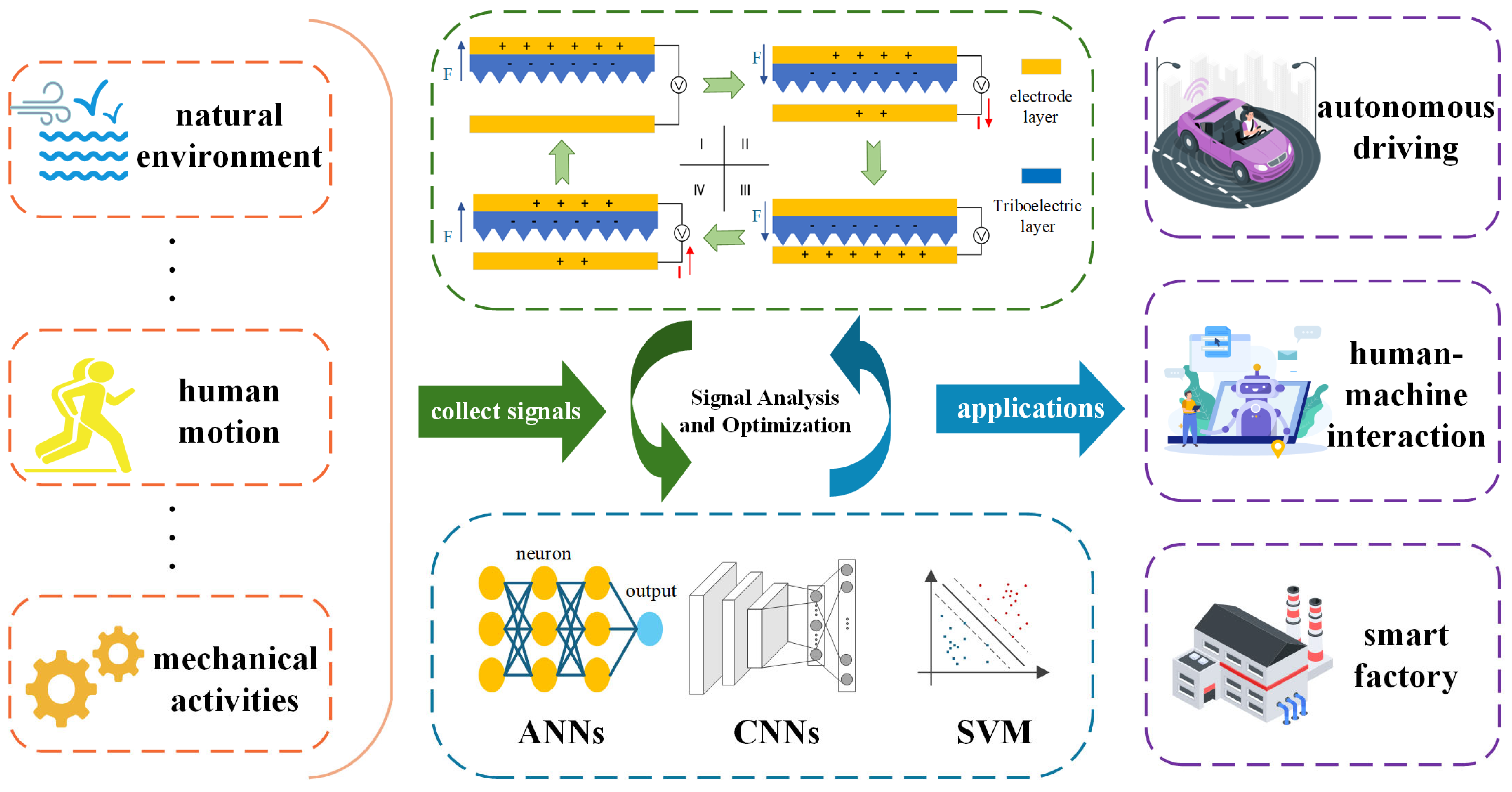
4. The Principle and Capacity of the Triboelectric Nanogenerator
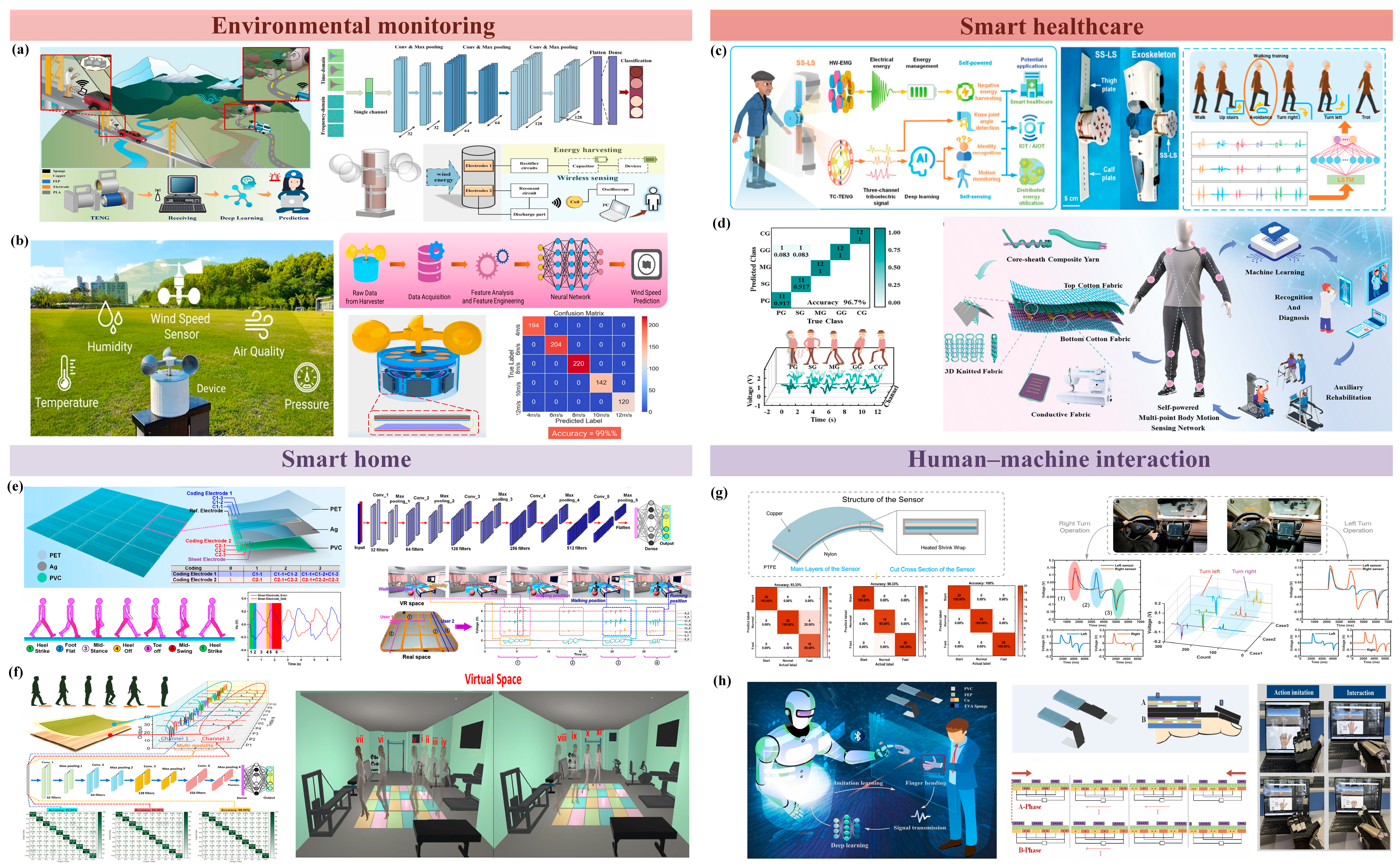
5. Triboelectric Sensors Combined with Neural Network Applications
6. Summary and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, X.; Buriak, J.M.; Salanne, M.; Xin, H. Nano & AI: A Nobel Partnership. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 32279–32282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S. An overview on the evolution and adoption of deep learning applications used in the industry. WIREs Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2018, 8, e1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, R.A.; Saeed, N.; Masood, M.; Fard, Y.M.; Alouini, M.S.; Al-Naffouri, T.Y. Deep Learning in the Industrial Internet of Things: Potentials, Challenges, and Emerging Applications. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 11016–11040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, K.R.M.; Tsokos, C.P. Deep and statistical learning in biomedical imaging: State of the art in 3D MRI brain tumor segmentation. Inf. Fusion 2023, 92, 450–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, A.; Selvaraj, P.; Gupta, D.; Sheikh, T.H.; Pareek, P.K.; Shankar, V. Internet of things and deep learning enabled healthcare disease diagnosis using biomedical electrocardiogram signals. Expert Syst. 2023, 40, e12864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taye, M.M. Understanding of Machine Learning with Deep Learning: Architectures, Workflow, Applications and Future Directions. Computers 2023, 12, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chai, J.; Cho, S. Deep learning in finance and banking: A literature review and classification. Front. Bus. Res. China 2020, 14, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Du, K.-L. Using Radial Basis Function Networks for Function Approximation and Classification. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2012, 2012, 324194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allinson, N.; Yin, H.; Allinson, L.; Slack, J. Advances in Self-Organising Maps; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.E.; Osindero, S.; Teh, Y. A Fast Learning Algorithm for Deep Belief Nets. Neural Comput. 2006, 18, 1527–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arel, I.; Rose, D.C.; Karnowski, T.P. Deep Machine Learning—A New Frontier in Artificial Intelligence Research [Research Frontier]. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2010, 5, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Xie, T.; Chen, Z. Wearable Sensors and Equipment in VR Games: A Review. In Transactions on Edutainment XV; Pan, Z., Cheok, A.D., Müller, W., Zhang, M., El Rhalibi, A., Kifayat, K., Eds.; Transactions on Edutainment XV; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Wu, H.; Wang, H.; Wu, H.; Lee, C. Self-Powered Gyroscope Ball Using a Triboelectric Mechanism. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1701300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Shi, Q.; Wang, H.; Wen, F.; Chen, T.; Ouyang, J.; Lee, C. Beyond energy harvesting—Multi-functional triboelectric nanosensors on a textile. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Dong, K.; Li, X.; An, J.; Wu, D.; Peng, X.; Yi, J.; Ning, C.; Cheng, R.; Yu, P.; et al. Stretchable, Washable, and Ultrathin Triboelectric Nanogenerators as Skin-Like Highly Sensitive Self-Powered Haptic Sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2005584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, K.-H.; Chung, C.-K. High-Performance Al/PDMS TENG with Novel Complex Morphology of Two-Height Microneedles Array for High-Sensitivity Force-Sensor and Self-Powered Application. Small 2020, 16, 2001209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Hou, X.; He, J.; Cui, M.; Wang, C.; Geng, W.; Mu, J.; Han, B.; Chou, X. Ultra-flexible and high-sensitive triboelectric nanogenerator as electronic skin for self-powered human physiological signal monitoring. Nano Energy 2020, 69, 104437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, Y.; Hao, D.; Chen, J.; Qi, L. A Self-Powered and Self-Sensing Lower-Limb System for Smart Healthcare. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2301254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, N.; Wang, Z.L.; Sun, Q. Machine learning enhanced rigiflex pillar-membrane triboelectric nanogenerator for universal stereoscopic recognition. Nano Energy 2024, 129, 109956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, A.; Sun, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Dong, F.; Wang, Z.; Si, J.; Zou, Y.; Xu, M. Recent advances in triboelectric tactile sensors for robot hand. Mater. Today Phys. 2024, 46, 101496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Lin, Y.; Zhao, F.; Chen, P.; Cao, S.; Zhou, K.; Gao, C.; Liu, Z.; et al. A comprehensive review on triboelectric sensors and AI-integrated systems. Mater. Today 2024, 80, 450–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Xiong, Y.; Sun, J.; Xie, X.; Sun, Q.; Wang, Z.L. Multidiscipline Applications of Triboelectric Nanogenerators for the Intelligent Era of Internet of Things. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 15, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Shen, M.; Cui, X.; Shao, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y. Triboelectric nanogenerator based self-powered sensor for artificial intelligence. Nano Energy 2021, 84, 105887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, R.; Chen, H.; Cai, X.; Shi, X.; Yang, Y.; Wei, X.