Unobtrusive Bed Monitor State of the Art
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sensing Devices Embedded in the Bed
2.1. History
2.2. Bed-Embedded Sensors
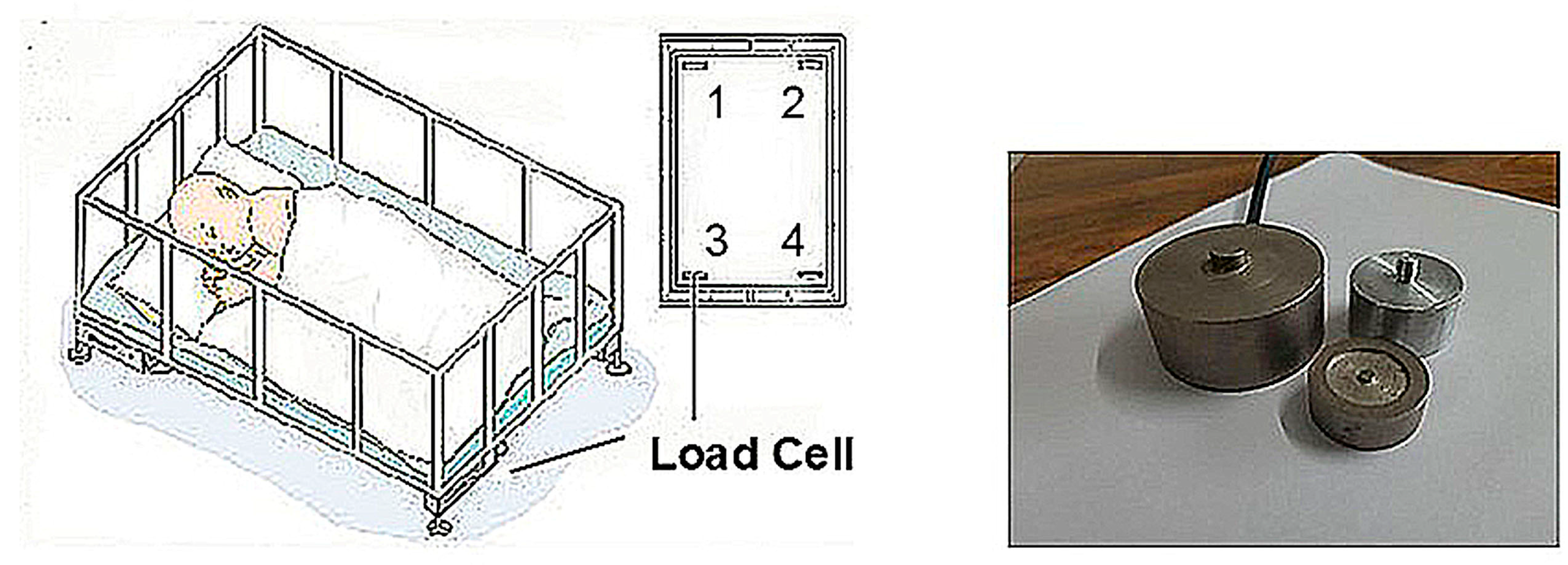
2.2.1. Load Cells for Force and Motion Detection
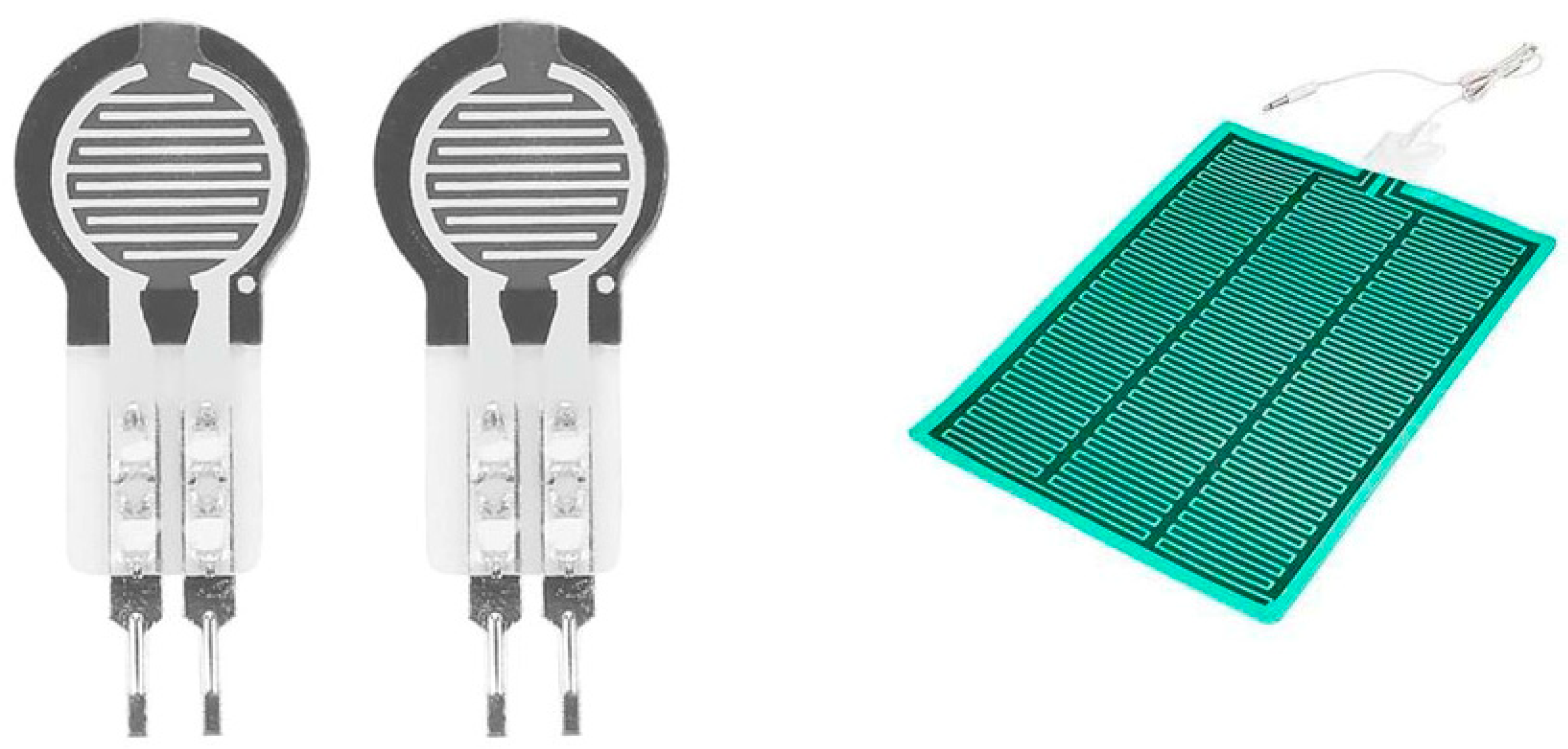
2.2.2. Pressure Sensors
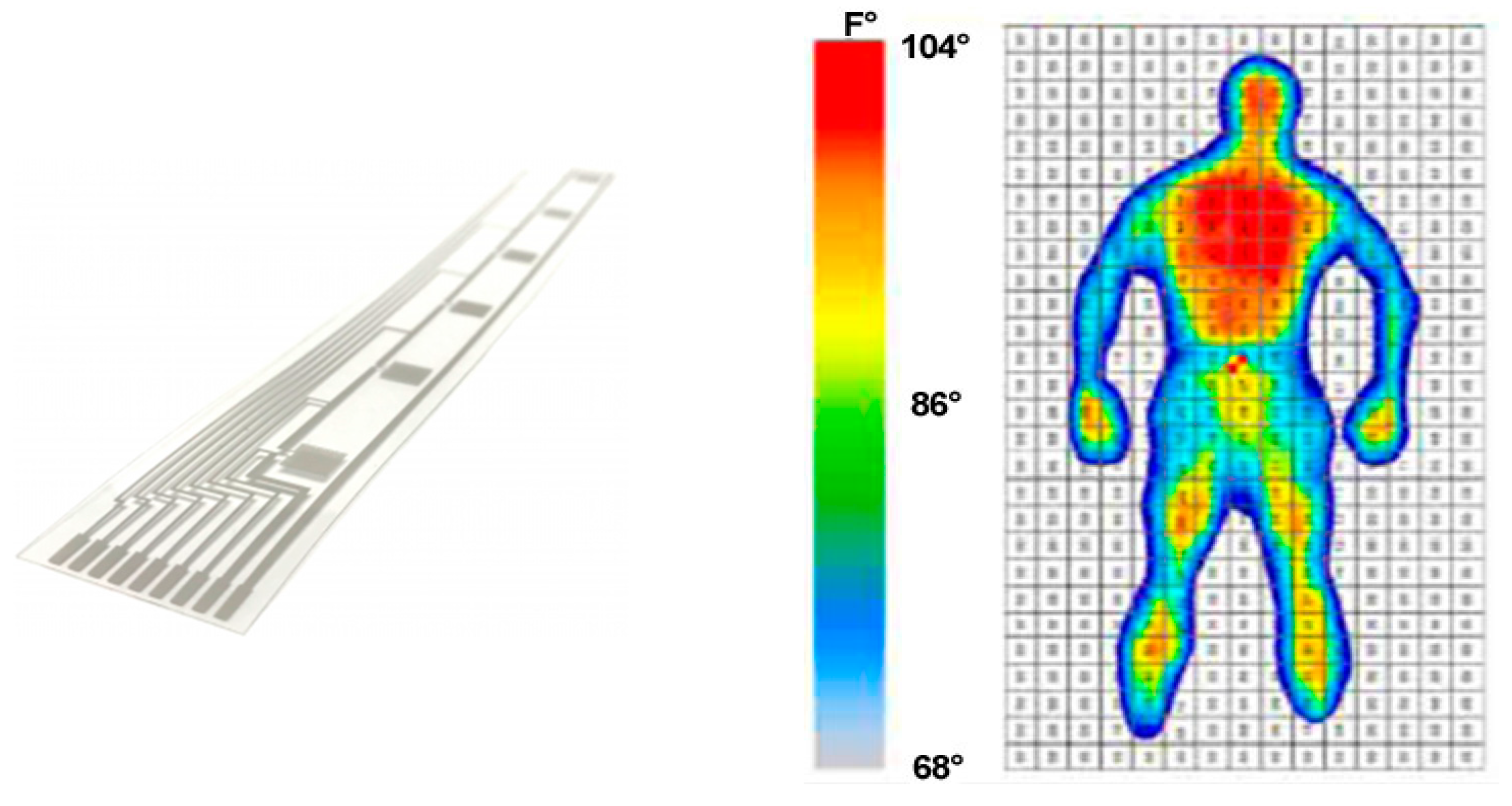
2.2.3. Temperature Sensors and Array
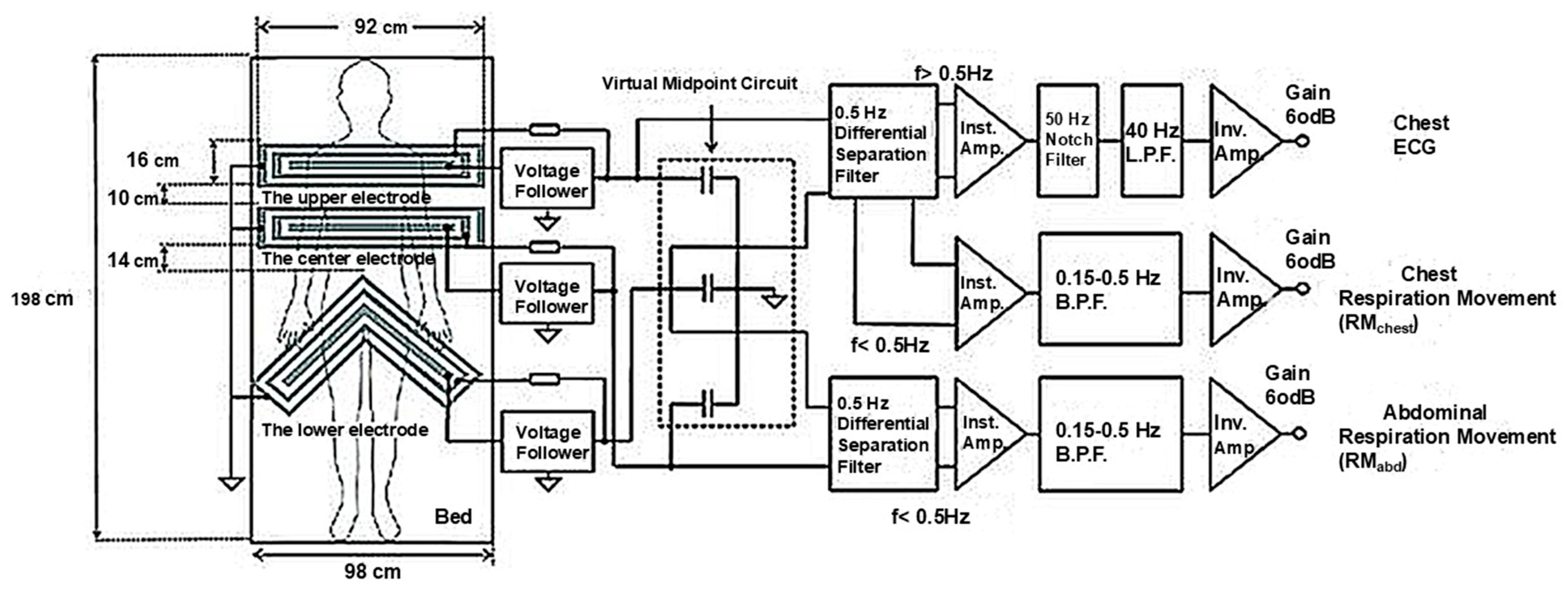
2.2.4. Electric Signals
- (a)
- ECG
- (b)
- Capacitive ECG
- (c)
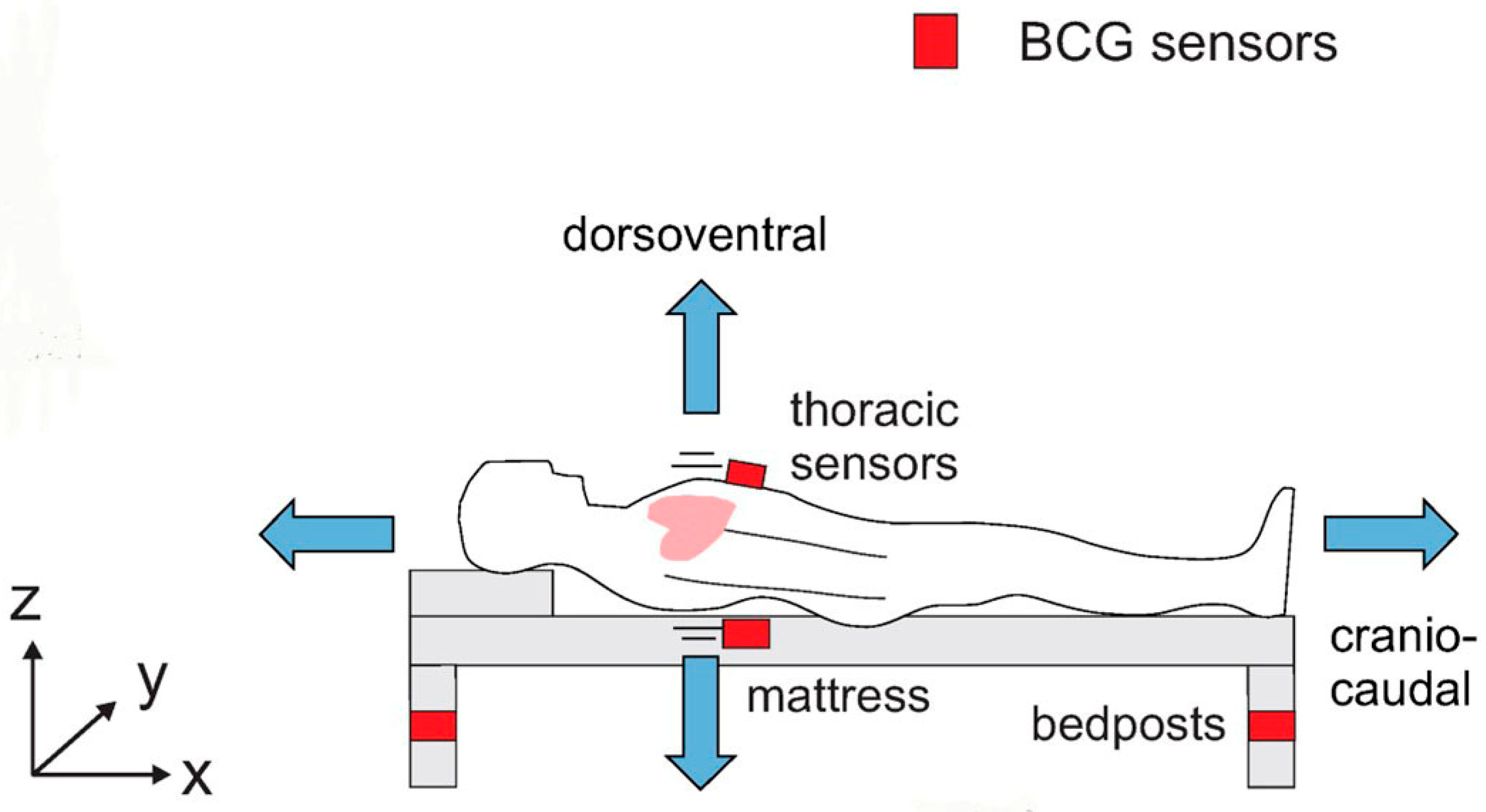
- BCG
- (d)
- Static Charge-Sensitive Bed (SCSB)
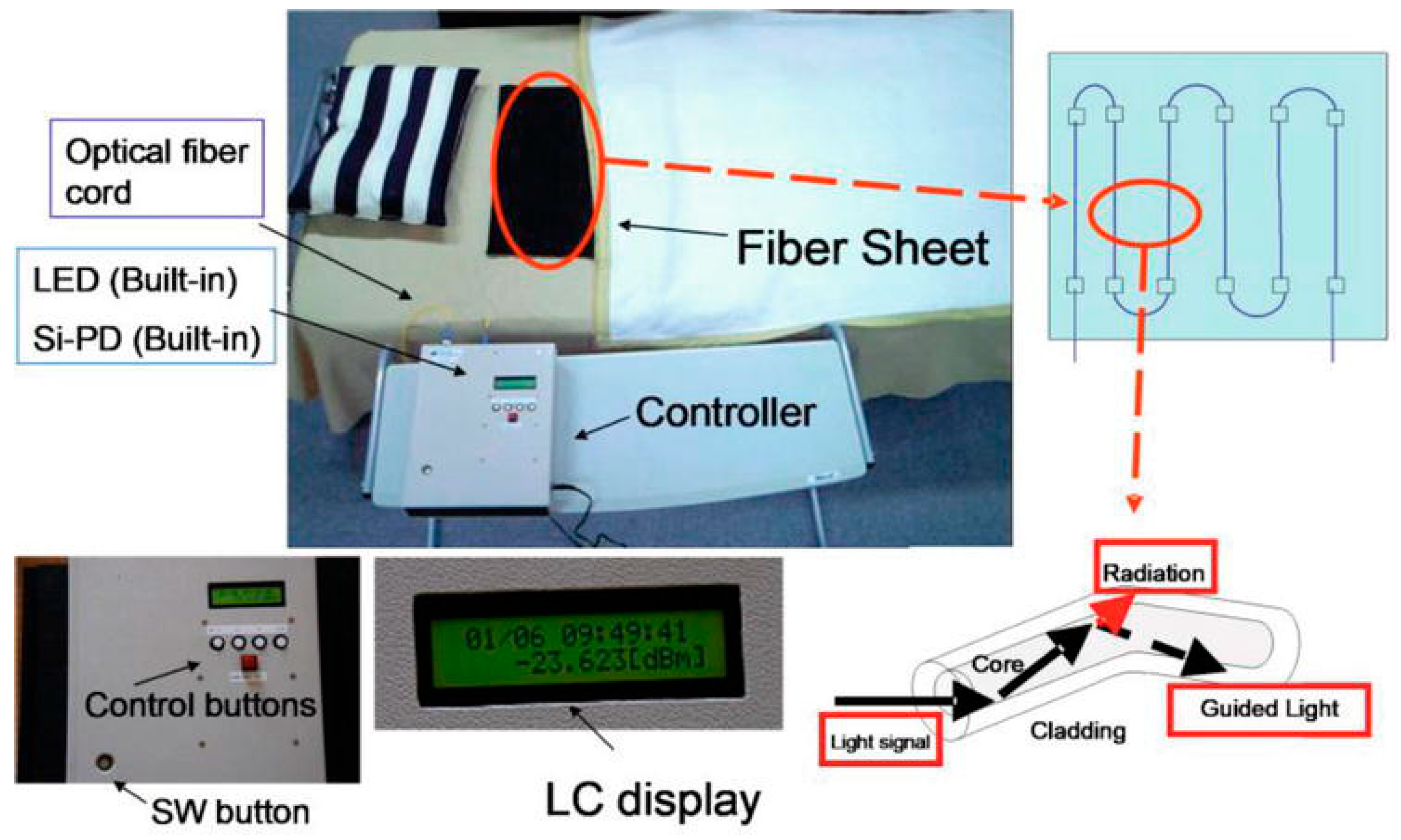
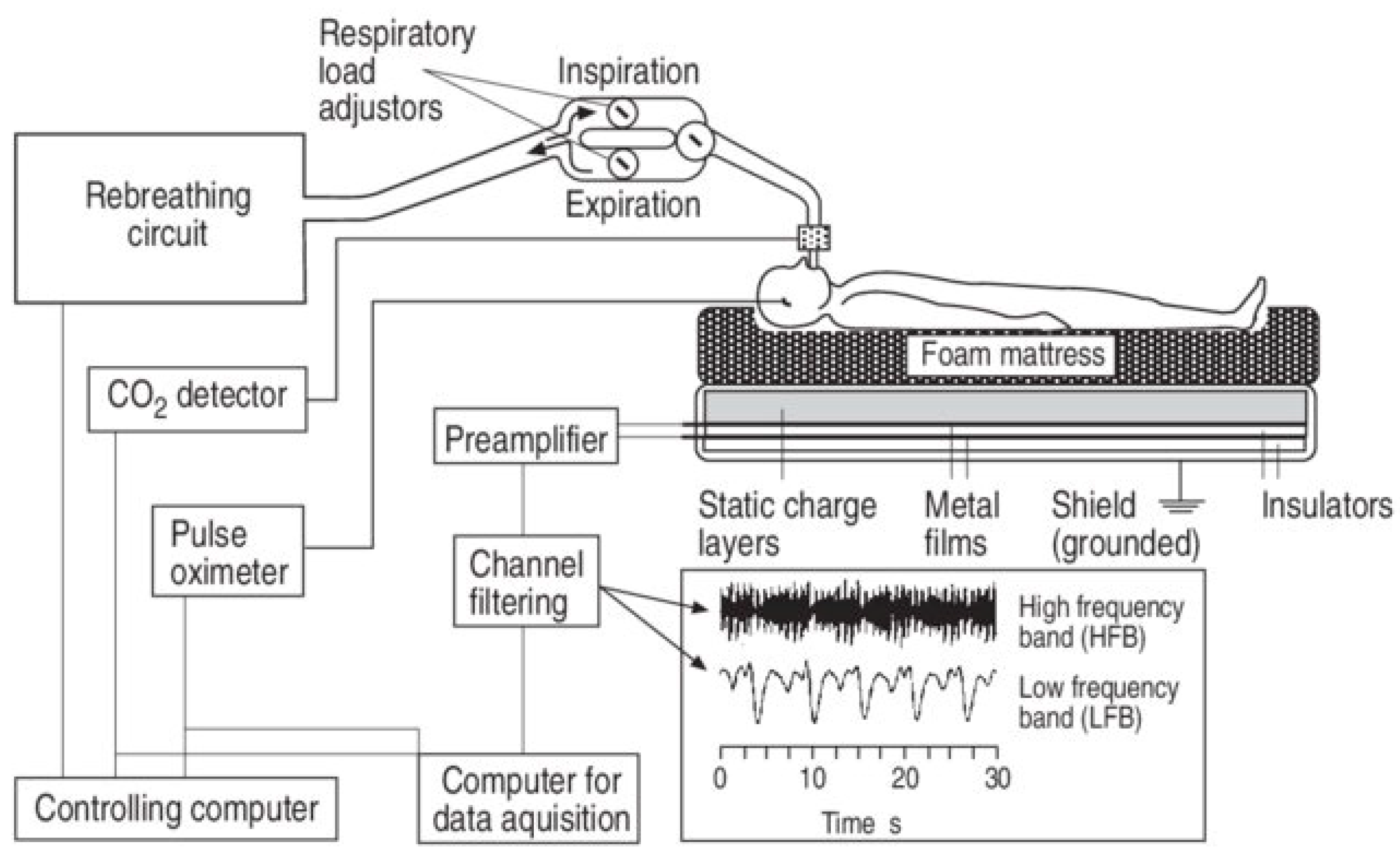
2.2.5. Gas Sensor
2.3. Indirect Sensing by Optical and Biomagnetic Sensors
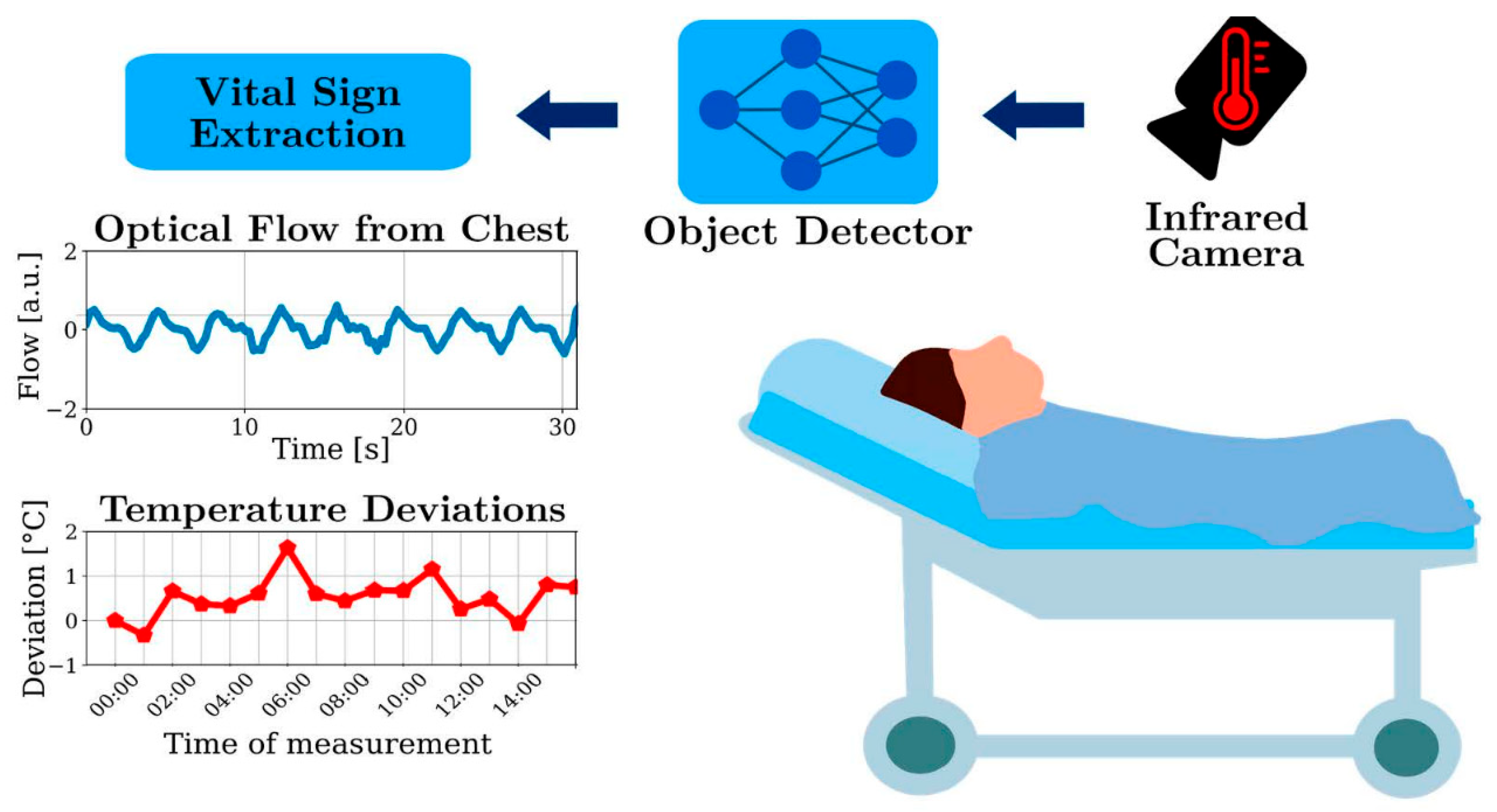
2.3.1. Video and Camera Images
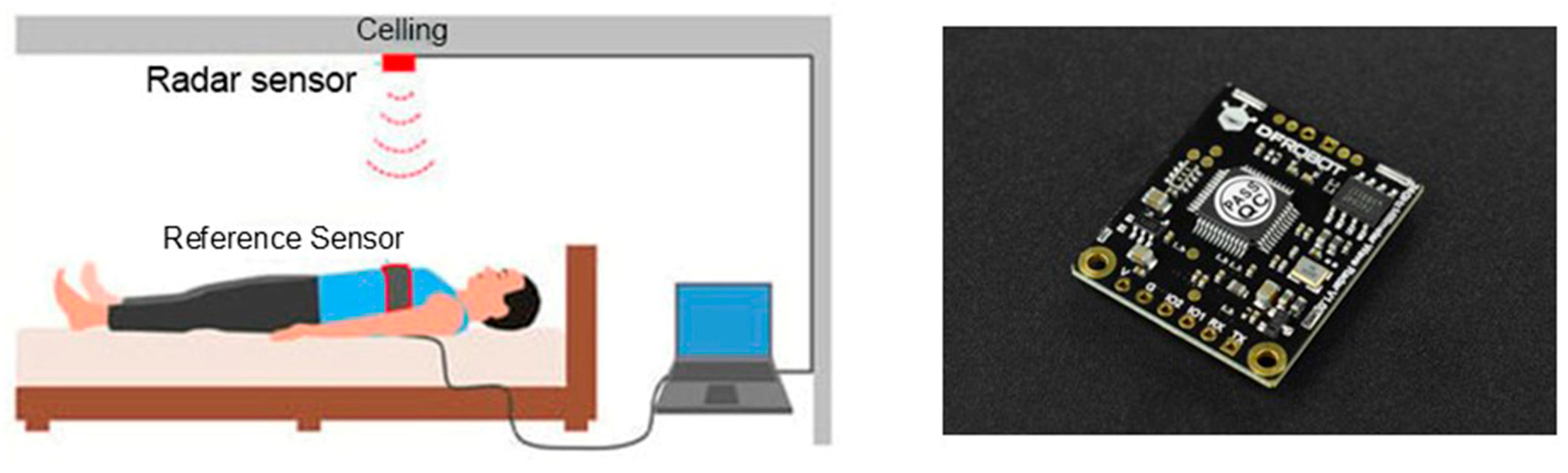
2.3.2. Radar Sensor
3. Physiological Parameters
3.1. Sleep Quality and Body Movement
3.2. Heart Rate and Respiratory Rate
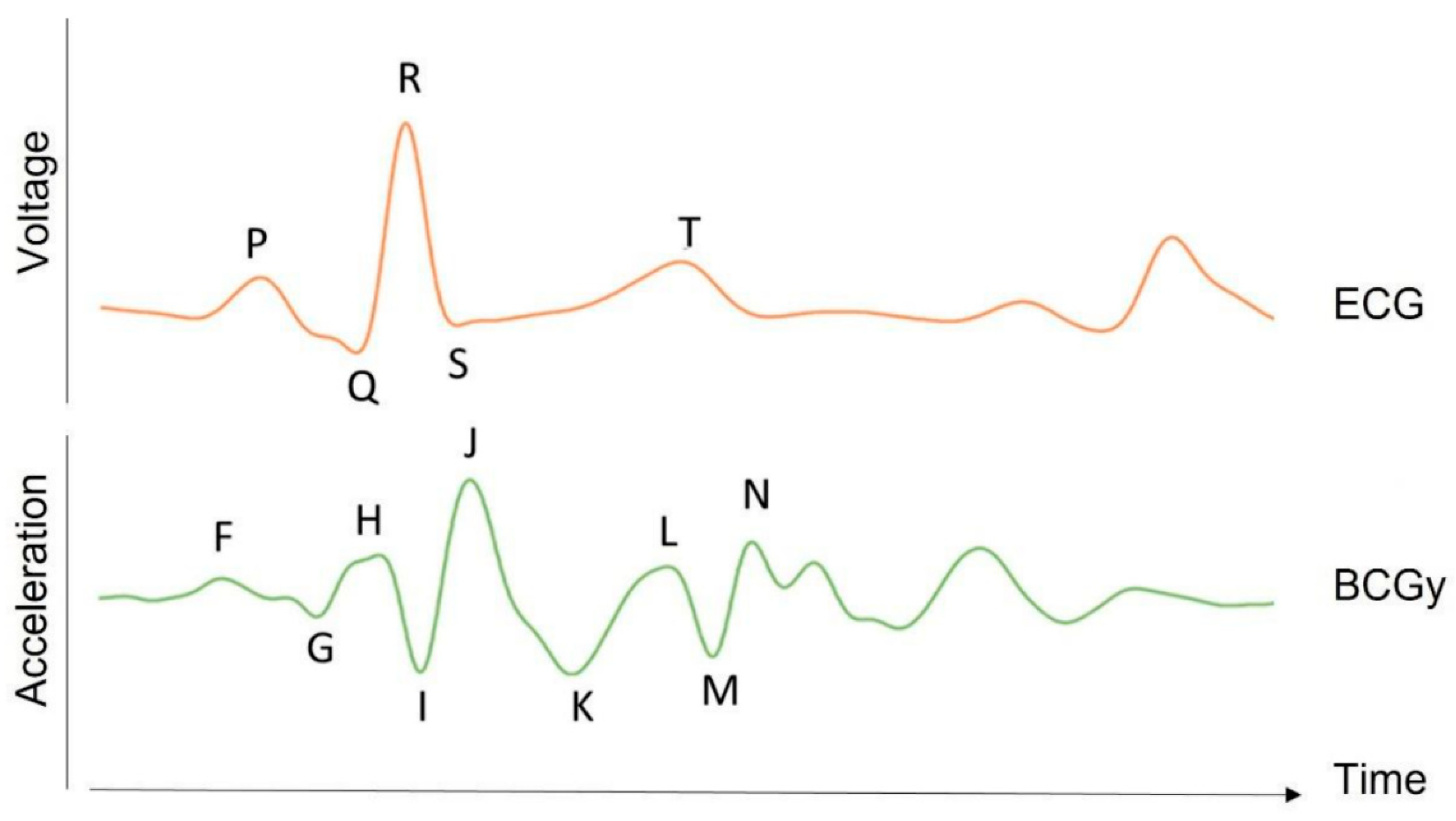
3.3. ECG and Ballistocardiogram
3.4. Blood Pressure
3.5. Body Temperature Measurement
3.6. Odor Sensing
4. Clinical Trials
4.1. Physiological Information for Babies
4.2. Intensive Care and Critical Care
4.3. Assistive Care in Nursing Homes
4.4. Sleep Apnea
4.5. Commercial Devices
5. Future Prospects
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alihanka, J.; Vaahtoranta, K. A static charge sensitive bed. A new method for recording body movements during sleep. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1979, 46, 731–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaziz, M.; Jia, Z.; Liu, J.; Howard, R.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. Motion Scale: A Body Motion Monitoring System Using Bed-Mounted Wireless Load Cells. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE First International Conference on Connected Health: Applications, Systems and Engineering Technologies (CHASE), Washington, DC, USA, 27–29 June 2016; pp. 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhai, A.A. Load-Cell Based Hospital Bed Control. U.S. Patent US20070268147A1, 22 November 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Togawa, T. Home health monitoring. J. Med. Dent. Sci. 1998, 45, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.K.; Yoon, H.; Han, C.; Joo, K.M.; Park, K.S. Physiological Signal Monitoring Bed for Infants Based on Load-Cell Sensors. Sensors 2016, 16, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adami, A.M.; Pavel, M.; Hayes, T.L.; Singer, C.M. Detection of Movement in Bed Using Unobtrusive Load Cell Sensors. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2010, 14, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indra, C.; D, A.; Das, M. Weighing the Weight of Bedridden Patient by using Strain Gauge (Weighing Scale)—Prototype. Int. J. Health Technol. Innov. 2023, 2, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoj, R.; Kumarasami, R.; Joseph, J.; George, B.; Sivaprakasam, M. Continuous Weight Monitoring System for ICU Beds using Air-filled Mattresses/Pads: A Proof of Concept. