Optical Camera-Based Integrated Sensing and Communication for V2X Applications: Model and Optimization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. System Model
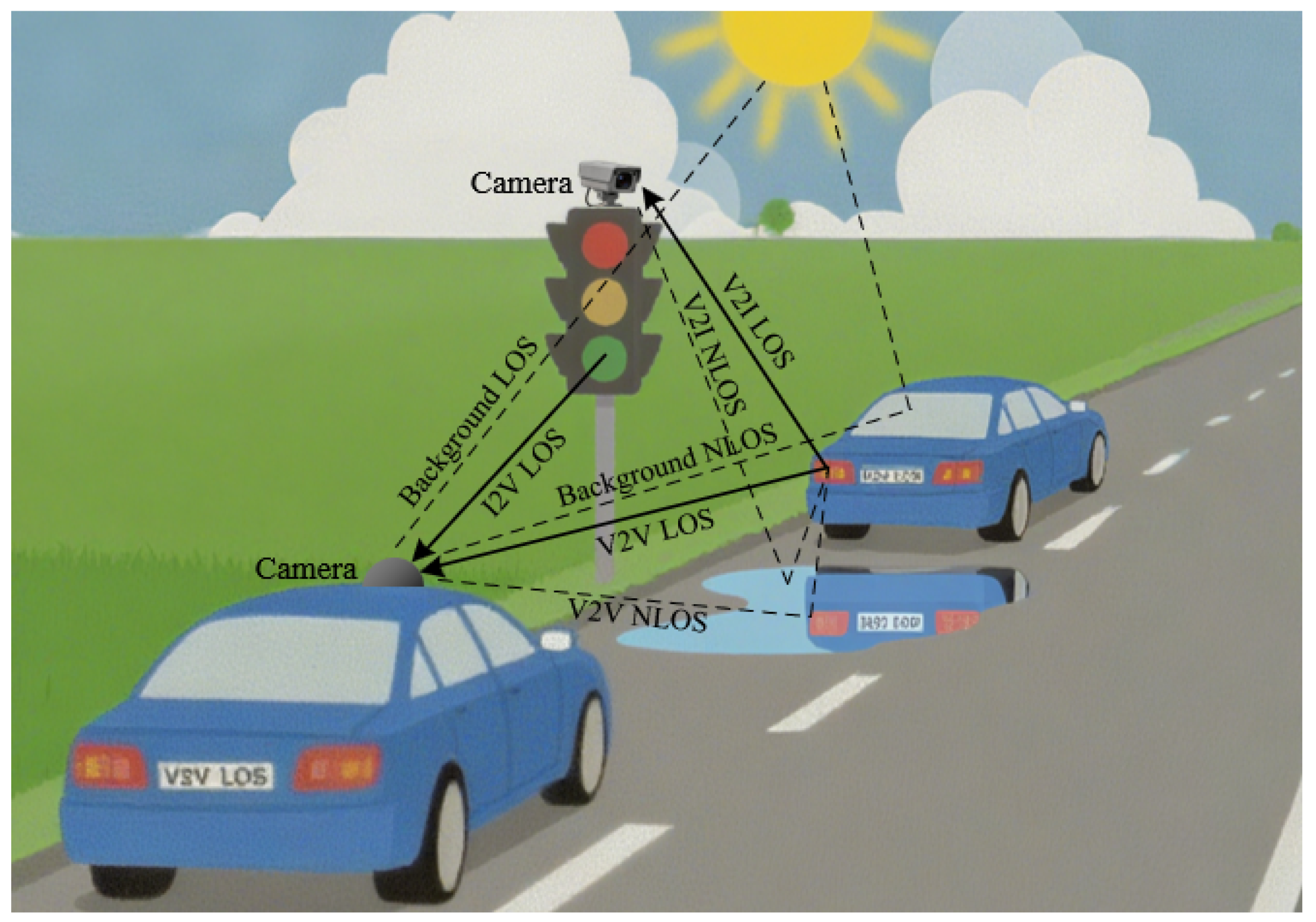
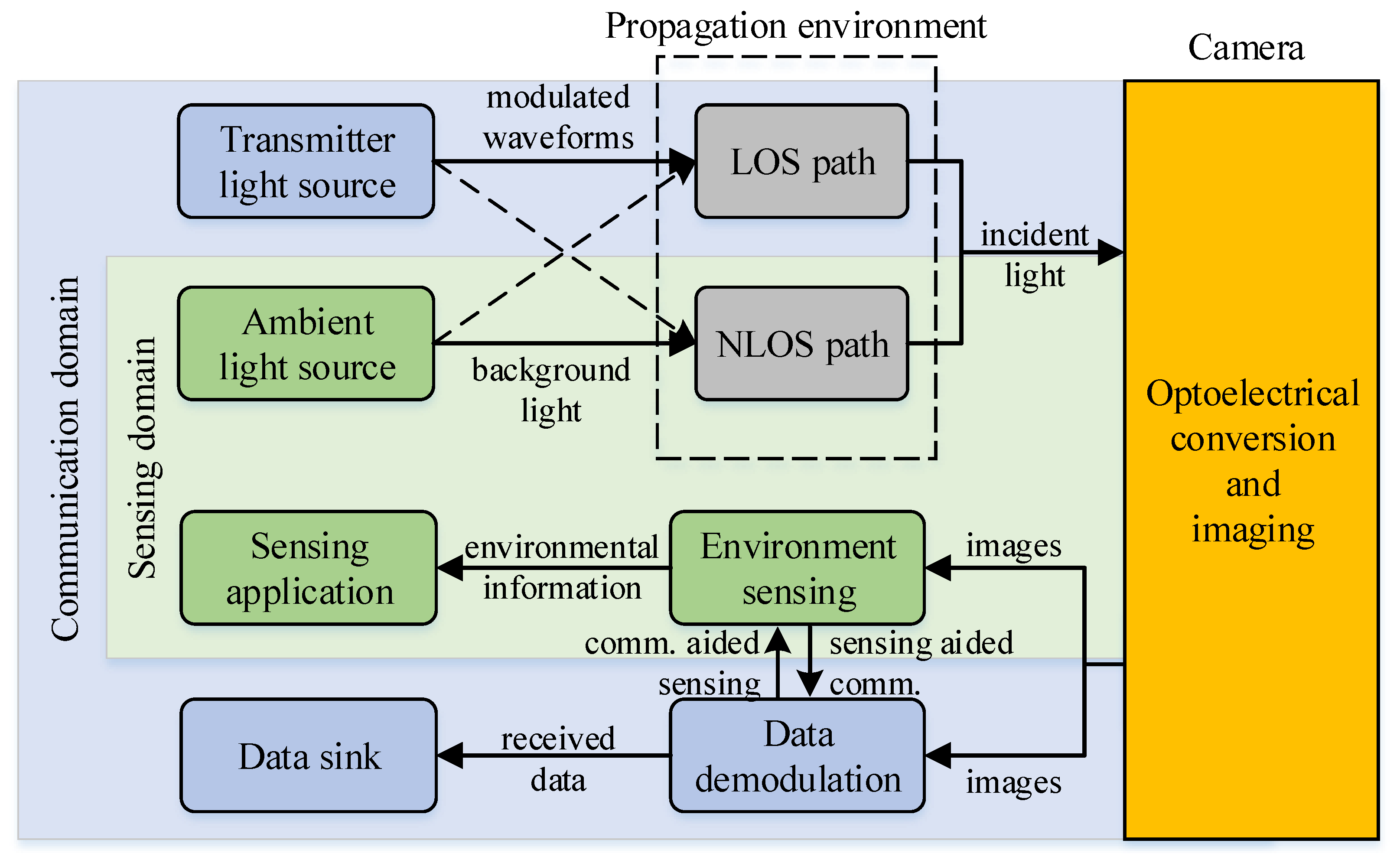
2.1. OC-ISAC Architecture
2.2. List of Symbols
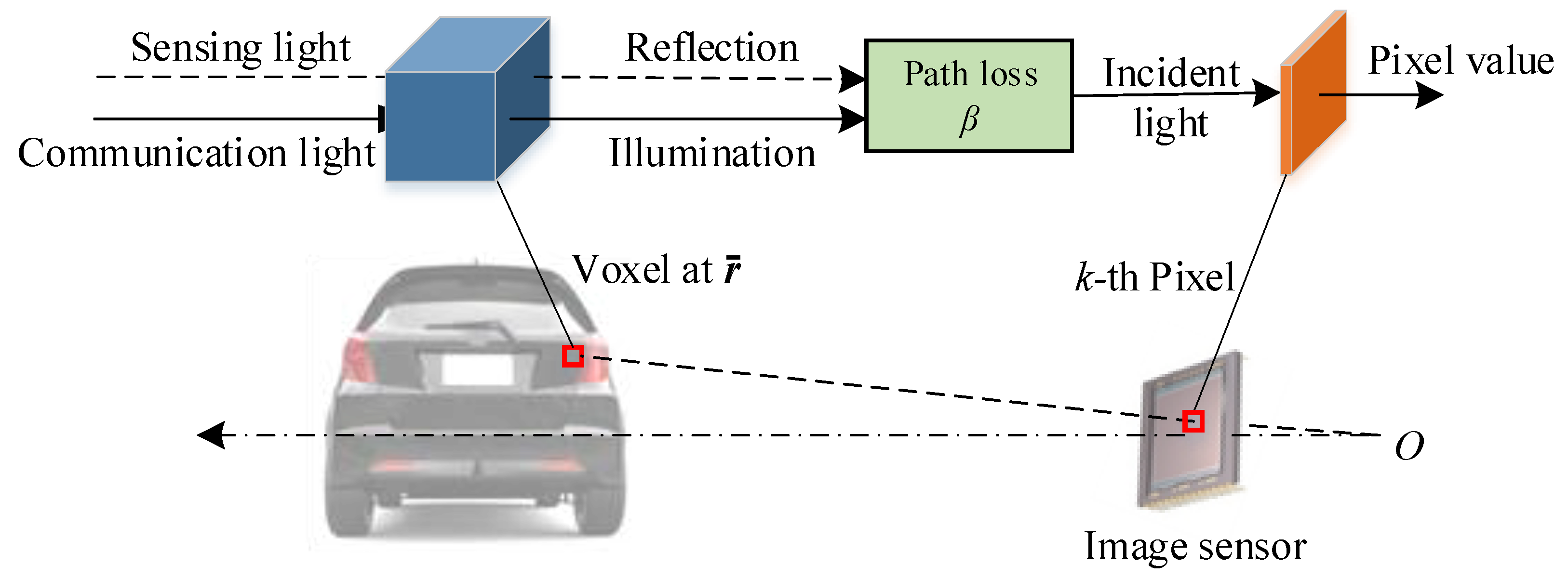
