Research on the Design of Micromixer Based on Acoustic Streaming-Driven Sharp-Edge Structures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Formulation and Numerical Method
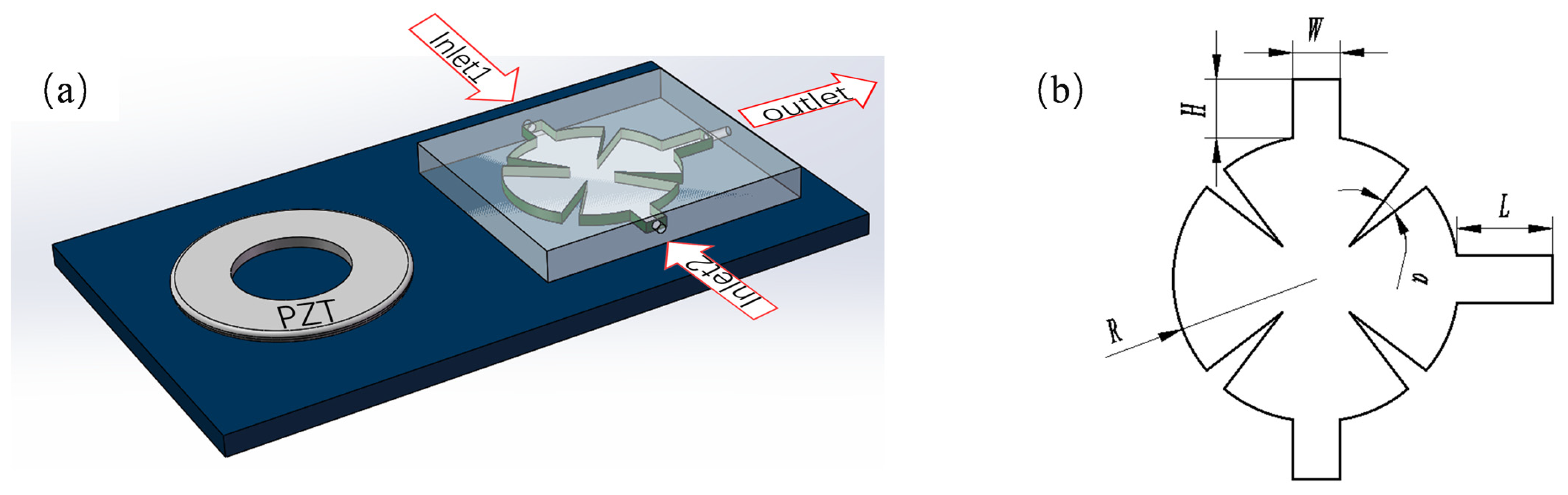
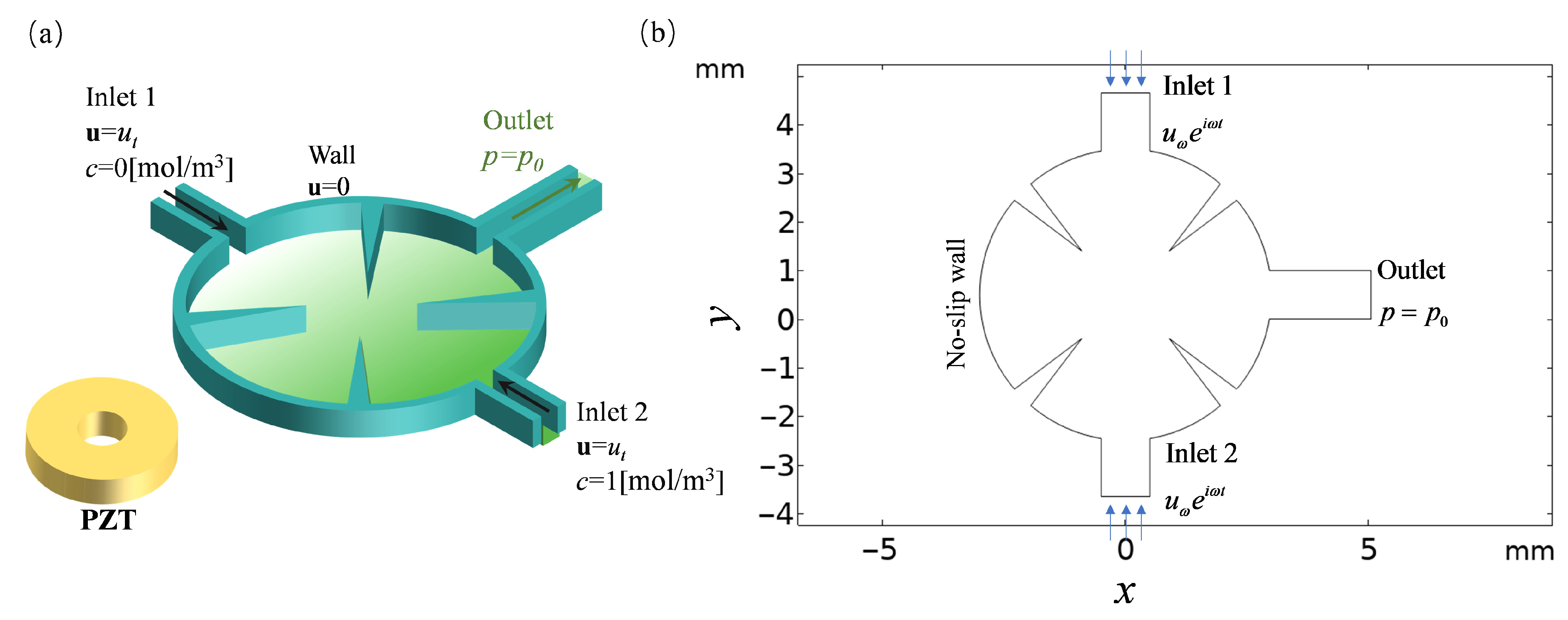
2.1. Geometric Structure
2.2. Mathematical Formulation
2.2.1. Fluid Flow
2.2.2. Acoustic Field
2.2.3. Material Transport
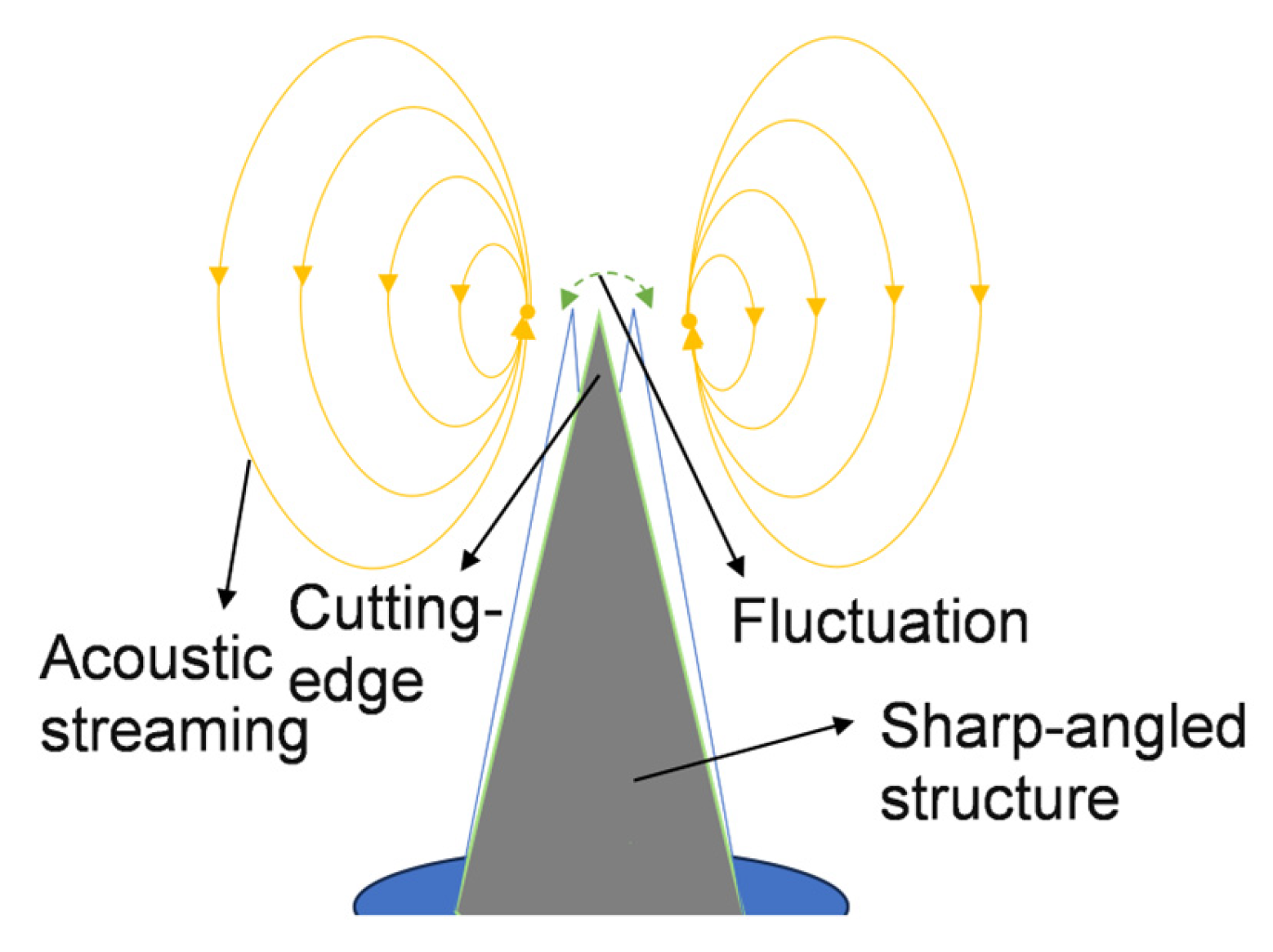
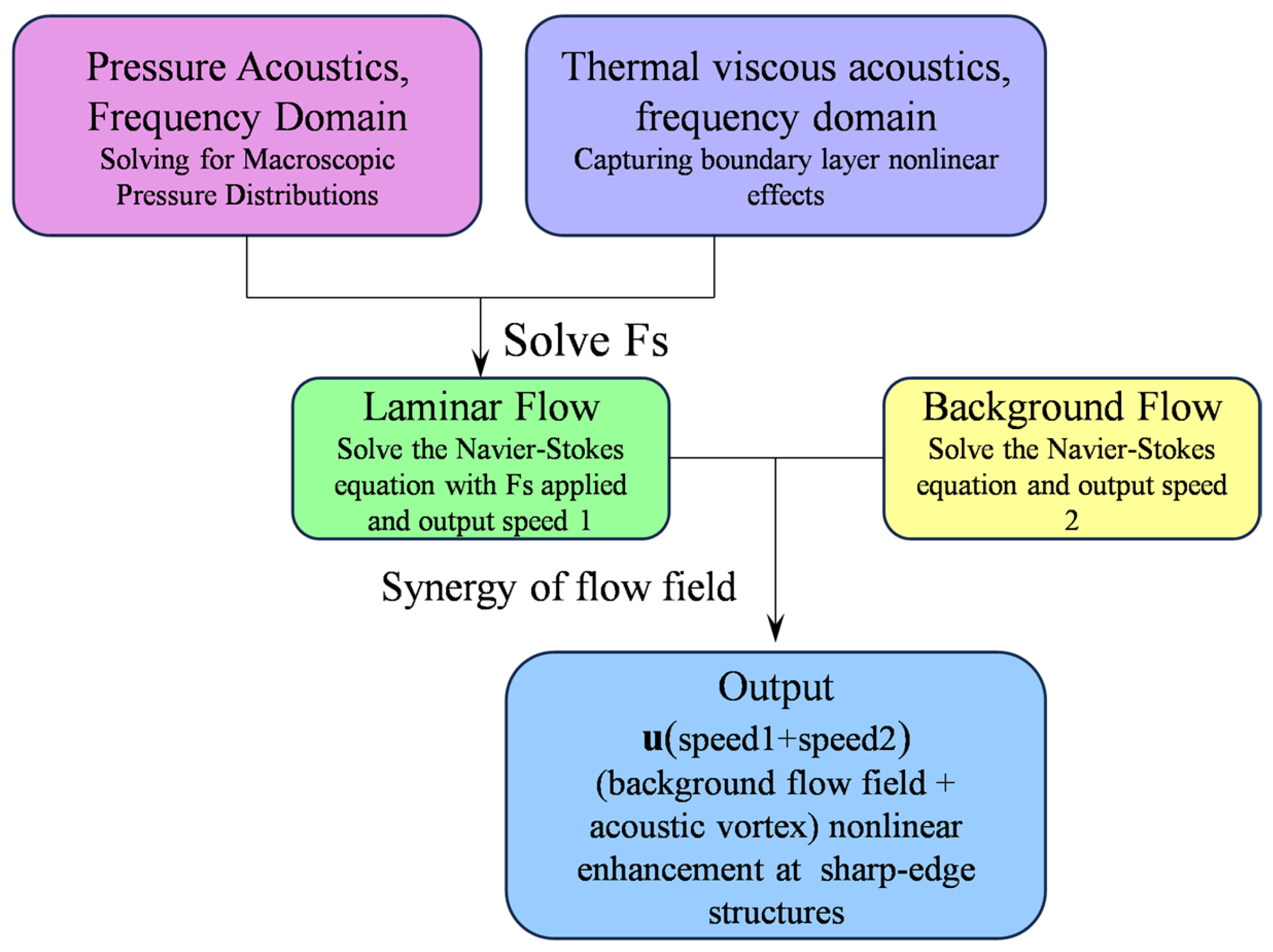
2.3. Acoustic–Fluid Coupling Mechanism
2.3.1. Principle of Acoustic–Fluid Coupling
2.3.2. Numerical Modeling of Acoustic Streaming
2.4. Mixing Efficiency
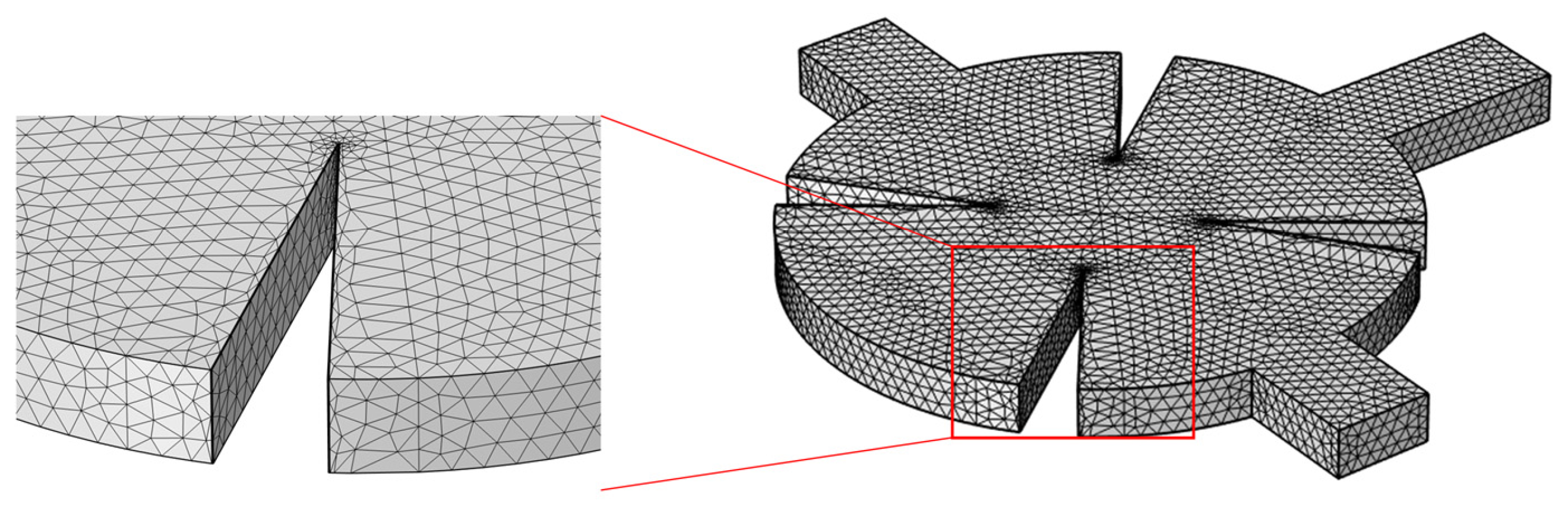
2.5. Grid Independence Test
3. Results and Discussion
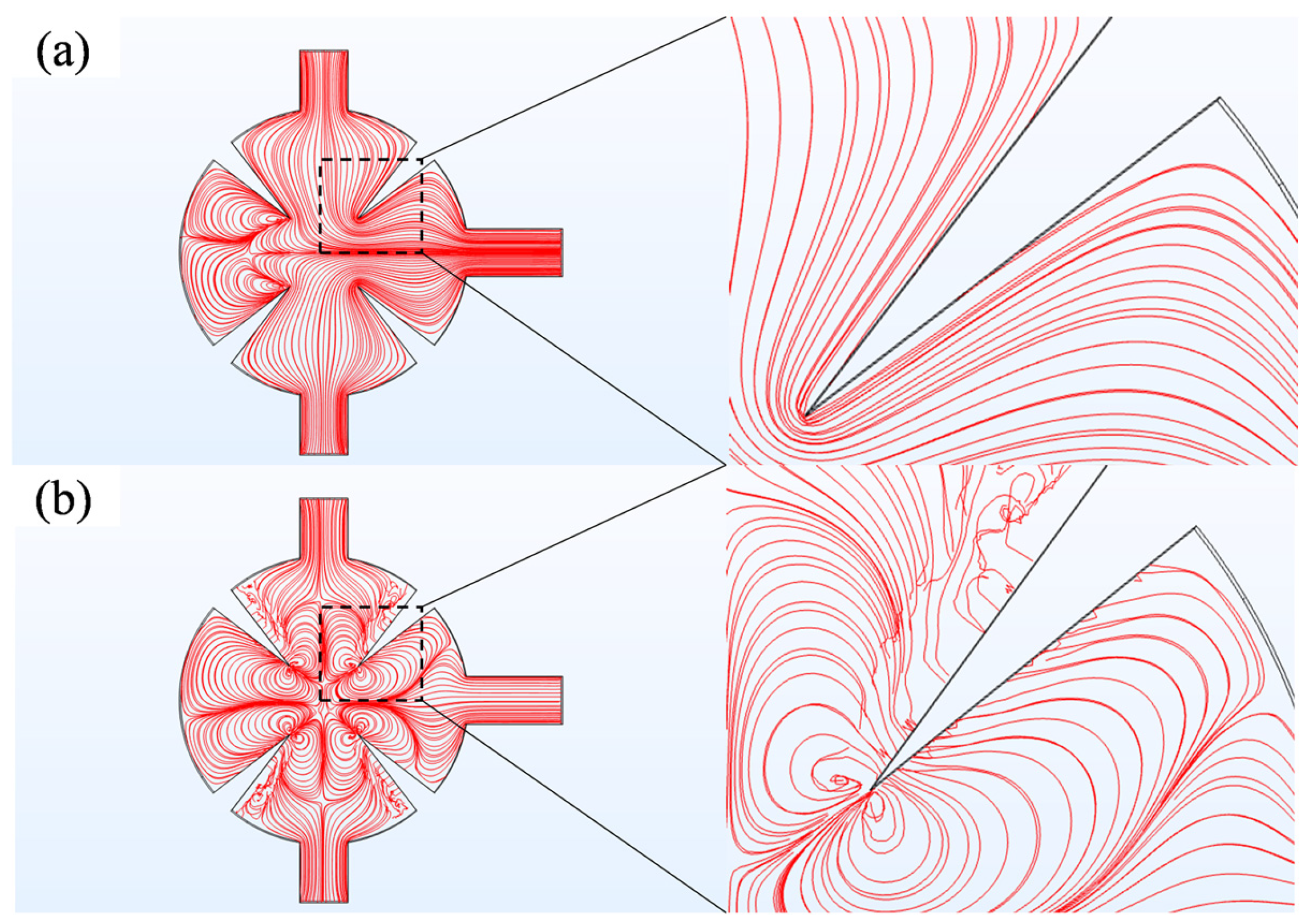
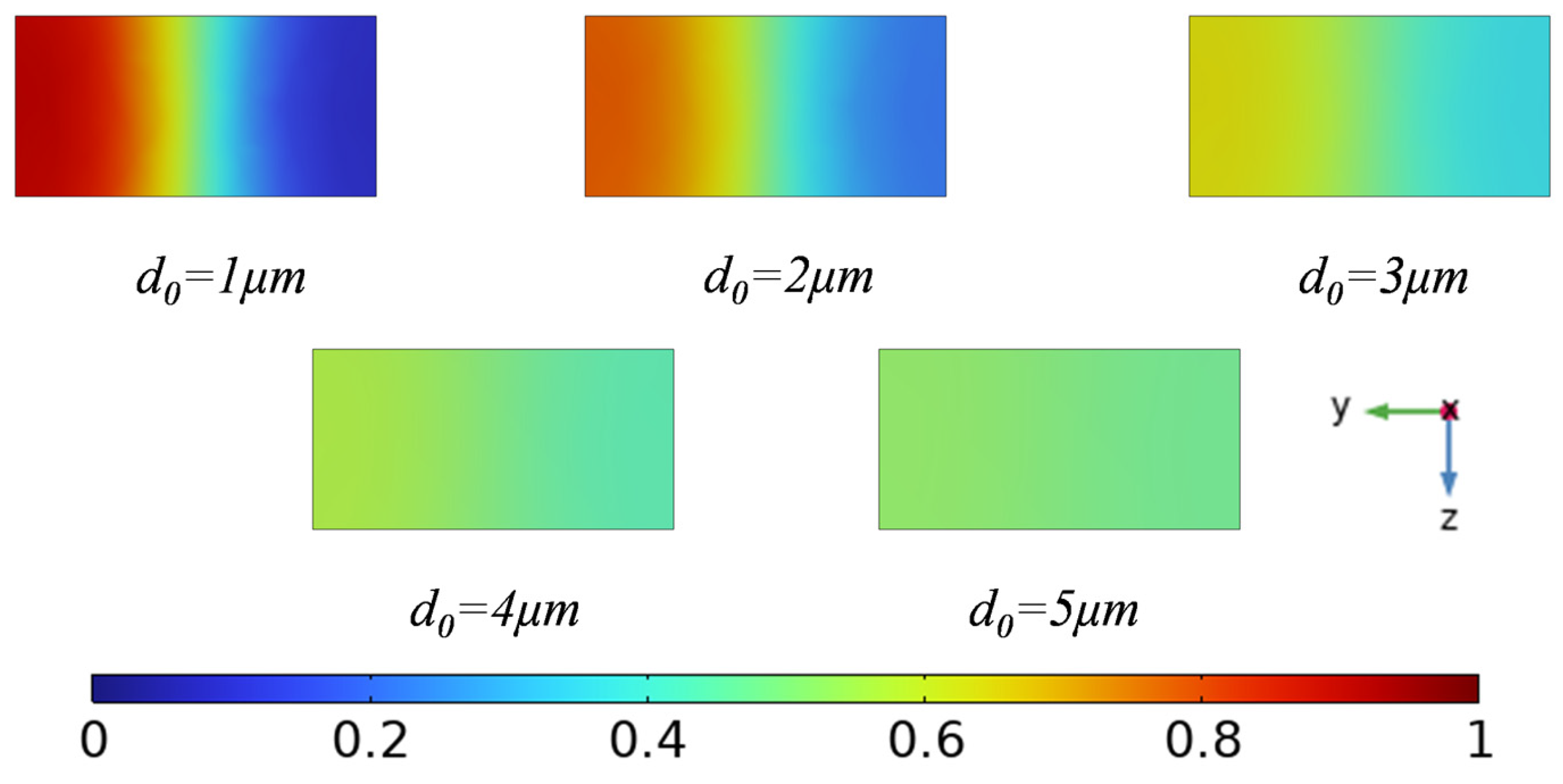
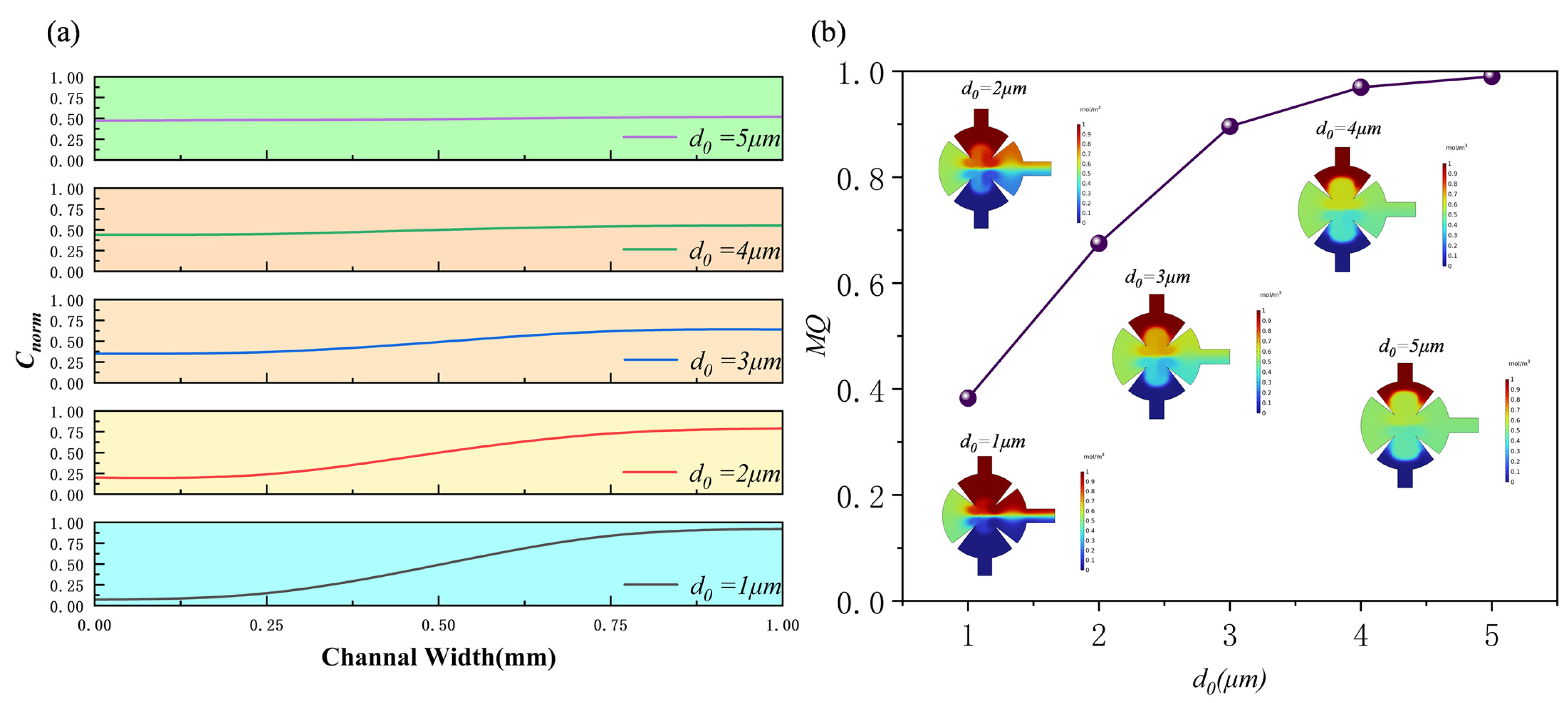
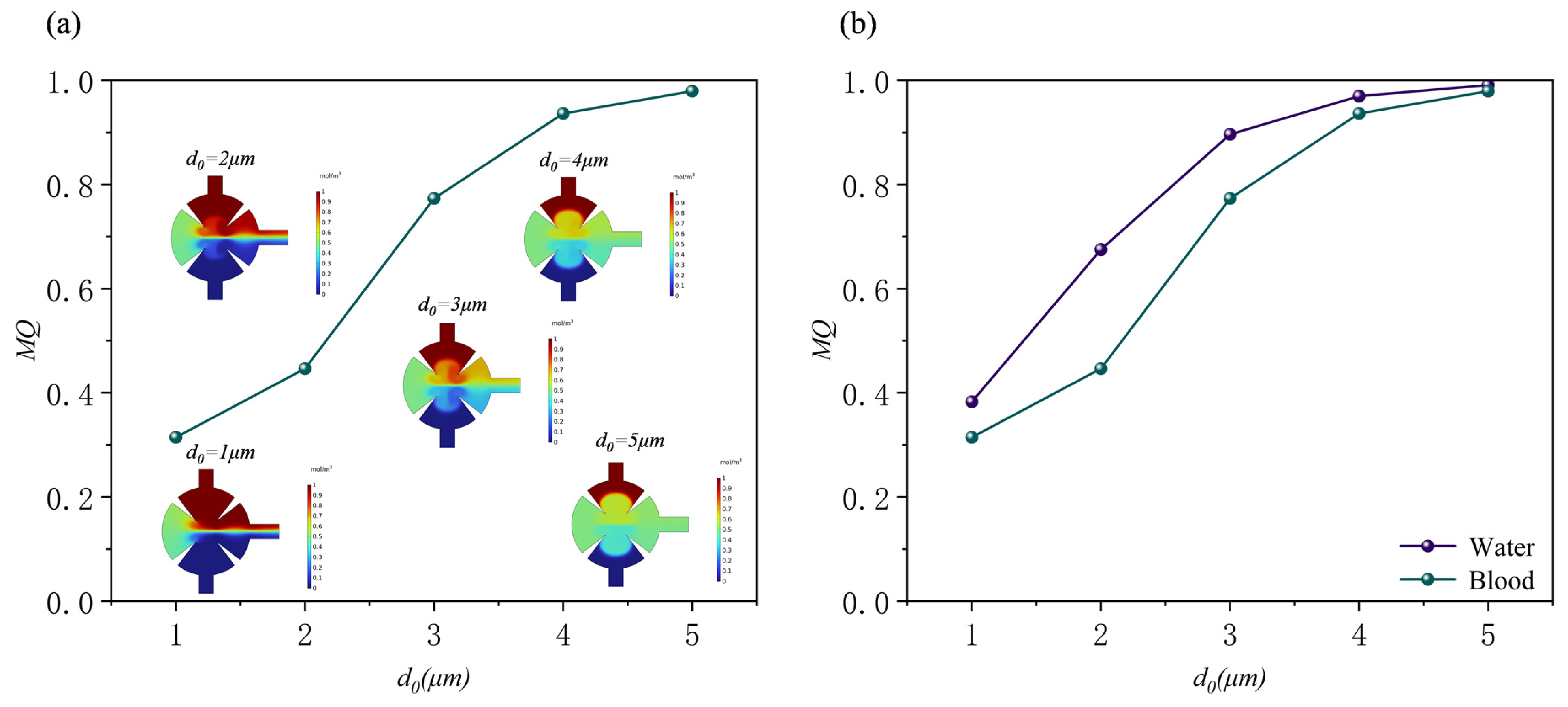
3.1. Effect of Displacement Amplitude
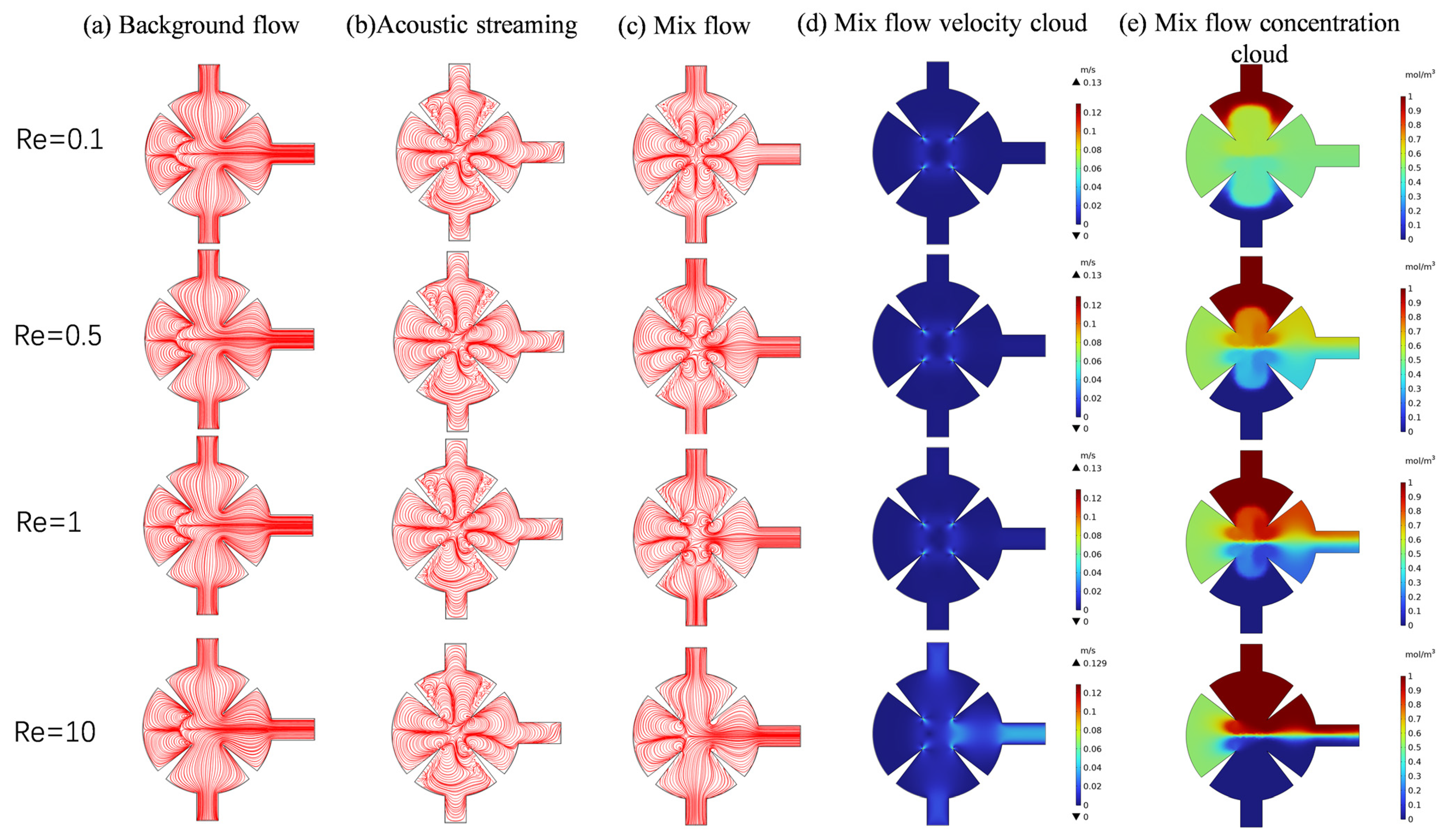
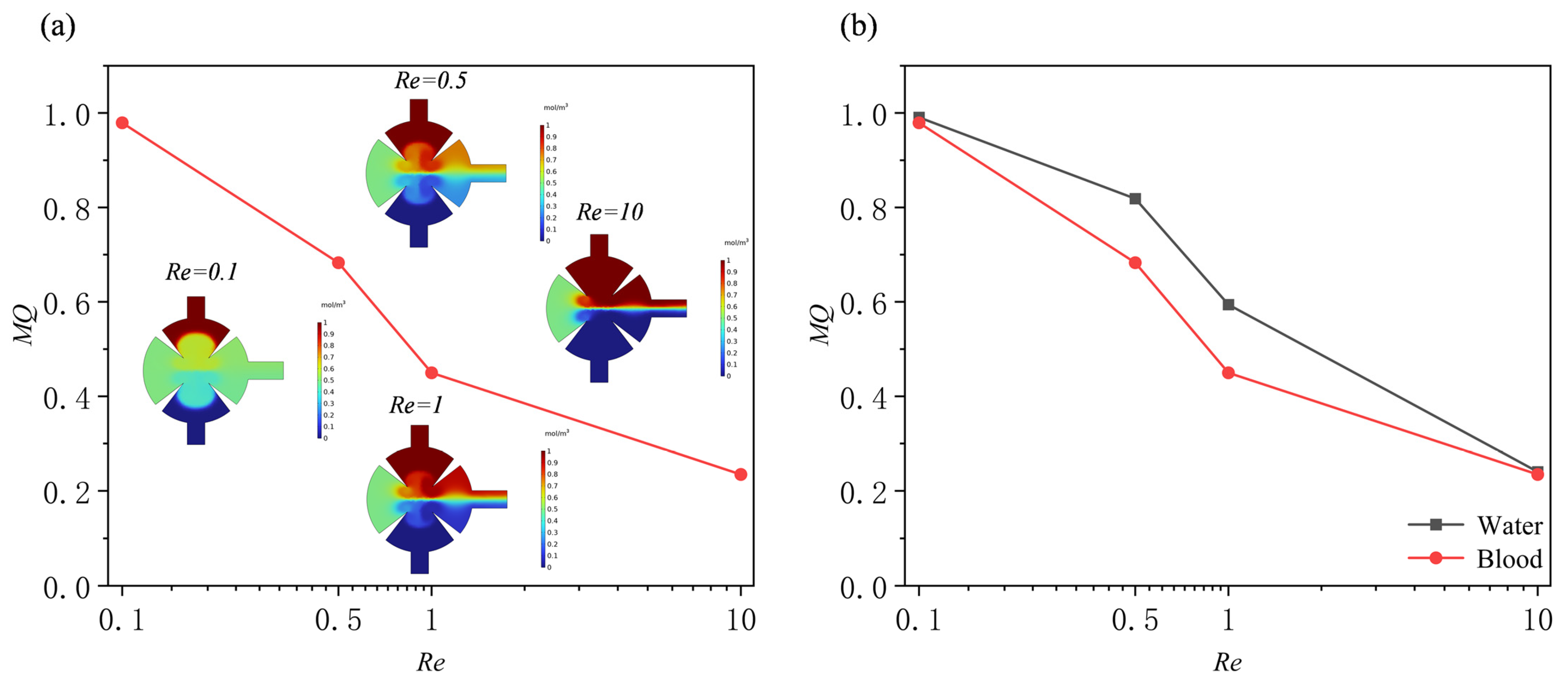
3.2. Effect of Reynolds Number
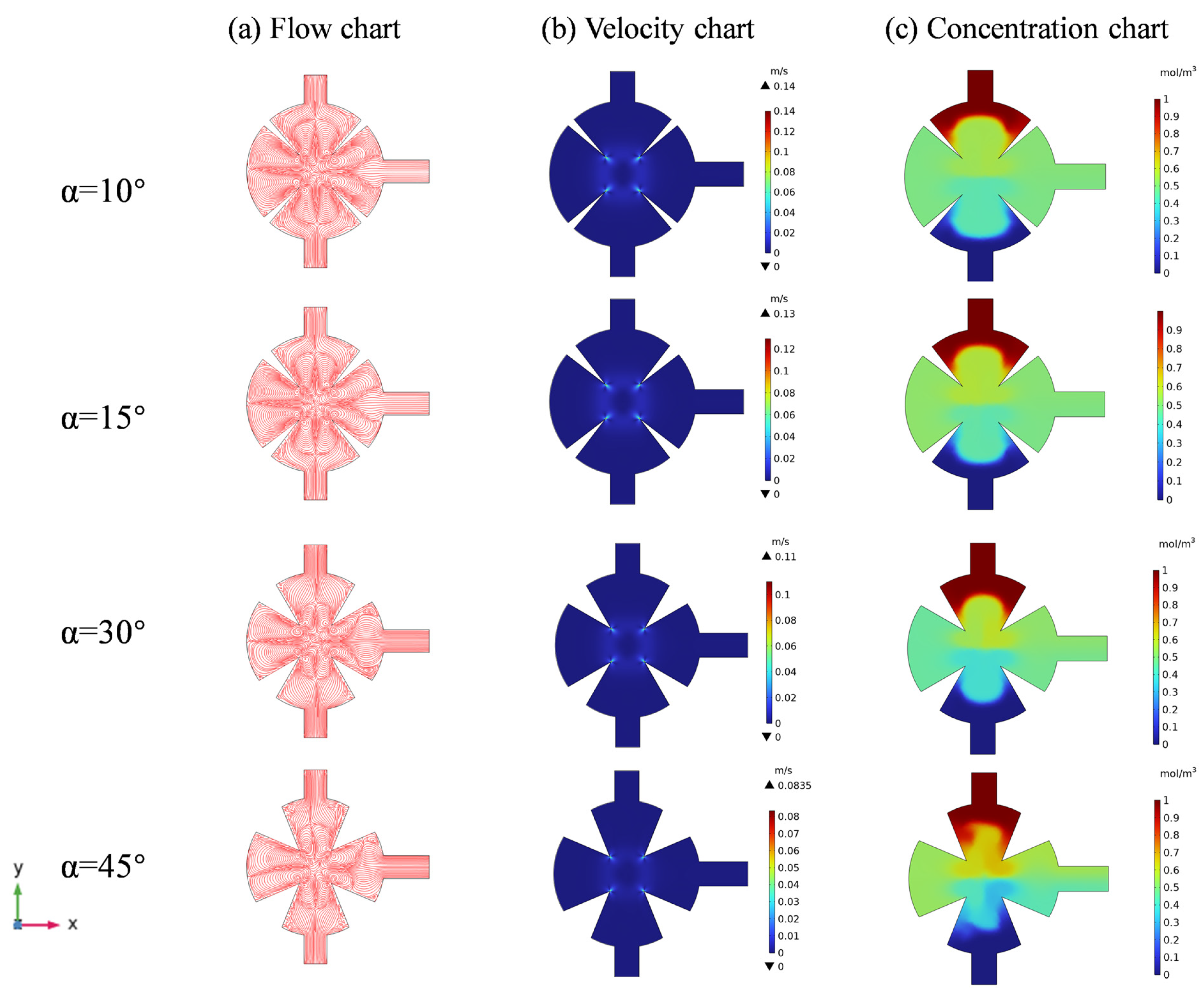
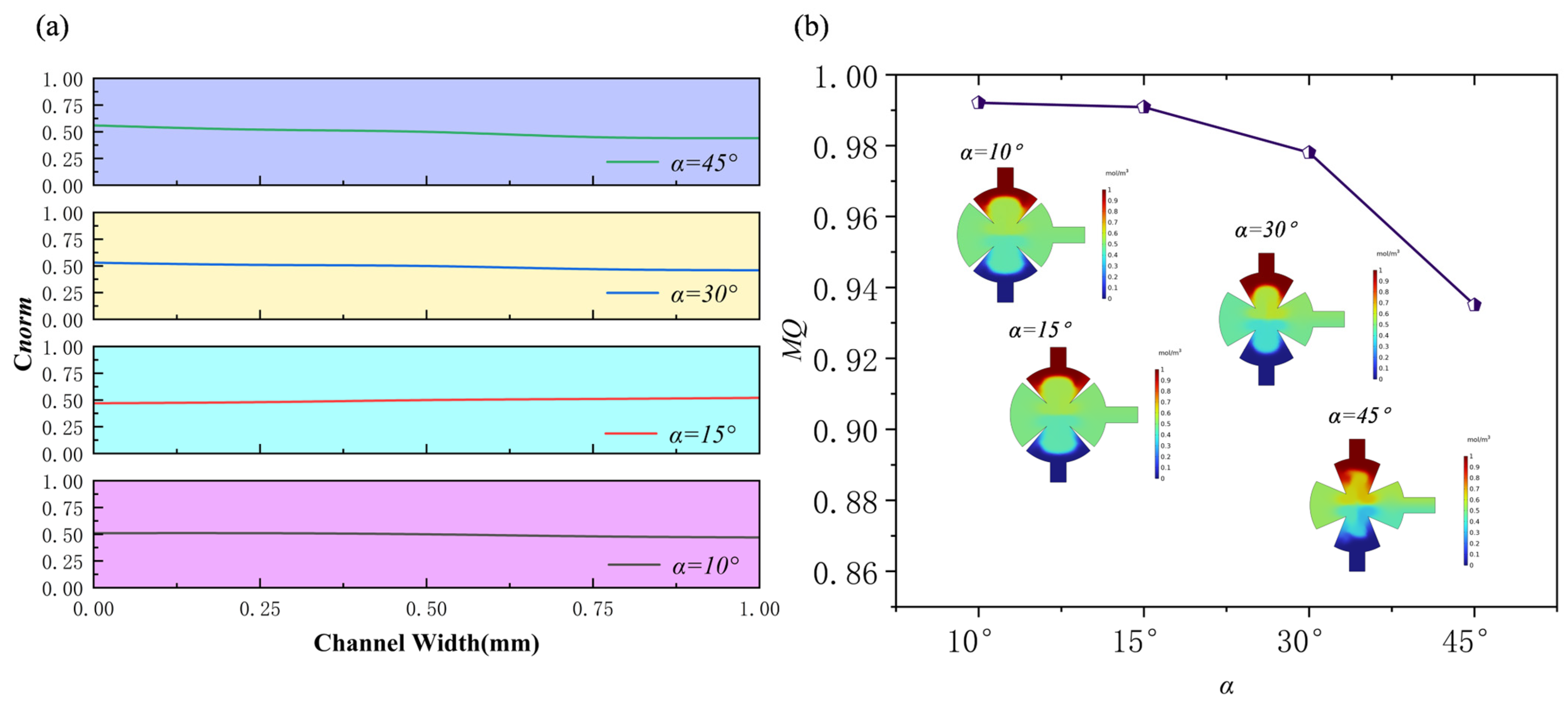
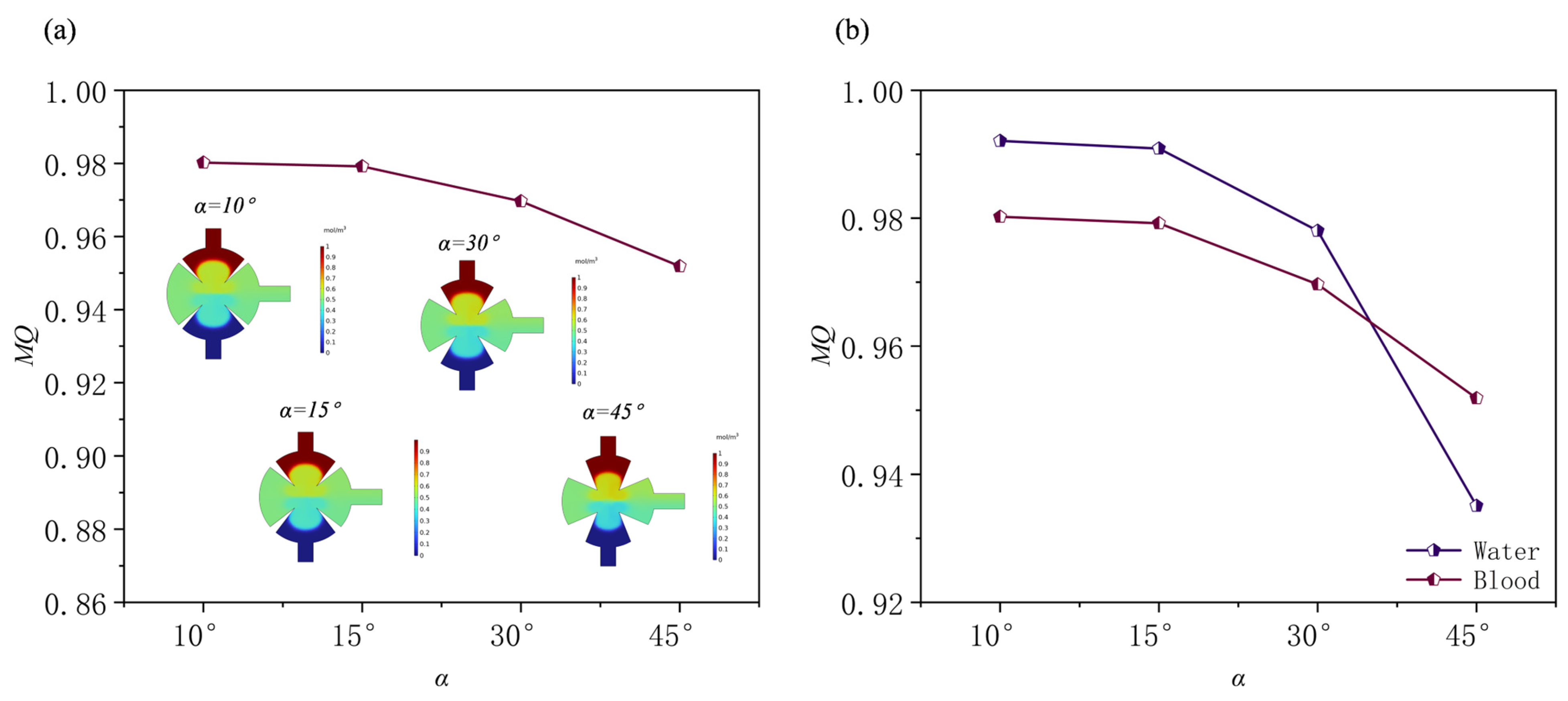
3.3. Effect of the Angles of Sharp Edges
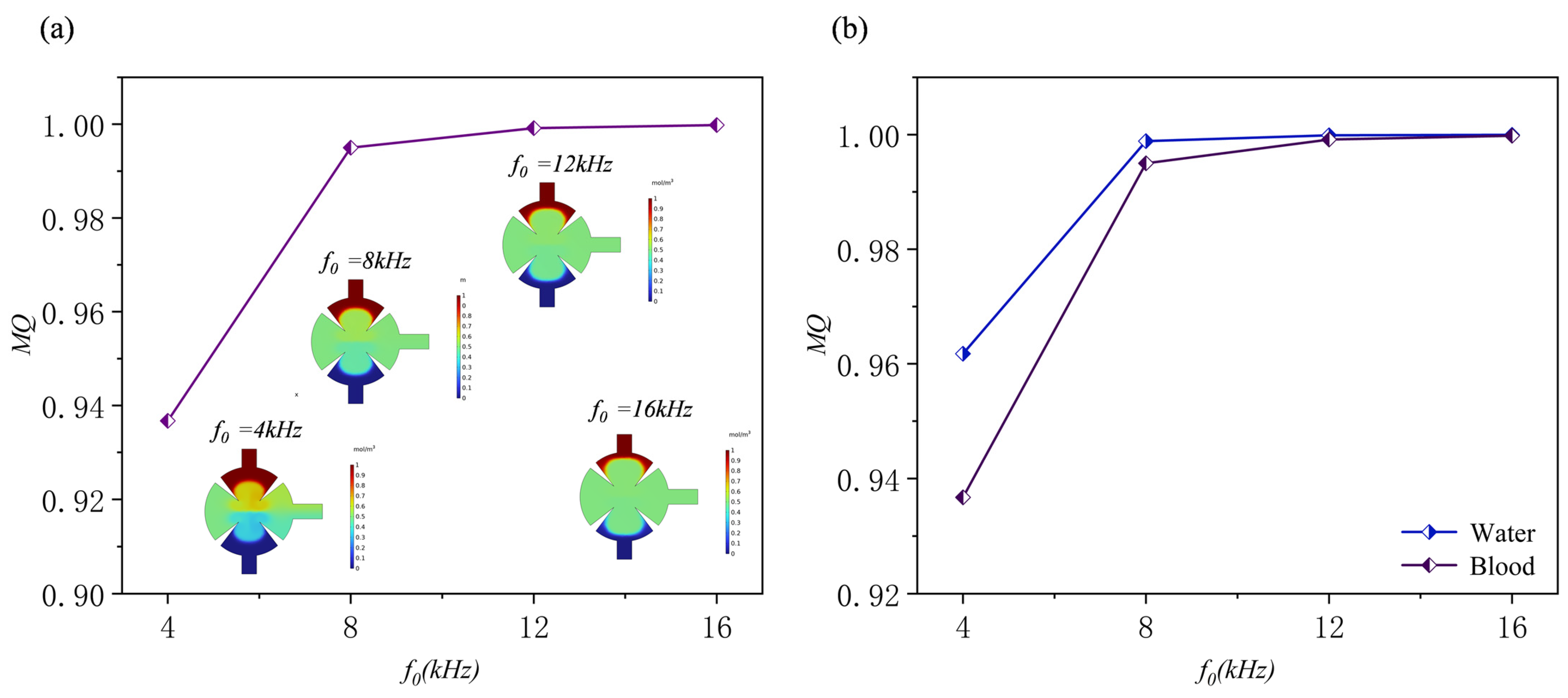
3.4. Effect of Applied Frequency
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Grid Independence Test
