A Beam Hardening Artifact Correction Method for CT Images Based on VGG Feature Extraction Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Beam Hardening Artifact Correction Method Based on Feature Extraction
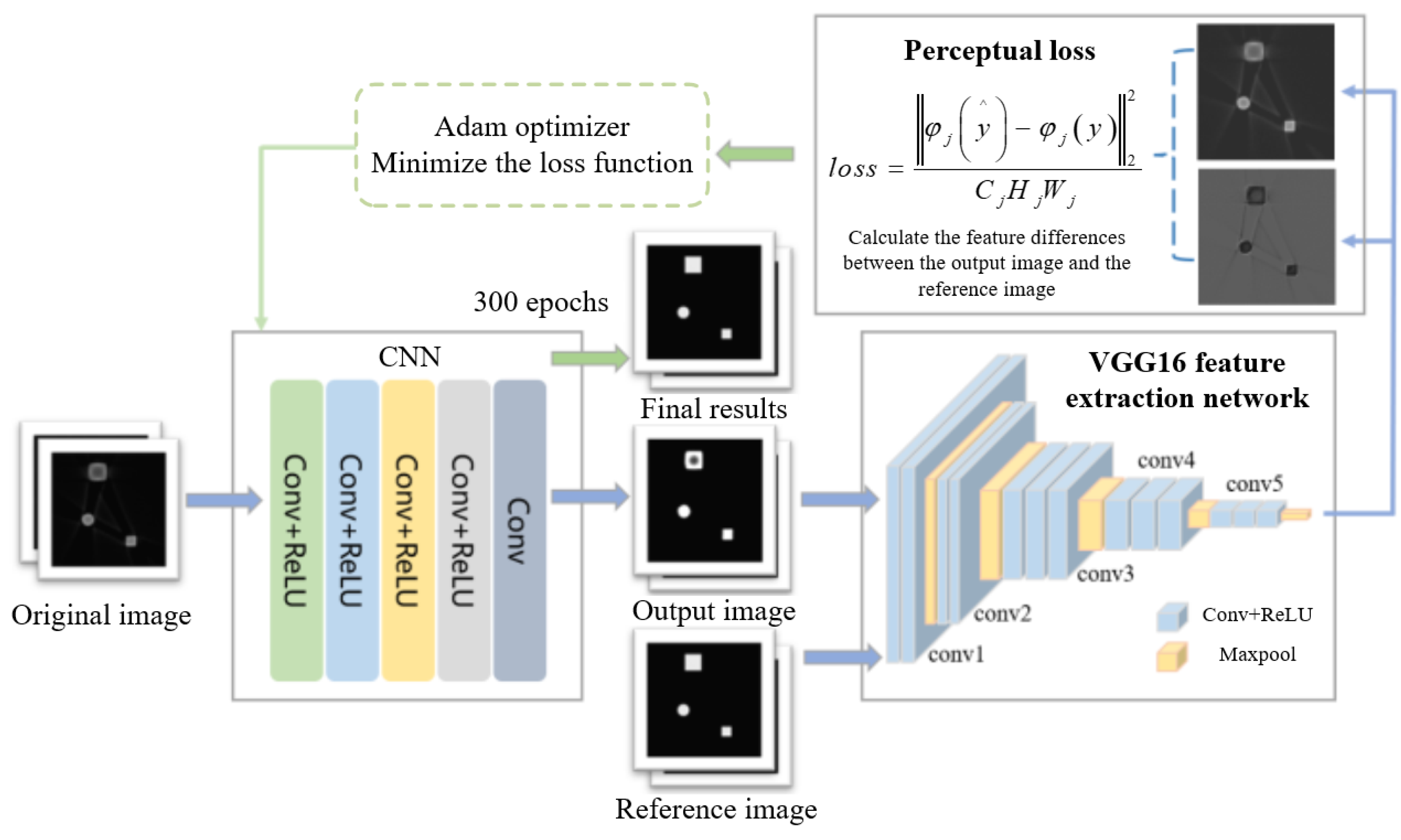
2.1. The Overall Structure of the Algorithm
2.2. The VGG-Net Feature Extraction Network
2.3. Loss Function
3. Data and Experiment
3.1. Data Acquisition
- (1)
- Simulating CT images of single-material objects: Simulated tomographic images were generated of objects composed of a single material.