2.3. Voxel-to-Pixel Channel Model
2.3.1. Communication Channel
2.3.2. Sensing Channel
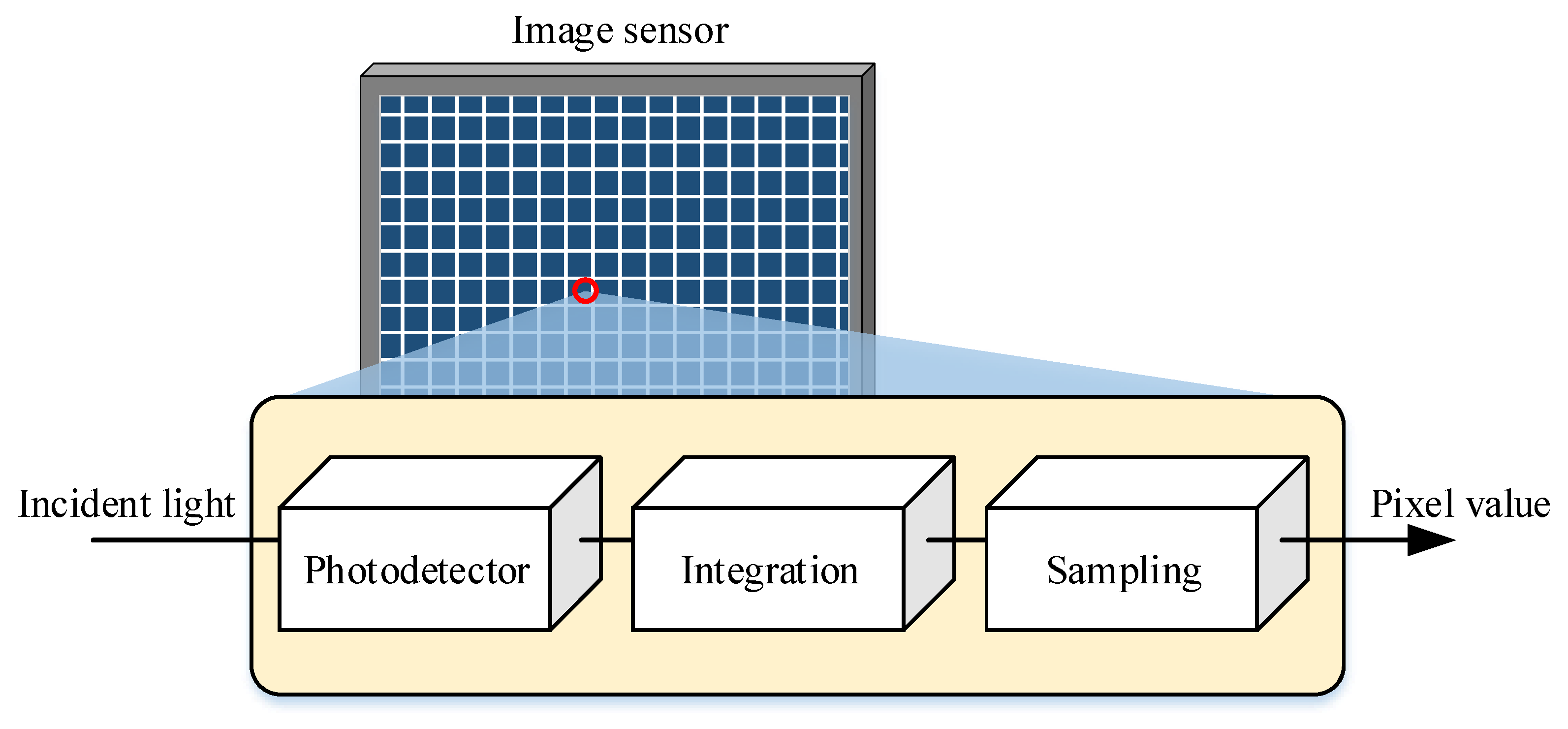
2.3.3. Pixel Value
2.4. Signal Model
2.4.1. Communication Signal
2.4.2. Sensing Signal
3. Performance Analysis
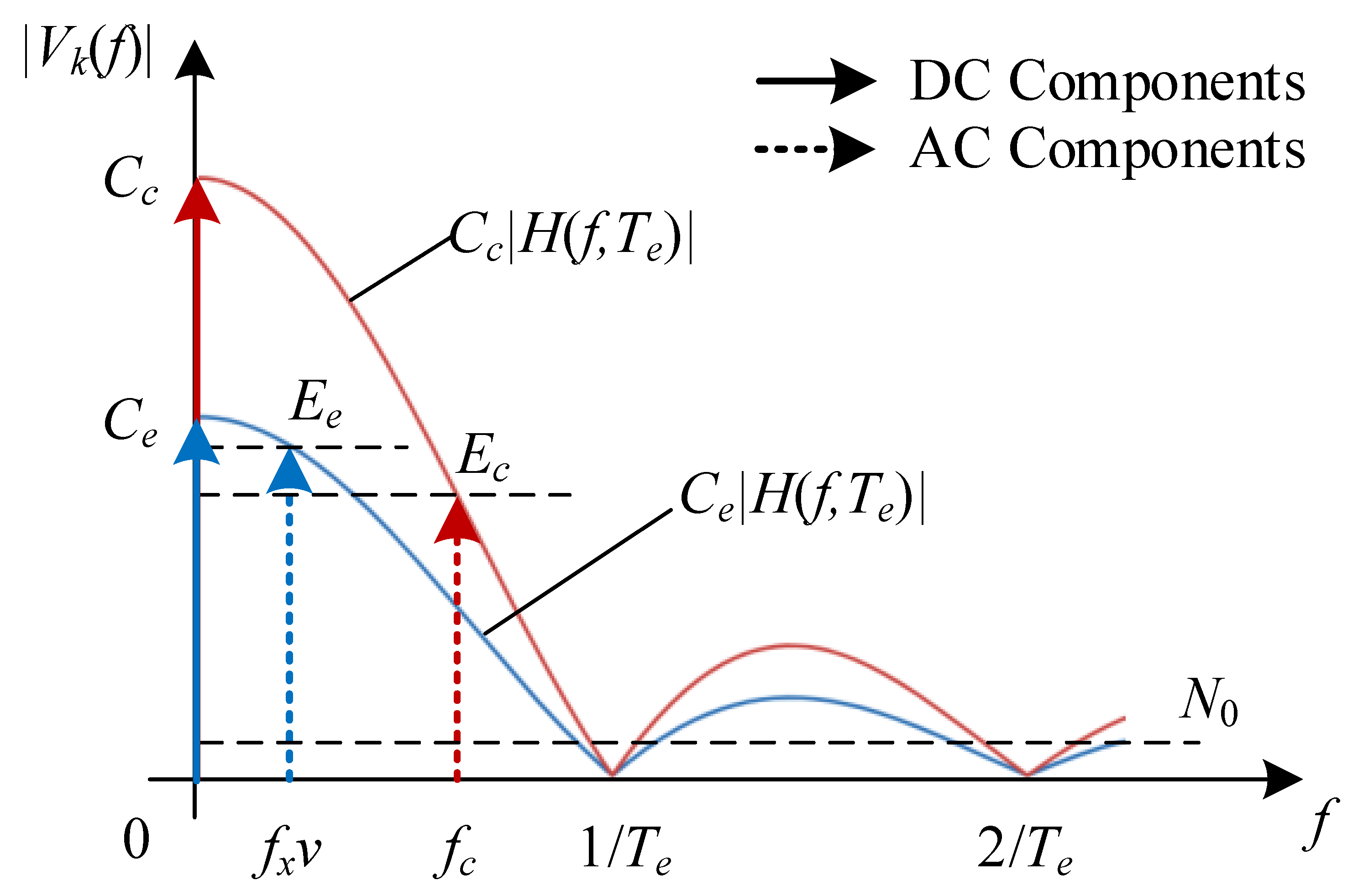
3.1. Exposure Effect
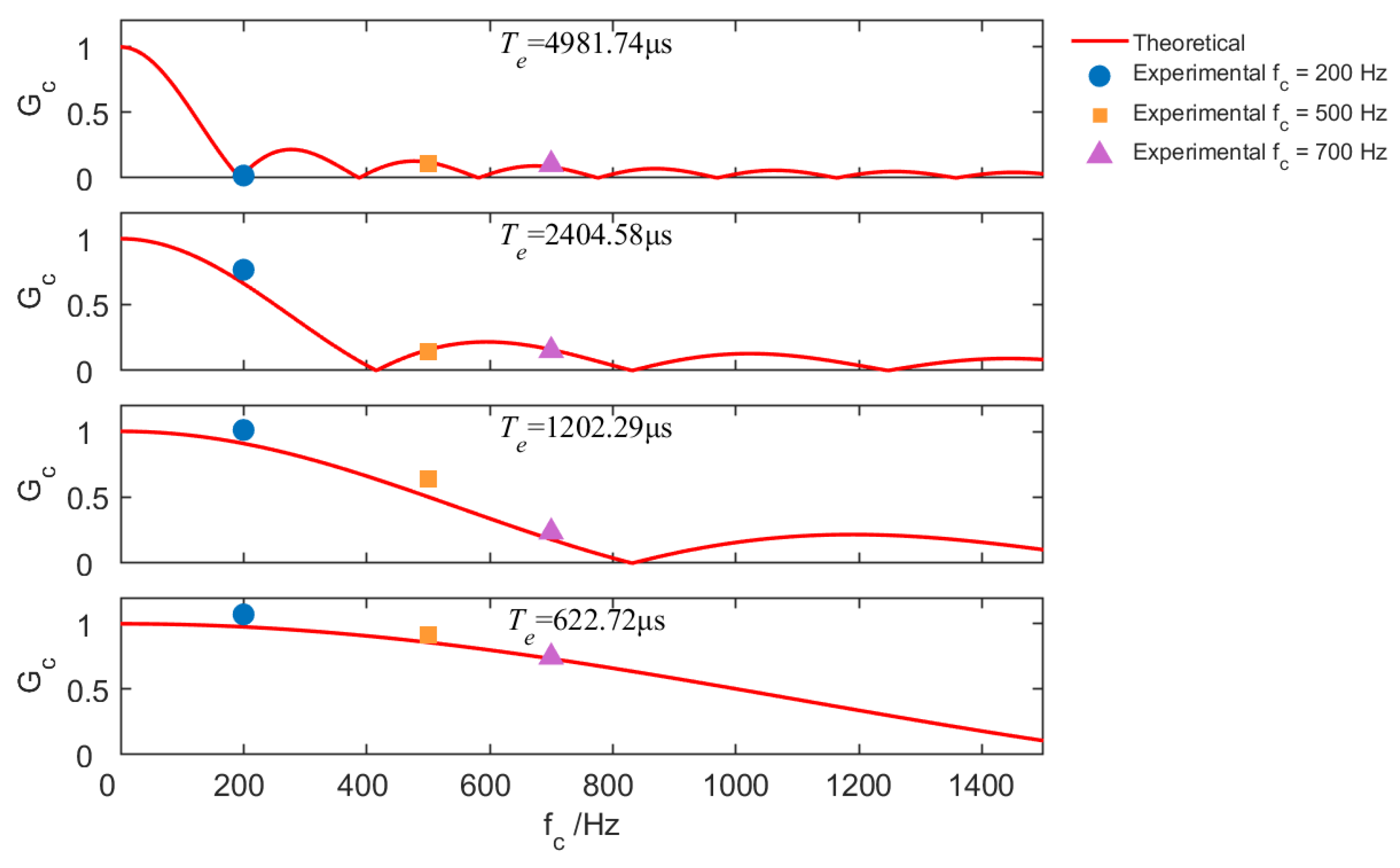