| Maximum Unit Size at the Angles of Sharp-Edge | Number of Cells | Mixed Quality (MQ) | Error (ξ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.025 | 103,139 | 0.87441 | 0 |
| 0.05 | 91,792 | 0.88636 | 1.3% |
| 0.1 | 86,938 | 0.89957 | 2.5% |
| 0.2 | 86,518 | 0.88335 | 1% |

Appendix B. Effect of Curvature Radius

References
- Whitesides, G.M. The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 2006, 442, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.M.; Wang, Y.N.; Liu, C.C. An integrated microfluidic chip for formaldehyde analysis in Chinese herbs. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 244, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvira, K.S.; I Solvas, X.C.; Wootton, R.C.R.; Demello, A.J. The past, present and potential for microfluidic reactor technology in chemical synthesis. Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Shang, L.; Ren, J.; Zhao, Y. Natural polysaccharide based complex drug delivery system from microfluidic electrospray for wound healing. Appl. Mater. 2021, 23, 101000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeming, K.K.; Thakor, N.V.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.-H. Real-time modulated nanoparticle separation with an ultra-large dynamic range. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irfan, M.; Shah, I.; Niazi, U.M.; Ali, M.; Ali, S.; Jalalah, M.S.; Khan, M.K.A.; Almawgani, A.H.M.; Rahman, S. Numerical analysis of non-aligned inputs M-type micromixers with different shaped obstacles for biomedical applications. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part E J. Process Mech. Eng. 2022, 236, 870–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Joo, S.W. An Enhanced One-Layer Passive Microfluidic Mixer with an Optimized Lateral Structure with the Dean Effect. J. Fluids Eng. 2015, 137, 91102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Wu, Z. Micromixers—A review. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2005, 15, R1–R16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, N.; Nie, Y.; Zhang, J.X.J. Microfluidics for silica biomaterials synthesis: Opportunities and challenges. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 2218–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, P.; Zhao, X.; Huang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hao, N. Sharp-edge acoustic microfluidics: Principles, structures, and applications. Appl. Mater. 2021, 25, 101239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Shi, Z.; Li, M.; Sha, J.; Zhong, M.; Chen, S.; Liu, X.; Jia, S. Numerical and experimental investigation of a magnetic micromixer under microwires and uniform magnetic field. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 551, 169141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Kim, K.Y. Analysis of a Two-Layer Nozzle-and-Diffuser Electroosmotic Micromixer. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2019, 42, 2164–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Brunet, P.; Royon, L.; Guo, X. Mixing intensification using sound-driven micromixer with sharp edges. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 410, 128252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nama, N.; Huang, P.H.; Huang, T.J.; Costanzo, F. Investigation of micromixing by acoustically oscillated sharp-edges. Biomicrofluidics 2016, 10, 24124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, D.; Mao, X.; Shi, J.; Juluri, B.K.; Huang, T.J. A millisecond micromixer via single-bubble-based acoustic streaming. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishor, R. Characterization of an acoustically coupled multilayered microfluidic platform on SAW substrate using mixing phenomena. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2015, 233, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani Kharaji, Z.; Bayareh, M.; Kalantar, V. A review on acoustic field-driven micromixers. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2021, 19, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.H.; Xie, Y.; Ahmed, D.; Rufo, J.; Nama, N.; Chen, Y.; Chan, C.Y.; Huang, T.J. An acoustofluidic micromixer based on oscillating sidewall sharp-edges. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Zhao, S.; Bachman, H.; Nama, N.; Li, Z.; Chen, C.; Yang, S.; Wu, M.; Zhang, S.P.; Huang, T.J. Acoustofluidic Synthesis of Particulate Nanomaterial. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, P.H.; Chen, C.; Bachman, H.; Zhao, S.; Yang, S.; Huang, T.J. Correction: Cell lysis via acoustically oscillating sharp edges. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doinikov, A.A.; Gerlt, M.S.; Pavlic, A.; Dual, J. Acoustic streaming produced by sharp-edge structures in microfluidic devices. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2020, 24, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Nama, N.; Huang, P.H.; Huang, T.J.; Costanzo, F. Investigation of acoustic streaming patterns around oscillating sharp edges. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 2824–2836. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Wang, F.; Burns, M.A.; Kurabayashi, K. Temperature-Programmed Natural Convection for Micromixing and Biochemical Reaction in a Single Microfluidic Chamber. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 4510–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachman, H.; Chen, C.; Rufo, J.; Zhao, S.; Yang, S.; Tian, Z.; Nama, N.; Huang, P.-H.; Huang, T.J. An acoustofluidic device for efficient mixing over a wide range of flow rates. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 1238–1248. [Google Scholar]
- Sekhwama, M.; Mpofu, K.; Sivarasu, S.; Mthunzi-Kufa, P. Applications of microfluidics in biosensing. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2024, 6, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotter, M.; Kalameitsev, A.V.; Govorov, A.O.; Ruile, W.; Wixforth, A. Charge conveyance and nonlinear acoustoelectric phenomena for intense surface acoustic waves on a semiconductor quantum well. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 82, 2171–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, D. Numerical Simulation of Acoustic Streaming on Surface Acoustic Wave-driven Biochips. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 2007, 29, 2352–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Li, P.; Lin, S.C.S.; Stratton, Z.S.; Nama, N.; Guo, F.; Slotcavage, D.; Mao, X.; Shi, J.; Costanzoa, F.; et al. Surface acoustic wave microfluidics. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srithan, K.; Strobl, C.J.; Schneider, M.F.; Wixforth, A.; Guttenberg, Z.V. Acoustic mixing at low Reynold’s numbers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 54102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovchinnikov, M.; Zhou, J.; Yalamanchili, S. Acoustic streaming of a sharp edge. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 136, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Guo, X.; Brunet, P.; Costalonga, M.; Royon, L. Acoustic streaming near a sharp structure and its mixing performance characterization. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2019, 23, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Guo, X.; Royon, L.; Brunet, P. Unveiling of the mechanisms of acoustic streaming induced by sharp edges. Phys. Rev. E 2020, 102, 43110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, G.K.; Morteza, B. Mixing intensification using an acoustic microfluidic device aided with multi-lobed sharp edges under various oscillation boundary conditions. Chem. Pap. 2025, 79, 1223–1240. [Google Scholar]




| Name | Notation | Worth |
|---|---|---|
| Density (water) | ρ | 997 kg/m3 |
| Density (blood) | ρd | 1060 kg/m3 |
| Speed of sound (water) | c0 | 1485 m/s |
| Speed of sound (blood) | cd | 1540 m/s |
