Hand–Object Pose Estimation Based on Anchor Regression from a Single Egocentric Depth Image
Abstract
1. Introduction
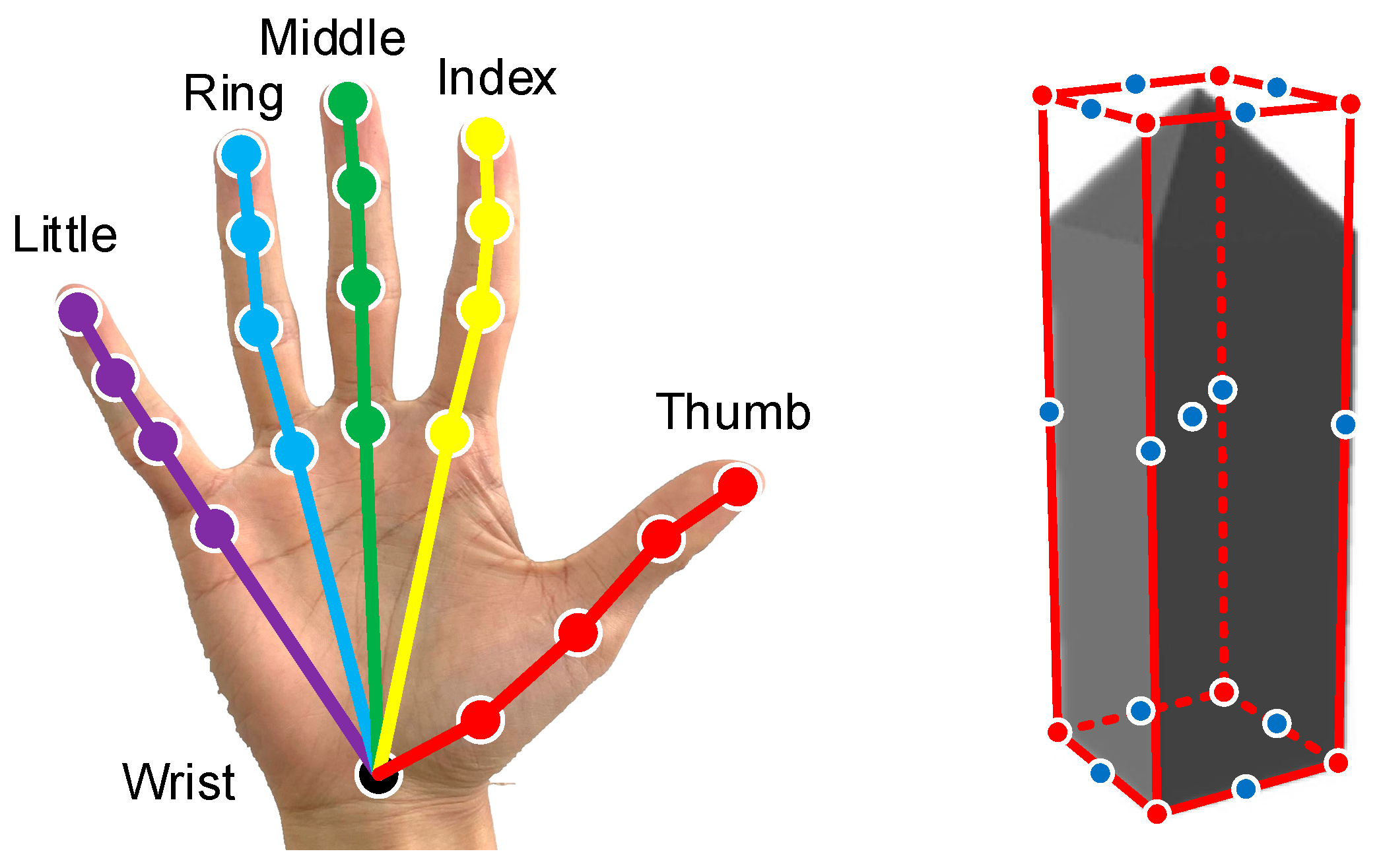
- A hand–object pose estimation method based on anchor regression is proposed. The pose of the manipulated object is parameterized with the same number of keypoints as the hand counterpart, and the keypoint locations of the hand and object are estimated simultaneously in the same framework.
- An anchor point weight allocation scheme is constructed considering the anchor point locations and keypoint prediction errors of both the hand and object.