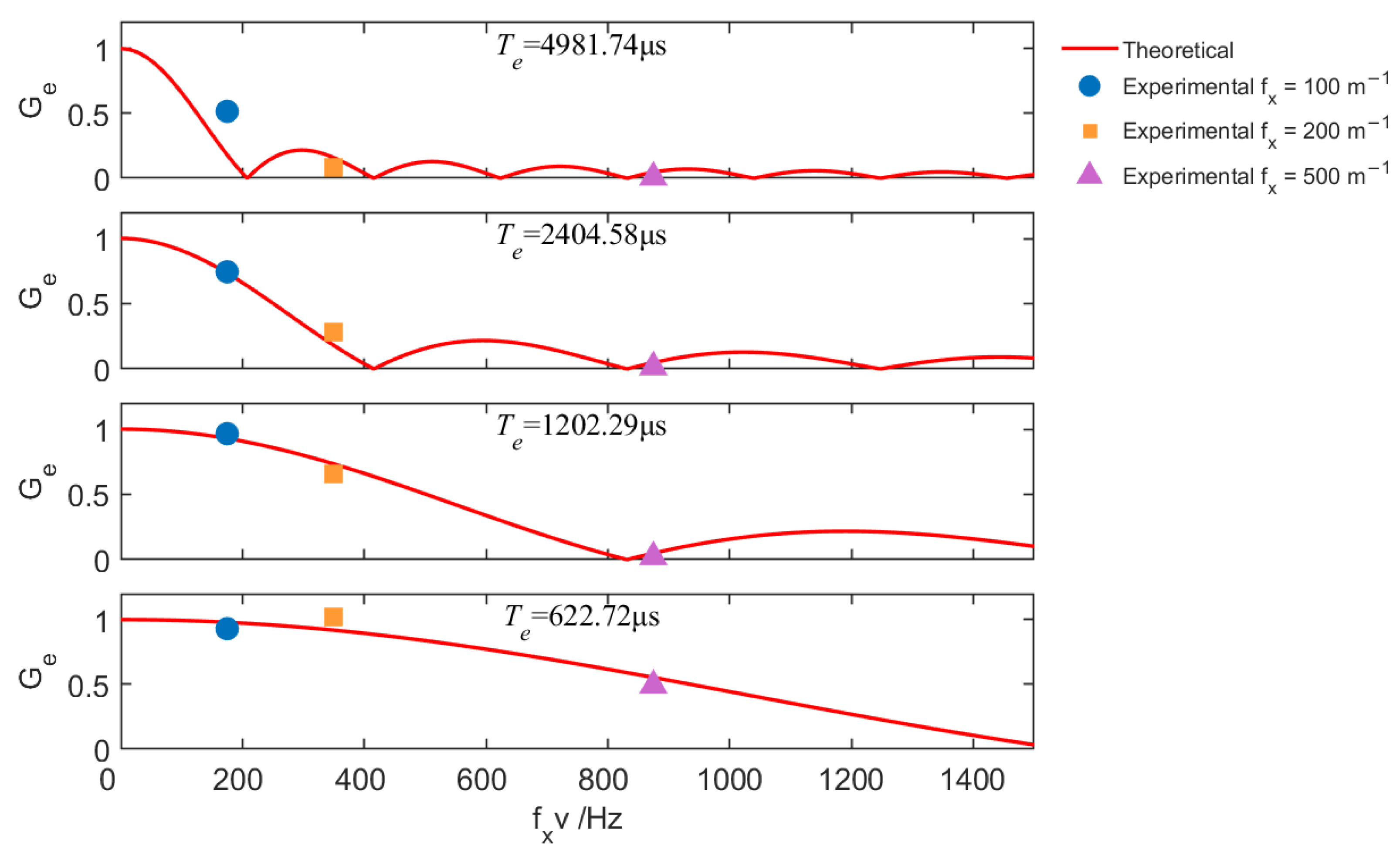
3.2. Normalized Gains for Communication and Sensing
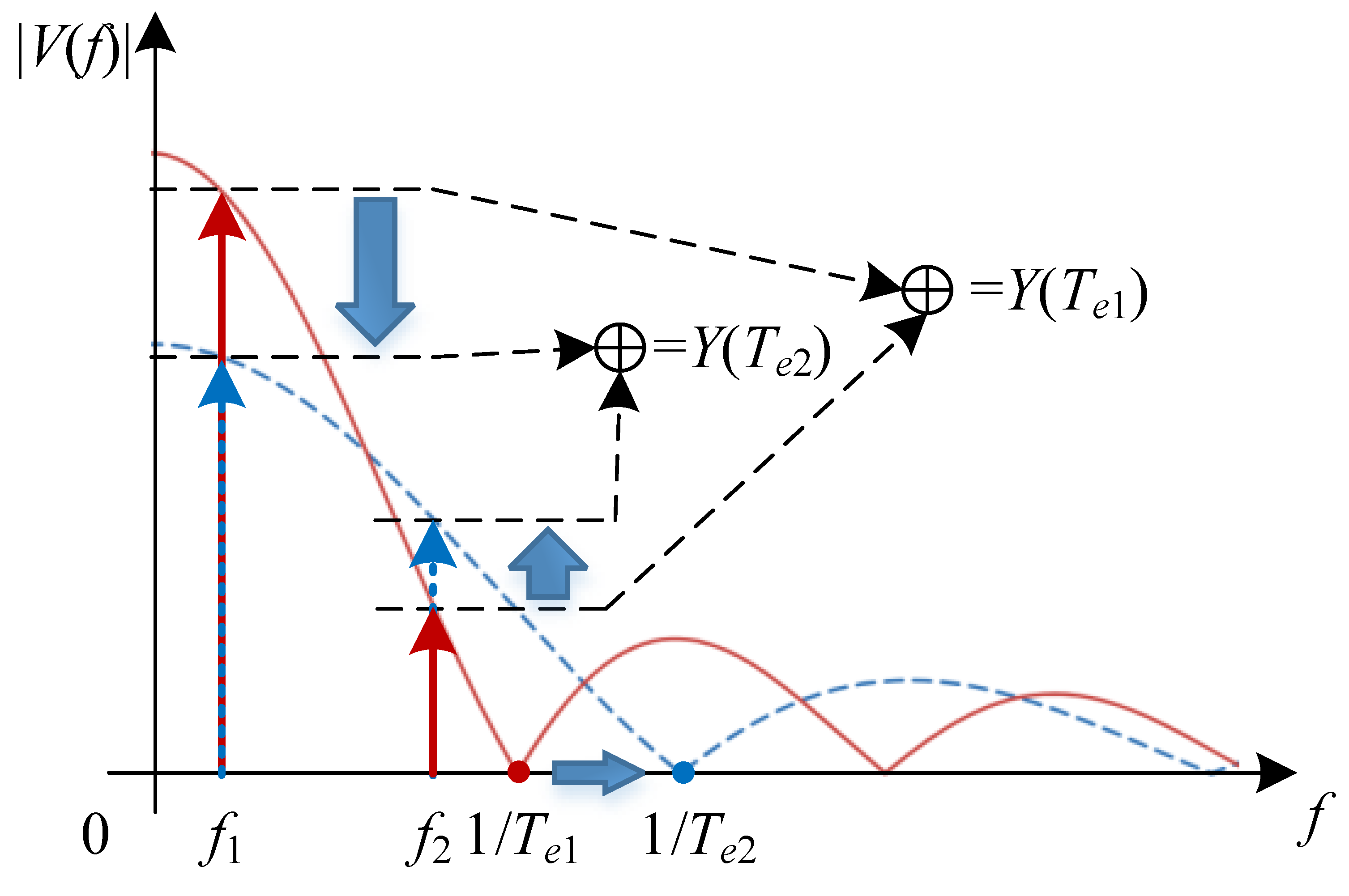
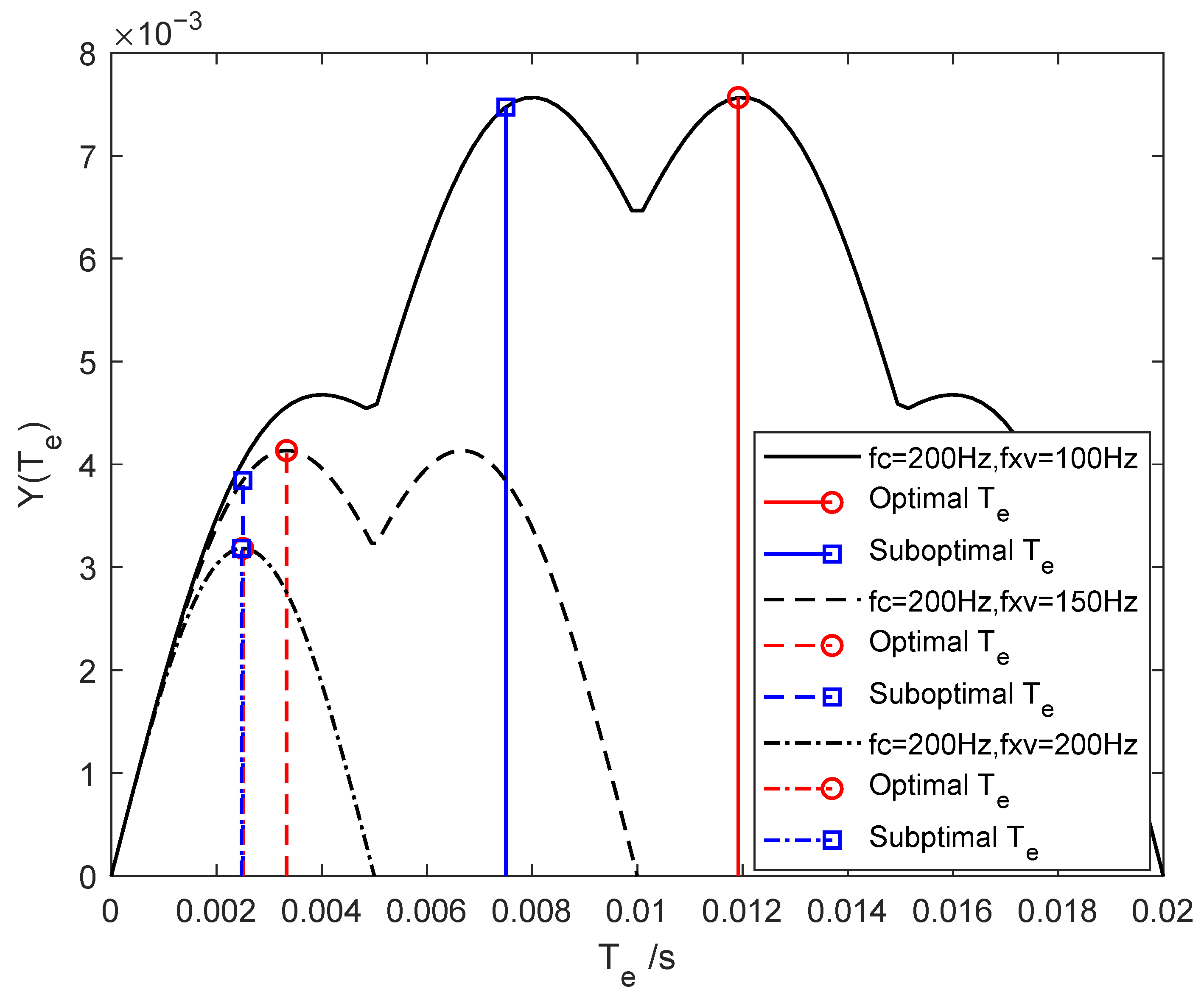
4. Optimization of the Camera’s Exposure Time
4.1. Problem Formulation
4.2. Suboptimal Solution
- Input parameters: Obtain the communication modulation frequency and the sensing frequency .
- Frequency classification: Determine the higher and lower characteristic frequencies:
- Compute the frequency ratio: Evaluate the ratiowhich reflects the disparity between the communication and sensing frequency components.
- Determine the side-lobe index: Estimate the integer parameter indicating the number of side lobes between and in the Sinc-shaped response:
- Compute the suboptimal exposure time: The exposure time that approximately maximizes the joint performance is given by the following:
- Output: The obtained represents the suboptimal exposure time balancing communication reliability and sensing accuracy in the OC-ISAC system.
