Prestimulus EEG Oscillations and Pink Noise Affect Go/No-Go ERPs
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Related Work
1.3. Key Contributions of This Study
- Examines within-task prestimulus EEG effects on ERPs and behaviour in an auditory equiprobable Go/No-Go task.
- Validly estimates and removes pink and white noise from the observed EEG, leaving the rhythmical oscillations.
- Extracts the noise-free EEG oscillation components using frequency PCA.
- Decomposes the Go and No-Go ERP components by separate temporal PCAs, avoiding misallocation of variance.
- Uses regression to search for novel within-task EEG/ERP/behaviour links.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Task and Procedure
2.3. Electrophysiological Recording
2.4. EEG Quantification
2.5. ERP Quantification
2.6. Statistical Analyses
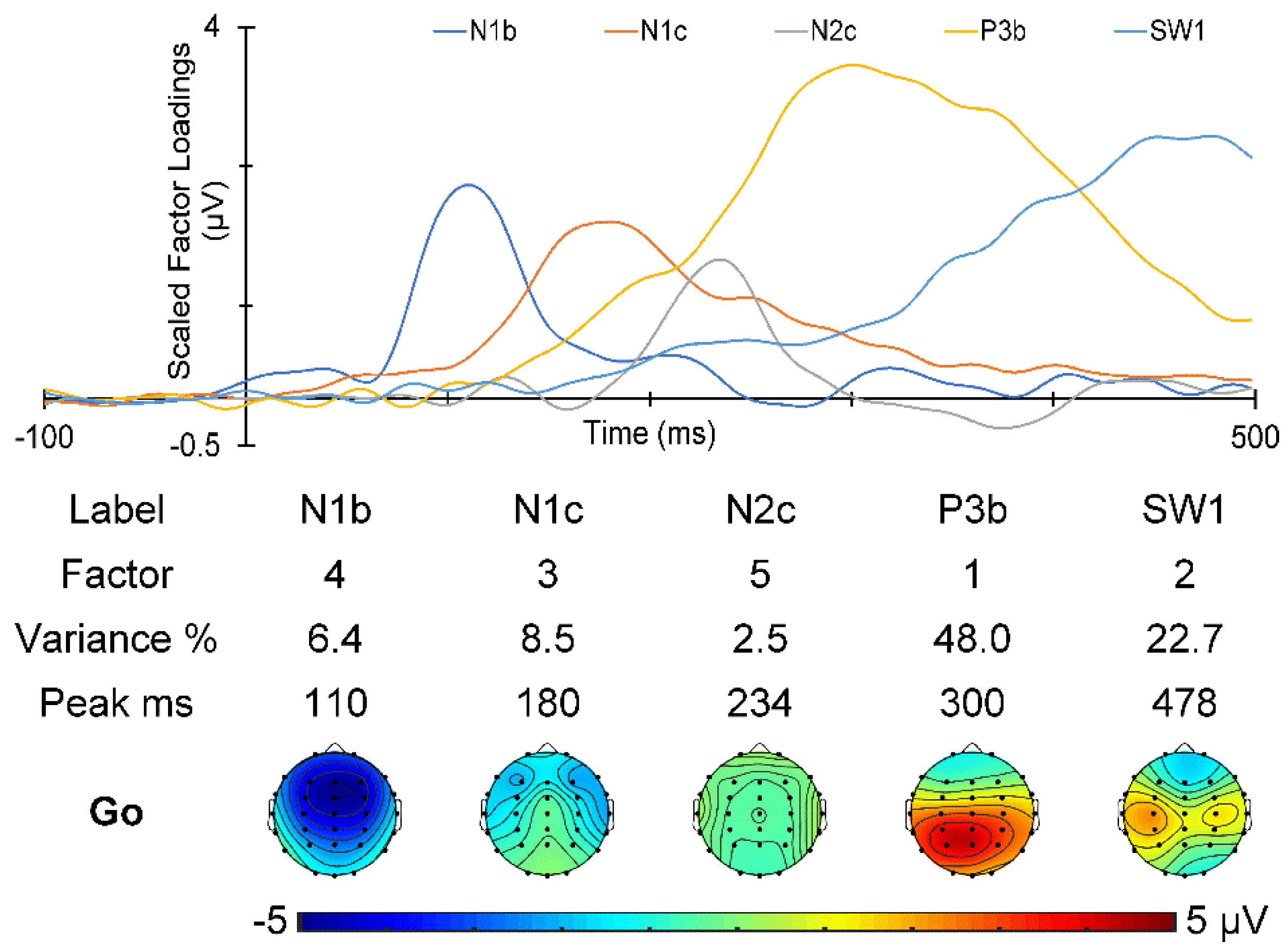
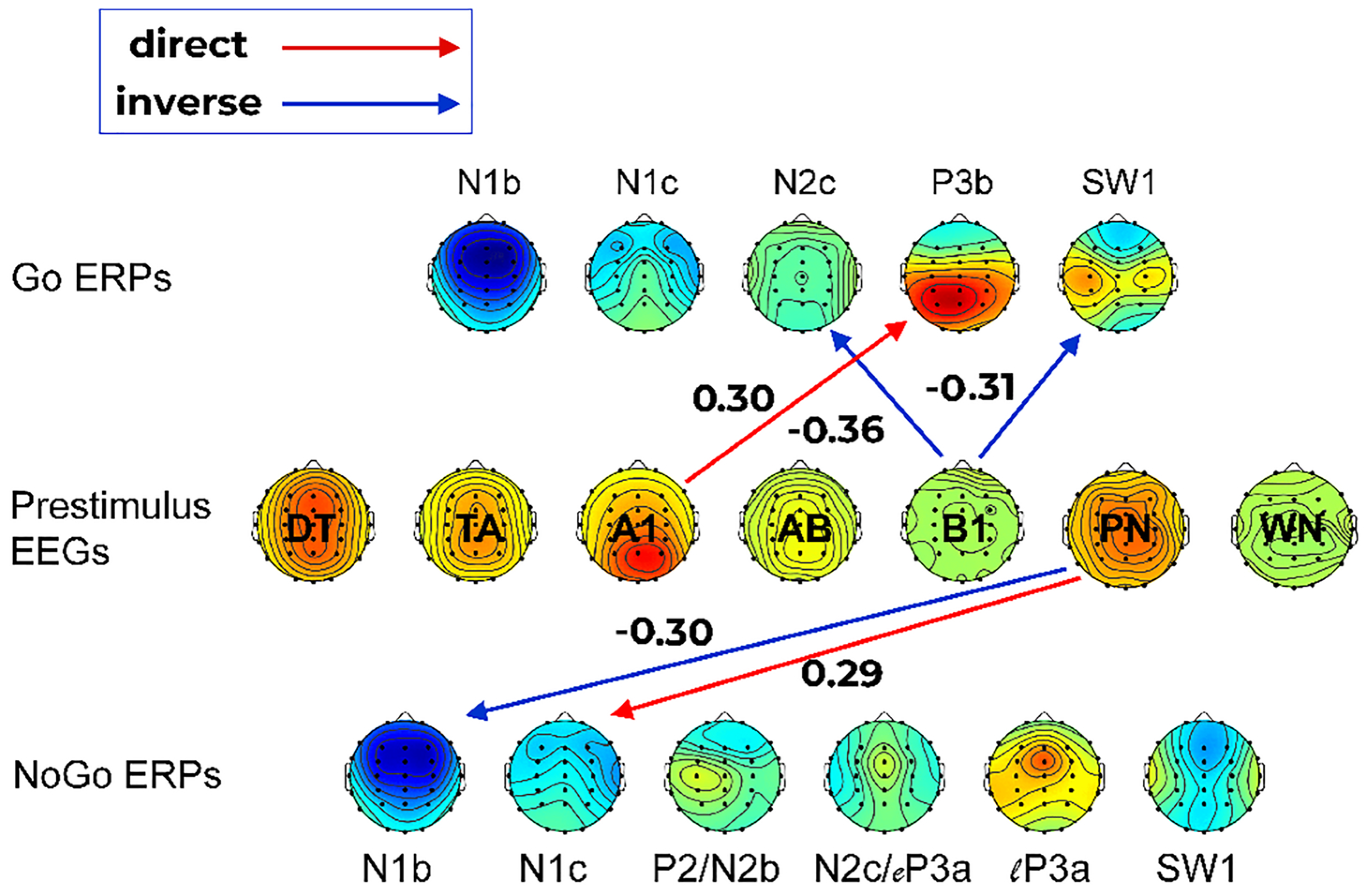
3. Results
3.1. Accepted Trials
3.2. Behaviour
3.3. Prestimulus EEG
3.4. Poststimulus ERPs
3.5. Regression Outcomes
4. Discussion
4.1. EEG Predictors
4.2. Dependent Variables
4.3. Regression Analyses
4.4. Limitations
4.5. Beyond the Auditory Go/No-Go Task
