Underground Ferromagnetic Pipeline Detection Using a Rotable Magnetic Sensor Array
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
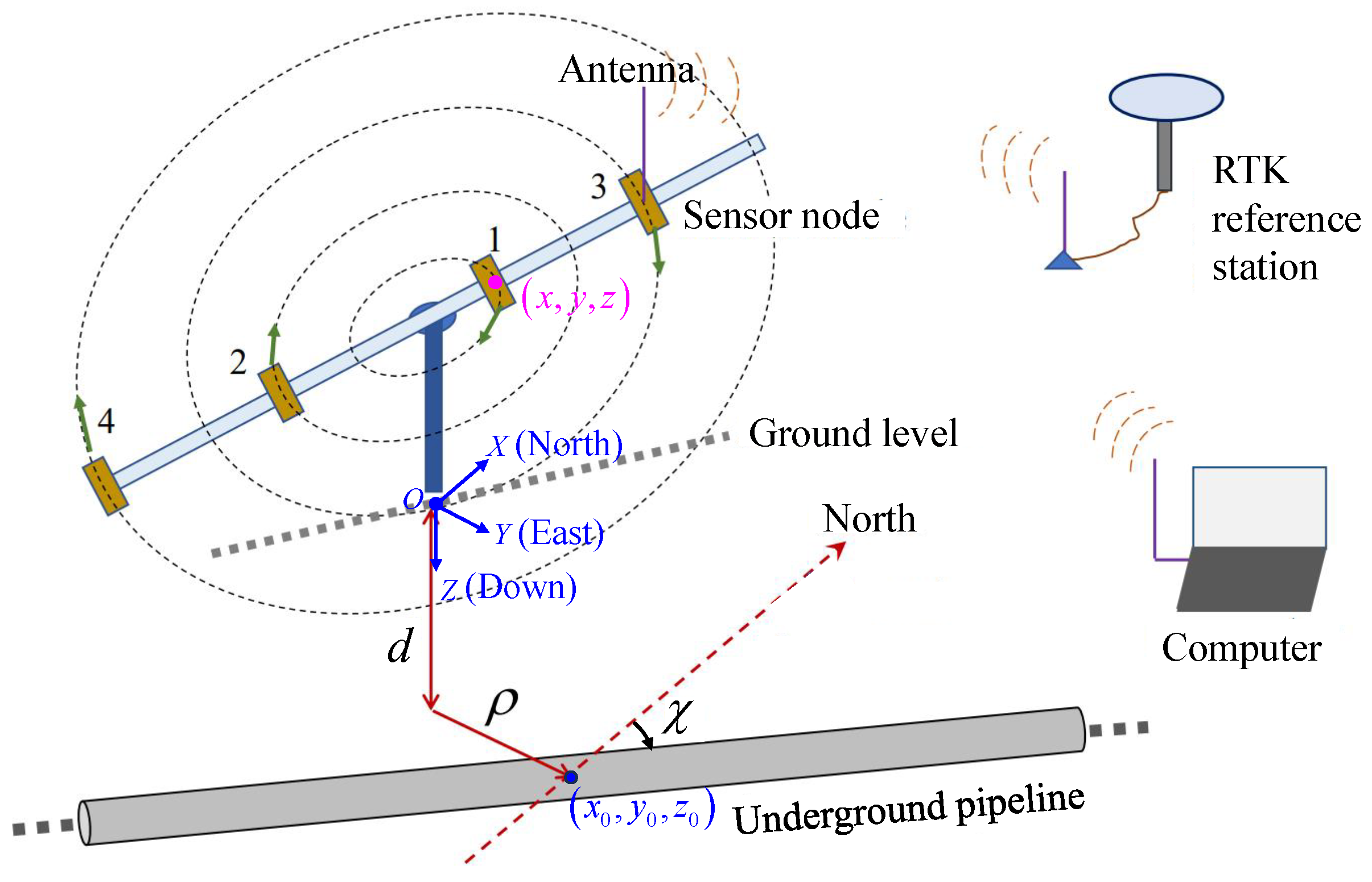
- Integration of sensor nodes: Each node can in real time collect the magnetic field at the node place, as well as the position and attitude information of the node, and wirelessly transmit all collected data to a working laptop.
- (2)
- Rotating scanning mode: Instead of the commonly used row or line scanning mode, we adopted rotating scanning, which is much more efficient to probe a specified area and applies to uneven or muddy ground.
- (3)
- Simple localization method: We did not need complex forward modeling or accurate measured values but simply inspected the periodic variations of measured data to obtain the horizontal offset and strike angle, which was very fast and robust.
2. Methodology
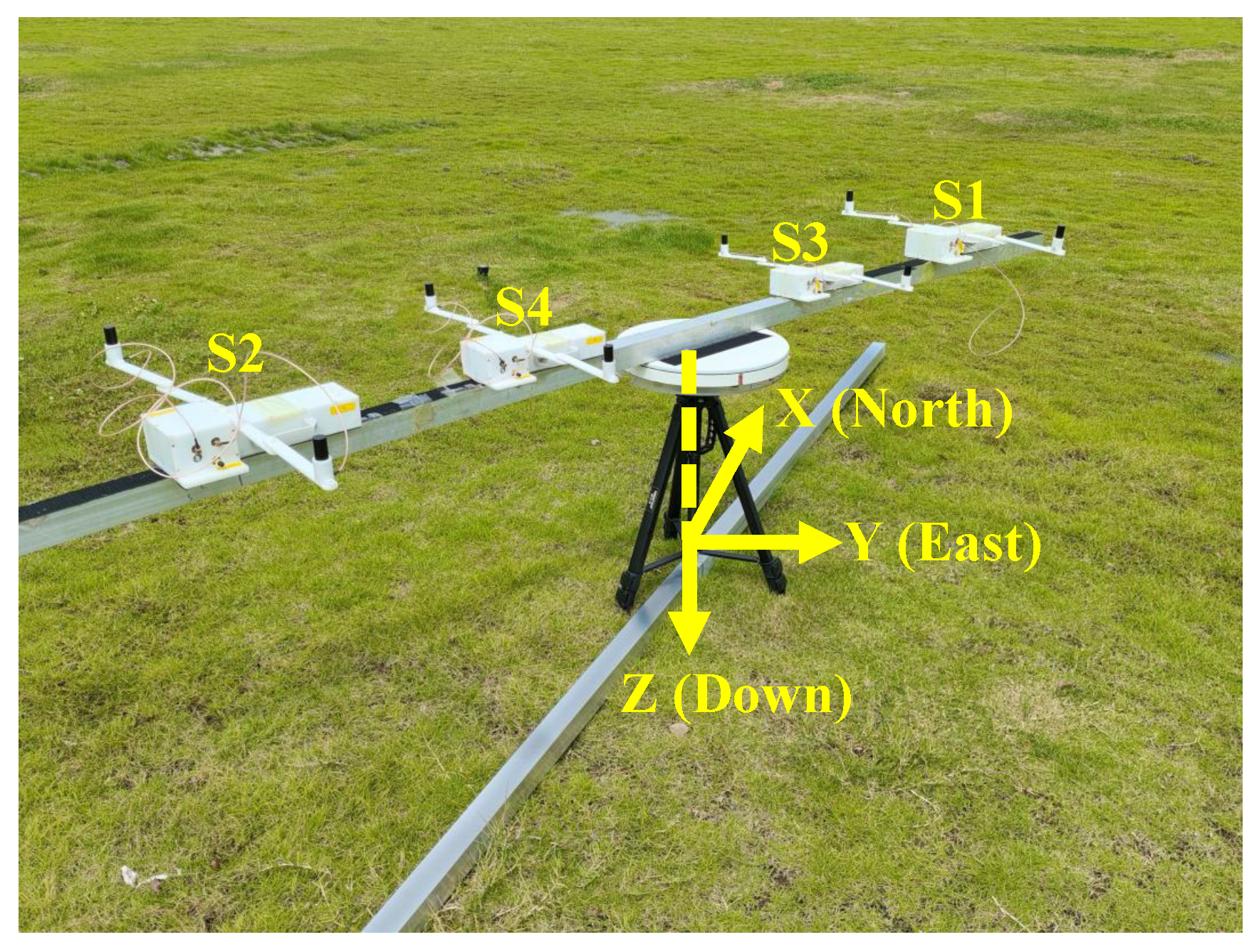
2.1. Composition of Measurement System
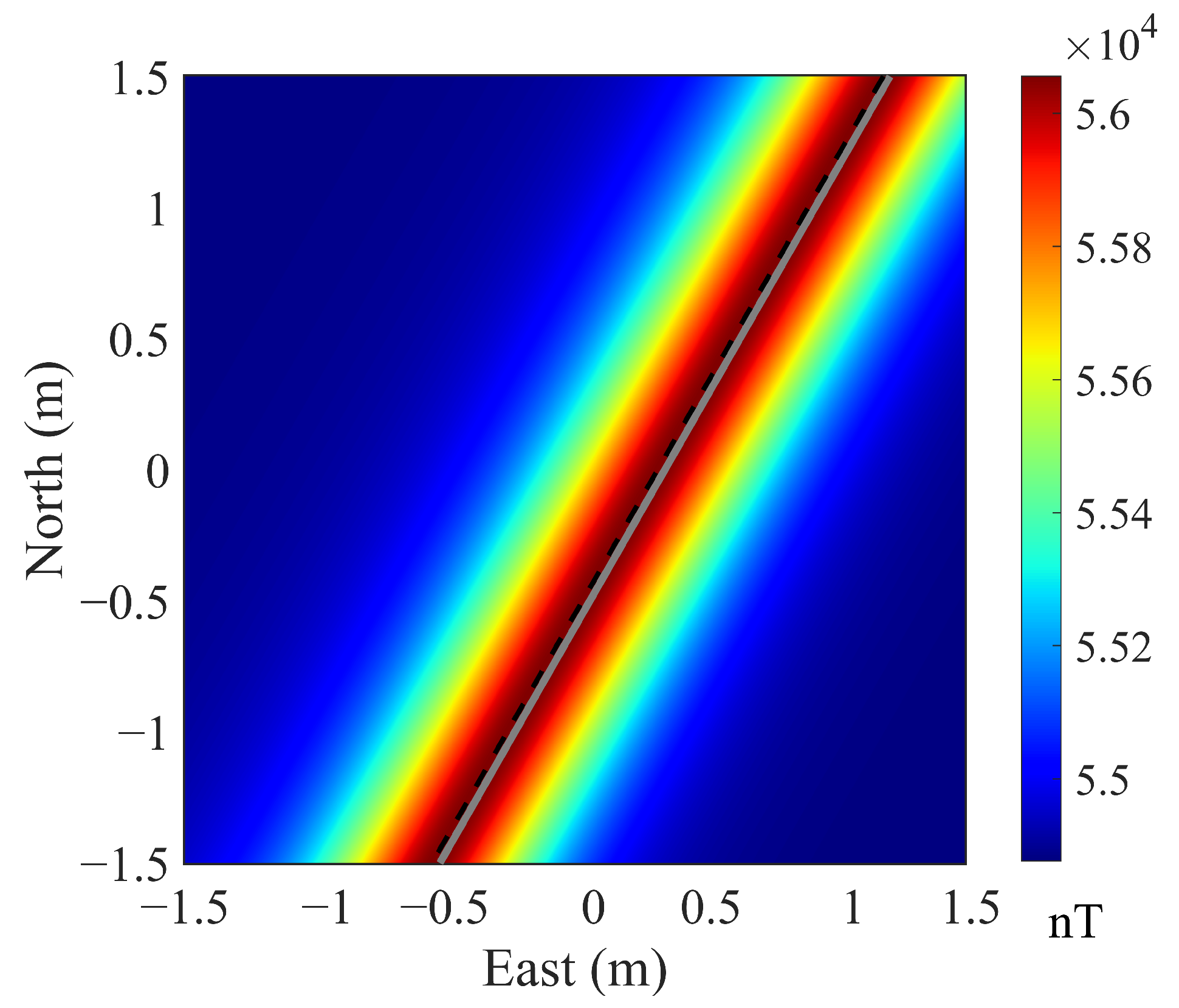
2.2. Theoretical Analysis of Pipeline Magnetic Anomalies
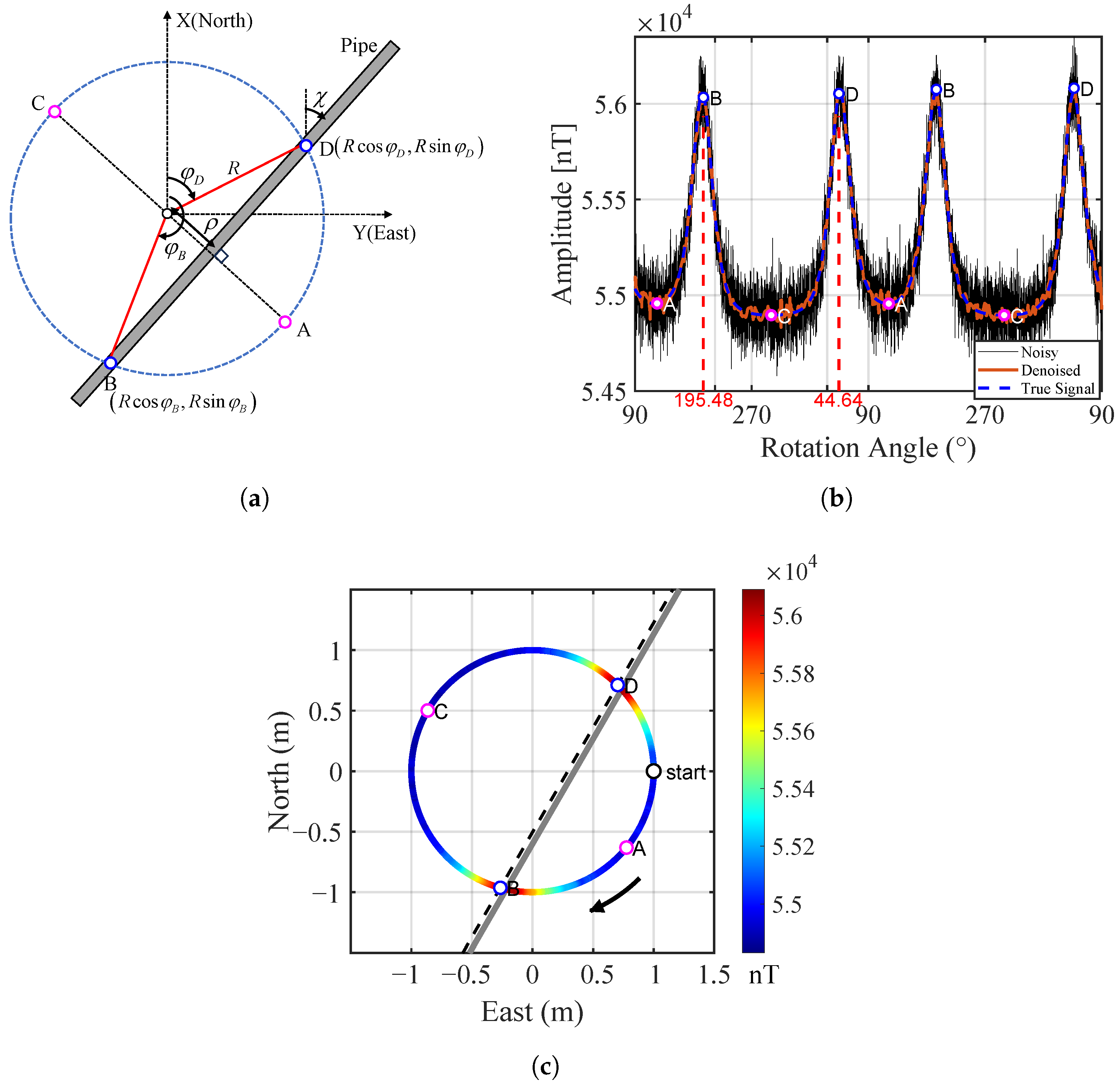
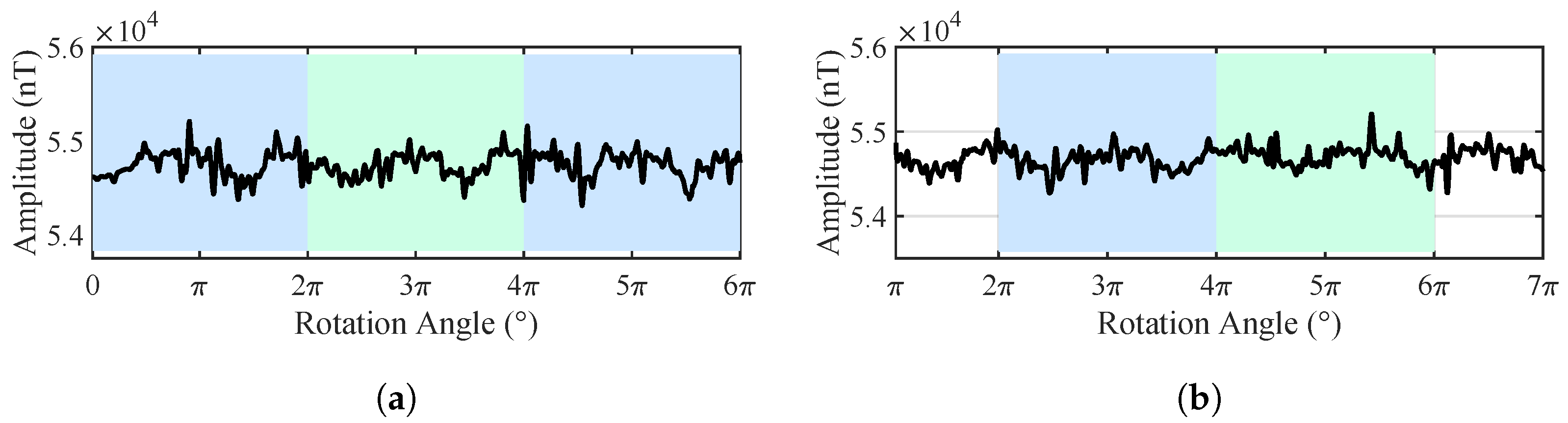
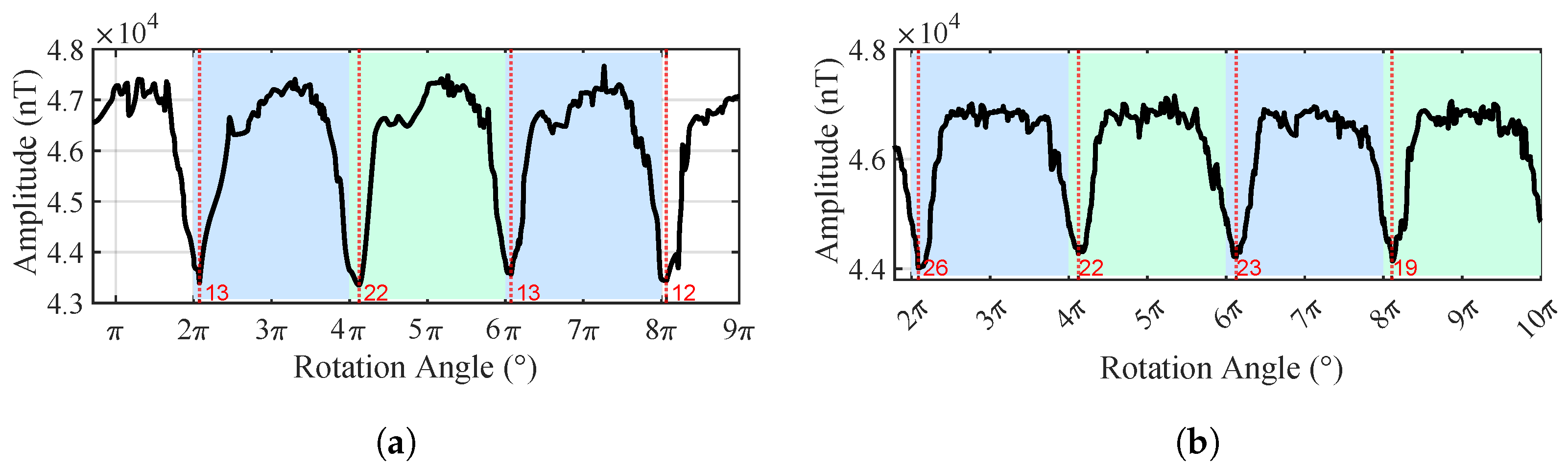
2.3. Rotating Scanning Measurement
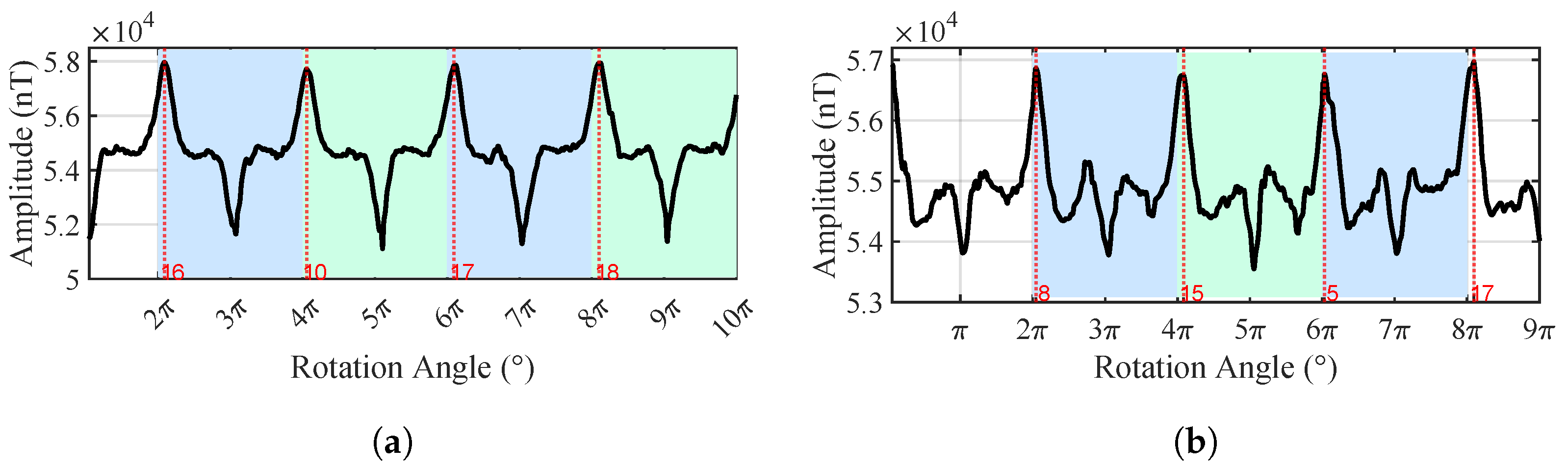
2.4. Estimate of Pipeline Location and Strike Angle
2.4.1. Horizontal Placement Estimation
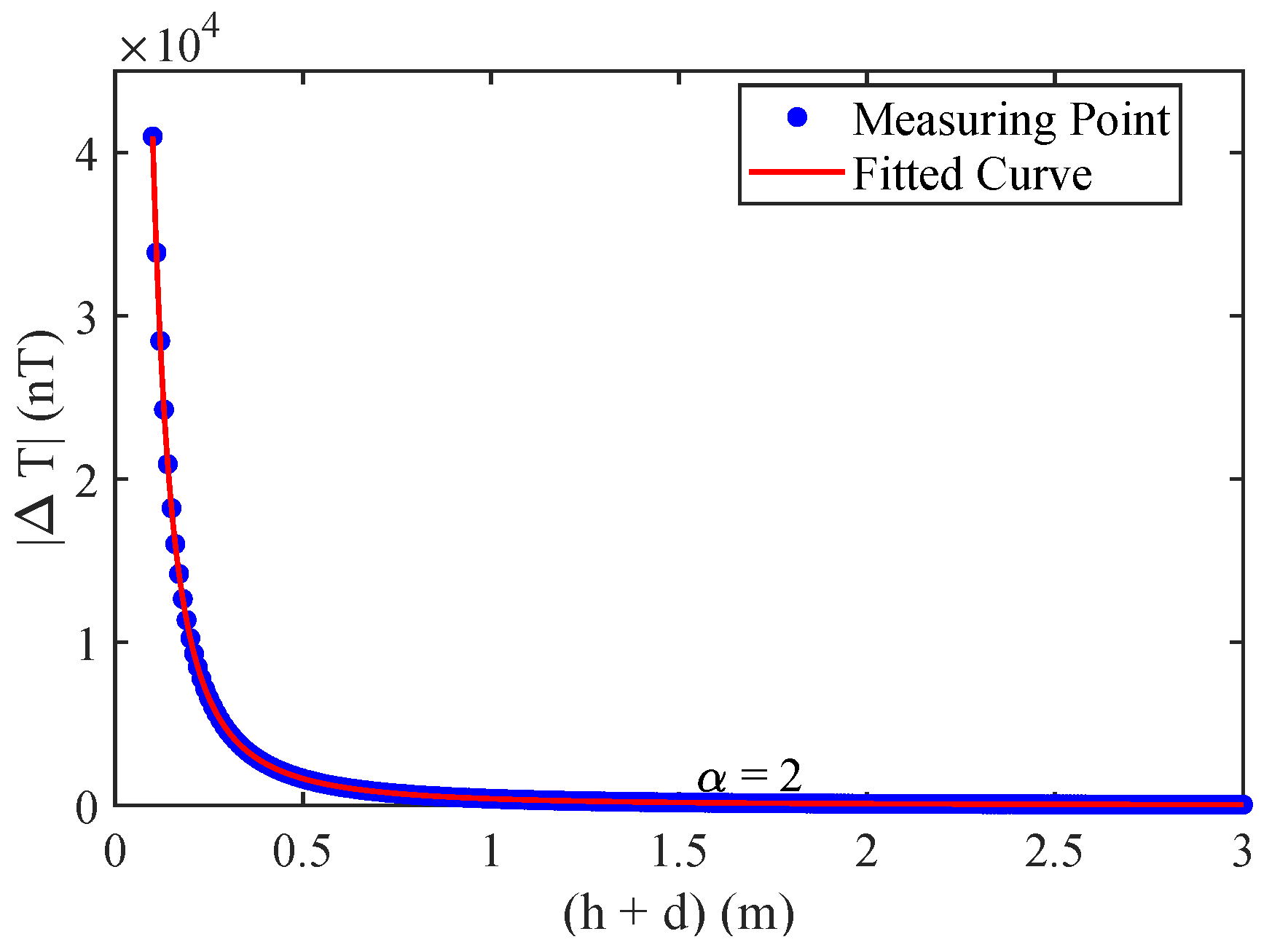
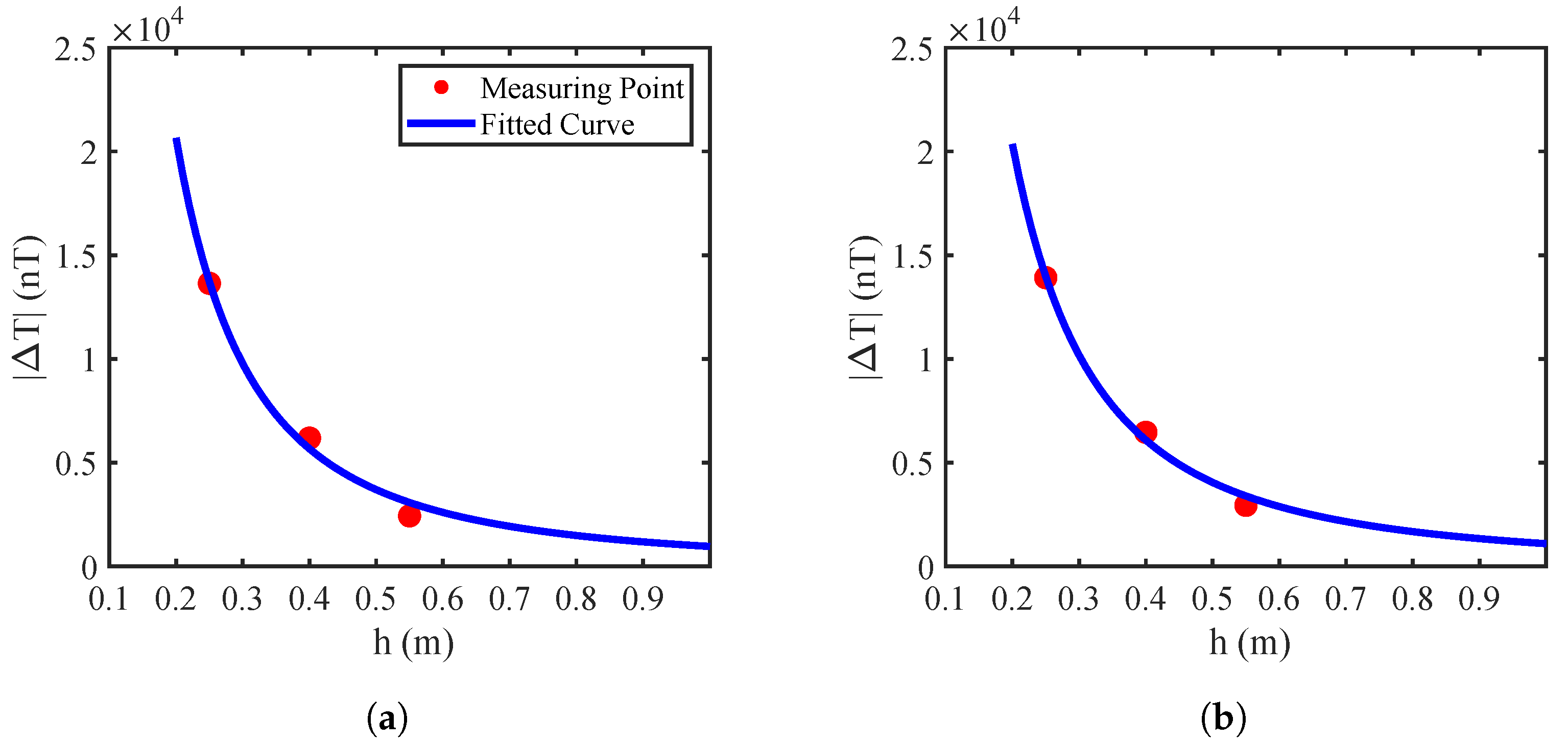
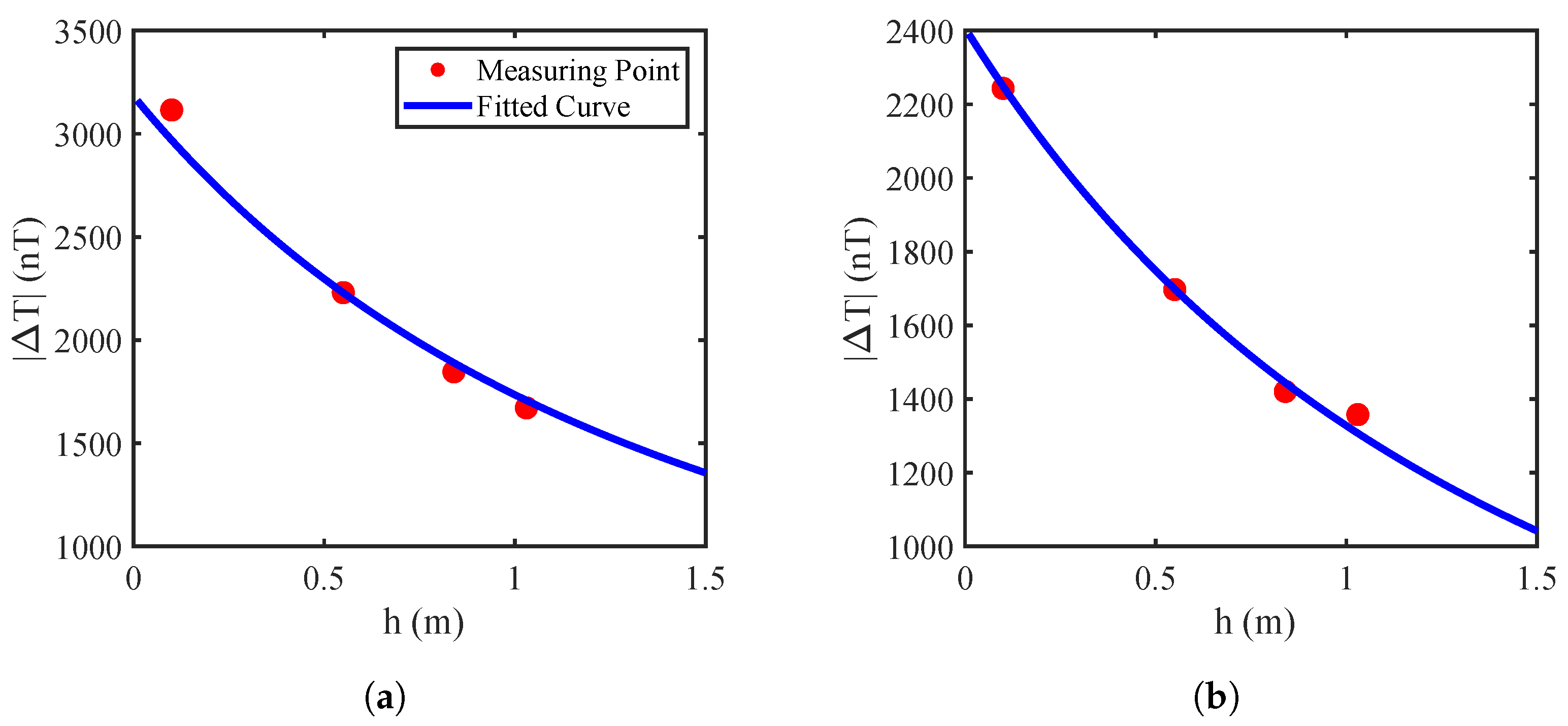
2.4.2. Buried Depth Estimation
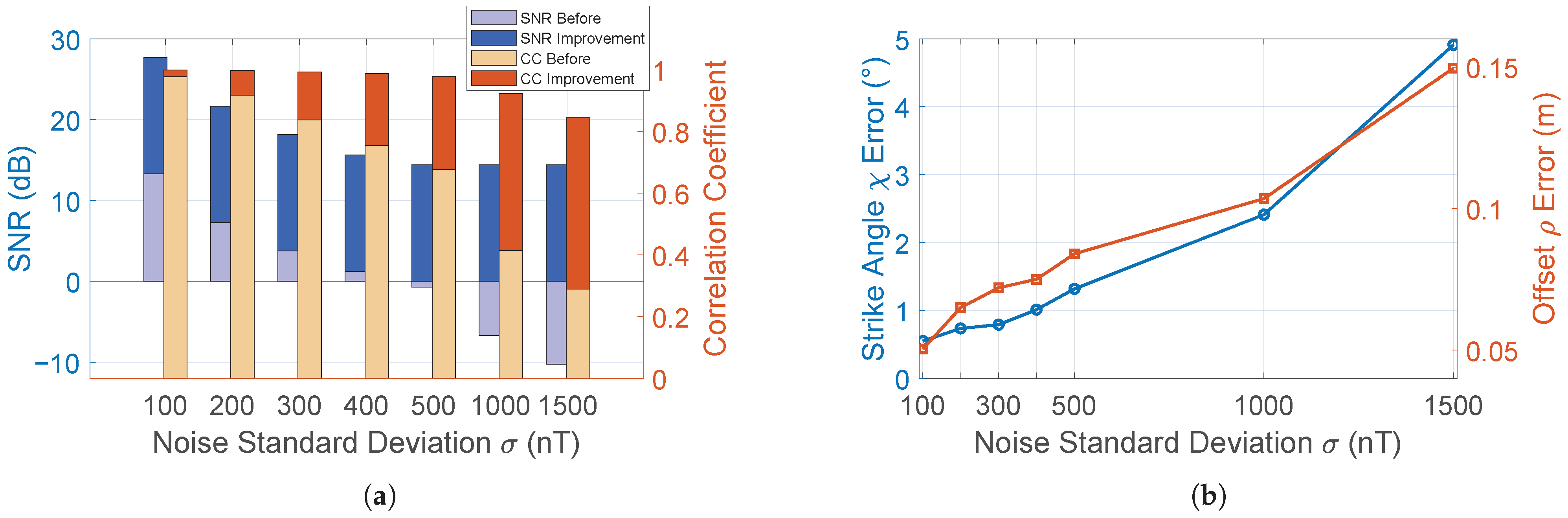
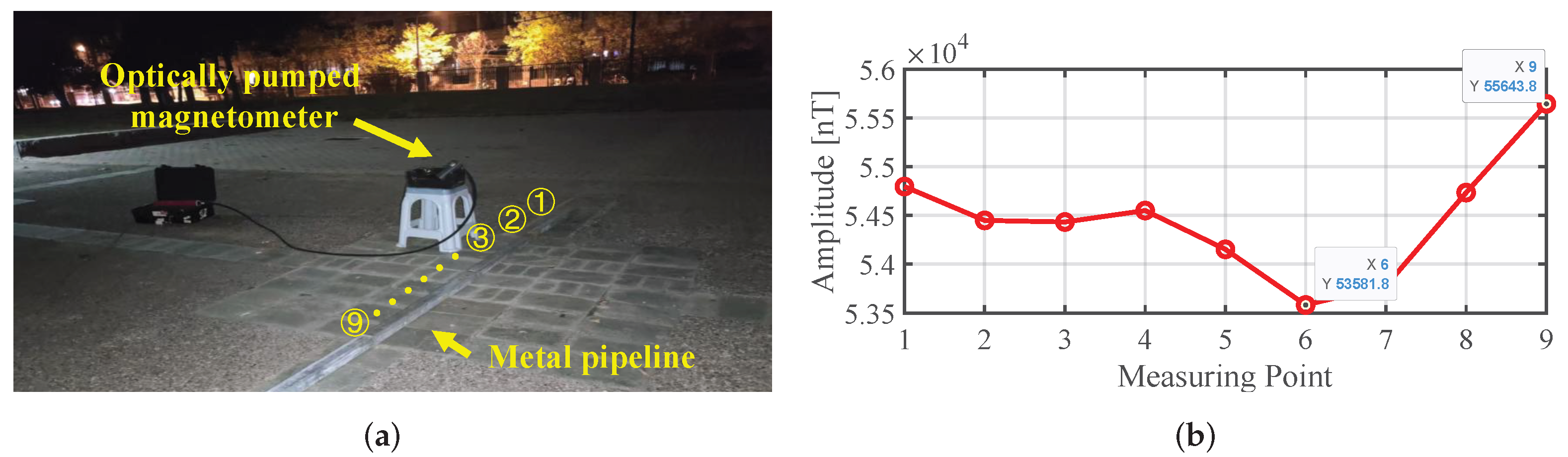
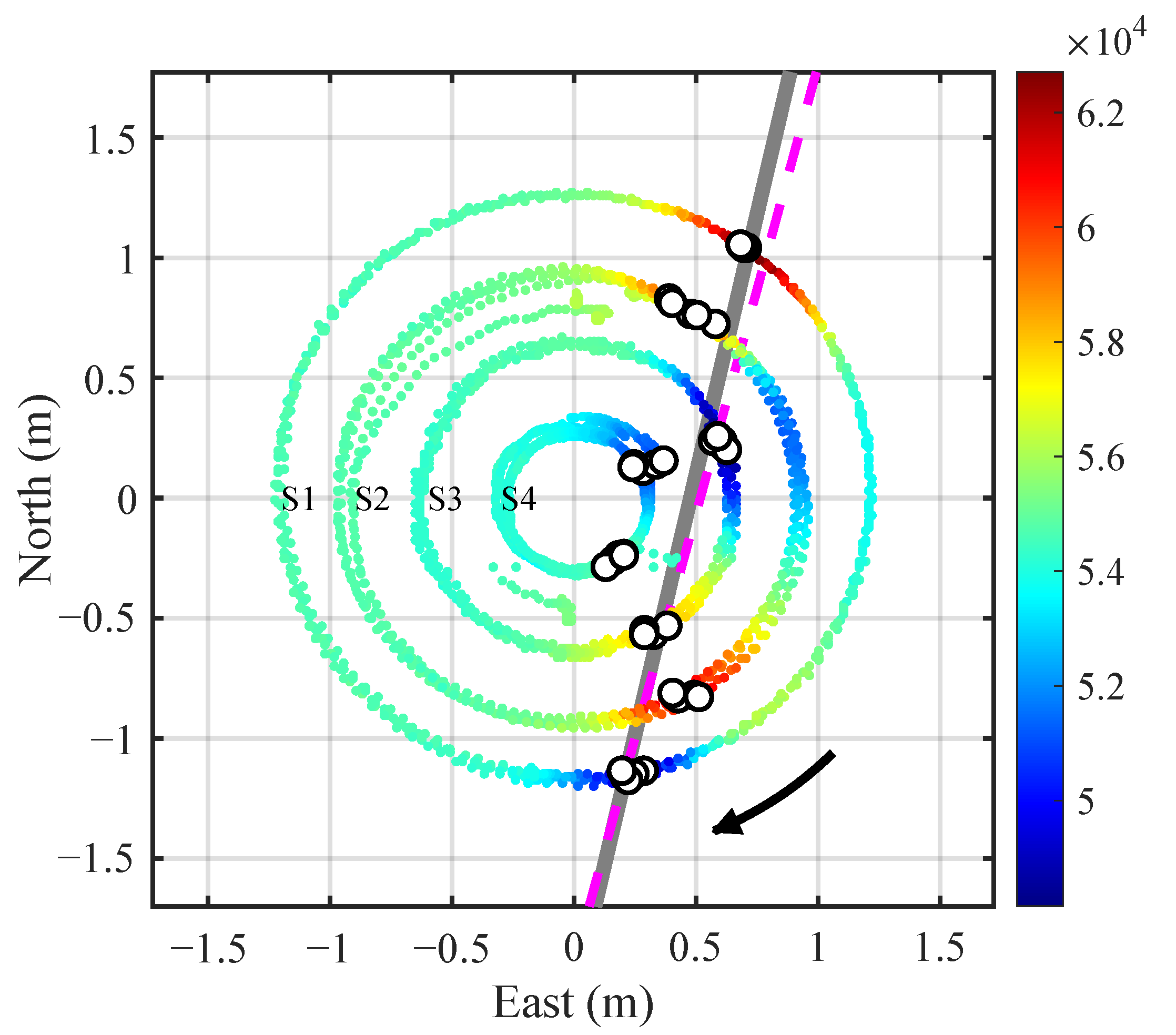
3. Field Experimental Results
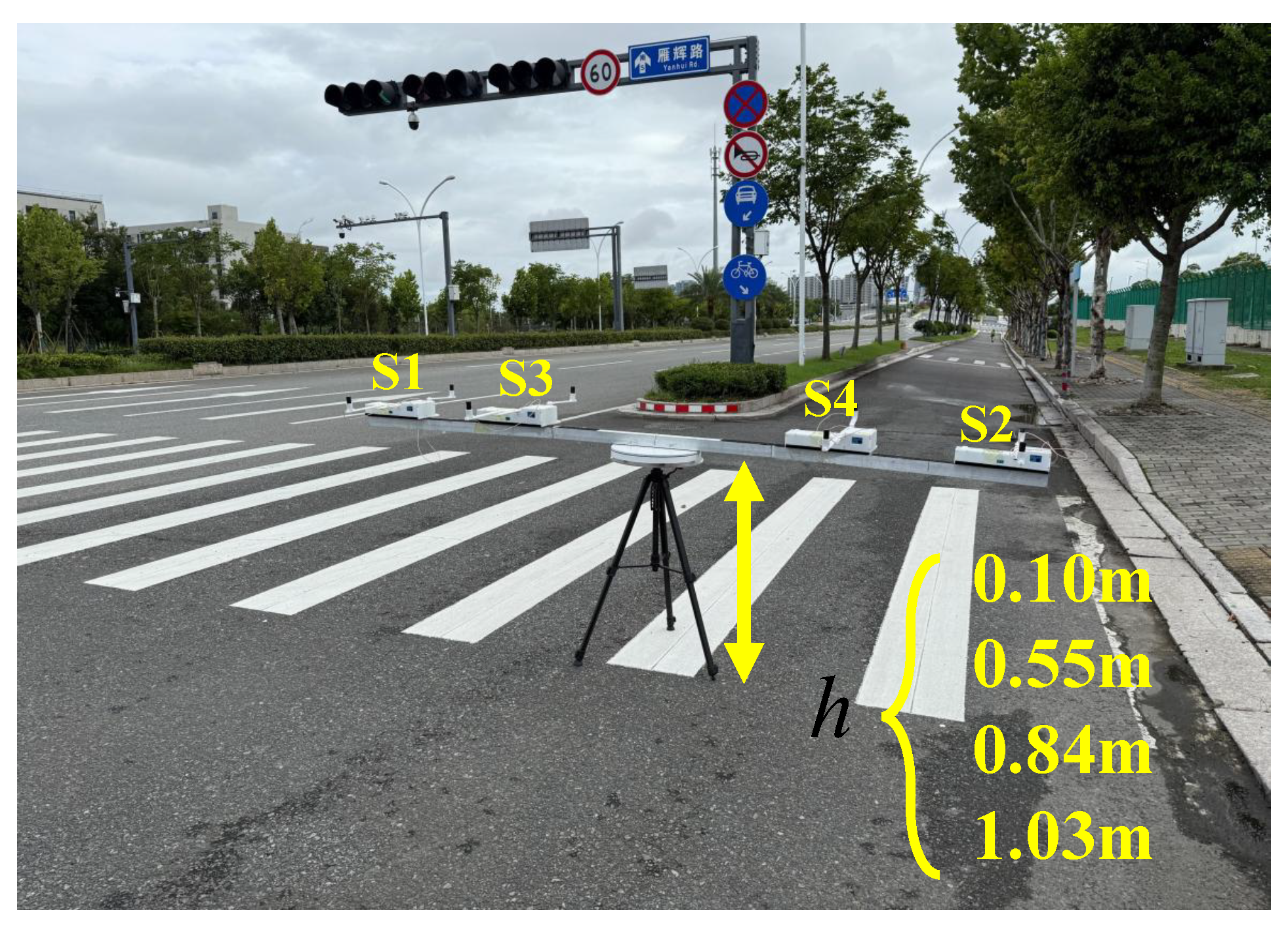
3.1. Experimental Setup
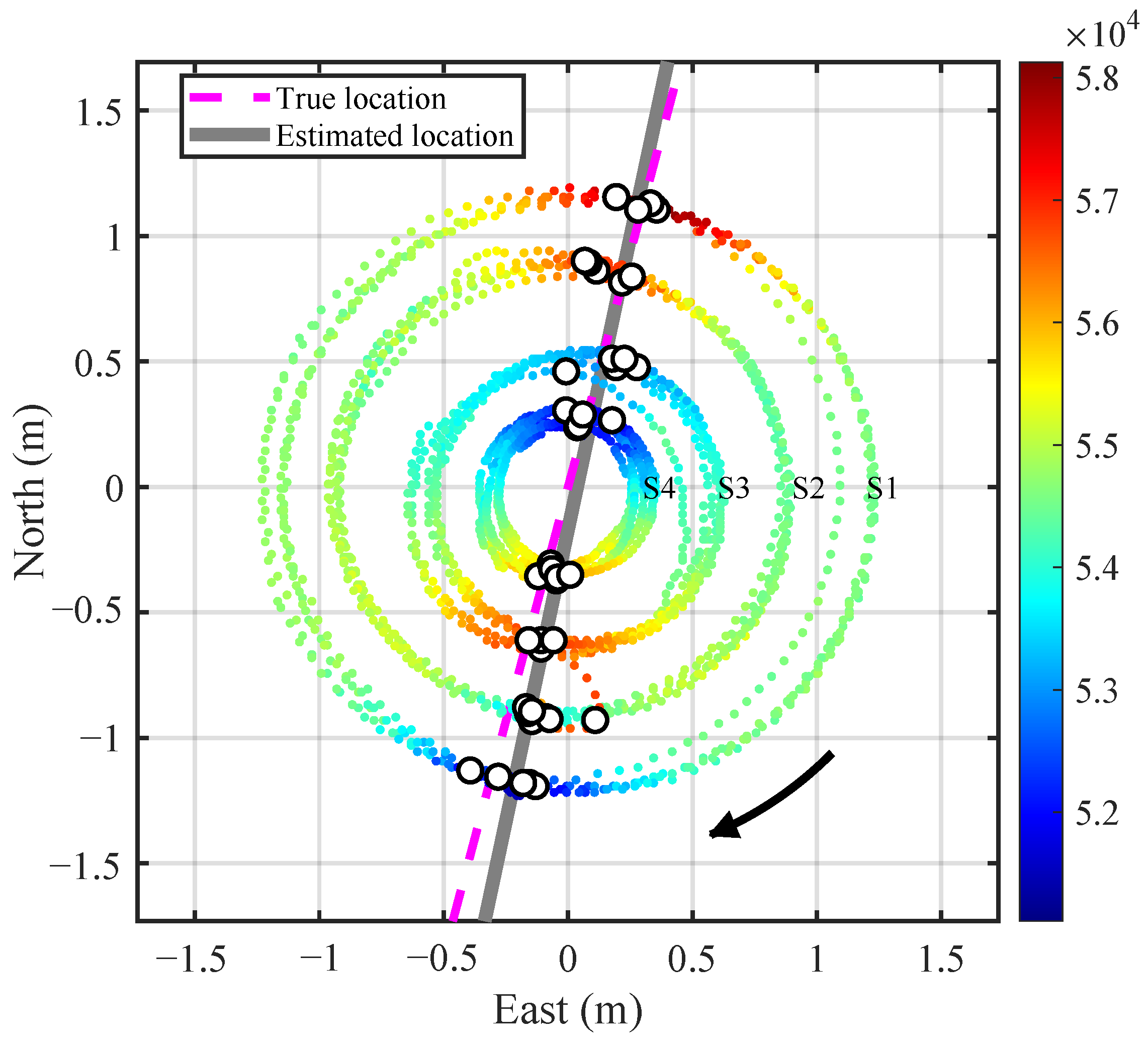
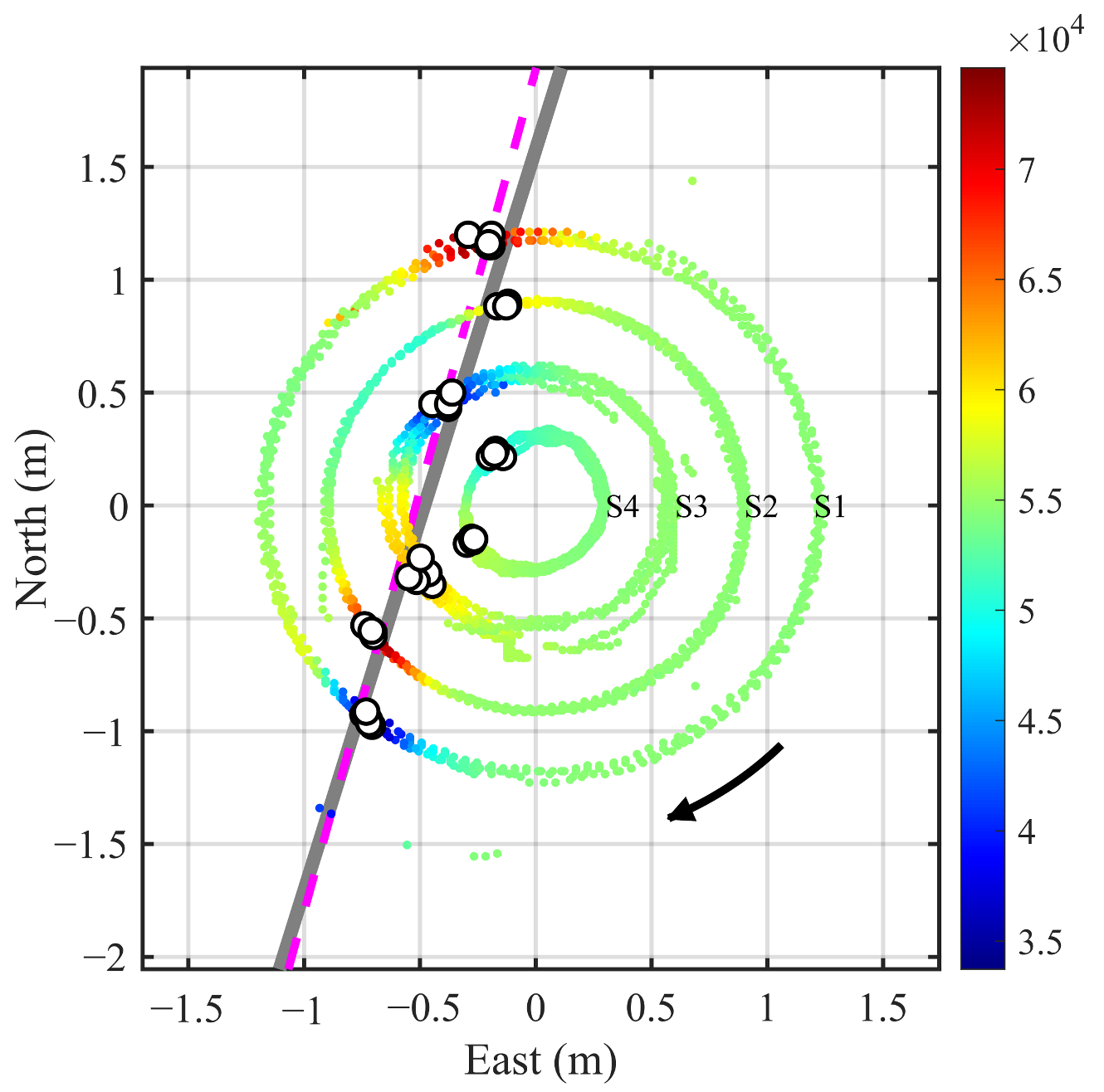
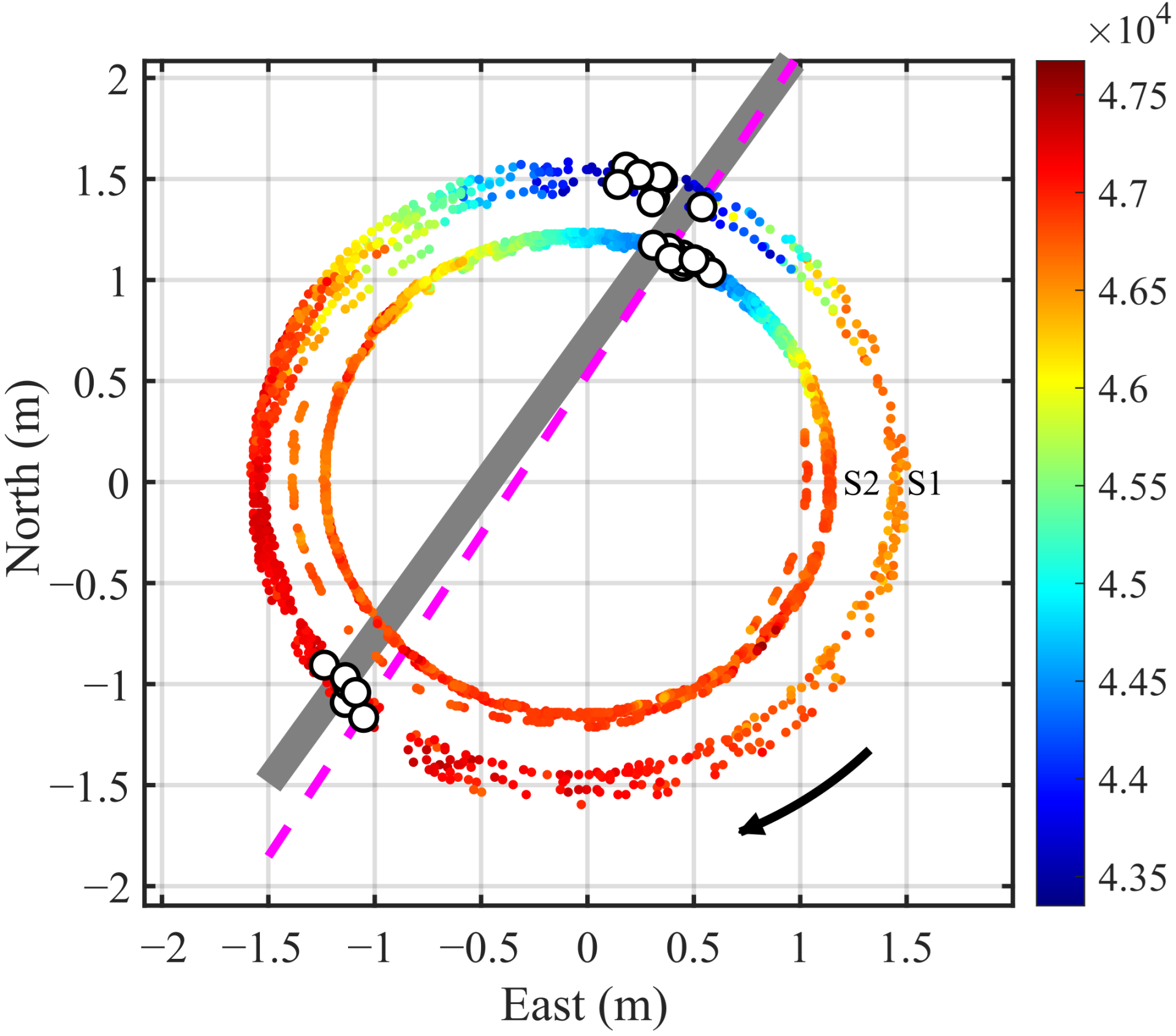
