Coelenterazine Analogs for Bioassays and Molecular Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Coelenterazine as a Common Substrate of Marine Luciferases
2.1. Chemical Structure of Coelenterazine
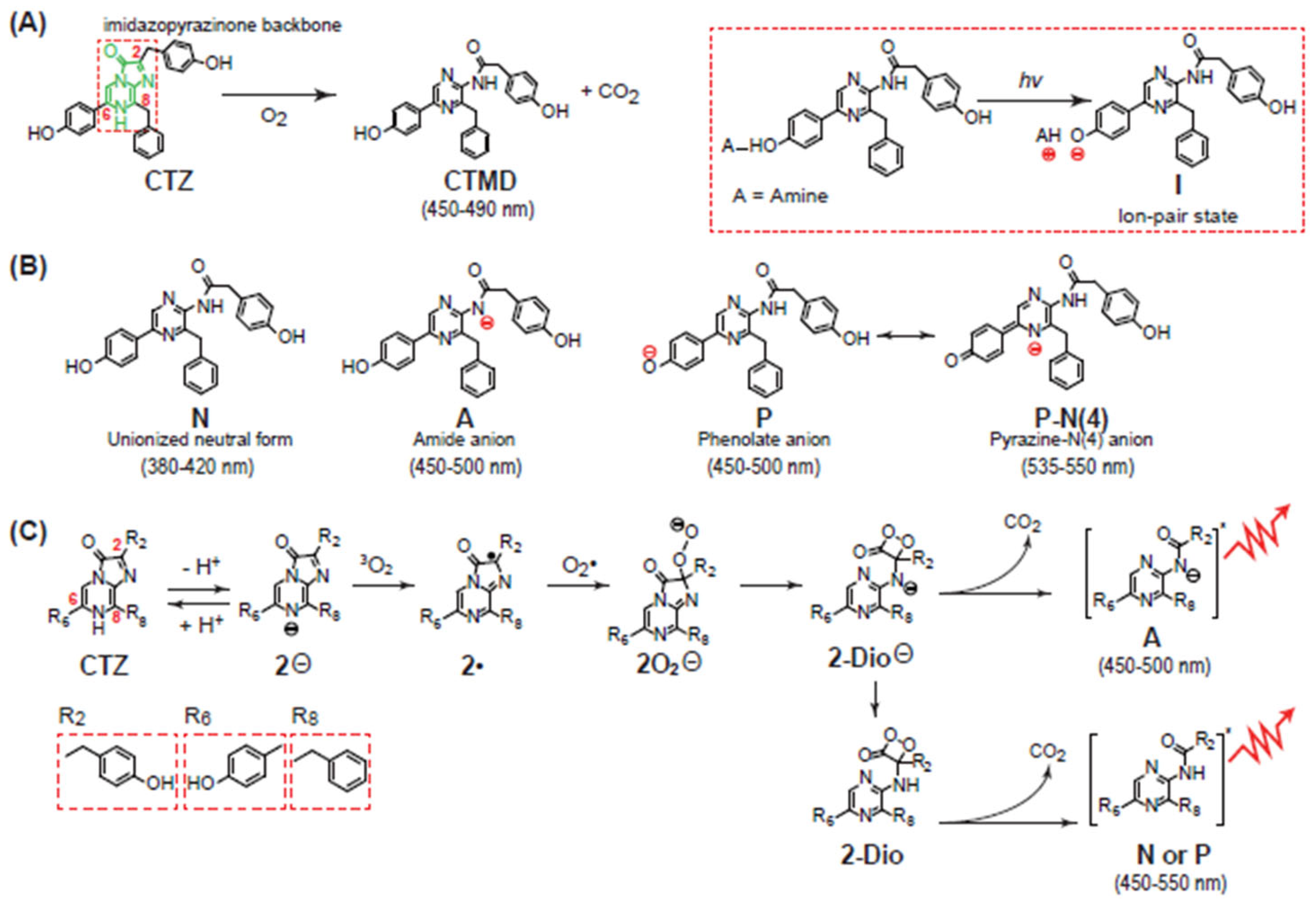
2.2. Chemiluminescence-Emitting Mechanism of CTZ
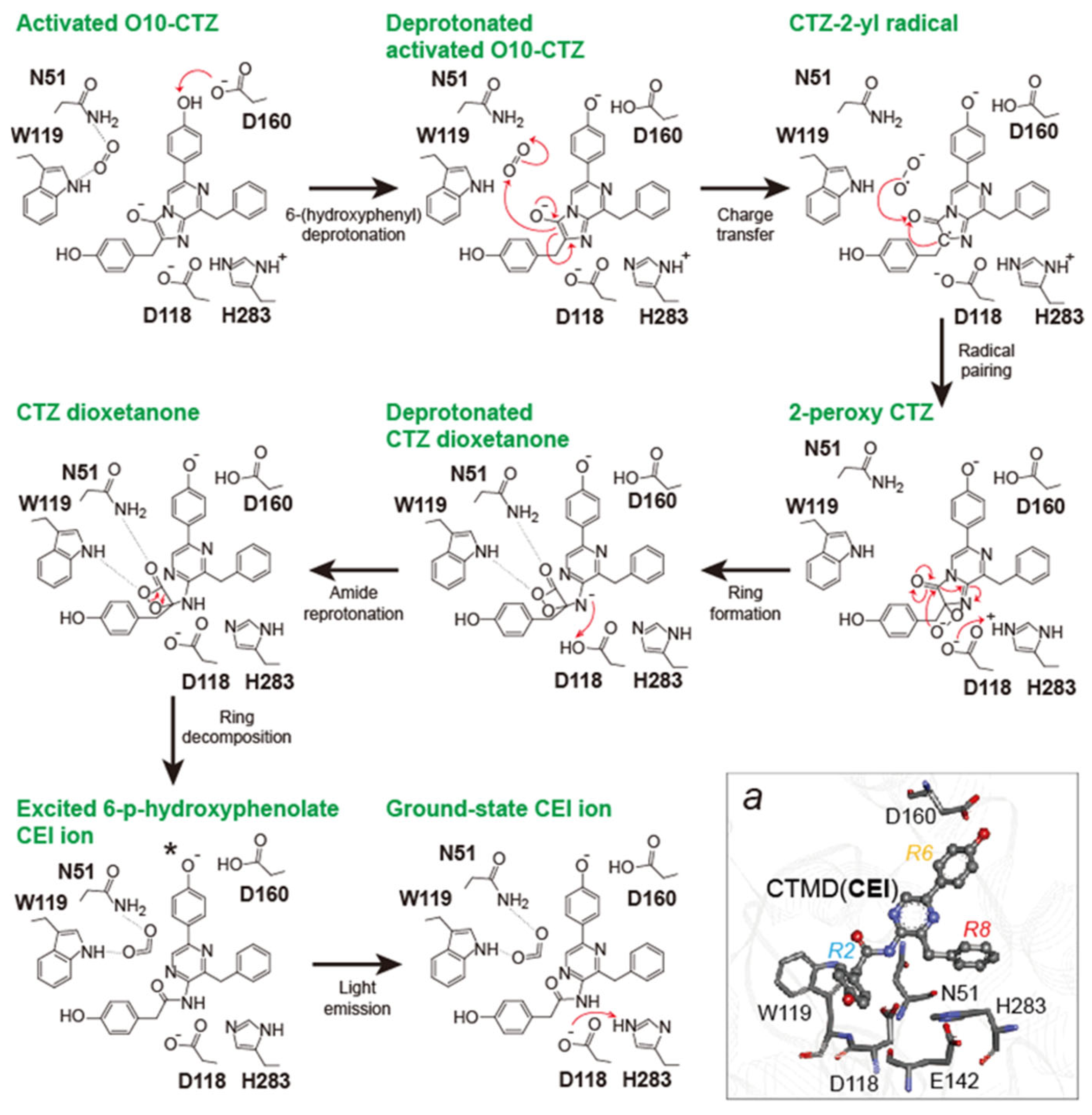
2.3. Bioluminescence-Emitting Mechanism of Coelenterazine
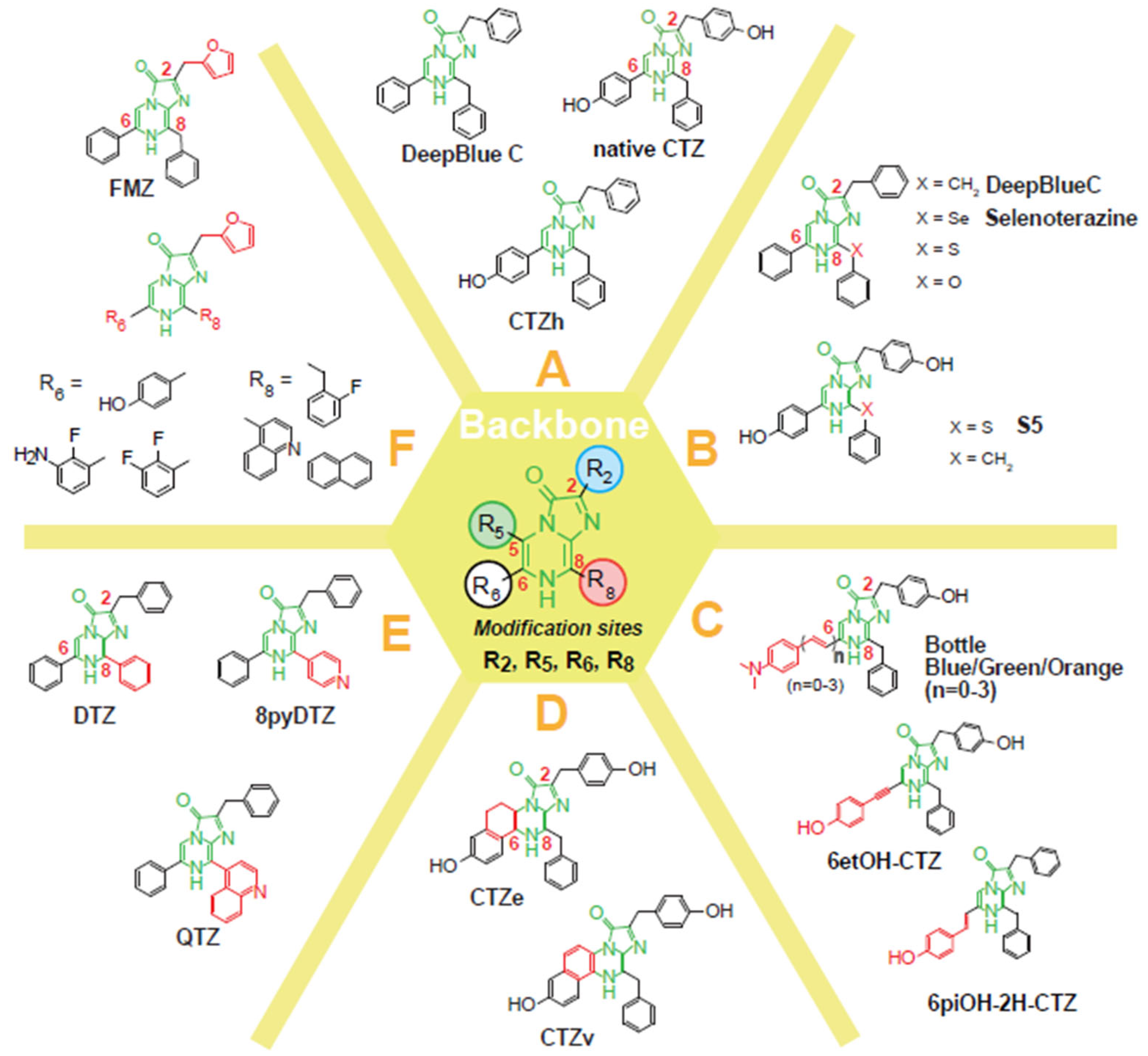
3. Creation of Coelenterazine Analogs
3.1. Categorization of Coelenterazine Analogs
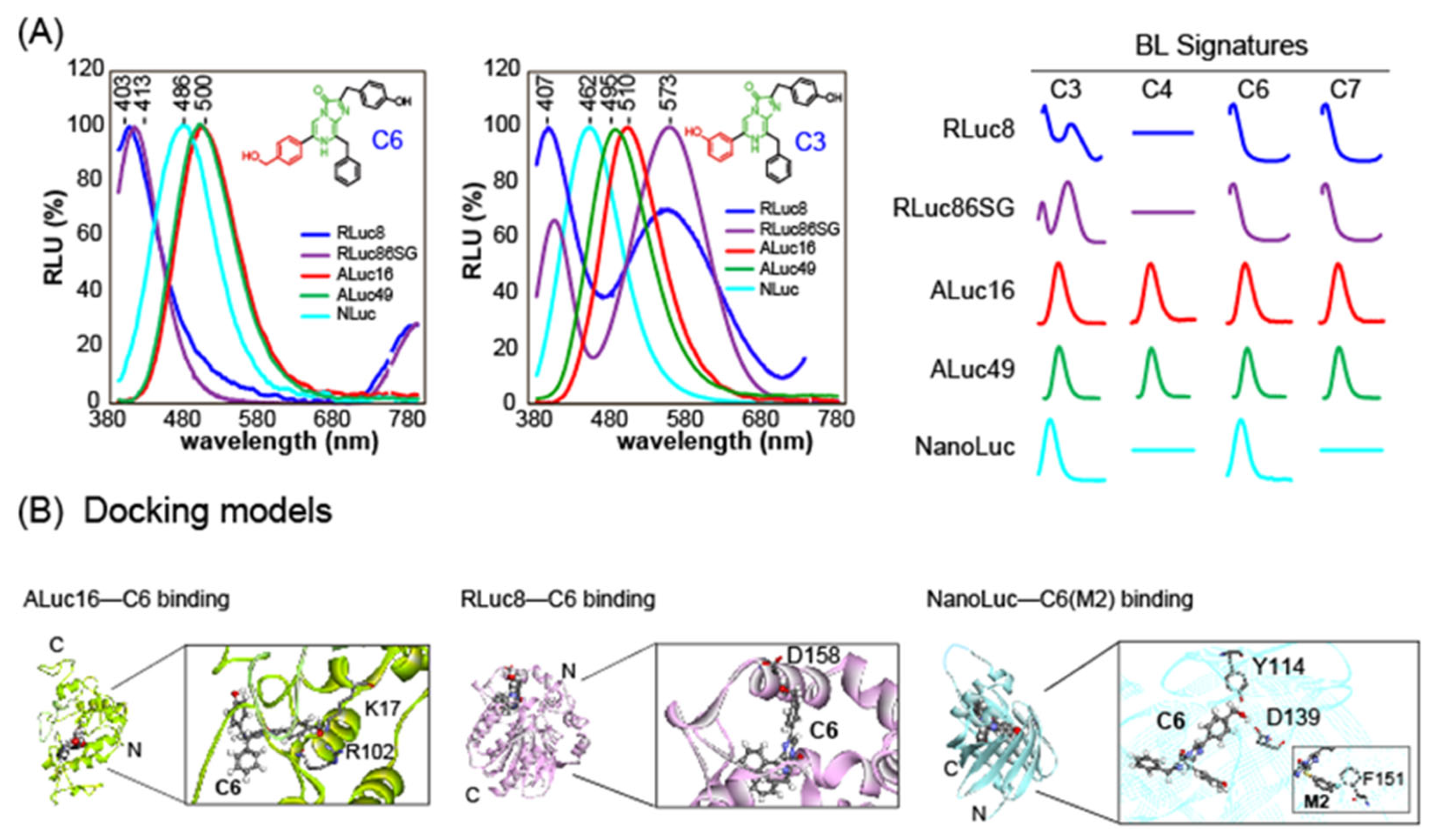
3.2. Color-Tunable Coelenterazine Analogs
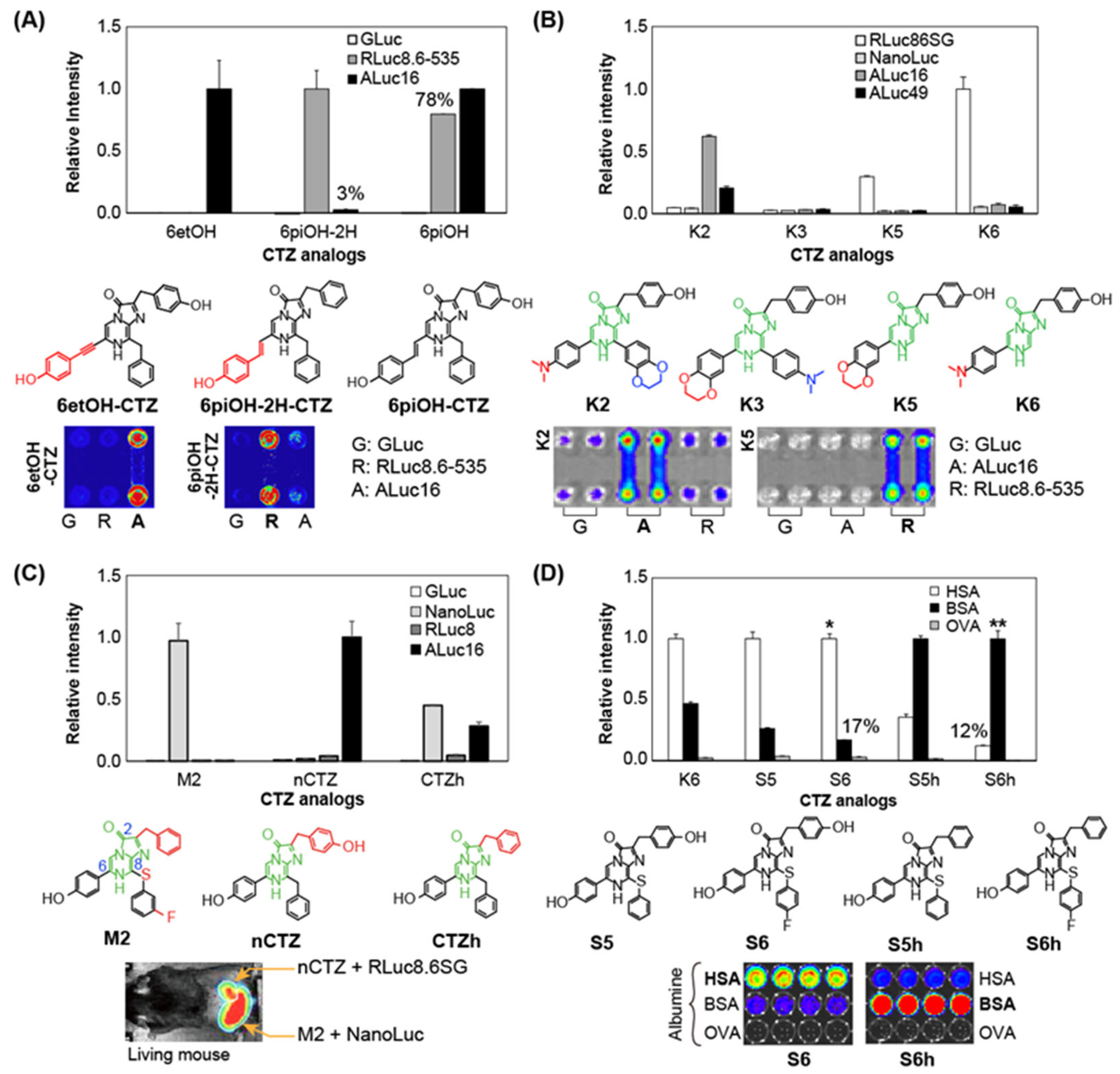
3.3. Luciferase-Specific Coelenterazine Analogs
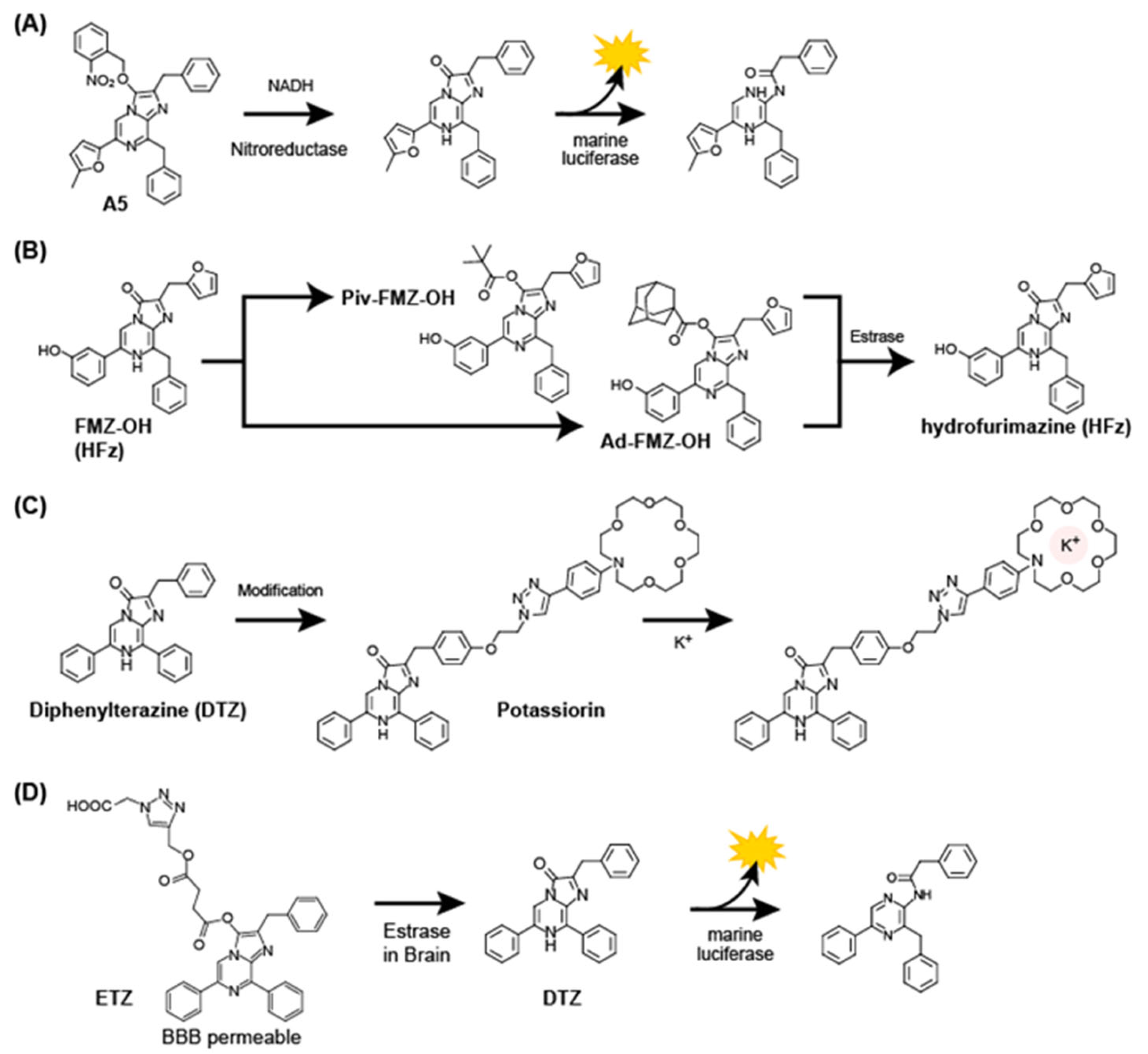
3.4. Activatable Coelenterazine Analogs
3.5. Coelenterazine Analogs as Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenger and Anticancer Drugs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shimomura, O. Bioluminescence—Chemical Principles and Methods; World Scientific Pub Co Pte Ltd.: Singapore, 2006; ISBN 978-981-256-801-4. [Google Scholar]
- Dale, N.C.; Johnstone, E.K.M.; White, C.W.; Pfleger, K.D.G. NanoBRET: The Bright Future of Proximity-Based Assays. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Li, B.; Ding, S.; Fan, Y.; Wang, S.; Sun, C.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, C.-X.; Zhang, F. NIR-II bioluminescence for in vivo high contrast imaging and in situ ATP-mediated metastases tracing. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, A.S.; Schwinn, M.K.; Hall, M.P.; Zimmerman, K.; Otto, P.; Lubben, T.H.; Butler, B.L.; Binkowski, B.F.; Machleidt, T.; Kirkland, T.A.; et al. NanoLuc Complementation Reporter Optimized for Accurate Measurement of Protein Interactions in Cells. ACS Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, L.; Di, L.-J. Applications of Protein Fragment Complementation Assays for Analyzing Biomolecular Interactions and Biochemical Networks in Living Cells. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 2987–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotlobay, A.A.; Sarkisyan, K.S.; Mokrushina, Y.A.; Marcet-Houben, M.; Serebrovskaya, E.O.; Markina, N.M.; Somermeyer, L.G.; Gorokhovatsky, A.Y.; Vvedensky, A.; Purtov, K.V.; et al. Genetically encodable bioluminescent system from fungi. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 12728–12732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meighen, E.A. Bacterial bioluminescence—Organization, regulation, and application of the lux genes. FASEB J. 1993, 7, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleiss, A.; Sarkisyan, K.S. A brief review of bioluminescent systems (2019). Curr. Genet. 2019, 65, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakhomov, A.A.; Martynov, V.I. GFP Family: Structural Insights into Spectral Tuning. Chem. Biol. 2008, 15, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimomura, O.; Johnson, F.H.; Saiga, Y. Extraction, Purification and Properties of Aequorin, a Bioluminescent Protein from the Luminous Hydromedusan, Aequorea. J. Cell. Comp. Physiol. 1962, 59, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimomura, O.; Johnson, F.H. Structure of the light-emitting moiety of aequorin. Biochemistry 1972, 11, 1602–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, S.; Sugiura, S.; Kakoi, H.; Hasizume, K.; Goto, T.; Iio, H. Squid Bioluminescence. 2. Isolation from Watasenia scintillans and Synthesis of 2-(Para-hydroxybenzyl)-6-(Para-hydroxyphenyl)-3,7-dihydroimidazo[1,2-a]pyrazin-3-one. Chem. Lett. 1975, 2, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oba, Y.; Kato, S.-I.; Ojika, M.; Inouye, S. Biosynthesis of luciferin in the sea firefly, Cypridina hilgendorfii: l-tryptophan is a component in Cypridina luciferin. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 2389–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessho-Uehara, M.; Huang, W.; Patry, W.L.; Browne, W.E.; Weng, J.-K.; Haddock, S.H. Evidence for de novo Biosynthesis of the Luminous Substrate Coelenterazine in Ctenophores. iScience 2020, 23, 101859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutant, E.P.; Janin, Y.L. Synthetic Routes to Coelenterazine and Other Imidazo[1,2-a]pyrazin-3-one Luciferins: Essential Tools for Bioluminescence-Based Investigations. Chem.–A Eur. J. 2015, 21, 17158–17171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimomura, O.; Teranishi, K. Light-emitters involved in the luminescence of coelenterazine. Luminescence 2000, 15, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimomura, O.; Goto, T.; Hirata, Y. Crystalline Cypridina Luciferin. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1957, 30, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, T. Chemistry of bioluminescence. Pure and Applied Chemistry 1968, 17, 421–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenkmayerova, A.; Toul, M.; Pluskal, D.; Baatallah, R.; Gagnot, G.; Pinto, G.P.; Santana, V.T.; Stuchla, M.; Neugebauer, P.; Chaiyen, P.; et al. A catalytic mechanism for Renilla-type bioluminescence. bioRxiv 2022. bioRxiv:2022.02.09.479090. [Google Scholar]
- Schenkmayerova, A.; Toul, M.; Pluskal, D.; Baatallah, R.; Gagnot, G.; Pinto, G.P.; Santana, V.T.; Stuchla, M.; Neugebauer, P.; Chaiyen, P.; et al. Catalytic mechanism for Renilla-type luciferases. Nat. Catal. 2023, 6, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-B.; Furuta, T. Bioluminescence from the bright and dark sides. Front. Chem. Biol. 2024, 3, 1459397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loening, A.M.; Dragulescu-Andrasi, A.; Gambhir, S.S. A red-shifted Renilla luciferase for transient reporter-gene expression. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimomura, O.; Musicki, B.; Kishi, Y. Semi-synthetic aequorin. An improved tool for the measurement of calcium ion concentration. Biochem. J. 1988, 251, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, K.; Cormier, M.J. Structure and Chemical Synthesis of a Biologically Active Form of Renilla (Sea Pansy) Luciferin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1973, 70, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, K.; Charbonneau, H.; Hart, R.C.; Cormier, M.J. Structure of native Renilla reinformis luciferin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 4285–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishihara, R.; Suzuki, H.; Hoshino, E.; Suganuma, S.; Sato, M.; Saitoh, T.; Nishiyama, S.; Iwasawa, N.; Citterio, D.; Suzuki, K. Bioluminescent coelenterazine derivatives with imidazopyrazinone C-6 extended substitution. Chem. Commun. 2014, 51, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiya, G.; Kitada, N.; Furuta, T.; Hirano, T.; Maki, S.; Kim, S.B. C-Series Coelenterazine-Driven Bioluminescence Signature Imaging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiya, G.; Kitada, N.; Furuta, T.; Hirano, T.; Maki, S.A.; Kim, S.