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA), Istanbul, Turkey, 26–28 June 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Liu, T.; Meng, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, S. Method of bed exit intention based on the internal pressure features in array air spring mattress. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Liu, S.; Fang, Z.; Wu, H.; Liang, M.; Deng, S.; Lin, J. A Novel Detection Method for Heart Rate Variability and Sleep Posture Based on a Flexible Sleep Monitoring Belt. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 25, 5178–5191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitachi, S.; Satoh, K.; Shimoyama, K.; Satoh, M.; Sugiyama, T. Optical Fiber-Based Sleep Apnea Syndrome Sensor. In Sino-Nasal and Olfactory System Disorders; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren-Smith, S.C.; Kilpatrick, A.D.; Wisal, K.; Nguyen, L.V. Multimode optical fiber specklegram smart bed sensor array. J. Biomed. Opt. 2022, 27, 067002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanellos, G.T.; Papaioannou, G.; Tsiokos, D.; Mitrogiannis, C.; Nianios, G.; Pleros, N. Two dimensional polymer-embedded quasi-distributed FBG pressure sensor for biomedical applications. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, T.; Togawa, T.; Murta, M. A bed temperature monitoring system for assessing body movement during sleep. Clin. Phys. Physiol. Meas. 1988, 9, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, T.; Zhou, J.; Mizukami, H.; Togawa, T. A system for monitoring temperature distribution in bed and its application to the assessment of body movement. Physiol. Meas. 1993, 14, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, T.; Miyasako, S.; Ogawa, M.; Togawa, T.; Fujimoto, T. Assessment of bed temperature monitoring for detecting body movement during sleep: Comparison with simultaneous video image recording and actigraphy. Med. Eng. Phys. 1999, 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Molina, G.; Winger, T.; Makaram, N.; Rao, M.R.; Chernega, P.; Shcherbakov, Y.; McGhee, L.; Chellamuthu, V.; Veneros, E.; Mills, R.; et al. Unobtrusive Skin Temperature Estimation on a Smart Bed. Sensors 2024, 24, 4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, T.; Kawarada, A.; Nambu, M.; Tsukada, A.; Sasaki, K.; Yamakoshi, K. E-healthcare at an experimental welfare techno house in Japan. Open Med. Inform. J. 2007, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.G.; Kim, K.K.; Park, K.S. ECG Recording on a Bed During Sleep Without Direct Skin-Contact. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 54, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peltokangas, M.; Verho, J.; Vehkaoja, A. Night-Time EKG and HRV Monitoring with Bed Sheet Integrated Textile Electrodes. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2012, 16, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.G.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, S.M.; Lee, H.J.; Park, K.S. Capacitive Measurement of ECG for Ubiquitous Healthcare. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 42, 2218–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, M.; Yamagishi, S.; Ohmuta, T.; Fukuoka, Y.; Ueno, A. Non-Contact Simultaneous Measurements of Electrocardiogram and Respiratory Movements Using Capacitive Sheet Electrodes. Adv. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 6, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, M.; Ueno, A. Noncontact In-Bed Measurements of Physiological and Behavioral Signals Using an Integrated Fabric-Sheet Sensing Scheme. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2019, 23, 618–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessard-Tremblay, M.; Weeks, J.; Morelli, L.; Cowan, G.; Gagnon, G.; Zednik, R.J. Contactless Capacitive Electrocardiography Using Hybrid Flexible Printed Electrodes. Sensors 2020, 20, 5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Kamiyama, N.; Arima, Y.; Nakamura, T. Capacitively Coupled Electrode Array Sensors for Body Posture and ECG Measurement During Sleep. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 24363–24372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Choi, S.; Koo, C.; Joung, Y. Development and Optimization of Silicon−Dioxide−Coated Capacitive Electrode for Ambulatory ECG Measurement System. Sensors 2022, 22, 8388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.S.; Ober, S.; McMurtry MFinegan, B.A.; Inan, O.T.; Mullamada, R.; Hahn, J.C. Ballistocardiogram: Mechanism and Potential for Unobtrusive Cardiovascular Health Monitoring. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsukura, Y.; Sumali, B.; Nagura, M.; Fukunaga, K.; Yasui, M. Sleep Stage Estimation from Bed Leg Ballistocardiogram Sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, N.; Cocconcelli, F.; Matrella, G.; Chiorboli, G.; Ciampolini, P. An accurate and stable bed-based ballistocardiogram measurement and analysis system. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Industry 4.0 & IoT (MetroInd4.0&IoT), Rome, Italy, 7–9 June 2021; pp. 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonhardt, S.; Leicht, L.; Teichmann, D. Unobtrusive Vital Sign Monitoring in Automotive Environments—A Review. Sensors 2018, 18, 3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balali, P.; Rabineau, J.; Hossein, A.; Tordeur, C.; Debeir, O.; van de Borne, P. Investigating Cardiorespiratory Interaction Using Ballistocardiography and Seismocardiography—A Narrative Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 9565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alihanka, J.; Vaahtoranta, K.; Saarikivi, I. A new method for long-term monitoring of the ballistocardiogram, heart rate, and respiration. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1981, 240, R384–R392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo, O.; Brissaud, L.; Sales, B.; Besset, A.; Billiard, M. The validity of the static charge sensitive bed in detecting obstructive sleep apnoeas. Eur. Respir. J. 1988, 1, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, B.H.; Larson, B.H.; Shankar, K. Monitoring of the ballistocardiogram with the static charge sensitive bed. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1991, 38, 748–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindqvist, A.; Pihlajamäki, K.; Jalonen, J.; Laaksonen, V.; Alihanka, J. Static-charge-sensitive bed ballistocardiography in cardiovascular monitoring. Clin. Physiol. 