3.2. Pipeline Location Results
3.3. Real-World Pipeline Localization Case
4. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Makana, L.; Metje, N.; Jefferson, I.; Sackey, M.; Rogers, C. Cost estimation of utility strikes: Towards proactive management of street works. Infrastruct. Asset Manag. 2018, 7, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- der Tann, L.V.; Sterling, R.; Zhou, Y.; Metje, N. Systems approaches to urban underground space planning and management—A review. Undergr. Space 2020, 5, 144–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alliance, C.G. 2023 Damage Information Reporting Tool (DIRT) Report. 2024. Available online: https://commongroundalliance.com/Tools-Resources/Resources-Library (accessed on 24 November 2024).
- Xiao, X.; Chen, S.; Xu, Y.; Ge, L.; Wu, J. Ground-penetrating radar (GPR)-based mapping of underground pipeline network distribution. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 19562–19576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Jin, S.; Li, Y.; Lu, W. Deep learning for 3-D magnetic inversion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5905410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimi, R.; Weiss, E.; Ram-Cohen, T.; Geron, N.; Yogev, I. A dedicated genetic algorithm for localization of moving magnetic objects. Sensors 2015, 15, 23788–23804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Li, J.; Du, C.; Peng, X.; Guo, H. An unmanned aerial vehicle magnetic detection system for archaeological exploration. Electromagn. Sci. 2025, 3, 0110122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, L.; Lee, Y.; Lee, B.; Lee, S.; Jung, S.; Choi, Y. Unmanned aerial vehicle for magnetic detection of metallic landmines in military applications. Instrum. Sci. Technol. 2025, 53, 515–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, L.S.