- (2)
- Simulating multienergy projection data: Multienergy spectra and material attenuation coefficients were used to simulate the multienergy projection data of the tomographic images.
- (3)
- Reconstruction with filtered back projection: The tomographic images containing beam hardening artifacts using the filtered back projection algorithm.
3.1.1. Artifact-Free Simulated Data
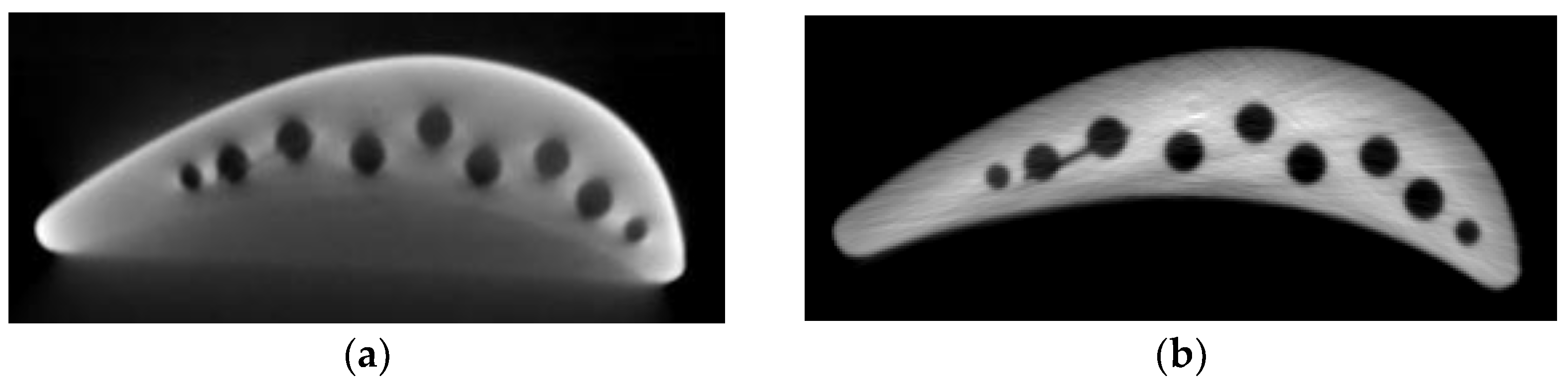
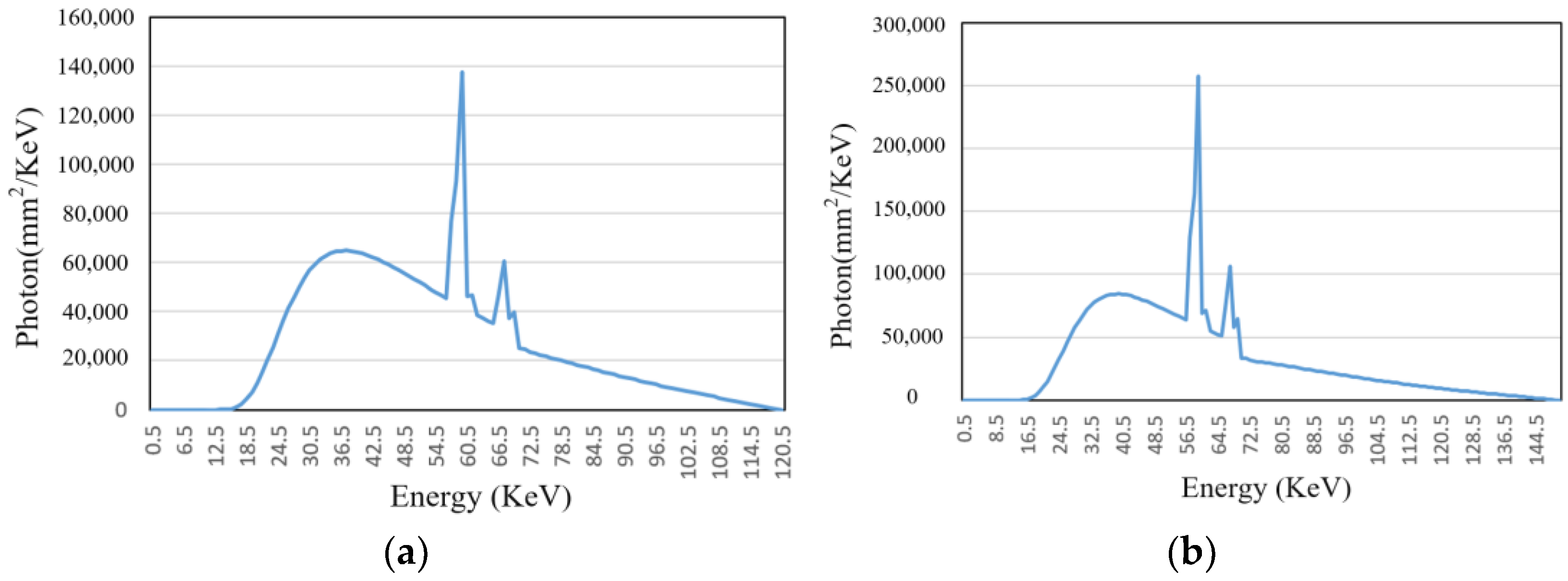
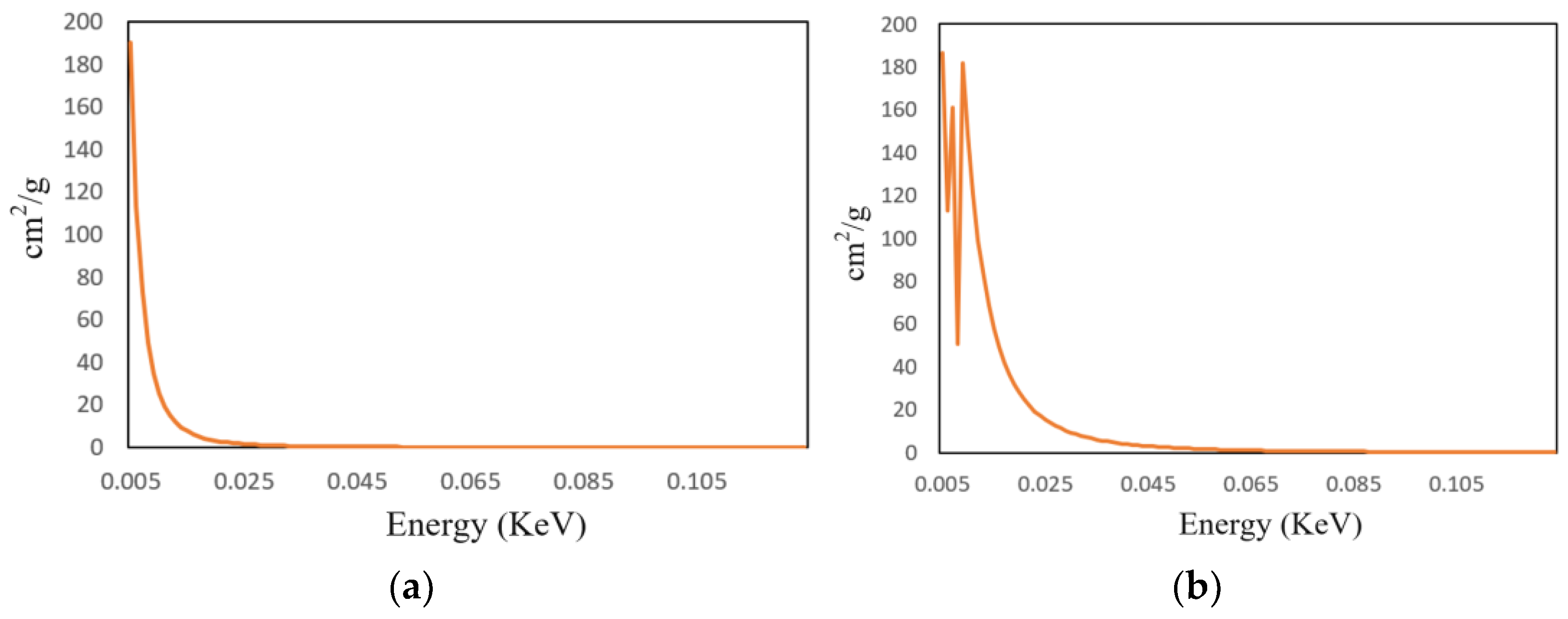
3.1.2. Generation of Simulated Artifact Data
3.2. Network Training
4. Experimental Results
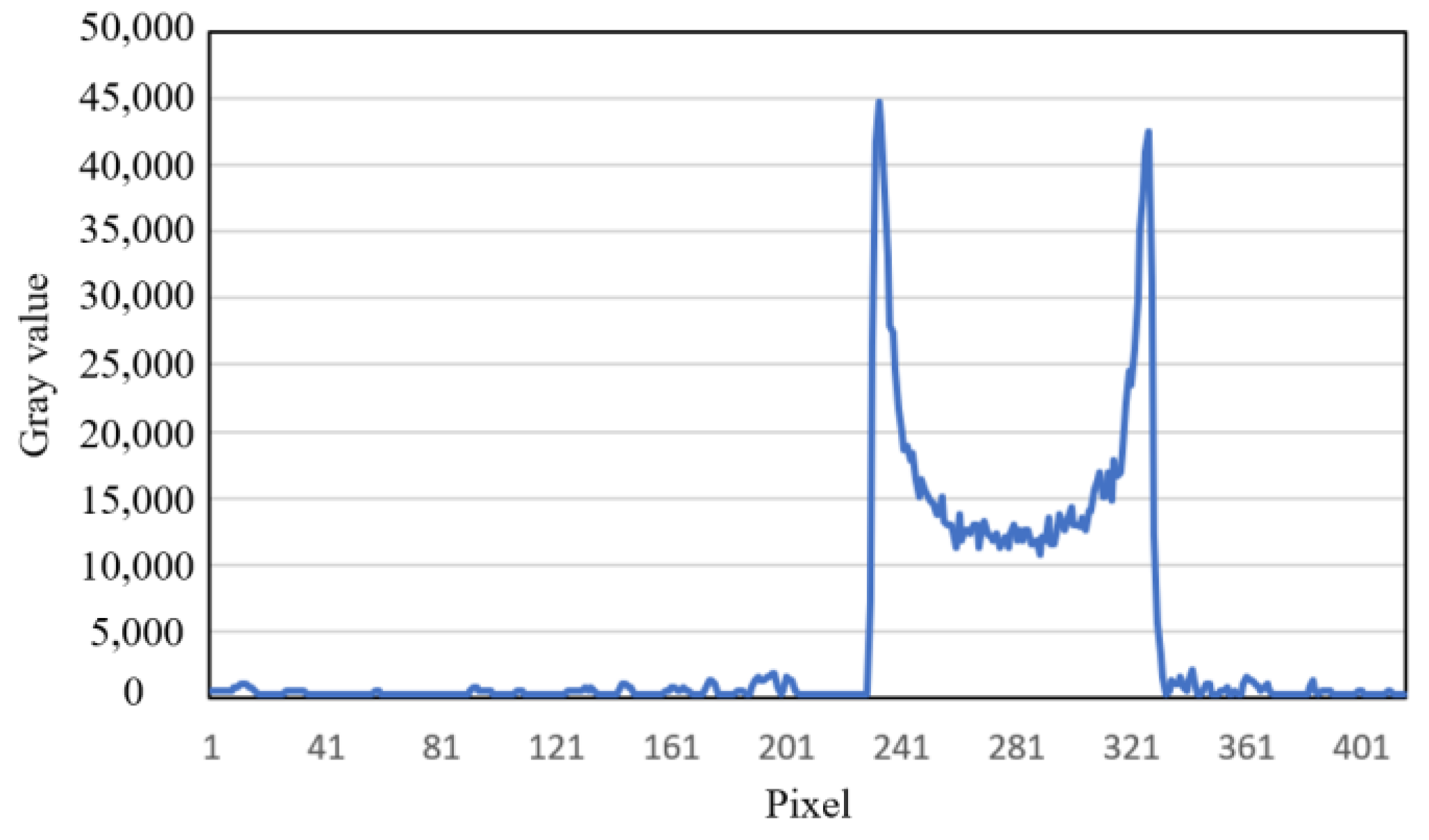
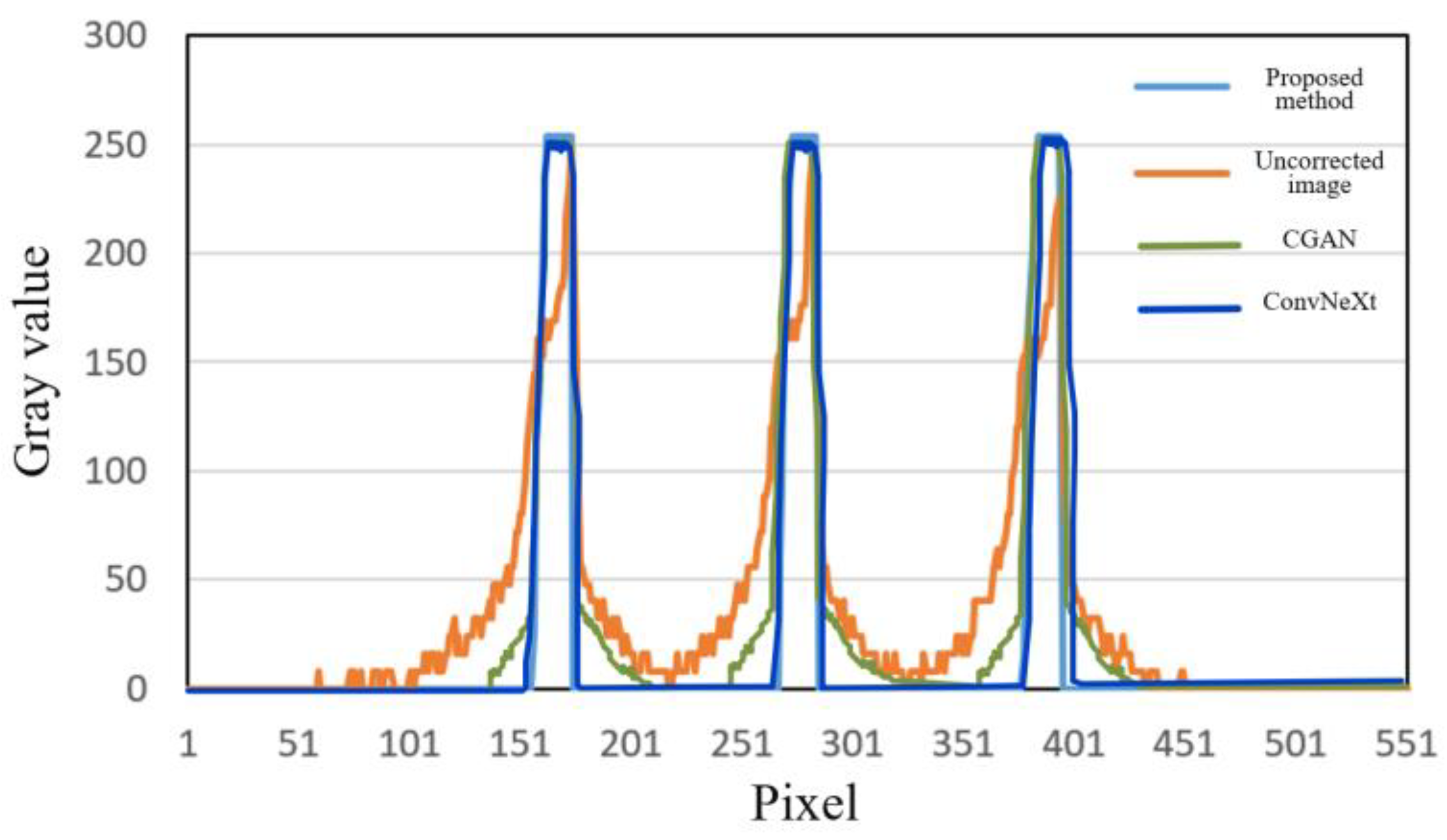
4.1. Simulated Experiment Results
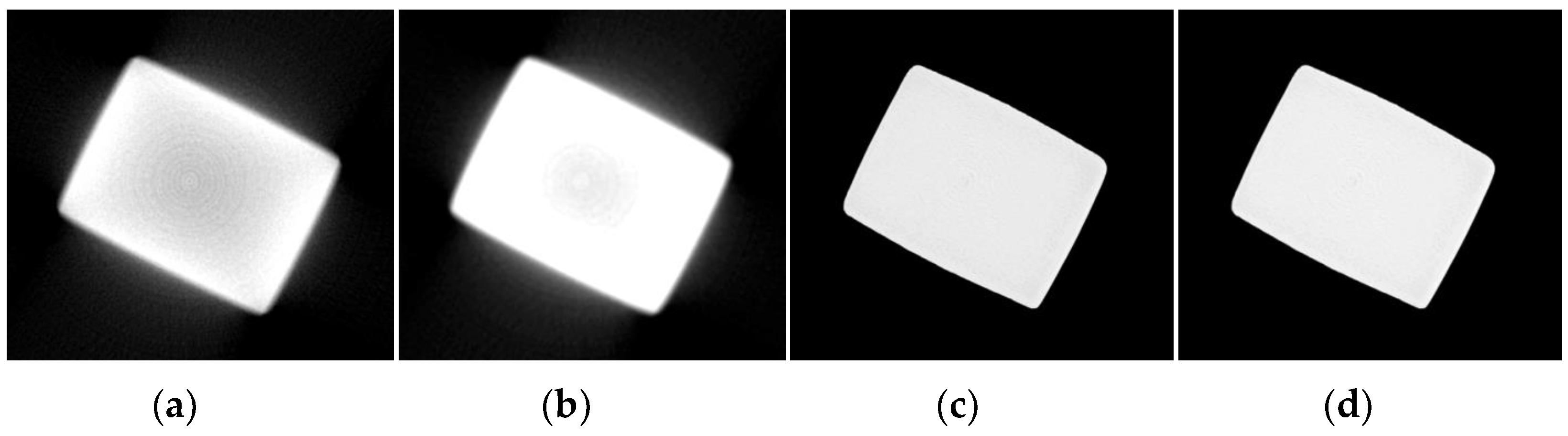
4.2. Real Data Experimental Results
4.2.1. Experiment 1: Additive Manufacturing of Titanium Alloy Samples
4.2.2. Experiment 2: Blisk Sample
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, H.S.; Hwang, D.; Seo, J.K. Metal Artifact Reduction for Polychromatic X-ray CT Based on a Beam-Hardening Corrector. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Han, Y.; Pan, J.; Chen, P. Multi-energy image sequence fusion based on variable energy X-ray imaging. J. X-Ray Sci. Technol. 2014, 22, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tward, D.J.; Siewerdsen, J.H. Cascaded systems analysis of the 3D noise transfer characteristics of flat-panel cone-beam CT. Med. Phys. 2009, 35, 5510–5529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbakri, I.; Fessler, J. Statistical