1996, 16, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirjavainen, T.; Polo, O.; McNamara, S.; Vaahtoranta, K.; Sullivan, C.E. Respiratory challenge induces high frequency spiking on the static charge sensitive bed (SCSB). Eur. Respir. J. 1996, 9, 1810–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortelainen, J.M.; Mendez, M.O.; Bianchi, A.M.; Matteucci, M.; Cerutti, S. Sleep staging based on signals acquired through bed sensor. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2010, 14, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Huang, G. Real time monitoring to the odour of excrement for health of infants and elderly completely bedridden. In Proceedings of the SPIE 10245, International Conference on Innovative Optical Health Science, Shanghai, China, 5 January 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ui, Y.; Akiba, Y.; Sugano, S.; Imai, R.; Tomiyama, K. Excretion Detection System with Gas Sensor—Proposal and Verification of Algorithm Based on Time-Series Clustering. J. Robot. Mechatron. 2017, 29, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugano, S.; Ui, Y.; Tanimoto, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Nakano, K.; Tomiyama, K. Excretion Detection Systems with Gas Sensors—Development of Prototype Devices Integrating Sensor and Operation Functions. J. Robot. Mechatron. 2021, 33, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugano, S.; Tanimoto, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Ui, Y. Excretion Detection Systems with Gas Sensors—Development of Excretion Detection Device with Non-Suction Utilizing Floor Cushion. J. Robot. Mechatron. 2023, 3, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Tamura, T. Development of real-time image sequence analysis for evaluating posture change and respiratory rate of a subject in bed. Physiol. Meas. 2001, 22, N21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Cheng, J.; Song, R.; Liu, Y.; Ward, R.K.; Wang, Z. Video-Based Heart Rate Measurement: Recent Advances and Future Prospects. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 68, 3600–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scebba, G.; Da Poian, G.; Karlen, W. Multispectral Video Fusion for Non-Contact Monitoring of Respiratory Rate and Apnea. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 68, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyra, S.; Mayer, L.; Ou, L.; Chen, D.; Timms, P.; Tay, A.; Chan, P.Y.; Ganse, B.; Leonhardt, S.; Hoog Antink, C. A Deep Learning-Based Camera Approach for Vital Sign Monitoring Using Thermography Images for ICU Patients. Sensors 2021, 21, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Goederen, R.; Pu, S.; Silos Viu, M.; Doan, D.; Overeem, S.; Serdijn, W.A.; Joosten, K.F.M.; Long, X.; Dudink, J. Radar-based sleep stage classification in children undergoing polysomnography: A pilot-study. Sleep Med. 2021, 82, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Aguila, M.; Olvera-Cervantes, J.L.; Perez-Ramos, A.E.; Corona-Chavez, A. Methodology for the determination of human respiration rate by using Doppler radar and Empirical Modal Decomposition. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.W.; Kim, D.H.; Koo, D.L.; Park, Y.; Nam, H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Hong, S.