DMC-LIBSAS: A Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy Analysis System with Double-Multi Convolutional Neural Network for Accurate Traceability of Chinese Medicinal Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
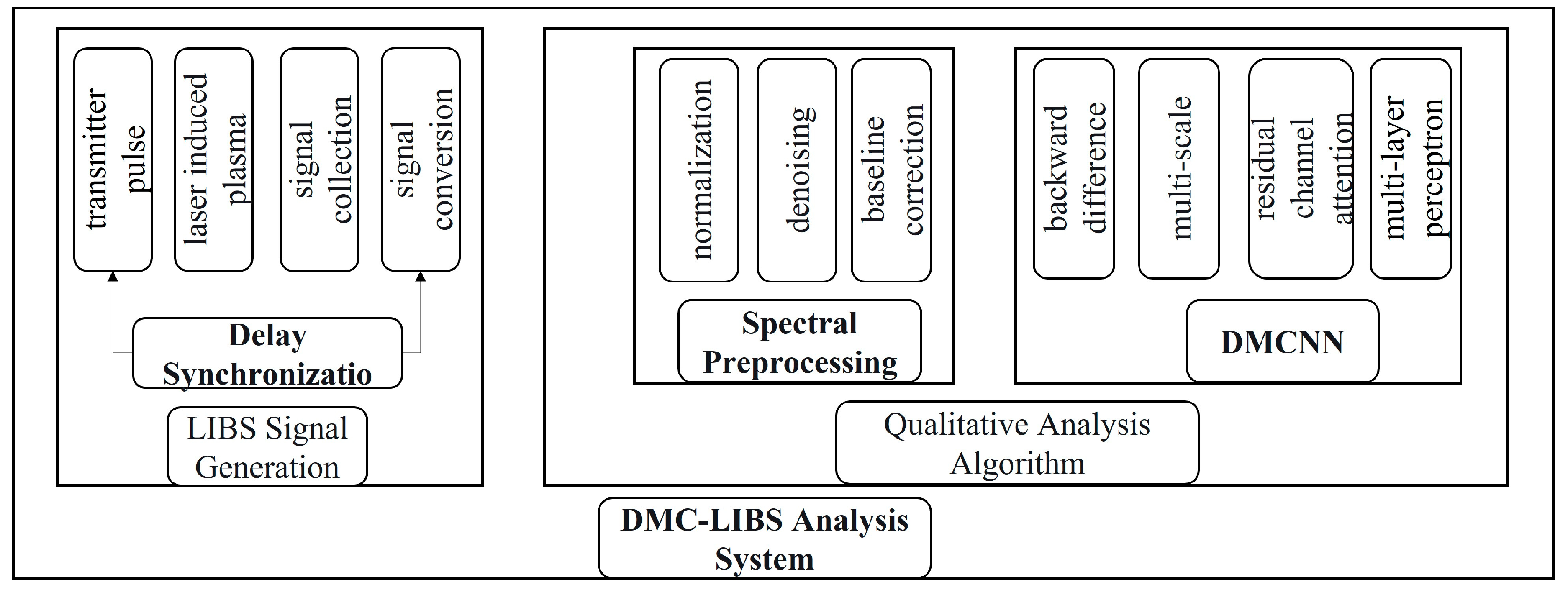
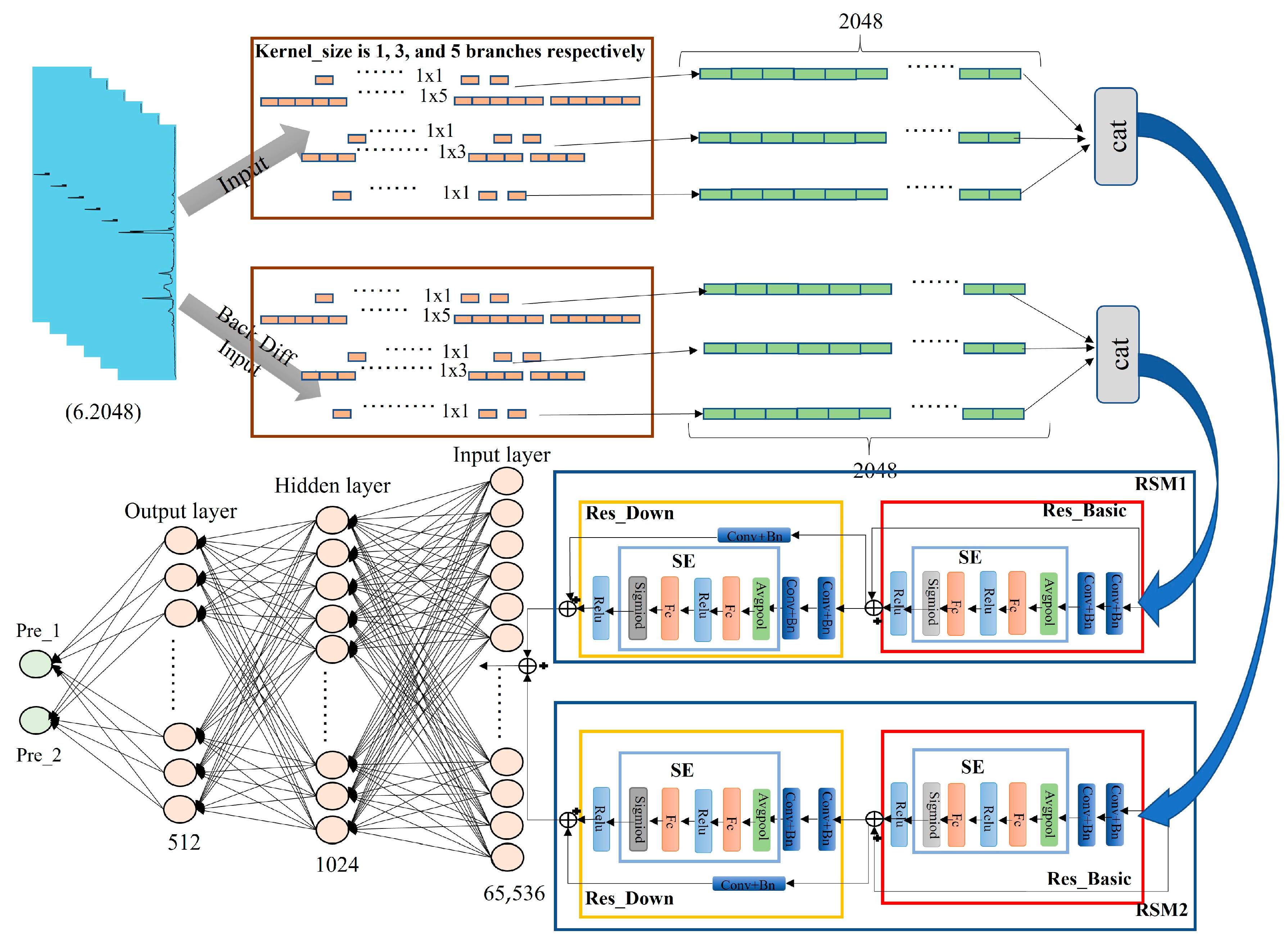
2.1. DMC-LIBSAS Architecture
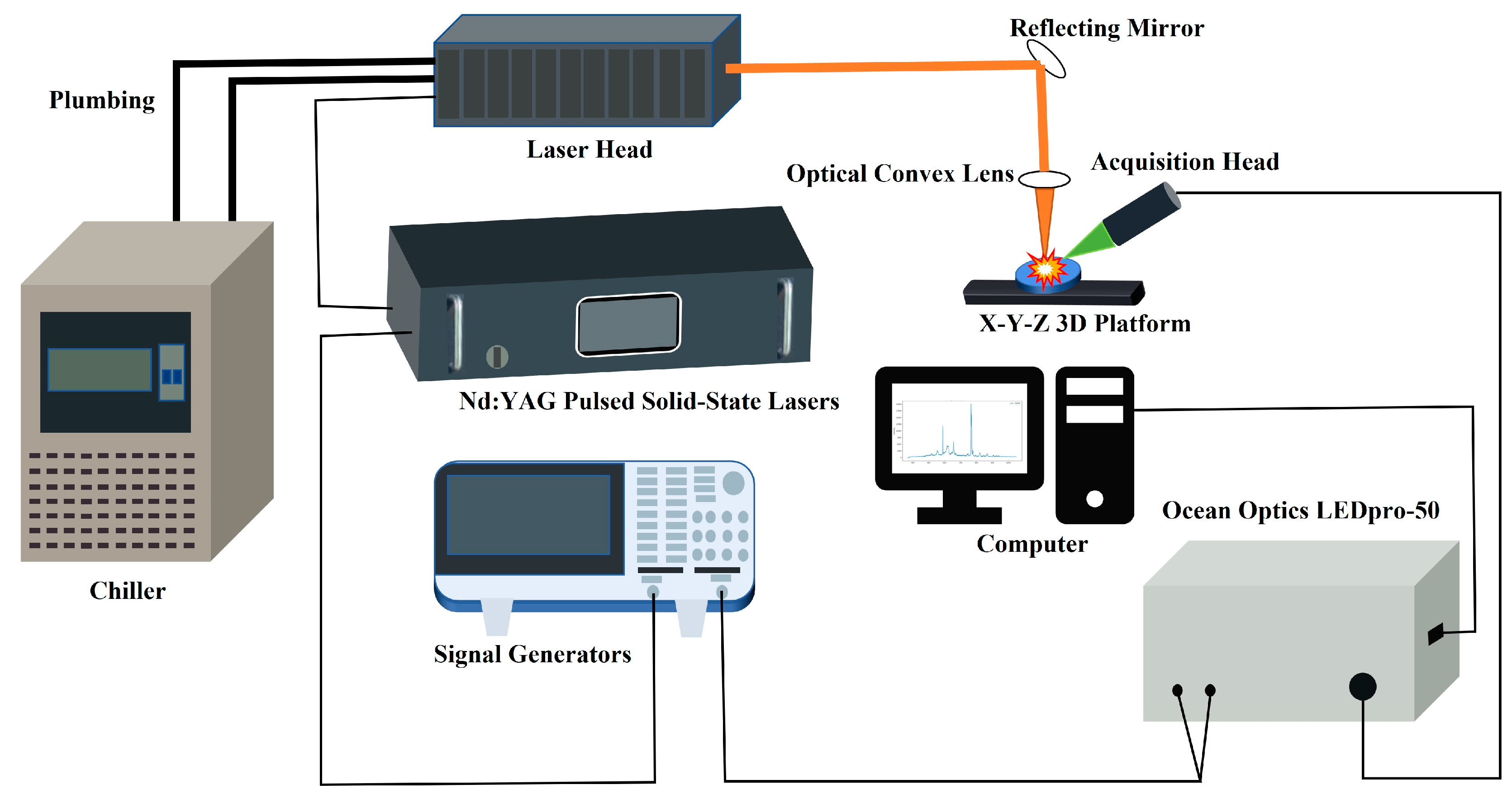
2.2. LIBS Spectral Signal Generation Module
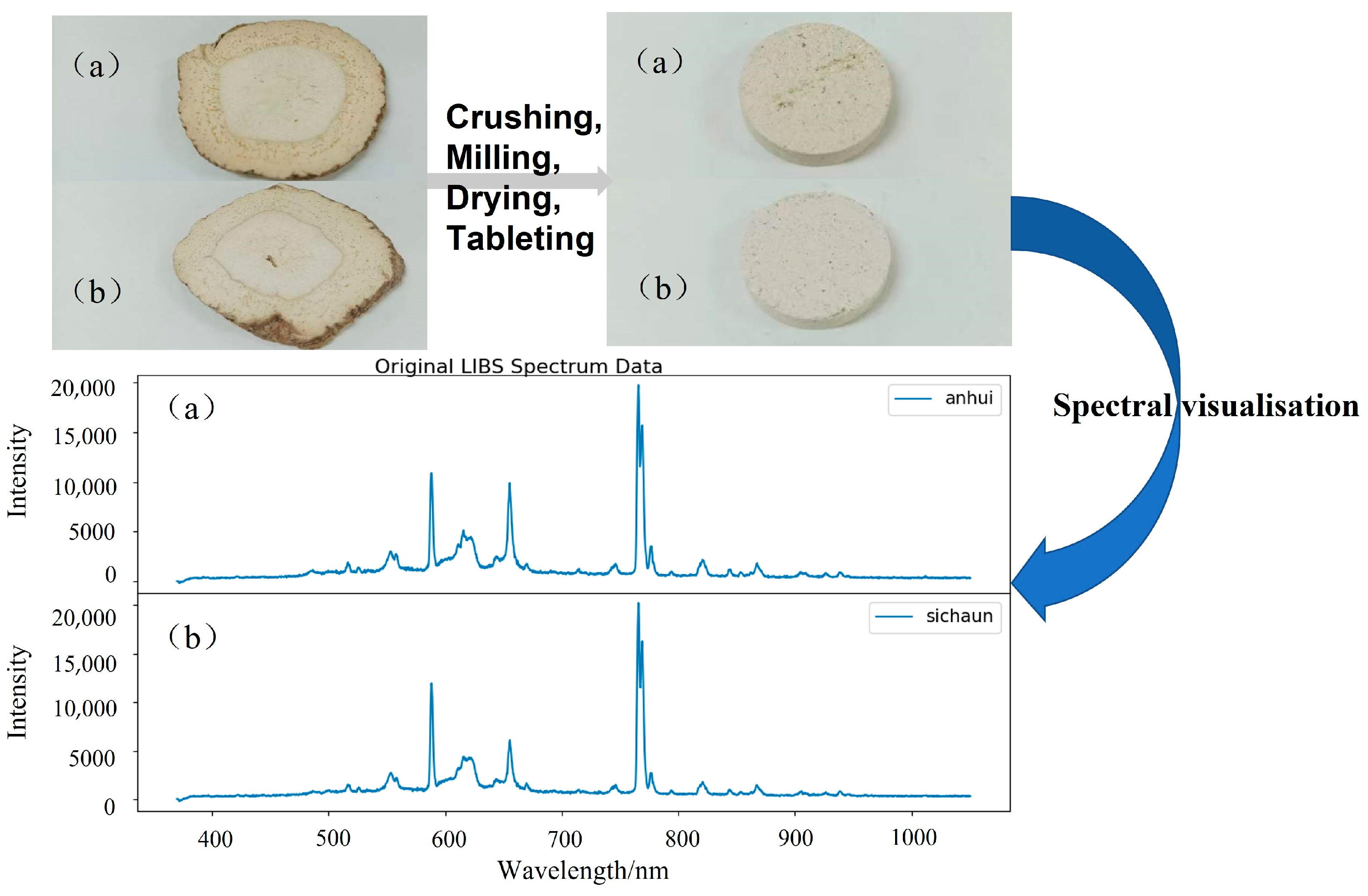
2.3. Sample Preparation and Data Collection
2.4. Spectral Preprocessing Module
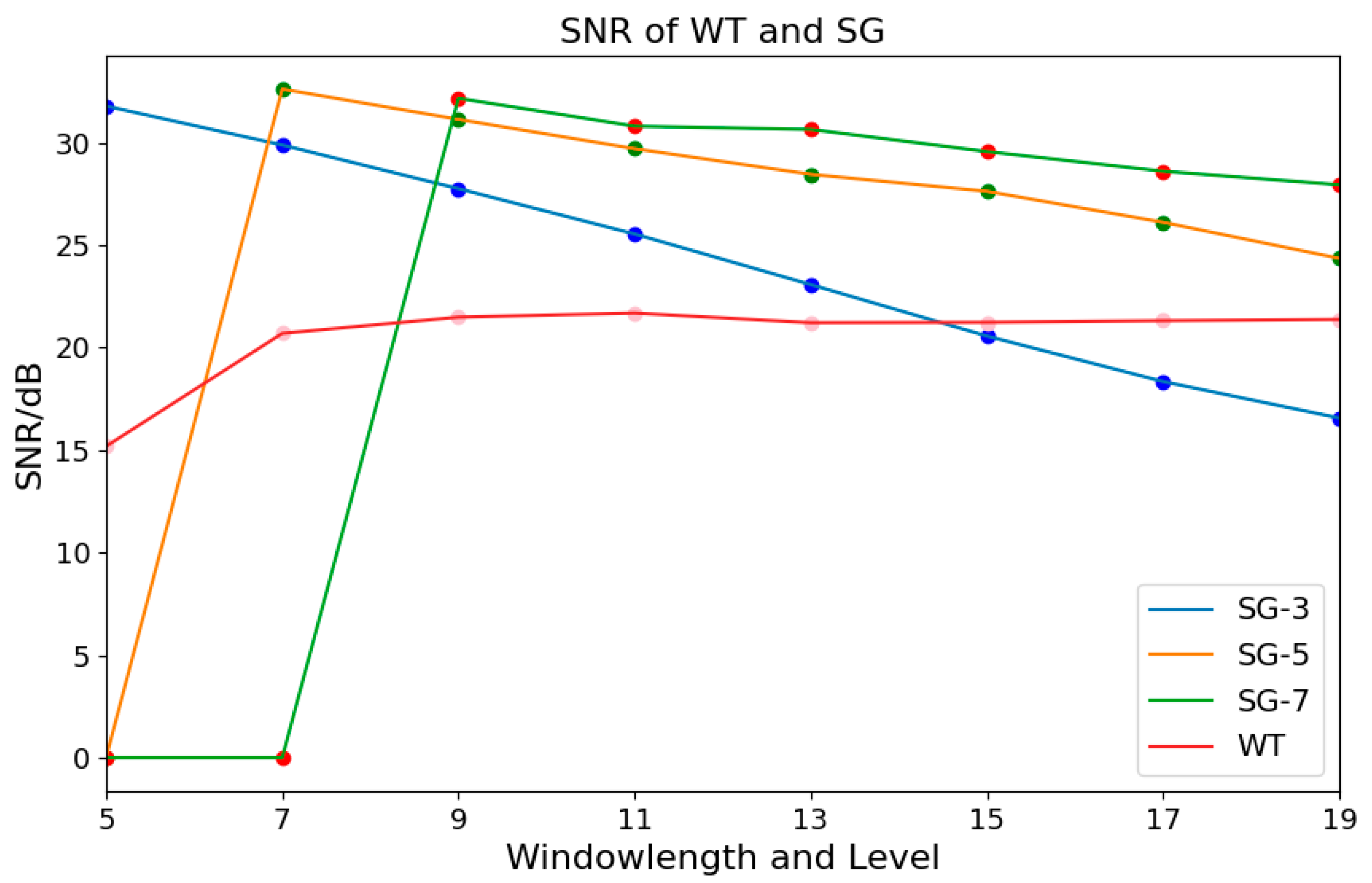
2.4.1. Savitzky–Golay Filtering
2.4.2. Min–Max Normalization
2.4.3. Polynomial Iterative Fitting
2.4.4. Spectral Preprocessing
2.5. DMCNN Module
2.5.1. Methods for the DNCNN Module
2.5.2. Structure of the DNCNN Module
2.5.3. Validation of the DNCNN Module
3. Results
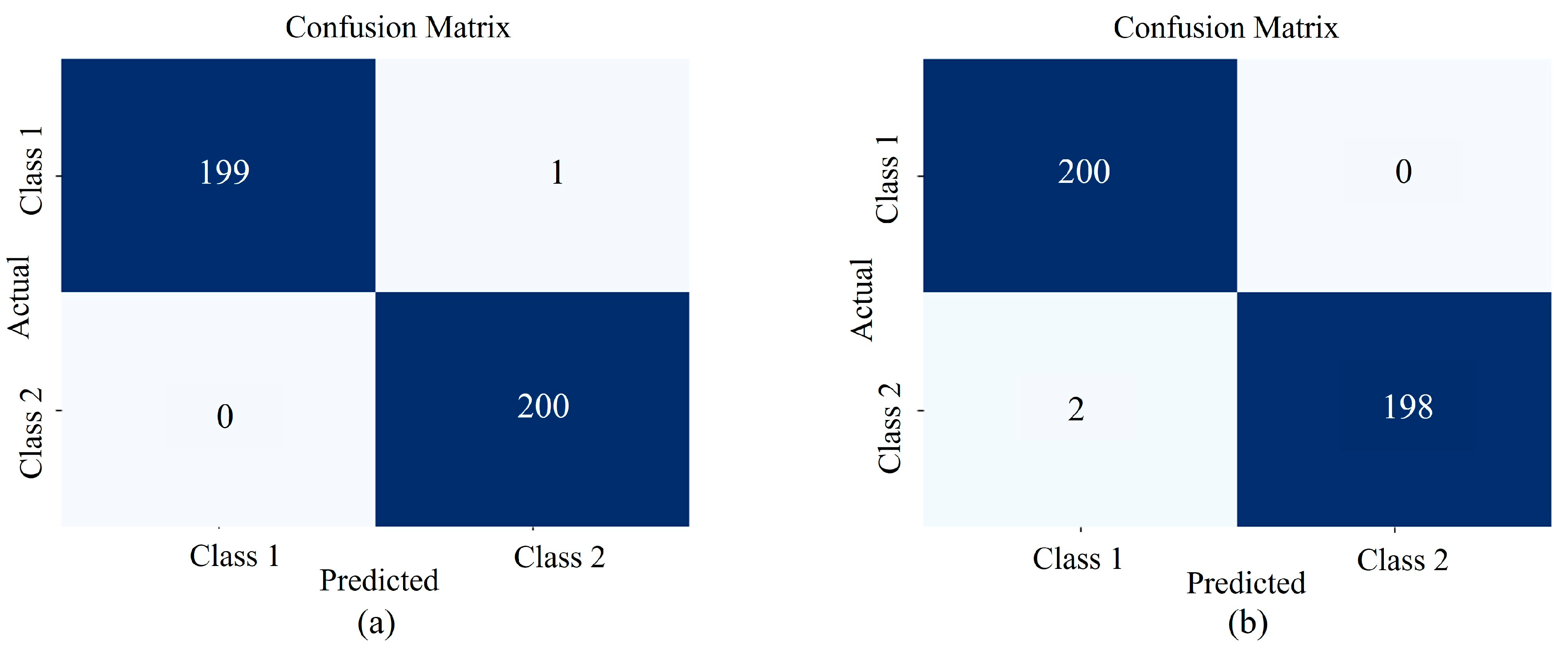
3.1. Model Performance Validation
3.2. Ablation Experiments
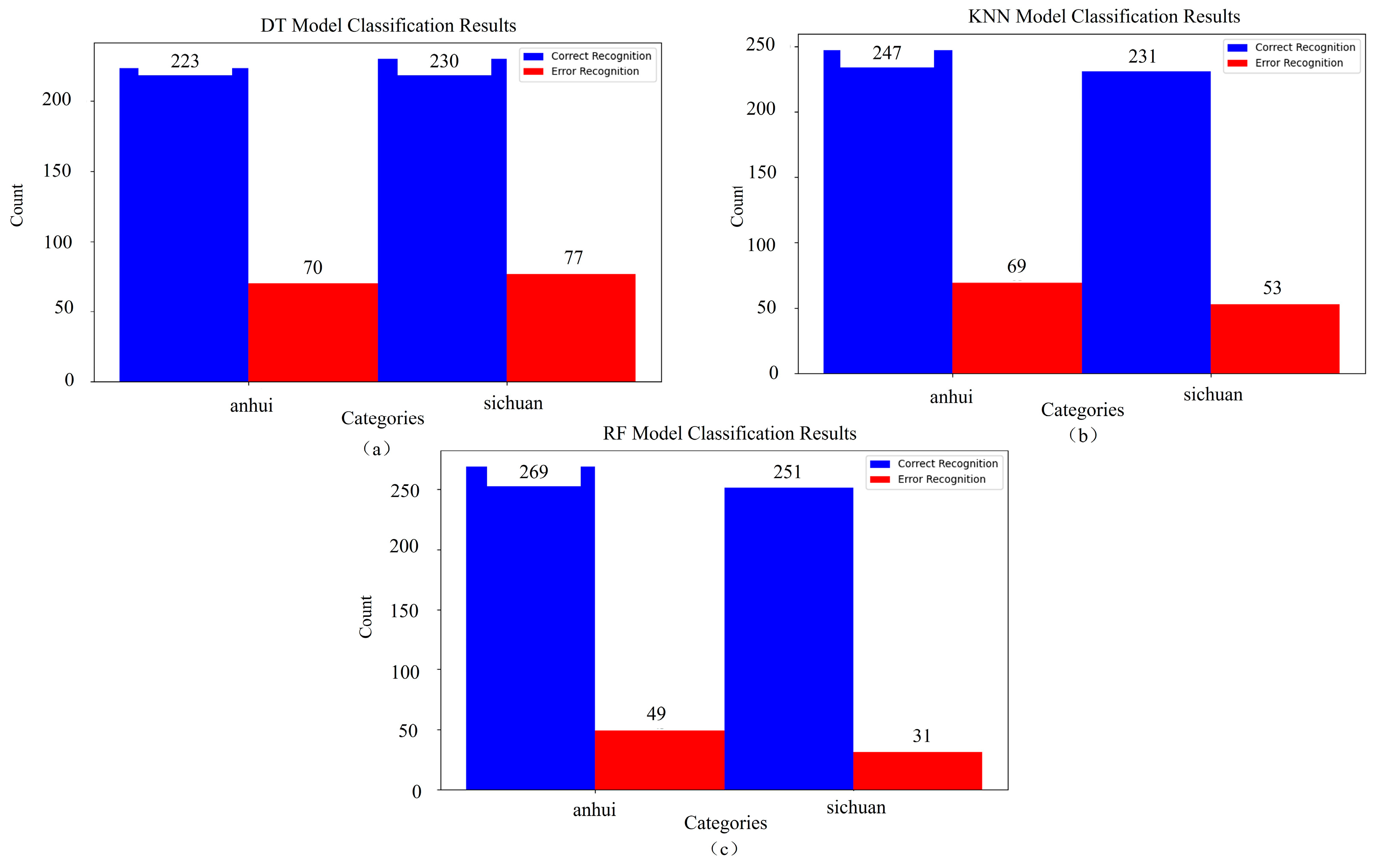
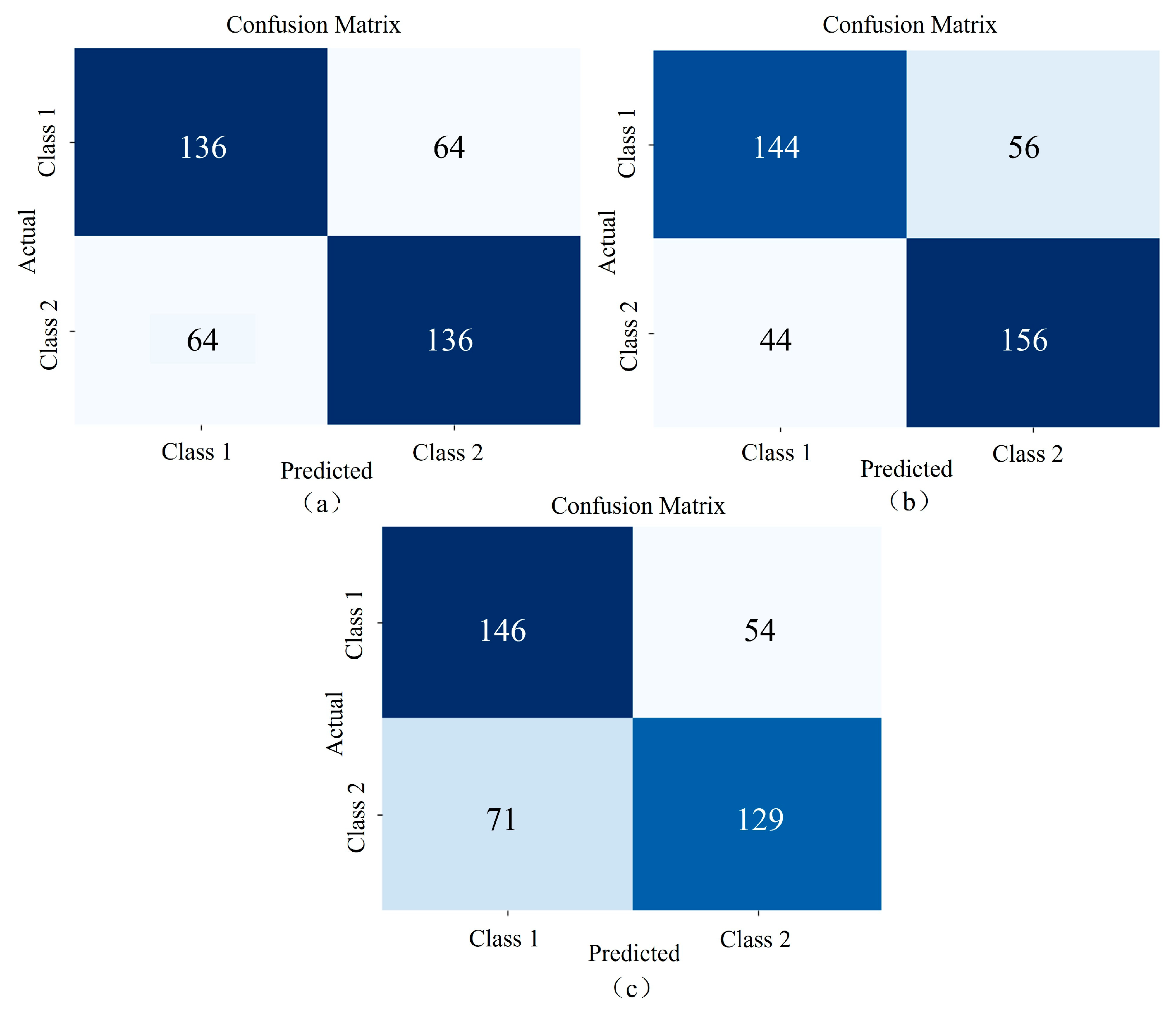
3.3. Comparative Experiments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LIBS | Laser-induced Breakdown Spectroscopy |
| DMC-LIBSAS | Double-Multi Convolutional Neural Network LIBS Analysis System |
| KNN | K-Nearest Neighbors |
| RF | Random Forest |
| DT | Decision Tree |
| DMCNN | Double-Multi Convolutional Neural Network |
