Lattice Surgery for Dummies
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation
1.2. Contribution
1.3. Paper Structure
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. A Brief Overview of QECCs
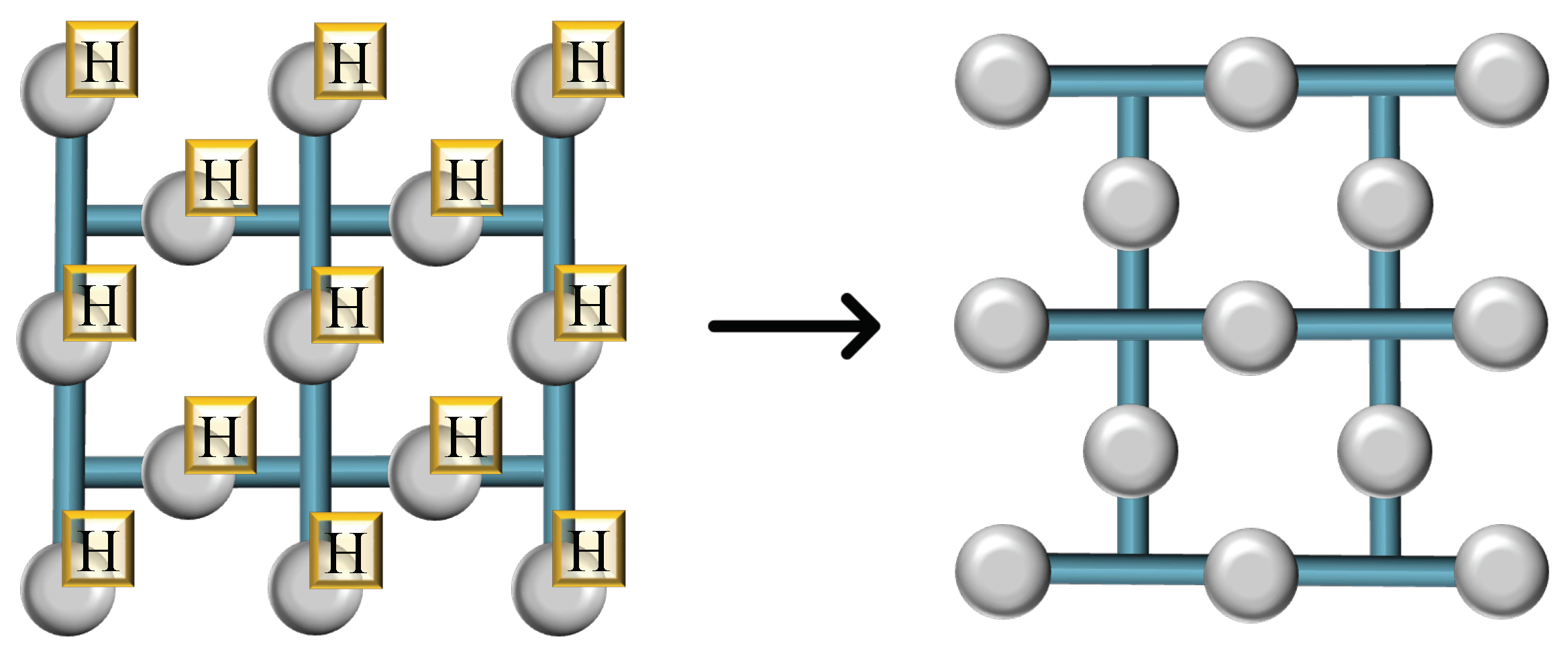
2.2. Surface Codes
2.3. Transversal Gates
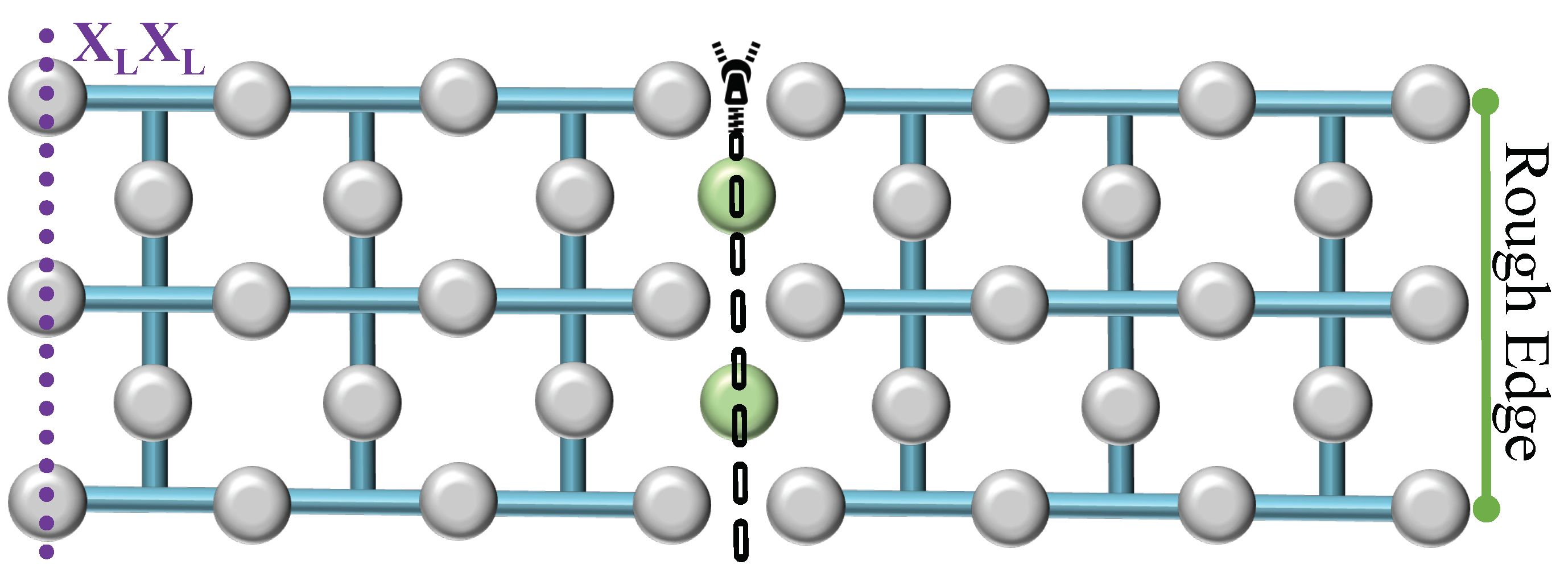
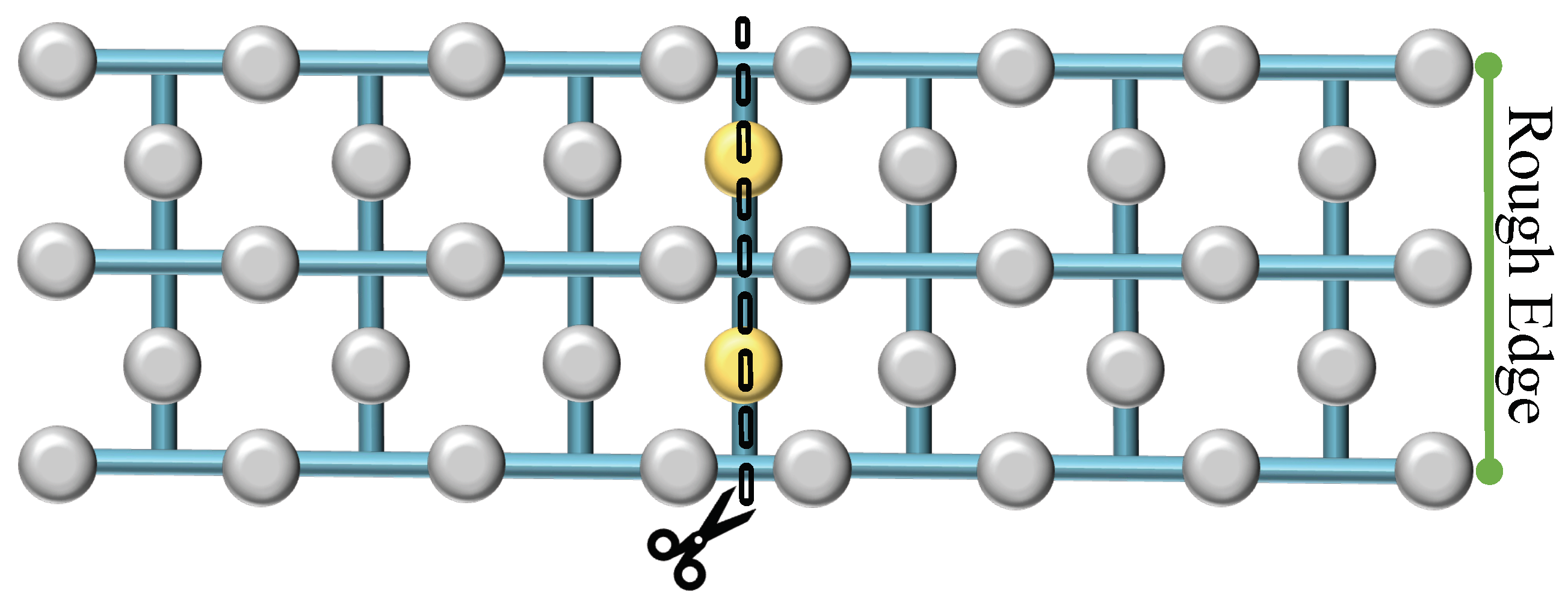
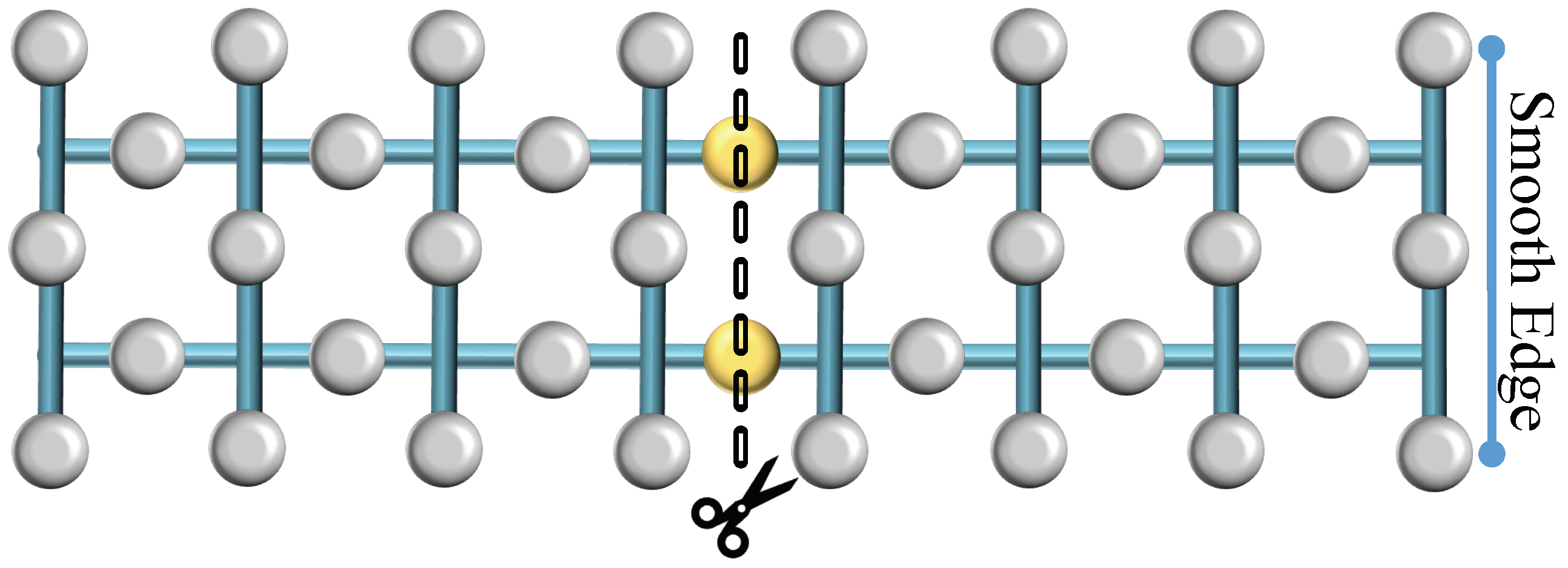
3. Lattice Surgery
3.1. Pivotal Idea
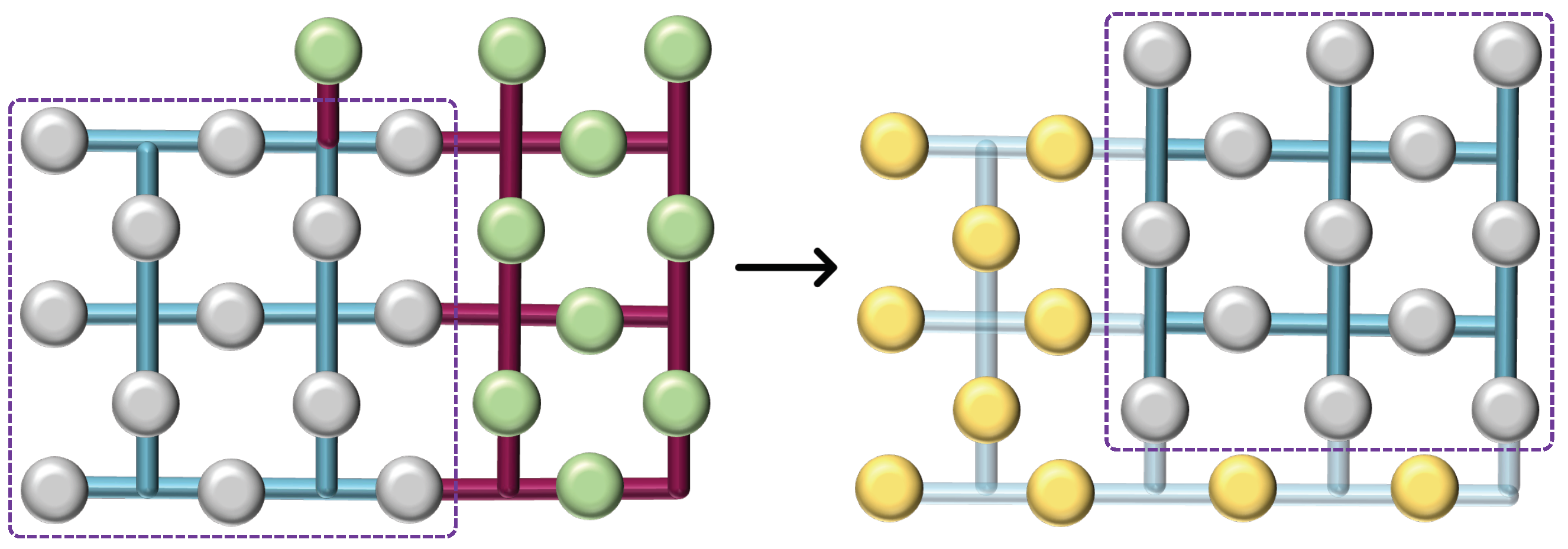
3.2. Lattice Merging
3.3. Lattice Splitting
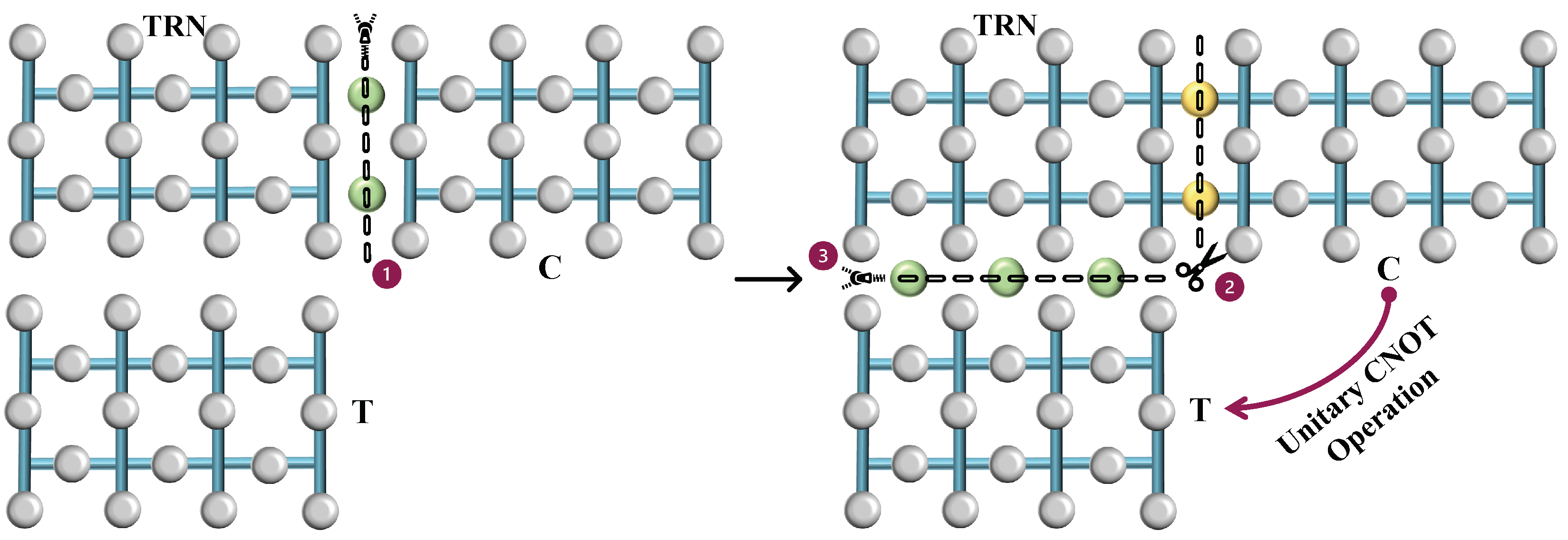
4. Operations with Lattice Surgery
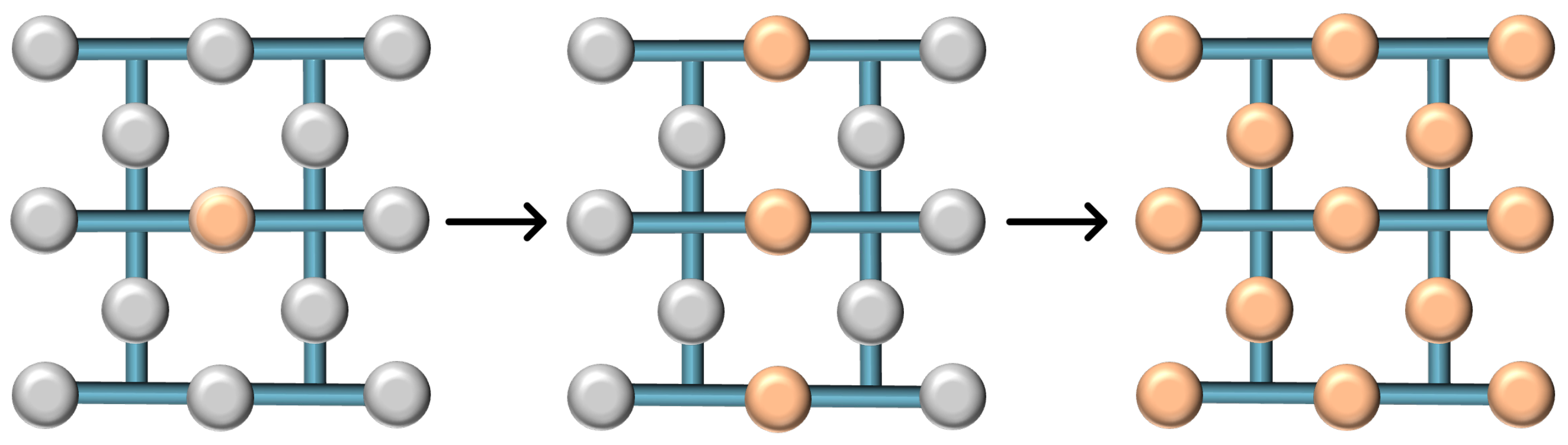
4.1. The CNOT Gate
4.2. The Hadamard Gate
4.3. Arbitrary Qubit Rotation Gates
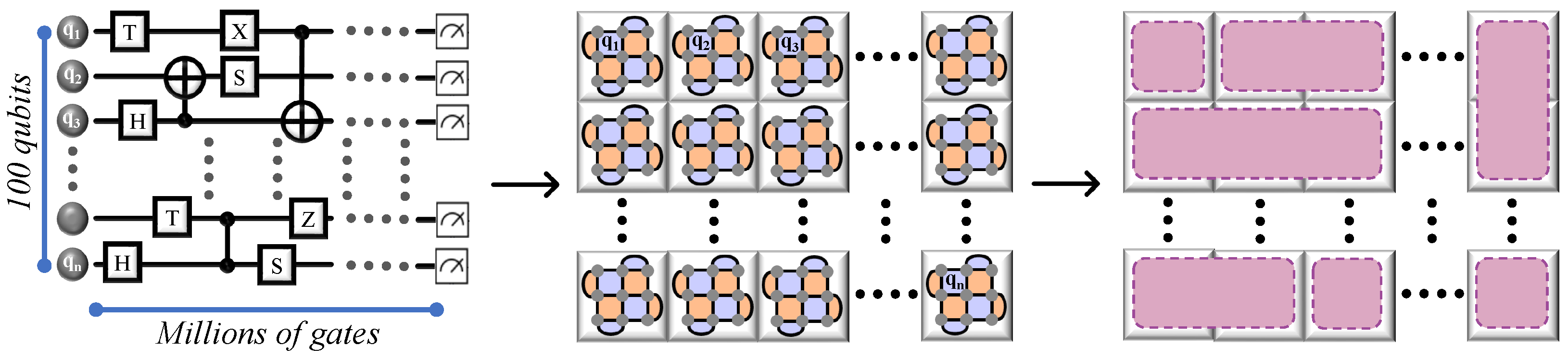
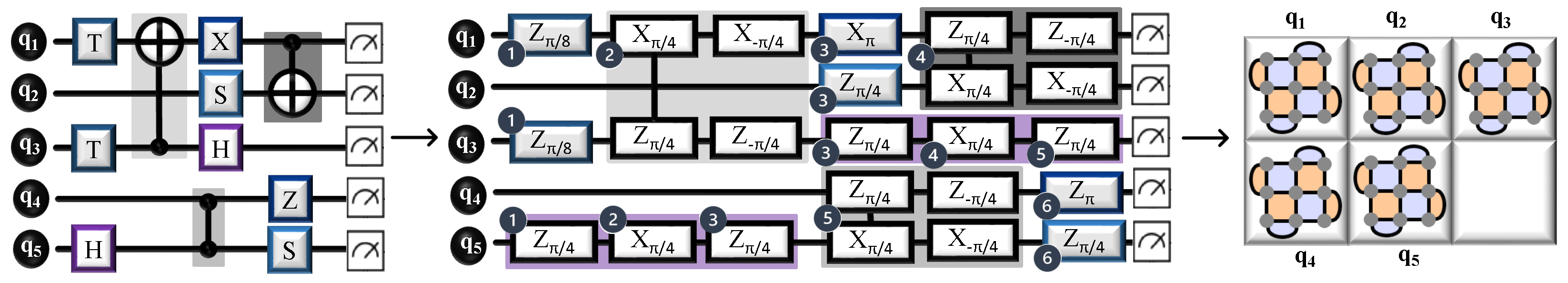
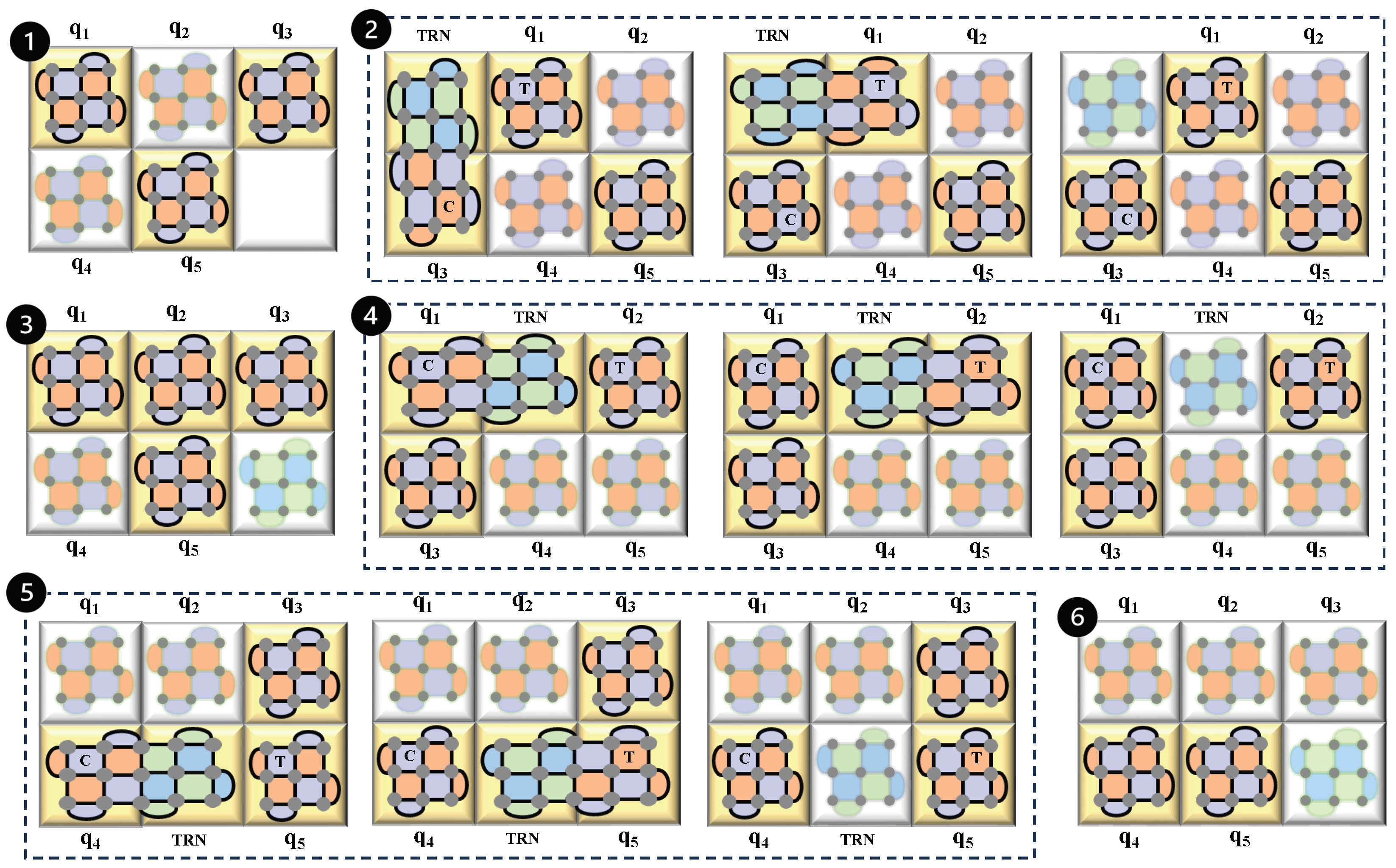
5. Application of QECC on Multi-Qubit Circuits
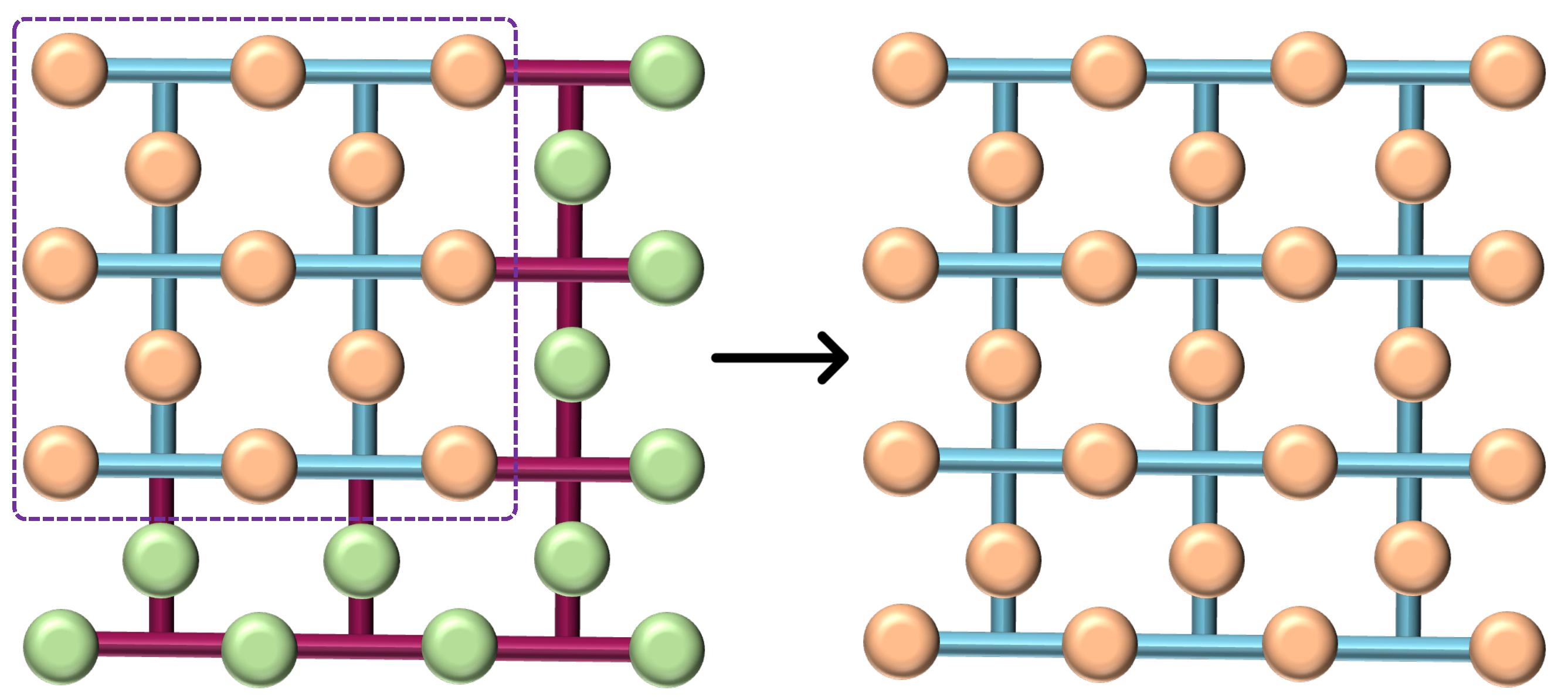
5.1. Moving Towards Fault-Tolerant Quantum Computing
5.2. Simplification of the Circuit
6. Feasibility and Implementation of Lattice Surgery
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reiher, M.; Wiebe, N.; Svore, K.M.; Wecker, D.; Troyer, M. Elucidating reaction mechanisms on quantum computers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 7555–7560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orús, R.; Mugel, S.; Lizaso, E. Quantum computing for finance: Overview and prospects. Rev. Phys. 2019, 4, 100028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuld, M.; Sinayskiy, I.; Petruccione, F. An introduction to quantum machine learning. Contemp. Phys. 2015, 56, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gachnang, P.; Ehrenthal, J.; Hanne, T.; Dornberger, R. Quantum Computing in Supply Chain Management State of the Art and Research Directions. Asian J. Logist. Manag. 