Effect of Annealing Treatment on Sensing Response of Inorganic Film Taste Sensor to Sweet Substances
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fabrication and Property Measurement Method of Inorganic Film Taste Sensors
2.2. Measurement Method of Taste Sensor
2.3. Sample Solutions
3. Results
3.1. Physical Properties (SEM, XRD)
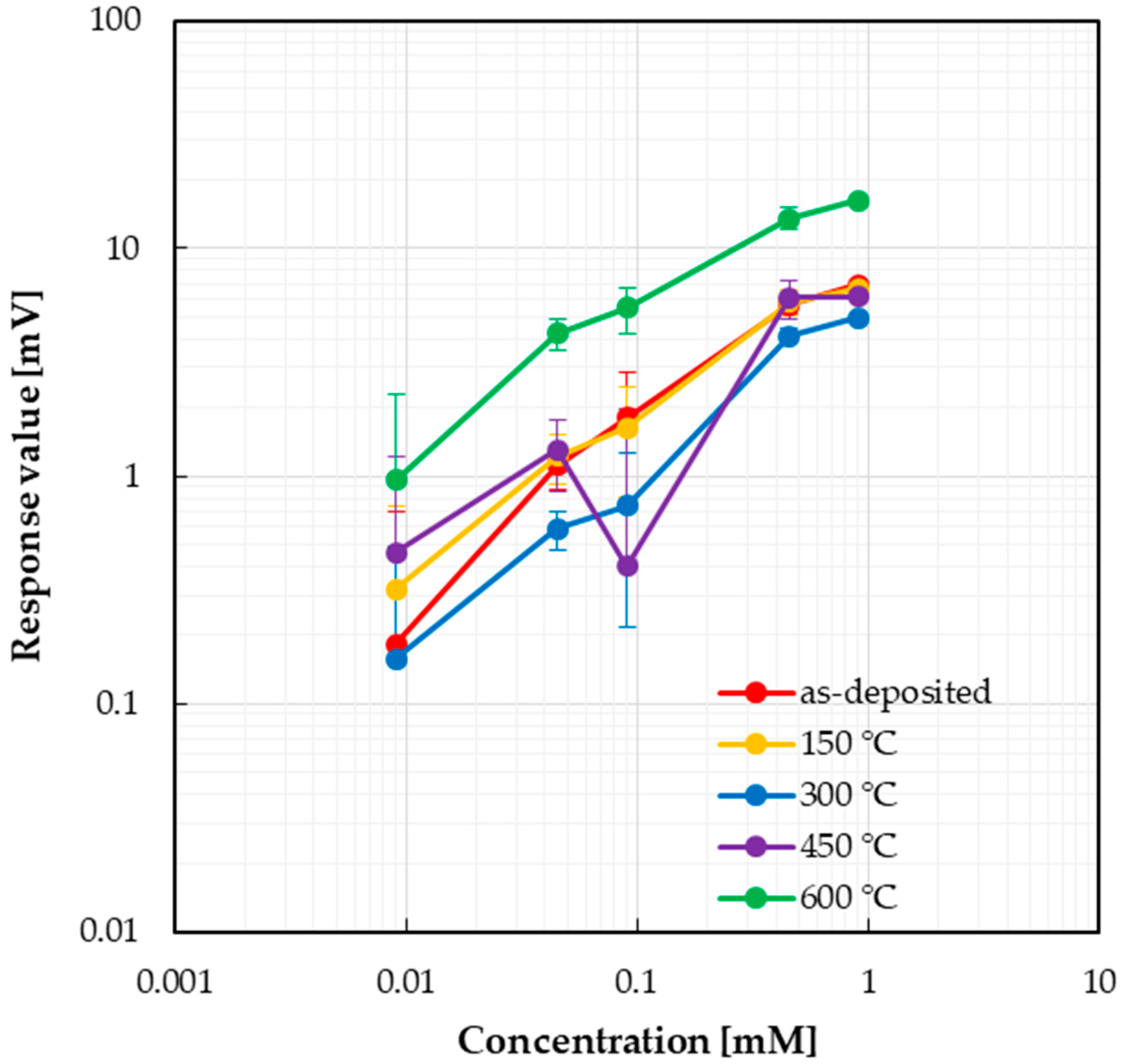
3.2. Sensor Response
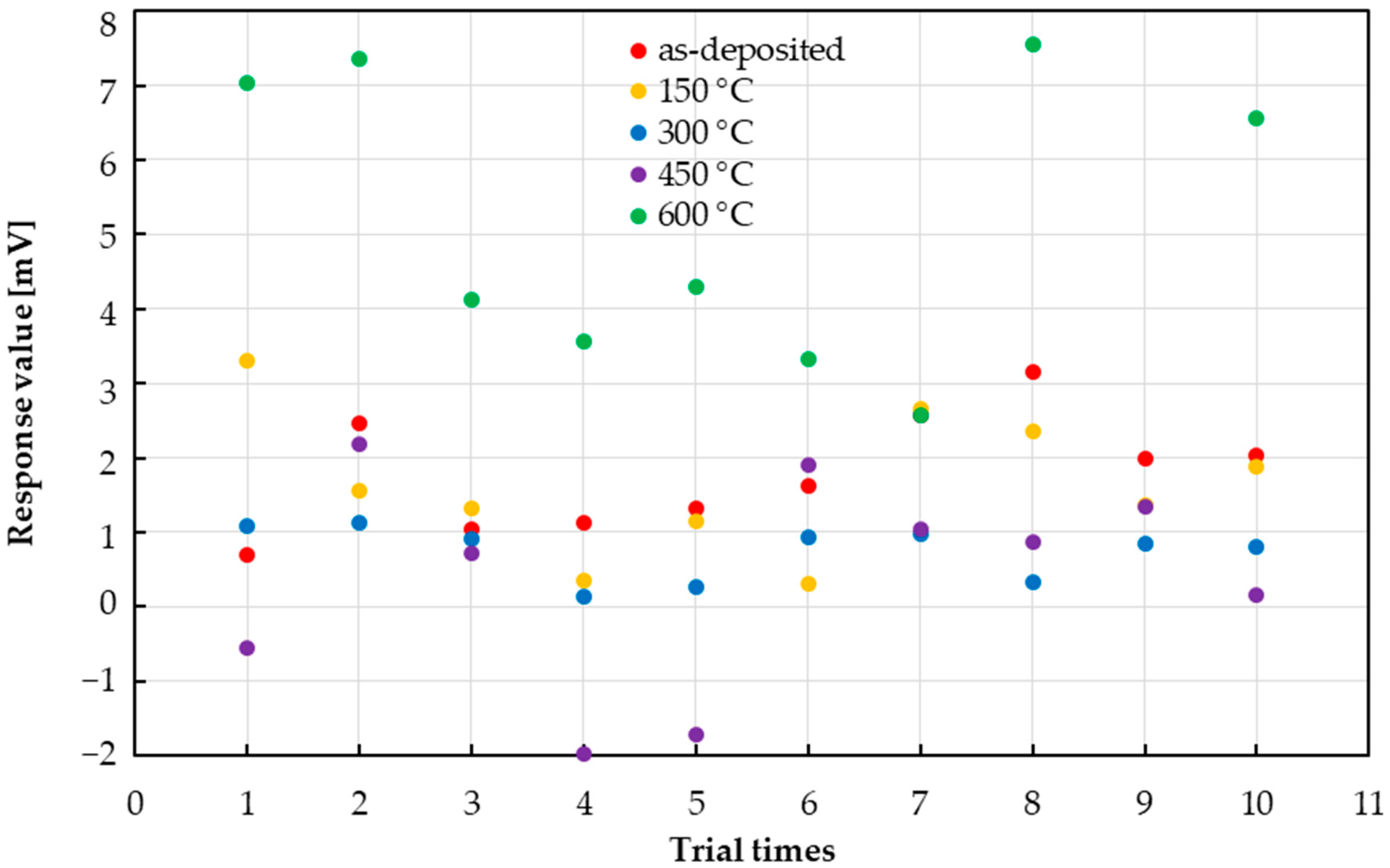
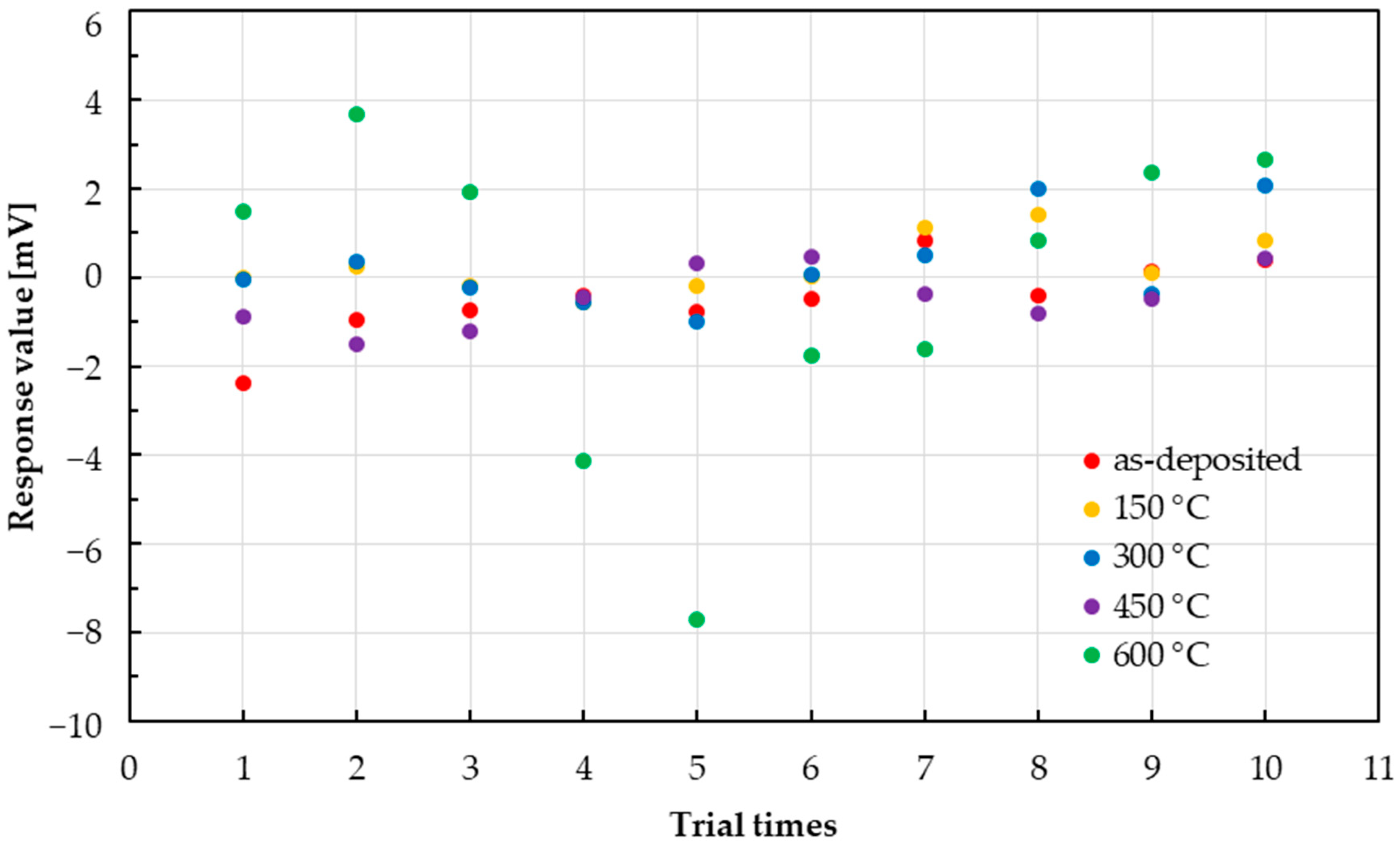
3.3. Variability in Sensor Responses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shand, C.A.; Wendler, R.; Dawson, L.; Yates, K.; Stephenson, H. Multivariate Analysis of Scotch Whisky by Total Reflection X-Ray Fluorescence and Chemometric Methods: A Potential Tool in the Identification of Counterfeits. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 976, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.W.; Zhou, H.H.; Lv, Y.; Wu, Q.; Pan, Y.; Peng, Z.X.; Zhang, X.H.; Yin, X.L. Geographical Origin Identification of Chinese Red Wines Using Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy Coupled with Machine Learning Techniques. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 119, 105265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Peterson, D.G. Identification of a Novel Umami Compound in Potatoes and Potato Chips. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, M.; Su, G.; Lin, L. Identification and Taste Characteristics of Novel Umami and Umami-Enhancing Peptides Separated from Peanut Protein Isolate Hydrolysate by Consecutive Chromatography and UPLC–ESI–QTOF–MS/MS. Food Chem. 2019, 278, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Luo, Q.; Yin, X. Quantification of Artificial Sweeteners in Alcoholic Drinks Using Direct Analysis in Real-Time QTRAP Mass Spectrometry. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tighrine, A.; Amir, Y.; Alfaro, P.; Mamou, M.; Nerín, C. Simultaneous Extraction and Analysis of Preservatives and Artificial Sweeteners in Juices by Salting out Liquid-Liquid Extraction Method Prior to Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Food Chem. 2019, 277, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ongkowijoyo, P.; Peterson, D.G. Identification of Compounds Contributing to Umami Taste of Pea Protein Isolate. Food Chem. 2023, 429, 136863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iiyama, S.; Kuga, H.; Ezaki, S.; Hayashi, K.; Toko, K. Peculiar Change in Membrane Potential of Taste Sensor Caused by Umami Substances. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 91, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuura, M.; Okazaki, H.; Tahara, Y.; Ikezaki, H.; Toko, K. Development of Sweetness Sensor with Selectivity to Negatively Charged High-Potency Sweeteners. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 201, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akitomi, H.; Tahara, Y.; Yasuura, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ikezaki, H.; Toko, K. Quantification of Tastes of Amino Acids Using Taste Sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 179, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iiyama, S.; Yahiro, M.; Toko, K. Measurements of Soy Sauce Using Taste Sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2000, 66, 205–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Onitake, H.; Haraguchi, T.; Tahara, Y.; Yatabe, R.; Yoshida, M.; Uchida, T.; Ikezaki, H.; Toko, K. Quantitative Prediction of Bitterness Masking Effect of High-Potency Sweeteners Using Taste Sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 235, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Song, F.; Kimura, S.; Onodera, T.; Uchida, T.; Toko, K. Taste Sensor for Detecting Non-Charged Bitter Substances: Xanthine Derivatives of Pharmaceutical Applications. Microchem. J. 2024, 200, 110248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iiyama, S.; Ezaki, S.; Toko, K.; Matsuno, T.; Yamafuji, K. Study