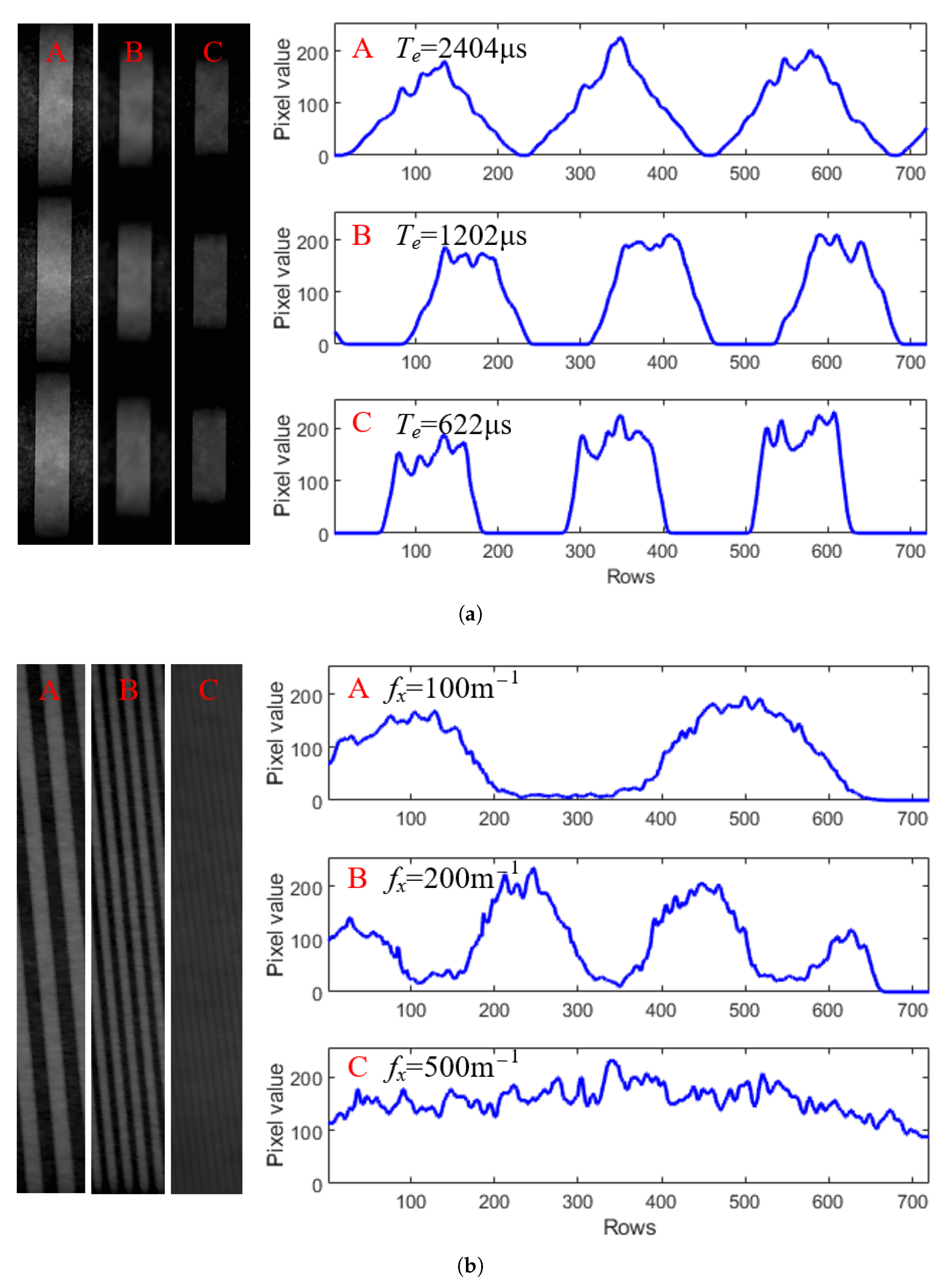
5. Experiment and Results
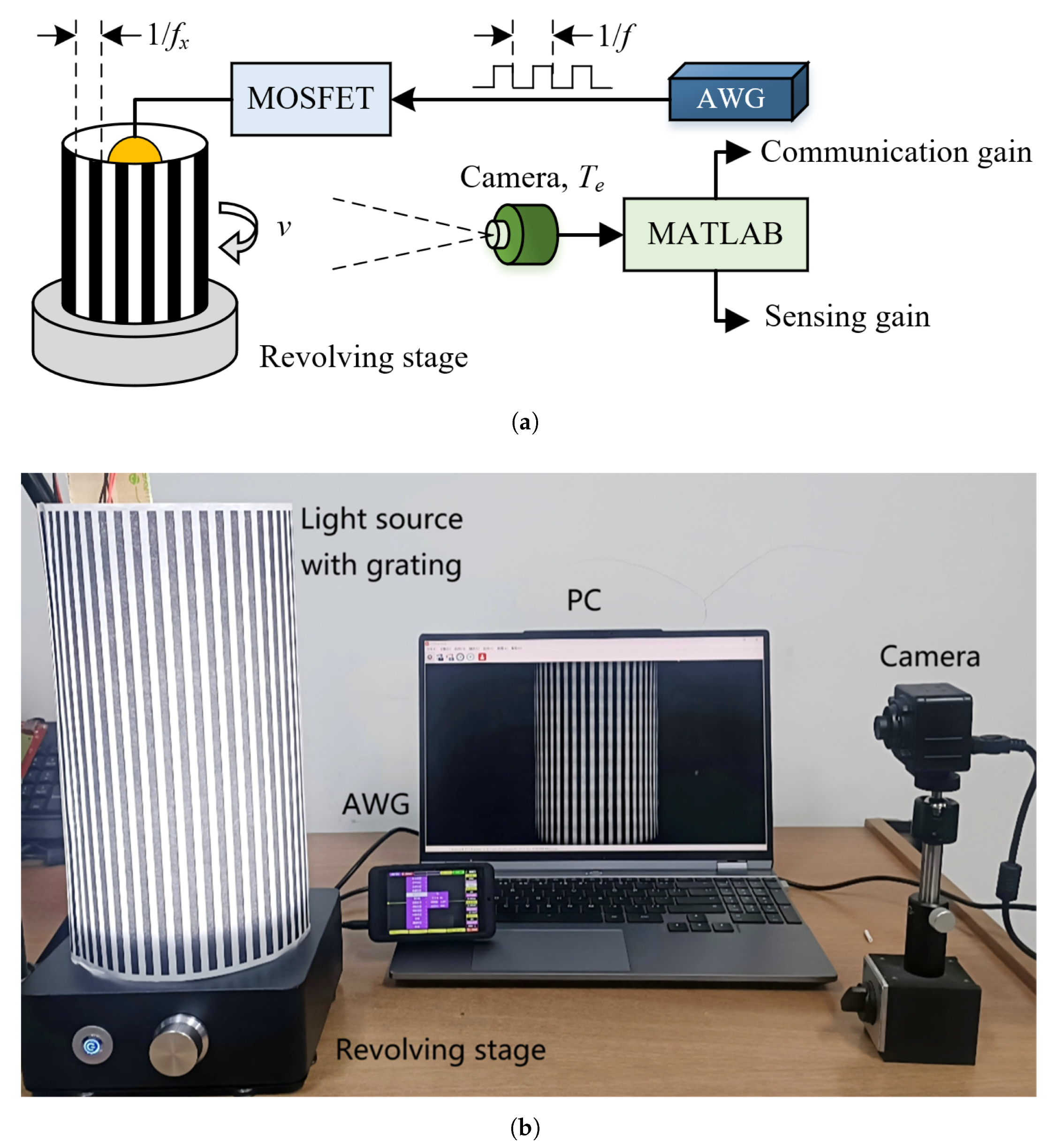
5.1. Experiment Setup
5.2. Methodology
- Input parameters: Confirm the parameter sets of {} and {} for communication and sensing scenarios, respectively.
- Pixel vector: In each scenario, select an arbitrary column of pixels from the output image (in the sensing scenario, choose a column that can be transmitted through the grating) to obtain the pixel value vector, for and .
- Fast Fourier Transformation (FFT): Compute an N-point FFT of to obtain its frequency spectrum vector, for .