2022, 1, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajagekar, A.; You, F. Quantum computing for energy systems optimization: Challenges and opportunities. Energy 2019, 179, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerk, A.A.; Devoret, M.H.; Girvin, S.M.; Marquardt, F.; Schoelkopf, R.J. Introduction to quantum noise, measurement, and amplification. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2010, 82, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouloudakis, G.; Lambropoulos, P. Entanglement instability in the interaction of two qubits with a common non-Markovian environment. Quantum Inf. Process. 2021, 20, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.K.; Spiller, T.; Popescu, S. Introduction to Quantum Computation and Information; World Scientific: Singapore, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Devitt, S.J.; Munro, W.J.; Nemoto, K. Quantum error correction for beginners. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2013, 76, 076001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamming, R.W. Error detecting and error correcting codes. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1950, 29, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wootters, W.K.; Zurek, W.H. The no-cloning theorem. Phys. Today 2009, 62, 76–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Neumann, J. Mathematical Foundations of Quantum Mechanics: New Edition; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2018; Volume 53. [Google Scholar]
- Sundaresan, N.; Yoder, T.J.; Kim, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, E.H.; Harper, G.; Thorbeck, T.; Cross, A.W.; Córcoles, A.D.; Takita, M. Matching and maximum likelihood decoding of a multi-round subsystem quantum error correction experiment. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.07205. [Google Scholar]
- Abobeih, M.; Wang, Y.; Randall, J.; Loenen, S.; Bradley, C.; Markham, M.; Twitchen, D.; Terhal, B.; Taminiau, T. Fault-tolerant operation of a logical qubit in a diamond quantum processor. Nature 2022, 606, 884–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacon, D. Operator quantum error-correcting subsystems for self-correcting quantum memories. Phys. Rev. A 2006, 73, 012340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitaev, A.Y. Quantum computations: Algorithms and error correction. Russ. Math. Surv. 1997, 52, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krinner, S.; Lacroix, N.; Remm, A.; Di Paolo, A.; Genois, E.; Leroux, C.; Hellings, C.; Lazar, S.; Swiadek, F.; Herrmann, J.; et al. Realizing repeated quantum error correction in a distance-three surface code. Nature 2022, 605, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombin, H.; Martin-Delgado, M.A. Topological quantum distillation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 180501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsman, D.; Fowler, A.G.; Devitt, S.; Van Meter, R. Surface code quantum computing by lattice surgery. New J. Phys. 2012, 14, 123011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landahl, A.J.; Ryan-Anderson, C. Quantum computing by color-code lattice surgery. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1407.5103. [Google Scholar]
- Cowtan, A. Qudit lattice surgery. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.13228. [Google Scholar]