| WT | Wavelet Transform |
| SNR | Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
| 1D-Grad-CAM | 1D Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping |
| TCM | Traditional Chinese Medicine |
| MLP | Multi-Layer Perceptron |
| SG | Savitzky–Golay |
| RSM | Residual and Channel Attention Module |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| Tra | Training Set |
| Val | Validation Set |
| Pre | Test Set |
| t-SNE | t-distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding |
References
- Chu, T.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Meng, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, F.; Chen, L. Analysis and Reflection on Thedevelopment Process and Market Status of Traditional Chinese Medicine Decoction Pieces. Glob. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2023, 3, 365–378. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Yuan, M.; Cao, Y.; Ma, Y. Comparative Study on Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Effect of Sulfur-Fumigation and Non-Sulfur-Fumigation Angelica dahurica. Pharm. Clin. Chin. Mater. Medica 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Sheng, Y.; Li, S.; Pan, Y.; Ao, H. Comparative Study on the Volatile Constituents of Baizhi from Six Different Producing Regions. Storage Process 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Ai, J.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, Q.; Yu, Q. Rapid Classification of Coffee Origin by Combining Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Coffee Aroma with Deep Learning. Food Chem. 2024, 446, 138811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Bakar, M.H.; Azeman, N.H.; Mobarak, N.N.; Nazri, N.A.A.; Daniyal, W.M.E.M.M.; Othman, M.Q.; Abdullah, F.; Bakar, A.A.A. Uv–Vis Spectroscopy for Simple Chloride Content Analysis in Edible Oil Using Charged Amino-Functionalized Carbon Quantum Dots Fluorophore Reagent. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2024, 317, 124419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronzi, B.; Brilli, C.; Beone, G.M.; Fontanella, M.C.; Ballabio, D.; Todeschini, R.; Consonni, V.; Grisoni, F.; Parri, F.; Buscema, M. Geographical Identification of Chianti Red Wine Based on ICP-MS Element Composition. Food Chem. 2020, 315, 126248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R. Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) in Biomedical Analysis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 181, 117992. [Google Scholar]
- Busser, B. Elemental Imaging Using Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy: A New and Promising Approach for Biological and Medical Applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 358, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.-L.; Wu, S.; Tang, H.