- Normalized gains: Compute the normalized gains by the following:where m is the index of the frequency component in DFT caused by data modulation and mobility, which is determined by the following:
5.3. Normalized Gains for Communication and Sensing
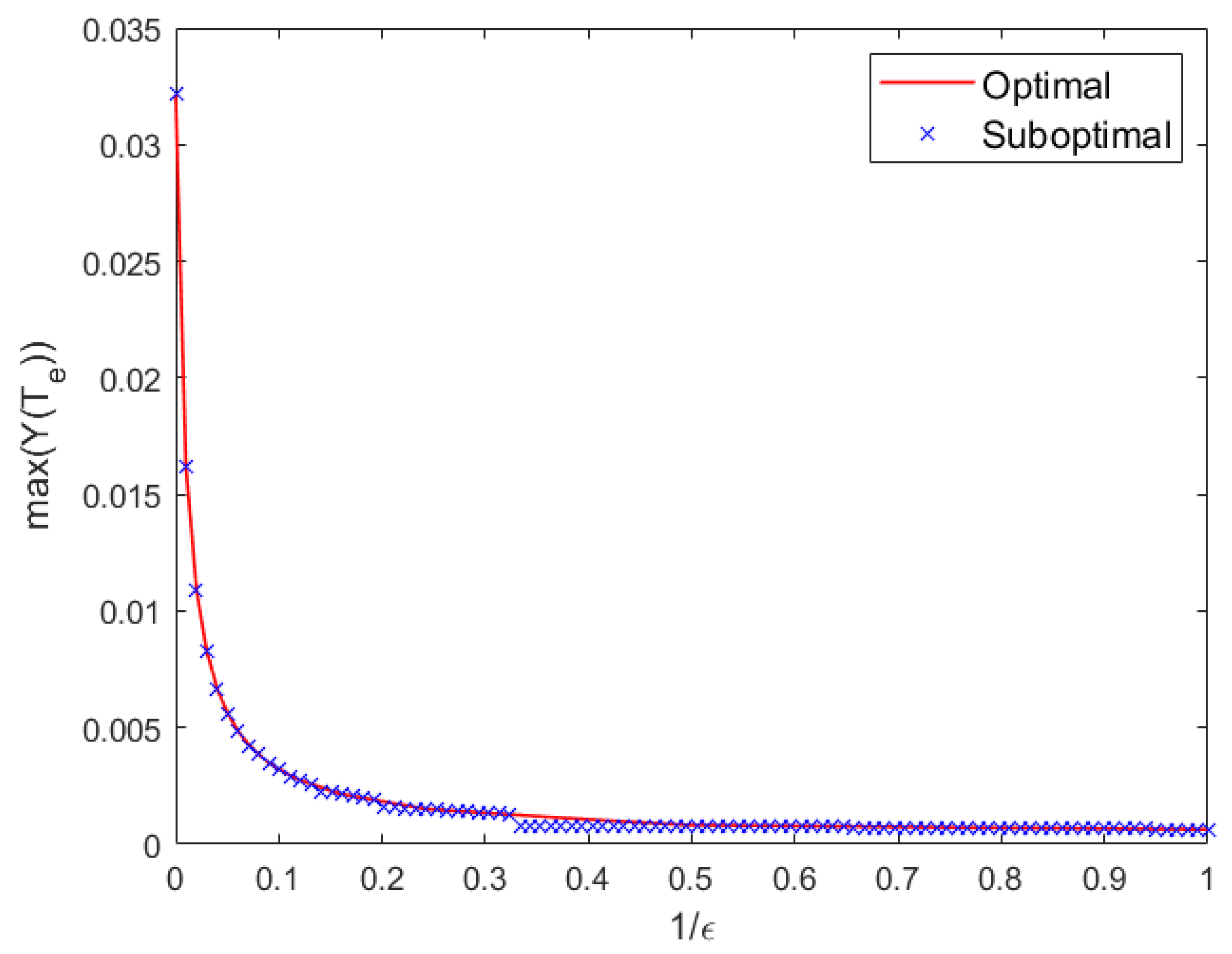
5.4. Optimization of Exposure Time
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohsan, S.A.H. Optical Camera Communications: Practical Constraints, Applications, Potential Challenges, and Future Directions. J. Opt. Technol. 2021, 88, 729–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teli, S.R.; Matus, V.; Younus, O.; Eöllős-Jarošíková, K.; Li, X.; Hassan, N.B.; Lin, B.; Figueiredo, M.; Alves, L.N.; Vegni, A.M.; et al. Optical Camera Communications: Concept, Marketing, Implementation, Challenges and Applications. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2025, 68, 201301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, Z.; Hu, X.; Sun, Y.; Deng, X.; Zhu, B.; Yang, Y. Constraints and Recent Solutions of Optical Camera Communication for Practical Applications. Photonics 2023, 10, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.K.; Ali, M.O.; Rahman, M.H.; Chowdhury, M.Z.; Jang, Y.M. Optical Camera Communication in Vehicular Applications: A Review. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 6260–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Yin, Y.; Tong, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, L.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Q.; Chen, M. Channel Characterization and Modeling for VLC-IoE Applications in 6G: A Survey. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 34872–34895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hassan, N.B.; Burton, A.; Ghassemlooy, Z.; Zvanovec, S.; Perez-Jimenez, R. A Simplified Model for the Rolling Shutter Based Camera in Optical Camera Communications. In Proceedings of the 2019 15th International Conference on Telecommunications (ConTEL), Graz, Austria, 3–5 July 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Rátosi, M.; Simon, G. Robust VLC Beacon Identification for Indoor Camera-Based Localization Systems. Sensors 2020, 20, 2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Zhang, M.; Ghassemlooy, Z.; Le Minh, H.; Tsai, H.M.; Tang, X.; Han, D. Experimental Demonstration of a 1024-QAM Optical Camera Communication System. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2016, 28, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; He, J.; Jiang, Z.W.; Chang, G.K. Modulation Format Shifting Scheme for Optical Camera Communication. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2020, 32, 1167–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lain, J.K.; Yang, Z.D.; Xu, T.W. Experimental DCO-OFDM Optical Camera Communication Systems With a Commercial Smartphone Camera. IEEE Photonics J. 2019, 11, 7906813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Lin, B.; Ghassemlooy, Z.; Huang, T.; Luo, J.; Ding, Y. Non-Line-of-Sight Optical Camera Communications Based on CPWM and a Convolutional Neural Network. Appl. Opt. 2023, 62, 7367–7372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; You, X.; Shi, J.; Chen, J.; Yu, C.; Gao, M.; Shen, G. Dimmable Optical Camera Communications With WDM Using RGB and Infrared LEDs. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2025, 37, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, C.W.; Shiu, R.J.; Liu, Y.C.; Liu, Y.; Yeh, C.H. Non-Flickering 100 m RGB Visible Light Communication Transmission Based on a CMOS Image Sensor. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 7079–7084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younus, O.I.; Hassan, N.B.; Ghassemlooy, Z.; Haigh, P.A.; Zvanovec, S.; Alves, L.N.; Minh, H.L. Data Rate Enhancement in Optical Camera Communications Using an Artificial Neural Network Equaliser. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 42656–42665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Ke, X.Z.; Wang, M.J. Equalization of Camera-Based Channel to Mitigate Uncertain Sampling for Optical Camera Communications. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 47776–47791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younus, O.I.; Hassan, N.B.; Ghassemlooy, Z.; Zvanovec, S.; Alves, L.N.; Le-Minh, H. The Utilization of Artificial Neural Network Equalizer in Optical Camera Communications. Sensors 2021, 21, 2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, P.P.; Sun, Y.M.; Deng, X.; Yang, Y.B.; Chen, L.Y. High-Speed Extraction of Regions of Interest in Optical Camera Communication Enabled by Grid Virtual Division. Sensors 2022, 22, 8375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Islam, A.; Jang, Y.M. Region-of-Interest Signaling Vehicular System Using Optical Camera Communications. IEEE Photonics J. 2017, 9, 7900720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Kong, M.; Wang, M. Error Performance Analysis for OOK Modulated Optical Camera Communication Systems. Opt. Commun. 2025, 574, 131121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, A.; Jain, S.; Gruteser, M.; Mandayam, N.; Yuan, W.; Dana, K. Capacity of Screen–Camera Communications under Perspective Distortions. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2015, 16, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Kong, M.; Su, W.; Ma, S.; Wang, M. Generalized Modulation for Distance-Aware Optical Camera Communication beyond Oversampled and Undersampled Schemes. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 16319–16332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 802.15.7a-2024; IEEE Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks—Part 15.7: Short-Range Optical Wireless Communications Amendment 1: Higher Rate, Longer Range Optical Camera Communication (OCC). Amendment to IEEE Std 802.15.7-2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2025; pp. 1–52.