-B. S-Series Coelenterazine-Driven Combinatorial Bioluminescence Imaging Systems for Mammalian Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaki, S.; Kitada, N.; Kiyama, M.; Fujii, R.; Hirano, T.; Kim, S.B.; Maki, S. Color-tunable bioluminescence imaging portfolio for cell imaging. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.P.; Unch, J.; Binkowski, B.F.; Valley, M.P.; Butler, B.L.; Wood, M.G.; Otto, P.; Zimmerman, K.; Vidugiris, G.; Machleidt, T.; et al. Engineered Luciferase Reporter from a Deep Sea Shrimp Utilizing a Novel Imidazopyrazinone Substrate. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 1848–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipunova, V.O.; Shilova, O.N.; Shramova, E.I.; Deyev, S.M.; Proshkina, G.M. A Highly Specific Substrate for NanoLUC Luciferase Furimazine Is Toxic in vitro and in vivo. Russ. J. Bioorganic Chem. 2018, 44, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Walker, J.R.; Park, Y.; Smith, T.P.; Liu, L.X.; Hall, M.P.; Labanieh, L.; Hurst, R.; Wang, D.C.; Encell, L.P.; et al. Novel NanoLuc substrates enable bright two-population bioluminescence imaging in animals. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Walker, J.R.; Hall, M.P.; Klein, M.A.; Wu, X.; Encell, L.P.; Casey, K.M.; Liu, L.X.; Hong, G.; Lin, M.Z.; et al. An optimized bioluminescent substrate for non-invasive imaging in the brain. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2023, 19, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakhmin, A.; Hall, M.P.; Machleidt, T.; Walker, J.R.; Wood, K.V.; Kirkland, T.A. Coelenterazine analogues emit red-shifted bioluminescence with NanoLuc. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 8559–8567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Reza, S.; Li, X.; Tian, X.; Ai, H.-W. Engineered Amber-Emitting Nano Luciferase and Its Use for Immunobioluminescence Imaging In Vivo. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 14101–14111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishihara, R.; Hoshino, E.; Kakudate, Y.; Kishigami, S.; Iwasawa, N.; Sasaki, S.