Investigation of Ultrasound Transmit–Receive Sequence That Enables Both High-Frame-Rate Vascular Wall Velocity Estimation and High-Contrast B-Mode Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
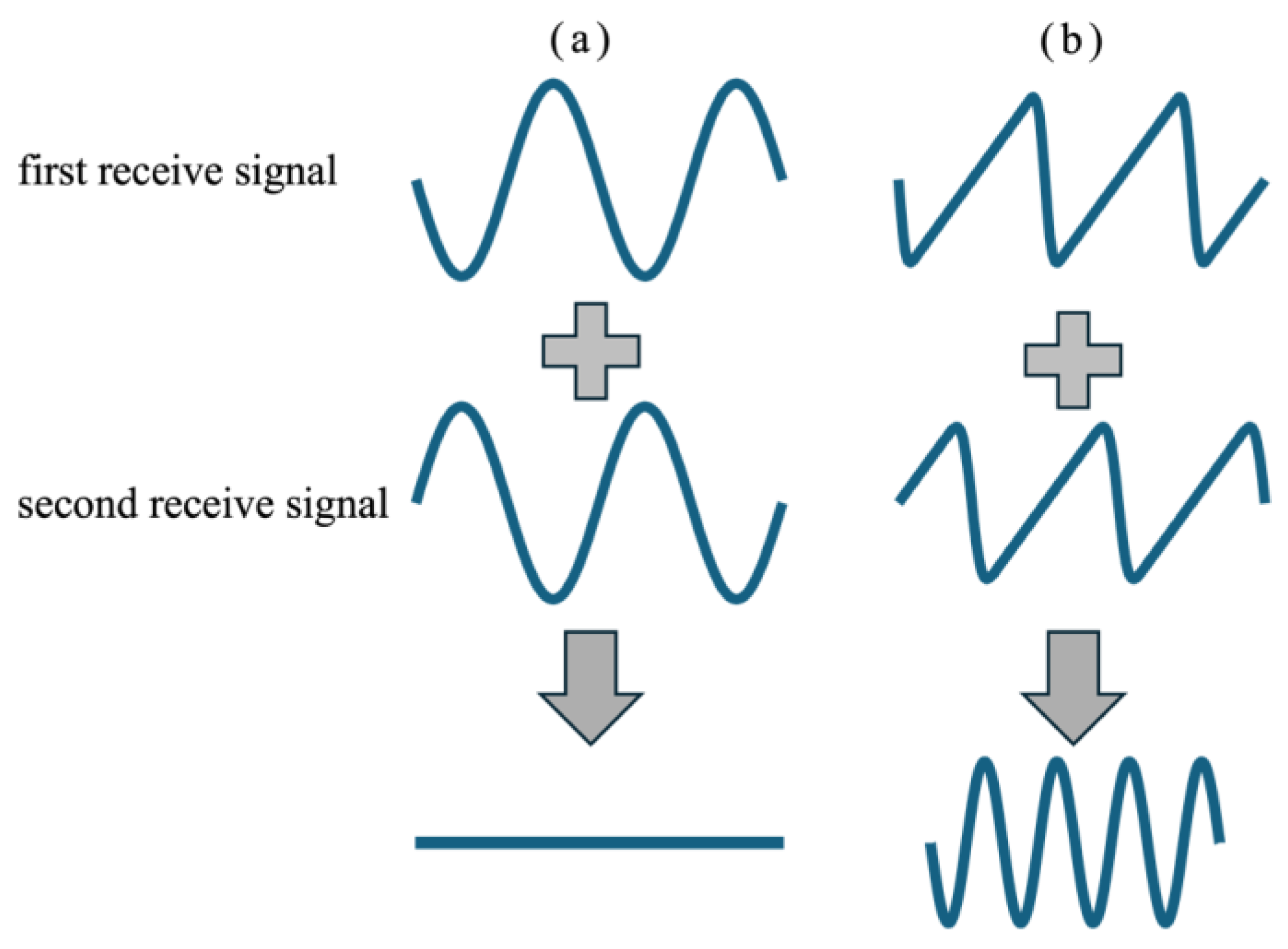
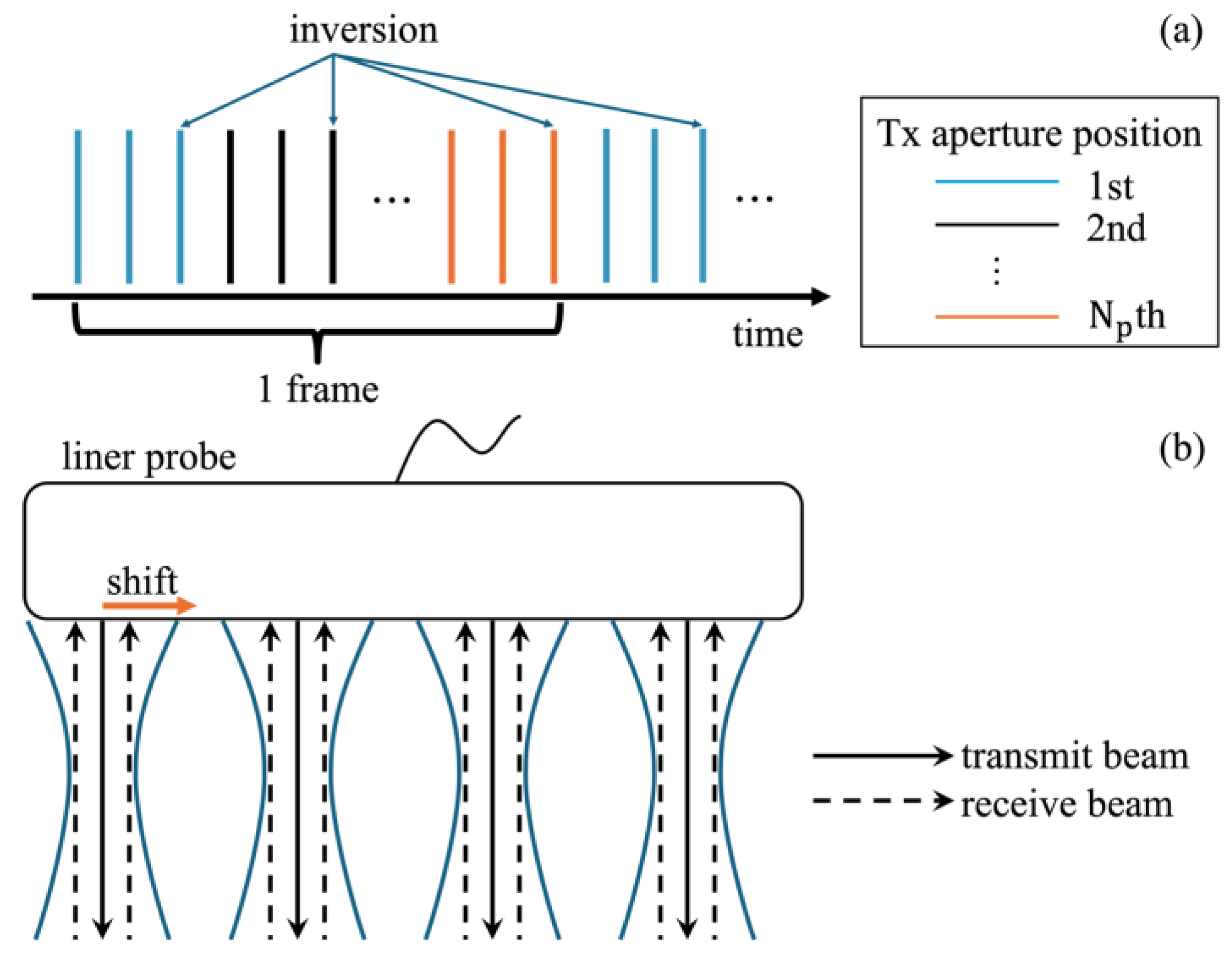
2.1. Tx-Rx Sequence
2.2. Basic Experimental Setup
2.3. In Vivo Experiment
3. Results
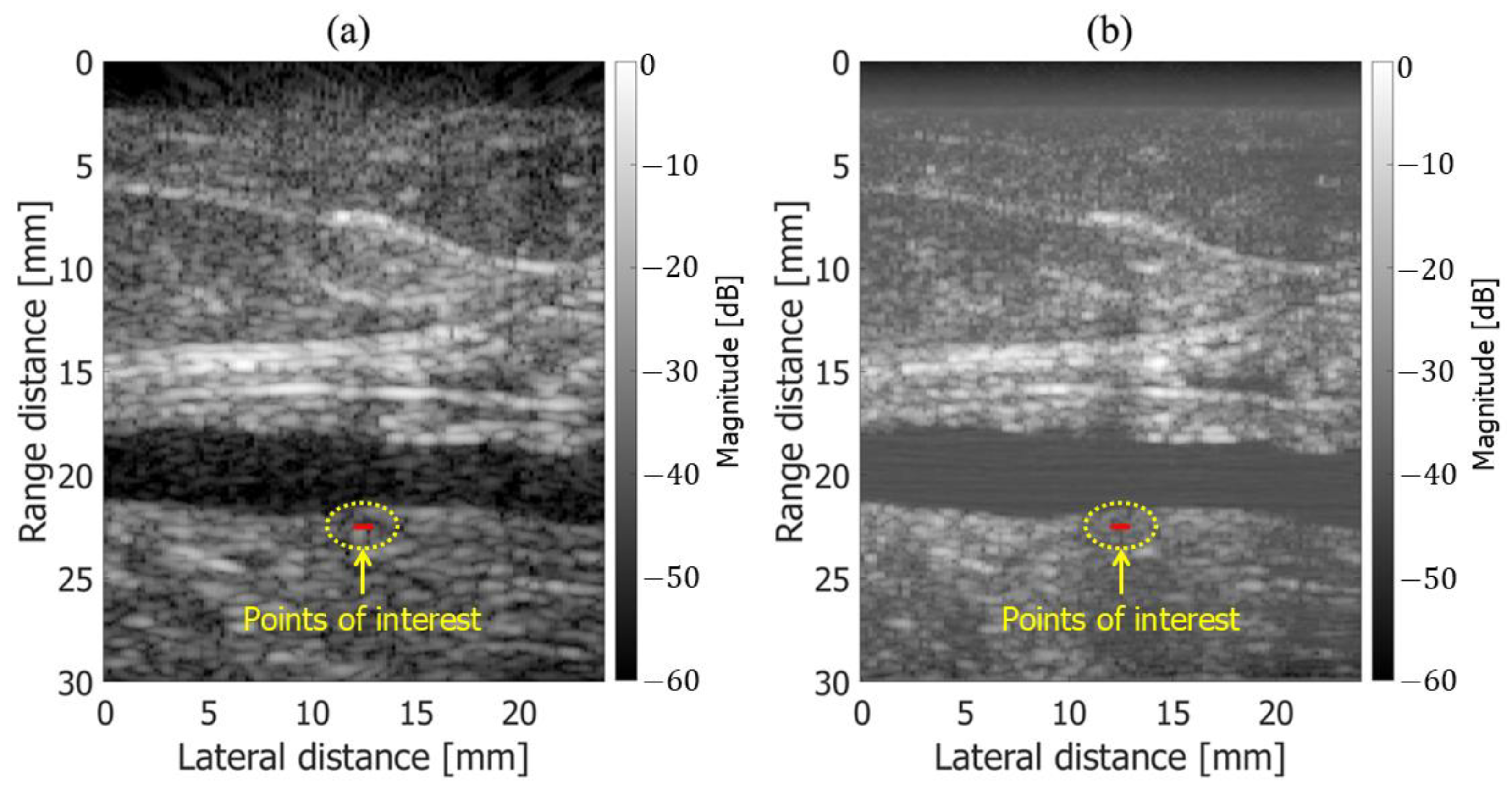
3.1. Basic Experimental Results
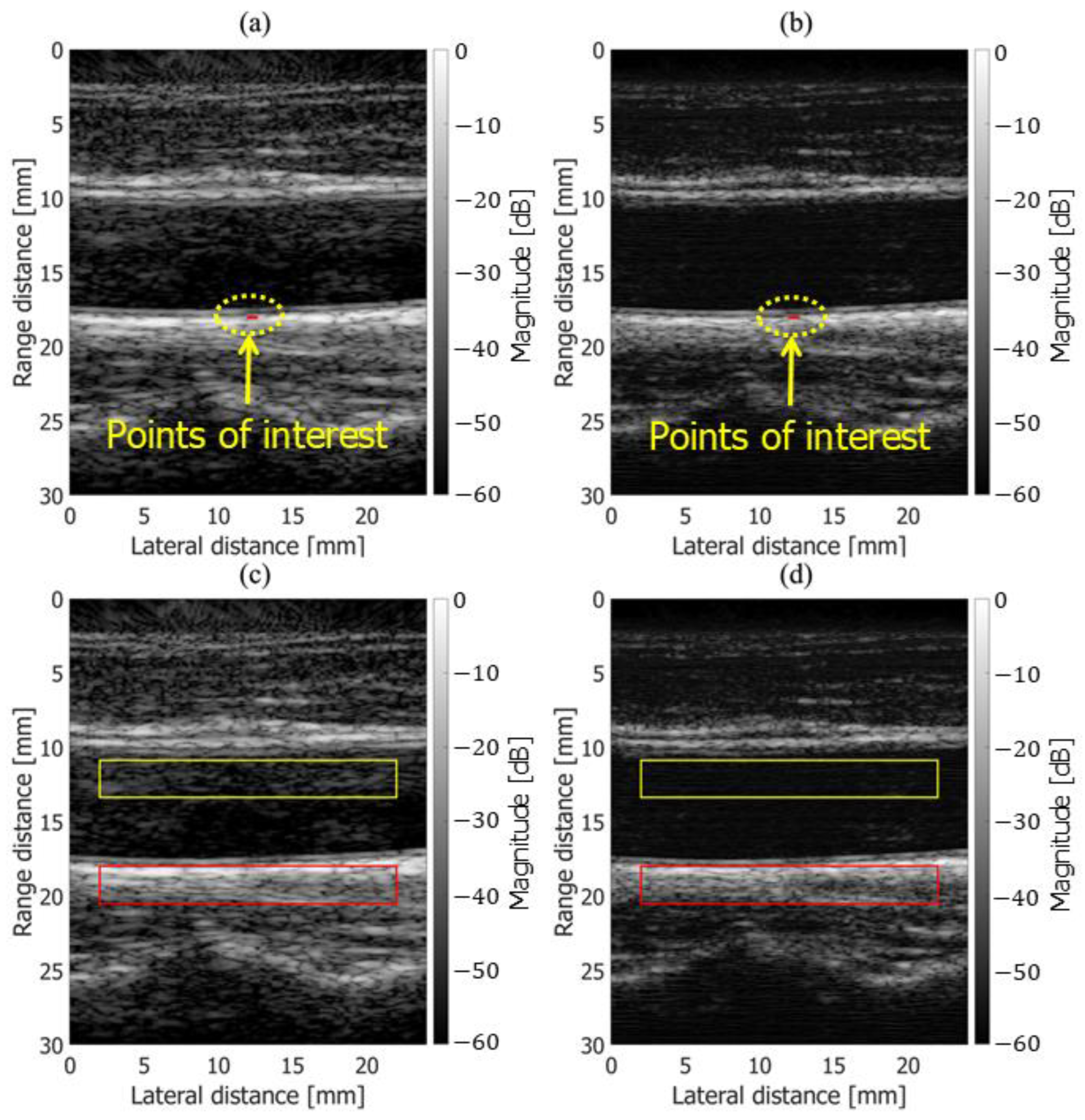
3.2. In Vivo Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nair, A.; Kuban, B.D.; Tuzcu, E.M.; Schoenhagen, P.; Nissen, S.E.; Vince, D.G. Coronary Plaque Classification With Intravascular Ultrasound Radiofrequency Data Analysis. Circulation 2002, 106, 2200–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picano, E.; Paterni, M. Ultrasound Tissue Characterization of Vulnerable Atherosclerotic Plaque. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 10121–10133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, Y.; Kodama, M.; Nishizawa, H.; Sakamoto, K.; Matsuhisa, M.; Kajimoto, Y.; Kosugi, K.; Shimizu, Y.; Kawamori, R.; Hori, M. Carotid intima-media thickness in Japanese type 2 diabetic subjects: Predictors of progression and relationship with incident coronary heart disease. Diab. Care. 2000, 23, 