4.6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Başar, E. Brain oscillations in neuropsychiatric disease. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 15, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, R.J.; De Blasio, F.M. Sequential processing in the equiprobable auditory Go/NoGo task: A temporal PCA study. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2013, 89, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donchin, E. A Multivariate Approach to the Analysis of Average Evoked Potentials. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1966, BME-13, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, R.J.; De Blasio, F.M.; Cave, A.E. Sequential processing in young and older adults in the equiprobable auditory Go/NoGo task. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 2273–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, R.J.; De Blasio, F.M. Performance and ERP components in the equiprobable go/no-go task: Inhibition in children. Psychophysiology 2015, 52, 1228–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, R.J.; De Blasio, F.M.; Fogarty, J.S. A processing schema for children in the auditory equiprobable Go/NoGo task: ERP components and behaviour. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2018, 123, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, R.J.; De Blasio, F.M.; Borchard, J.P. Sequential processing in the equiprobable auditory Go/NoGo task: Children vs. adults. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2014, 125, 1995–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, R.J.; De Blasio, F.M.; Cave, A.E. Development of children’s performance and ERP components in the equiprobable Go/NoGo task. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2022, 171, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahn, E.; Basar, E. Prestimulus EEG-activity strongly influences the auditory evoked vertex response: A new method for selective averaging. Int. J. Neurosci. 1993, 69, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, A.; Callieco, R.; Cosi, V. Prestimulus spectral EEG patterns and the evoked auditory vertex response. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1988, 70, 270–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzaro, I.; Gordon, E.; Whitmont, S.; Meares, R.; Clarke, S. The modulation of late component event related potentials by pre-stimulus EEG theta activity in ADHD. Int. J. Neurosci. 