-N.; Jang, G.; Lim, S.; et al. Automated Detection of Sleep Apnea-Hypopnea Events Based on 60 GHz Frequency-Modulated Continuous-Wave Radar Using Convolutional Recurrent Neural Networks: A Preliminary Report of a Prospective Cohort Study. Sensors 2022, 22, 7177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Eun-Kyoung Lee, O.; Feng, F.; Vitiello, M.V.; Wang, W.; Benson, H.; Fricchione, G.L.; Denninger, J.W. The effect of meditative movement on sleep quality: A systematic review. Sleep Med. Rev. 2016, 30, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Hwang, S.H.; Lee, S.M.; Lim, Y.G.; Park, K.S. Estimation of Body Postures on Bed Using Unconstrained ECG Measurements. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2013, 17, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, Y.; Liu, T.; Shen, L.-M. Method of recognizing sleep postures based on air pressure sensor and convolutional neural network: For an air spring mattress. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 121, 106009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, A.; Zheng, T.; Xiao, H.; Huang, R. The Relationship between Sleeping Position and Sleep Quality: A Flexible Sensor-Based Study. Sensors 2022, 22, 6220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.H.; Chung, G.C.; Lee, J.-S.; Jeong, D.-U.; Park, K.S. Slow-wave sleep estimation on a load-cell-installed bed: A non-constrained method. Physiol. Meas. 2009, 30, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tal, A.; Shinar, Z.; Shaki, D.; Codish, S.; Goldbart, A. Validation of contact-free sleep monitoring device with comparison to polysomnography. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2017, 13, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siyahjani, F.; Garcia Molina, G.; Barr, S.; Mushtaq, F. Performance Evaluation of a Smart Bed Technology against Polysomnography. Sensors 2022, 22, 2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, E.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xu, G.; Chen, L. The past, present, and future of sleep quality assessment and monitoring. Brain Res. 2023, 1810, 148333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaiduk, M.; Stoffers, M.; Stoffers, M.; Taheri, N.; Penzel, T.; Madrid, N.M. Evolution of Bed-Based Sensor Technology in Unobtrusive Sleep Monitoring: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 29545–29563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Lyu, W.; Zhou, J.; Yu, J. Sleep condition detection and assessment with optical fiber interferometer based on machine learning. iScience 2023, 26, 107244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukai, T.; Matsuo, K.; Kato, Y.; Shimizu, A.; Guo, S. Determination of locations on a tactile sensor suitable for respiration and heartbeat measurement of a person on a bed. In Proceedings of the 2014 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Chicago, IL, USA, 26–30 August 2014; pp. 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Guo, S.; Xiao, S.; Zhao, X. Unconstrained Identification of the Positions of Chest and Abdomen and Detection of Respiratory Motions in Sleep by Using a Bed-Size Tactile Sensor Sheet. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 16276–16286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isono, S. Contact-free assessments of respiratory rate and volume with load cells under the bed legs in ventilated patients: A prospective exploratory observational study. J. Appl. Physiol. 1985, 134, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, G.S.; Choi, B.H.; Jeong, D.-U.; Park, K.S. Noninvasive Heart Rate Variability Analysis Using Loadcell-Installed Bed During Sleep. In Proceedings of the 2007 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Lyon, France, 22–26 August 2007; pp. 2357–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Watanabe, T.; Watanabe, H.; Ando, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Kobayashi, K. Noninvasive measurement of heartbeat, respiration, snoring and body movements of a subject in bed via a pneumatic method. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 52, 2100–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortelainen, J.M.; van Gils, M.; Pärkkä, J. Multichannel bed pressure sensor for sleep monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2012 Computing in Cardiology, Krakow, Poland, 9–12 September 2012; pp. 313–316. [Google Scholar]
- Gaiduk, M.; Wehrle, D.; Seepold, R.; Ortega, J.A. Non-obtrusive system for overnight respiration and heartbeat tracking. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 176, 2746–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Hwang, S.H.; Yoon, H.N.; Lee, W.K.; Park, K.S. Heart Rate Variability Monitoring during Sleep Based on Capacitively Coupled Textile Electrodes on a Bed. Sensors 2015, 15, 11295–11311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, L.; Su, B.Y.; Skubic, M.; Ho, K.C. Heart Rate Monitoring Using Hydraulic Bed Sensor Ballistocardiogram. J. Ambient Intell. Smart Environ. 2017, 9, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Kimball, J.P.; Receveur, T.; Agdeppa, E.D.; Inan, O.T. Accurate Ballistocardiogram Based Heart Rate Estimation Using an Array of Load Cells in a Hospital Bed. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2021, 25, 3373–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Du, L.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, X.; Sun, J.; Man, Z.; Cao, B.; Fang, Z. Accurate Estimation of Heart and Respiration Rates Based on an Optical Fiber Sensor Using Adaptive Regulations and Statistical Classifications Spectrum Analysis. Front. Digit. Health 2021, 3, 747460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alivar, A.; Carlson, C.; Suliman, A.; Warren, S.; Prakash, P.; Thompson, D.E.; Natarajan, B. Motion Artifact Detection and Reduction in Bed-Based Ballistocardiogram. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 13693–13703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranjec, K.; Beguš, S.; Geršak, G.; Drnovšek, J. Non-contact heart rate and heart rate variability measurements: A review. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2014, 13, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harford, M.; Catherall, J.; Gerry, S.; Young, J.D.; Watkinson, P. Availability and performance of image-based, non-contact methods of monitoring heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and oxygen saturation: A systematic review. Physiol. Meas. 2019, 40, 06TR01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, I.; Biswas, J.; Abdulrazak, B. Ballistocardiogram signal processing: A review. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 2019, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serhani, M.A.; El Kassabi, H.T.; Ismail, H.; Navaz, A.N. ECG Monitoring Systems: Review, Architecture, Processes, and Key Challenges. Sensors 2020, 20, 1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeetha, T.; Kumutha, D.; Bharathi, M.D.; Surendran, R. Smart mattress integrated with pressure sensor and IoT functions for sleep apnea detection. Meas. Sens. 2022, 24, 100450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recmanik, M.; Martinek, R.; Nedoma, J.; Jaros, R.; Pelc, M.; Hajovsky, R.; Velicka, J.; Pies, M.; Sevcakova, M.; Kawala-Sterniuk, A. A Review of Patient Bed Sensors for Monitoring of Vital Signs. Sensors 2024, 24, 4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Li, H.; Chen, Q.; Jiang, C.; Dong, W.-F. Blood pressure monitoring with piezoelectric bed sensor systems. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2024, 87 Pt A, 105479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.Y.; Ryan, N.P.; Chen, D.; McNeil, J.; Hopper, I. Novel wearable and contactless heart rate, respiratory rate, and oxygen saturation monitoring devices: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Anaesthesia 2022, 77, 1268–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.-T.; Yeh, C.-Y.; Chen, C.-C.; Lai, C.-H.; Lin, Y.-H.; Lin, C.-Y.; Shu, Y.-C.; Ko, N.-Y. Early changes in skin surface temperature predict body temperature increases in patients with fever: A pilot study. Care Nurs. 2024, 83, 10365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, W.; Long, X.; Meftah, M.; Tan, T.; Shan, C.; Aarts, R.M.; de With, P.H.N. Respiration Monitoring for Premature Neonates in NICU. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastwood-Sutherland, C.; Lim, K.; Gale, T.J.; Wheeler, K.I.; Dargaville, P.A. Detection of respiratory activity in newborn infants using a noncontact vision-based monitor. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2023, 58, 1753–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dore, H.; Aviles-Espinosa, R.; Luo, Z.; Anton, O.; Rabe, H.; Rendon-Morales, E. Characterisation of Textile Embedded Electrodes for Use in a Neonatal Smart Mattress Electrocardiography System. Sensors 2021, 21, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Hu, M.; Zhai, G.; Zhu, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.P. Lightweight Video-Based Respiration Rate Detection Algorithm: An Application Case on Intensive Care. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 1761–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Sakai, I.; Amemiya, A.; Komatsu, R.; Sakuraba, S.; Isono, S. Long-term body weight change assessed by non-contact load cells under the bed in older people with and without eating assistance: A preliminary study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contact-Free Sleep Sensors. Available online: https://emfit.com (accessed on 2 December 2024).