-S.; Wang, K.; Duan, Y.-X.; Li, H. Progress of Chemometrics in Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy Analysis. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 43, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noll, R. LIBS Analyses for Industrial Applications—An Overview of Developments from 2014 to 2018. Crit. Rev. 2018, 33, 945–956. [Google Scholar]
- Jean-Noëla, M.K.; Arthurb, K.T.; Jean-Marcc, B. LIBS Technology and Its Application: Overview of the Different Research Areas. J. Environ. Sci. Public Health 2020, 4, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markiewicz-Keszycka, M.; Cama-Moncunill, X.; Casado-Gavalda, M.P.; Dixit, Y.; Cama-Moncunill, R.; Cullen, P.J.; Sullivan, C. Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) for Food Analysis: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 65, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lamine Guindo, M.; Xu, X.; Sun, M.; Peng, J.; Liu, F.; He, Y. Deep Learning Associated with Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) for the Prediction of Lead in Soil. Appl. Spectrosc. 2019, 73, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Ma, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, J.; Huo, L. Study on Tea Classification Based on Provenance via Random Forests and Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy. In Proceedings of the AOPC 2021: Optical Spectroscopy and Imaging, Beijing, China, 20–22 June 2021; Zhao, H., Liu, J., Xu, L., Wang, Y., Eds.; SPIE: Beijing, China, 2021; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Jiao, L.; Yan, N.; Yan, C.; Qu, L.; Zhang, S.; Ma, L. Identification of Salvia Miltiorrhiza From Different Origins by Laser InducedBreakdown Spectroscopy Combined with Artificial Neural Network. Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 2023, 43, 3098–3104. [Google Scholar]
- Khalilian, P.; Rezaei, F.; Darkhal, N.; Karimi, P.; Safi, A.; Palleschi, V.; Melikechi, N.; Tavassoli, S.H. Jewelry Rock Discrimination as Interpretable Data Using Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy and a Convolutional LSTM Deep Learning Algorithm. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, H.; Nian, F. Quantitative Analysis of Steel Alloy Elements Based on LIBS and Deep Learning of Multi-Perspective Features. Electronics 2023, 12, 2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Xiao, D. Identification of Coal, Gangue, and Surrounding Rock Based on LIBS and Deep Learning. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Yan, Z.; Li, J.; Fu, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, B. Coal Identification Based on Reflection Spectroscopy and Deep Learning: Paving the Way for Efficient Coal Combustion and Pyrolysis. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 23919–23928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Y.; Fu, X.; Zhao, S.; He, P.; Zhao, C.; Li, G. Improved Convolutional Neural Network-Assisted Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy for Identification of Soil Contamination Types. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2024, 215, 106910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Li, Y.; Lin, X.; Che, C. Fusion of Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy Technology and Deep Learning: A New Method to Identify Malignant and Benign Lung Tumors with High Accuracy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawash, Y.Z.; Al-Naami, B.; Alfraihat, A.; Owida, H.A. Advanced Low-Pass Filters for Signal Processing: A Comparative Study on Gaussian, Mittag-Leffler, and Savitzky-Golay Filters. MMEP 2024, 11, 1841–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Tao, M.; Fang, Y. Infrared Spectrum Baseline Correction Method Based on Improved Iterative Polynomial Fitting. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2020, 57, 033001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, M.; Anwar-ul-Haq, M.; Shah, A.; Sher Afgan, M.; Haq, S.U.; Abbas Khan, R.; Aslam Baig, M. Self-Absorption Effect in Calibration-Free Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy: Analysis of Mineral Profile in Maerua Oblongifolia Plant. Microchem. J. 2022, 175, 107106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial Pyramid Pooling in Deep Convolutional Networks for Visual Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-Based Localization. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2020, 128, 336–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Methods | Decision Coefficient for Fitting Accuracy | Computational Time |
|---|---|---|
| SG–Normalization–Polynomial Iterative Fitting | 0.99 | 0.009 |
| SG–Normalization–Polynomial Fitting | 0.09 | 0.004 |
| SG–Normalization–Linear Fitting | 0.05 | 0 |
| Model | Tra (%) | Val (%) | Pre (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base Module | 100.00 | 92.50 | 92.75 |
| Introduction of backward difference | 100.00 | 95.00 | 93.50 |
| Introduction of multiscale | 100.00 | 94.75 | 93.25 |
| Machine Learning Method | Main Parameter | Test Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|
| KNN | n_neighbors = 5 | 79.7 |
| RF | n_estimators = 100, random_state = 42 | 86.7 |
| DT | random_state = 42 | 75.5 |
| Model | Tra (%) | Val (%) | Pre (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LeNet | 71.5 | 70 | 68 |
| AlexNet | 73.25 | 73.75 | 75 |
