The Riemannian Means Field Classifier for EEG-Based BCI Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preprocessing, Processing, and Feature Extraction
2.1.1. ADCSP
2.1.2. Robust Power Mean Estimation (RPME)
2.1.3. Classification Pipelines
2.2. Data
2.3. Statistical Analysis
- -
- -
- The Wilcoxon one-sided signed-rank test, which basically is equivalent to a permutation test performed on the ranked data, if the number of subjects ≥ 20.
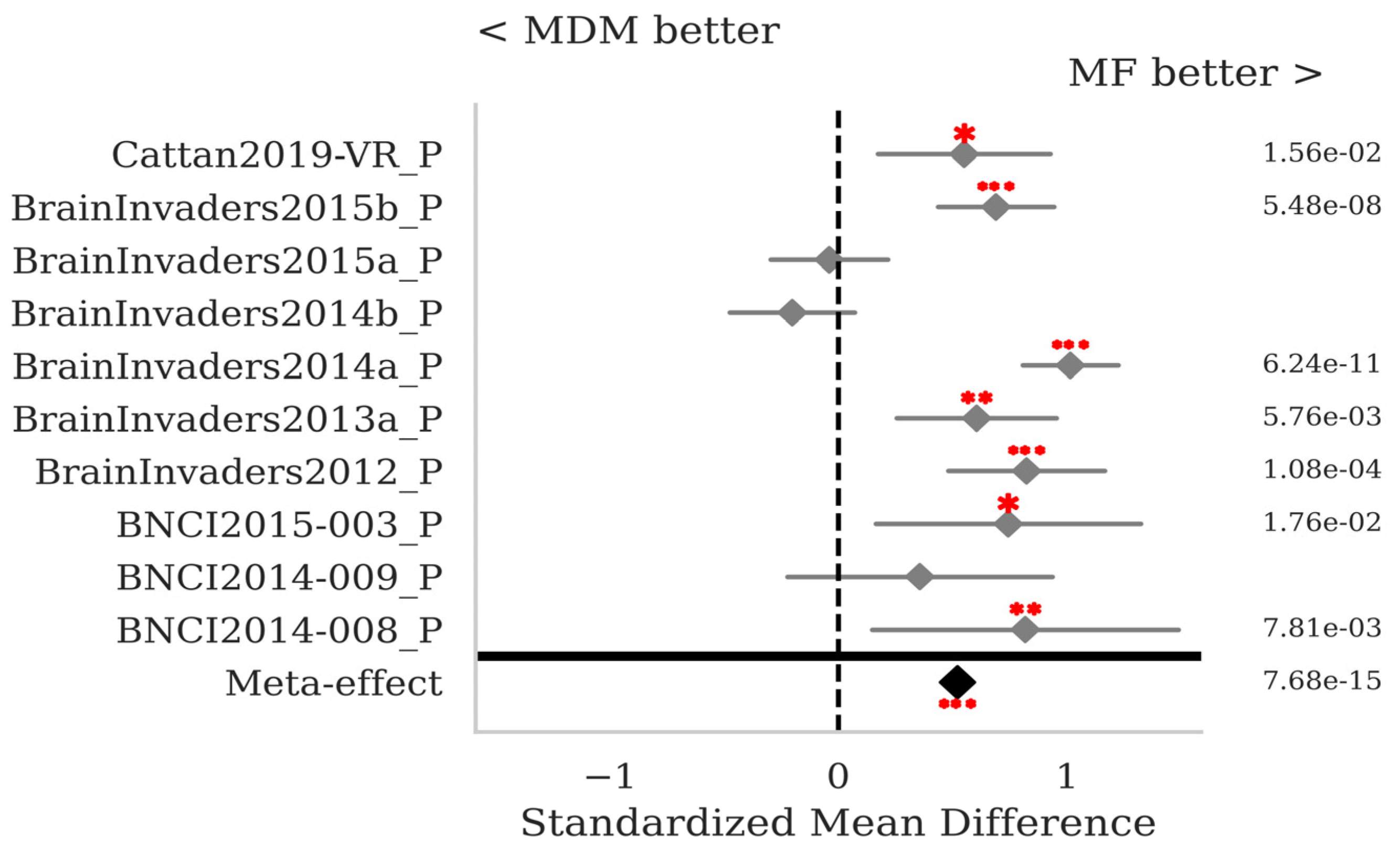
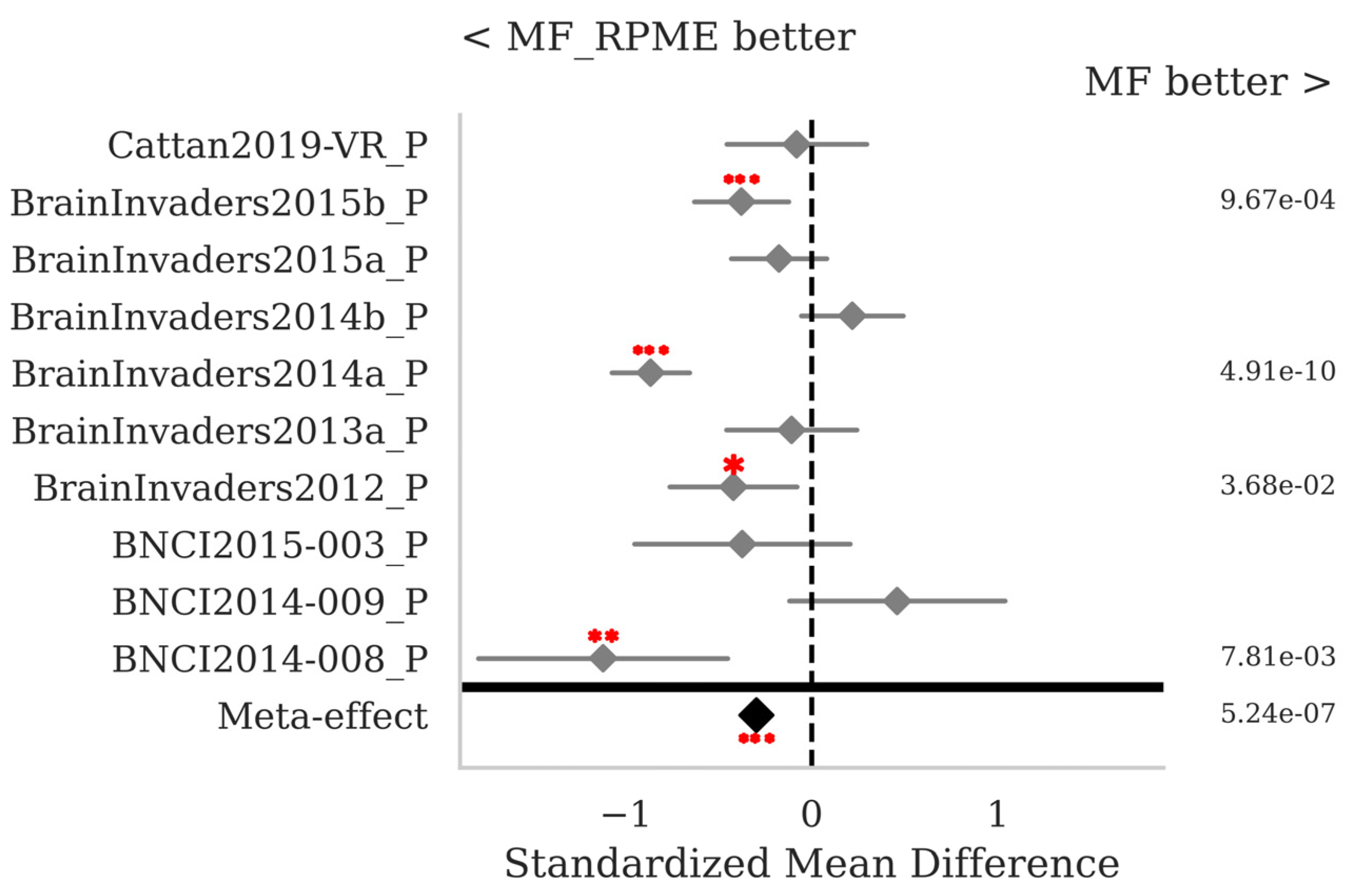
3. Results
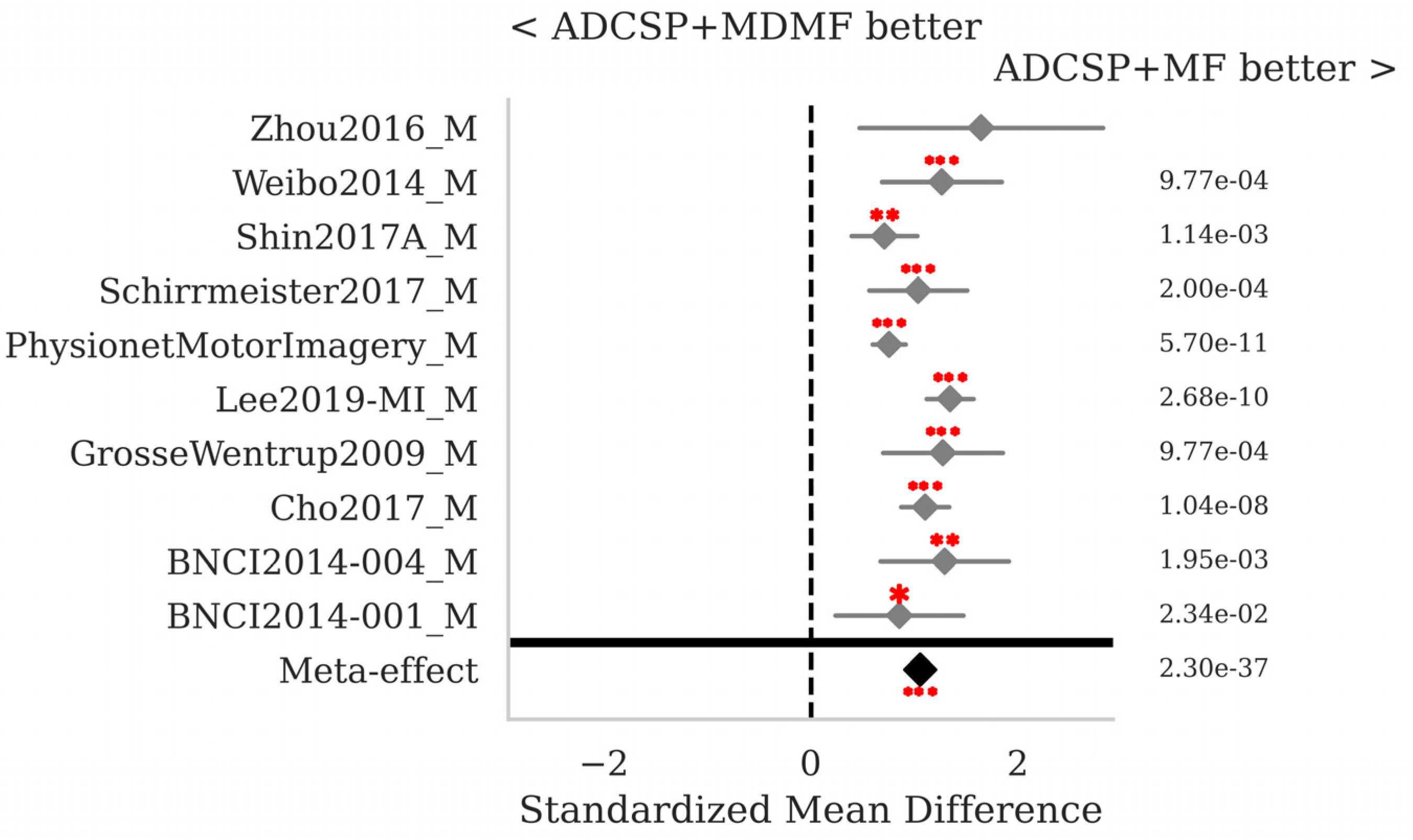
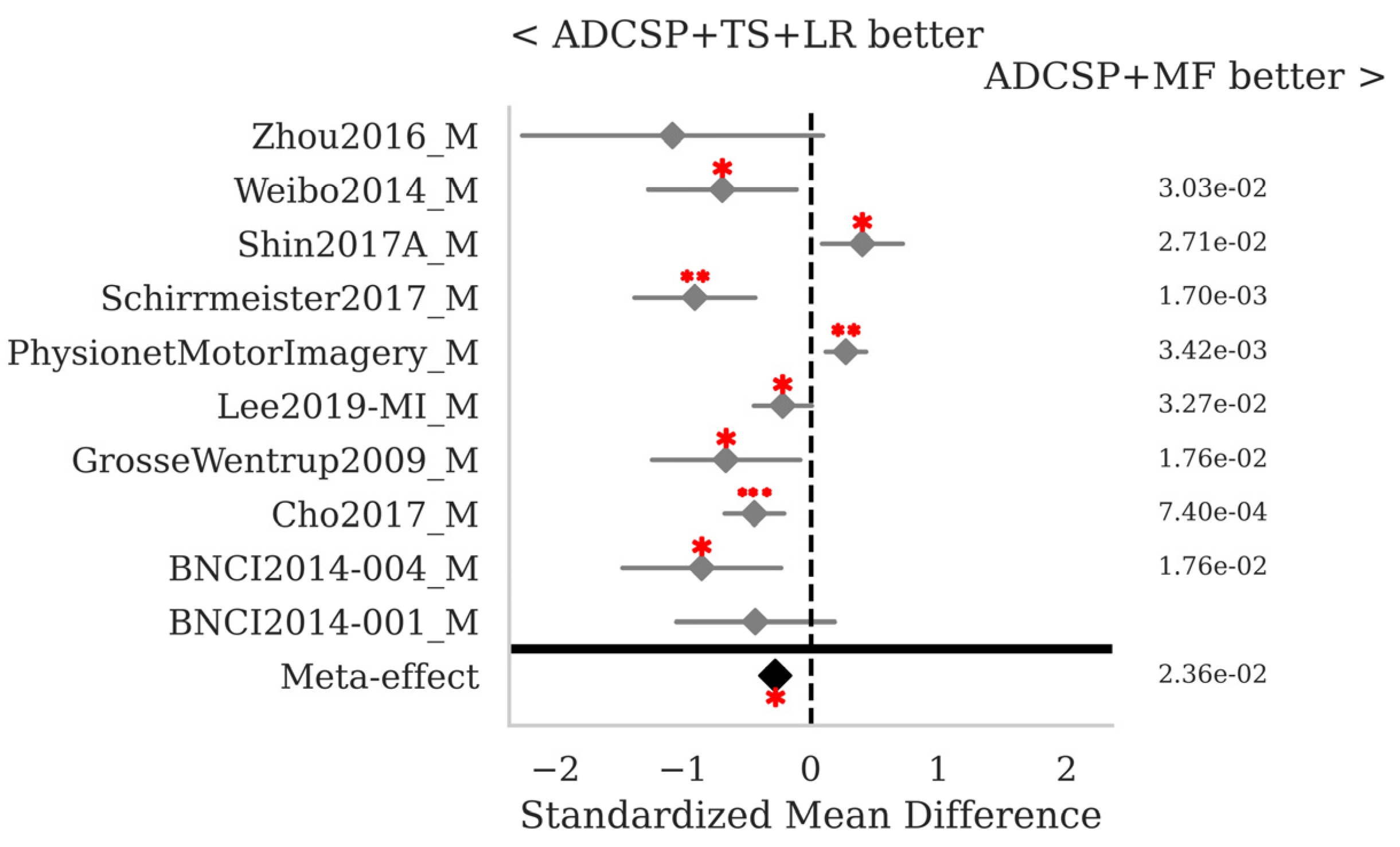
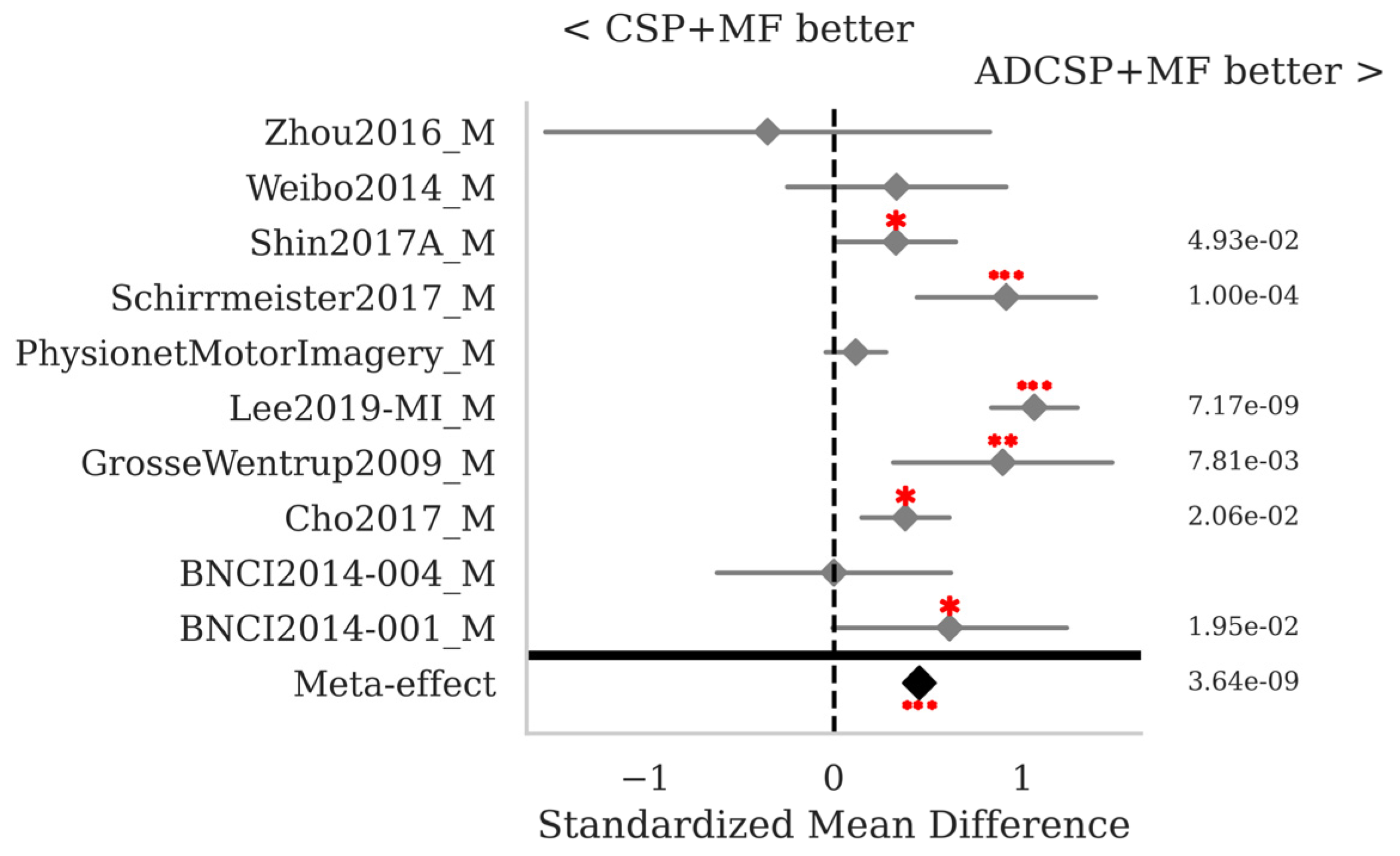
3.1. Motor Imagery
3.2. P300 ERPs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chevallier, S.; Carrara, I.; Aristimunha, B.; Guetschel, P.; Sedlar, S.; Lopes, B.; Velut, S.; Khazem, S.; Moreau, T. The largest EEG-based BCI reproducibility study for open science: The MOABB benchmark. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.15319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotte, F.; Bougrain, L.; Cichocki, A.; Clerc, M.; Congedo, M.; Rakotomamonjy, A.; Yger, F. A review of classification algorithms for EEG-based brain–computer interfaces: A 10 year update. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 15, 031005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levi-Civita, T. Lezioni Di Calcolo Differenziale Assoluto; Nicola Zanichelli Editore: Bologna, Italy, 1925. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia, R. Positive Definite Matrices; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Barachant, A.; Bonnet, S.; Congedo, M.; Jutten, C. Multiclass brain-computer interface classification by Riemannian geometry. IEEE Trans. Bio-Med. Eng. 2012, 59, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congedo, M. EEG Source Analysis. Habilitation