image reconstruction for polyenergetic X-ray computed tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2002, 21, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, P.; Weckenmann, A. Multi-energy image stack fusion in computed tomography. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2010, 21, 045105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, J.R. A method for comparing beam-hardening filter materials for diagnostic radiology. Med. Phys. 1988, 15, 588–599. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Y.; Kiekens, K.; Welkenhuyzen, F.; Kruth, J.P.; Dewulf, W. Beam Hardening Correction and Its Influence on the Measurement Accuracy and Repeatability For CT Dimensional Metrology Applications. In Proceedings of the Conference on Industrial Computed Tomography, Wels, Austria, 19–21 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, G.; Yu, Z.; Yan, L. Beam hardening correction based on Monte Carlo simulation method. Chin. Phys. C 2006, 2, 178–182. [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakou, Y.; Meyer, E.; Prell, D.; Kachelrieß, M. Empirical beam hardening correction (EBHC) for CT. Med. Phys. 2010, 37, 5179–5187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Man, B.; Nuyts, J.; Dupont, P.; Marchal, G.; Suetens, P. An iterative maximum-likelihood polychromatic algorithm for CT. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2001, 20, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menvielle, N.; Goussard, Y.; Orban, D.; Soulez, G. Reduction of beam-hardening artifacts in X-ray CT. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology 27th Annual Conference, Shanghai, China, 17–18 January 2006; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 1865–1868. [Google Scholar]