- A 3D center detection method based on YOLOv3 is proposed that can estimate the 3D location of the hand–object center efficiently. With this method, local images only containing the hand and object can be quickly extracted from the original depth images to avoid the influence of irrelevant image information on the accuracy of pose estimation.
- The proposed hand–object pose estimation framework can simultaneously estimate the poses of the hand and the manipulated object from a single-frame egocentric depth image. It can also provide high prediction accuracy without introducing additional time constraints.
2. Related Work
2.1. Hand Center Detection
2.2. Hand Pose Estimation
2.3. 6D Object Pose Estimation
2.4. Hand–Object Pose Estimation
3. Method
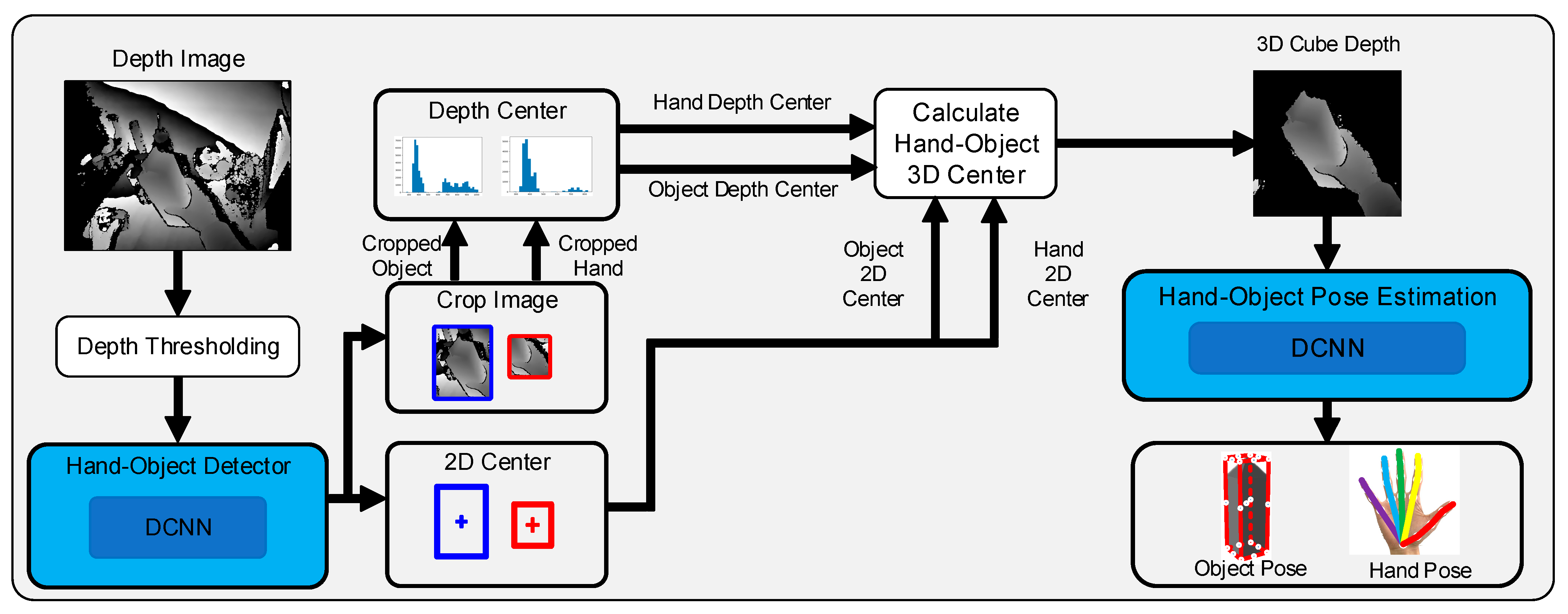