1310–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubozono, T.; Miyata, M.; Kawasoe, S.; Ojima, S.; Yoshifuku, S.; Miyahara, H.; Maenohara, S.; Ohishi, M. High Pulse Wave Velocity Has a Strong Impact on Early Carotid Atherosclerosis in a Japanese General Male Population. Circ. J. 2017, 81, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bots, M.L.; Hoes, A.W.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Hofman, A.; Grobbee, D.E. Common carotid intima-media thickness and risk of stroke and myocardial infarction: The Rotterdam Study. Circulation 1997, 96, 1432–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezu, T.; Hosomi, N.; Aoki, S.; Matsumoto, M. Carotid Intima-Media Thickness for Atherosclerosis. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2016, 23, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, Y.; Barthez, D.; Léveillé, R.; Peter, V.; Scrivani, D. Side lobes and grating lobes artifacts in ultrasound imaging. Veter- Radiol. Ultrasound 1997, 38, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.T.; Hangiandreou, N.; Timmerman, R.; Rice, M.J.; Smith, W.B.; Deitte, L.; Janelle, G.M. Imaging Artifacts in Echocardiography. Anesth. Analg. 2016, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averkiou, M.; Roundhill, D.; Powers, J. A new imaging technique based on the nonlinear properties of tissues. In Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium Proceedings. An International Symposium, Toronto, ON, Canada, 5–8 October 1997; pp. 1561–1566. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, R.S.; Wagreich, J.; Parsons, R.B.; Stancato-Pasik, A.; Yeh, H.C.; Lao, R. Tissue harmonic imaging sonography: Evaluation of image quality compared with conventional sonography. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1998, 171, 1203–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desser, T.S.; Jeffrey, R.B., Jr.; Lane, M.J.; Ralls, P.W. Tissue harmonic imaging: Utility in abdominal and pelvic sonography. Clin. Ultrasound 1999, 27, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hann, L.E.; Bach, A.M.; Cramer, L.D.; Siegel, D.; Yoo, H.H.; Garcia, R.; Hann, A.M.B.L.E.; Shapiro, R.S.; Wagreich, J.; Parsons, R.B.; et al. Hepatic sonography: Comparison of tissue harmonic and standard sonography techniques. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1999, 173, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tranquart, F.; Grenier, N.; Eder, V.; Pourcelot, L. Clinical use of ultrasound tissue harmonic imaging. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 1999, 25, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, S.J.; Jones, P.H.; Wetzel, L.H. Phase Inversion Tissue Harmonic Sonographic Imaging. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2001, 176, 1393–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, N.; Bouakaz, A.; Cate, F.J.T. Contrast harmonic imaging. Ultrasonics 2002, 40, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Averkiou, M.A.; Bruce, M.F.; Powers, J.E.; Sheeran, P.S.; Burns, P.N. Imaging Methods for Ultrasound Contrast Agents. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2020, 46, 498–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brands, P.J.; Willigers, J.M.; Ledoux, L.A.; Reneman, R.S.; Hoeks, A.P. A noninvasive method to estimate pulse wave velocity in arteries locally by means of ultrasound. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 1998, 24, 1325–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabben, S.I.; Stergiopulos, N.; Hellevik, L.R.; Smiseth, O.A.; Slørdahl, S.; Urheim, S.; Angelsen, B. An ultrasound-based method for determining pulse wave velocity in superficial arteries. J. Biomech. 2004, 37, 1615–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunmire, B.; Beach, K.; Labs, K.-H.; Plett, M.; Strandness, D. Cross-beam vector Doppler ultrasound for angle-independent velocity measurements. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2000, 26, 1213–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortoli, P.; Dallai, A.; Boni, E.; Francalanci, L.; Ricci, S. An Automatic Angle Tracking Procedure for Feasible Vector Doppler Blood Velocity Measurements. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2010, 36, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohs, L.; Geiman, B.; Anderson, M.; Gebhart, S.; Trahey, G. Speckle tracking for multi-dimensional flow estimation. Ultrasonics 2000, 38, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albinsson, J.; Brorsson, S.; Ahlgren, Å.R.; Cinthio, M. Improved Tracking Performance of Lagrangian Block-Matching Methodologies Using Block Expansion in the Time Domain: In Silico, Phantom and in Vivo Evaluations. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2014, 40, 2508–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, H. Phase-Sensitive 2D Motion Estimators Using Frequency Spectra of Ultrasonic Echoes. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H.; Omura, M.; Nagaoka, R.; Saito, K. Two-Dimensional Wavenumber Analysis Implemented in Ultrasonic Vector Doppler Method with Focused Transmit Beams. Sensors 2022, 22, 9787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Zhao, H.; Urban, M.W.; Manduca, A.; Pislaru, S.V.; Kinnick, R.R.; Pislaru, C.; Greenleaf, J.F.; Chen, S. Improved Shear Wave Motion Detection Using Pulse-Inversion Harmonic Imaging With a Phased Array Transducer. IEEE Trans. Med Imaging 2013, 32, 2299–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duck, F.A. Nonlinear acoustics in diagnostic ultrasound. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2002, 28, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carstensen, E.; Law, W.; McKay, N.; Muir, T. Demonstration of nonlinear acoustical effects at biomedical frequencies and intensities. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 1980, 6, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, W.; Frizzell, L.; Dunn, F. Determination of the nonlinearity parameter B/A of biological media. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 1985, 11, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


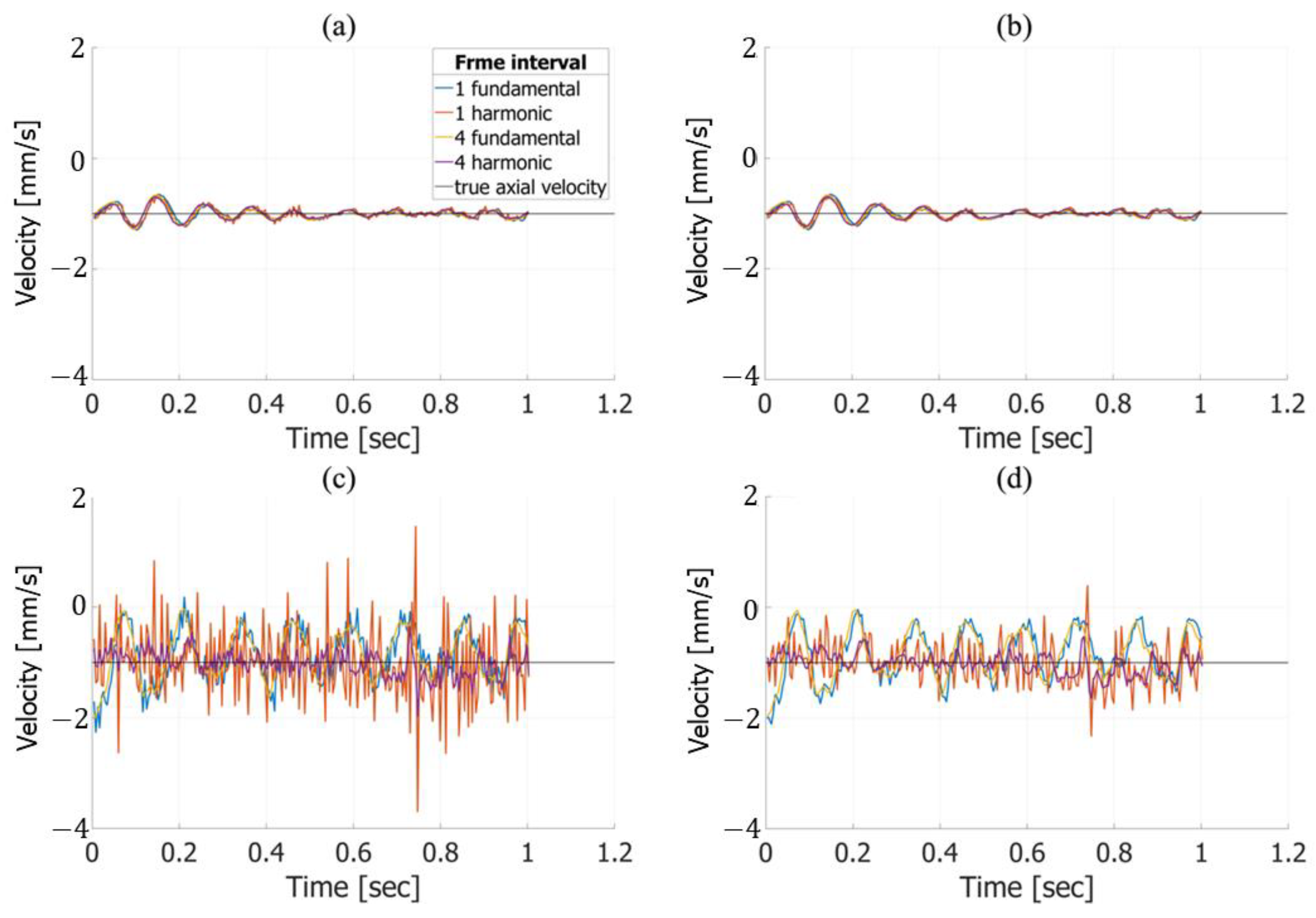

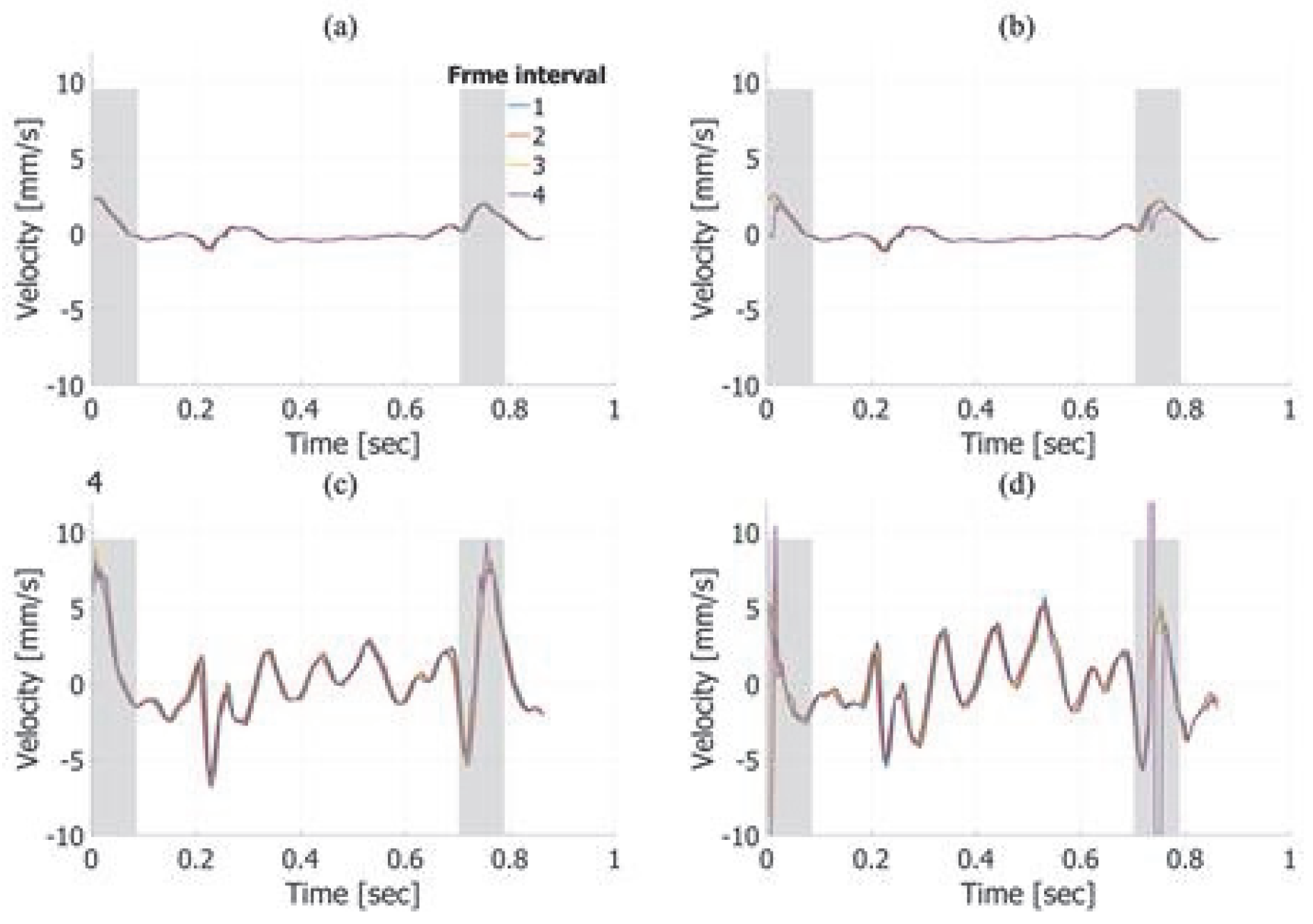
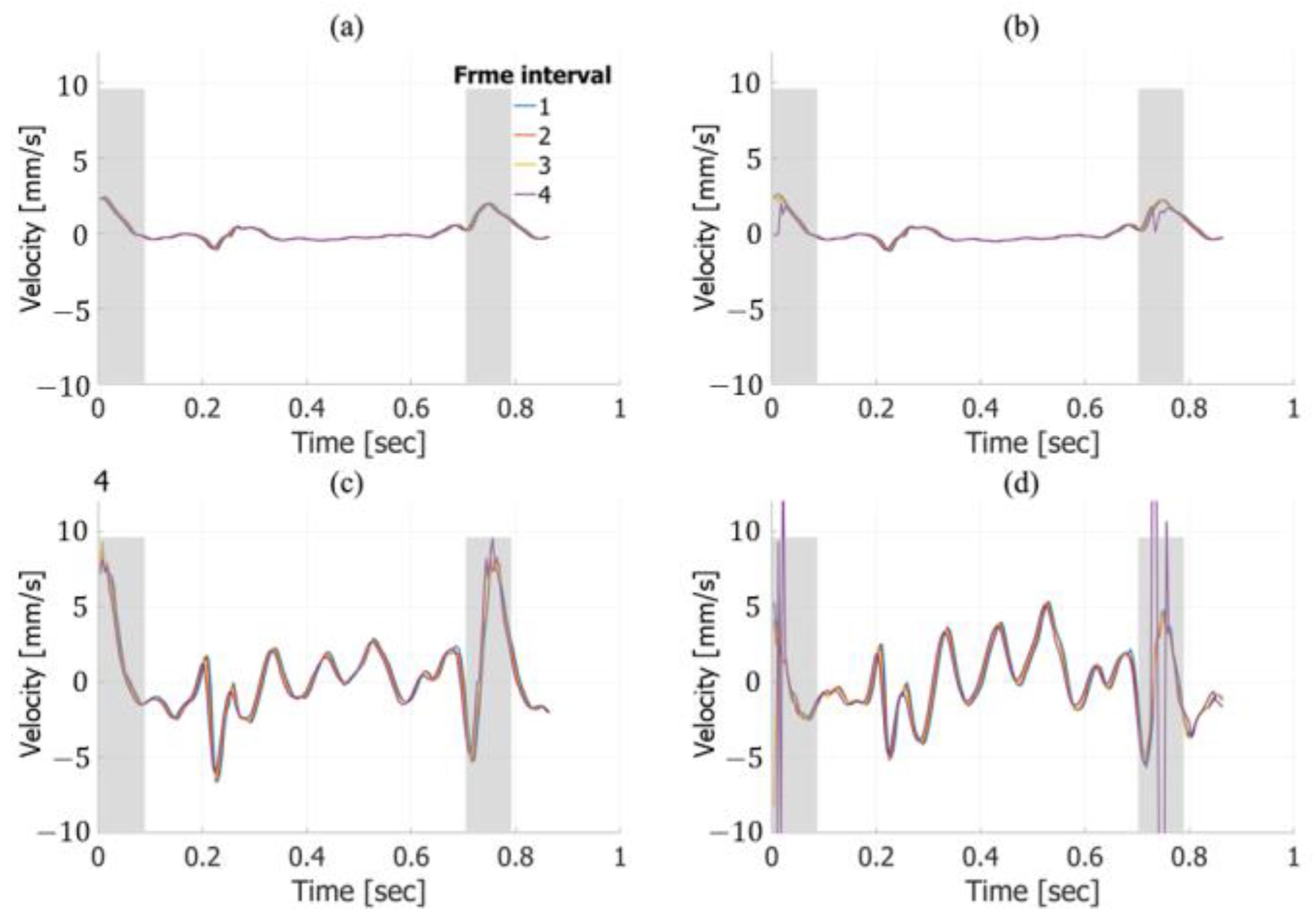
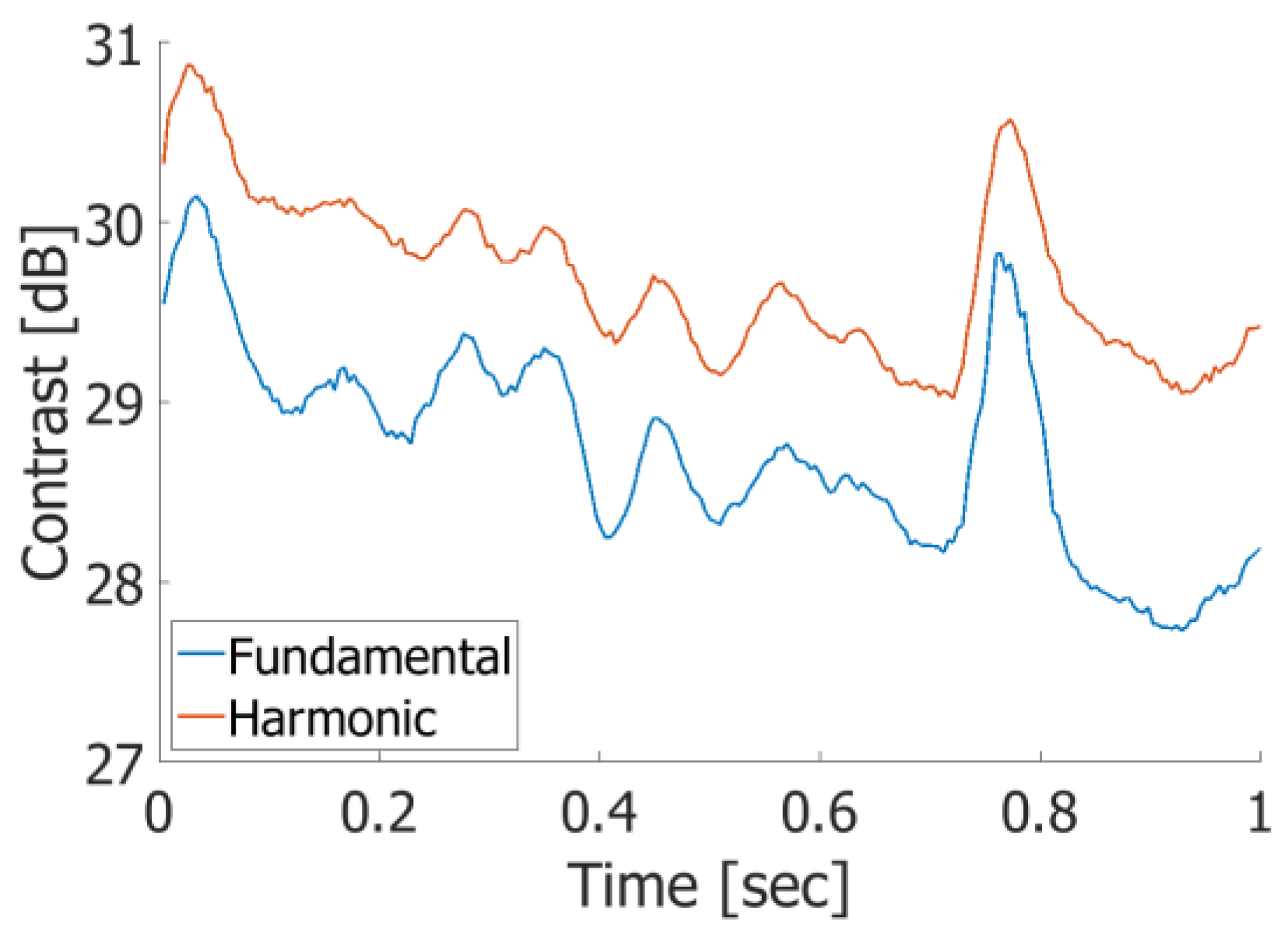
| RMSE of Axial Velocity Estimation Results in Fundamental Imaging [%] | ||
|---|---|---|
| frame interval | without frame averaging | with frame averaging |
| 1 | 6.038 | 5.919 |
| 2 | 5.906 | 5.786 |
| 3 | 5.721 | 5.610 |
| 4 | 5.506 | 5.393 |
| RMSE of axial velocity estimation results in harmonic imaging [%] | ||
| frame interval | without frame averaging | with frame averaging |
| 1 | 7.034 | 6.491 |
| 2 | 6.495 | 6.323 |
| 3 | 6.264 | 6.130 |
| 4 | 6.027 | 5.883 |
| RMSE of lateral velocity estimation results in fundamental imaging [%] | ||
| frame interval | without frame averaging | with frame averaging |
| 1 | 46.571 | 44.743 |
| 2 | 43.959 | 43.455 |
| 3 | 42.531 | 42.019 |