- O’Sullivan, J.A.; Benac, J. Alternating Minimization Algorithms for Transmission Tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2007, 26, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, J.F.; Whiting, B.R.; Benac, J.; Murphy, R.J.; Blaine, G.J.; O’Sullivan, J.A.; Politte, D.G.; Snyder, D.L. Prospects for quantitative computed tomography imaging in the presence of foreign metal bodies using statistical image reconstruction. Med. Phys. 2002, 29, 2404–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishna, K.; Muralidhar, K.; Munshi, P. Beam-hardening in simulated X-ray tomography. NDT E Int. 2006, 39, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Samei, E. An efficient polyenergetic SART (pSART) reconstruction algorithm for quantitative myocardial CT perfusion. Med. Phys. 2014, 41, 461–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, R.E.; Macovski, A. Energy-selective reconstructions in X-ray computerised tomography. Phys. Med. Biol. 1976, 21, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Leng, S.; McCollough, C.H. Dual-energy CT-based monochromatic imaging. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2012, 199, S9–S15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, J. Exact Reconstruction for Dual Energy Computed Tomography Using an H-L Curve Method. In Proceedings of the IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference 2006, San Diego, CA, USA, 29 October–4 November 2006; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2006; Volume 6, pp. 3485–3488. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, R.E.; Seibert, J.A.; Thompson, S.K. Comparison of dual energy detector system performance. Med. Phys. 2004, 31, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olasz, C.; Varga, L.G.; Nagy, A. Beam hardening artifact removal by the fusion of FBP and deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Digital Image Processing, Singapore, 30 June 2021; Volume 11878, pp. 350–360. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.S.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, H.P.; Seo, J.K.; Chung, Y.E. CT sinogram-consistency learning for metal-induced beam hardening correction. Med. Phys. 2018, 45, 5376–5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinto, E.T. Singularities of the X-Ray Transform and Limited Data Tomography in R2 and R3. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 1993, 24, 1215–1225. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G. A Perspective on Deep Imaging. IEEE Access 2017, 4, 8914–8924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Qiao, K.; Wang, L.; Yan, B.; Li, L.; Hu, G. Image Prediction for Limited-angle Tomography via Deep Learning with Convolutional Neural Network. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1607.08707. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Kalra, M.K.; Lin, F.; Chen, Y.; Liao, P.; Zhou, J.; Wang, G. Low-Dose CT With a Residual Encoder-Decoder Convolutional Neural Network (RED-CNN). IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 2524–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Sun, H.; Lv, Y.; Liao, P.; Zhou, J.; Wang, G. LEARN: Learned Experts’ Assessment-Based Reconstruction Network for Sparse-Data CT. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 1333–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, H. Convolutional Neural Network Based Metal Artifact Reduction in X-Ray Computed Tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 1370–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalare, K.; Bajpai, M.; Sarkar, S.; Munshi, P. Deep neural network for beam hardening artifacts removal in image reconstruction. Appl. Intell. 2021, 52, 6037–6056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, K.; Pan, K.; Huang, W. Image defect classification of surface mount technology welding based on the improved ResNet model. J. Eng. Res. 2024, 12, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| VGG-Net | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | A-LRN | B | C | D | E |
| 11 weight layers | 11 weight layers | 13 weight layers | 16 weight layers | 16 weight layers | 19 weight layers |
| Input image (512 pixels × 512 pixels) | |||||
| conv-64 | conv-64 LRN | conv-64 conv-64 | conv-64 conv-64 | conv-64 conv-64 | conv-64 conv-64 |
| Max pooling | |||||
