Multimodal Optimal Base Station Selection Network for Intelligent Communications
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Multimodal Optimal Base Station Selection Network. We propose MOBS-Net, which combines two complementary modules: a real-time base station judgment network and a sequential base station prediction network. This unified framework enables both accurate current-time base station selection and proactive prediction of the optimal base station at future time slots.
- Real-time multimodal judgment network. The judgment module utilizes a convolutional neural network for image feature extraction and a Transformer-based mechanism for multimodal fusion. By integrating channel state, user location, and environmental perception data, this approach enhances the accuracy and robustness of optimal base station selection.
- Sequential multimodal prediction network. The prediction module exploits multimodal temporal data and introduces a large-scale multimodal model to capture sequential semantics and refine task-specific predictions. This design enhances the continuity of environment understanding and enables preemptive base station switching before LOS link blockage occurs. Experimental results demonstrate that our framework achieves accuracy for base station judgment and for prediction, significantly outperforming single-modal approaches.
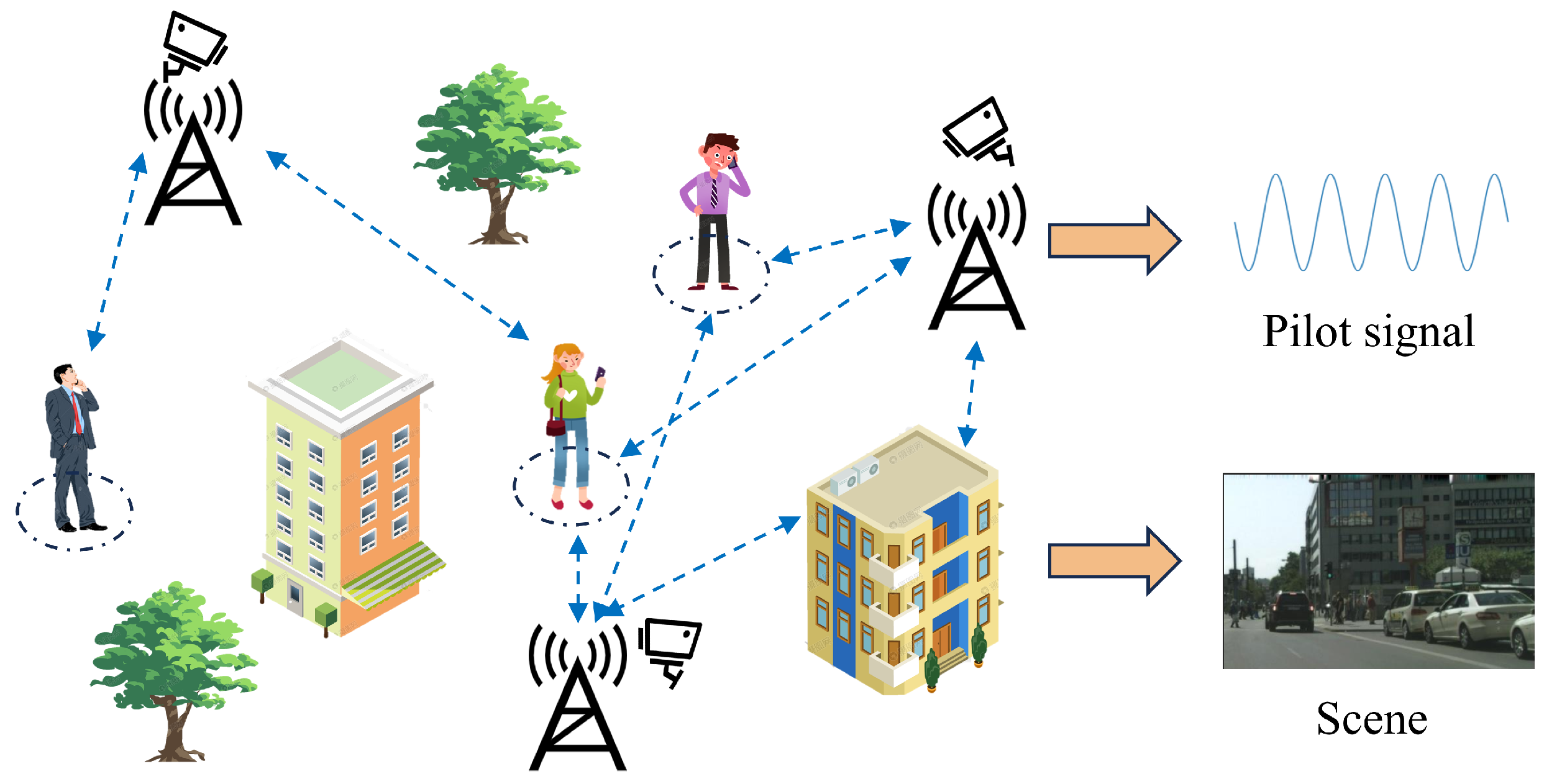
2. High-Frequency Wireless Communication System Modeling
2.1. System Model
2.2. Channel Model
2.3. Problem Formulation
2.3.1. Optimal Base Station Identification Problem
