High-Quality Text-to-Speech Implementation via Active Shallow Diffusion Mechanism
Abstract
1. Introduction
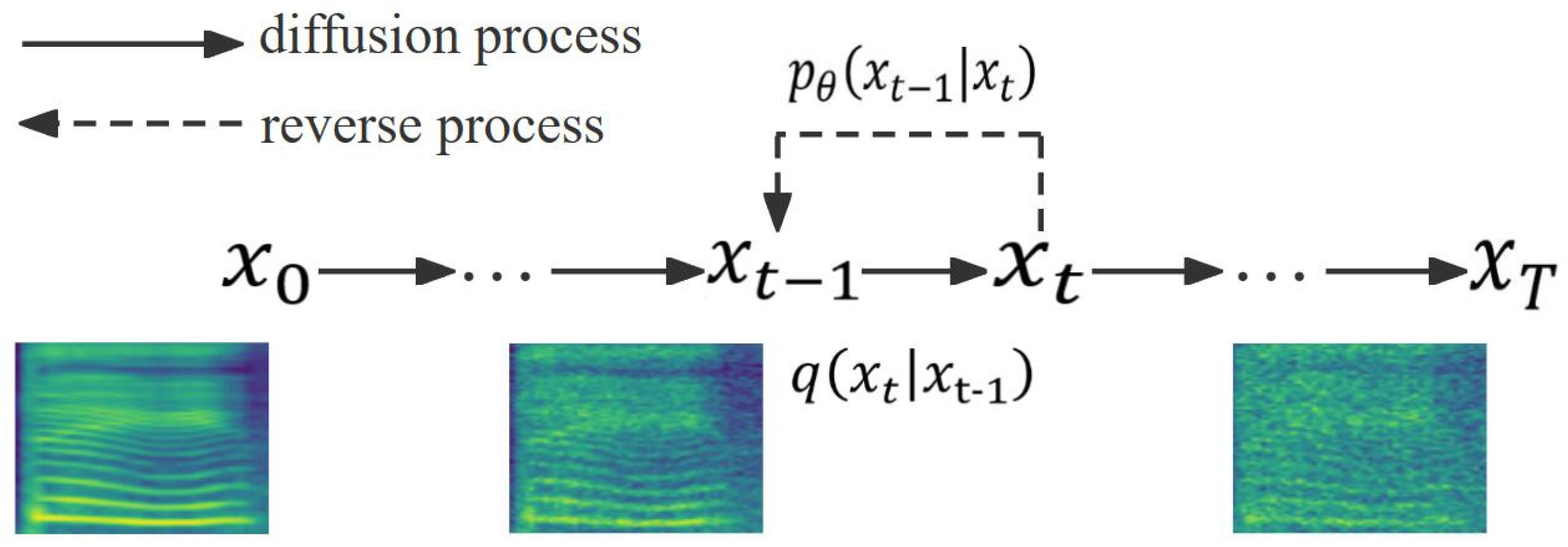
2. Diffusion Model
3. The CMG-TTS Model
3.1. Motivation
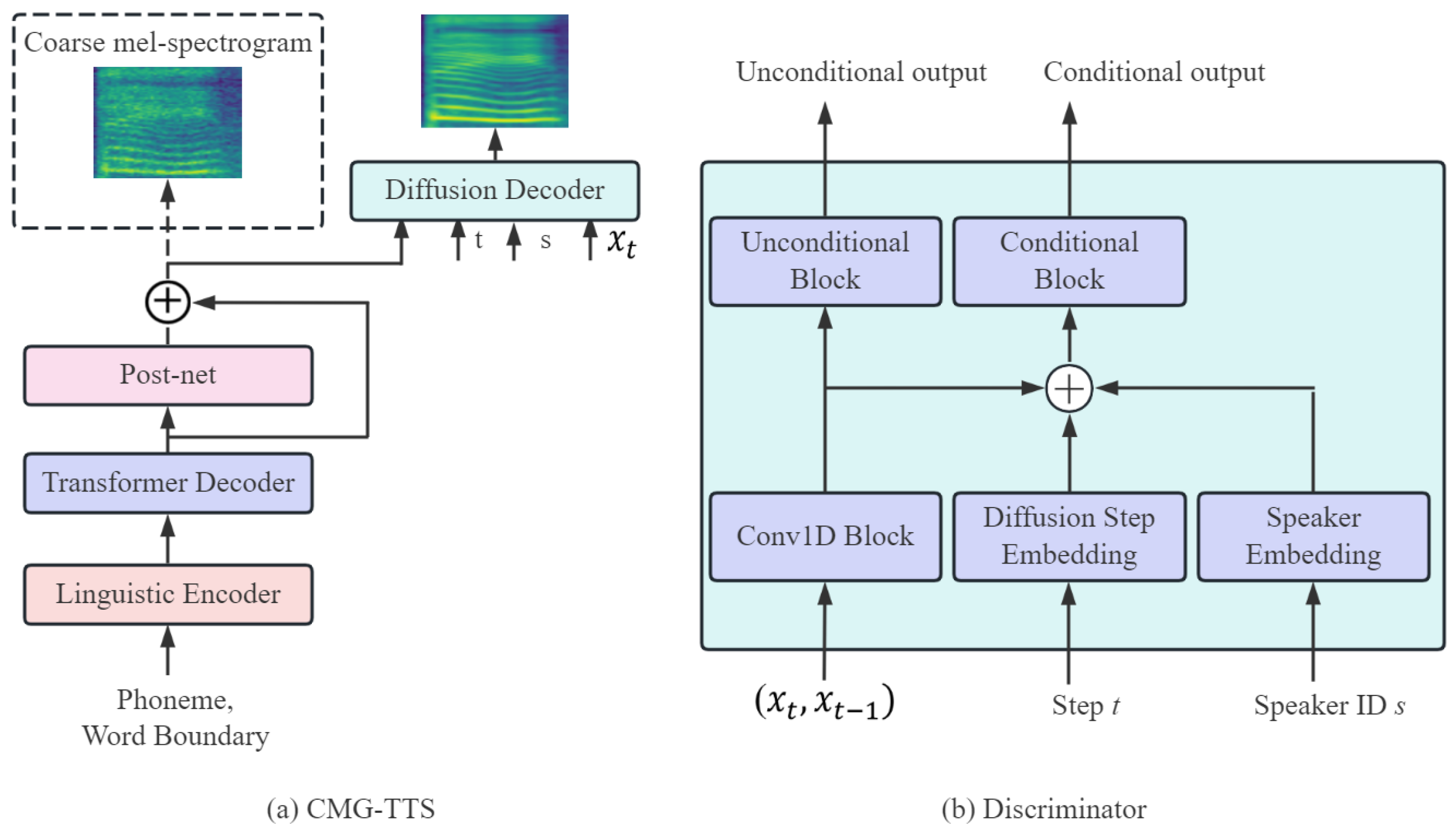
3.2. The Basic Model Architecture
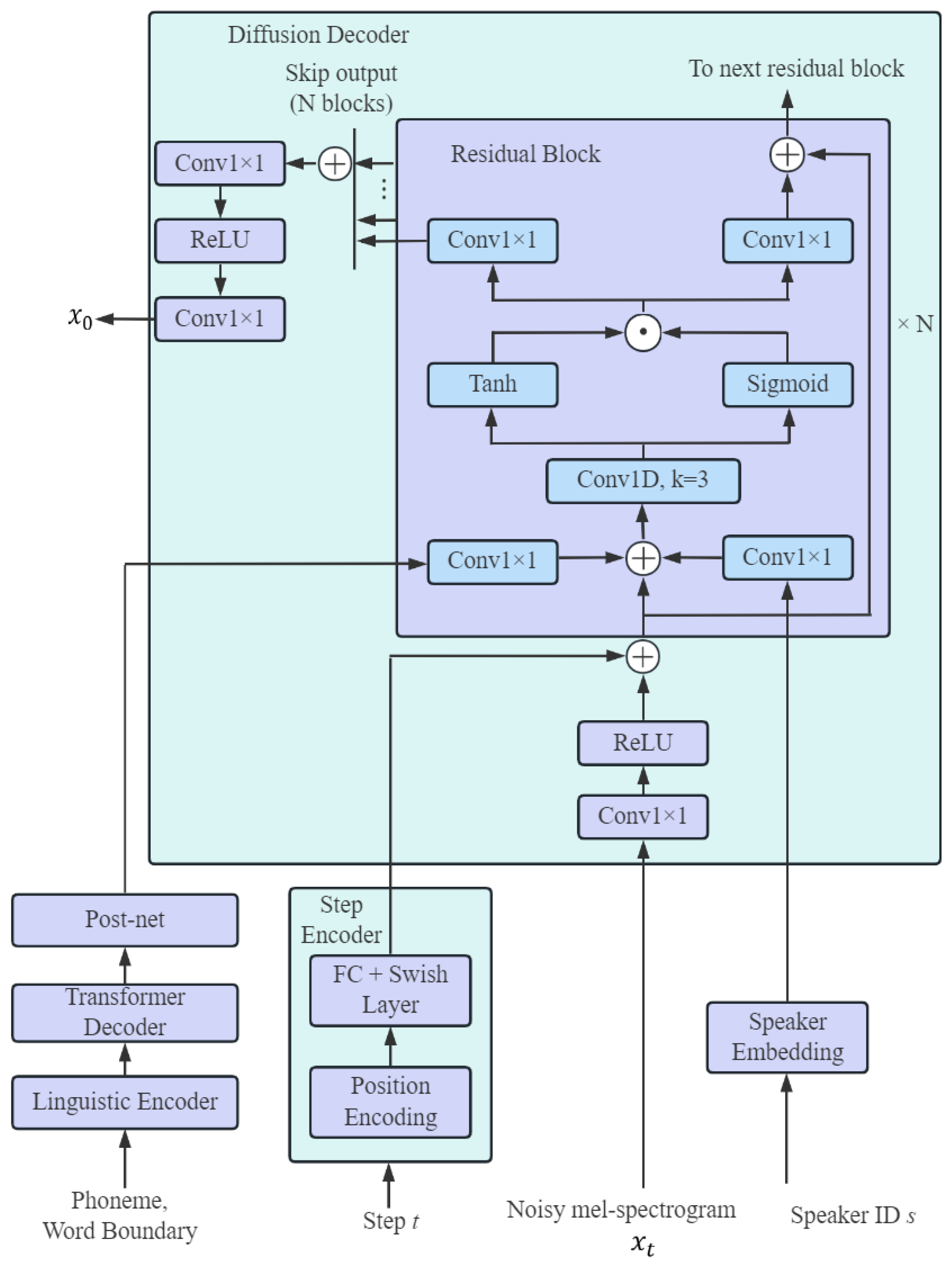
3.3. Diffusion Decoder and Discriminator
3.4. Active Shallow Diffusion Mechanism
3.5. Training Loss
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Setup
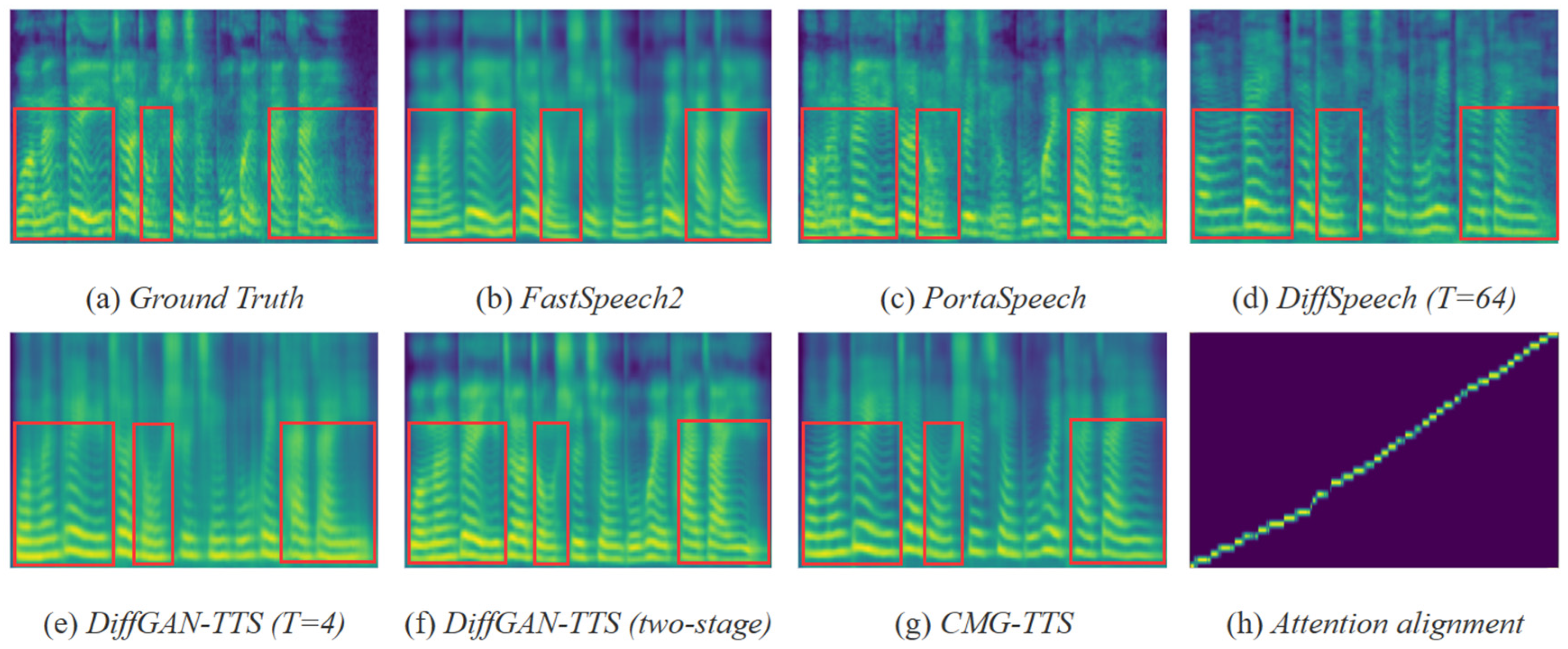
4.2. Experimental Results
4.3. Ablation Tests
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deng, Y.; Wu, N.; Qiu, C.; Luo, Y.; Chen, Y. MixGAN-TTS: Efficient and Stable Speech synthesis Based on Diffusion Model. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 57674–57682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wu, N.; Qiu, C.; Chen, Y.; Gao, X. Research on Speech Synthesis Based on Mixture Alignment Mechanism. Sensors 2023, 23, 7283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Song, X.