Compact Optical Visual Magnification System with a Wide Field of View
Highlights
- A Power-Corrector (PC) group positioned between the objective and intermediate image enables unified optimization of the optical system, achieving superior performance with an 86° apparent field of view while maintaining compact dimensions.
- The PC-based design demonstrates significantly improved optical quality with ~5% distortion compared to ~24% in conventional designs and achieves 42.5% length reduction and 44.9% diameter reduction compared to Nagler-based systems with identical specifications.
- The PC group enables practical wide-field optical devices with 1.6× larger FOV diameter (~2.56× viewing area) than conventional monoculars of identical physical dimensions, enhancing scene scanning efficiency for applications requiring stationary observation with eye movement scanning.
- This technology enables compact, high-performance monoculars, binoculars, and spotting scopes suitable for bird watching, hunting, sports, military, and astronomical applications, addressing the traditional trade-off between field of view and system compactness.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Power-Corrector Group Design Methodology
2.2. Design Methodology
3. Results
3.1. Design and Performance
3.2. Enhanced Compactness and Field of View Performance
3.3. Comparison of Field of View Performance Between PC-Equipped and Standard Monoculars
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Definition |
| PC | Power-Corrector |
| FOV | Field of View |
| ExP | Exit Pupil |
| ER | Eye Relief |
| MTF | Modulation Transfer Function |
| EFL | Effective Focal Length |
References
- Smith, G.H.; Ceragioli, R.; Berry, R. Telescopes, Eyepieces and Astrographs: Design, Analysis and Performance of Modern Astronomical Optics; Willmann Bell: Richmond, VA, USA, 2012; ISBN 0943396964, 9780943396965. [Google Scholar]
- Rutten, H.G.; van Venrooij, M.A. Telescope Optics: Evaluation and Design; Willmann Bell: Richmond, VA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, R.E.; Tadic-Galeb, B.; Yoder, P.R. Optical System Design, 2nd ed.; McGraw Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://www.telescope-optics.net/ (accessed on 17 September 2025).
- Nagler, A. Ultrawide Angle Flat Field Eyepiece. U.S. Patent No. 4,286,844, 1 September 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Dilworth, D.C. Telephoto Lens System. U.S. Patent No. 4,720,183, 19 January 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Wirth-Singh, A.; Fröch, J.E.; Yang, F.; Martin, L.