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y. Machine Learning-Enhanced Triboelectric Sensing Application. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2024, 9, 2301316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Wu, H.; Hu, X.; Xie, M.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, X.; Ou-Yang, W. Machine learning-assisted self-powered intelligent sensing systems based on triboelectricity. Nano Energy 2023, 113, 108559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoudi, M.; An, C.-Y.; Kim, D.-E. A Review on Triboelectric Nanogenerators, Recent Applications, and Challenges. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2024, 11, 1317–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Guo, H.; Wang, P.; Li, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, D. An Advanced Strategy to Enhance TENG Output: Reducing Triboelectric Charge Decay. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2209895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Sun, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, G.; Chen, T.; Tian, Y.; Hou, X.; et al. Triboelectric nanogenerator sensors for soft robotics aiming at digital twin applications. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Pan, J.; Cui, T.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; Ren, T.-L. Recent Progress of Tactile and Force Sensors for Human–Machine Interaction. Sensors 2023, 23, 1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Xu, B.; Li, B.; Fu, H. Advanced Design of Soft Robots with Artificial Intelligence. Nano-Micro Lett. 2024, 16, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Zhang, L.; Su, Y.; Gao, G.; Liu, Y.; Na, Z.; Xu, Q.; Ding, T.; Xiao, L.; Li, L.; et al. A space crawling robotic bio-paw (SCRBP) enabled by triboelectric sensors for surface identification. Nano Energy 2023, 105, 108013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Ma, T.; Zhou, N.; Feng, J.; Huayan, P.; Luo, J.; Pennacchi, P.; Chu, F.; Han, Q. Extremely compact and lightweight triboelectric nanogenerator for spacecraft flywheel system health monitoring. Nano Energy 2024, 122, 109330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zheng, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Guan, T.; Fu, X.; Xu, M.; Xie, G.; et al. Deep-Learning-Assisted Underwater 3D Tactile Tensegrity. Research 2023, 6, 0062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Liu, J.; Liu, B.; Li, Y.; Jin, H.; Mu, Z.; Guan, T.; Xie, G.; Wang, H.; Xu, M. Deep-learning-assisted triboelectric whisker for near field perception and online state estimation of underwater vehicle. Nano Energy 2024, 129, 110011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Dong, B.; Jin, H.; Zhu, P.; Mu, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Meng, Z.; Zhou, X.; Xu, P.; et al. Deep-Learning-Assisted Triboelectric Whisker Sensor Array for Real-Time Motion Sensing of Unmanned Underwater Vehicle. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2025, 10, 2401053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCulloch, W.S.; Pitts, W. A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull. Math. Biophys. 1943, 5, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblatt, F. The perceptron: A probabilistic model for information storage and organization in the brain. Psychol. Rev. 1958, 65, 386–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taye, M.M. Theoretical Understanding of Convolutional Neural Network: Concepts, Architectures, Applications, Future Directions. Computation 2023, 11, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Boser, B.; Denker, J.S.; Henderson, D.; Howard, R.E.; Hubbard, W.; Jackel, L.D. Backpropagation Applied to Handwritten Zip Code Recognition. Neural Comput. 1989, 1, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long Short-Term Memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smagulova, K.; James, A.P. A survey on LSTM memristive neural network architectures and applications. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2019, 228, 2313–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2012, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, USA, 8–13 December 2014; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; Volume 2, pp. 2672–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, A.; Mittal, M.; Battineni, G. Generative adversarial network: An overview of theory and applications. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 2021, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Nagarajan, T.; Kumar, A.; Rennie, S.; Davis, L.S.; Grauman, K.; Feris, R. BlockDrop: Dynamic Inference Paths in Residual Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8817–8826. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Guo, J.; Liu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Xiao, A.; Xu, C.; Xu, Y.; et al. A Survey on Vision Transformer. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 87–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.-W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Narasimhan, K. Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training. 2018. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:49313245 (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Huang, S.; Cai, N.; Pacheco, P.P.; Narrandes, S.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W. Applications of Support Vector Machine (SVM) Learning in Cancer Genomics. Cancer Genom.-Proteom. 2018, 15, 41–51. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Li, J. KNN Classification with One-Step Computation. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2023, 35, 2711–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:abs/2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Huda, Z.; Peng, B.; Algburi, R.N.A.; Al-antari, M.A.; Al-Jarazi, R.; Zhai, D. A hybrid deep learning pavement crack semantic segmentation. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 122, 106142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Yang, K.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z. Photovoltaic power forecasting: A hybrid deep learning model incorporating transfer learning strategy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 162, 112473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Sohoni, M.M.; Wright, L.G.; Stein, M.M.; Ma, S.-Y.; Onodera, T.; Anderson, M.G.; McMahon, P.L. Image sensing with multilayer nonlinear optical neural networks. Nat. Photonics 2023, 17, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennel, L.; Symonowicz, J.; Wachter, S.; Polyushkin, D.K.; Molina-Mendoza, A.J.; Mueller, T. Ultrafast machine vision with 2D material neural network image sensors. Nature 2020, 579, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, L.A.; Coelho da Silva, T.L.; Magalhães, R.P.; Melo, W.C.D.; Cordeiro, M.; de Macedo, J.A.F.; Zeitouni, K. Modeling Trajectories Obtained from External Sensors for Location Prediction via NLP Approaches. Sensors 2022, 22, 7475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.H.; Pham, T.X.; Issa, D.; Wang, H.S.; Lee, J.H.; Chung, M.; Lee, B.-Y.; Kim, G.; Yoo, C.D.; Lee, K.J. Deep learning-based noise robust flexible piezoelectric acoustic sensors for speech processing. Nano Energy 2022, 101, 107610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, C.; Sun, Q.; Gu, H.; Li, J.; Tu, X.; Nie, B.; Sun, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Neuromorphic Computing-Assisted Triboelectric Capacitive-Coupled Tactile Sensor Array for Wireless Mixed Reality Interaction. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 17041–17052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, Q.; He, T.; Liu, H.; Chen, T.; Lee, C. Haptic-feedback smart glove as a creative human-machine interface (HMI) for virtual/augmented reality applications. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz8693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.H.; Zhang, Z.; An, K.; He, T.; Sun, Z.; Pu, X.; Lee, C. A Wearable Multidimensional Motion Sensor for AI-Enhanced VR Sports. Research 2023, 6, 0154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Yang, G.; Pang, G.; Ye, Z.; Lv, H.; Yu, Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, X.V.; Xu, K.; Yang, H. Bioinspired Co-Design of Tactile Sensor and Deep Learning Algorithm for Human–Robot Interaction. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2022, 4, 2200050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Hu, Y.; Wang, L.; Song, G.; Waslander, S.L.; Liu, Y.; Li, H. LMDrive: Closed-Loop End-to-End Driving with Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 15120–15130. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, A.S.S.; Pachori, R.B. Multivariate Dynamic Mode Decomposition for Automatic Imagined Speech Recognition Using Multichannel EEG Signals. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2024, 8, 6001604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Microsoft Kinect Sensor and Its Effect. IEEE MultiMed. 2012, 19, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.; Kumar, P.; Kaur, B.; Roy, P.P.; Dogra, D.P.; Santosh, K.C. Kinect sensor-based interaction monitoring system using the BLSTM neural network in healthcare. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2019, 10, 2529–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthu, B.; Sivaparthipan, C.B.; Manogaran, G.; Sundarasekar, R.; Kadry, S.; Shanthini, A.; Dasel, A. IOT based wearable sensor for diseases prediction and symptom analysis in healthcare sector. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 2020, 13, 2123–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsar, M.M.; Saqib, S.; Aladfaj, M.; Alatiyyah, M.H.; Alnowaiser, K.; Aljuaid, H.; Jalal, A.; Park, J. Body-Worn Sensors for Recognizing Physical Sports Activities in Exergaming via Deep Learning Model. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 12460–12473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.-Y.; Heo, W.; Yang, H.; Park, H. A Neural Network-Based Gait Phase Classification Method Using Sensors Equipped on Lower Limb Exoskeleton Robots. Sensors 2015, 15, 27738–27759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Dai, H.N.; Tang, H. Graph Neural Networks for Anomaly Detection in Industrial Internet of Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 9214–9231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Yen, S.-C.; Sheshadri, S.; Wang, J.; Lee, S.; Liu, Y.-H.; Liao, L.-D.; Thakor, N.V.; Lee, C. Progress of Flexible Electronics in Neural Interfacing—A Self-Adaptive Non-Invasive Neural Ribbon Electrode for Small Nerves Recording. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4472–4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. From contact electrification to triboelectric nanogenerators. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2021, 84, 096502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, W.; Hu, J.; He, W.; Yang, H.; Ling, C.; Xi, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, A.; Hu, C. Two voltages in contact-separation triboelectric nanogenerator: From asymmetry to symmetry for maximum output. Nano Energy 2020, 69, 104452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Jiang, T.; Tang, W.; Xu, L.; Kim, T.W.; Wu, C.; Chen, X.; Chen, B.; Xiao, T.; Bai, Y. Studying about applied force and the output performance of sliding-mode triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2018, 48, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xie, Y.; Niu, S.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z.L. Freestanding Triboelectric-Layer-Based Nanogenerators for Harvesting Energy from a Moving Object or Human Motion in Contact and Non-contact Modes. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2818–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjari Padhan, A.; Hajra, S.; Sahu, M.; Nayak, S.; Joon Kim, H.; Alagarsamy, P. Single-electrode mode TENG using ferromagnetic NiO-Ti based nanocomposite for effective energy harvesting. Mater. Lett. 2022, 312, 131644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Mo, J.; Fu, Q.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Wang, S.; Nie, S. Enhancement of Triboelectric Charge Density by Chemical Functionalization. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2004714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, G.; Nam, M.; Cho, S.; Kim, R.; Heo, Y.-W.; Lee, S. Droplet-based triboelectric devices using liquid dielectrics for self-powered sensing applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 497, 155659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Yao, Y.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Pan, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Li, T. Wireless Online Rotation Monitoring System for UAV Motors Based on a Soft-Contact Triboelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 46516–46526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xiongsong, T.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Gao, M.; Li, H.; Dai, G.; Yang, J. Constructing Ultra-High Current Direct-Current Tribo-Photovoltaic Nanogenerators via Cu/Perovskite Schottky Junction. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 34803–34814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Yu, A.; Wang, W.; Guo, D.; Jia, M.; Guo, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhai, J. p-n Junction Based Direct-Current Triboelectric Nanogenerator by Conjunction of Tribovoltaic Effect and Photovoltaic Effect. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 10099–10106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Deng, L.; Zhu, X.; Xu, C.; Xie, L.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, H. Efficient electrical energy conversion strategies from triboelectric nanogenerators to practical applications: A review. Nano Energy 2024, 132, 110383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Hu, X.; Chen, Z.; Yang, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Gao, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y. Textile-Based TENG Woven with Fluorinated Polyimide Yarns for Motion and Position Monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 17, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, Z.; Qu, X.; Gai, Y.; Xue, J.; Chao, S.; Huang, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Self-encapsulated ionic fibers based on stress-induced adaptive phase transition for non-contact depth-of-field camouflage sensing. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, X.; Zhai, S.; Bi, X.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, T. Harvesting Broadband Breeze Vibration Energy via Elastic Bistable Triboelectric Nanogenerator for In Situ, Self-Powered Monitoring of Power Transmission Lines. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 15, 2403318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; An, S.; Wang, P.; Xiong, S.; Wang, J.; Xu, S.; Wu, H.; Li, K.; Li, W.; Tong, L.; et al. Transverse-Asymmetric Electrode Structure Design to Eliminate Charge Transfer Loss for Enhancing Output Performance of Sliding Mode TENG. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2413359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.; Gu, G.; Zhang, W.; Luo, H.; Wang, T.; Zhang, B.; Guo, J.; Cui, P.; Yang, F.; Cheng, G.; et al. Rotational pulsed triboelectric nanogenerators integrated with synchronously triggered mechanical switches for high efficiency self-powered systems. Nano Energy 2021, 82, 105725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Sun, X.; Pan, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Li, X. An Inductive-Filtering Strategy of Submodule Ripple-Power in Triple-Port MMC-Based SST Applied to Hybrid Medium and Low Voltage AC/DC Interface. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 8015–8032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Lei, W.; Gao, L.; Chen, X.; Tong, D.; Yuan, P.; Mu, X.; Yu, H. Regulating the high-voltage and high-impedance characteristics of triboelectric nanogenerator toward practical self-powered sensors. Nano Energy 2021, 87, 106137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranjape, M.V.; Manchi, P.; Kurakula, A.; Kavarthapu, V.S.; Lee, J.K.; Graham, S.A.; Yu, J.S. Generalized utilization of energy harvesting ability of TENG for concurrent energy storage and motion sensing application with effective external circuitry. Nano Energy 2024, 129, 109983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tan, H.