| conv-128 | conv-128 | conv-128 conv-128 | conv-128 conv-128 | conv-128 conv-128 | conv-128 conv-128 |
| Max pooling | |||||
| conv-256conv-256 | conv-256 conv-256 | conv-256 conv-256 | conv-256 conv-256 conv-256 | conv-256 conv-256 conv-256 | conv-256 conv-256 conv-256 conv-256 |
| Max pooling | |||||
| conv-512 conv-512 | conv-512 conv-512 | conv-512 conv-512 | conv-512 conv-512 conv-512 | conv-512 conv-512 conv-512 | conv-512 conv-512 conv-512 conv-512 |
| Max pooling | |||||
| conv-512 conv-512 | conv-512 conv-512 | conv-512 conv-512 | conv-512 conv-512 conv-512 | conv-512 conv-512 conv-512 | conv-512 conv-512 conv-512 conv-512 |
| Max pooling | |||||
| Index | CGAN | ConvNeXt | Proposed | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | RMSE | 2.6118 | 0.8242 | 0.4156 |
| PSNR | 20.5411 | 26.7854 | 28.3647 | |
| SSIM | 0.9274 | 0.9566 | 0.9638 | |
| Sample 2 | RMSE | 2.8112 | 1.6514 | 0.9574 |
| PSNR | 21.9457 | 24.3789 | 27.6621 | |
| SSIM | 0.9348 | 0.9470 | 0.9513 |
| Index | CGAN | ConvNeXt | Proposed | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | RMSE | 3.1020 | 2.5564 | 1.2128 |
| PSNR | 19.3123 | 25.7412 | 26.3147 | |
| SSIM | 0.9236 | 0.9571 | 0.9634 | |
| Sample 2 | RMSE | 3.2401 | 2.3697 | 1.5441 |
| PSNR | 21.0496 | 25.3412 | 27.8741 | |
| SSIM | 0.9034 | 0.9367 | 0.9501 |
| Flat Panel Detector | Pixel Size | Resolution | Ratio | Integration Time | Projection Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amorphous silicon | 0.139 mm | 900 × 900 | 5.545 | 1 s | 720 |
| Index | CGAN | ConvNeXt | Proposed |