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, B.; Pan, F.; Wu, Z. LightGrad: Lightweight Diffusion Probabilistic Model for Text-to-Speech. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023-2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 4–10 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Du, C.; Ma, Z.; Chen, X.; Yu, K. VoiceFlow: Efficient Text-to-Speech with Rectified Flow Matching. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.05027. [Google Scholar]
- Oord, A.V.D.; Dieleman, S.; Zen, H.; Simonyan, K.; Vinyals, O.; Graves, A.; Kalchbrenner, N.; Senior, A.; Kavukcuoglu, K. Wavenet: A generative model for raw audio. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.03499. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, J.; Kim, J.; Bae, J. Hifi-gan: Generative adversarial networks for efficient and high fidelity speech synthesis. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 17022–17033. [Google Scholar]
- Prenger, R.; Valle, R.; Catanzaro, B. Waveglow: A flow-based generative network for speech synthesis. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019-2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 3617–3621. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Skerry-Ryan, R.J.; Stanton, D.; Wu, Y.; Weiss, R.J.; Jaitly, N.; Yang, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Bengio, S.; et al. Tacotron: Towards end-to-end speech synthesis. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.10135. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Pang, R.; Weiss, R.J.; Schuster, M.; Jaitly, N.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Skerrv-Ryan, R.; et al. Natural tts synthesis by conditioning wavenet on mel spectrogram predictions. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AL, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 4779–4783. [Google Scholar]
- Gibiansky, A.; Arik, S.; Diamos, G.; Miller, J.; Peng, K.; Ping, W.; Raiman, J.; Zhou, Y. Deep voice 2: Multi-speaker neural text-to-speech. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30. Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2017/hash/c59b469d724f7919b7d35514184fdc0f-Abstract.html (accessed on 27 January 2025).
- Ping, W.; Peng, K.; Gibiansky, A.; Arik, S.O.; Kannan, A.; Narang, S.; Raiman, J.; Miller, J. Deep voice 3: Scaling text-to-speech with convolutional sequence learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.07654. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Liu, M. Neural speech synthesis with transformer network. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; Volume 33, pp. 6706–6713. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Runa, Y.; Tan, X.; Qin, T.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, T.-Y. FastSpeech: Fast, robust and controllable text to speech. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1905.09263 (accessed on 27 January 2025).