- Erhard, A.; Poulsen Nautrup, H.; Meth, M.; Postler, L.; Stricker, R.; Stadler, M.; Negnevitsky, V.; Ringbauer, M.; Schindler, P.; Briegel, H.J.; et al. Entangling logical qubits with lattice surgery. Nature 2021, 589, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, A.G.; Gidney, C. Low overhead quantum computation using lattice surgery. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1808.06709. [Google Scholar]
- Litinski, D. A game of surface codes: Large-scale quantum computing with lattice surgery. Quantum 2019, 3, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herr, D.; Paler, A.; Devitt, S.J.; Nori, F. Lattice surgery on the Raussendorf lattice. Quantum Sci. Technol. 2018, 3, 035011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberland, C.; Campbell, E.T. Circuit-level protocol and analysis for twist-based lattice surgery. Phys. Rev. Res. 2022, 4, 023090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberland, C.; Campbell, E.T. Universal quantum computing with twist-free and temporally encoded lattice surgery. PRX Quantum 2022, 3, 010331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herr, D.; Nori, F.; Devitt, S.J. Optimization of lattice surgery is NP-hard. Npj Quantum Inf. 2017, 3, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Beaudrap, N.; Horsman, D. The ZX calculus is a language for surface code lattice surgery. Quantum 2020, 4, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuillot, C.; Lao, L.; Criger, B.; Almudéver, C.G.; Bertels, K.; Terhal, B.M. Code deformation and lattice surgery are gauge fixing. New J. Phys. 2019, 21, 033028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.A.; Chuang, I.L. Quantum Computation and Quantum Information; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, A.; Phalak, K.; Ghosh, S. Quantum error correction for dummies. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Quantum Computing and Engineering (QCE), Bellevue, WA, USA, 17–22 September 2023; Volume 1, pp. 70–81. [Google Scholar]
- Chiaverini, J.; Leibfried, D.; Schaetz, T.; Barrett, M.D.; Blakestad, R.; Britton, J.; Itano, W.M.; Jost, J.D.; Knill, E.; Langer, C.; et al. Realization of quantum error correction. Nature 2004, 432, 602–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, E.; Kitaev, A.; Landahl, A.; Preskill, J. Topological quantum memory. J. Math. Phys. 2002, 43, 4452–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, A.G.; Mariantoni, M.; Martinis, J.M.; Cleland, A.N. Surface codes: Towards practical large-scale quantum computation. Phys. Rev. A 2012, 86, 032324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, V. Blossom V: A new implementation of a minimum cost perfect matching algorithm. Math. Program. Comput. 2009, 1, 43–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, Y.; Svore, K.M. Low-distance surface codes under realistic quantum noise. Phys. Rev. A 2014, 90, 062320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, M.H.; Meyer, D.A. Projective plane and planar quantum codes. Found. Comput. Math. 2001, 1, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravyi, S.B.; Kitaev, A.Y. Quantum codes on a lattice with boundary. arXiv 1998, arXiv:quant-ph/9811052. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, N.C.; Van Meter, R.; Fowler, A.G.; McMahon, P.L.; Kim, J.; Ladd, T.D.; Yamamoto, Y. A layered architecture for quantum computing using quantum dots. arXiv 2010, arXiv:1010.5022. [Google Scholar]