3.1. Overall Framework
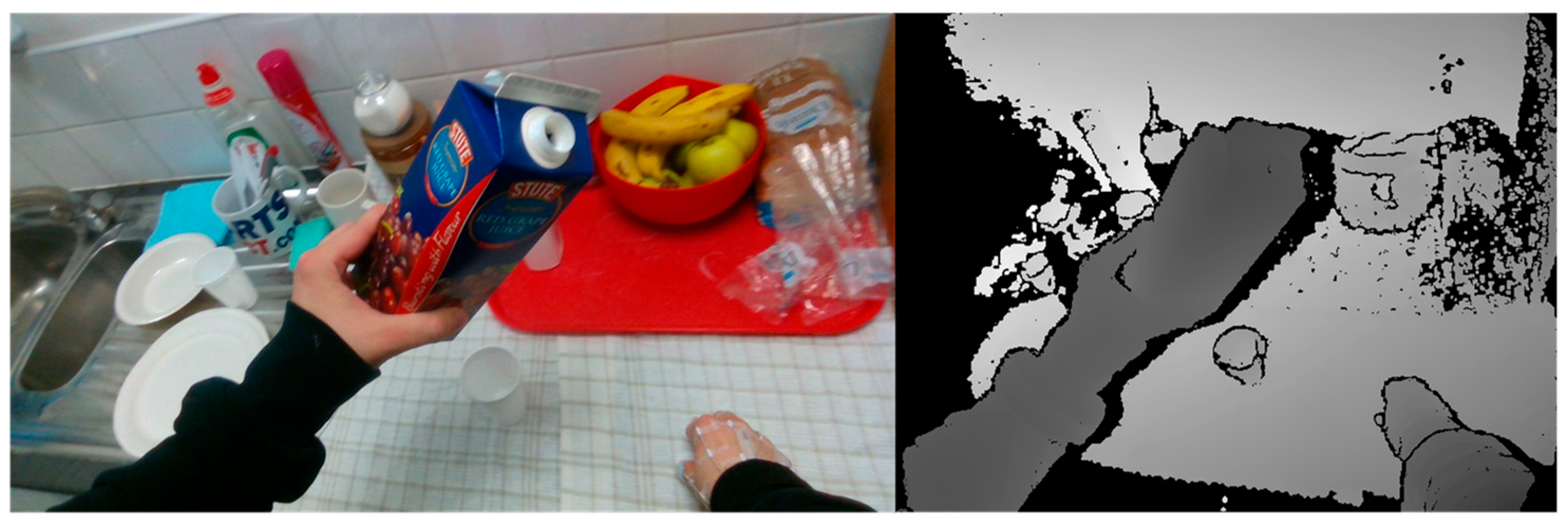
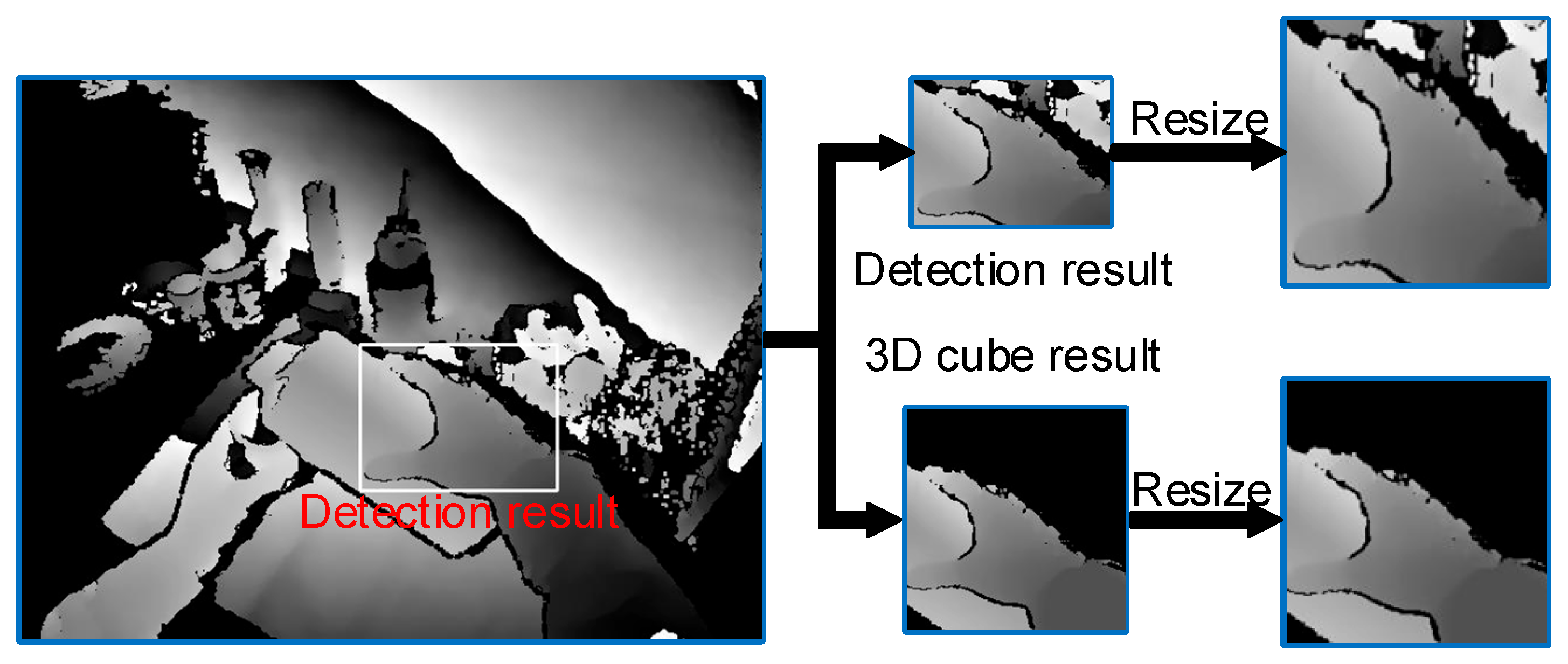
3.2. Hand–Object 3D Center Detection Module
3.2.1. Hand–Object 2D Center Estimation
3.2.2. Hand–Object Depth Center Estimation
3.2.3. Hand–Object 3D Center Calculation
