Toward Detection of Inert PFAS: Single/Few-CNT Devices for Sensing PFOA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
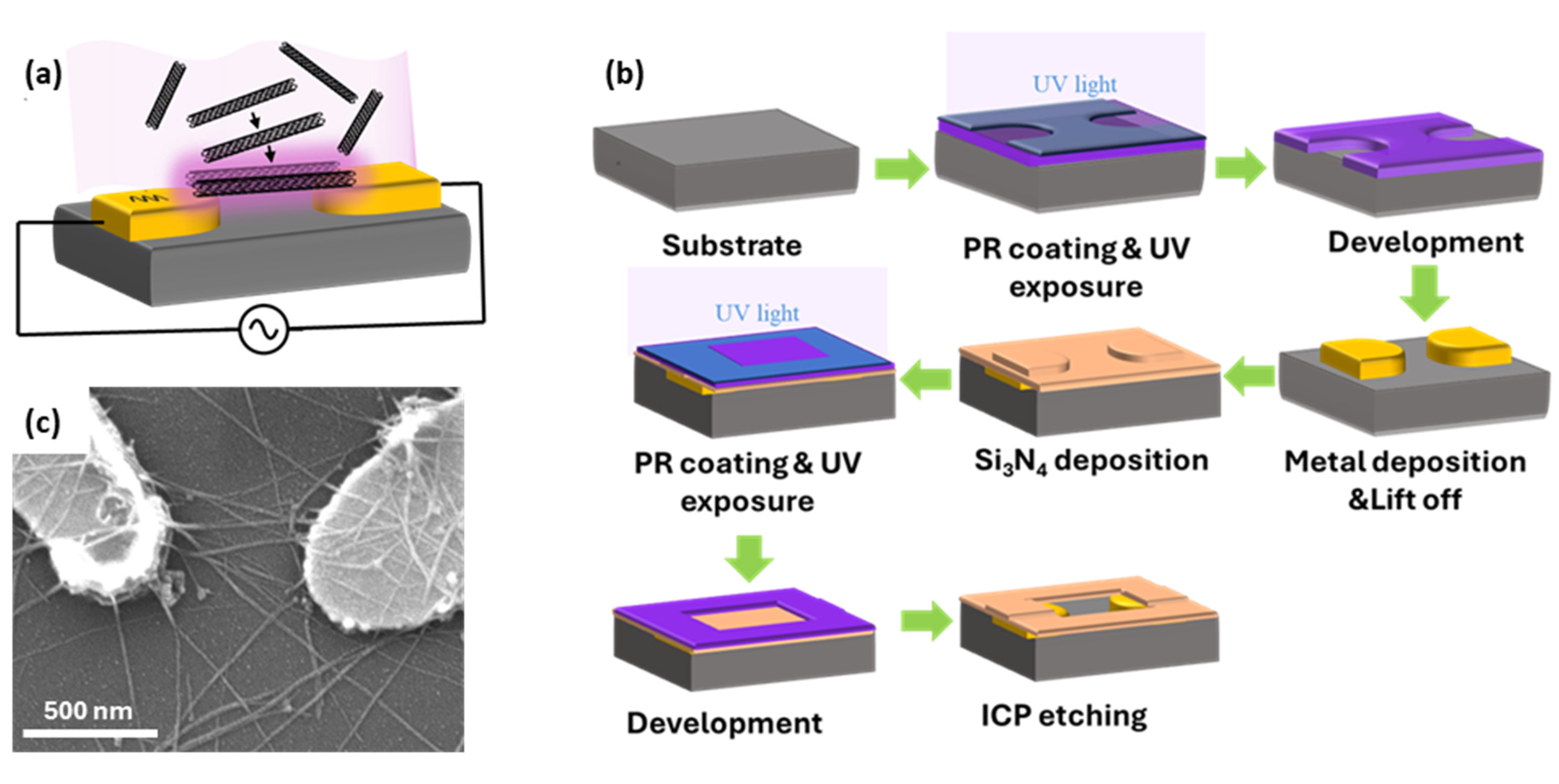
2.1. Nanoelectrode Fabrication
2.2. DEP Manipulation of SWCNTs
2.3. Characterization Methods
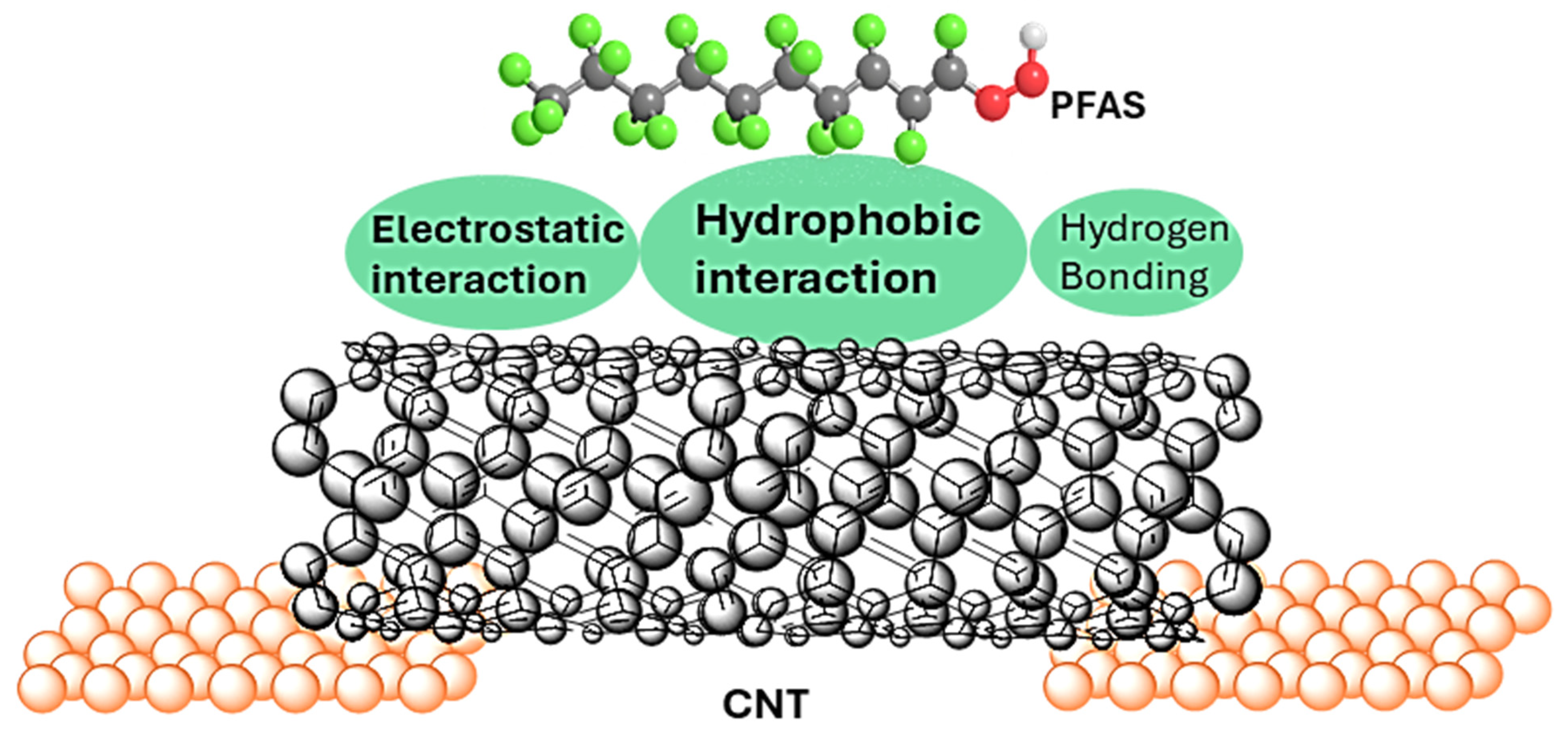
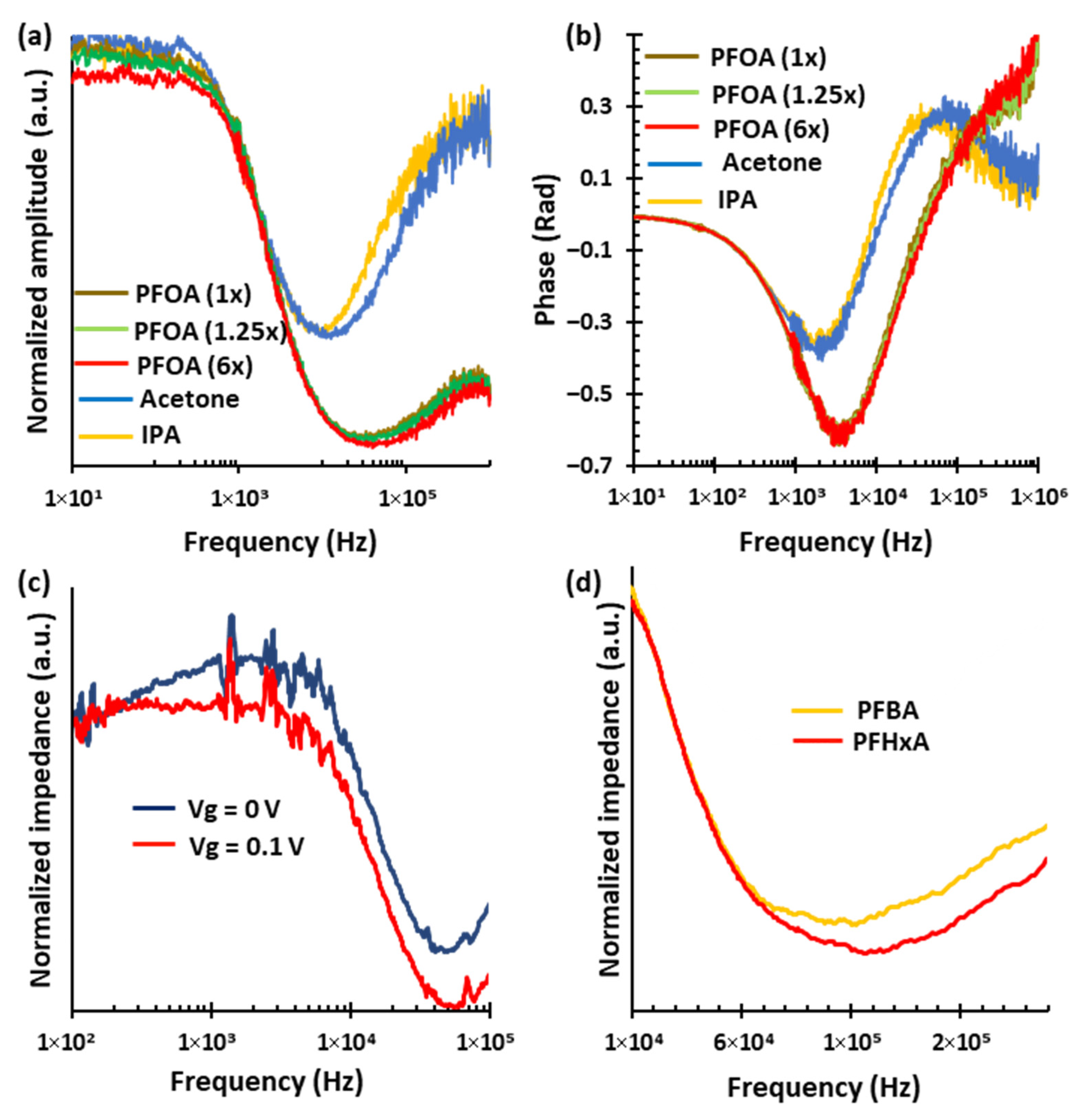
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jariwala, D.; Sangwan, V.K.; Lauhon, L.J.; Marks, T.J.; Hersam, M.C. Carbon nanomaterials for electronics, optoelectronics, photovoltaics, and sensing. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2824–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghomian, T.; Jeong, H.; Pan, V.; Celik, K.; Alangari, M.; Ke, Y.; Hihath, J. High-Throughput Dielectrophoretic Trapping and Detection of DNA Origami. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2001476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.H.; Pioch, T.N.; Swager, T.M. Chemi-Impeditive Sensing Platform Based on Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 31486–31496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddique, I. Carbon nanotube-based sensors—A review. SSRN Electron. J. 2024. published online. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffman, D.R.; Star, A. Carbon Nanotube Gas and Vapor Sensors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 6550–6570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, V.; Savagatrup, S.; He, M.; Lin, S.; Swager, T.M. Carbon Nanotube Chemical Sensors. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 599–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-L.; Shang, Y.; Yan, K.-C.; Sedgwick, A.C.; Gan, H.-Q.; Chen, G.-R.; He, X.-P.; James, T.D.; Chen, D. Low-dimensional nanomaterials for antibacterial applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 3640–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas Martins, E.; Pinotti, L.F.; De Carvalho Castro Silva, C.; Rocha, A.R. Addressing the Theoretical and Experimental Aspects of Low-Dimensional-Materials-Based FET Immunosensors: A Review. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.Q.; Xia, X.; Zhu, M.; Xu, L.H.; Zhang, Y.X.; Li, S.S. Cobalt encapsulated in bamboo-like N-doped carbon nanotubes for highly sensitive electroanalysis of Pb(II): Enhancement based on adsorption and catalysis. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 2147–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dariyal, P.; Sharma, S.; Chauhan, G.S.; Singh, B.P.; Dhakate, S.R. Recent trends in gas sensing via carbon nanomaterials: Outlook and challenges. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 6514–6544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Mahajan, A.; Saini, R.; Bedi, R.; Kumar, S.; Debnath, A.; Aswal, D. Reversible and fast responding ppb level Cl2 sensor based on noncovalent modified carbon nanotubes with Hexadecafluorinated copper phthalocyanine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Mahajan, A.; Bedi, R.K.; Kumar, S.; Debnath, A.K.; Aswal, D.K. Non-covalently anchored multi-walled carbon nanotubes with hexa-decafluorinated zinc phthalocyanine as ppb level chemiresistive chlorine sensor. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 427, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, N.D.; Van Cat, V.; Nam, M.H.; Phan, V.N.; Le, A.T.; Van Quy, N. Enhanced SO2 sensing characteristics of multi-wall carbon nanotubes based mass-type sensor using two-step purification process. Sens Actuators Phys. 2019, 295, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perebeinos, V.; Rotkin, S.V.; Petrov, A.G.; Avouris, P. The Effects of Substrate Phonon Mode Scattering on Transport in Carbon Nanotubes. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Jang, C.; Xiao, S.; Ishigami, M.; Fuhrer, M.S. Intrinsic and extrinsic performance limits of graphene devices on SiO2. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerw, R.; Foley, B.; Tekleab, D.; Rubio, A.; Ajayan, P.M.; Carroll, D.L. Substrate-interface interactions between carbon nanotubes and the supporting substrate. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 66, 033408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Villagrán, D. Design of nanomaterials for the removal of per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in water: Strategies, mechanisms, challenges, and opportunities. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Zhang, Q.; Nie, Y.; Wei, H.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Yu, G.; Xing, B. Sorption mechanisms of perfluorinated compounds on carbon nanotubes. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 168, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, S.C.E.; Wanninayake, D.; Chen, D.; Nguyen, N.T.; Li, Q. Physicochemical properties and interactions of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS)-Challenges and opportunities in sensing and remediation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 166764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasian Chaleshtari, Z.; Foudazi, R. A Review on Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Remediation: Separation Mechanisms and Molecular Interactions. ACS EST Water 2022, 2, 2258–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, D.; Shafi, T.; Chowdhury, S.; Dubey, B.K.; Sen, R. Progress and perspectives on carbon-based materials for adsorptive removal and photocatalytic degradation of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Chemosphere 2024, 351, 141164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lin, H.; Jin, F.; Li, Y.; Niu, J. Electrochemically enhanced removal of perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) from aqueous solution by CNTs-graphene composite electrode. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 328, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tsui, M.M.; Ruan, Y.; Lin, H.; Zhao, Z.; Ku, J.P.; Sun, H.; Lam, P.K. Occurrence and distribution of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in the seawater and sediment of the South China sea coastal region. Chemosphere 2019, 231, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staii, C.; Johnson, A.T.; Chen, M.; Gelperin, A. DNA-Decorated Carbon Nanotubes for Chemical Sensing. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 1774–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, W.; Hu, Y.; Cui, Y. Carbon Nanotube Field-Effect Transistor-Based Chemical and Biological Sensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Han Sjen Tulevski, G.S.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, D.D.; Haensch, W. Arrays of single-walled carbon nanotubes with full surface coverage for high-performance electronics. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Zhao, J.; Shen, L.; Xia, J.; Meng, H.; Yu, W.; Huang, Q.; Han, H.; Liang, X.; Peng, L. Large-area and highly uniform carbon nanotube film for high-performance thin film transistors. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 4356–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, Y.; Brady, G.J.; Kanimozhi, C.; Ko, J.; Shea, M.J.; Strand, M.T.; Arnold, M.S.; Gopalan, P. Polymer-Free Electronic-Grade Aligned Semiconducting Carbon Nanotube Array. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 28859–28867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinkins, K.R.; Chan, J.; Jacobberger, R.M.; Berson, A.; Arnold, M.S. Substrate-Wide Confined Shear Alignment of Carbon Nanotubes for Thin Film Transistors. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2019, 5, 1800593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, N.; Lin, A.; Myers, E.R.; Wong, H.S.P.; Mitra, S. Integrated wafer-scale growth and transfer of directional Carbon Nanotubes and misaligned-Carbon-Nanotube-immune logic structures. In 2008 Symposium on VLSI Technology; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 205–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinkins, K.R.; Chan, J.; Jacobberger, R.M.; Berson, A.; Arnold, M.S. Fabrication of carbon nanotube field-effect transistors in commercial silicon manufacturing facilities. Nat. Electron. 