-I.; Nakajima, T.; Sato, M.; Nishiyama, S.; Citterio, D.; et al. Azide- and Dye-Conjugated Coelenterazine Analogues for a Multiplex Molecular Imaging Platform. Bioconjugate Chem. 2018, 29, 1922–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, M.; Nishihara, R.; Ikeda, Y.; Nakajima, T.; Sato, M.; Iwasawa, N.; Nishiyama, S.; Paulmurugan, R.; Citterio, D.; Kim, S.B.; et al. Near-Infrared Bioluminescence Imaging with a through-Bond Energy Transfer Cassette. ChemBioChem 2019, 20, 1919–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-B.; Furuta, T.; Ohmuro-Matsuyama, Y.; Kitada, N.; Nishihara, R.; Maki, S.A. Bioluminescent imaging systems boosting near-infrared signals in mammalian cells. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2023, 22, 1267–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widder, E.A.; Latz, M.I.; Case, J.F. Marine Bioluminescence Spectra Measured with an Optical Multichannel Detection System. Biol. Bull. 1983, 165, 791–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Song, J.; Zhang, Y. Coelenterazine-Type Bioluminescence-Induced Optical Probes for Sensing and Controlling Biological Processes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrion-Perdigones, A.; Chang, L.; Gonzalez, Y.; Gallego-Flores, T.; Young, D.W.; Venken, K.J.T. Examining multiple cellular pathways at once using multiplex hextuple luciferase assaying. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammon, S.T.; Leevy, W.M.; Gross, S.; Gokel, G.W.; Piwnica-Worms, D. Spectral Unmixing of Multicolored Bioluminescence Emitted from Heterogeneous Biological Sources. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 1520–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishihara, R.; Abe, M.; Nishiyama, S.; Citterio, D.; Suzuki, K.; Kim, S.B. Luciferase-Specific Coelenterazine Analogues for Optical Contamination-Free Bioassays. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamiya, G.; Kitada, N.; Maki, S.; Kim, S.B. Multiplex quadruple bioluminescent assay system. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamiya, G.; Kitada, N.; Furuta, T.; Thangudu, S.; Natarajan, A.; Paulmurugan, R.; Kim, S.