of Astringency and Pungency with Multichannel Taste Sensor Made of Lipid Membranes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1995, 24, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, M.; Aoki, Y.; Tamai, N.; Matsuki, H. Effect of Pressure on Bilayer Phase Behavior of N-Methylated Di-O-Hexadecylphosphatidylethanolamines: Relevance of Head-Group Modification on the Bilayer Interdigitation. Biophys. Chem. 2017, 231, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, M.; Endo, T.; Yano, T.; Tamai, N.; Kohlbrecher, J.; Matsuki, H. Comprehensive Characterization of Temperature- and Pressure-Induced Bilayer Phase Transitions for Saturated Phosphatidylcholines Containing Longer Chain Homologs. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 128, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuki, H.; Endo, S.; Sueyoshi, R.; Goto, M.; Tamai, N.; Kaneshina, S. Thermotropic and Barotropic Phase Transitions on Diacylphosphatidylethanolamine Bilayer Membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 1222–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, Y.; Uchida, H.; Hasegawa, Y. Study on Inorganic Film Taste Sensor for Hot Drink Evaluation. IEEJ Trans. Sens. Micromach. 2016, 136, 180–185. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankova, M.; Vilanova, X.; Llobet, E.; Calderer, J.; Bittencourt, C.; Pireaux, J.J.; Correig, X. Influence of the Annealing and Operating Temperatures on the Gas-Sensing Properties of Rf Sputtered WO3 Thin-Film Sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 105, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamlesh; Suthar, D.; Sharma, R.; Chasta, G.; Panwar, S.; Himanshu; Purohit, L.P.; Dhaka, M.S. Exploration of Annealing Effect on Physical Properties of Indium Oxide Films for Gas Sensors. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2024, 675, 415622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, J.; Chen, X.; Xu, J. Annealing Temperature Dependence of Mechanical and Structural Properties of Chromium-Gold Films on the Silica Glass Substrate. Thin Solid Films 2023, 774, 139849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, T.; Bissig, B.; Döbeli, M.; Tiwari, A.N.; Romanyuk, Y.E. Thin Films of SnO2:F by Reactive Magnetron Sputtering with Rapid Thermal Post-Annealing. Thin Solid Films 2014, 553, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Das, A.; Singha, C.; Bhattacharyya, A. Al, Mg Co-Doped ZnO Thin Films: Effect of the Annealing Temperature on the Resistivity and Ultraviolet Photoconductivity. Thin Solid Films 