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, H.; Tanguy, Q.T.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, L.; John, D.D.; et al. Wide field of view large aperture meta doublet eyepiece. Light Sci. Appl. 2024, 13, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Hugot, E.; Muslimov, E.; Lombardo, S. Compact off-axis reflective optical system design combining freeform mirror and freeform detector. Opt. Commun. 2024, 565, 130675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushibiki, K.; Ozaki, S.; Takeda, M.; Hosobata, T.; Yamagata, Y.; Morita, S.-Y.; Tsuzuki, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Saiki, T.; Ohtake, Y.; et al. Development of a near-infrared wide-field integral field unit by ultra-precision diamond cutting. J. Astron. Telesc. Instrum. Syst. 2024, 10, 015004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, K.P.; Rolland, J.P. Freeform optical surfaces: A revolution in imaging optical design. Opt. Photonics News 2012, 23, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falaggis, K.; Rolland, J.; Duerr, F.; Sohn, A. Freeform optics: Introduction. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 6450–6455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Chen, L.; Li, X.; Yuan, Q.; Gao, Z. Review of optical freeform surface representation technique and its application. Opt. Eng. 2017, 56, 110901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippman, D.H.; Kochan, N.S.; Yang, T.; Schmidt, G.R.; Bentley, J.L.; Moore, D.T. Freeform gradient-index media: A new frontier in freeform optics. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 36997–37012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, C.; Meng, Q. Reflecting optical systems desensitization: Modulation by freeform surfaces. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2024, 180, 108317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Ma, X.; Ke, J. Freeform surface based optical design of a broadband compressive spectral imager with co-aperture coding. Appl. Opt. 2024, 63, 6165–6172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Shi, C.; Li, Z.; Yang, C.; Liu, B.; Zhu, X.; Liang, H.; Cai, C.; et al. Freeform optical design via surface type conversion: A dual optimization strategy for miniaturized high resolution imaging system. J. Opt. 2025, 27, 075702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yan, C.; Shao, M. Design method of freeform surface optical systems with low coupling position error