| 4 | 41.056 | 40.518 |
| RMSE of lateral velocity estimation results in harmonic imaging [%] | ||
| frame interval | without frame averaging | with frame averaging |
| 1 | 53.576 | 30.256 |
| 2 | 30.490 | 23.265 |
| 3 | 21.985 | 17.896 |
| 4 | 18.820 | 15.631 |
| RMSE of Axial Velocity Estimation Results in Fundamental Imaging [%] | ||
|---|---|---|
| frame interval | without frame averaging | with frame averaging |
| 1 | 3.519 | 3.516 |
| 2 | 3.494 | 3.493 |
| 3 | 3.496 | 3.455 |
| 4 | 3.476 | 3.408 |
| RMSE of axial velocity estimation results in harmonic imaging [%] | ||
| frame interval | without frame averaging | with frame averaging |
| 1 | 3.563 | 3.164 |
| 2 | 3.161 | 3.062 |
| 3 | 3.047 | 2.994 |
| 4 | 3.802 | 3.684 |
| RMSE of lateral velocity estimation results in fundamental imaging [%] | ||
| frame interval | without frame averaging | with frame averaging |
| 1 | 18.963 | 18.432 |
| 2 | 18.096 | 17.657 |
| 3 | 17.735 | 17.313 |
| 4 | 17.528 | 17.010 |
| RMSE of lateral velocity estimation results in harmonic imaging [%] | ||
| frame interval | without frame averaging | with frame averaging |
| 1 | 33.152 | 22.361 |
| 2 | 21.872 | 18.883 |
| 3 | 17.669 | 16.002 |
| 4 | 153.275 | 148.791 |
| Single-Line Tx | MLTI | Unfocused Tx | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frame rate | <100 Hz | <1000 Hz | >1000 Hz |