- Guo, M.; Zhang, P.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y. Object Recognition in Optical Camera Communication Enabled by Image Restoration. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 37026–37037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhou, B. Vehicle Positioning Scheme Based on Visible Light Communication Using a CMOS Camera. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 27278–27290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifthekhar, M.S.; Le, N.T.; Hossain, M.A.; Nguyen, T.; Jang, Y.M. Neural Network-Based Indoor Positioning Using Virtual Projective Invariants. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2016, 86, 1813–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Duan, D.; Gao, S.; Yang, L. Integrated Sensing and Communications (ISAC) for Vehicular Communication Networks (VCN). IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 23441–23451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Liu, F.; Li, Y.X.; Yuan, W.J.; Cui, Y.H.; Zhang, Z.H.; Masouros, C.; Ai, B. Toward ISAC-Empowered Vehicular Networks: Framework, Advances, and Opportunities. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2025, 32, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.W.; Li, S.B.; Li, D.Y.; Zhu, J.Z.; Guan, Q.S. Transformer-Based Predictive Beamforming for Integrated Sensing and Communication in Vehicular Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 20690–20705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Mo, R.; Zhang, P.; Wang, C.; Sheng, Z.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Y. VehicleTalk: Lightweight V2V Network Enabled by Optical Wireless Communication and Sensing. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 99th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2024-Spring), Singapore, 24–27 June 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, C.; Pan, Y.; Xu, Z. Unified ultraviolet communication and sensing: Modeling and system optimization. J. Commun. 2023, 44, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Wu, J.; Wei, Z.; Sun, Y.; Deng, R.; Yang, Y. Channel Modeling for NLoS Visible Light Networks with Integrated Sensing and Communication. Opt. Lett. 2024, 49, 2861–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Yang, F.; Song, J.; Han, Z. Optical Integrated Sensing and Communication: Architectures, Potentials and Challenges. IEEE Internet Things Mag. 2024, 7, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, N.; Yang, F.; Cheng, L.; Song, J.; Han, Z. Free Space Optical Communications for Intelligent Transportation Systems: Potentials and Challenges. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2023, 18, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Yang, F.; Dong, Y.; Song, J.; Zhang, X.P.; Ding, W. Integrated Sensing, Lighting and Communication Based on Visible Light Communication: A Review. Digit. Signal Process. 2024, 145, 104340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
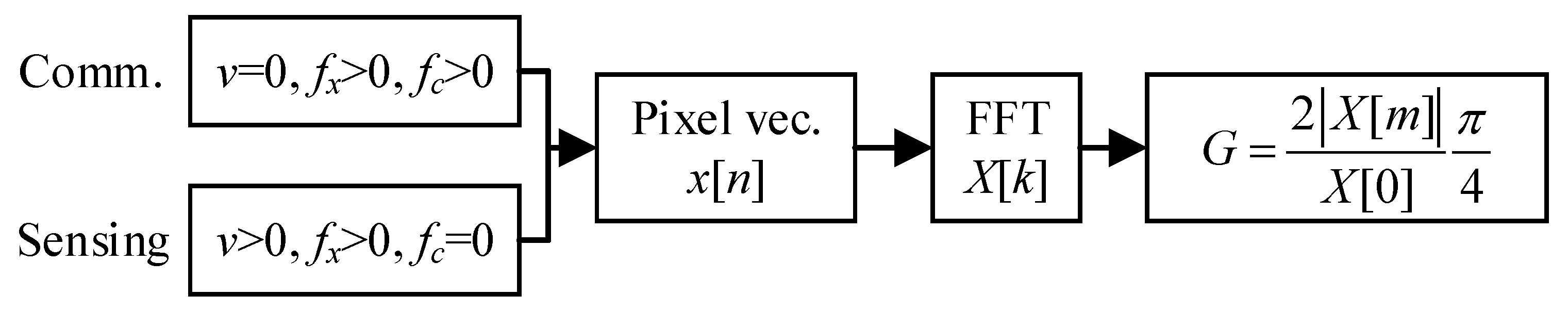
| Symbol | Description | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| A | Conversion gain of the image sensor | - |
| Signal attenuation for light propagation over distance d | - | |
| Exposure time of image sensor | μs | |
| Position vector in 3-D space | m | |
| Maximum intensity of the communication light source | ||
| , , | Amplitude, frequency, and phase of the communication carrier | V, Hz, rad |
| Maximum intensity of the sensing light source | ||
| , | Spatial frequency and phase of sensing along given direction x | Hz, rad |
| v | Speed of motion | m/s |
| Luminous factor caused by data modulation | - | |
| Reflective factor caused by environmental mobility | - |
| Parameter | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Image sensor | - | SONY IM291 (Shenzhen, China) |
| Image resolution, | - | |
| Frame rate | FPS | 30 |
| Readout time, | μs | 22.2 |
| Exposure time, | μs | 622, 1202, 2404, 4981 |
| Camera distance | m | 0.3 |
| Annular grating diameter, | m | 0.15 |
| Turntable rotation speed, | rpm | 223 |
| Communication frequency, | Hz | 0, 200, 500, 700 |
| Grating width | m | 0.01, 0.005, 0.002 |
| Environmental complexity, | m−1 | 100, 200, 500 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, K.; Cao, W.; Wang, M. Optical Camera-Based Integrated Sensing and Communication for V2X Applications: Model and Optimization. Sensors 2025, 25, 7061. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25227061
Dong K, Cao W, Wang M. Optical Camera-Based Integrated Sensing and Communication for V2X Applications: Model and Optimization. Sensors. 2025; 25(22):7061. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25227061
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Ke, Wenying Cao, and Mingjun Wang. 2025. "Optical Camera-Based Integrated Sensing and Communication for V2X Applications: Model and Optimization" Sensors 25, no. 22: 7061. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25227061
APA StyleDong, K., Cao, W., & Wang, M. (2025). Optical Camera-Based Integrated Sensing and Communication for V2X Applications: Model and Optimization. Sensors, 25(22), 7061. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25227061