sensitivity. Sensors 2024, 24, 4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Su, R.; Ottevaere, H. Freeform optical system design with differentiable three-dimensional ray tracing and unsupervised learning. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 7450–7465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kim, S.J. Meta-Optics for Optical Engineering of Next Generation AR/VR Near Eye Displays. Micromachines 2025, 16, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milman, U.; Kaufmann, J.; Safra, E.; Arieli, Y. Uri Milman Compact Magnifying Optical System with Wide Field of View. U.S. Patent No. 8928975, 6 January 2025. [Google Scholar]
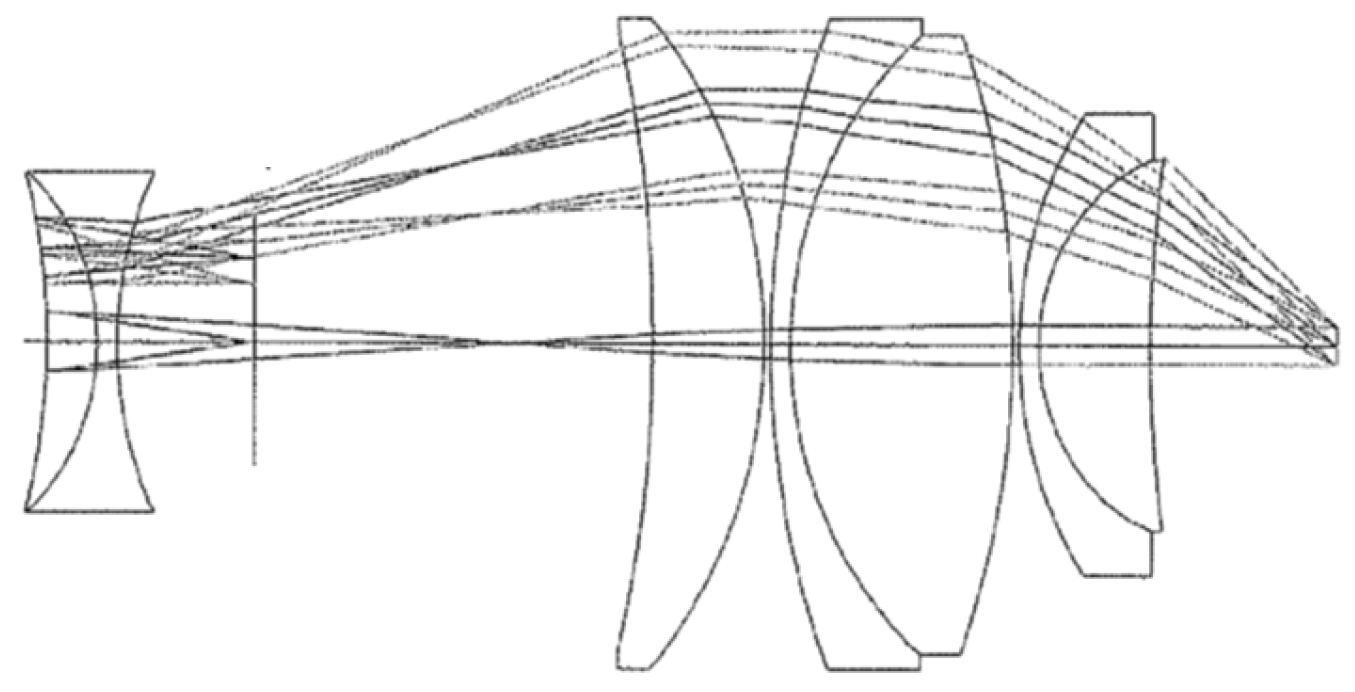
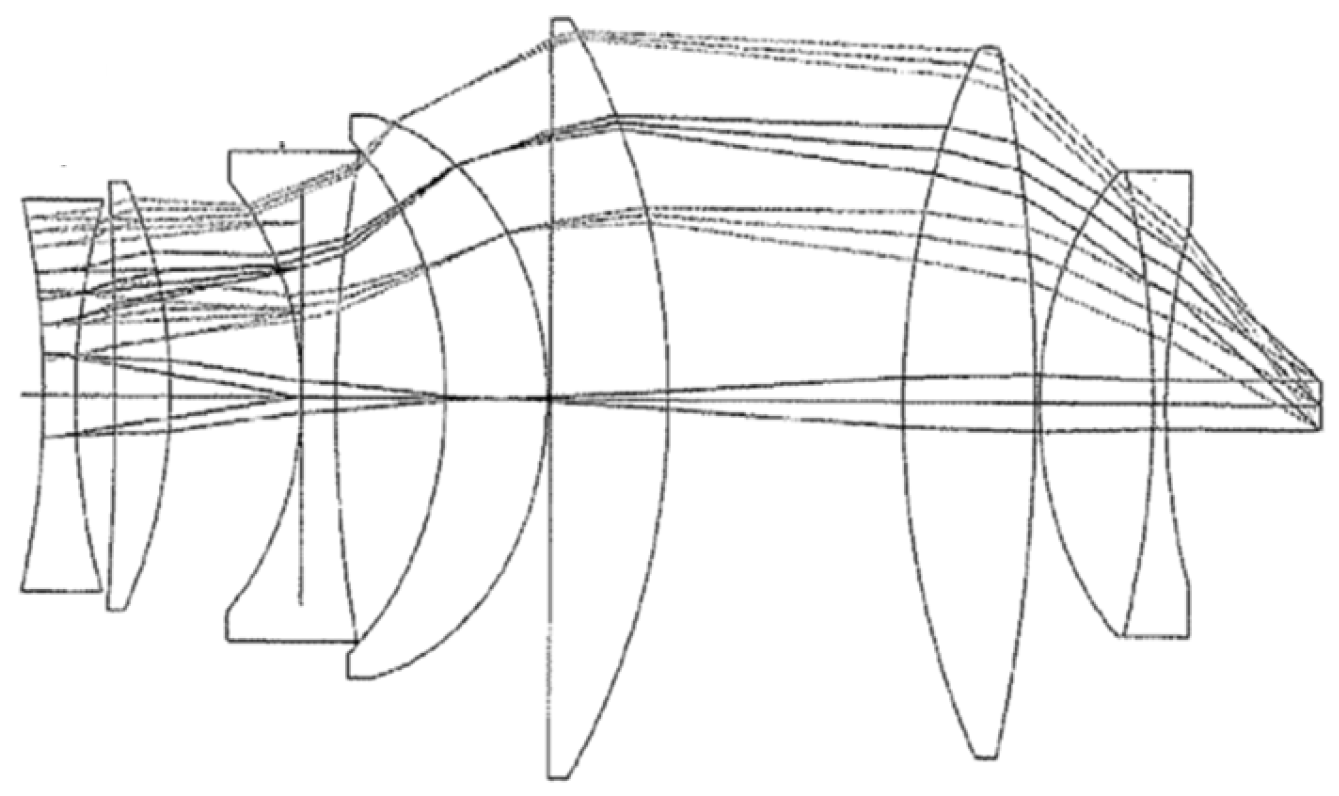
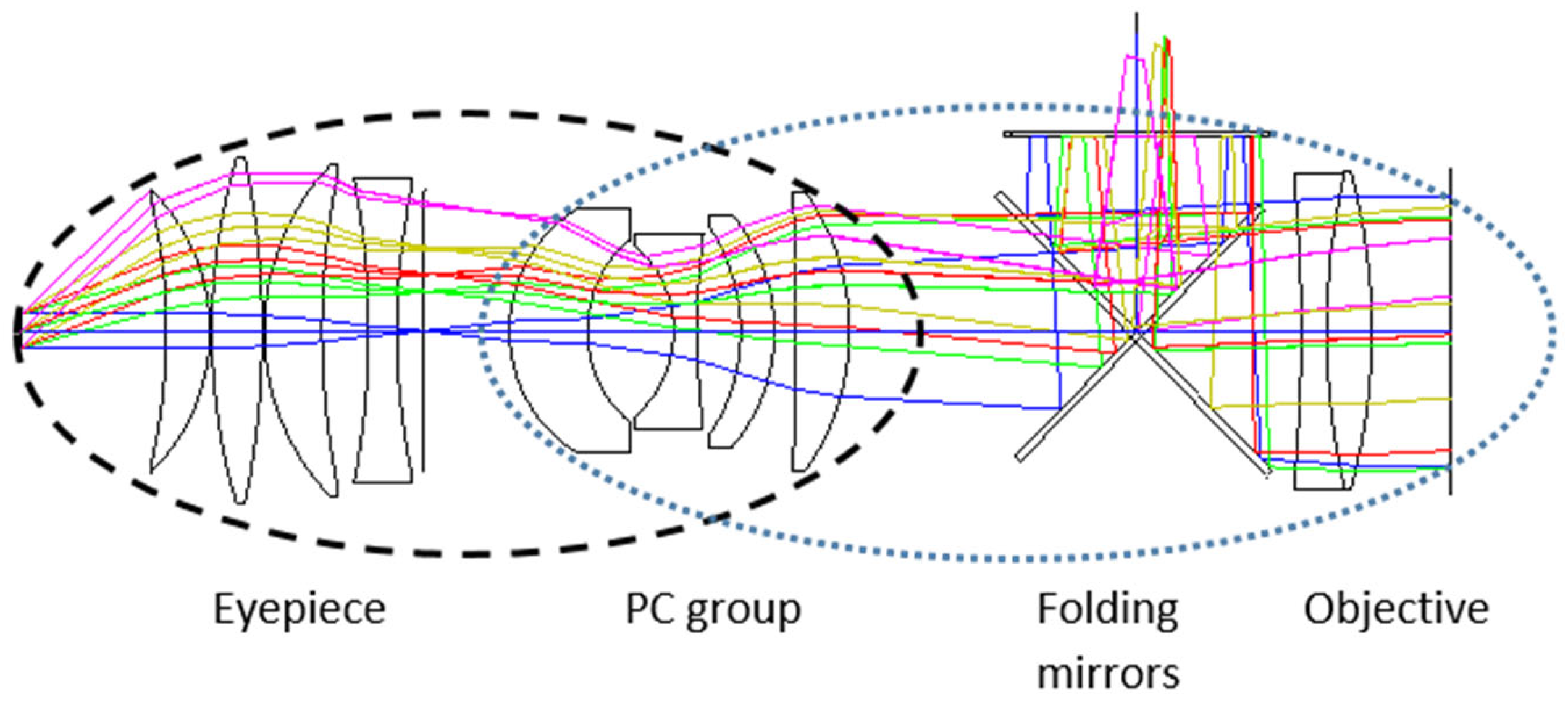
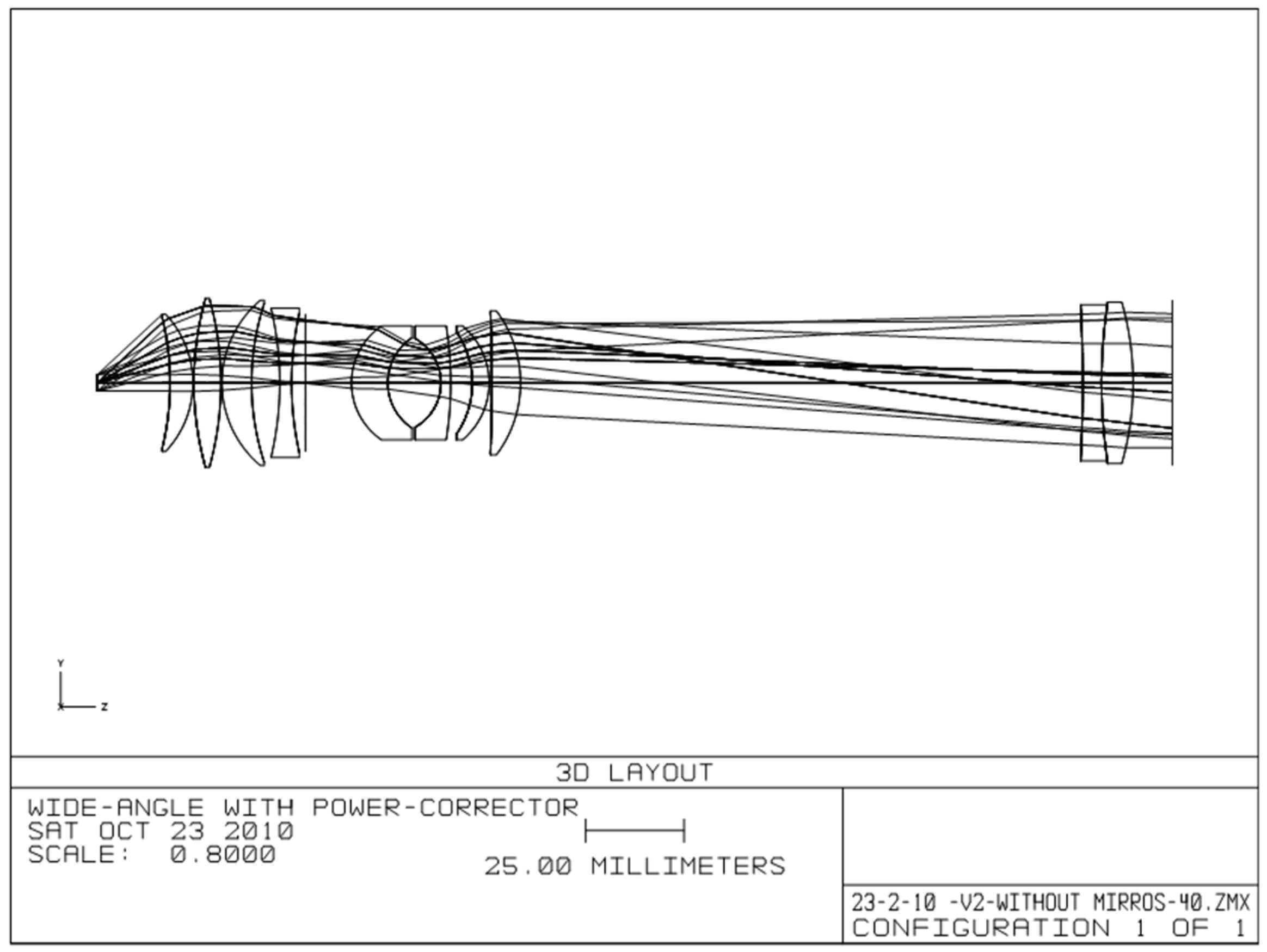
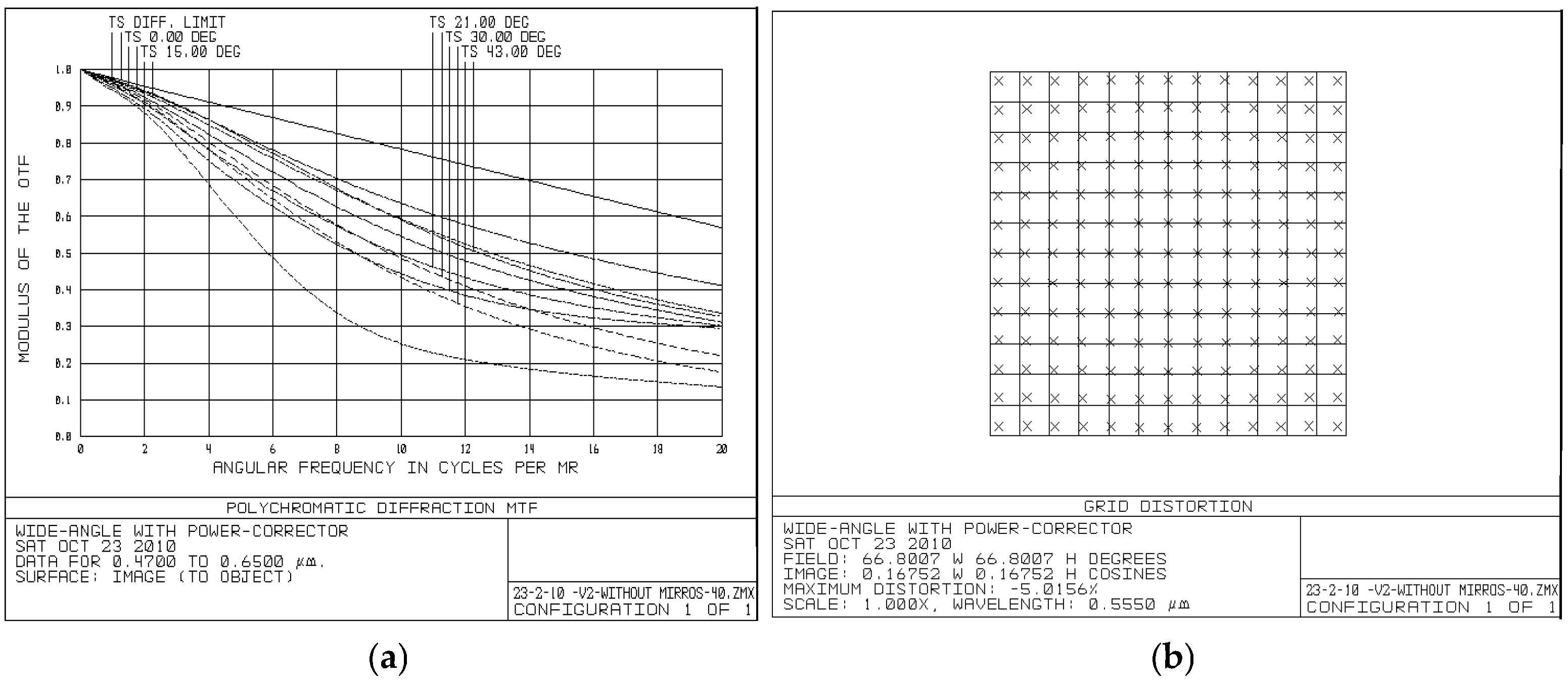
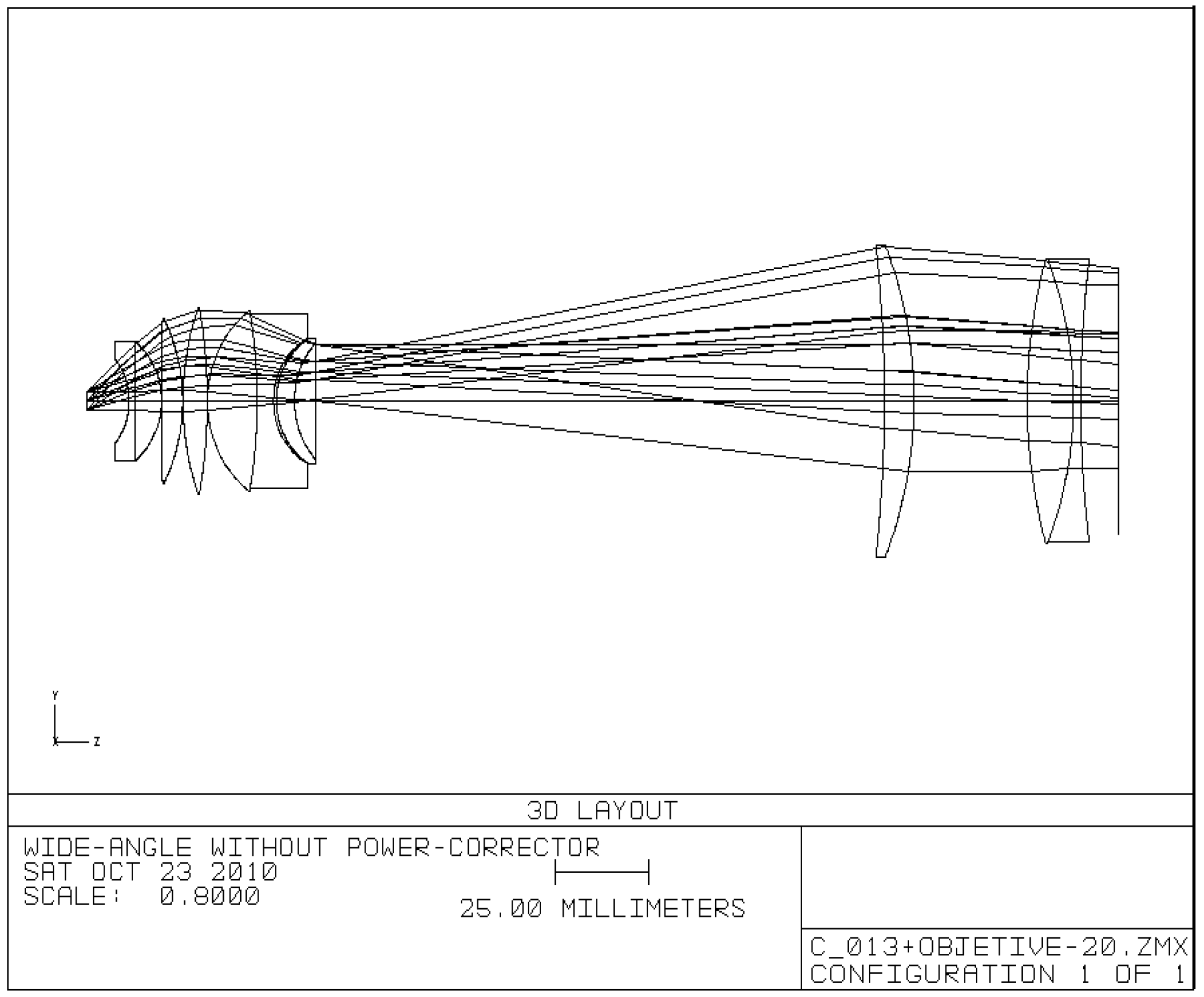
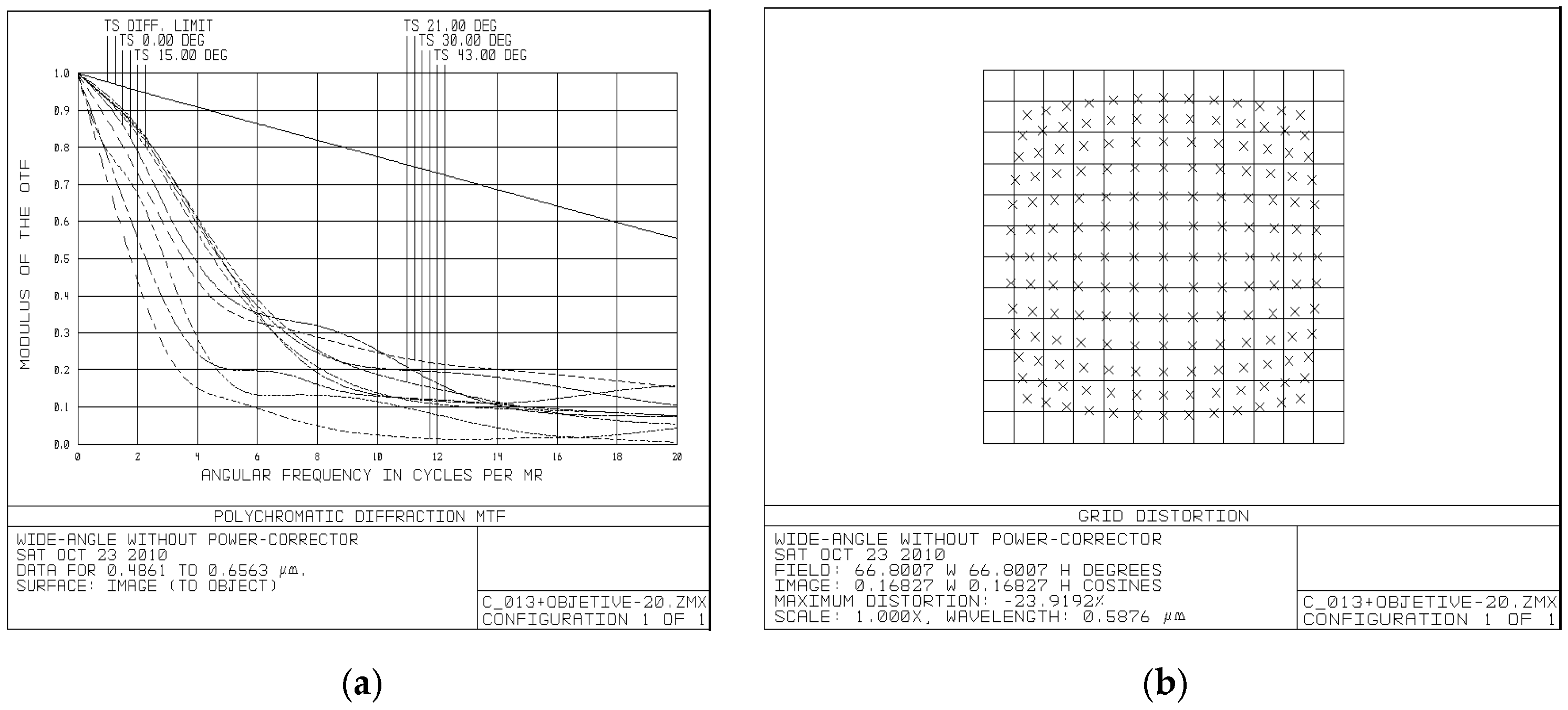


| Surf | Comment | Type | Radius | Thickness | Glass | Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OBJ | STANDARD | Infinity | Infinity | 0 | ||
| STO | Exit Pupil | STANDARD | Infinity | 18.5 | 4.2 | |
| 2 | Eyepiece lens 1 | STANDARD | −69.99975 | 5.807029 | N-LASF43 | 33 |