| Tissue harmonic | Applicable | Applicable | N/A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hirano, H.; Suzuki, R.; Omura, M.; Nagaoka, R.; Saito, K.; Hasegawa, H. Investigation of Ultrasound Transmit–Receive Sequence That Enables Both High-Frame-Rate Vascular Wall Velocity Estimation and High-Contrast B-Mode Images. Sensors 2025, 25, 2441. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082441
Hirano H, Suzuki R, Omura M, Nagaoka R, Saito K, Hasegawa H. Investigation of Ultrasound Transmit–Receive Sequence That Enables Both High-Frame-Rate Vascular Wall Velocity Estimation and High-Contrast B-Mode Images. Sensors. 2025; 25(8):2441. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082441
Chicago/Turabian StyleHirano, Hitoshi, Rikuto Suzuki, Masaaki Omura, Ryo Nagaoka, Kozue Saito, and Hideyuki Hasegawa. 2025. "Investigation of Ultrasound Transmit–Receive Sequence That Enables Both High-Frame-Rate Vascular Wall Velocity Estimation and High-Contrast B-Mode Images" Sensors 25, no. 8: 2441. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082441
APA StyleHirano, H., Suzuki, R., Omura, M., Nagaoka, R., Saito, K., & Hasegawa, H. (2025). Investigation of Ultrasound Transmit–Receive Sequence That Enables Both High-Frame-Rate Vascular Wall Velocity Estimation and High-Contrast B-Mode Images. Sensors, 25(8), 2441. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082441