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, Y.K.; Jung, S.K.; Choi, Y. Application of a drone magnetometer system to military mine detection in the demilitarized zone. Sensors 2021, 21, 3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Ge, X.; Gao, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J. Speedy aeromagnetic detection technology for underwater heritage sites: A case study of the flying tigers P40 wrecked aircraft. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2025, 22, 7507605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadran, V.; Shukla, A.; Karki, H. Non-contact flaw detection and condition monitoring of subsurface metallic pipelines using magnetometric method. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 28, 860–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, T.; Chen, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, T.; Ju, H. Non-contact harmonic magnetic field detection for parallel steel pipeline localization and defects recognition. Measurement 2021, 180, 109534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Dang, X.; Li, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, B. Application of non-contact magnetic corresponding on the detection for natural gas pipeline. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 185, 01090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ma, Z.; He, L.; Wang, D.; Zhang, H.; Ren, J. Quantitative study on the propagation characteristics of MMM signal for stress internal detection of long distance oil and gas pipeline. NDT E Int. 2018, 100, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Wan, F.; He, S.; Yu, R.Q. Non-magnetization detection of arbitrary direction defects in coiled tubing based on fluxgate sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 7661–7668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.M.; Ghorbel, F.H.; Stanley, R.K. Simulation and analysis of 3-D magnetic flux leakage. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 1966–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Zhao, C. Magnetic-charge element method for magnetic flux leakage inspection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 6007910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Bian, Y.; Jiang, P.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y. Improving pipeline magnetic flux leakage (MFL) detection performance with mixed attention mechanisms (AMs) and deep residual shrinkage networks (DRSNs). IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 5162–5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.Y.; Liu, D.J.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, Y.Y. Forward modeling of total magnetic anomaly over a pseudo-2D underground ferromagnetic pipeline. J. Appl. Geophys. 2015, 113, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Liu, D.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z. Vertical magnetic field and its analytic signal applicability in oil field underground pipeline detection. J. Geophys. Eng. 2015, 12, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Guo, Z.; Du, J.; Liu, Z.; Xu, W.; Liu, G. Geometric modeling of underground ferromagnetic pipelines for magnetic dipole reconstruction-based magnetic anomaly detection. Petroleum 2020, 6, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.J.; Guo, Z.Y.; Zhu, H.H.; Pan, Q.; Ai, Q.H. Voxel partitioning strategy of magnetic dipole reconstruction for underground ferrous pipeline magnetic anomaly. Prog. Geophys. 2016, 31, 2756–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Liu, D.; Cheng, X.; Fang, H.; Li, C. A new segmentation strategy for processing magnetic anomaly detection data of shallow depth ferromagnetic pipeline. J. Appl. Geophys. 