| 3 | Eyepiece lens 1 | STANDARD | −25.44476 | 0.2402004 | 35 | |
| 4 | Eyepiece lens 2 | STANDARD | 79.79214 | 6.887695 | N-LAK9 | 43 |
| 5 | Eyepiece lens 2 | STANDARD | −79.79214 | 0.2499943 | 43 | |
| 6 | Eyepiece lens 3 | STANDARD | 27.59204 | 7.534562 | N-SF1 | 42.09881 |
| 7 | Eyepiece lens 3 | STANDARD | 65.36421 | 7.185632 | 40.5138 | |
| 8 | Eyepiece lens 4 | STANDARD | −81.64127 | 3 | N-BASF2 | 38.04538 |
| 9 | Eyepiece lens 4 | STANDARD | 81.64127 | 3.5 | 35.50076 | |
| 10 | intermediate image | STANDARD | Infinity | 11.72949 | 34.88509 | |
| 11 | PC lens 5 | STANDARD | 17.6026 | 9.235033 | N-SF57 | 29 |
| 12 | PC lens 5 | STANDARD | 13.83732 | 13.52949 | 23 | |
| 13 | PC lens 6 | STANDARD | −12.99517 | 2.48984 | N-LAF7 | 22.616 |
| 14 | PC lens 6 | STANDARD | −91.26436 | 5.492719 | 29 | |
| 15 | PC lens 7 | STANDARD | −23.0725 | 4.277042 | N-SF5 | 26 |
| 16 | PC lens 7 | STANDARD | −18.97247 | 0.6944073 | 29 | |
| 17 | PC lens 8 | STANDARD | −457.7323 | 7.284854 | N-BASF64 | 35.774 |
| 18 | PC lens 8 | STANDARD | −30.42477 | 143 | 36.67637 | |
| 19 | Objective lens 9 | STANDARD | −381.2483 | 4.796475 | N-SF6 | 38.49232 |
| 20 | Objective lens 10 | STANDARD | 133.6307 | 8.012712 | N-BAK2 | 39.79242 |
| 21 | Objective lens 10 | STANDARD | −75.35432 | 10 | 41.15424 | |
