RAFF-AMACNet: Adaptive Multi-Rate Atrous Convolution Network with Residual Attentional Feature Fusion for Satellite Signal Recognition
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We design an adaptive multi-rate atrous convolution module with a set of preset dilation rates that adaptively selects and combines features from both global and local contexts to generate robust fused representations.
- A residual attentional feature fusion module based on a dual-attention collaborative mechanism is developed. This module utilizes a channel attention mechanism in the main branch to enhance feature map extraction, while concurrently applying an attentional feature fusion mechanism to integrate features from the skip branch, collaboratively optimizing and compensating for feature map shifts.
2. Related Works
2.1. Multi-Scale Neural Networks
2.2. Modulation Recognition for Satellite Signals
3. Proposed Methods
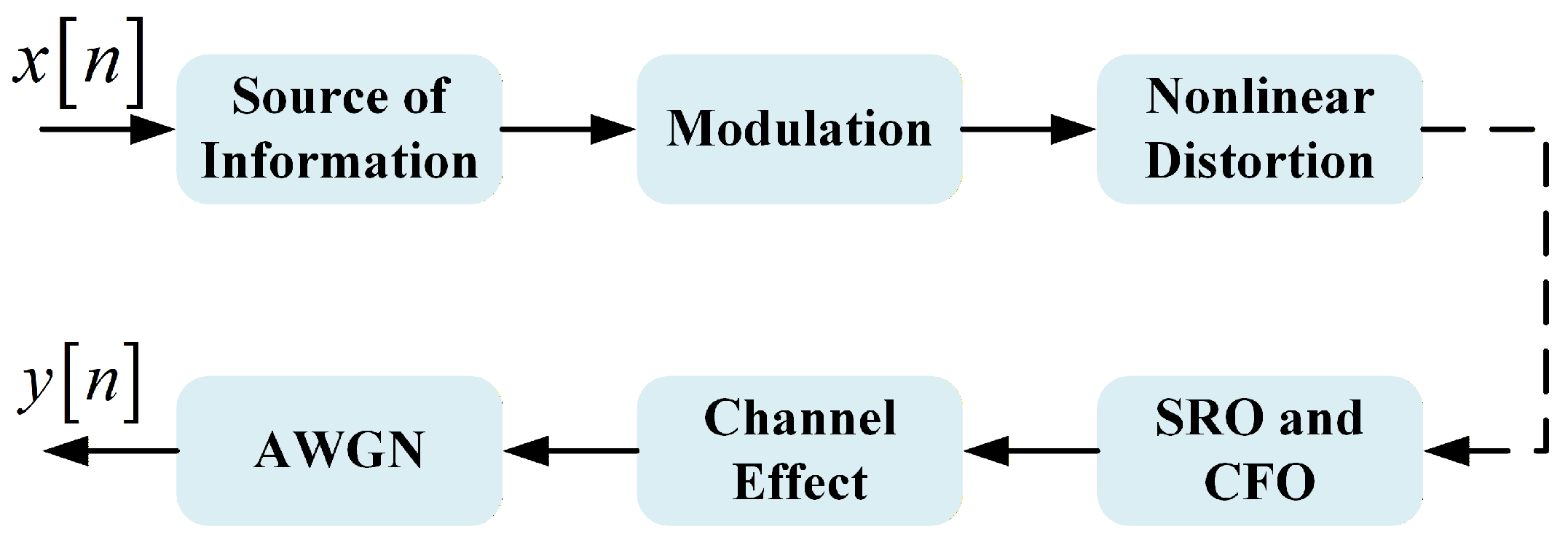
3.1. Signal Model
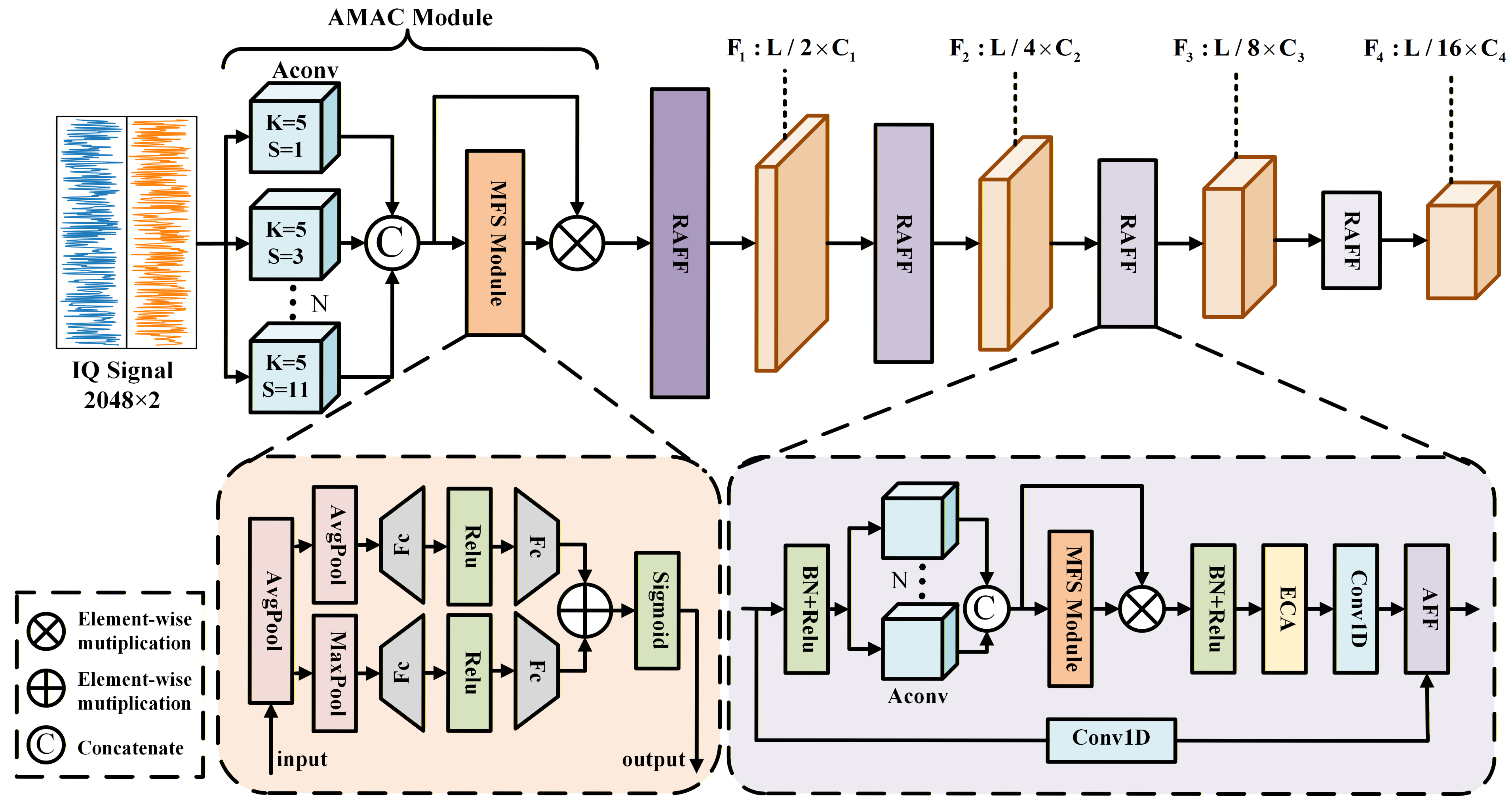
3.2. The Framework of RAFF-AMACNet
3.2.1. Adaptive Multi-Rate Atrous Convolution Module (AMAC)
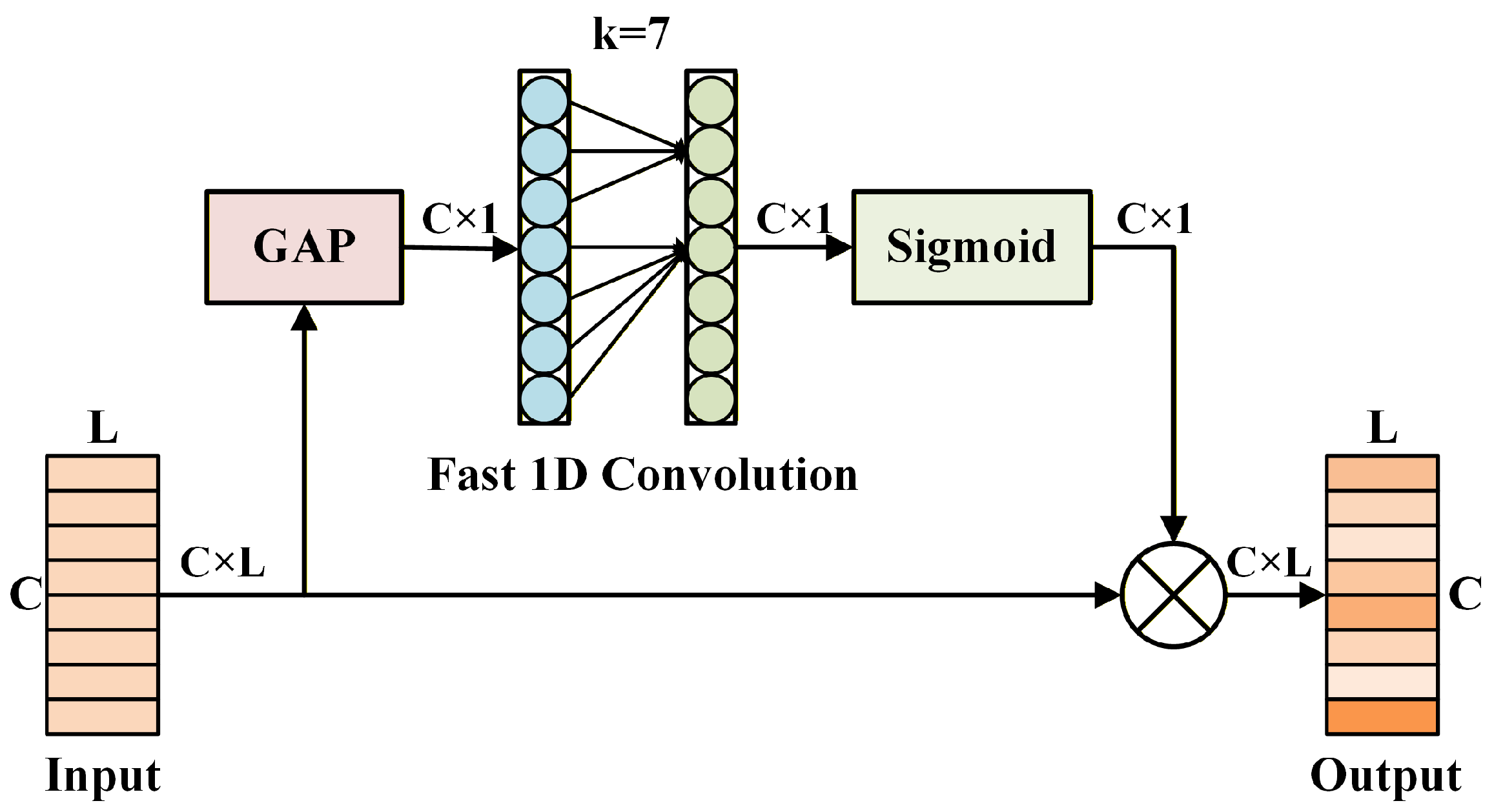
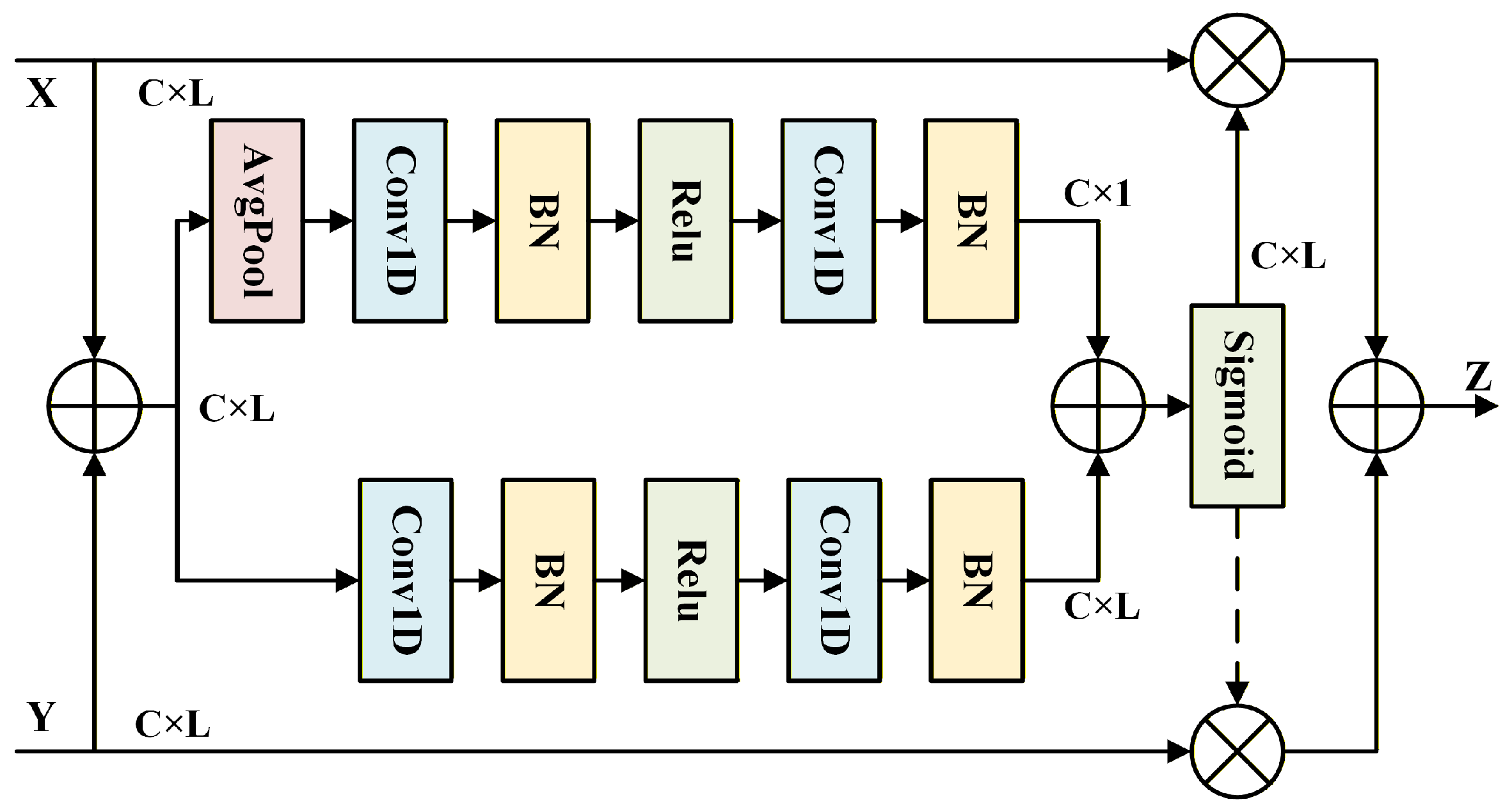
3.2.2. Residual Attentional Feature Fusion Module (RAFF)
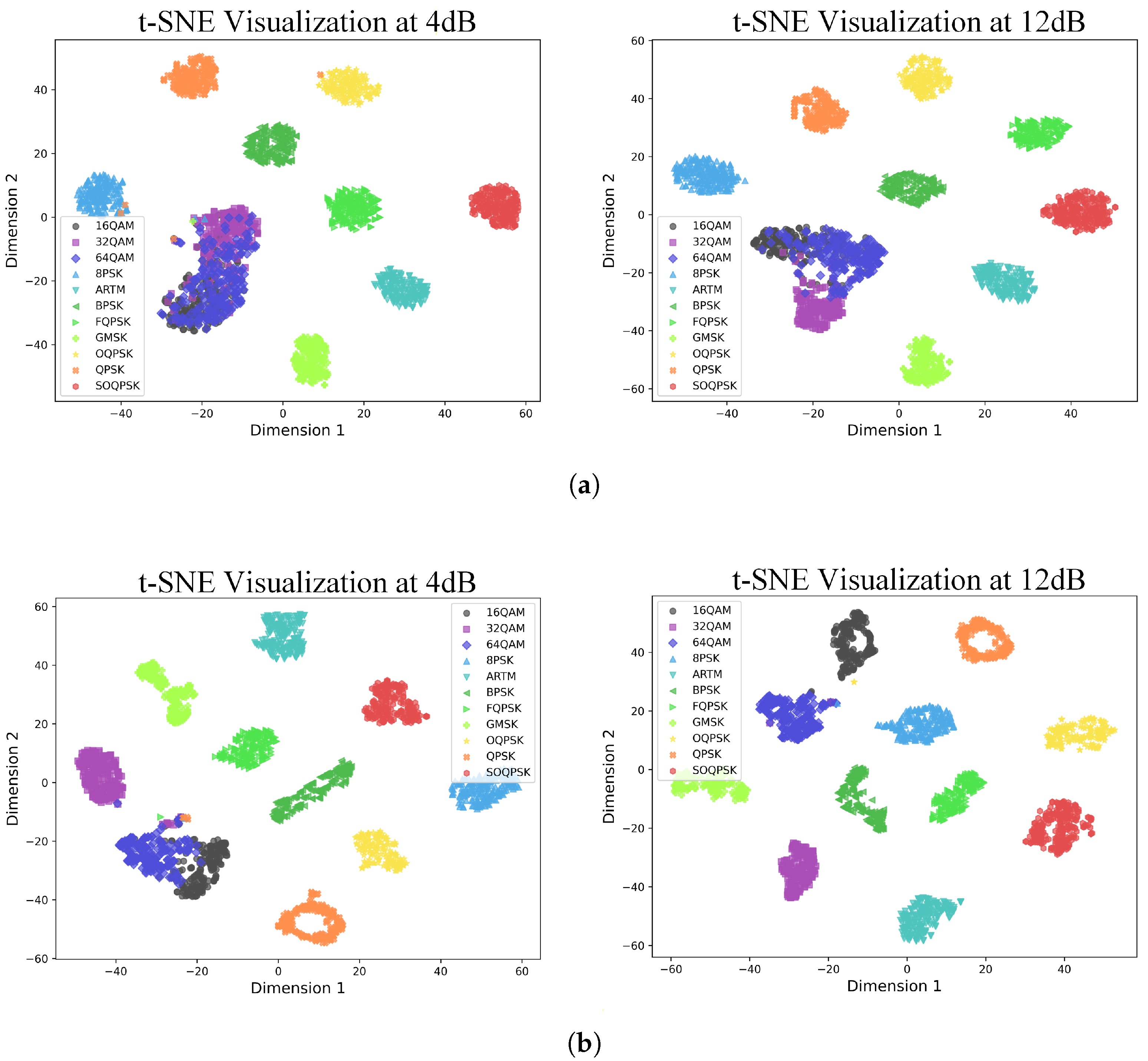
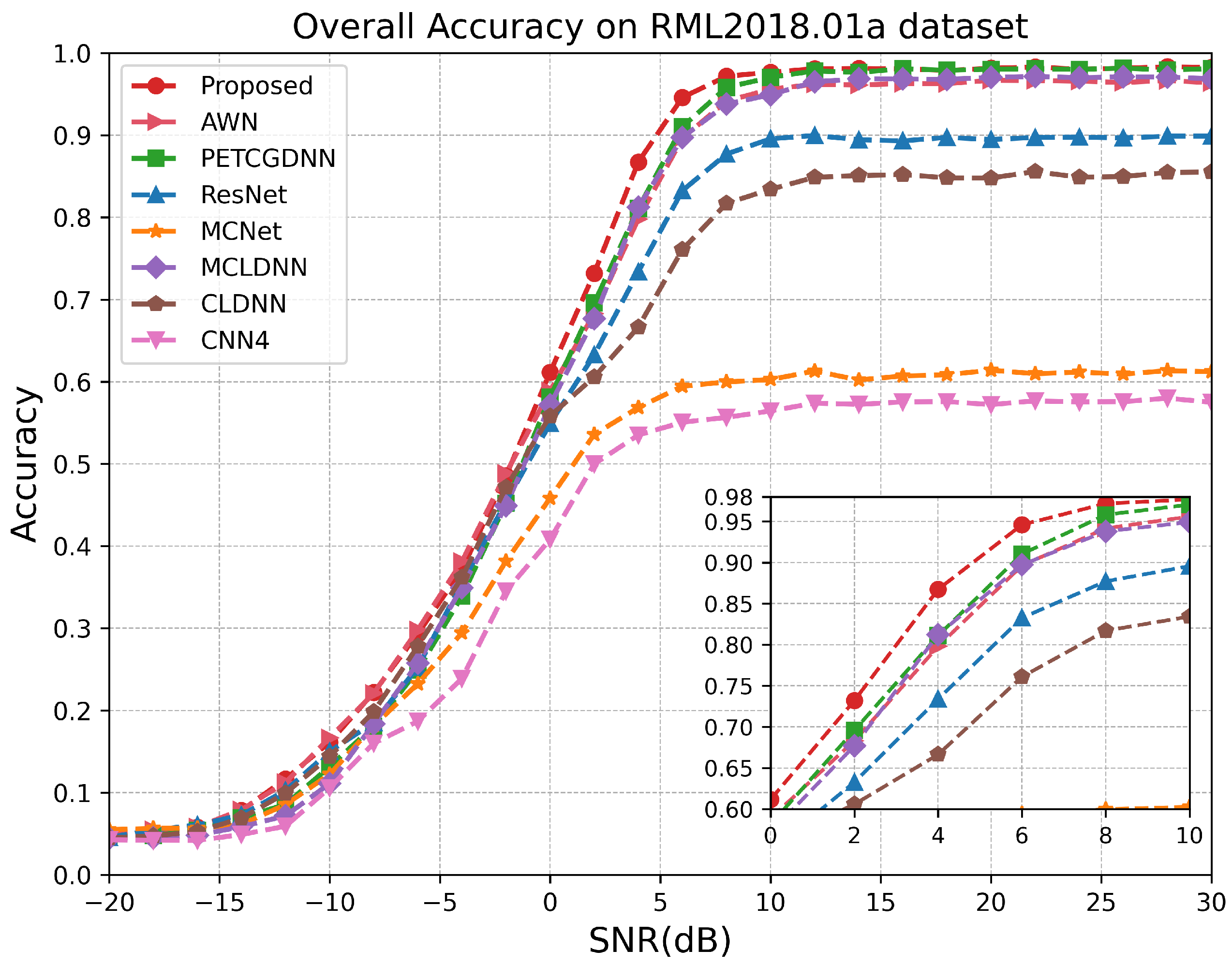
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
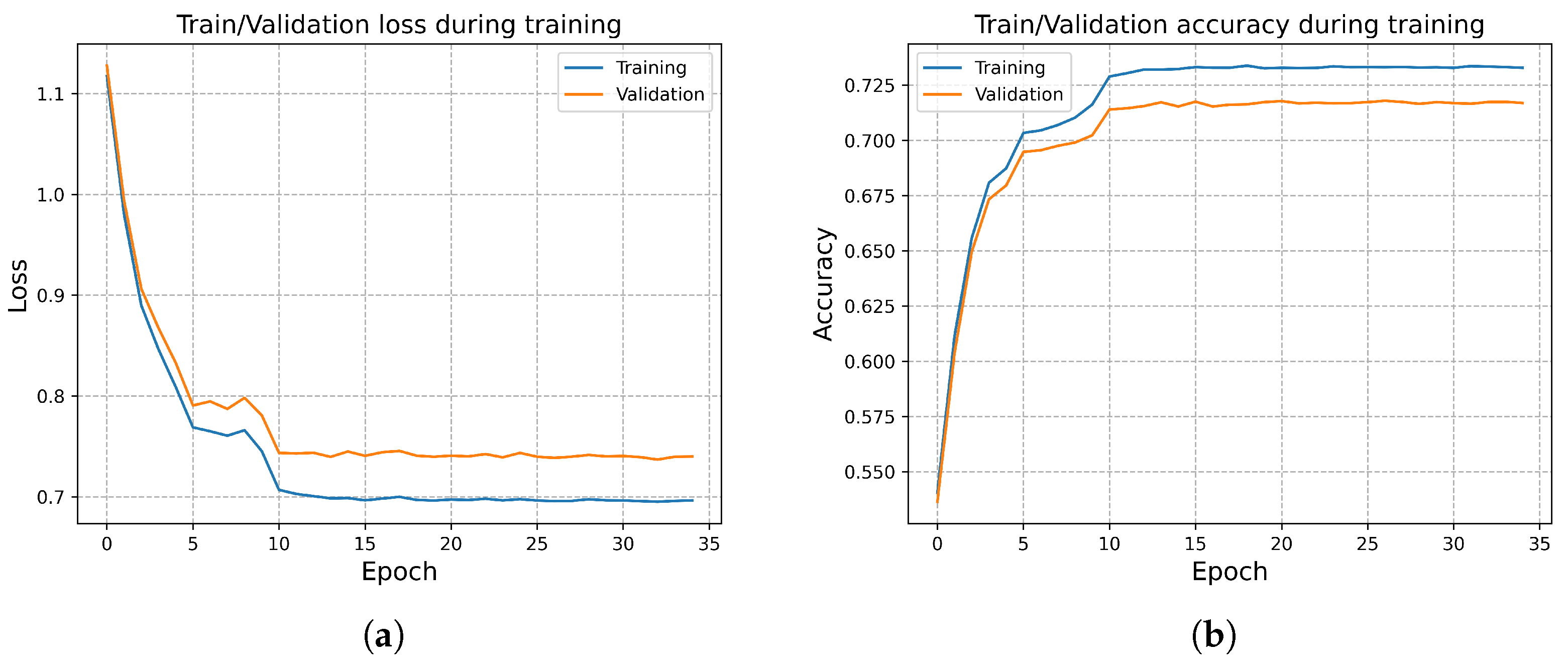
4.2. Experimental Setup
