A Progressive Feature Learning Network for Cordyceps sinensis Image Recognition
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- We propose PFL-Net, capable of accurately extracting and relating discriminative features. To the best of our knowledge, PFL-Net is the first study on recognizing C. sinensis.
- (2)
- The SSRM is designed to model spatial contextual, mining multi-scale discriminative features of C. sinensis. The MCPM relates the feature extracted at multiple scales to avoid the loss of C. sinensis features.
- (3)
- The CD loss decouples the features within the channel dimension and guides the network to focus on the C. sinensis features.
- (4)
- C. sinensis has significant medicinal value, we construct the first dataset for CSD. We perform extensive experiments on CSD and three fine-grained classification benchmarks demonstrating the superior performance of PFL-Net.
2. Related Work
2.1. General Image Classification
2.2. Fine-Grained Image Classification
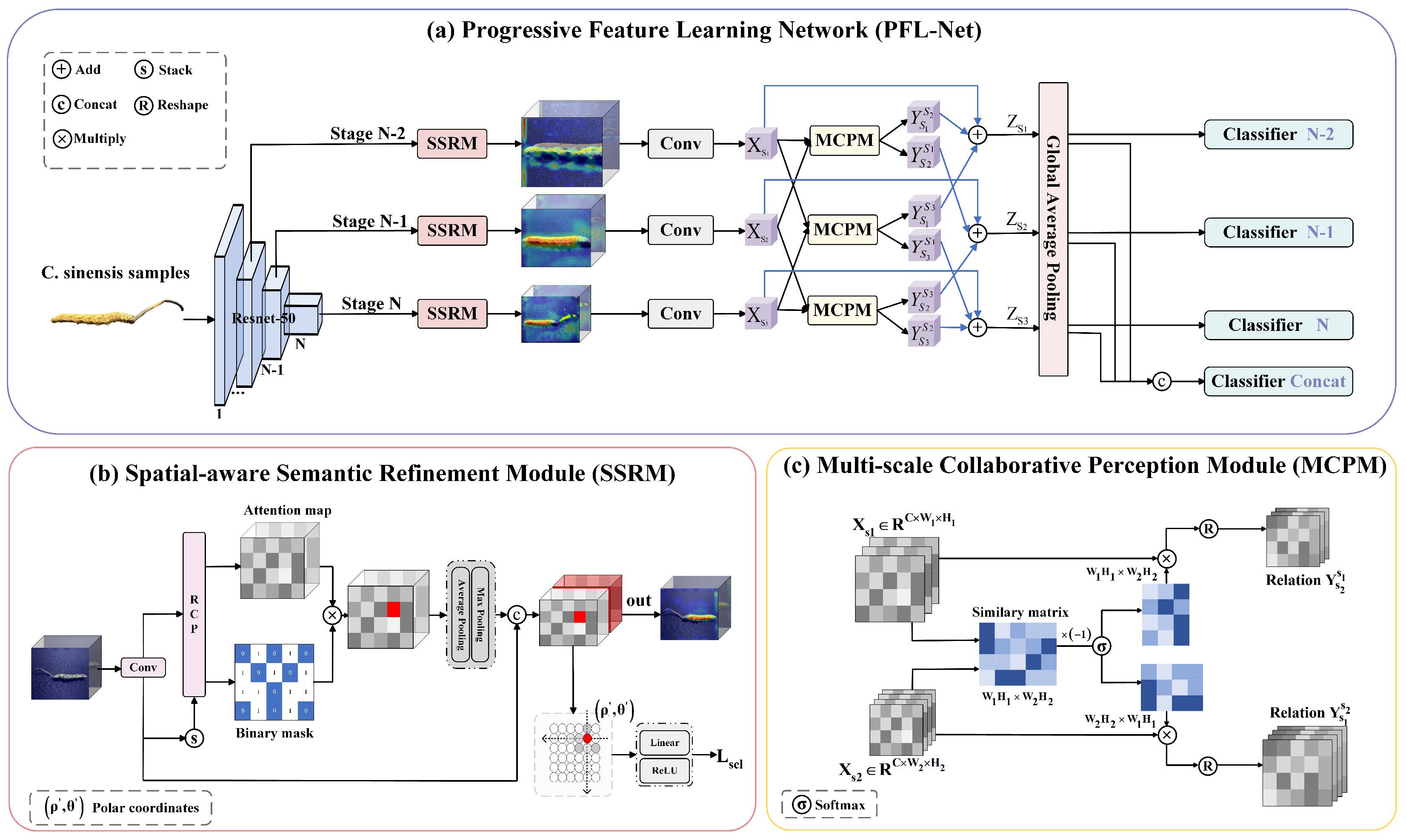
3. Method
3.1. Overview Architecture
3.2. Spatial-Aware Semantic Refinement Module
3.3. Multi-Scale Collaborative Perception Module
3.4. Loss Function
4. Data Collection and Construction
4.1. Material Preparation
4.2. Data Collection and Annotation
Environmental Considerations and Optical Stability
5. Experiments
5.1. Datasets and Settings
5.2. Comparison with State of the Arts
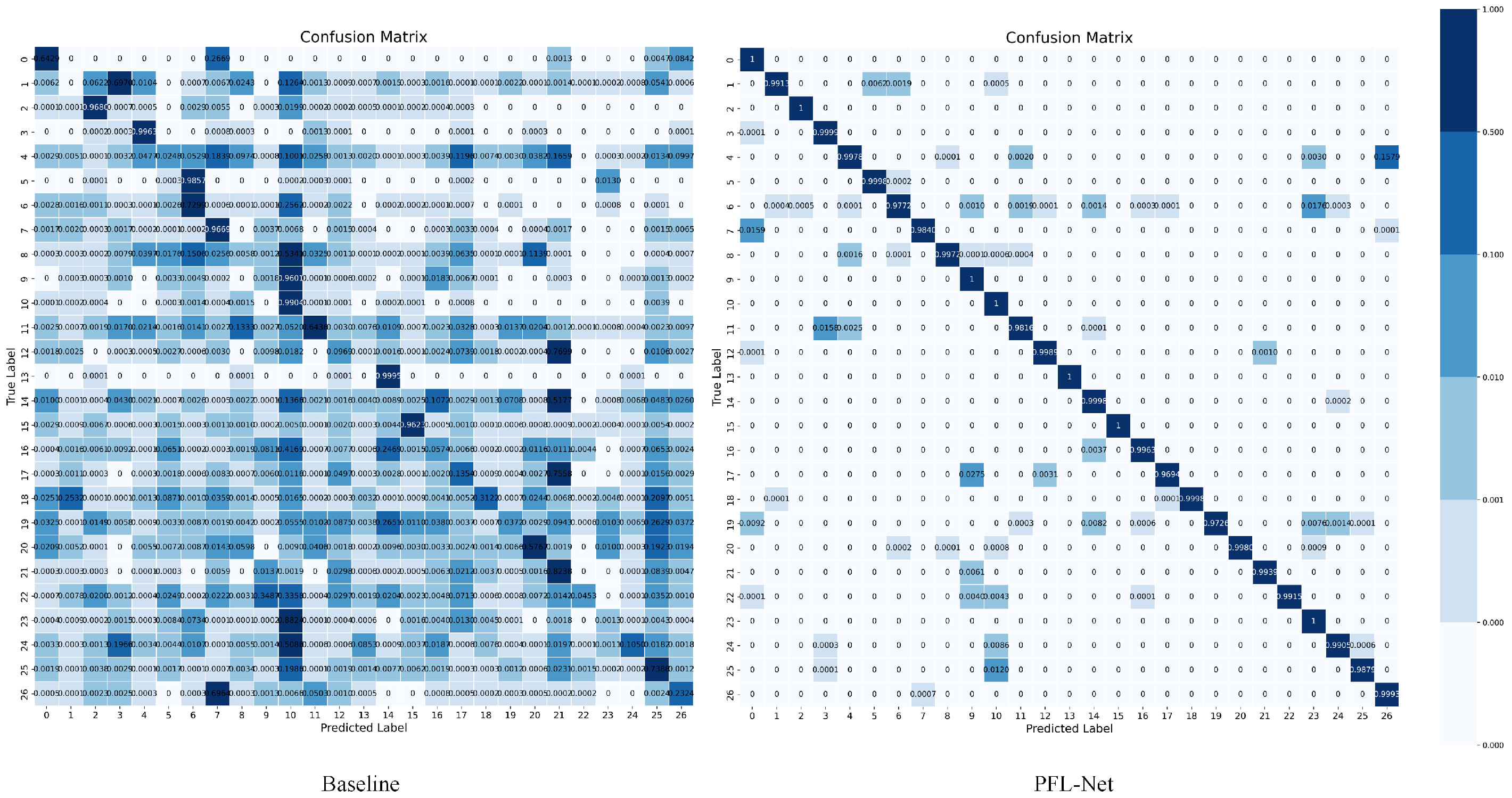
5.3. Ablation Studies
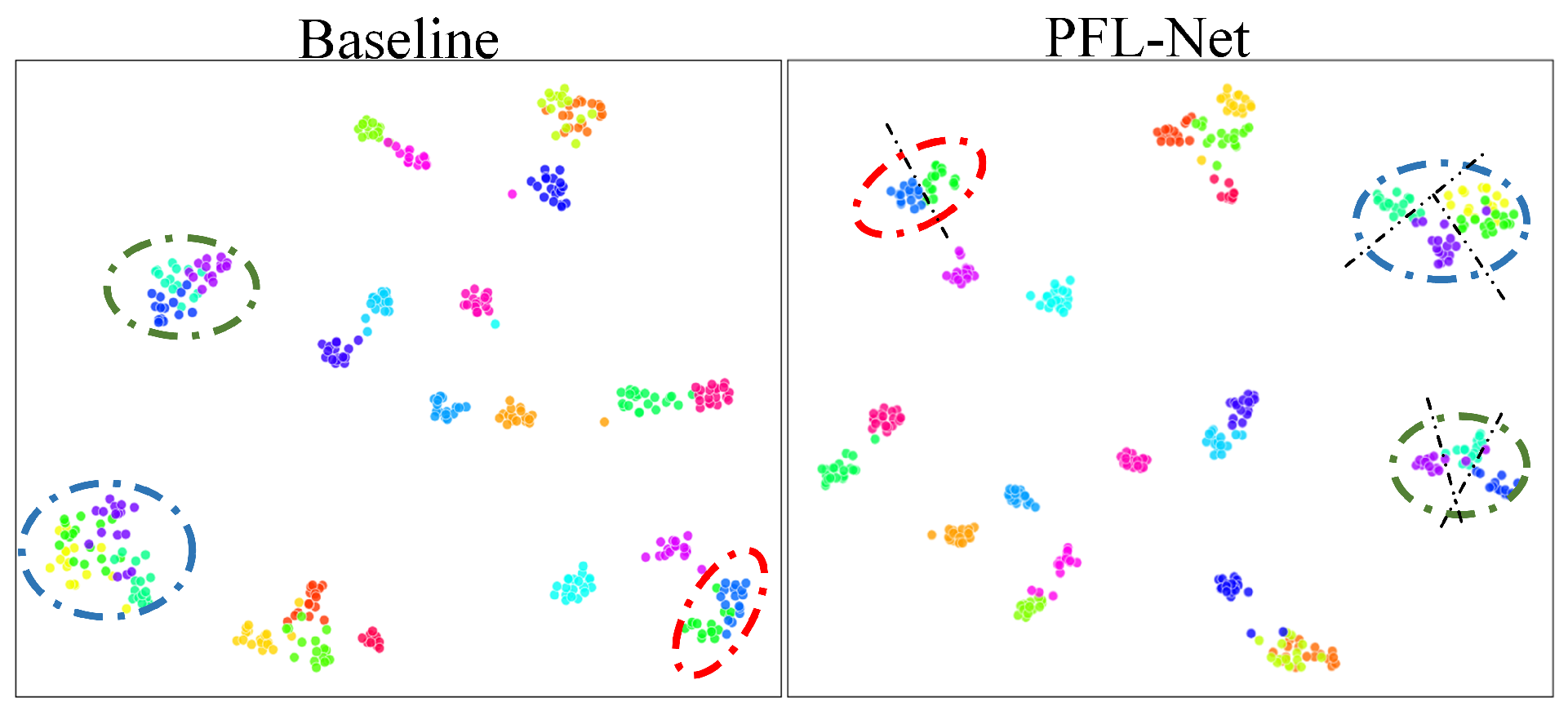
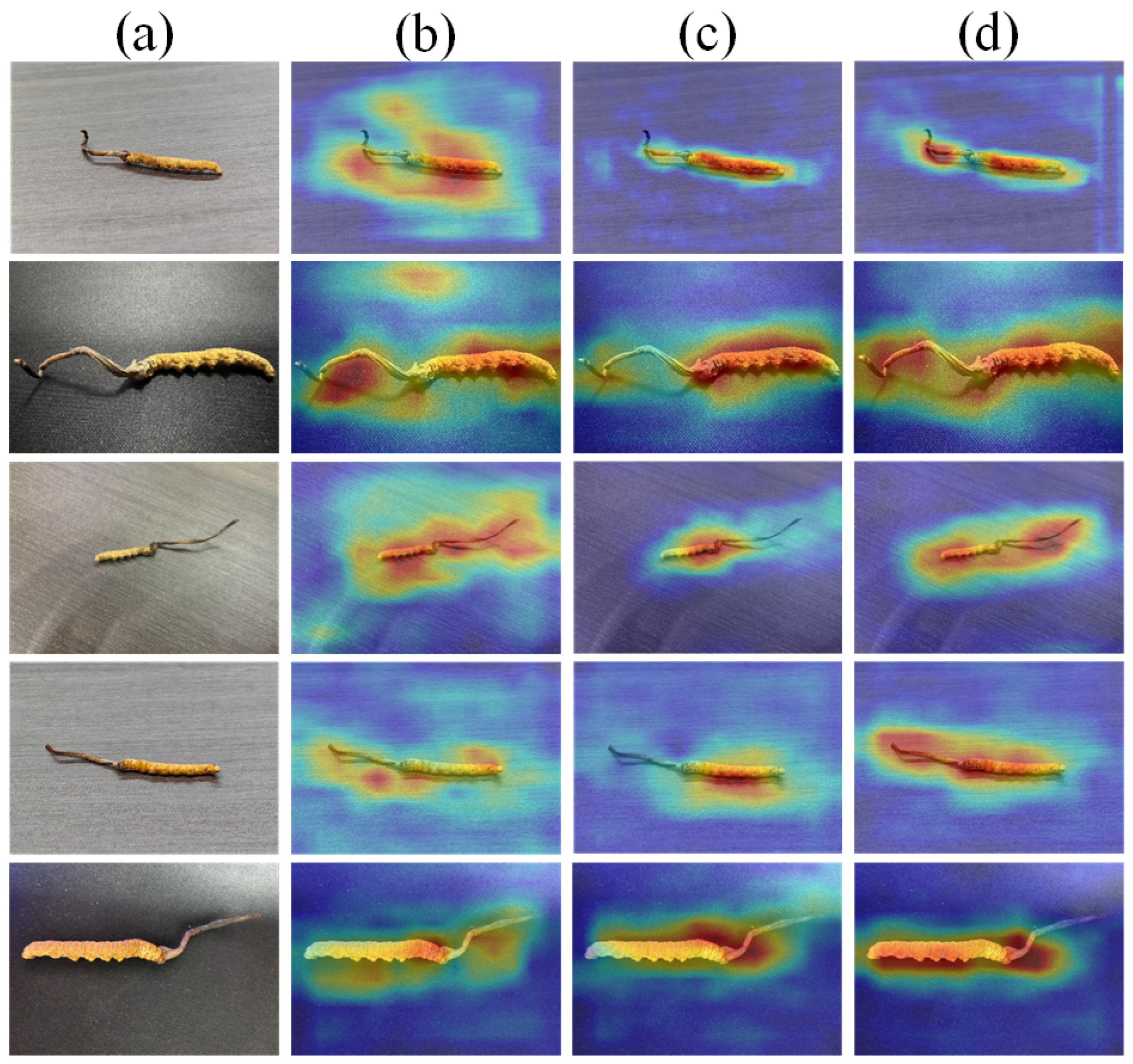
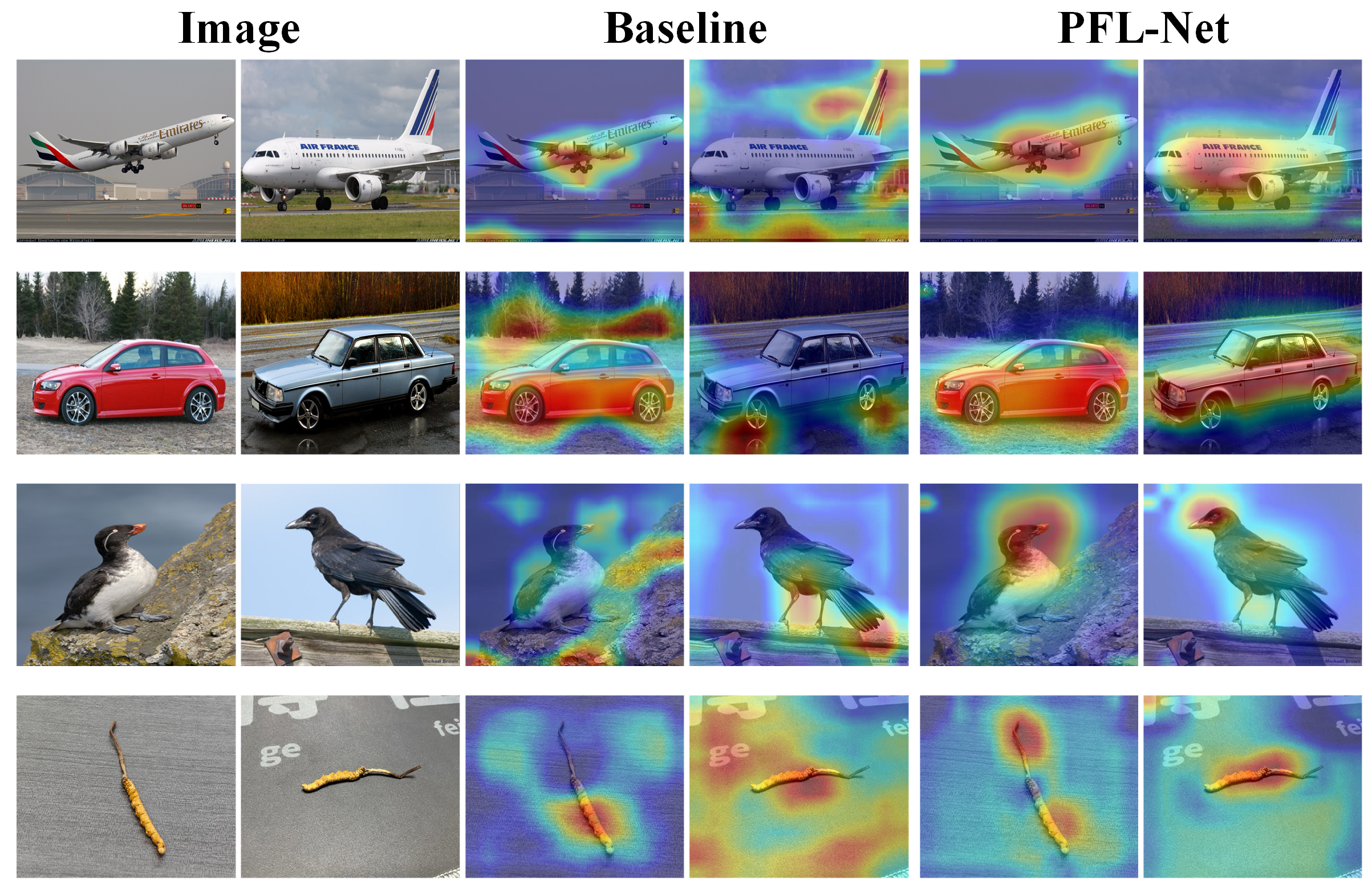
5.4. Visualizations
6. Conclusions