2023, 780, 139958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhara, S.; Giri, P.K. Stable P-Type Conductivity and Enhanced Photoconductivity from Nitrogen-Doped Annealed ZnO Thin Film. Thin Solid Films 2012, 520, 5000–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuprenaite, S.; Abrutis, A.; Kubilius, V.; Murauskas, T.; Saltyte, Z.; Plausinaitiene, V. Effects of Annealing Conditions and Film Thickness on Electrical and Optical Properties of Epitaxial Al-Doped ZnO Films. Thin Solid Films 2016, 599, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehraj, S.; Ansari, M.S. Alimuddin Annealed SnO2 Thin Films: Structural, Electrical and Their Magnetic Properties. Thin Solid Films 2015, 589, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmanov, A.A.; Beauchamp, G.K. Taste Receptor Genes. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2007, 27, 389–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.; Henderson, D.; Hjelm, M.; Hård, T.; Hernandez Salazar, L.T.; Laska, M. Taste Responsiveness of Chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes) and Black-Handed Spider Monkeys (Ateles geoffroyi) to Eight Substances Tasting Sweet to Humans. Physiol. Behav. 2021, 238, 113470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Liu, H.; Qin, N.; Ren, X.; Zhu, B.; Xia, X. Impact of Food Additives on the Composition and Function of Gut Microbiota: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 99, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Guo, J.; Shao, T.; Kou, H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Tian, S. Enhanced Ethanol Gas Sensing Performance of Ag/SnO2 Composites. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2025, 423, 136721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
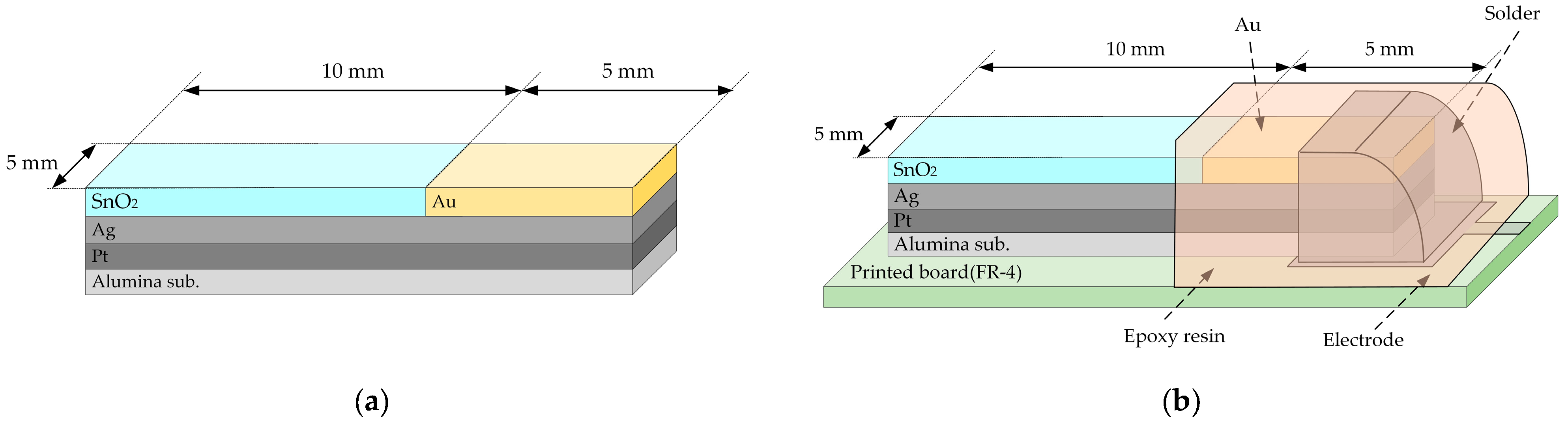


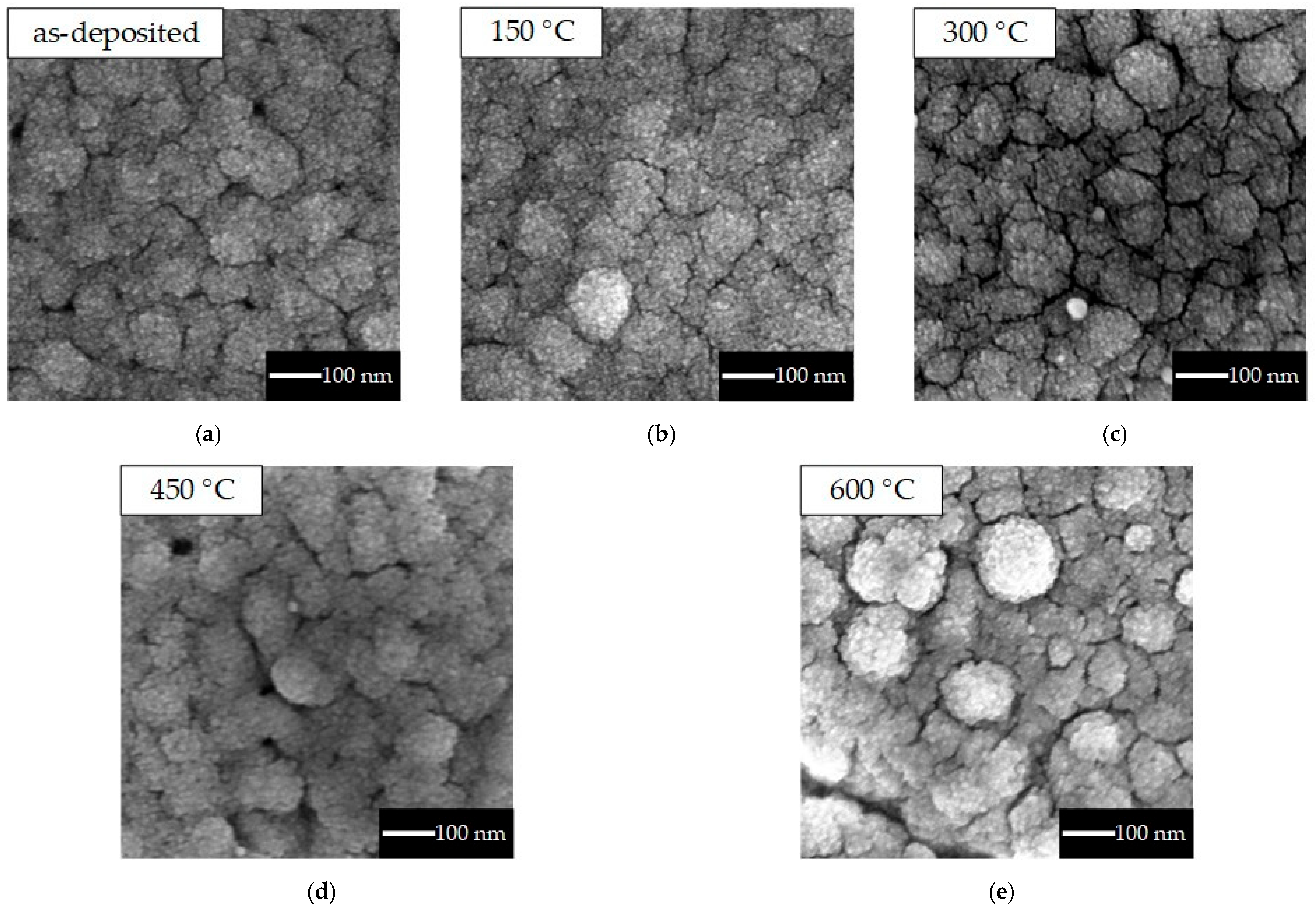
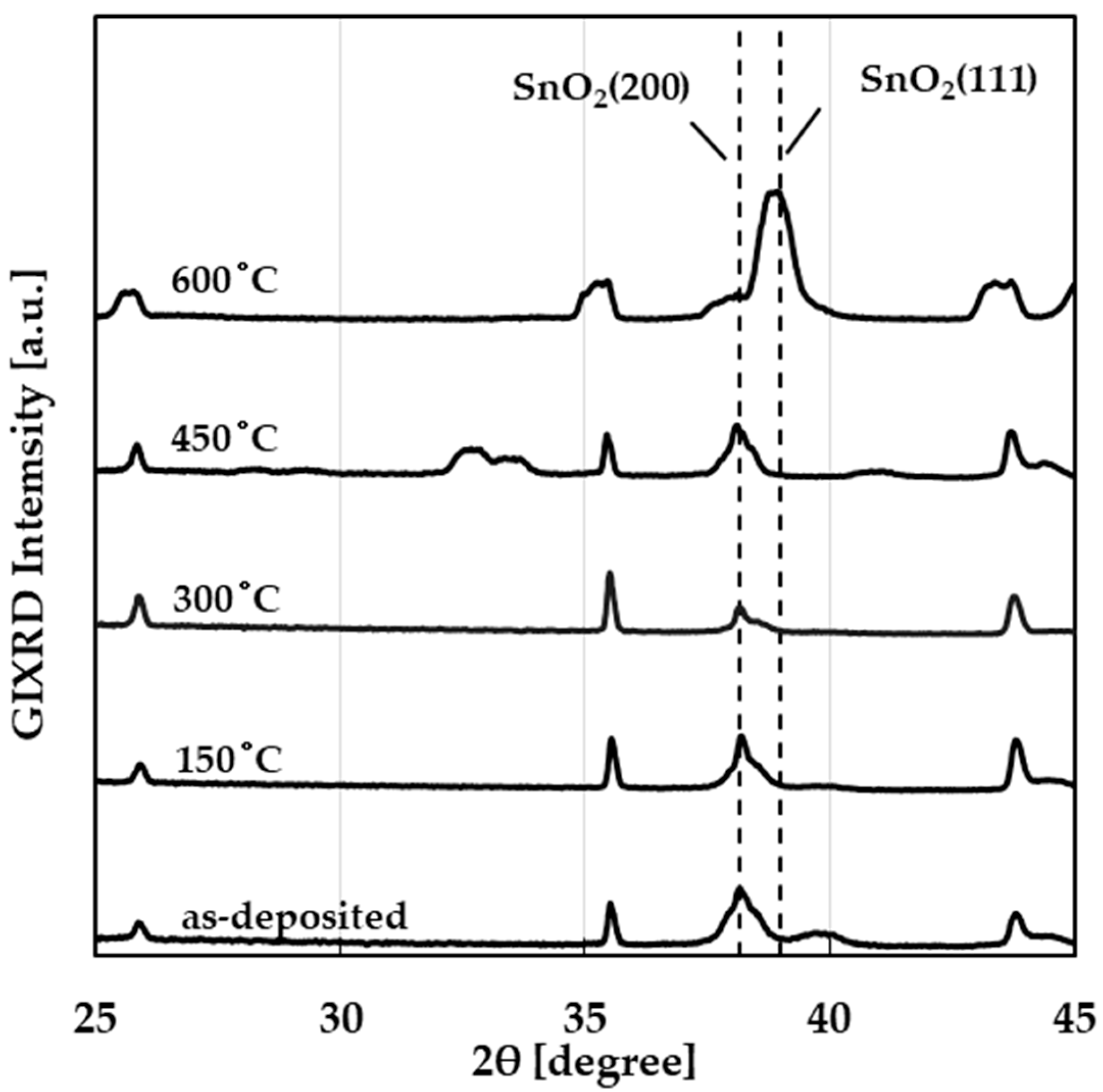
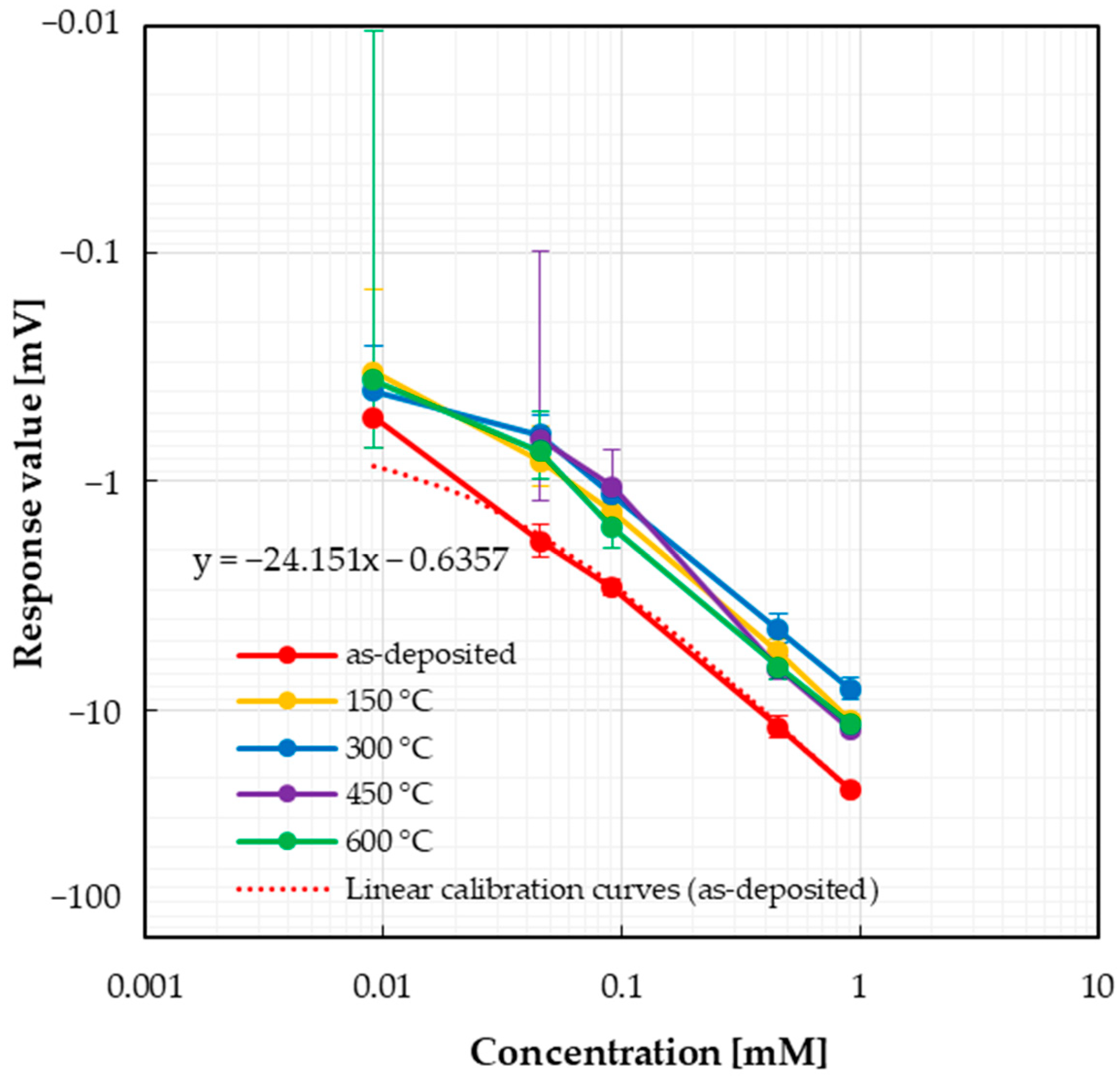


| Parameters | Conditions |
|---|---|
| Target | Pt, Ag, Au, SnO2 (4N) |
| Substrate | Alumina (3N) |
| Deposited temperature | R.T. |
| Deposited time | 5 min |
| Sputtering power | 50 W |
| Source gas | Ar (6N) |
| Flow rate | 0.5 mL/m |
| Sample (Taste Threshold) | Chemical Formula (Molecular Weight) | Properties | In Water |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acesulfame potassium (0.5 mM) [27,28] | C4H4KNO4S (201.24) | Water-soluble, electrolytes, low hydrophobicity | K+ + C4H4NO4S− |
| Aspartame (0.5 mM) [27,28] | C14H18N2O5 (294.30) | Water-soluble, non-electrolytes, hydrophilic–hydrophobic | C14H18N2O5 |