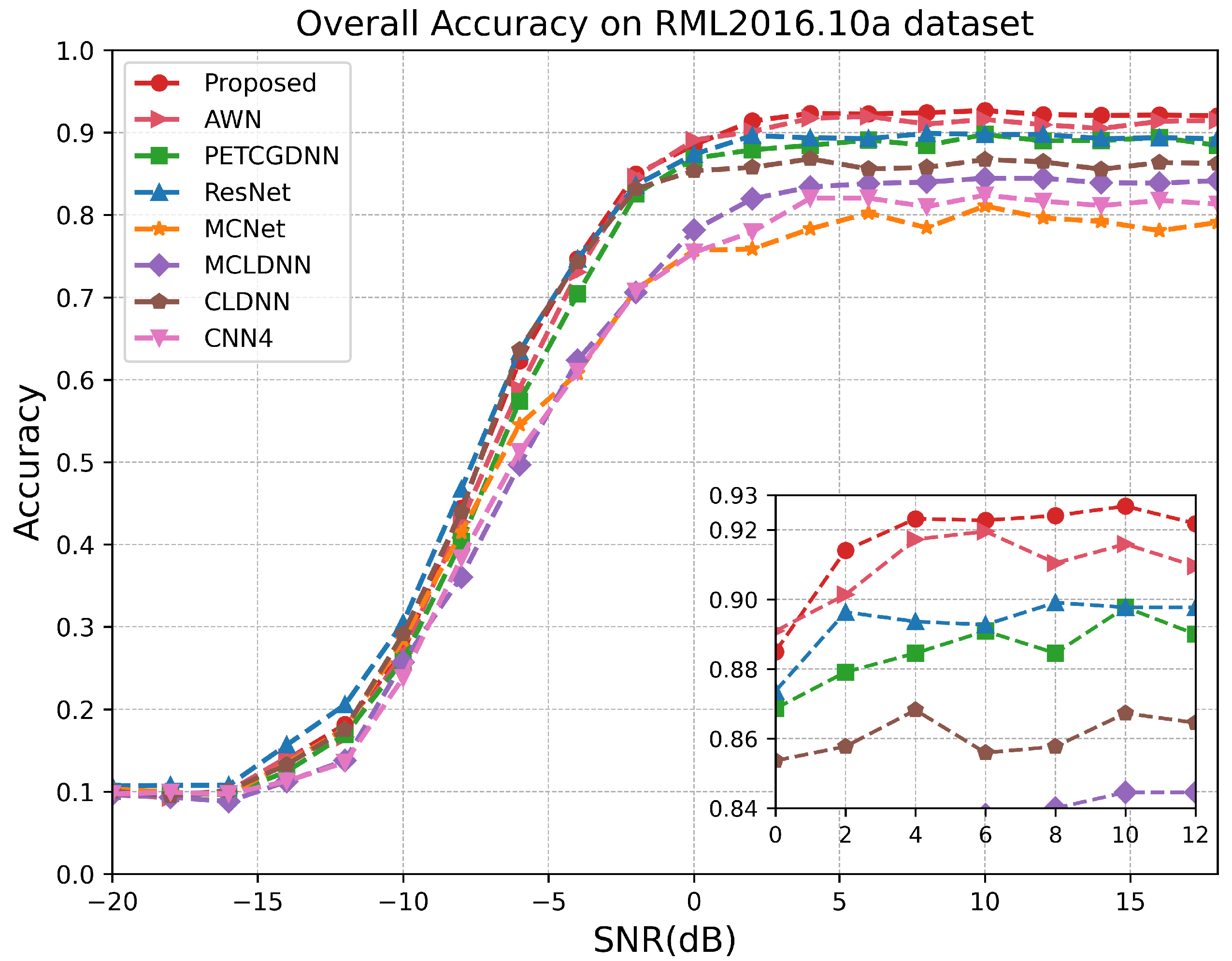
4.3. Comparisons with Other Methods
4.4. Ablation Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, M.; Park, S.; Lee, Y. A survey on satellite communication system security. Sensors 2024, 24, 2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Sun, S.; Kang, S. System integration of terrestrial mobile communication and satellite communication—The trends, challenges and key technologies in B5G and 6G. China Commun. 2021, 17, 156–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, L.J. Radiowave Propagation in Satellite Communications; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bazzi, A.; Bomfin, R.; Mezzavilla, M.; Rangan, S.; Rappaport, T.; Chafii, M. Upper mid-band spectrum for 6G: Vision, opportunity and challenges. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.17914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, K.; Masouros, C.; Petropulu, A.P.; Hanzo, L. Cooperative ISAC networks: Opportunities and challenges. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2024, 32, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navandar, R.K.; Ananthanarayanan, A.; Joshi, S.M.; Venu, N. Advanced Estimation and Feedback of Wireless Channels State Information for 6G Communication via Recurrent Conditional Wasserstein Generative Adversarial Network. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2025, 38, e70033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourati, F.; Alouini, M.S. Artificial intelligence for satellite communication: A review. Intell. Converg. Netw. 2021, 2, 213–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, F.; Dobre, O.A.; Popescu, D.C. On the likelihood-based approach to modulation classification. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2009, 8, 5884–5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazza, A.; Shoaib, M.; Alshebeili, S.A.; Fahad, A. An overview of feature-based methods for digital modulation classification. In Proceedings of the 2013 1st International Conference on Communications, Signal Processing, and Their Applications (ICCSPA), Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 12–14 February 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Fang, S.; Fan, Y.; Wang, M.; Ma, Z. A method of noise reduction for radio communication signal based on ragan. Sensors 2023, 23, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Shang, S.; Song, X.; Zhang, S.; You, T.; Zhang, L. Intelligent radar jamming recognition in open set environment based on deep learning networks. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III 18. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, G.; Yan, L. PCR: A parallel convolution residual network for traffic flow prediction. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. 2025, 9, 3072–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, D.; Lu, Y.; Deng, K.; Yuan, Z.; Huang, M.; Jiang, T. A mutual cross-attention fusion network for surface roughness prediction in robotic machining process using internal and external signals. J. Manuf. Syst. 2025, 82, 284–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, F.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Gao, E.; Cai, Y.; Zhou, X.; Li, C. A multi-scale enhanced feature fusion model for aircraft detection from SAR images. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2025, 18, 2507842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Xu, G.; Song, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W. Performance Analysis of LEO Satellite-assisted Deep Space Communication Systems. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2025, 61, 12628–12648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.; Park, H. Robust Symbol Timing Synchronization for Initial Access under LEO Satellite Channel. Sensors 2023, 23, 8320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, B.; Jung, H.; Lee, I.H. Survey on doppler characterization and compensation schemes in leo satellite communication systems. In Proceedings of the 2022 27th Asia Pacific Conference on Communications (APCC), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 19–21 October 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 637–638. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zang, B.; Ji, H.; Li, L.; Li, S.; Chen, L. Cognitive radio for satellite tt & c system: A general dataset using software-defined radio (rml24). TechRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Shea, T.J.; Corgan, J.; Clancy, T.C. Convolutional radio modulation recognition networks. In Proceedings of the Engineering Applications of Neural Networks: 17th International Conference, EANN 2016, Aberdeen, UK, 2–5 September 2016; Proceedings 17. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 213–226. [Google Scholar]
- O’Shea, T.J.; Roy, T.; Clancy, T.C. Over-the-air deep learning based radio signal classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2018, 12, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Luo, C.; Parr, G.; Luo, Y. A spatiotemporal multi-channel learning framework for automatic modulation recognition. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2020, 9, 1629–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; He, X.; Li, P.; Tian, T.; Cheng, X.; Qiao, M.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, B.; Chang, Z.; Fan, T. Multi-scale attention network for building extraction from high-resolution remote sensing images. Sensors 2024, 24, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, H.; Hao, J.; Tian, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, B. FADC: A High-Efficiency CNN-Based Deep Neural Network for Automatic Modulation Recognition. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=5682697 (accessed on 3 October 2025).