2.3.2. Optimal Base Station Prediction Problem
3. Multimodal Optimal Base Station Selection Network
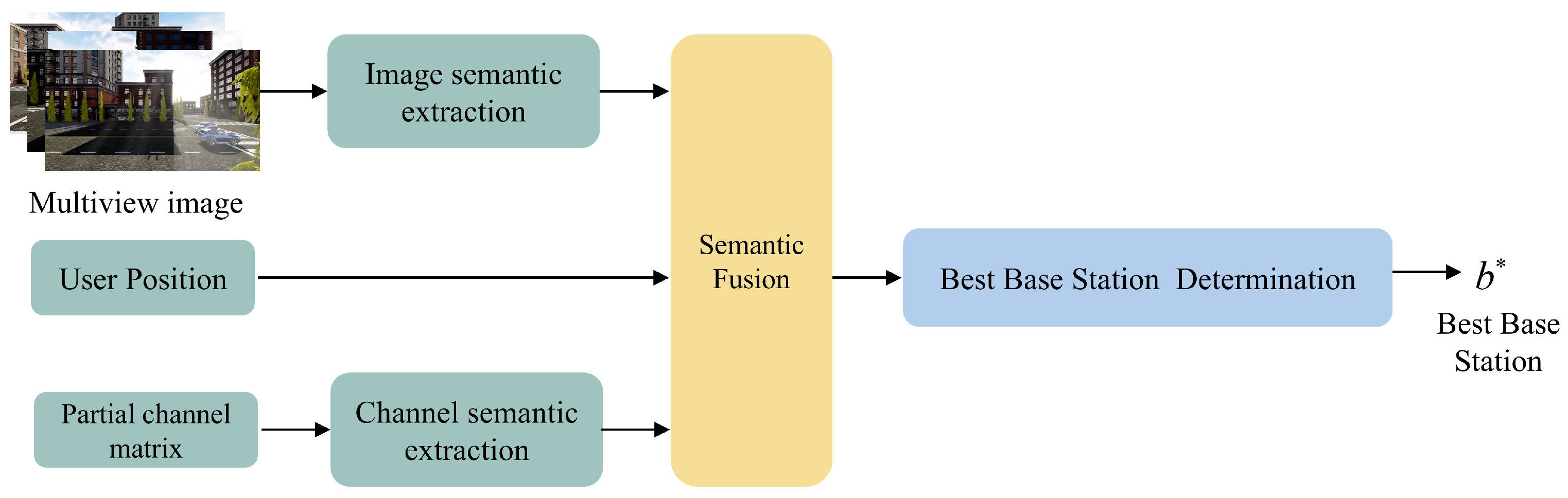
3.1. Optimal Base Station Judgment Network
3.2. Multimodal Semantic Fusion and Optimal Base Station Classification Network
3.3. Multimodal Large Model-Enabled Optimal Base Station Prediction Network
4. Simulation and Analysis
4.1. Simulation Setup
4.2. Configuration of Base Station Networks
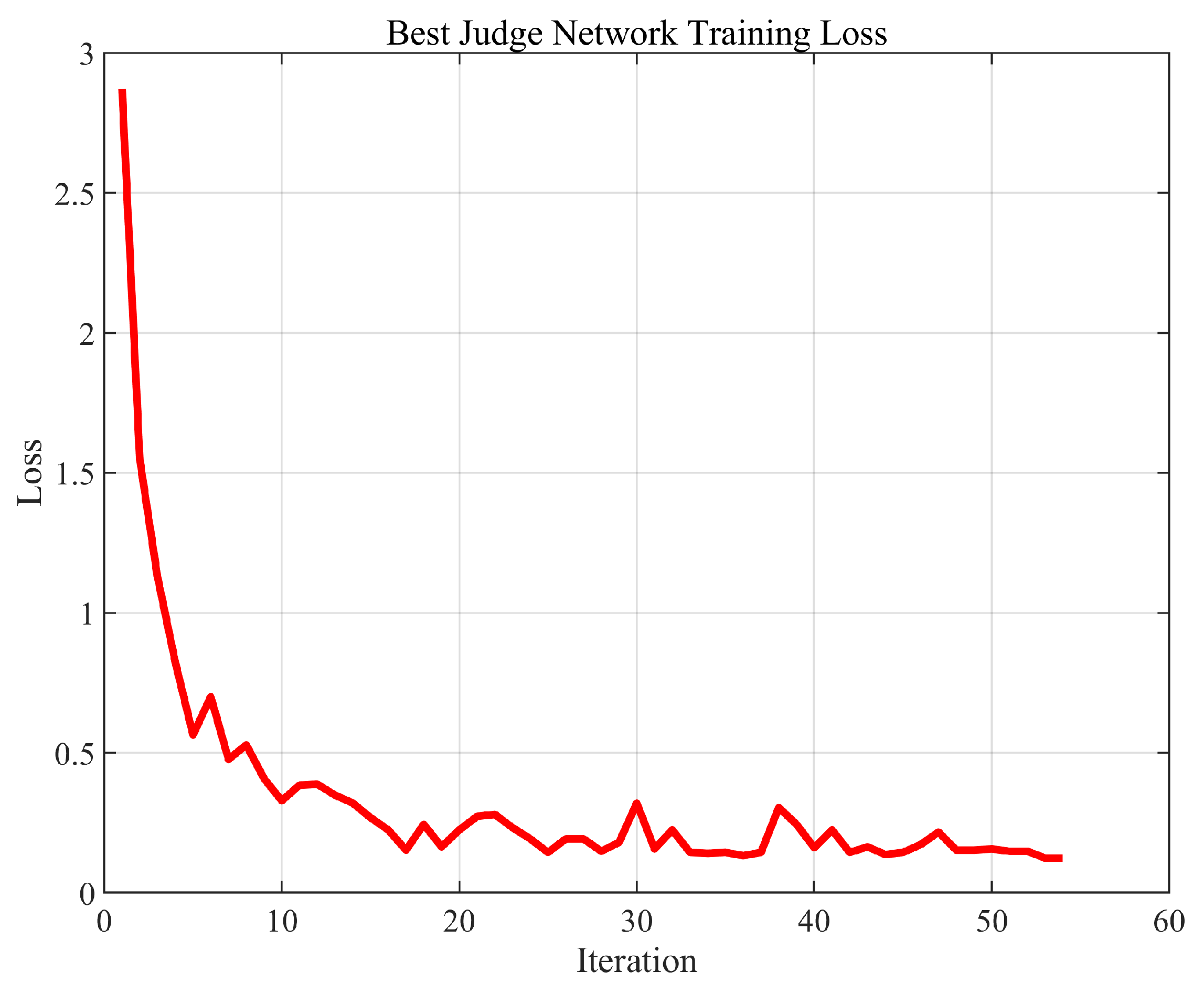
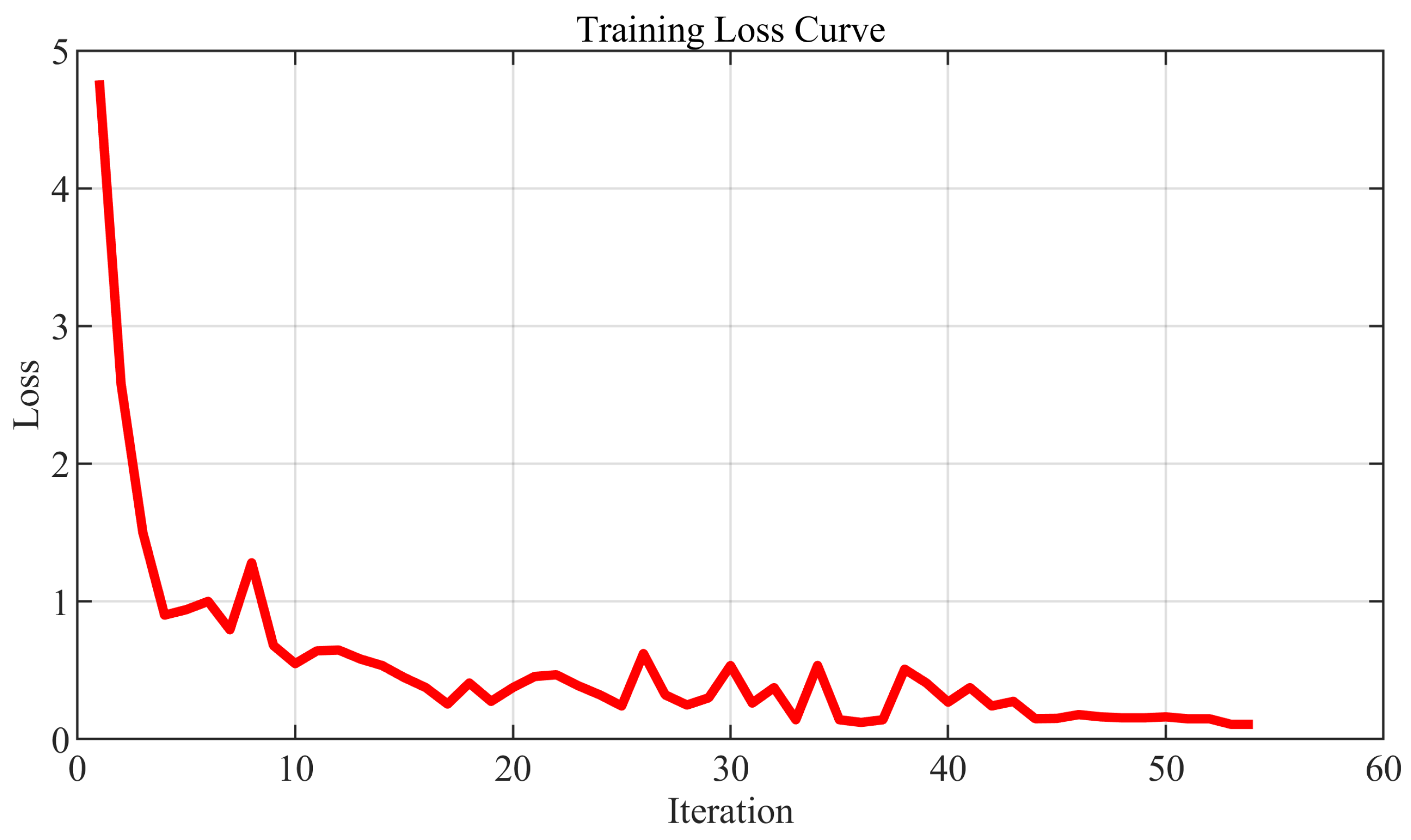
4.2.1. Base Station Judgment Network Configuration
4.2.2. Base Station Prediction Network Configuration
4.3. Simulation Results and Analysis
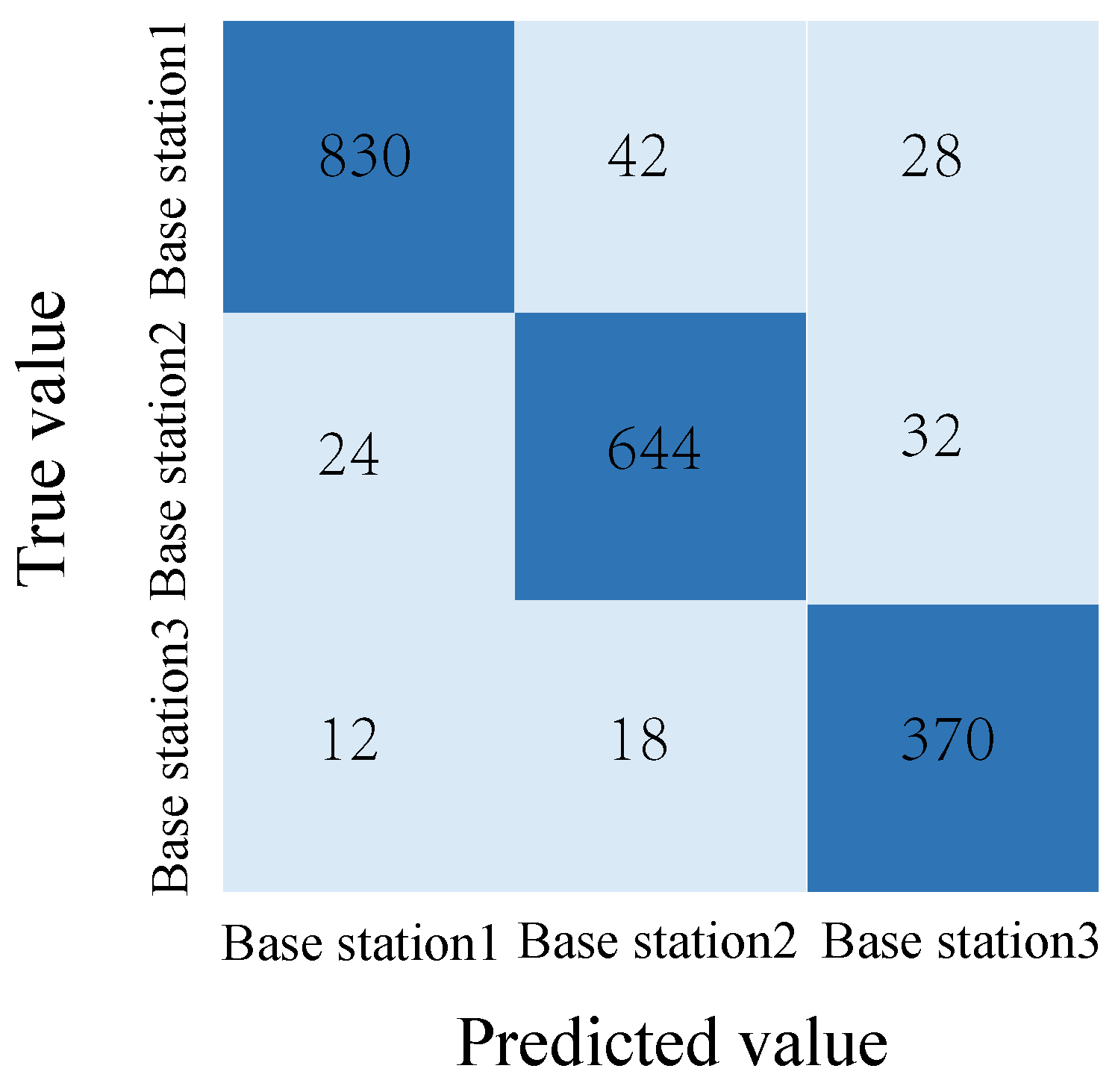
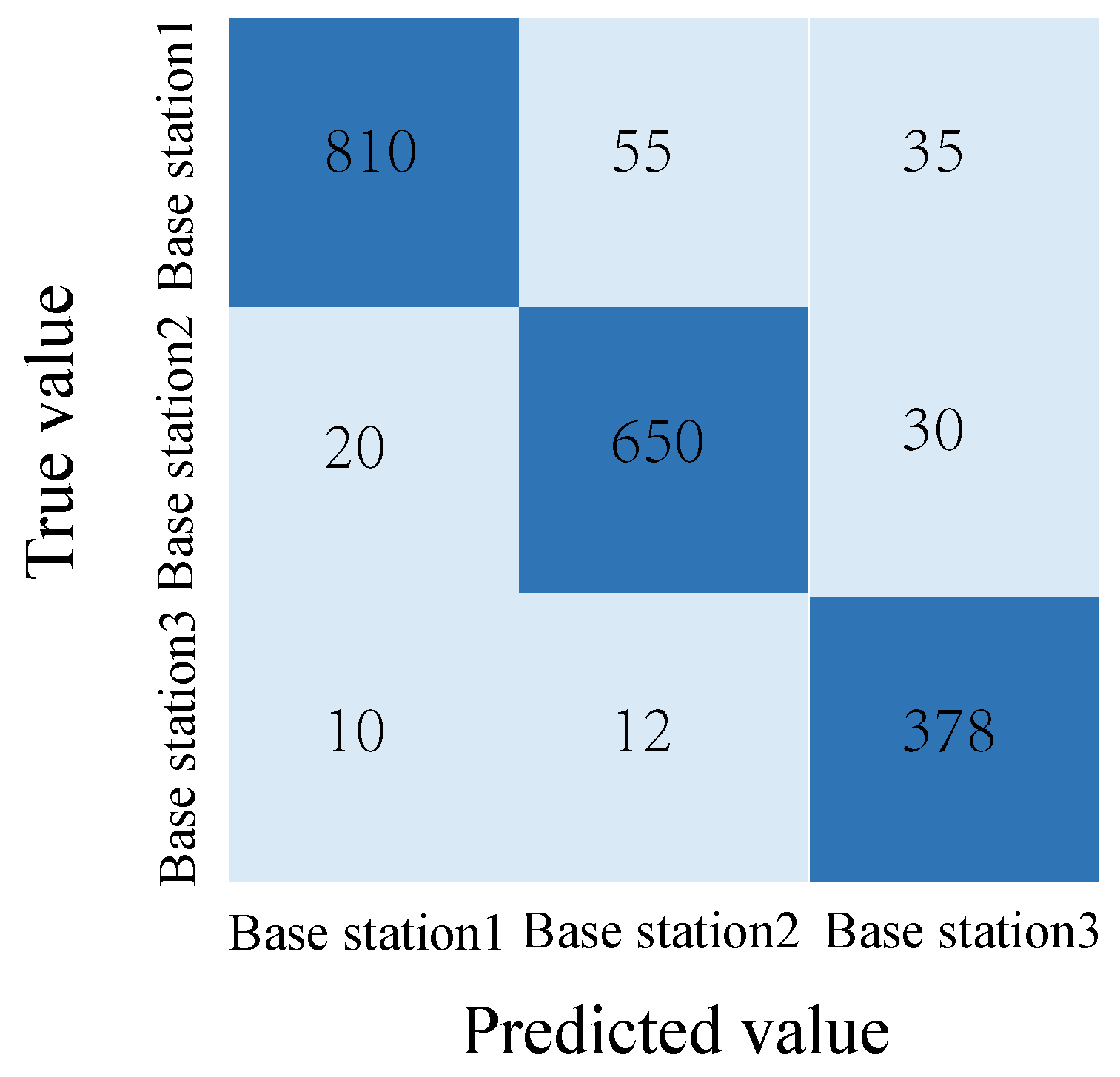
4.3.1. Base Station Judgment Network
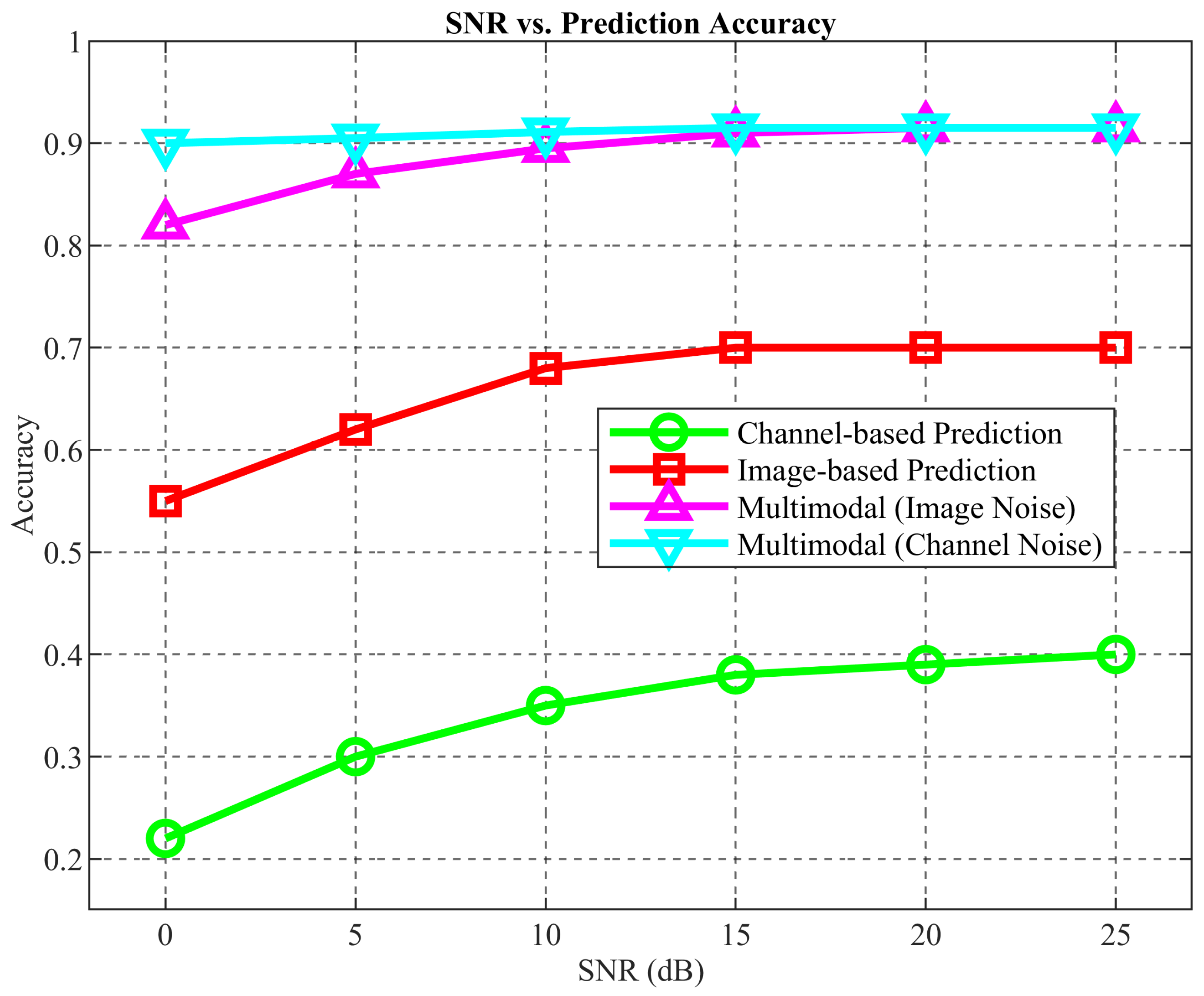
4.3.2. Multimodal Base Station Prediction Network
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, M.; Liu, M.; Wang, W.; Dou, H.; Wang, L. Cross-modal semantic communications in 6g. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China (ICCC), Dalian, China, 10–12 August 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Li, A.; Lou, J.; Chen, M.; Zhang, X.; Kang, B. An attention-based bidirectional gated recurrent unit network for location prediction. In Proceedings of the 2021 13th International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing (WCSP), Changsha, China, 20–22 October 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Rong, Y.; Mao, Y.; He, X.; Chen, M. Large-scale traffic flow forecast with lightweight llm in edge intelligence. IEEE Internet Things Mag. 2025, 8, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, M.; Ahmed, I.; Rubaai, A.; Pu, C.; Rawat, D.B. Gan-based channel estimation for irs-aided communication systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 73, 6012–6017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y.; Mao, Y.; Cui, H.; He, X.; Chen, M. Edge computing enabled large-scale traffic flow prediction with gpt in intelligent autonomous transport system for 6g network. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 26, 17321–17338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingkai, C.; Minghao, L.; Zhe, Z.; Zhiping, X.; Lei, W. Task-oriented semantic communication with foundation models. China Commun. 2024, 21, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Liu, M.; Wang, C.; Song, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, Y.; Wang, L. Cross-modal graph semantic communication assisted by generative ai in the metaverse for 6g. Research 2024, 7, 0342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhao, L.; Chen, J.; Wei, X.; Guizani, M. Modal-aware resource allocation for cross-modal collaborative communication in iiot. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 14952–14964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yin, A.; Jiang, X.; Chen, M.; Dev, K.; Qureshi, N.M.F.; Yao, J.; Zheng, B. Resource allocation for multi-traffic in cross-modal communications. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2022, 20, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wei, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Zhou, L. Integration and provision for city public service in smart city cloud union: Architecture and analysis. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2020, 27, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Li, J.; Shi, H. Deep learning based channel estimation for ofdm systems with doubly selective channel. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2022, 26, 2067–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Ahn, Y.; Kim, J.; Shim, B. Towards deep learning-aided wireless channel estimation and channel state information feedback for 6g. J. Commun. Netw. 2023, 25, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charan, G.; Alrabeiah, M.; Alkhateeb, A. Vision-aided 6g wireless communications: Blockage prediction and proactive handoff. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 10193–10208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charan, G.; Alrabeiah, M.; Alkhateeb, A. Vision-aided dynamic blockage prediction for 6g wireless communication networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–23 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Charan, G.; Osman, T.; Hredzak, A.; Thawdar, N.; Alkhateeb, A. Vision-position multi-modal beam prediction using real millimeter wave datasets. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Austin, TX, USA, 10–13 April 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 2727–2731. [Google Scholar]