2017, 139, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.F.; Liu, D.J.; Zhai, Y.; Xie, Y.; Sun, Y. The effect of parallel pipeline parameters on the characteristics of gravity and magnetic surveys. J. Appl. Geophys. 2019, 166, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Meng, T.; Shuai, Y.; Chen, Y. Magnetic anomaly detection of adjacent parallel pipelines using deep learning neural networks. Comput. Geosci. 2022, 159, 104987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Song, Y.; Dong, L.; Tao, C.; Lin, X. Magnetic anomalies of submarine pipeline based on theoretical calculation and actual measurement. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2019, 55, 6500410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Guo, Z. High-precision inversion of buried depth in urban underground iron pipelines based on AM-PSO algorithm for magnetic anomaly. Prog. Electromagn. Res. C 2020, 100, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Liu, D.J.; Guo, Z.Y.; Fang, H.F.; Feng, M.Q. Magnetic anomaly inversion using magnetic dipole reconstruction based on the pipeline section segmentation method. J. Geophys. Eng. 2016, 13, 242–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, D.; Meng, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y. The positioning of buried pipelines from magnetic data. Geophysics 2020, 85, J111–J120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; He, T.; Liao, K.; Deng, S.; Chen, D. Experimental and numerical analysis of non-contact magnetic detecting signal of girth welds on steel pipelines. ISA Trans. 2022, 125, 681–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Liao, K.; Tang, J.; He, G.; Deng, S.; Qin, M. Quantitative study of sensor-pipe distance in noncontact magnetic detection of ferromagnetic pipelines. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 7879–7894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Cui, D. Technology of detecting deep underground metal pipeline by magnetic gradient method. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 660, 012074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Lee, W.K.; Hou, Y.; Pong, P.W. Underground power cable detection and inspection technology based on magnetic field sensing at ground surface level. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 6200605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossinger, R.; Keplinger, F.; Mehmood, N.; Espina-Hernandez, J.H.; Araujo, J.; Eisenmenger, C.; Poppenberger, K.; Hallen, J.M. Magnetic and microstructural investigations of pipeline steels. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2008, 44, 3277–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Ham, Y.; Park, H. Underground metal pipeline localization using low-cost wireless magnetic sensors mounted on an excavator. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 10674–10683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khiyavi, O.A.; Seo, J.; Lin, X. Three-dimensional metal pipe detection for autonomous excavators using inexpensive magnetometer sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 24383–24392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tan, D.; Liu, L. Particle swarm optimization algorithm: An overview. Soft Comput. 2018, 22, 387–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
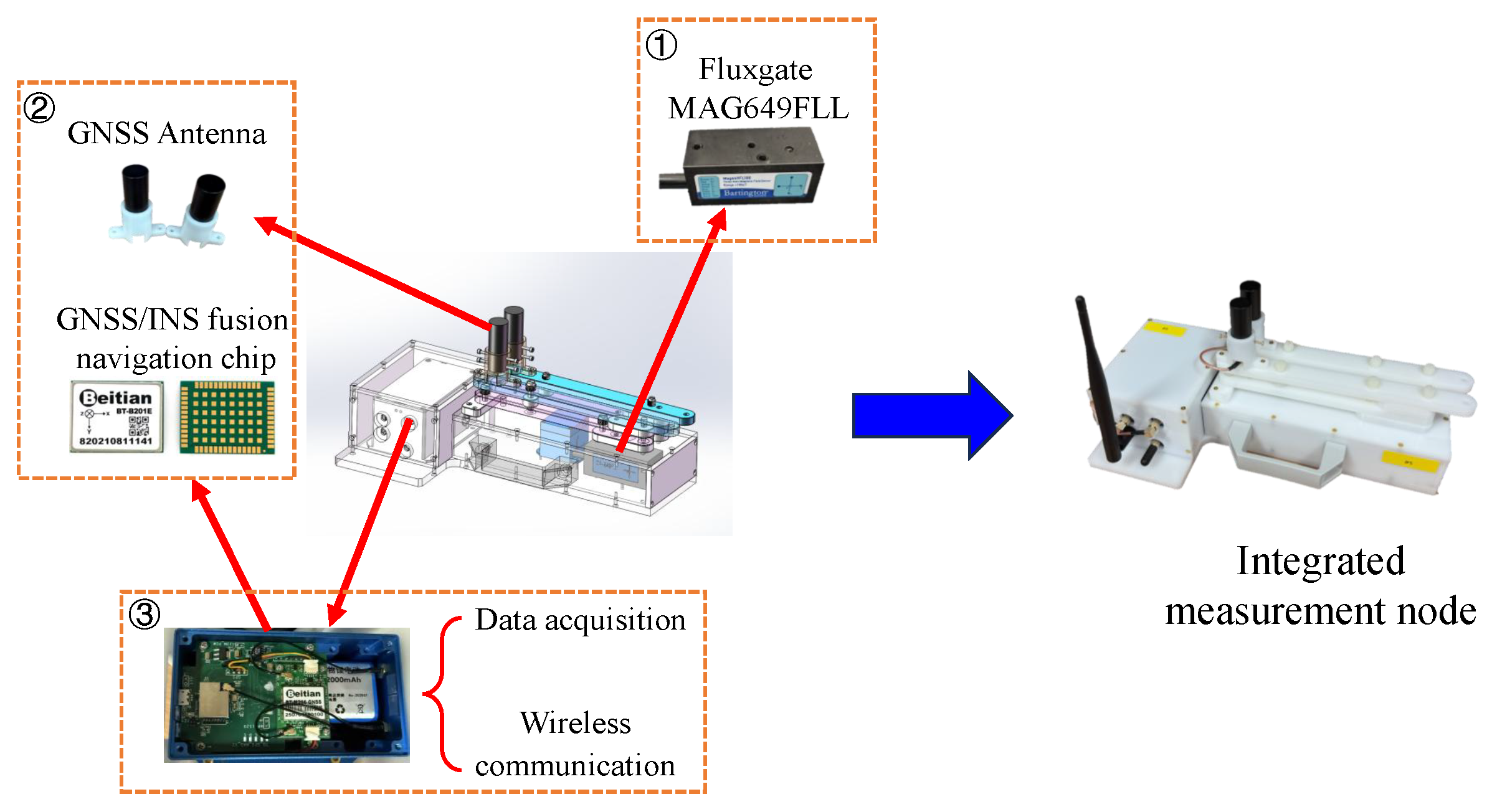

| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Magnetometer Module | |
| Sensors | Bartington Mag649FLL |
| Measuring Range | ±100 T |
| Orthogonality Error | <1° error between axes |
| Magnetic Field Resolution | 0.01 nT |
| GNSS/Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) Modules | |