- Junnila, S.; Kailanto, H.; Merilahti, J.; Vainio, A.-M.; Vehkaoja, A.; Zakrzewski, M.; Hyttinen, J. Wireless, Multipurpose In-Home Health Monitoring Platform: Two Case Trials. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2010, 14, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüser, C.; Winter, S.; Leonhardt, S. Unsupervised Heart Rate Variability Estimation from Ballistocardiograms. Int. J. Bioelectromagn. 2013, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Tenhunen, M.; Hyttinen, J.; Lipponen, J.A.; Virkkala, J.; Kuusimäki, S.; Tarvainen, M.P.; Karjalainen, P.A.; Himanen, S.-L. Heart rate variability evaluation of Emfit sleep mattress breathing categories in NREM sleep. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, M.M.S.; van Lotringen, J.H.; Vos-van der Hulst, M.; Keijsers, N.L.W. Bed Sensor Technology for Objective Sleep Monitoring Within the Clinical Rehabilitation Setting: Observational Feasibility Study. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2021, 9, e24339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleeptracker-AI. Available online: https://sleeptracker.com (accessed on 2 December 2024).
- Ding, F.; Cotton-Clay, A.; Fava, L.; Easwar, V.; Kinsolving, A.; Kahn, P.; Rama, A.; Kushida, C. Polysomnographic validation of an under-mattress monitoring device in estimating sleep architecture and obstructive sleep apnea in adults. Sleep Med. 2022, 96, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NemuriScan. Available online: https://www.paramount.co.jp/english/product/detail/index/20/96 (accessed on 2 December 2024).
- Nagatomo, K.; Masuyama, T.; Iizuka, Y.; Makino, J.; Shiotsuka, J.; Sanui, M. Validity of an under-mattress sensor for objective sleep measurement in critically ill patients: A prospective observational study. J. Intensive Care 2020, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Product Name | Emfit QS Sleep Tracker | Sleeptracker-AI® | NSCAN |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Emfit Ltd., Vaajakoski, Finland | Sleeptracker, Santa Cruz, CA, USA | Paramount Bed Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan |
| Principle | Ballistocardiography | Force | Pressure |
| Parameters | HR HRV Sleep period Sleep stage | BR Snoring HR, RR Sleep stage | HR, RR Sleep stage |
| Dimensions | 542 mm L × 70 mm W × 1.4 mm THK | 146.6 mm L × 77 mm W × 15 mm THK | 245 mm L × 780 mm W × 15 mm THK |
| Sensor | Emfit‘s proprietary dynamic ferroelectret sensor | Piezoelectric sensors | A flexible, stretchable, and soft rubber-based tactile sensor sheet |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tamura, T.; Huang, M. Unobtrusive Bed Monitor State of the Art. Sensors 2025, 25, 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061879
Tamura T, Huang M. Unobtrusive Bed Monitor State of the Art. Sensors. 2025; 25(6):1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061879
Chicago/Turabian StyleTamura, Toshiyo, and Ming Huang. 2025. "Unobtrusive Bed Monitor State of the Art" Sensors 25, no. 6: 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061879
APA StyleTamura, T., & Huang, M. (2025). Unobtrusive Bed Monitor State of the Art. Sensors, 25(6), 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061879