-B.; Maki, S.A. Regiospecific Coelenterazine Analogs for Bioassays and Molecular Imaging. Bioconjugate Chem. 2024, 35, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishihara, R.; Niwa, K.; Tomita, T.; Kurita, R. Coelenterazine Analogue with Human Serum Albumin-Specific Bioluminescence. Bioconjugate Chem. 2020, 31, 2679–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-B.; Kamiya, G.; Furuta, T.; Kitada, N.; Maki, S.A. Coelenterazine Indicators for the Specific Imaging of Human and Bovine Serum Albumins. Sensors 2023, 23, 6020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishihara, R.; Dokainish, H.M.; Kihara, Y.; Ashiba, H.; Sugita, Y.; Kurita, R. Pseudo-Luciferase Activity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein for Luciferin. ACS Central Sci. 2024, 10, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, J.J.; Medici, V.; Heffern, M.C. A caged imidazopyrazinone for selective bioluminescence detection of labile extracellular copper(ii). Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 4352–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.C.; Cheng, L.; Dong, G.P.; Han, G.X.; Yang, X.Y.; Tang, C.C.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.B.; Du, L.P.; Li, M.Y. Novel photoactivatable substrates for Renilla luciferase imaging in vitro and in vivo. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 4789–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, R.; Takakura, H.; Kamiya, M.; Kobayashi, E.; Komatsu, T.; Ueno, T.; Terai, T.; Hanaoka, K.; Nagano, T.; Urano, Y. Development of a Sensitive Bioluminogenic Probe for Imaging Highly Reactive Oxygen Species in Living Rats. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 14768–14771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffern, M.C.; Park, H.M.; Au-Yeung, H.Y.; Van de Bittner, G.C.; Ackerman, C.M.; Stahl, A.; Chang, C.J. In vivo bioluminescence imaging reveals copper deficiency in a murine model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 14219–14224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, T.; Ai, H.-W. A luciferase prosubstrate and a red bioluminescent calcium indicator for imaging neuronal activity in mice. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aron, A.T.; Heffern, M.C.; Lonergan, Z.R.; Wal, M.N.V.; Blank, B.R.; Spangler, B.; Zhang, Y.; Park, H.M.; Stahl, A.; Renslo, A.R.; et al. In vivo bioluminescence imaging of labile iron accumulation in a murine model of Acinetobacter baumannii infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 12669–12674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, Z.; Jiang, T.; Du, L.; Li, M. A coelenterazine-type bioluminescent probe for nitroreductase imaging. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 16, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orioka, M.; Eguchi, M.; Mizui, Y.; Ikeda, Y.; Sakama, A.; Li, Q.; Yoshimura, H.; Ozawa, T.; Citterio, D.; Hiruta, Y. A Series of Furimazine Derivatives for Sustained Live-Cell Bioluminescence Imaging and Application to the Monitoring of Myogenesis at the Single-Cell Level. Bioconjugate Chem. 2022, 33, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Xiong, Y.; Sunnapu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, X.; Ai, H.-W. Bioluminescence Imaging of Potassium Ion Using a Sensory Luciferin and an Engineered Luciferase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 13406–13416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielonka, J.; Kalyanaraman, B. Small-molecule luminescent probes for the detection of cellular oxidizing and nitrating species. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 128, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, L.P.; Núnez-Montenegro, A.; Magalhães, C.M.; Ferreira, P.J.; Duarte, D.; González-Berdullas, P.; Rodríguez-Borges, J.E.; Vale, N.; da Silva, J.C.E. Single-molecule chemiluminescent photosensitizer for a self-activating and tumor-selective photodynamic therapy of cancer. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 183, 111683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shramova, E.I.; Chumakov, S.P.; Shipunova, V.O.; Ryabova, A.V.; Telegin, G.B.; Kabashin, A.V.; Deyev, S.M.; Proshkina, G.M. Genetically encoded BRET-activated photodynamic therapy for the treatment of deep-seated tumors. Light. Sci. Appl. 2022, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronsart, L.L.; Stokes, C.; Contag, C.H. Multimodality Imaging of Cancer Superoxide Anion Using the Small Molecule Coelenterazine. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2015, 18, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, S.; Hu, S.; Li, X.-L.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, D.; Huang, T.; Luo, W.; Zhao, Z.; Duan, L.; Su, S.-J.; et al. Heavy Atom Effect of Bromine Significantly Enhances Exciton Utilization of Delayed Fluorescence Luminogens. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 17327–17334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.P.; González-Berdullas, P.; Pereira, M.; Duarte, D.; Rodríguez-Borges, J.E.; Vale, N.; da Silva, J.C.E.; da Silva, L.P. Evaluation of the anticancer activity and chemiluminescence of a halogenated coelenterazine analog. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 2022, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Berdullas, P.; Pereira, R.B.; Teixeira, C.; Silva, J.P.; Magalhães, C.M.; Rodríguez-Borges, J.E.; Pereira, D.M.; da Silva, J.C.G.E.; da Silva, L.P. Discovery of the Anticancer Activity for Lung and Gastric Cancer of a Brominated Coelenteramine Analog. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magalhaes, C.M.; Dučić, T.; Pereira, R.B.; González-Berdullas, P.; Rodríguez-Borges, J.E.; Pereira, D.M.; da Silva, J.C.E.; Algarra, M.; da Silva, L.P. Synchrotron-based FTIR evaluation of biochemical changes in cancer and noncancer cells induced by brominated marine coelenteramine. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2023, 743, 109660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magalhães, C.M.; Pereira, R.B.; Erbiai, E.H.; González-Berdullas, P.; da Silva, J.C.E.; Pereira, D.M.; da Silva, L.P. Comparative investigation into the anticancer activity of analogs of marine coelenterazine and coelenteramine. Bioorganic Chem. 2024, 144, 107083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.-B.; Kamiya, G.; Furuta, T.; Maki, S.A. Coelenterazine Analogs for Bioassays and Molecular Imaging. Sensors 2025, 25, 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061651
Kim S-B, Kamiya G, Furuta T, Maki SA. Coelenterazine Analogs for Bioassays and Molecular Imaging. Sensors. 2025; 25(6):1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061651
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Sung-Bae, Genta Kamiya, Tadaomi Furuta, and Shojiro A. Maki. 2025. "Coelenterazine Analogs for Bioassays and Molecular Imaging" Sensors 25, no. 6: 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061651
APA StyleKim, S.-B., Kamiya, G., Furuta, T., & Maki, S. A. (2025). Coelenterazine Analogs for Bioassays and Molecular Imaging. Sensors, 25(6), 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061651