2001, 107, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stampfer, H.; Baslar, E. Does frequency analysis lead to better understanding of human event related potentials. Int. J. Neurosci. 1985, 26, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, R.J.; Kirkaikul, S.; Hodder, D. EEG alpha activity and the ERP to target stimuli in an auditory oddball paradigm. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2000, 39, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasiukaitis, P.; Hakerem, G. The effect of prestimulus alpha activity on the P300. Psychophysiology 1988, 25, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Blasio, F.M.; Barry, R.J. Prestimulus delta and theta determinants of ERP responses in the Go/NoGo task. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2013, 87, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Blasio, F.M.; Barry, R.J. Prestimulus alpha and beta determinants of ERP responses in the Go/NoGo task. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2013, 89, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, R.J.; De Blasio, F.M.; Karamacoska, D. Data-driven derivation of natural EEG frequency components: An optimised example assessing resting EEG in healthy ageing. J. Neurosci. Methods 2019, 321, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, R.J.; De Blasio, F.M. EEG frequency PCA in EEG-ERP dynamics. Psychophysiology 2018, 55, e13042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, R.J.; De Blasio, F.M.; Clarke, A.R.; Duda, A.T.; Munford, B.S. Age-Related Differences in Prestimulus EEG Affect ERPs and Behaviour in the Equiprobable Go/NoGo Task. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.B. The Schottky effect in low frequency circuits. Phys. Rev. 1925, 26, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, R.J.; De Blasio, F.M. Characterizing pink and white noise in the human electroencephalogram. J. Neural Eng. 2021, 18, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donoghue, T.; Haller, M.; Peterson, E.J.; Varma, P.; Sebastian, P.; Gao, R.; Noto, T.; Lara, A.H.; Wallis, J.D.; Knight, R.T.; et al. Parameterizing neural power spectra into periodic and aperiodic components. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 1655–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, R.J.; De Blasio, F.M.; Fogarty, J.S.; Karamacoska, D. ERP Go/NoGo condition effects are better detected with separate PCAs. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2016, 106, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croft, R.J.; Barry, R.J. EOG correction of blinks with saccade coefficients: A test and revision of the aligned-artefact average solution. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2000, 111, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tony. RAAA EOG Correction Program. MATLAB Central File Exchange. 2024. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/17456-raaa-eog-correction-program (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foti, D.; Hajcak, G.; Dien, J. Differentiating neural responses to emotional pictures: Evidence from temporal-spatial PCA. Psychophysiology 2009, 46, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dien, J. The ERP PCA Toolkit: An open source program for advanced statistical analysis of event-related potential data. J. Neurosci. Methods 2010, 187, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogarty, J.S.; Barry, R.J.; De Blasio, F.M.; Steiner, G.Z. ERP components and behavior in the auditory equiprobable go/no-go task: Inhibition in young adults. Psychophysiology 2018, 55, e13065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogarty, J.S.; Barry, R.J.; Steiner, G.Z. The first 250 ms of auditory processing: No evidence of early processing negativity in the Go/NoGo task. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebenthal, E.; Ellingson, M.L.; Spanaki, M.V.; Prieto, T.E.; Ropella, K.M.; Binder, J.R. Simultaneous ERP and fMRI of the auditory cortex in a passive oddball paradigm. Neuroimage 2003, 19, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Blasio, F.M.; Barry, R.J. Prestimulus alpha and beta contributions to equiprobable Go/NoGo processing in healthy ageing. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2020, 155, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clements, G.M.; Bowie, D.C.; Gyurkovics, M.; Low, K.A.; Fabiani, M.; Gratton, G. Spontaneous alpha and theta oscillations are related to complementary aspects of cognitive control in younger and older adults. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 621620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bender, R.; Lange, S. Adjusting for multiple testing—When and how? J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2001, 54, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