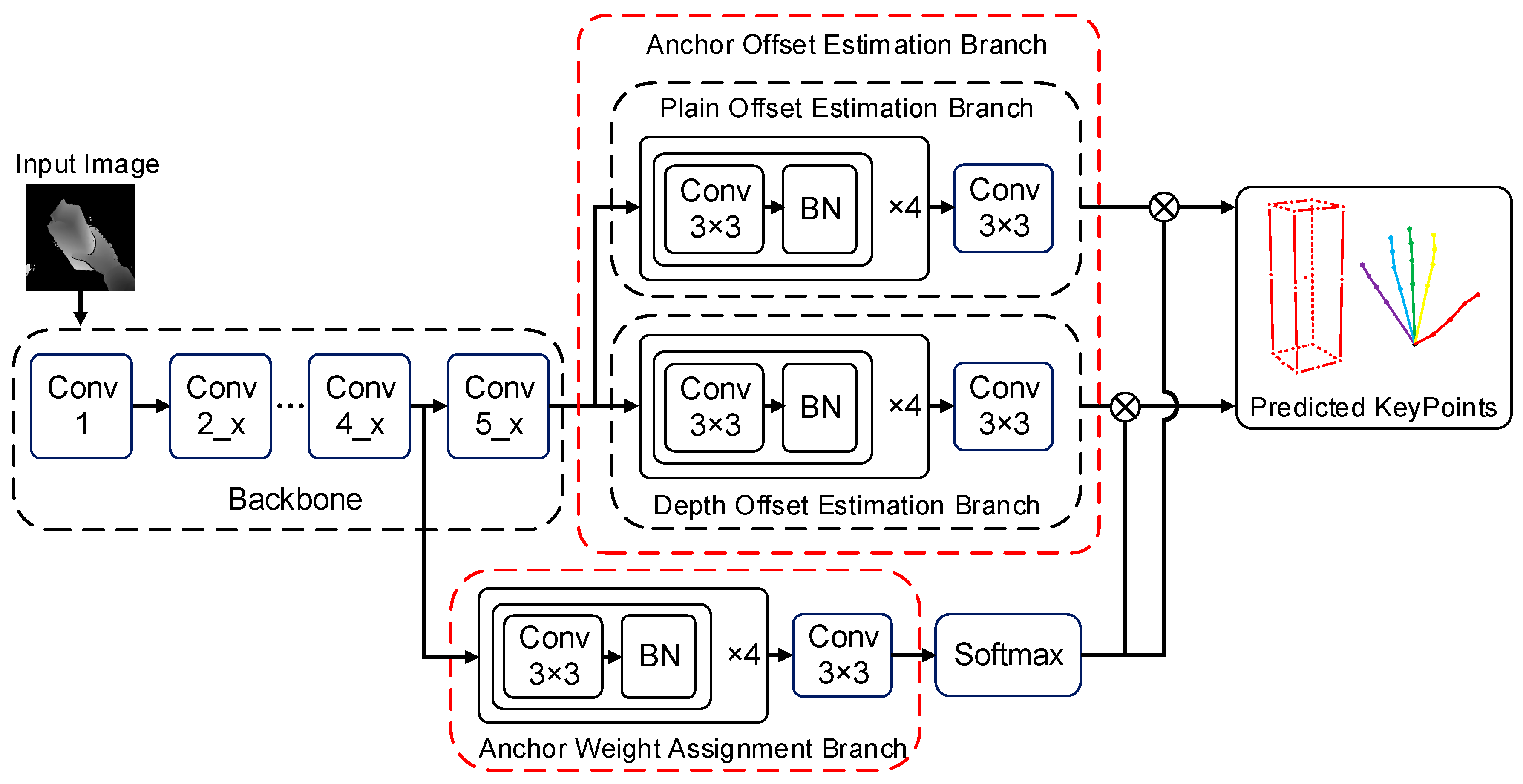
3.3. Hand–Object Pose Estimation Module Based on Anchor Regression
3.3.1. Backbone Network for Feature Extraction
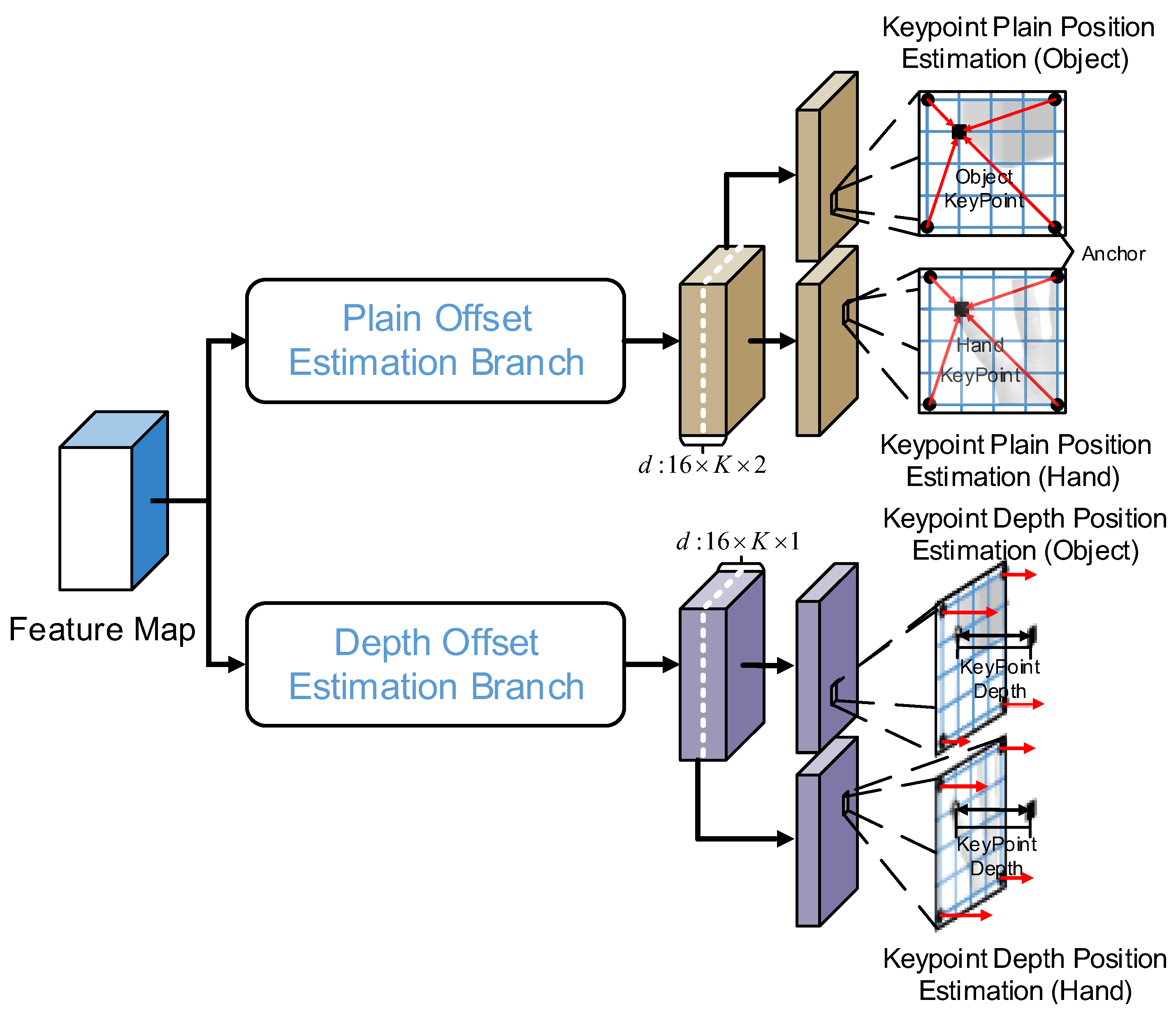
3.3.2. Anchor Point Offset Estimation Branch