- Ren, Y.; Hu, C.; Tan, X.; Qin, T.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, T.Y. Fastspeech 2: Fast and high-quality end-to-end text to speech. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.04558. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Z. PortaSpeech: Portable and high-quality generative text-to-speech. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 13963–13974. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Kong, J.; Yoon, S. Glow-tts: A generative flow for text-to-speech via monotonic alignment search. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 8067–8077. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, C.; Liang, S.; Chen, M.; Ma, J.; Wang, S.; Xiao, J. Flow-tts: A non-autoregressive network for text to speech based on flow. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Virtual, 4–9 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.G.; Kim, H.; Shin, C.; Tan, X.; Liu, C.; Meng, Q.; Qin, T.; Chen, W.; Yoon, S.; Liu, T.Y. Priorgrad: Improving conditional denoising diffusion models with data-dependent adaptive prior. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.06406. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Wu, Y.; Leng, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, H.; Tan, X.; Cui, Y.; Wang, K.; He, L. Resgrad: Residual denoising diffusion probabilistic models for text to speech. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.14518. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, J.; Jain, A.; Abbeel, P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 6840–6851. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Z.; Kreis, K.; Vahdat, A. Tackling the generative learning trilemma with denoising diffusion gans. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.07804. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Li, C.; Ren, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhao, Z. Diffsinger: Singing voice synthesis via shallow diffusion mechanism. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Online, 22 February–1 March 2022; Volume 36, pp. 11020–11028. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Su, D.; Yu, D. DiffGAN-TTS: High-Fidelity and Efficient Text-to-Speech with Denoising Diffusion GANs. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.11972. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Bu, H.; Xu, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, M. Aishell-3: A multi-speaker mandarin tts corpus and the baselines. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11567. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, X.; Li, Q.; Xie, H.; Lau, R.Y.; Wang, Z.; Smolley, S.P. Least squares generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2794–2802. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Bae, J.-S.; Bak, T.; Kim, Y.; Cho, H.-Y. Ganspeech: Adversarial training for high-fidelity multi-speaker speech synthesis. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.15153. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, A.B.L.; Sønderby, S.K.; Larochelle, H.; Winther, O. Autoen-coding beyond pixels using a learned similarity metric. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, New York City, NY, USA, 19–24 June 2016; pp. 1558–1566. [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana, H.; Uenoyama, K.; Aihara, S. Efficiently trainable text-to-speech system based on deep convolutional networks with guided attention. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AL, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 4784–4788. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, M.; Peng, H. Objective Measure for Estimating Mean Opinion Score of Synthesized Speech. US Patent 7,024,362, 4 April 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kubichek, R. Mel-cepstral distance measure for objective speech quality assessment. In Proceedings of the IEEE Pacific Rim Conference on Communications Computers and Signal Processing, Victoria, BC, Canada, 19–21 May 1993; Volume 1, pp. 125–128. [Google Scholar]
- Rix, A.W.; Beerends, J.G.; Hollier, M.P.; Hekstra, A.P. Perceptual evaluation of speech quality (PESQ)-a new method for speech quality assessment of telephone networks and codecs. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 7–11 May 2001, Proceedings (Cat. No. 01CH37221); IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2001; Volume 2, pp. 749–752. [Google Scholar]