| Sensors | BT-B201E |
| Accelerometer | ±16 g |
| Gyroscope | ±1000 deg/s |
| Satellite System | Beidou, GPS, Gallileo, Glonass |
| Horizontal Accuracy | ≤8 mm ± 1 ppm |
| Roll/Pitch Accuracy | ≤0.02° (1) |
| Yaw Accuracy | ≤0.2° (1) |
| Data Acquisition and Communication Card | |
| Sampling Rate | 10 Hz |
| Wireless Module | ESP32-WROOM-32 Wi-Fi |
| Height of Nodes Above Ground (m) | a | b (m) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.55 | 4.655 | 3.141 | 4.676 | −0.169 | 1.539 | −2.541 | 0.9479 | 0.8558 | 0.8694 |
| 0.40 | 4.464 | 2.990 | 4.663 | −0.178 | 1.554 | −2.238 | 0.8850 | 0.9288 | 0.9142 |
| 0.25 | 4.193 | 3.283 | 4.866 | −0.176 | 1.577 | −2.517 | 0.9403 | 0.9132 | 0.9620 |
| Overall | 4.501 | 3.138 | 4.735 | −0.174 | 1.557 | −2.432 | 0.913 | ||
| Node Index | k () | d (m) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1000.07 | 0.020 | 0.9895 |
| 2 | 1185.99 | 0.041 | 0.9945 |
| 3 | 1027.84 | 0.000 | 0.9947 |
| 4 | 1112.65 | 0.010 | 0.9945 |
| Overall | 1081.64 | 0.0177 | 0.9933 |
| Experiment Index | Inversion Parameters | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| χ (°) | x0 (m) | y0 (m) | d (m) | ||||||||
| 1 | True | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||
| Estimate | 12.12 | 12.62 | 13.41 | −0.007 | −0.009 | −0.009 | 0.035 | 0.038 | 0.040 | 0.018 | |
| Error | 2.88 | 2.37 | 1.59 | 0.007 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.034 | 0.038 | 0.040 | 0.018 | |
| 2 | True | 15 | 0.129 | −0.483 | 0 | ||||||
| Estimate | 17.66 | 18.49 | 16.94 | 0.142 | 0.156 | 0.134 | −0.445 | −0.467 | −0.440 | 0.014 | |
| Error | 2.66 | 3.50 | 1.94 | 0.013 | 0.027 | 0.005 | 0.038 | 0.015 | 0.043 | 0.014 | |
| 3 | True | 15 | −0.129 | 0.483 | 0 | ||||||
| Estimate | 12.07 | 12.10 | 11.61 | −0.111 | −0.098 | −0.102 | 0.520 | 0.459 | 0.496 | 0.018 | |