- Charan, G.; Alkhateeb, A. Computer vision aided blockage prediction in real-world millimeter wave deployments. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 4–8 December 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1711–1716. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, B.; Gao, F.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, C.; Liu, G. Multi-camera view based proactive bs selection and beam switching for v2x. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.05299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, M.; Pourahmadi, V.; Sheikhzadeh, H. Pilot pattern design for deep learning-based channel estimation in ofdm systems. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2020, 9, 2173–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Song, J. Deep learning-based channel estimation algorithm over time selective fading channels. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2019, 6, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, K.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Rajatheva, N.; Wei, J. Performance analysis on machine learning-based channel estimation. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2021, 69, 5183–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, Z. Lstm and resnets deep learning aided end-to-end intelligent communication systems. In Proceedings of the 2021 2nd Information Communication Technologies Conference (ICTC), Nanjing, China, 7–9 May 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 156–160. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Al-Nahhal, I.; Dobre, O.A.; Wang, F. Deep-learning channel estimation for irs-assisted integrated sensing and communication system. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 72, 6181–6193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ji, T.; Shi, H.; Li, C.; Huang, Y.; Yang, L. A self-supervised learning-based channel estimation for irs-aided communication without ground truth. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2023, 22, 5446–5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Zhong, C. Deep learning for joint channel estimation and signal detection in ofdm systems. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 24, 2780–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Gao, F.; Xing, C.; An, J.; Dobre, O.A. Deep learning based channel extrapolation for large-scale antenna systems: Opportunities, challenges and solutions. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2021, 28, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Gu, Y.; He, X.; Wang, S.; Huang, F.; Wang, L. Explainable artificial intelligence enhance image semantic communication system in 6g-iot. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Pan, C.; Xu, Y.; Li, C. Generative adversarial networks-based channel estimation for intelligent reflecting surface assisted mmwave mimo systems. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2024, 10, 1883–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Trivedi, A.; Saxena, D. Generative channel estimation for intelligent reflecting surface-aided wireless communication. Wirel. Netw. 2024, 30, 2753–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Singh, K.; Janu, D.; Kumar, S.; Singh, G. Deep learning-driven channel estimation for intelligent reflecting surfaces aided networks: A comprehensive survey. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 154, 110861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, M.S.; Pourahmadi, V.; Sodagari, S. Deep ul2dl: Data-driven channel knowledge transfer from uplink to downlink. IEEE Open J. Veh. Technol. 2019, 1, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Gao, F.; Xu, C.; Ma, J.; Dobre, O.A. Deep learning based antenna selection for channel extrapolation in fdd massive mimo. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing (WCSP), Nanjing, China, 21–23 October 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 182–187. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Ng, D.W.K.; Yuan, J. Deep residual learning for channel estimation in intelligent reflecting surface-assisted multi-user communications. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 21, 898–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A. An image is worth 16 × 16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Batra, D.; Parikh, D.; Lee, S. Vilbert: Pretraining task-agnostic visiolinguistic representations for vision-and-language tasks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual Event, 18–24 July 2021; PMLR: Cambridge MA, USA, 2021; pp. 8748–8763. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Li, D.; Savarese, S.; Hoi, S. Blip-2: Bootstrapping language-image pre-training with frozen image encoders and large language models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023; PMLR: Cambridge MA, USA, 2023; pp. 19730–19742. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Huang, Z.; Bai, L.; Zhang, H.; Sun, M.; Liu, B.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Lee, M. M3SC: A generic dataset for mixed multi-modal (mmm) sensing and communication integration. China Commun. 2023, 20, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Base Station | X Coordinate | Y Coordinate | Z Coordinate | Roll | Pitch | Yaw |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base Station 1 | −9.7702 | −54.9763 | 0.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Base Station 2 | −8.1531 | −87.2525 | 0.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Base Station 3 | 20.7087 | −87.1356 | 0.4 | 0 | 0 | 90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dou, H.; Zhan, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, T.; Wang, L. Multimodal Optimal Base Station Selection Network for Intelligent Communications. Sensors 2025, 25, 6895. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25226895
Dou H, Zhan X, Zhang X, Zhu T, Wang L. Multimodal Optimal Base Station Selection Network for Intelligent Communications. Sensors. 2025; 25(22):6895. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25226895
Chicago/Turabian StyleDou, Haie, Xinyu Zhan, Xinyu Zhang, Taojie Zhu, and Lei Wang. 2025. "Multimodal Optimal Base Station Selection Network for Intelligent Communications" Sensors 25, no. 22: 6895. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25226895
APA StyleDou, H., Zhan, X., Zhang, X., Zhu, T., & Wang, L. (2025). Multimodal Optimal Base Station Selection Network for Intelligent Communications. Sensors, 25(22), 6895. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25226895






