Deep Guided Exposure Correction with Knowledge Distillation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We present a deep guided exposure correction method, which can learn different prior knowledge for over- and under-exposure correction at the same time.
- We design a deep guided network to automatically exploit color guidance information by considering the sensitive property of different channels.
- We introduce a knowledge distillation strategy to effectively learn a unified network by distilling varying well-learned prior knowledge.
2. Related Work
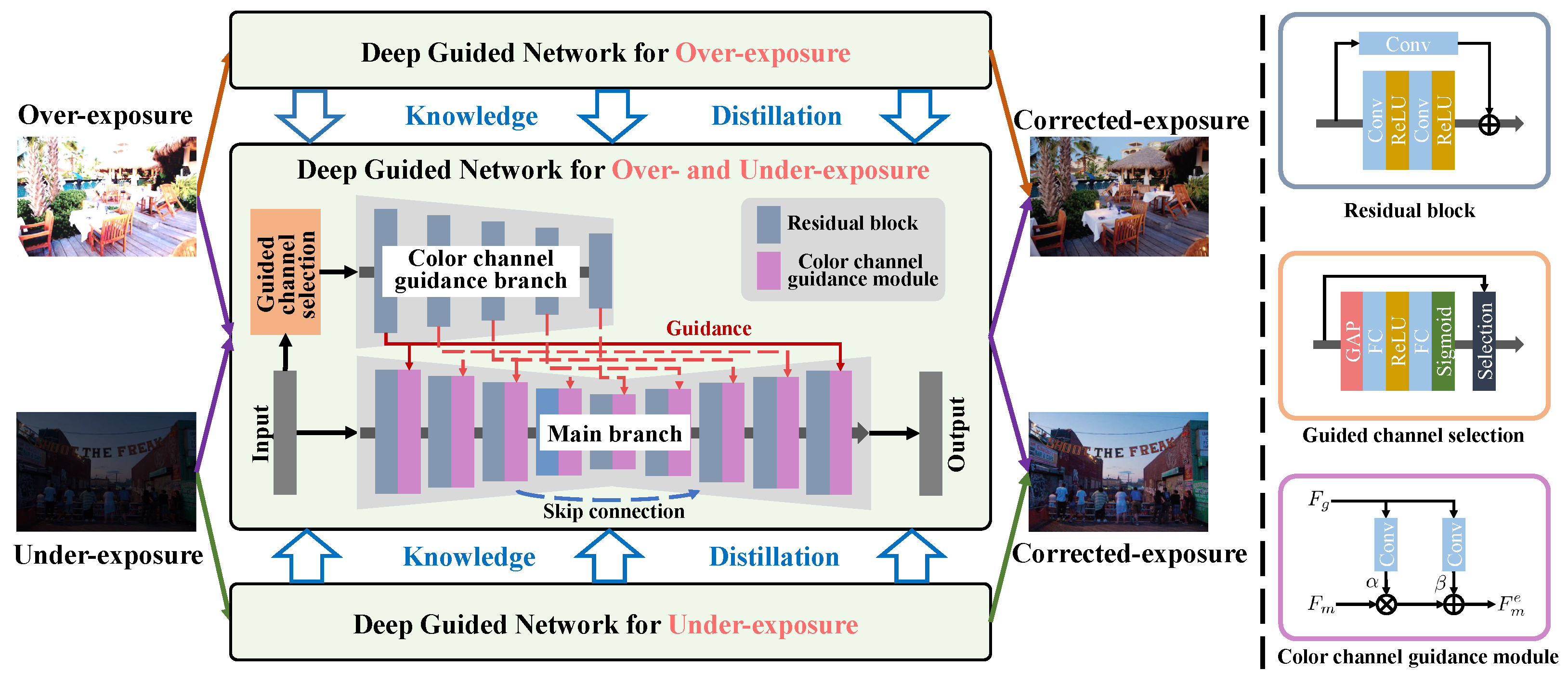
3. Method
3.1. Motivation
3.2. Deep Guided Network
3.3. Knowledge Distillation
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Settings
4.3. Evaluation of Exposure Correction
4.4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdullah-Al-Wadud, M.; Kabir, M.H.; Dewan, M.A.A.; Chae, O. A dynamic histogram equalization for image contrast enhancement. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2007, 53, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arici, T.; Dikbas, S.; Altunbasak, Y. A histogram modification framework and its application for image contrast enhancement. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2009, 18, 1921–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.C.; Cohen, L.D. Global and local contrast adaptive enhancement for non-uniform illumination color images. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 3023–3030. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.; Zeng, D.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.P.; Ding, X. A weighted variational model for simultaneous reflectance and illumination estimation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2782–2790. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Ling, H. LIME: Low-light image enhancement via illumination map estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 26, 982–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, J.; Fang, F.; Li, F.; Zhang, G. Luminance-aware pyramid network for low-light image enhancement. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2020, 23, 3153–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, D.; Yang, W.; Fan, M.; Huang, H. Benchmarking low-light image enhancement and beyond. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 1153–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Wang, W.; Yang, W.; Liu, J. Deep retinex decomposition for low-light enhancement. In Proceedings of the Conference on British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), Newcastle, UK, 3–6 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Wang, S.; Fang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J. From fidelity to perceptual quality: A semi-supervised approach for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 3063–3072. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Li, C.; Guo, J.; Loy, C.C.; Hou, J.; Kwong, S.; Cong, R. Zero-reference deep curve estimation for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 1780–1789. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, F.; Liu, B.; Lu, F. Fast enhancement for non-uniform illumination images using light-weight CNNs. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Multimedia (MM), Seattle, WA, USA, 12–16 October 2020; pp. 1450–1458. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Jin, D.; Liu, R.; Fan, X.; Luo, Z. Joint over and under exposures correction by aggregated retinex propagation for image enhancement. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2020, 27, 1210–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afifi, M.; Derpanis, K.G.; Ommer, B.; Brown, M.S. Learning multi-scale photo exposure correction. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 9157–9167. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Zhou, M.; Liu, Y.; Yao, M.; Zhao, F.; Xiong, Z. Exposure-Consistency Representation Learning for Exposure Correction. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Multimedia (MM), Lisboa, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022; pp. 6309–6317. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.; Zheng, X.; Li, J.; Zhan, R.; Dong, J.; Wen, Y.; Mao, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y. Tone Mapping of HDR Images via Meta-Guided Bayesian Optimization and Virtual Diffraction Modeling. Sensors 2025, 25, 6577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistellato, M.; Fatima, T.; Wimmer, M. Exploiting light polarization for deep hdr imaging from a single exposure. Sensors 2023, 23, 5370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reza, A.M. Realization of the contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE) for real-time image enhancement. J. VLSI Signal Process. Syst. Signal Image Video Technol. 2004, 38, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, E.H. The retinex theory of color vision. Sci. Am. 1977, 237, 108–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yuan, G.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, L.; Zheng, W.S. High-quality exposure correction of underexposed photos. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Multimedia (MM), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 22–26 October 2018; pp. 582–590. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Liu, J.; Yang, W.; Sun, X.; Guo, Z. Structure-revealing low-light image enhancement via robust retinex model. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 2828–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Kim, W. DSLR: Deep stacked Laplacian restorer for low-light image enhancement. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2020, 23, 4272–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranasinghe, P.; Patra, D.; Banerjee, B.; Raval, S. LiDAR Point Cloud Colourisation Using Multi-Camera Fusion and Low-Light Image Enhancement. Sensors 2025, 25, 6582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Zhu, C.; Liu, A.; Zhang, C.; Feng, X. RICNET: Retinex-Inspired Illumination Curve Estimation for Low-Light Enhancement in Industrial Welding Scenes. Sensors 2025, 25, 5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucherit, I.; Kheddar, H. Reinforced Residual Encoder–Decoder Network for Image Denoising via Deeper Encoding and Balanced Skip Connections. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L.; Huang, H. Coded hyperspectral image reconstruction using deep external and internal learning. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 3404–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, D.; Huang, H. Joint camera spectral response selection and hyperspectral image recovery. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 44, 256–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liang, Z.; Fu, Y. Joint spatial-spectral pattern optimization and hyperspectral image reconstruction. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2022, 16, 636–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X. Kindling the darkness: A practical low-light image enhancer. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Multimedia (MM), Amherst, MA, USA, 18–21 June 2019; pp. 1632–1640. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, W.; Liu, S.; Ma, L.; Xu, Q.; Xu, X.; Cao, X.; Du, J.; Yang, M.H. Low-light image enhancement via a deep hybrid network. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 4364–4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jiang, J.; Wu, M.; Feng, Z.; Shi, X. Illumination-guided dual-branch fusion network for partition-based image exposure correction. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2025, 106, 104342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Sun, J.; Tang, X. Guided image filtering. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 35, 1397–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, T.W.; Loy, C.C.; Tang, X. Depth map super-resolution by deep multi-scale guidance. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 353–369. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, J. Guided hyperspectral image denoising with realistic data. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2022, 130, 2885–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Fu, Y.; Li, C. Deep spatial adaptive network for real image demosaicing. In Proceedings of the Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), Arlington, VA, USA, 17–19 November 2022; Volume 36, pp. 3326–3334. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, G.; Fu, Y.; Li, K.; Liu, Y. Cross-MPI: Cross-scale Stereo for Image Super-Resolution using Multiplane Images. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 14842–14851. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, D.; Huang, H. Hyperspectral image super-resolution with optimized RGB guidance. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 11661–11670. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Huang, J.B.; Ahuja, N.; Yang, M.H. Deep joint image filtering. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 154–169. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, J. Deep guided attention network for joint denoising and demosaicing in real image. Chin. J. Electron. 2024, 33, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Li, Y.; Gool, L.V.; Timofte, R. Self-guided network for fast image denoising. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 2511–2520. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Jia, X.; Liu, J.; Tian, Q. Joint demosaicing and denoising with self guidance. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 2240–2249. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.; Vinyals, O.; Dean, J. Distilling the knowledge in a neural network. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1503.02531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, A.; Ballas, N.; Kahou, S.E.; Chassang, A.; Gatta, C.; Bengio, Y. Fitnets: Hints for thin deep nets. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6550. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, H.; Li, X.; Tan, X. Progressive Blockwise Knowledge Distillation for Neural Network Acceleration. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), Stockholm, Sweden, 13–19 July 2018; pp. 2769–2775. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, X.; Feng, J. Distilling object detectors with fine-grained feature imitation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 4933–4942. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, K.; Liu, C.; Qin, Z.; Luo, Z.; Wang, J. Structured knowledge distillation for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 2604–2613. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Qiao, J.; Liao, J.; Li, W.; Li, S.; Xie, J.; Shen, Y.; Hu, J.; Lin, S. Dynamic Contrastive Knowledge Distillation for Efficient Image Restoration. In Proceedings of the Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 25 February–4 March 2025; Volume 39, pp. 10861–10869. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Feng, C.; Zhang, F.; Bull, D. Mtkd: Multi-teacher knowledge distillation for image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; pp. 364–382. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Min, Q.; Lu, W.; Yao, W.; Ma, Y.; Du, J.; Lu, T.; Liu, G. An automated cloud detection method based on the green channel of total-sky visible images. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 4671–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.T.; Huang, Z.K.; Tsai, C.C.; Yang, H.H.; Ding, J.J.; Kuo, S.Y. Learning Multiple Adverse Weather Removal via Two-Stage Knowledge Learning and Multi-Contrastive Regularization: Toward a Unified Model. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 17653–17662. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Park, T.; Liu, M.Y.; Wang, T.C.; Zhu, J.Y. Semantic image synthesis with spatially-adaptive normalization. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 2337–2346. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, J. Low-light raw video denoising with a high-quality realistic motion dataset. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 25, 8119–8131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yan, C.; Timofte, R. Calibration-Free Raw Image Denoising via Fine-Grained Noise Estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2025, 47, 5368–5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. PyTorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. In Proceedings of the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; pp. 8024–8035. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Ma, L.; Zhang, J.; Fan, X.; Luo, Z. Retinex-inspired unrolling with cooperative prior architecture search for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 10561–10570. [Google Scholar]
- Nsamp, N.; Hu, Z.; Wang, Q. Learning Exposure Correction Via Consistency Modeling. In Proceedings of the Conference on British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), Online, 22–25 November 2021; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
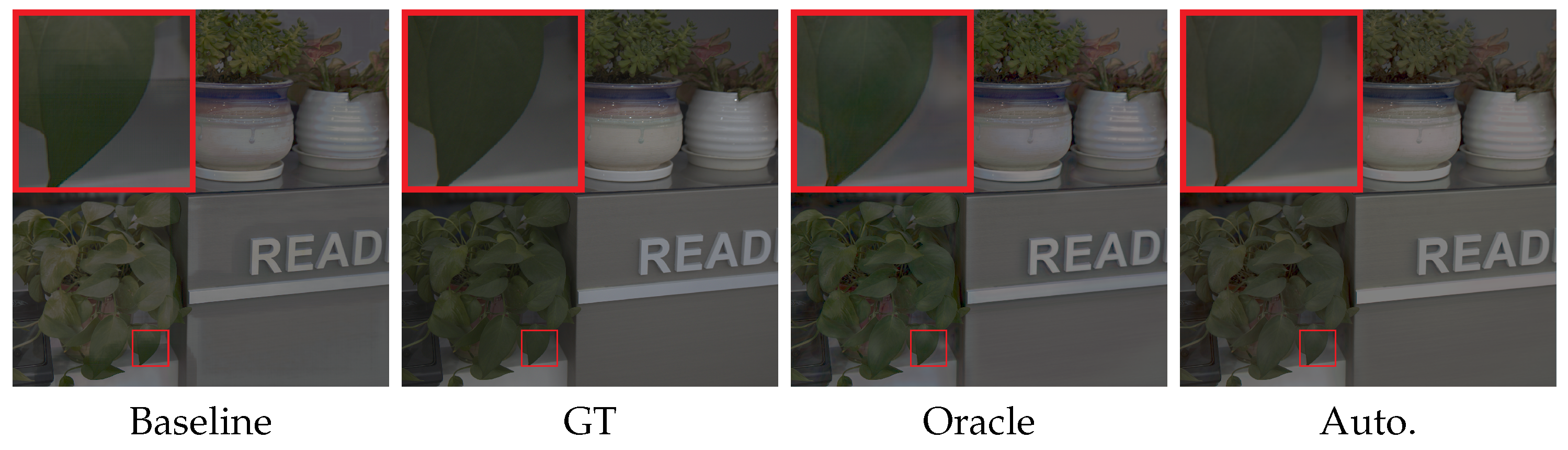




| Cases | Metrics | Zero-DCE | RUAS | MSEC | ECCM | ECLNet | IDFN | DGKD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [10] | [56] | [13] | [57] | [57] | [30] | (Ours) | ||
| Over | PSNR | 20.215 | 25.349 | 20.812 | 27.118 | 27.641 | 27.634 | 27.828 |
| SSIM | 0.8382 | 0.9243 | 0.8991 | 0.9371 | 0.9432 | 0.9402 | 0.9505 | |
| Under | PSNR | 15.830 | 19.231 | 20.038 | 20.334 | 20.674 | 21.057 | 21.479 |
| SSIM | 0.4103 | 0.6407 | 0.6507 | 0.6676 | 0.6788 | 0.6791 | 0.6859 | |
| Average | PSNR | 18.022 | 22.290 | 20.425 | 23.726 | 24.158 | 24.345 | 24.653 |
| SSIM | 0.6243 | 0.7825 | 0.7749 | 0.8024 | 0.8110 | 0.8097 | 0.8182 | |
| Inference Time (ms) | 2.92 | 14.64 | 5.77 | 14.83 | 18.54 | 9.25 | 9.18 | |
| Cases | Metrics | Baseline | +Color Guidance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oracle | Auto. | |||
| Over | PSNR | 27.009 | 27.867 | 27.828 |
| SSIM | 0.9367 | 0.9508 | 0.9505 | |
| Under | PSNR | 20.293 | 21.485 | 21.479 |
| SSIM | 0.6783 | 0.6862 | 0.6859 | |
| Average | PSNR | 23.651 | 24.676 | 24.653 |
| SSIM | 0.8075 | 0.8185 | 0.8182 | |
| Cases | Metrics | Separated | Unified | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| w/o KD | w/KD | |||
| Over | PSNR | 27.934 | 27.671 | 27.828 |
| SSIM | 0.9535 | 0.9431 | 0.9505 | |
| Under | PSNR | 21.618 | 21.125 | 21.479 |
| SSIM | 0.6897 | 0.6807 | 0.6859 | |
| Average | PSNR | 24.776 | 24.398 | 24.653 |
| SSIM | 0.8216 | 0.8119 | 0.8182 | |
| Cases | Metrics | S2S | R2S | R2R |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Over | PSNR | 23.589 | 27.542 | 27.828 |
| SSIM | 0.8834 | 0.9418 | 0.9505 | |
| Under | PSNR | 17.867 | 20.594 | 21.479 |
| SSIM | 0.6213 | 0.6808 | 0.6859 | |
| Average | PSNR | 20.728 | 24.068 | 24.653 |
| SSIM | 0.7524 | 0.8113 | 0.8182 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Zhang, T. Deep Guided Exposure Correction with Knowledge Distillation. Sensors 2025, 25, 7606. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25247606
Liu S, Zhang T. Deep Guided Exposure Correction with Knowledge Distillation. Sensors. 2025; 25(24):7606. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25247606
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Songrong, and Tao Zhang. 2025. "Deep Guided Exposure Correction with Knowledge Distillation" Sensors 25, no. 24: 7606. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25247606
APA StyleLiu, S., & Zhang, T. (2025). Deep Guided Exposure Correction with Knowledge Distillation. Sensors, 25(24), 7606. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25247606