- Liu, X.; Song, Y.; Zhu, J.; Shu, F.; Qian, Y. An Efficient Deep Learning Model for Automatic Modulation Classification. Radioengineering 2024, 33, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh-The, T.; Hua, C.H.; Pham, Q.V.; Kim, D.S. MCNet: An efficient CNN architecture for robust automatic modulation classification. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 24, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, S. Double-Branch Multi-Scale Contextual Network: A Model for Multi-Scale Street Tree Segmentation in High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Sensors 2024, 24, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouldieff, V.; Palicot, J.; Daumont, S. Blind modulation classification for cognitive satellite in the spectral coexistence context. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 65, 3204–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Qiu, S.; Li, J. Modulation recognition method of satellite communication based on CLDNN model. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 30th International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), Kyoto, Japan, 20–23 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- An, Z.; Xu, Y.; Tahir, A.; Wang, J.; Ma, B.; Pedersen, G.F.; Shen, M. Collaborative Learning-Based Modulation Recognition for 6G Multibeam Satellite Communication Systems via Blind and Semiblind Channel Equalization. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024, 60, 5226–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Deep learning-based satellite signal modulation identification and doppler shift impact study. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication Security (ICSPCS 2024), Gold Coast, Australia, 16–18 December 2024; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2024; Volume 13222, pp. 174–181. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Ji, H.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y. Satellite Signal Recognition Based on Deep Approximate Representation Network. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Milan, Italy, 24–27 March 2025; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2025; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Y.; Lu, Z.; Zeng, R.; Wang, J.; Wang, J. Enhancing automatic modulation recognition through robust global feature extraction. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 74, 4192–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Koltun, V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.07122. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 11534–11542. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.; Gieseke, F.; Oehmcke, S.; Wu, Y.; Barnard, K. Attentional feature fusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Virtual, 5–9 January 2021; pp. 3560–3569. [Google Scholar]
- Tekbıyık, K.; Ekti, A.R.; Görçin, A.; Kurt, G.K.; Keçeci, C. Robust and fast automatic modulation classification with CNN under multipath fading channels. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 91st Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2020-Spring), Antwerp, Belgium, 25–28 May 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Yang, D.; El Gamal, A. Deep neural network architectures for modulation classification. In Proceedings of the 2017 51st Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 29 October–1 November 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 915–919. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Feng, Z.; Yang, S. Toward the automatic modulation classification with adaptive wavelet network. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2023, 9, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Luo, C.; Xu, J.; Luo, Y. An efficient deep learning model for automatic modulation recognition based on parameter estimation and transformation. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 3287–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Layer | Type | Detailed Parameters | Output Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Input | None | (B,2,2048) |
| 2 | AMAC | K = 5, S = 1, N = 6, C = 5 | (B,30,2048) |
| 3 | RAFF1 | (ECA):K = 7 (AFF):R = 2 | (B,30,1024) |
| 4 | RAFF2 | (B,60,512) | |
| 5 | RAFF3 | (B,60,256) | |
| 6 | RAFF4 | (B,60,128) | |
| 7 | GAP | None | (B,60,1) |
| 8 | Fc | Out Channel = 11 | (B,11) |
| Method | Dataset | Params (K) | FLOPs (M) | Inference Time (ms) | OA (%) | Macro-F1 (%) | Kappa (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN4 [41] | A * | 418.21 | 78.77 | 0.580 | 54.16 | 54.44 | 49.58 |
| B * | 811.43 | 155.12 | 0.520 | 38.92 | 39.72 | 36.27 | |
| C * | 1335.72 | 314.33 | 0.523 | 53.79 | 52.33 | 49.18 | |
| CLDNN [32] | A | 1323.78 | 65.57 | 0.420 | 59.00 | 60.52 | 54.90 |
| B | 7058.18 | 524.60 | 0.882 | 54.58 | 57.39 | 52.61 | |
| C | 13,611.78 | 1049.20 | 0.920 | 65.78 | 65.69 | 62.37 | |
| MCLDNN [25] | A | 406.19 | 49.09 | 0.240 | 56.25 | 56.25 | 51.88 |
| B | 406.19 | 402.39 | 0.243 | 61.94 | 63.08 | 60.29 | |
| C | 406.19 | 806.16 | 0.237 | 55.13 | 52.80 | 50.65 | |
| MCNet [29] | A | 184.97 | 1.41 | 0.460 | 53.84 | 55.08 | 49.23 |
| B | 184.97 | 11.24 | 0.480 | 41.18 | 38.65 | 38.63 | |
| C | 184.97 | 22.55 | 0.650 | 57.66 | 57.20 | 53.43 | |
| ResNet [42] | A | 3849.95 | 21.99 | 0.405 | 60.16 | 61.93 | 56.18 |
| B | 3849.95 | 175.92 | 0.432 | 57.75 | 57.75 | 55.92 | |
| C | 3849.95 | 351.83 | 0.480 | 63.74 | 63.23 | 60.12 | |
| PETCGDNN [44] | A | 72.07 | 9.33 | 0.014 | 59.80 | 62.19 | 55.78 |
| B | 74.95 | 71.92 | 0.038 | 63.00 | 63.27 | 61.35 | |
| C | 75.91 | 149.28 | 0.043 | 63.89 | 63.61 | 60.28 | |
| AWN [43] | A | 124.04 | 12.11 | 0.391 | 61.83 | 64.15 | 58.01 |
| B | 376.71 | 140.03 | 0.468 | 62.43 | 62.41 | 60.76 | |
| C | 376.71 | 279.36 | 0.507 | 64.87 | 64.76 | 61.36 | |
| RAFF-AMACNet | A | 123.06 | 6.87 | 0.109 | 62.51 | 64.86 | 58.76 |
| B | 123.06 | 54.71 | 0.144 | 63.90 | 63.98 | 62.33 | |
| C | 123.06 | 109.39 | 0.146 | 71.74 | 71.55 | 68.91 |
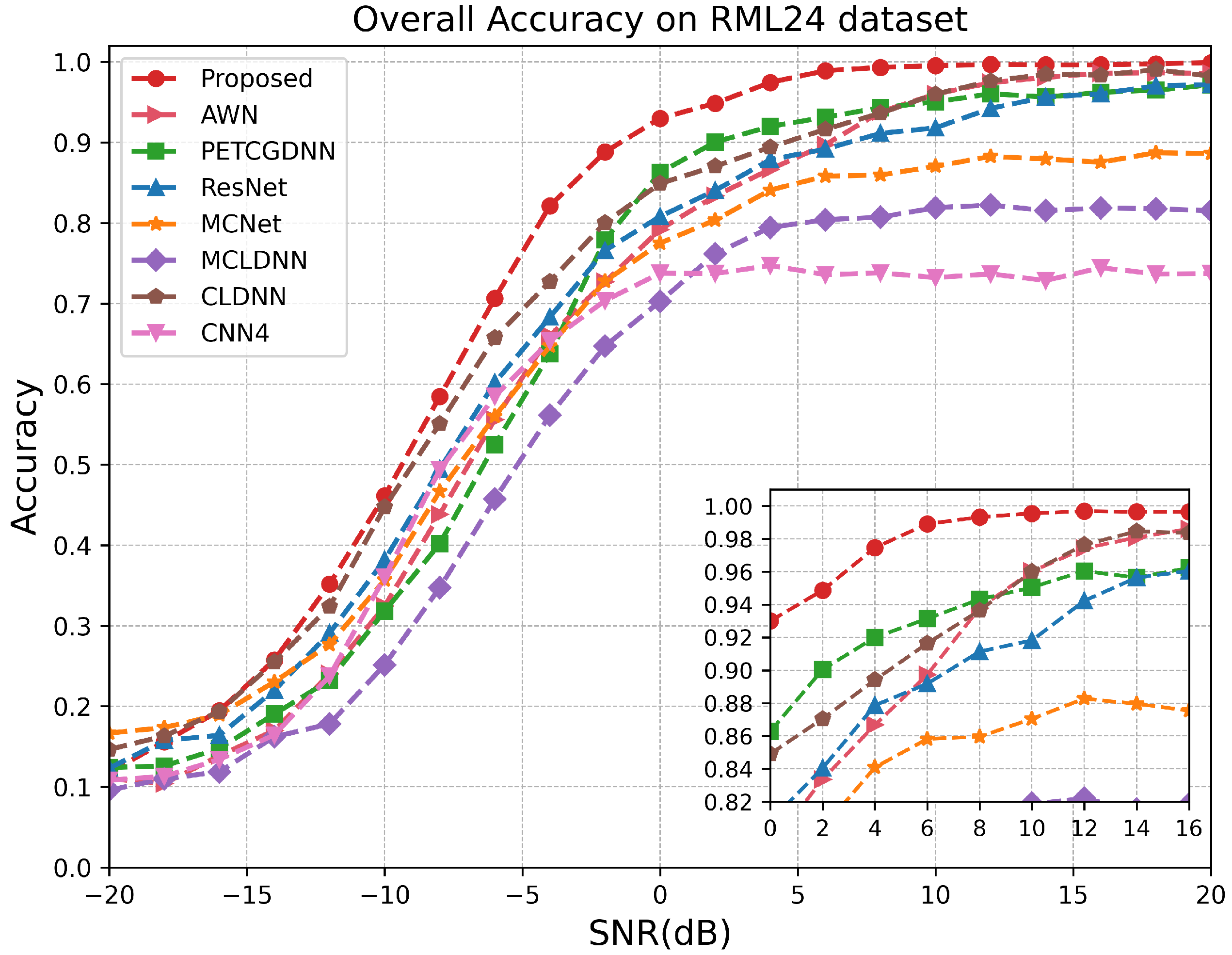
| Method | −18 dB | −12 dB | −6 dB | 0 dB | 6 dB | 12 dB | 18 dB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN4 | 11.31 | 23.77 | 58.50 | 73.77 | 73.59 | 73.68 | 73.68 |
| CLDNN | 16.31 | 32.36 | 65.77 | 84.90 | 91.63 | 97.63 | 99.04 |
| MCLDNN | 11.00 | 17.81 | 45.72 | 70.27 | 80.40 | 82.22 | 82.77 |
| MCNet | 17.36 | 27.68 | 55.99 | 77.49 | 85.81 | 88.27 | 88.72 |
| ResNet | 15.77 | 29.09 | 60.18 | 80.81 | 89.18 | 94.22 | 97.04 |
| PETCGDNN | 12.59 | 23.22 | 52.45 | 86.27 | 93.13 | 96.04 | 96.50 |
| AWN | 10.41 | 24.02 | 55.61 | 79.19 | 89.72 | 97.41 | 98.66 |
| RAFF-AMACNet | 15.59 | 35.18 | 70.63 | 92.99 | 98.90 | 99.68 | 99.77 |
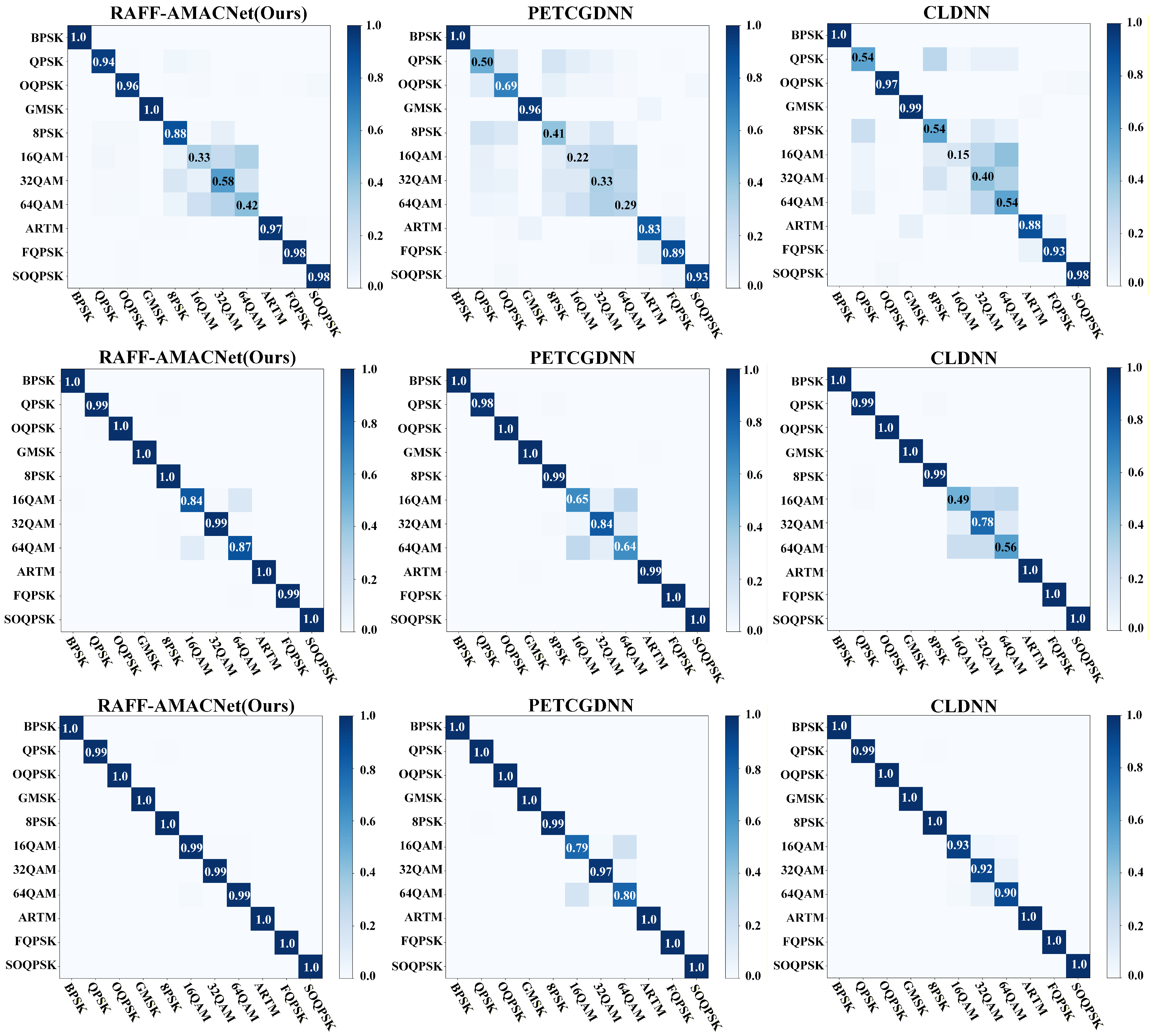