Limitations and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, J.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Tang, C.; Wang, T.; Li, Y. Suitability and regionalization of Chinese cordyceps in Qinghai Province, Northwest China. Mycosystema 2022, 41, 1772–1785. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, F.; Li, X.; Zhang, N. Mechanism of cordyceps sinensis and its extracts in the treatment of diabetic kidney disease: A review. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 881835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, K.V.; Ulhas, R.S.; Malaviya, A. Bioactive compounds from Cordyceps and their therapeutic potential. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2024, 44, 753–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residualearning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Du, F.; Yang, P.; Jia, Q.; Nan, F.; Chen, X.; Yang, Y. Global and local mixture consistency cumulative learning for long-tailed visual recognitions. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 10–22 June 2023; pp. 15814–15823. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, F.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Q. Localizing discriminative regions for fine-grained visual recognition: One could be better than many. Neurocomputing 2024, 610, 128611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.H.; Cheng, M.M.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, X.Y.; Yang, M.H.; Torr, P. Res2net: A new multi-scale backbone architecture. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 43, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. Efficientnetv2: Smaller models and faster training. In Proceedings of the ICML, Online, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 10096–10106. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, X.; Ma, N.; Han, J.; Ding, G.; Sun, J. Repvgg: Making vgg-style convnets great again. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Online, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 13733–13742. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Mao, H.; Wu, C.Y.; Feichtenhofer, C.; Darrell, T.; Xie, S. A convnet for the 2020s. In Proceedings of the CVPR, New Orleans, LS, USA, 21–24 June 2022; pp. 11976–11986. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Debnath, S.; Hu, R.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Kweon, I.S.; Xie, S. Convnext v2: Co-designing and scaling convnets with masked autoencoders. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 10–22 June 2023; pp. 16133–16142. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Xiong, S. Maskcov: A random mask covariance network for ultra-fine-grained visual categorization. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 119, 108067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Yang, R. Feature boosting, suppression, and diversification for fine-grained visual classification. In Proceedings of the IJCNN, Shenzhen, China, 18–22 July 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, Y. SPARE: Self-supervised part erasing for ultra-fine-grained visual categorization. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 128, 108691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Chen, J.N.; Liu, S.; Kortylewski, A.; Yang, C.; Bai, Y.; Wang, C. Transfg: A transformer architecture for fine-grained recognition. In Proceedings of the AAAI, Online, 22 February–1 March 2022; Volume 36, pp. 852–860. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, E.; Wang, W.; Ding, M.; Zhang, R.; Luo, P. Polarmask++: Enhanced polar representation for single-shot instance segmentation and beyond. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 5385–5400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, A.; Wharton, Z.; Hewage, P.R.; Bera, A. Context-aware attentional pooling (cap) for fine-grained visual classification. In Proceedings of the AAAI, Online, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 929–937. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Xie, H.; Zha, Z.J.; Ma, L.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Y. Filtration and distillation: Enhancing region attention for fine-grained visual categorization. In Proceedings of the AAAI, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 11555–11562. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Tian, Y. Part-guided relational transformers for fine-grained visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 9470–9481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.; Cholakkal, H.; Khan, S.; Khan, F.; Shao, L. Fine-grained recognition: Accounting for subtle differences between similar classes. In Proceedings of the AAAI, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 12047–12054. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, K.P. Probabilistic Machine Learning: An Introduction; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Khorin, P.; Dzyuba, A.; Khonina, S. Optical wavefront aberration: Detection, recognition, and compensation techniques—A comprehensive review. Opt. Laser Technol. 2025, 191, 113342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welinder, P.; Branson, S.; Mita, T.; Wah, C.; Schroff, F.; Belongie, S.; Perona, P. Caltech-UCSD Birds 200; Caltech: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dataset, E. Novel datasets for fine-grained image categorization. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; Volume 5, p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Maji, S.; Rahtu, E.; Kannala, J.; Blaschko, M.; Vedaldi, A. Fine-grained visual classification of aircraft. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1306.5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, J.; Li, M. Bag of tricks for image classification with convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 558–567. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Pan, X.; Song, S.; Zhang, H.; Huang, G.; Wu, C. Implicit semantic data augmentation for deep networks. NeurIPS 2019, 32, 12614–12623. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.X.; Chen, Z.D.; Zhao, L.J.; Zhang, Z.C.; Luo, X.; Xu, X.S. Cross-Layer and Cross-Sample Feature Optimization Network for Few-Shot Fine-Grained Image Classification. In Proceedings of the AAAI, Vancouver, BC, USA, 20–28 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 4136–4144. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Chang, D.; Sain, A.; Li, X.; Ma, Z.; Cao, J.; Guo, J.; Song, Y.Z. Bi-directional feature reconstruction network for fine-grained few-shot image classification. In Proceedings of the AAAI, Washington, DC, USA, 7–15 February 2023; Volume 37, pp. 2821–2829. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, Y.; Han, Y.; Wang, Y.; Feng, J.; Deng, C.; Huang, G. Fine-grained recognition with learnable semantic data augmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2024, 33, 3130–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, S.; Koniusz, P.; Wang, L.; Zhou, L.; Moghadam, P.; Sun, C. Learning partial correlation based deep visual representation for image classification. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Vancouver, BC, USA, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 6231–6240. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Ma, Z.; Wen, S.; Xie, J.; Chang, D.; Si, Z.; Wu, M.; Ling, H. AP-CNN: Weakly supervised attention pyramid convolutional neural network for fine-grained visual classification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 2826–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, R.; Wen, L.; Zhang, L.; Du, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Liu, X.; Huang, F. Attention convolutional binary neural tree for fine-grained visual categorization. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 10468–10477. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, P.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, Y. Learning attentive pairwise interaction for fine-grained classification. In Proceedings of the AAAI, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 13130–13137. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Ye, Q.; Jiao, J. Selective sparse sampling for fine-grained image recognition. In Proceedings of the ICCV, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6599–6608. [Google Scholar]
- Du, R.; Chang, D.; Bhunia, A.K.; Xie, J.; Ma, Z.; Song, Y.Z.; Guo, J. Fine-grained visual classification via progressive multi-granularity training of jigsaw patches. In Proceedings of the ECCV, Online, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 153–168. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, W.; Mei, T. Destruction and construction learning for fine-grained image recognition. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 5157–5166. [Google Scholar]
- Alexey, D. An image is worth 16 × 16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. In Proceedings of the ICLR, Virtual Event, 3–7 May 2021; p. 11929. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, K.; Xu, Y.; Tian, Y. Fine-grained object classification via self-supervised pose alignment. In Proceedings of the CVPR, New Orleans, LS, USA, 19–23 June 2022; pp. 7399–7408. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the ICCV, Nicosia, Cyprus, 24–25 April 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Maaten, L.; Hinton, G. Visualizing data using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9, 2579–2605. [Google Scholar]
- Wattenberg, M.; Viégas, F.; Johnson, I. How to Use t-SNE Effectively. Distill 2016, 1, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkina, A.C.; Ciccolella, C.O.; Anno, R.; Spidlen, J.; Snyder-Cappione, J.E. Automated optimal parameters for t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding improve visualization and allow analysis of large datasets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5415. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]




| Origin | Specification | Image | Origin | Specification | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yushu | 1000 | 636 | Guoluo | 1000 | 600 |
| 1200 | 626 | 1200 | 640 | ||
| 1500 | 620 | 1500 | 640 | ||
| 2000 | 568 | 2000 | 592 | ||
| 2500 | 616 | 3000 | 576 | ||
| Haixi | 2000 | 636 | Huangnan | 1000 | 616 |
| 2500 | 640 | 1200 | 584 | ||
| 3000 | 616 | 1500 | 636 | ||
| 3500 | 616 | 2000 | 640 | ||
| Haibei | 2000 | 616 | Hainan | 1000 | 640 |
| 2500 | 640 | 1200 | 624 | ||
| 3000 | 636 | 1500 | 600 | ||
| 3500 | 640 | 2000 | 640 | ||
| Counterfeit | / | 3167 |
| Dataset | Classes | Training | Testing |
|---|---|---|---|
| CUB-200-2011 [24] | 200 | 5994 | 5794 |
| Stanford Cars [25] | 196 | 8144 | 8041 |
| FGVC-Aircraft [26] | 100 | 6667 | 3333 |
| Method | Venue | C. sinensis Dataset | CUB-200-2011 | Stanford Cars | FGVC-Aircraft |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISDA [28] | NeurIPS19 | 81.4 | 85.3 | 91.7 | 93.2 |
| C2-Net [29] | AAAI24 | 88.5 | 84.6 | - | 88.9 |
| Bi-FRN [30] | AAAI23 | 89.9 | 85.4 | - | 88.4 |
| LearnableISDA [31] | TIP24 | 90.2 | 86.7 | 92.7 | 94.3 |
| iSICE [32] | CVPR23 | 90.2 | 85.9 | 93.5 | 92.7 |
| AP-CNN [33] | TIP21 | 90.5 | 87.2 | 92.2 | 93.6 |
| ACNet [34] | CVPR20 | 90.6 | 88.1 | 92.4 | 94.6 |
| API-Net [35] | AAAI20 | 91.0 | 87.7 | 93.0 | 94.8 |