|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 3.1062 | 1.6472 | 0.8873 |
| PSNR | 25.3601 | 28.9647 | 30.1422 |
| SSIM | 0.9320 | 0.9698 | 0.9731 |
| Index | CGAN | ConvNeXt | Proposed |
|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 1.9873 | 1.0035 | 0.8423 |
| PSNR | 26.3041 | 27.7415 | 28.4762 |
| SSIM | 0.9598 | 0.9773 | 0.9841 |
| Index | CGAN | ConvNeXt | Proposed |
|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 3.0193 | 2.3676 | 1.3647 |
| PSNR | 28.5511 | 30.6470 | 33.1478 |
| SSIM | 0.9632 | 0.9796 | 0.9821 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Ma, Z.; Kang, D.; Yang, M. A Beam Hardening Artifact Correction Method for CT Images Based on VGG Feature Extraction Networks. Sensors 2025, 25, 2088. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072088
Zhang H, Ma Z, Kang D, Yang M. A Beam Hardening Artifact Correction Method for CT Images Based on VGG Feature Extraction Networks. Sensors. 2025; 25(7):2088. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072088
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hong, Zhaoguang Ma, Da Kang, and Min Yang. 2025. "A Beam Hardening Artifact Correction Method for CT Images Based on VGG Feature Extraction Networks" Sensors 25, no. 7: 2088. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072088
APA StyleZhang, H., Ma, Z., Kang, D., & Yang, M. (2025). A Beam Hardening Artifact Correction Method for CT Images Based on VGG Feature Extraction Networks. Sensors, 25(7), 2088. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072088