| IMA | To object | STANDARD | Infinity | 41.97317 |
| Surf | Comment | Type | Radius | Thickness | Glass | Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OBJ | STANDARD | Infinity | Infinity | 0 | ||
| STO | Exit pupil | STANDARD | Infinity | 11.22352 | 4.2 | |
| 2 | Eyepiece lens 1 | STANDARD | −15.9638 | 1.471002 | SF12 | 20.16894 |
| 3 | Eyepiece lens 2 | STANDARD | 343.0037 | 7.166386 | SK16 | 28.65183 |
| 4 | Eyepiece lens 2 | STANDARD | −18.3646 | 0.1 | 29.18207 | |
| 5 | Eyepiece lens 3 | STANDARD | 1020.46 | 5.542679 | SK16 | 39.27781 |
| 6 | Eyepiece lens 3 | STANDARD | −42.42625 | 0.1 | 39.78866 | |
| 7 | Eyepiece lens 4 | STANDARD | 65.24167 | 6.441244 | SK16 | 44.99595 |
| 8 | Eyepiece lens 6 | STANDARD | −125.3955 | 0.08242904 | 45.03692 | |
| 9 | Eyepiece lens 5 | STANDARD | 27.17794 | 13.26808 | SK16 | 43.59262 |
| 10 | Eyepiece lens 6 | STANDARD | −118.7091 | 4.314647 | SF12 | 42.57508 |
| 11 | Eyepiece lens 6 | STANDARD | 17.23902 | 0.8302175 | 30.22803 | |
| 12 | Eyepiece lens 7 | STANDARD | 17.74849 | 4.768924 | SF12 | 30.44236 |
| 13 | Eyepiece lens 7 | STANDARD | 20.49193 | 5.827407 | 28.59791 | |
| 14 | Intermediate image | STANDARD | Infinity | 151.5005 | 28.59794 | |
| 15 | Objective lens 8 | STANDARD | −323.258 | 7.926562 | N-LASF31A | 74.83004 |
| 16 | Objective lens 8 | STANDARD | −96.83467 | 30.21642 | 75.60162 | |
| 17 | Objective lens 9 | STANDARD | 123.8577 | 12.32034 | N-K5 | 68.80706 |
| 18 | Objective lens 10 | STANDARD | −89.16053 | 1.912899 | P-SF8 | 68.52388 |
| 19 | Objective lens 10 | STANDARD | 252.4839 | 10 | 66.56563 | |
| IMA | to object | STANDARD | Infinity | 64.54548 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Milman, U.; Kaufmann, J.; Arieli, Y. Compact Optical Visual Magnification System with a Wide Field of View. Sensors 2025, 25, 7025. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25227025
Milman U, Kaufmann J, Arieli Y. Compact Optical Visual Magnification System with a Wide Field of View. Sensors. 2025; 25(22):7025. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25227025
Chicago/Turabian StyleMilman, Uri, Jacob Kaufmann, and Yoel Arieli. 2025. "Compact Optical Visual Magnification System with a Wide Field of View" Sensors 25, no. 22: 7025. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25227025
APA StyleMilman, U., Kaufmann, J., & Arieli, Y. (2025). Compact Optical Visual Magnification System with a Wide Field of View. Sensors, 25(22), 7025. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25227025