| D(+)-glucose (100 mM) [29] | C6H12O6 (180.16) | Water-soluble, non-electrolytes | C6H12O6 |
| Sample | As-Deposited | 150 °C | 300 °C | 450 °C | 600 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acesulfame potassium | −24.151 | −11.941 | −8.645 | −13.576 | −12.499 |
| Aspartame | 7.3915 | 7.128 | 5.561 | - | 16.002 |
| D(+)-glucose | - | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shinta, T.; Uchida, H.; Hasegawa, Y. Effect of Annealing Treatment on Sensing Response of Inorganic Film Taste Sensor to Sweet Substances. Sensors 2025, 25, 1859. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061859
Shinta T, Uchida H, Hasegawa Y. Effect of Annealing Treatment on Sensing Response of Inorganic Film Taste Sensor to Sweet Substances. Sensors. 2025; 25(6):1859. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061859
Chicago/Turabian StyleShinta, Tomoki, Hidekazu Uchida, and Yuki Hasegawa. 2025. "Effect of Annealing Treatment on Sensing Response of Inorganic Film Taste Sensor to Sweet Substances" Sensors 25, no. 6: 1859. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061859
APA StyleShinta, T., Uchida, H., & Hasegawa, Y. (2025). Effect of Annealing Treatment on Sensing Response of Inorganic Film Taste Sensor to Sweet Substances. Sensors, 25(6), 1859. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061859