- Herrera-Martí, D.A.; Fowler, A.G.; Jennings, D.; Rudolph, T. Photonic implementation for the topological cluster-state quantum computer. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 82, 032332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiVincenzo, D.P. Fault-tolerant architectures for superconducting qubits. Phys. Scr. 2009, 2009, 014020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groszkowski, P.; Fowler, A.G.; Motzoi, F.; Wilhelm, F.K. Tunable coupling between three qubits as a building block for a superconducting quantum computer. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 144516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, J.; Gierl, C.; Schlosser, M.; Birkl, G. Reconfigurable site-selective manipulation of atomic quantum systems in two-dimensional arrays of dipole traps. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 81, 060308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, N.Y.; Jiang, L.; Gorshkov, A.V.; Maurer, P.C.; Giedke, G.; Cirac, J.I.; Lukin, M.D. Scalable architecture for a room temperature solid-state quantum information processor. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumph, M.; Brownnutt, M.; Blatt, R. 2 Dimensional Arrays of RF Ion Traps with Addressable Interactions. New J. Phys. 2011, 13, 073043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crick, D.; Donnellan, S.; Ananthamurthy, S.; Thompson, R.; Segal, D. Fast shuttling of ions in a scalable Penning trap array. Rev. Sci. Instruments 2010, 81, 013111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuer, H.P.; Laine, E.M.; Piilo, J. Measure for the degree of non-Markovian behavior of quantum processes in open systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 