| ResNet18 | 100% | 79% | 72.50% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, T.; Bi, W.; Song, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, L.; Sun, J.; Jiang, C. DMC-LIBSAS: A Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy Analysis System with Double-Multi Convolutional Neural Network for Accurate Traceability of Chinese Medicinal Materials. Sensors 2025, 25, 2104. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072104
Huang T, Bi W, Song Y, Yu X, Wang L, Sun J, Jiang C. DMC-LIBSAS: A Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy Analysis System with Double-Multi Convolutional Neural Network for Accurate Traceability of Chinese Medicinal Materials. Sensors. 2025; 25(7):2104. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072104
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Tianhe, Wenhao Bi, Yuxiao Song, Xiaolin Yu, Le Wang, Jing Sun, and Chenyu Jiang. 2025. "DMC-LIBSAS: A Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy Analysis System with Double-Multi Convolutional Neural Network for Accurate Traceability of Chinese Medicinal Materials" Sensors 25, no. 7: 2104. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072104
APA StyleHuang, T., Bi, W., Song, Y., Yu, X., Wang, L., Sun, J., & Jiang, C. (2025). DMC-LIBSAS: A Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy Analysis System with Double-Multi Convolutional Neural Network for Accurate Traceability of Chinese Medicinal Materials. Sensors, 25(7), 2104. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072104