Thesis, Université de Grenoble, Saint-Martin-d’Hères, France, 2013. Available online: https://tel.archives-ouvertes.fr/tel-00880483 (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Carrara, I. Advanced Methods for BCI-EEG Processing for Improved Classification Performance and Reproducibility. Phdthesis, Université Côte d’Azur, 2024. Available online: https://inria.hal.science/tel-04797267 (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Congedo, M.; Barachant, A.; Bhatia, R. Riemannian geometry for EEG-based brain-computer interfaces; a primer and a review. Brain-Comput. Interfaces 2017, 4, 155–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yger, F.; Berar, M.; Lotte, F. Riemannian Approaches in Brain-Computer Interfaces: A Review. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 25, 1753–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korczowski, L.; Congedo, M.; Jutten, C. Single-trial classification of multi-user P300-based brain-computer interface using riemannian geometry. In Proceedings of the 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 1769–1772. [Google Scholar]
- Mayaud, L.; Cabanilles, S.; Van Langhenhove, A.; Congedo, M.; Barachant, A.; Pouplin, S.; Filipe, S.; Pétégnief, L.; Rochecouste, O.; Azabou, E.; et al. Brain-computer interface for the communication of acute patients: A feasibility study and a randomized controlled trial comparing performance with healthy participants and a traditional assistive device. Brain Comput. Interfaces 2016, 3, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korczowski, L.; Ostaschenko, E.; Andreev, A.; Cattan, G.; Rodrigues, P.L.C.; Gautheret, V.; Congedo, M. Brain Invaders Calibration-Less P300-Based BCI Using Dry EEG Electrodes Dataset (bi2014a); GIPSA-lab, Research Report, juillet; 2019. Available online: https://hal.science/hal-02171575 (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Andreev, A.; Barachant, A.; Lotte, F.; Congedo, M. Recreational Applications of OpenViBE: Brain Invaders and Use-the-Force; chap. 14; John Wiley, Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; Available online: https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01366873/document (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Moakher, M. A Differential Geometric Approach to the Geometric Mean of Symmetric Positive-Definite Matrices. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 2005, 26, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.; Pálfia, M. Matrix power means and the Karcher mean. J. Funct. Anal. 2012, 262, 1498–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pálfia, M. Operator means of probability measures and generalized Karcher equations. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1601.06777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, J.; Lim, Y. Weighted means and Karcher equations of positive operators. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 110, 15626–15632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, J.; Lim, Y. Karcher means and Karcher equations of positive definite operators. Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. Ser. B 2014, 1, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congedo, M.; Barachant, A.; Bhatia, R. Fixed Point Algorithms for Estimating Power Means of Positive Definite Matrices. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 65, 2211–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congedo, M.; Rodrigues, P.L.C.; Jutten, C. The Riemannian Minimum Distance to Means Field Classifier. In Proceedings of the BCI 2019—8th International Brain-Computer Interface Conference, Graz, Austria, 16–20 September 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, A.; Igor, C.; Pierre, G.; Sara, S.; Pedro, R.; Jan, S.; Divyesh, N.; Erik, B.; Barthelemy, Q.; Tibor, S.R.; et al. Mother of All BCI Benchmarks, version v1.0.0; Zenodo: Genève, Switzerland, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Jayaram, V.; Barachant, A. MOABB: Trustworthy algorithm benchmarking for BCIs. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 15, 066011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barachant, A.; Barthélemy, Q.; King, J.-R.; Gramfort, A.; Chevallier, S.; Rodrigues, P.L.C.; Olivetti, E.; Goncharenko, V.; Berg, G.W.v.; Reguig, G.; et al. pyRiemann, version v0.8; Zenodo: Genève, Switzerland, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Blankertz, B.; Tomioka, R.; Lemm, S.; Kawanabe, M.; Muller, K. Optimizing Spatial filters for Robust EEG Single-Trial Analysis. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2008, 25, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivet, B.; Souloumiac, A.; Attina, V.; Gibert, G. Xdawn algorithm to enhance evoked potentials: Application to brain-computer interface. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 56, 2035–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T. Joint Approximate Diagonalization of Positive Definite Hermitian Matrices. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 2001, 22, 1136–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthélemy, Q.; Mayaud, L.; Ojeda, D.; Congedo, M. The Riemannian Potato Field: A Tool for Online Signal Quality Index of EEG. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 27, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangermann, M.; Müller, K.R.; Aertsen, A.; Birbaumer, N.; Braun, C.; Brunner, C.; Leeb, R.; Mehring, C.; Miller, K.J.; Müller-Putz, G.R.; et al. Review of the BCI Competition IV. Front. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeb, R.; Lee, F.; Keinrath, C.; Scherer, R.; Bischof, H.; Pfurtscheller, G. Brain-computer communication: Motivation, aim, and impact of exploring a virtual apartment. IEEE Trans. Neural. Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2007, 15, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Ahn, M.; Ahn, S.; Kwon, M.; Jun, S.C. EEG datasets for motor imagery brain-computer interface. Gigascience 2017, 6, gix034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosse-Wentrup, M.; Liefhold, C.; Gramann, K.; Buss, M. Beamforming in noninvasive brain-computer interfaces. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 56, 1209–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.H.; Kwon, O.Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, H.K.; Lee, Y.E.; Williamson, J.; Fazli, S.; Lee, S.W. EEG dataset and OpenBMI toolbox for three BCI paradigms: An investigation into BCI illiteracy. Gigascience 2019, 8, giz002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalk, G.; McFarland, D.J.; Hinterberger, T.; Birbaumer, N.; Wolpaw, J.R. BCI2000: A general-purpose brain-computer interface (BCI) system. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 51, 1034–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirrmeister, R.T.; Springenberg, J.T.; Fiederer, L.D.J.; Glasstetter, M.; Eggensperger, K.; Tangermann, M.; Hutter, F.; Burgard, W.; Ball, T. Deep learning with convolutional neural networks for EEG decoding and visualization. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2017, 38, 5391–5420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; von Lühmann, A.; Blankertz, B.; Kim, D.W.; Jeong, J.; Hwang, H.J.; Müller, K.R. Open Access Dataset for EEG+NIRS Single-Trial Classification. IEEE Trans. Neural. Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 25, 1735–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.; Qiu, S.; Wang, K.; Qi, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, P.; He, F.; Ming, D. Evaluation of EEG oscillatory patterns and cognitive process during simple and compound limb motor imagery. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Wu, X.; Lv, Z.; Zhang, L.; Guo, X. A Fully Automated Trial Selection Method for Optimization of Motor Imagery Based Brain-Computer Interface. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccio, A.; Simione, L.; Schettini, F.; Pizzimenti, A.; Inghilleri, M.; Belardinelli, M.O.; Mattia, D.; Cincotti, F. Attention and P300-based BCI performance in people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aricò, P.; Aloise, F.; Schettini, F.; Salinari, S.; Mattia, D.; Cincotti, F. Influence of P300 latency jitter on event related potential-based brain-computer interface performance. J. Neural Eng. 2014, 11, 035008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guger, C.; Daban, S.; Sellers, E.; Holzner, C.; Krausz, G.; Carabalona, R.; Gramatica, F.; Edlinger, G. How many people are able to control a P300-based brain-computer interface (BCI)? Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 462, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Veen, G.F.P.; Barachant, A.; Andreev, A.; Cattan, G.; Rodrigues, P.L.C.; Congedo, M. Building Brain Invaders: EEG Data of An Experimental Validation. GIPSA-Lab, Research Report 1, mai 2019. Available online: https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-02126068 (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Vaineau, E.; Barachant, A.; Andreev, A.; Rodrigues, P.C.; Cattan, G.; Congedo, M. Brain Invaders Adaptive Versus Non-Adaptive P300 Brain-Computer Interface Dataset. GIPSA-LAB, Research Report 1, avril 2019. Available online: https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-02103098 (accessed on 2 July 2019).