210401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, Á.; Huelga, S.F.; Plenio, M.B. Entanglement and non-Markovianity of quantum evolutions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 050403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chruściński, D.; Kossakowski, A.; Rivas, Á. Measures of non-Markovianity: Divisibility versus backflow of information. Phys. Rev. A—At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2011, 83, 052128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varsamopoulos, S.; Criger, B.; Bertels, K. Decoding small surface codes with feedforward neural networks. Quantum Sci. Technol. 2017, 3, 015004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen Nautrup, H.; Friis, N.; Briegel, H.J. Fault-tolerant interface between quantum memories and quantum processors. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, G.; Nguyen, H.M.; Watkins, K.; Pearce, S.; Lau, H.K.; Paler, A. A high performance compiler for very large scale surface code computations. Quantum 2024, 8, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riverlane and Rigetti. Introducing the World’s First Low-Latency QEC Experiment. 2023. Available online: https://www.riverlane.com/news/introducing-the-world-s-first-low-latency-qec-experiment (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Riverlane and Rigetti. World’s First Low-Latency Quantum Error Correction Experiment. 2023. Available online: https://quantumcomputingreport.com/riverlane-and-rigetti-achieve-worlds-first-low-latency-quantum-error-correction-experiment (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- IQM, Riverlane, and Zurich Instruments. Developing a Real-Time Quantum Error Correction Platform. 