| Error | 2.93 | 2.90 | 3.39 | 0.018 | 0.031 | 0.027 | 0.037 | 0.024 | 0.013 | 0.018 | |
| Average error | 2.68 ± 0.63 | 0.016 ± 0.010 | 0.031 ± 0.011 | 0.017 ± 0.002 | |||||||
| 0.039 ± 0.015 | |||||||||||
| Node Index | k () | d (m) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25,318.39 | 2.82 | 0.9802 |
| 2 | 20,025.93 | 2.88 | 0.9936 |
| Overall | 22,672.16 | 2.85 | 0.9869 |
| Experiment Index | Inversion Parameters | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| χ (°) | x0 (m) | y0 (m) | d (m) | |||||||||||
| 1 | True | 32.14 | 0.204 | −0.208 | 3.00 | |||||||||
| Estimate | 34.55 | 37.63 | 38.39 | 38.82 | 0.322 | 0.347 | 0.360 | 0.364 | −0.222 | −0.268 | −0.286 | −0.293 | 2.85 | |
| Error | 2.41 | 5.49 | 6.25 | 6.68 | 0.118 | 0.143 | 0.156 | 0.160 | 0.014 | 0.060 | 0.078 | 0.085 | 0.15 | |
| Average error | 5.21 ± 1.93 | 0.144 ± 0.019 | 0.059 ± 0.032 | 0.15 | ||||||||||
| 0.216 | ||||||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Yuan, Z.; Xia, M. Underground Ferromagnetic Pipeline Detection Using a Rotable Magnetic Sensor Array. Sensors 2025, 25, 7153. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25237153
Liu X, Yuan Z, Xia M. Underground Ferromagnetic Pipeline Detection Using a Rotable Magnetic Sensor Array. Sensors. 2025; 25(23):7153. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25237153
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xingen, Zifan Yuan, and Mingyao Xia. 2025. "Underground Ferromagnetic Pipeline Detection Using a Rotable Magnetic Sensor Array" Sensors 25, no. 23: 7153. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25237153
APA StyleLiu, X., Yuan, Z., & Xia, M. (2025). Underground Ferromagnetic Pipeline Detection Using a Rotable Magnetic Sensor Array. Sensors, 25(23), 7153. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25237153