- Korczowski, L.; Ostaschenko, E.; Andreev, A.; Cattan, G.; Rodrigues, P.L.C.; Gautheret, V.; Congedo, M. Brain Invaders Solo Versus Collaboration: Multi-User P300-Based Brain-Computer Interface Dataset (bi2014b); GIPSA-lab, Research Report, juillet; 2019. Available online: https://hal.science/hal-02173958/ (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Korczowski, L.; Cederhout, M.; Andreev, A.; Cattan, G.; Rodrigues, P.L.C.; Gautheret, V.; Congedo, M. Brain Invaders Calibration-less P300-Based BCI with Modulation of Flash Duration Dataset (bi2015a); GIPSA-lab, Research Report, juillet; 2019. Available online: https://hal.science/hal-02172347 (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Korczowski, L.; Cederhout, M.; Andreev, A.; Cattan, G.; Rodrigues, P.L.; Gautheret, V.; Congedo, M. Brain Invaders Cooperative Versus Competitive: Multi-User P300-based Brain-Computer Interface Dataset (bi2015b); GIPSA-lab, Research Report, juillet; 2019. Available online: https://hal.science/hal-02173913v1 (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Cattan, G.; Andreev, A.; Rodrigues, P.; Congedo, M. Dataset of an EEG-Based BCI Experiment in Virtual Reality and on a Personal Computer; GIPSA-lab; IHMTEK, Research Report, 2019. Available online: https://hal.science/hal-02078533v3 (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Edgington, E.S. Randomization Tests, 3rd ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Huson, L.W. Multivariate Permutation Tests: With Applications in Biostatistics. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. D Stat. 2003, 52, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congedo, M.; Afsari, B.; Barachant, A.; Moakher, M. Approximate Joint Diagonalization and Geometric Mean of Symmetric Positive Definite Matrices. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
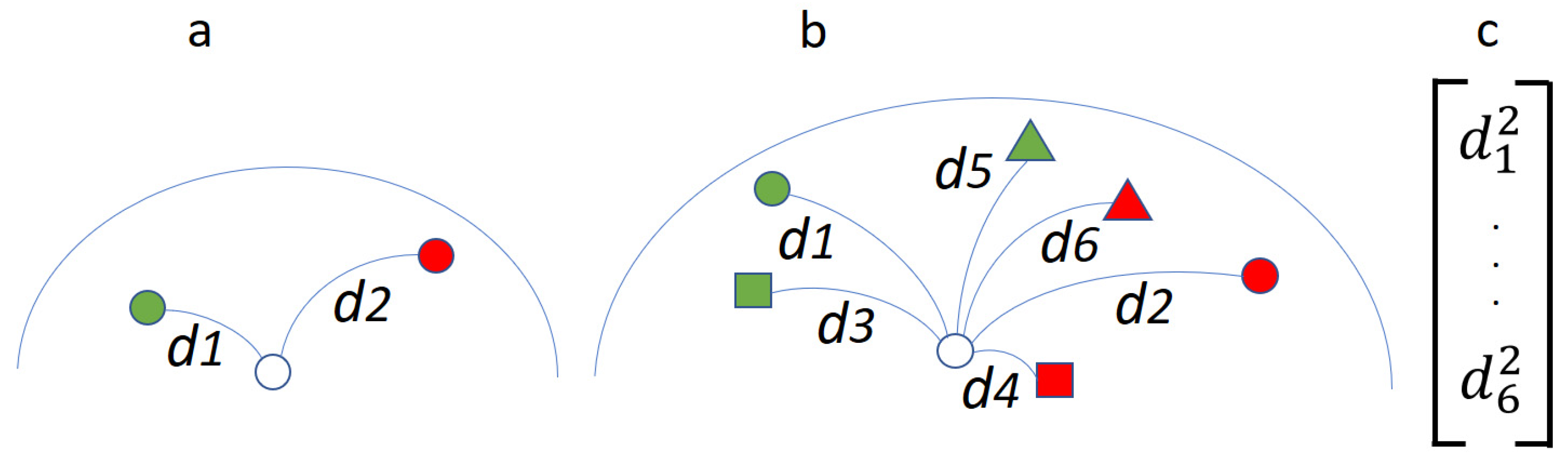




| Name | Number of Channels | Number of Sessions | Number of Subjects |
|---|---|---|---|
| BNCI2014-001 [28] | 22 | 2 | 9 |
| BNCI2014-004 [29] | 3 | 5 | 9 |
| Cho 2017 [30] | 64 | 1 | 52 |
| Grosse Wentrup 2009 [31] | 128 | 1 | 10 |
| Lee2019 MI [32] | 62 | 2 | 54 |
| Physionet Motor Imagery [33] | 64 | 1 | 109 |
| Schirrmeister 2017 [34] | 128 | 1 | 14 |
| Shin 2017A [35] | 30 | 3 | 29 |
| Weibo 2014 [36] | 60 | 1 | 10 |
| Zhou 2016 [37] | 14 | 3 | 4 |
| Name | Number of Channels | Number of Sessions | Number of Subjects |
|---|---|---|---|
| BNCI2014-008 [38] | 8 | 1 | 8 |
| BNCI2014-009 [39] | 16 | 3 | 10 |
| BNCI2015-003 [40] | 8 | 1 | 10 |
| Brain Invaders 2012 [41] | 16 | 2 | 25 |
| Brain Invaders 2013a [42] | 16 | 1/8 | 24 |
| Brain Invaders 2014a [12] | 16 | 3 | 64 |
| Brain Invaders 2014b [43] | 32 | 3 | 38 |
| Brain Invaders 2015a [44] | 32 | 3 | 43 |
| Brain Invaders 2015b [45] | 32 | 1 | 44 |
| Cattan 2019 VR [46] | 16 | 2 | 21 |
| Pipeline | Mean AUC-ROC | StD AUC-ROC | Mean Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| ADCSP + MDM | 0.685 | 0.187 | 0.15 |