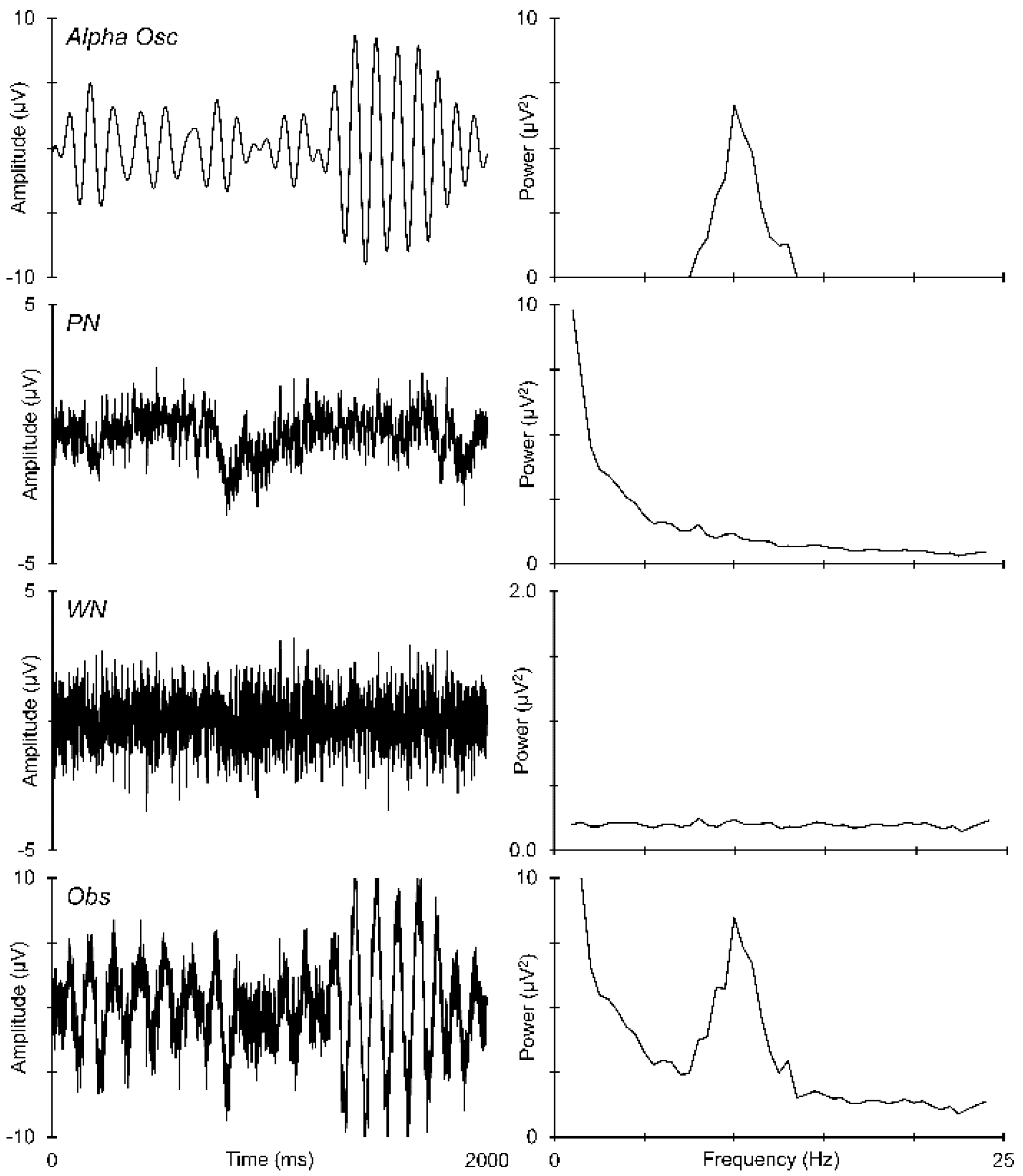
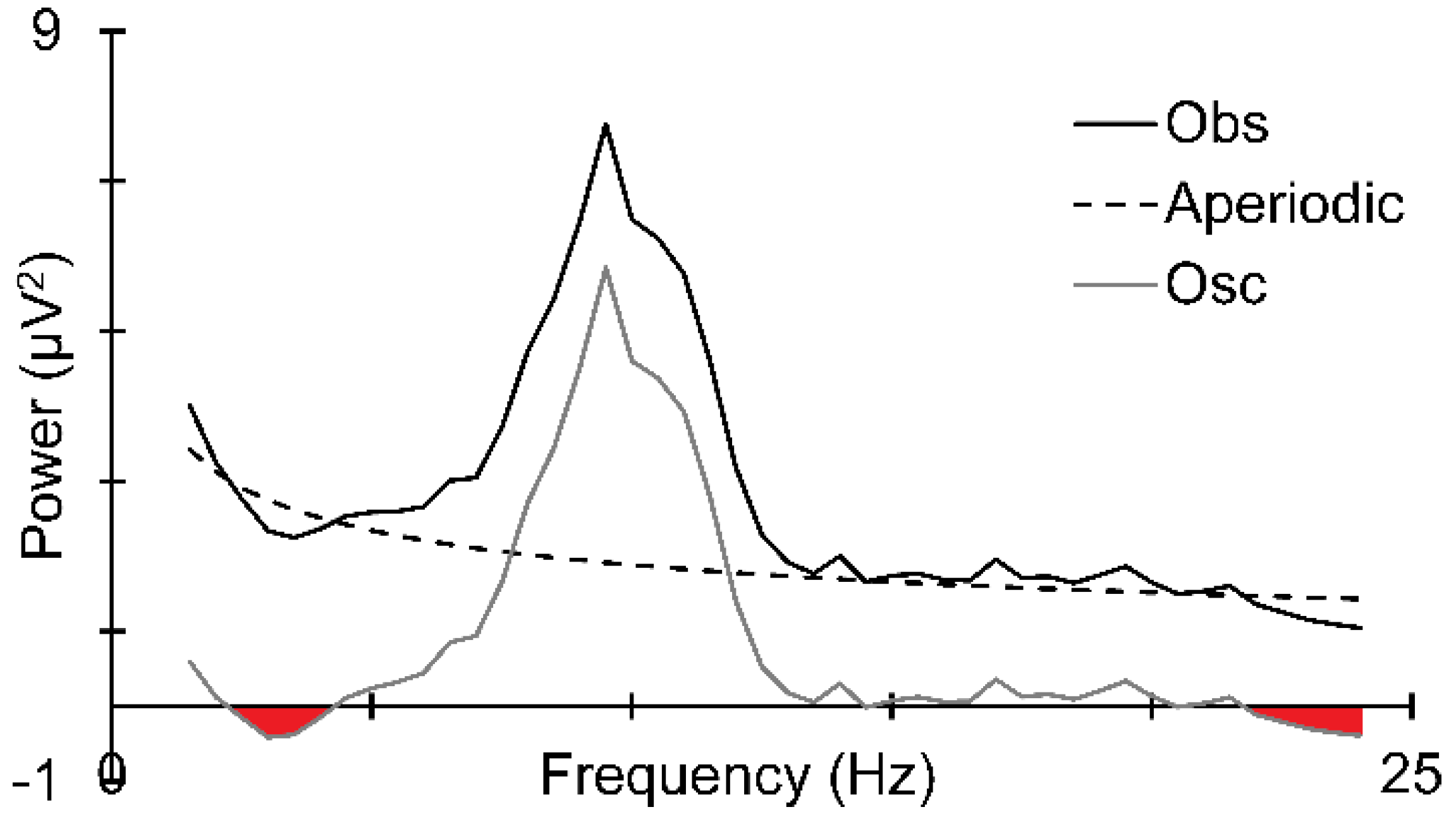
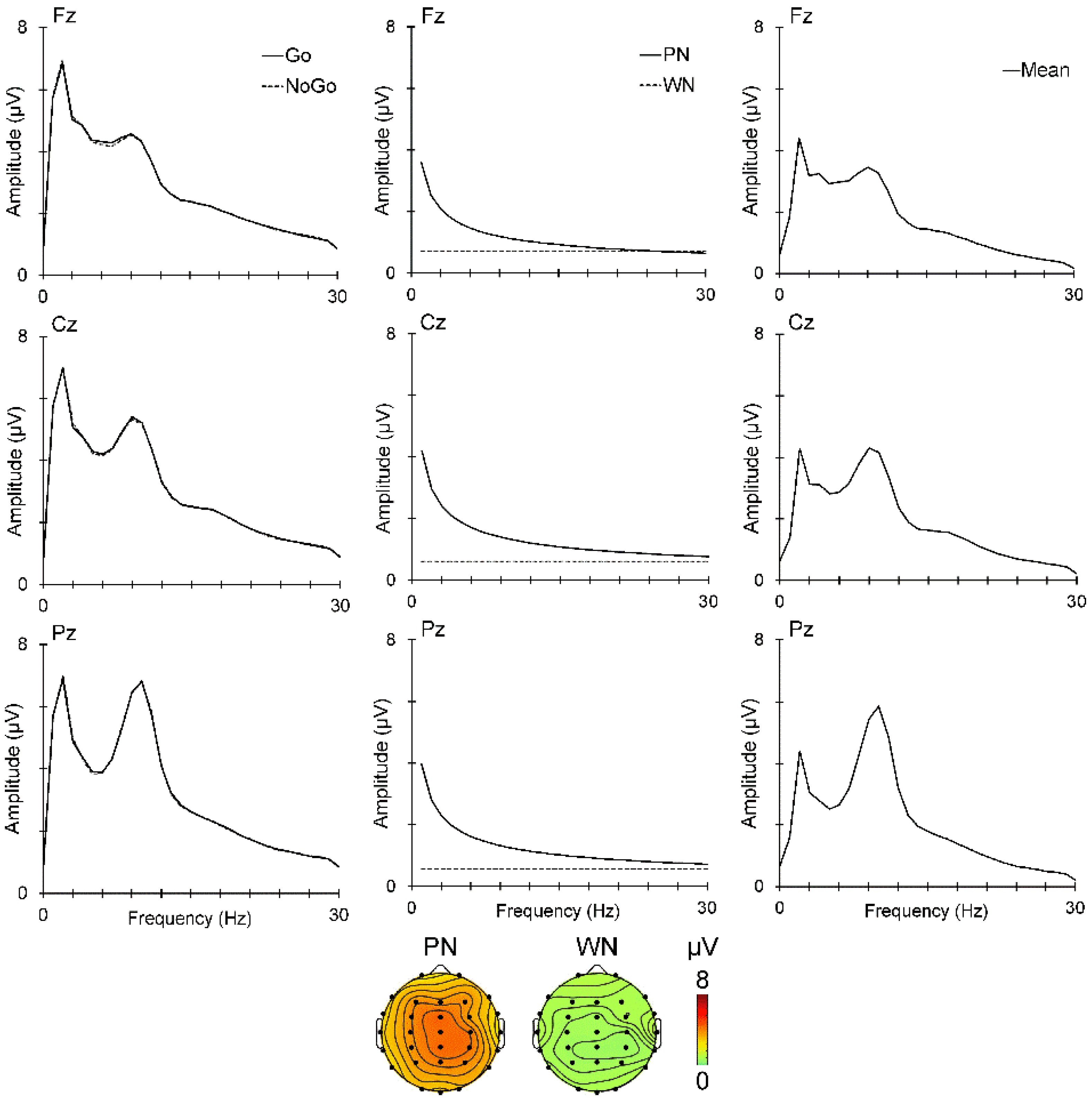
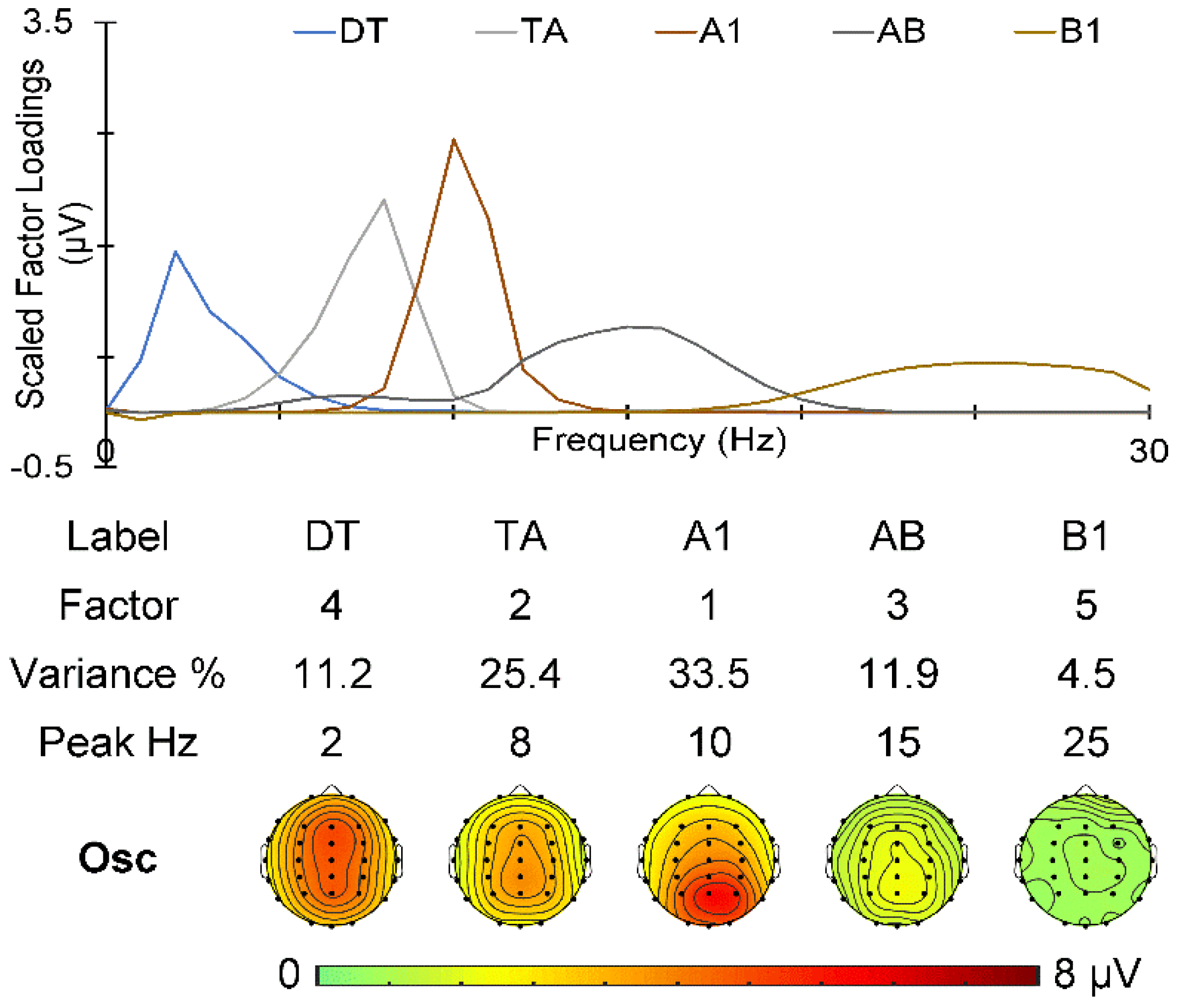


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barry, R.J.; De Blasio, F.M.; Duda, A.T.; Munford, B.S. Prestimulus EEG Oscillations and Pink Noise Affect Go/No-Go ERPs. Sensors 2025, 25, 1733. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061733
Barry RJ, De Blasio FM, Duda AT, Munford BS. Prestimulus EEG Oscillations and Pink Noise Affect Go/No-Go ERPs. Sensors. 2025; 25(6):1733. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061733
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarry, Robert J., Frances M. De Blasio, Alexander T. Duda, and Beckett S. Munford. 2025. "Prestimulus EEG Oscillations and Pink Noise Affect Go/No-Go ERPs" Sensors 25, no. 6: 1733. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061733
APA StyleBarry, R. J., De Blasio, F. M., Duda, A. T., & Munford, B. S. (2025). Prestimulus EEG Oscillations and Pink Noise Affect Go/No-Go ERPs. Sensors, 25(6), 1733. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061733