| S3Ns [36] | ICCV19 | 91.2 | 88.5 | 92.8 | 94.7 |
| PMG [37] | ECCV20 | 92.1 | 88.9 | 92.8 | 95.0 |
| DCL [38] | CVPR19 | 92.8 | 87.8 | 93.0 | 94.5 |
| ViT [39] | ICLR21 | 93.1 | 90.3 | 94.2 | 94.8 |
| P2P-Net [40] | CVPR22 | 93.2 | 90.2 | 94.9 | 94.2 |
| TransFG [15] | AAAI22 | 93.7 | 91.7 | 94.8 | - |
| PFL-Net (our) | - | 94.4 | 91.2 | 94.9 | 95.1 |
| Index | Component | Accuracy (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | SSRM | MCPM | CD | CSD | CUB | |
| 0 | √ | 91.64 | 88.88 | |||
| 1 | √ | √ | 92.80 | 89.02 | ||
| 2 | √ | √ | 91.87 | 89.93 | ||
| 3 | √ | √ | 93.03 | 89.41 | ||
| 4 | √ | √ | √ | 93.34 | 90.95 | |
| 5 | √ | √ | √ | 94.19 | 90.55 | |
| 6 | √ | √ | √ | 93.75 | 90.41 | |
| 7 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 94.43 | 91.26 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Wu, W.; Chen, H.; You, S.; Lu, J.; Mao, L.; Zhang, F.; Ji, Y. A Progressive Feature Learning Network for Cordyceps sinensis Image Recognition. Sensors 2025, 25, 7082. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25227082
Liu S, Wu W, Chen H, You S, Lu J, Mao L, Zhang F, Ji Y. A Progressive Feature Learning Network for Cordyceps sinensis Image Recognition. Sensors. 2025; 25(22):7082. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25227082
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shangdong, Wenxiang Wu, Haijun Chen, Shuai You, Jiahuan Lu, Lin Mao, Fan Zhang, and Yimu Ji. 2025. "A Progressive Feature Learning Network for Cordyceps sinensis Image Recognition" Sensors 25, no. 22: 7082. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25227082
APA StyleLiu, S., Wu, W., Chen, H., You, S., Lu, J., Mao, L., Zhang, F., & Ji, Y. (2025). A Progressive Feature Learning Network for Cordyceps sinensis Image Recognition. Sensors, 25(22), 7082. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25227082