- Taal, C.H.; Hendriks, R.C.; Heusdens, R.; Jensen, J. A short-time objective intelligibility measure for time-frequency weighted noisy speech. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Dallas, TX, USA, 14–19 March 2010; pp. 4214–4217. [Google Scholar]
- Donahue, J.; Dieleman, S.; Bińkowski, M.; Elsen, E.; Simonyan, K. End-to-end adversarial text-to-speech. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.03575. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, C.; Shuang, L.; Liu, Z.; Minchuan, C.; Ma, J.; Wang, S.; Xiao, J. Efficients: An efficient and high-quality text-to-speech architecture. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 7700–7709. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, C.; Shuang, L.; Liu, Z.; Minchuan, C.; Ma, J.; Wang, S.; Xiao, J. Wave-tacotron: Spectrogram-free end-to-end text-to-speech synthesis. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021-2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 5679–5683. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Kong, J.; Son, J. Conditional variational autoencoder with adversarial learning for end-to-end text-to-speech. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 5530–5540. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, D.; Jung, S.; Kim, E. JETS: Jointly training FastSpeech2 and HiFi-GAN for end to end text to speech. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.16852. [Google Scholar]


| Method | MOS (↑) | MCD (↓) | F0 RMSE (↓) | PESQ (↑) | STOI (↑) | SegSNR (↑) | RTF (↓) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ground Truth | 4.27 ± 0.06 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| FastSpeech2 | 3.83 ± 0.07 | 17.808 | 0.724 | 1.061 | 0.146 | −8.271 | 0.096 |
| PortaSpeech | 4.02 ± 0.07 | 17.665 | 0.719 | 1.069 | 0.158 | −8.121 | 0.115 |
| DiffSpeech (T = 64) | 4.04 ± 0.06 | 17.721 | 0.748 | 1.059 | 0.157 | −8.191 | 0.184 |
| DiffGAN-TTS (T = 4) | 3.93 ± 0.06 | 17.746 | 0.745 | 1.058 | 0.161 | −8.177 | 0.167 |
| DiffGAN-TTS (two-stage) | 3.89 ± 0.07 | 17.704 | 0.783 | 1.054 | 0.155 | −8.124 | 0.144 |
| CMG-TTS | 4.03 ± 0.07 | 17.611 | 0.743 | 1.078 | 0.165 | −7.858 | 0.121 |
| Method | MOS (↑) | MCD (↓) | F0 RMSE (↓) | PESQ (↑) | STOI (↑) | SegSNR (↑) | RTF (↓) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ground Truth | 4.34 ± 0.07 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| FastSpeech2 | 3.94 ± 0.06 | 6.973 | 0.306 | 1.062 | 0.251 | −6.049 | 0.044 |
| PortaSpeech | 4.06 ± 0.07 | 6.694 | 0.301 | 1.074 | 0.274 | −5.781 | 0.071 |
| DiffSpeech (T = 64) | 4.09 ± 0.05 | 6.758 | 0.303 | 1.071 | 0.271 | −5.793 | 0.126 |
| DiffGAN-TTS (T = 4) | 4.02 ± 0.06 | 6.801 | 0.309 | 1.599 | 0.268 | −5.867 | 0.108 |
| DiffGAN-TTS (two-stage) | 3.99 ± 0.07 | 6.737 | 0.311 | 1.601 | 0.261 | −5.691 | 0.096 |
| CMG-TTS | 4.08 ± 0.06 | 6.671 | 0.298 | 1.667 | 0.276 | −5.661 | 0.087 |
| Method | MOS (↑) | MCD (↓) | F0 RMSE (↓) | PESQ (↑) | STOI (↑) | SegSNR (↑) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMG-TTS | 4.03 ± 0.07 | 17.611 | 0.743 | 1.078 | 0.165 | −7.858 |
| Remove post-net | 3.95 ± 0.07 | 17.707 | 0.776 | 1.063 | 0.146 | −8.136 |
| Remove post-net and two-stage | 3.99 ± 0.06 | 17.645 | 0.756 | 1.075 | 0.168 | −8.091 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, J.; Hou, R.; Deng, Y.; Long, Y.; Wu, N. High-Quality Text-to-Speech Implementation via Active Shallow Diffusion Mechanism. Sensors 2025, 25, 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25030833
Deng J, Hou R, Deng Y, Long Y, Wu N. High-Quality Text-to-Speech Implementation via Active Shallow Diffusion Mechanism. Sensors. 2025; 25(3):833. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25030833
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Junlin, Ruihan Hou, Yan Deng, Yongqiu Long, and Ning Wu. 2025. "High-Quality Text-to-Speech Implementation via Active Shallow Diffusion Mechanism" Sensors 25, no. 3: 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25030833
APA StyleDeng, J., Hou, R., Deng, Y., Long, Y., & Wu, N. (2025). High-Quality Text-to-Speech Implementation via Active Shallow Diffusion Mechanism. Sensors, 25(3), 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25030833