| Kinetic viscosity (water) | μ | 1 × 10−3 Pa·s |
| Bulk viscosity (water) | μb | 2.47 × 10−3 Pa·s |
| Bulk viscosity (blood) | μd | 0.056 Pa·s |
| Diffusion coefficient | D | 1 × 10−9 m2/s |
| Frequency | f | 5.5 kHz |
| Temperature | T | 296 K |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, K.; Qiao, H.; Cai, J.; Hu, J.; Wang, Z. Research on the Design of Micromixer Based on Acoustic Streaming-Driven Sharp-Edge Structures. Sensors 2025, 25, 6886. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25226886
Bai K, Qiao H, Cai J, Hu J, Wang Z. Research on the Design of Micromixer Based on Acoustic Streaming-Driven Sharp-Edge Structures. Sensors. 2025; 25(22):6886. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25226886
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Kaihao, Heting Qiao, Jixiang Cai, Jinlong Hu, and Zhiqi Wang. 2025. "Research on the Design of Micromixer Based on Acoustic Streaming-Driven Sharp-Edge Structures" Sensors 25, no. 22: 6886. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25226886
APA StyleBai, K., Qiao, H., Cai, J., Hu, J., & Wang, Z. (2025). Research on the Design of Micromixer Based on Acoustic Streaming-Driven Sharp-Edge Structures. Sensors, 25(22), 6886. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25226886