| Class | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | Macro-F1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BPSK | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| QPSK | 92.71 | 94.17 | 93.44 |
| OQPSK | 93.84 | 95.65 | 94.73 |
| 8PSK | 72.00 | 87.56 | 79.02 |
| GMSK | 99.55 | 1.00 | 99.78 |
| 16QAM | 51.09 | 33.01 | 40.11 |
| 32QAM | 45.26 | 57.59 | 50.69 |
| 64QAM | 47.97 | 42.41 | 45.02 |
| SOQPSK-TG | 97.39 | 98.42 | 97.90 |
| FQPSK | 97.87 | 98.39 | 98.13 |
| ARTM | 98.42 | 97.41 | 97.91 |
| Model | AMAC (w/o MFS) | AMAC (w/ MFS) | RAFF (ECA) | RAFF (AFF) | Params (K) | FLOPs (M) | Inference Time (ms) | OA (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 96.91 | 99.54 | 0.088 | 66.51 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | 97.75 | 99.55 | 0.109 | 68.18 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | 97.78 | 99.89 | 0.122 | 68.26 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | 123.04 | 109.05 | 0.137 | 68.69 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 123.06 | 109.39 | 0.146 | 71.74 |
| Number of Layers | Params (K) | FLOPs (M) | OA (%) | Macro-F1 | Kappa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11.39 | 30.47 | 55.20 | 53.50 | 50.73 |
| 2 | 41.59 | 66.79 | 67.87 | 67.66 | 64.66 |
| 3 | 82.33 | 95.19 | 70.14 | 69.88 | 67.15 |
| 4 | 123.06 | 109.39 | 71.74 | 71.55 | 68.91 |
| 5 | 163.80 | 116.50 | 69.50 | 69.41 | 66.45 |
| Channels | Params (K) | FLOPs (M) | OA (%) | Macro-F1 | Kappa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (30,30,30,30) | 43.05 | 55.96 | 68.43 | 68.22 | 65.28 |
| (30,30,30,60) | 62.71 | 61.41 | 67.51 | 67.21 | 64.27 |
| (30,30,60,60) | 92.89 | 77.41 | 69.06 | 68.92 | 65.97 |
| (30,60,60,60) | 123.06 | 109.39 | 71.74 | 71.55 | 68.91 |
| (60,60,60,60) | 153.25 | 173.36 | 69.51 | 69.26 | 66.46 |
| N/Dilation Rate | Params (K) | FLOPs (M) | OA (%) | Macro-F1 | Kappa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2/(1,3) | 14.68 | 13.31 | 62.35 | 64.51 | 58.59 |
| 4/(1,3,5,7) | 55.69 | 49.78 | 68.51 | 68.27 | 65.37 |
| 6/(1,3,5,7,9,11) | 123.06 | 109.39 | 71.74 | 71.55 | 68.91 |
| 8/(1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15) | 216.79 | 192.15 | 69.30 | 69.15 | 66.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Zang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Wei, H.; Liu, X.; Wu, M. RAFF-AMACNet: Adaptive Multi-Rate Atrous Convolution Network with Residual Attentional Feature Fusion for Satellite Signal Recognition. Sensors 2025, 25, 7514. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25247514
Chen L, Zang B, Zhang Y, Li L, Wei H, Liu X, Wu M. RAFF-AMACNet: Adaptive Multi-Rate Atrous Convolution Network with Residual Attentional Feature Fusion for Satellite Signal Recognition. Sensors. 2025; 25(24):7514. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25247514
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Leyan, Bo Zang, Yi Zhang, Lin Li, Haitao Wei, Xudong Liu, and Meng Wu. 2025. "RAFF-AMACNet: Adaptive Multi-Rate Atrous Convolution Network with Residual Attentional Feature Fusion for Satellite Signal Recognition" Sensors 25, no. 24: 7514. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25247514
APA StyleChen, L., Zang, B., Zhang, Y., Li, L., Wei, H., Liu, X., & Wu, M. (2025). RAFF-AMACNet: Adaptive Multi-Rate Atrous Convolution Network with Residual Attentional Feature Fusion for Satellite Signal Recognition. Sensors, 25(24), 7514. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25247514