2020, 3, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathinavel, S.; Priyadharshini, K.; Panda, D. A review on carbon nanotube: An overview of synthesis, properties, functionalization, characterization, and the application. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 268, 115095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghomian, T.; Hihath, J. Review of Dielectrophoretic Manipulation of Micro and Nanomaterials: Fundamentals, Recent Developments, and Challenges. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 70, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pethig, R. Dielectrophoresis: Theory, Methodology, and Biological Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dudina, A.; Seichepine, F.; Chen, Y.; Stettler, A.; Hierlemann, A.; Frey, U. Monolithic CMOS sensor platform featuring an array of 9′216 carbon-nanotube-sensor elements and low-noise, wide-bandwidth and wide-dynamic-range readout circuitry. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 279, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dormena, C.; Appiah, O.; Ghomian, T. Toward Detection of Inert PFAS: Single/Few-CNT Devices for Sensing PFOA. Sensors 2025, 25, 7653. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25247653
Dormena C, Appiah O, Ghomian T. Toward Detection of Inert PFAS: Single/Few-CNT Devices for Sensing PFOA. Sensors. 2025; 25(24):7653. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25247653
Chicago/Turabian StyleDormena, Collins, Obed Appiah, and Taher Ghomian. 2025. "Toward Detection of Inert PFAS: Single/Few-CNT Devices for Sensing PFOA" Sensors 25, no. 24: 7653. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25247653
APA StyleDormena, C., Appiah, O., & Ghomian, T. (2025). Toward Detection of Inert PFAS: Single/Few-CNT Devices for Sensing PFOA. Sensors, 25(24), 7653. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25247653