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Chen, F.; Jiang, X.; Lu, X.; Hu, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, J.; et al. Real-Time Non-Driving Behavior Recognition Using Deep Learning-Assisted Triboelectric Sensors in Conditionally Automated Driving. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2210580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Sun, D.; Guo, H.; Wang, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, F.; Gao, M. LDIPRS: A novel longitudinal driving intention prior recognition technique empowered by TENG and deep learning. Nano Energy 2024, 129, 110087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Hu, T.; Zhao, X.; Su, Y.; Yin, D.; Lee, C.; Wang, Z.L. Innovative smart gloves with Phalanges-based triboelectric sensors as a dexterous teaching interface for Embodied Artificial Intelligence. Nano Energy 2025, 133, 110491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, K.; Maharjan, P.; Bhatta, T.; Sharma, S.; Rahman, M.T.; Lee, S.; Salauddin, M.; Rana, S.S.; Park, J.Y. A High-Performance Rotational Energy Harvester Integrated with Artificial Intelligence-Powered Triboelectric Sensors for Wireless Environmental Monitoring System. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2022, 24, 2200286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhao, X.; Hu, T.; Liang, F.; Guo, B.; Tao, K. Deep-learning-assisted self-powered wireless environmental monitoring system based on triboelectric nanogenerators with multiple sensing capabilities. Nano Energy 2024, 132, 110301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, S.; Gupta, A.K.; Saha, U.; Krasnoslobodtsev, A.V.; Gupta, R.K.; Malhotra, B.D. Triboelectric Nanogenerator-based smart biomedical sensors for healthcare. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2023, 57, 103233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Jin, T.; Cai, J.; Xu, L.; He, T.; Wang, T.; Tian, Y.; Li, L.; Peng, Y.; Lee, C. Wearable Triboelectric Sensors Enabled Gait Analysis and Waist Motion Capture for IoT-Based Smart Healthcare Applications. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2103694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Luo, J.; Luo, J.; Li, X.; Han, K.; Li, D.; Cao, X.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible Wood-Based Triboelectric Self-Powered Smart Home System. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 3341–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Jiao, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Cao, X. Natural wood-based triboelectric nanogenerator as self-powered sensing for smart homes and floors. Nano Energy 2020, 75, 104957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Wu, F.; Lee, C.; Yuce, M.R. Self-powered control interface based on Gray code with hybrid triboelectric and photovoltaics energy harvesting for IoT smart home and access control applications. Nano Energy 2020, 70, 104456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhou, F.; Yan, H.; Gao, G.; Li, H.; Li, R.; Chen, T. Anti-freezing organohydrogel triboelectric nanogenerator toward highly efficient and flexible human-machine interaction at −30 °C. Nano Energy 2021, 90, 106614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Wang, A.C.; Wu, C.; Guo, H.; Wang, Z.L. Human–Machine Interfacing Enabled by Triboelectric Nanogenerators and Tribotronics. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Du, J.; Yang, P.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yang, D.; Zheng, L.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.L. Human–Machine Interaction via Dual Modes of Voice and Gesture Enabled by Triboelectric Nanogenerator and Machine Learning. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 17009–17018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Cheng, R.; Ning, C.; Wei, X.; Peng, X.; Lv, T.; Sheng, F.; Dong, K.; Wang, Z.L. A Self-Powered Body Motion Sensing Network Integrated with Multiple Triboelectric Fabrics for Biometric Gait Recognition and Auxiliary Rehabilitation Training. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2303562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Shan, X.; Salam, B.; Lee, C. Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT) Enabled Floor Monitoring System for Smart Home Applications. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 18312–18326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Shan, X.; Salam, B.; Lee, C. Robust triboelectric information-mat enhanced by multi-modality deep learning for smart home. InfoMat 2023, 5, e12360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yuan, K.; Chen, S.; Huang, Y.; Askari, H.; Yu, N.; Mo, J.; Xu, N.; Wu, M.; Chen, H.; et al. Triboelectric nanogenerator sensors for intelligent steering wheel aiming at automated driving. Nano Energy 2023, 113, 108575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Tian, H.; Cheng, J.; Zhu, F.; Liu, B.; Wei, S.; Ji, L.; Wang, Z.L. Decoding lip language using triboelectric sensors with deep learning. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Yao, P.; Ju, Z.; Sheng, Y.; Xu, B.; Liu, Y.; Hu, H. Conductive chenille yarn-based triboelectric carpet fabrics with enhanced flexibility and comfort for smart home monitoring. Mater. Today Energy 2024, 41, 101527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.-C.; Zhou, T.; Chang, S.-D.; Zou, H.-X.; Gao, Q.-H.; Wu, Z.-Y.; Yan, G.; Wei, K.