2023. Available online: https://quantumcomputingreport.com/iqm-riverlane-and-zurich-instruments-develop-real-time-quantum-error-correction-platform/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- IQM, Riverlane, and Zurich Instruments. Unveiling the World’s First Quantum Error Correction Platform. 2023. Available online: https://www.meetiqm.com/newsroom/blog/iqm-riverlane-and-zurich-instruments-join-forces-to-launch-worlds-first-quantum-error-correction-platform (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- IQM, Riverlane, and Zurich Instruments. IQM, Riverlane, and Zurich Instruments Join Forces to Launch the World’s First Quantum Error Correction Platform. 2023. Available online: https://www.riverlane.com/press-release/iqm-riverlane-and-zurich-instruments-join-forces-to-launch-world-s-first-quantum-error-correction-platform (accessed on 11 March 2025).


| Quantum Gates | Rotational Form | |
|---|---|---|
| Single Qubit | X | |
| Y | ||
| Z | ||
| RX | ||
| RY | ||
| RZ | ||
| H | ||
| S | ||
| T | ||
| Multi Qubit | CNOT | |
| C(P1, P2) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chatterjee, A.; Das, S.; Ghosh, S. Lattice Surgery for Dummies. Sensors 2025, 25, 1854. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061854
Chatterjee A, Das S, Ghosh S. Lattice Surgery for Dummies. Sensors. 2025; 25(6):1854. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061854
Chicago/Turabian StyleChatterjee, Avimita, Subrata Das, and Swaroop Ghosh. 2025. "Lattice Surgery for Dummies" Sensors 25, no. 6: 1854. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061854
APA StyleChatterjee, A., Das, S., & Ghosh, S. (2025). Lattice Surgery for Dummies. Sensors, 25(6), 1854. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061854