| ADCSP + MDMF | 0.699 | 0.189 | 0.188 |
| ADCSP + MF | 0.765 | 0.18 | 0.186 |
| ADCSP + MF_RPME | 0.766 | 0.177 | 0.247 |
| ADCSP + TS + LR | 0.757 | 0.189 | 0.143 |
| CSP + MF | 0.728 | 0.187 | 0.149 |
| MDM | 0.655 | 0.185 | 0.251 |
| MDMF | 0.668 | 0.189 | 2.884 |
| MF | 0.756 | 0.175 | 2.58 |
| TS + LR | 0.763 | 0.188 | 0.264 |
| Mean | 0.724 | 0.185 | - |
| StD | 0.044 | 0.005 | - |
| Pipeline Database | ADCSP + MDM | ADCSP + MDMF | ADCSP + MF | ADCSP + TS + LR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BNCI2014-001 | 0.821 | 0.833 | 0.856 | 0.862 |
| BNCI2014-004 | 0.777 | 0.783 | 0.796 | 0.801 |
| Cho2017 | 0.672 | 0.689 | 0.737 | 0.745 |
| GrosseW.2009 | 0.74 | 0.765 | 0.857 | 0.864 |
| Lee2019-MI | 0.728 | 0.747 | 0.822 | 0.826 |
| PhysionetMI | 0.592 | 0.599 | 0.682 | 0.66 |
| Schirrm.2017 | 0.756 | 0.78 | 0.867 | 0.883 |
| Shin2017A | 0.64 | 0.655 | 0.722 | 0.692 |
| Weibo2014 | 0.65 | 0.677 | 0.816 | 0.83 |
| Zhou2016 | 0.906 | 0.908 | 0.931 | 0.941 |
| Mean | 0.728 | 0.744 | 0.809 | 0.81 |
| StD | 0.094 | 0.091 | 0.076 | 0.088 |
| Pipeline | MeanAUC ROC | StDAUC-ROC | Mean Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| MDM | 0.879 | 0.097 | 0.178 |
| MDMF | 0.879 | 0.095 | 1.064 |
| MF | 0.89 | 0.088 | 0.955 |
| MF_RPME | 0.893 | 0.086 | 2.823 |
| TS + LR | 0.898 | 0.084 | 0.181 |
| Mean | 0.888 | 0.09 | - |
| StD | 0.009 | 0.006 | - |
| Pipeline Dataset | Xdawn + MDM | Xdawn + MDMF | Xdawn + MF | Xdawn + TS + LR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BNCI2014-008 | 0.776 | 0.797 | 0.831 | 0.858 |
| BNCI2014-009 | 0.92 | 0.926 | 0.931 | 0.93 |
| BNCI2015-003 | 0.831 | 0.829 | 0.834 | 0.838 |
| BrainInv.2012 | 0.882 | 0.883 | 0.901 | 0.907 |
| BrainInv.2013a | 0.91 | 0.914 | 0.922 | 0.922 |
| BrainInv.2014a | 0.809 | 0.807 | 0.834 | 0.857 |
| BrainInv.2014b | 0.916 | 0.916 | 0.914 | 0.913 |
| BrainInv.2015a | 0.926 | 0.923 | 0.925 | 0.927 |
| BrainInv.2015b | 0.835 | 0.834 | 0.839 | 0.843 |
| Cattan2019-VR | 0.899 | 0.901 | 0.913 | 0.913 |
| Mean | 0.87 | 0.873 | 0.884 | 0.891 |
| StD | 0.053 | 0.051 | 0.044 | 0.037 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andreev, A.; Cattan, G.; Congedo, M. The Riemannian Means Field Classifier for EEG-Based BCI Data. Sensors 2025, 25, 2305. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072305
Andreev A, Cattan G, Congedo M. The Riemannian Means Field Classifier for EEG-Based BCI Data. Sensors. 2025; 25(7):2305. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072305
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndreev, Anton, Gregoire Cattan, and Marco Congedo. 2025. "The Riemannian Means Field Classifier for EEG-Based BCI Data" Sensors 25, no. 7: 2305. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072305
APA StyleAndreev, A., Cattan, G., & Congedo, M. (2025). The Riemannian Means Field Classifier for EEG-Based BCI Data. Sensors, 25(7), 2305. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072305