-X.; Yeatman, E.M.; Meng, G.; et al. A disposable cup inspired smart floor for trajectory recognition and human-interactive sensing. Appl. Energy 2024, 357, 122524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yin, J.; Fang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Zou, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, J. Deep learning assisted ternary electrification layered triboelectric membrane sensor for self-powered home security. Nano Energy 2023, 113, 108524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, D.; Chu, H.; Ding, Y.; Fu, Z.; Yao, X.; Zhu, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, R.; Xu, T.; et al. Ultra-stretchable triboelectric touch pad with sandpaper micro-surfaces for Transformer-assisted gesture recognition. Nano Energy 2024, 130, 110110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, K.; Pradhan, G.B.; Bhatta, T.; Sharma, S.; Lee, S.; Song, H.; Jeong, S.; Park, J.Y. Intermediate nanofibrous charge trapping layer-based wearable triboelectric self-powered sensor for human activity recognition and user identification. Nano Energy 2023, 108, 108180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Cai, H.; Wang, J.; Li, K. Machine-learning-assisted wearable PVA/Acrylic fluorescent layer-based triboelectric sensor for motion, gait and individual recognition. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 478, 147075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Li, W.; Shi, Y.; Wei, S.; Liu, K.; Cheng, J.; Ji, L.; Lu, Y. Stretchable self-adhesive and self-powered smart bandage for motion perception and motion intention recognition. Nano Energy 2023, 109, 108245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Yao, C.; Liu, Z.; Huang, S.; Huang, X.; Zheng, S.; Liu, J.; Shi, P.; Zhang, T.; Chen, H.; et al. Machine learning-coupled vertical graphene triboelectric pressure sensors array as artificial tactile receptor for finger action recognition. Nano Energy 2024, 123, 109395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, C.; Xu, Z.; Xie, X.; Guo, H.; Peng, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Xie, S. Structure-Crack Detection and Digital Twin Demonstration Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Intelligent Maintenance. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2302443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Kong, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Hong, H. Monitoring Downhole Machinery Operations Using Noncontact Triboelectric Nanogenerators and Deep Learning. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 25414–25421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, C.; Ma, T.; Wang, T.; Gao, S.; Dai, Q.; Han, Q.; Chu, F. Tooth backlash inspired comb-shaped single-electrode triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered condition monitoring of gear transmission. Nano Energy 2024, 123, 109429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, D.; Mao, R.; Zhou, L.; Yang, C.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ji, Y. MoS2-based charge trapping layer enabled triboelectric nanogenerator with assistance of CNN-GRU model for intelligent perception. Nano Energy 2024, 127, 109753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Liang, J.; Wang, S.; Huang, J.; Chen, Z. A multimodal PDMS triboelectric nanogenerator sensor based on anodised aluminium oxide template preparation for object recognition. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 24158–24168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Miao, K.; Cui, M.; Ao, T.; Zhang, J.; Ban, D.; Zheng, H. Intelligent Sound Monitoring and Identification System Combining Triboelectric Nanogenerator-Based Self-Powered Sensor with Deep Learning Technique. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2112155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Bing, Z.; Wu, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhou, Z.; Fang, F.; Liang, S.; Guo, R.; Tu, S.; Pan, G.; et al. A multi-dimensional tactile perception system based on triboelectric sensors: Towards intelligent sorting without seeing. Nano Energy 2024, 123, 109398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Yang, Z.; Cheng, J.; Li, Z.; Ji, L. Development and application of nanogenerators in humanoid robotics. Nano Trends 2023, 3, 100013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Sun, Z.; Lee, C. Augmented Tactile Perception of Robotic Fingers Enabled by AI-Enhanced Triboelectric Multimodal Sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2409558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Xia, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, X. Wearable Pressure Sensor Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Information Encoding, Gesture Recognition, and Wireless Real-Time Robot Control. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 2419209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.-h.; Lee, H.; Song, M.; Ro, Y.G.; Kwak, M.S.; Kim, J.; Jung, G.; Park, J.; Kim, Y.-R.; Lee, J.; et al. A Self-Powered, Highly Sensitive, and Frequency-Tunable Triboelectric Acoustic Sensor Inspired by the Human Cochlea. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2408344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.-Y.; Han, J.-K.; Lee, S.-W.; Yu, J.-M.; Jeon, S.-B.; Choi, Y.-K. Self-aware artificial auditory neuron with a triboelectric sensor for spike-based neuromorphic hardware. Nano Energy 2023, 109, 108322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajra, S.; Panda, S.; Khanberh, H.; Vivekananthan, V.; Chamanehpour, E.; Mishra, Y.K.; Kim, H.J. Revolutionizing self-powered robotic systems with triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2023, 115, 108729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Jiang, Y.; Ren, T.; Chen, B.; Zhang, R.; Mao, Y. Recent advances in nature inspired triboelectric nanogenerators for self-powered systems. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2024, 6, 062003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Wang, L.; Fu, Z.; Xu, L.; Guo, W.; Huang, J.; Wang, Z.L.; Wu, H. Anatomically Designed Triboelectric Wristbands with Adaptive Accelerated Learning for Human–Machine Interfaces. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2205960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Fan, H.; Karimi, H.R.; Su, H. An adaptive reinforcement learning-based multimodal data fusion framework for human–robot confrontation gaming. Neural Netw. 2023, 164, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, Y.-R.; Zhou, M.; Peng, A.; Zhu, N.; Torres-Sospedra, J. Signal Processing and Machine Learning for Smart Sensing Applications. Sensors 2023, 23, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Manshaii, F.; Xiao, X.; Chen, J. Artificial intelligence assisted nanogenerator applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2025, 13, 832–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wei, D.; Wang, Z. Synergizing Machine Learning Algorithm with Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Advanced Self-Powered Sensing Systems. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagwari, A.; Logeshwaran, J.; Usha, K.; Raju, K.; Alsharif, M.H.; Uthansakul, P.; Uthansakul, M. An Enhanced Energy Optimization Model for Industrial Wireless Sensor Networks Using Machine Learning. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 96343–96362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, A.; Mandal, D. Roadmap to Human–Machine Interaction through Triboelectric Nanogenerator and Machine Learning Convergence. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2024, 7, 822–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wei, F.; Zhai, Z.; Zhang, R.; Liu, W.; Zhao, Z. A flexible dual-mode triboelectric sensor for strain and tactile sensing toward human-machine interface applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2024, 365, 114909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Zhu, M.; Sun, L.; Ding, T.; Huang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Su, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, T.; Lee, C. Scalable self-attaching/assembling robotic cluster (S2A2RC) system enabled by triboelectric sensors for in-orbit spacecraft application. Nano Energy 2022, 93, 106894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, L.H.; Wang, X.; Dove, A.; Horányi, M. Laboratory investigations of triboelectric charging of dust by rover wheels. Adv. Space Res. 2023, 72, 1861–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.; Cao, L.N.Y.; Shang, Y.; Li, C.; Zhou, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Tang, W.; Chen, B.; Guo, W.; et al. Conformal self-powered high signal-to-noise ratio biomimetic in-situ aircraft surface turbulence mapping system. Nano Energy 2025, 136, 110694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhang, S.; Wei, Z.; Luo, B.; Cai, C.; Chi, M.; Wang, S.; Nie, S. Dynamic Thermostable Cellulosic Triboelectric Materials from Multilevel-Non-Covalent Interactions. Small 2024, 20, 2307504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, T.; Qiu, Y.; Hou, Z.; Cai, C.; Li, M.; Xu, Y.; Mou, Y.; Luo, S.; Lu, D. Elastic Yet Strength Triboelectric Aerogel Enabled by Constructing a Supramolecular System. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2417067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, L.; Ding, X.; Wu, S.; Wu, Q.; Shao, Y. Signal processing collaborated with deep learning: An interpretable FIRNet for industrial intelligent diagnosis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2024, 212, 111314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wan, J.; Zhao, X.; Li, H.; Chen, Z.; Xia, H.; Gui, C. Vibration wave transfer management strategy inside triboelectric nanogenerator device for enhancing recognition accuracy. Nano Energy 2024, 124, 109474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, T.; Pradhan, G.B.; Shrestha, K.; Jeong, S.H.; Zhang, S.; Kim, H.S.; Park, J.Y. All elastomeric pillars-based triboelectric vibration sensor for self-powered broad range machinery condition monitoring. Nano Energy 2023, 117, 108929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, T.; Wei, Z.; Luo, B.; Chi, M.; Zhang, S.; Cai, C.; Gao, C.; Zhao, T.; et al. Triboelectric tactile sensor for pressure and temperature sensing in high-temperature applications. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhou, H.; Xu, S.; Lee, C. Advances in Machine-Learning Enhanced Nanosensors: From Cloud Artificial Intelligence Toward Future Edge Computing at Chip Level. Small Struct. 2024, 5, 2300325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.C.; Dai, Z.; Ma, H.; Zheng, J.; Leng, J.; Xie, C.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, W.; Yalikun, Y.; Song, X.; et al. Self-powered and speed-adjustable sensor for abyssal ocean current measurements based on triboelectric nanogenerators. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Zheng, J.; Guan, T.; Liu, X.; Wang, T.; Chen, T.; Wang, H.; Xie, G.; et al. A Self-powered Triboelectric Coral-Like Sensor Integrated Buoy for Irregular and Ultra-Low Frequency Ocean Wave Monitoring. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 2101098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, P.; Han, J.; Liang, X.; Ming, Y.; Liu, S.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z.L. High-performance triboelectric nanogenerator based on a double-spiral zigzag-origami structure for continuous sensing and signal transmission in marine environment. Interdiscip. Mater. 2025, 4, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Qu, C.; Lv, L.; Chen, H.; Song, G. Highly Adaptive Liquid–Solid Triboelectric Nanogenerator-Assisted Self-Powered Water Wave Motion Sensor. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2022, 4, 3870–3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Liu, L.; Xu, X.; Liu, A.; Wu, H.; Li, J.; Ou-Yang, W. A self-powered acoustic sensor excited by ultrasonic wave for detecting and locating underwater ultrasonic sources. Nano Energy 2022, 104, 107879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Sun, C.; Lin, Z.; Feng, Z.; Si, S.; Yang, J. Triboelectric hydrophone for underwater detection of low-frequency sounds. Nano Energy 2022, 99, 107428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowacki, B.; Mistewicz, K.; Hajra, S.; Joon Kim, H. 3D printed triboelectric nanogenerator for underwater ultrasonic sensing. Ultrasonics 2023, 133, 107045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Yuan, Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xu, F.; Fan, Q.; Zhang, M.; Qian, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; et al. All-in-one strain-triboelectric sensors based on environment-friendly ionic hydrogel for wearable sensing and underwater soft robotic grasping. Nano Energy 2023, 111, 108387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, B.; Liu, C.; Chen, R.; Qu, G.; Sui, H.; Chen, N.; Xing, G. A self-powered sensor for detecting slip state and pressure of underwater actuators based on triboelectric nanogenerator. Mater. Today Nano 2023, 24, 100391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, B.; Xu, P.; Liu, J.; Dai, X.; Yu, A.; Wang, T.; Guo, L.; Guan, T.; Song, L.; et al. A palm-like 3D tactile sensor based on liquid-metal triboelectric nanogenerator for underwater robot gripper. Nano Res. 2024, 17, 10008-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Xu, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, F.; Qu, L.; Tian, M. Underwater Gesture Recognition Meta-Gloves for Marine Immersive Communication. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 10818–10828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Model | Advantages | Disadvantages | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | Good generalization and robustness | Slightly high computational complexity | Text classification, image recognition, and financial risk assessment. |
| Handle linear and nonlinear problems effectively, even in high-dimensional spaces | Sensitive to missing data | ||
| Hyperparameter tuning is challenging | |||
| LSTM | Effectively captures long-distance dependencies in sequences | Higher computational complexity than traditional RNNs | Machine translation, text generation, sentiment analysis, weather forecasting, stock trend prediction. |
| Mitigate gradient vanishing to some extent | Require large data volumes, and limited data can weaken generalization capabilities | ||
| Well suited for time-sensitive data | |||
| ResNet | Residual blocks alleviate gradient explosion and vanishing problems | Deep model structure requires significant computing resources | Object detection and segmentation, image classification, audio signal processing. |
| High accuracy and suitable for transfer learning | Limited generalization on small datasets, risk of overfitting | ||
| GAN | Capable of generating realistic images, audio, etc. | Susceptible to “mode collapse”, causing generator degradation | Image and video synthesis, anomaly detection, data augmentation, privacy encryption and protection. |
| Works in an unsupervised fashion without labeled data | Challenging to evaluate generation quality, requires human intervention | ||
| Highly flexible and scalable | |||
| Transformer | Multi-head attention mechanism enables parallel computation | High data requirements for effective training. | Natural language processing, computer vision, code generation, program understanding. |
| Captures global dependencies with strong contextual understanding | High computational cost, complex hyperparameters, difficult tuning | ||
| Adaptable across multiple tasks. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, Y.; Yin, D.; Zhao, X.; Hu, T.; Liu, L. Exploration of Advanced Applications of Triboelectric Nanogenerator-Based Self-Powered Sensors in the Era of Artificial Intelligence. Sensors 2025, 25, 2520. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082520
Su Y, Yin D, Zhao X, Hu T, Liu L. Exploration of Advanced Applications of Triboelectric Nanogenerator-Based Self-Powered Sensors in the Era of Artificial Intelligence. Sensors. 2025; 25(8):2520. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082520
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Yifeng, Dezhi Yin, Xinmao Zhao, Tong Hu, and Long Liu. 2025. "Exploration of Advanced Applications of Triboelectric Nanogenerator-Based Self-Powered Sensors in the Era of Artificial Intelligence" Sensors 25, no. 8: 2520. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082520
APA StyleSu, Y., Yin, D., Zhao, X., Hu, T., & Liu, L. (2025). Exploration of Advanced Applications of Triboelectric Nanogenerator-Based Self-Powered Sensors in the Era of Artificial Intelligence. Sensors, 25(8), 2520. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082520