3.3.3. Anchor Point Weight Estimation Branch
3.3.4. Loss Function
4. Experiments and Discussion
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Experimental Platform and Parameter Settings
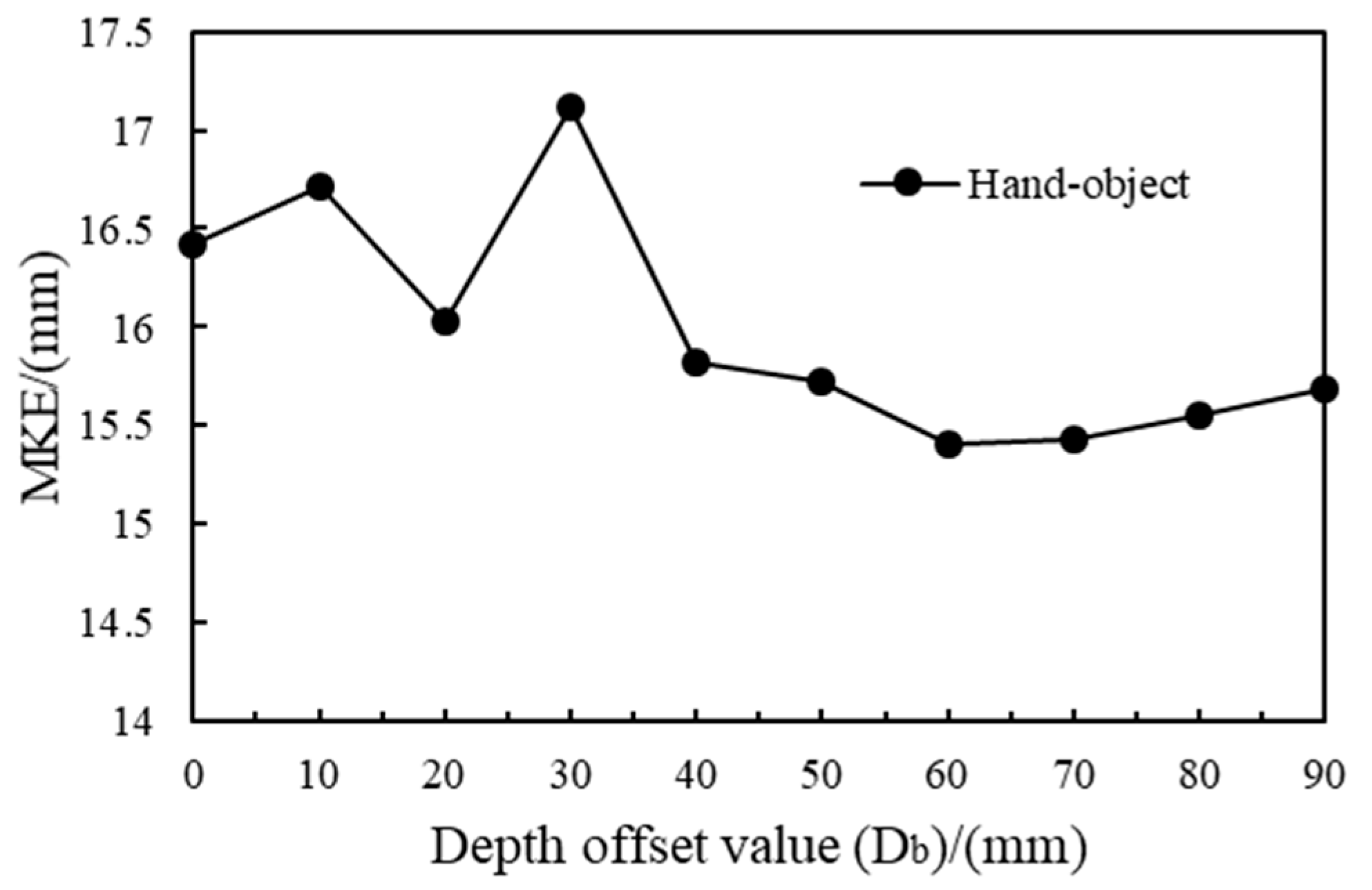
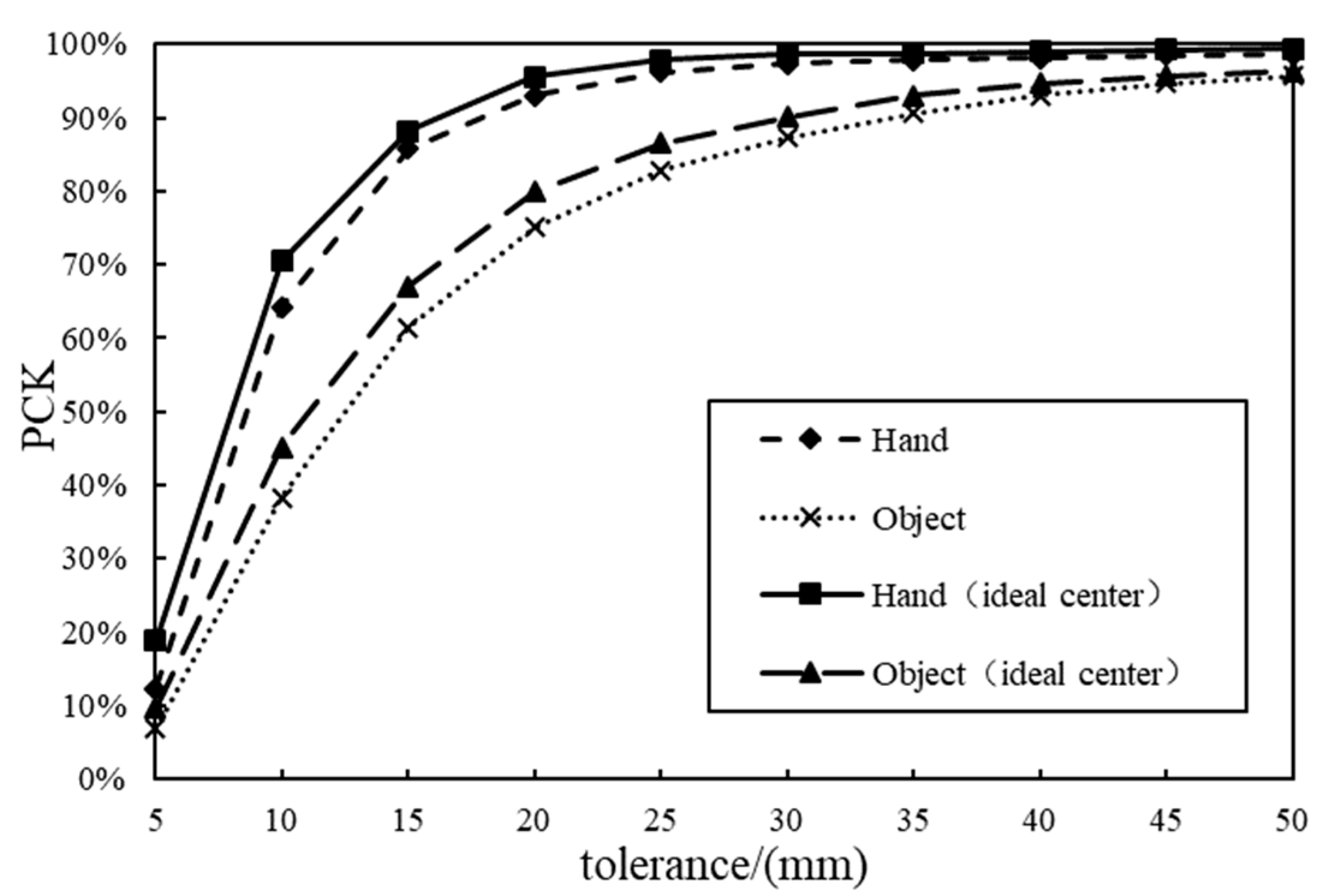
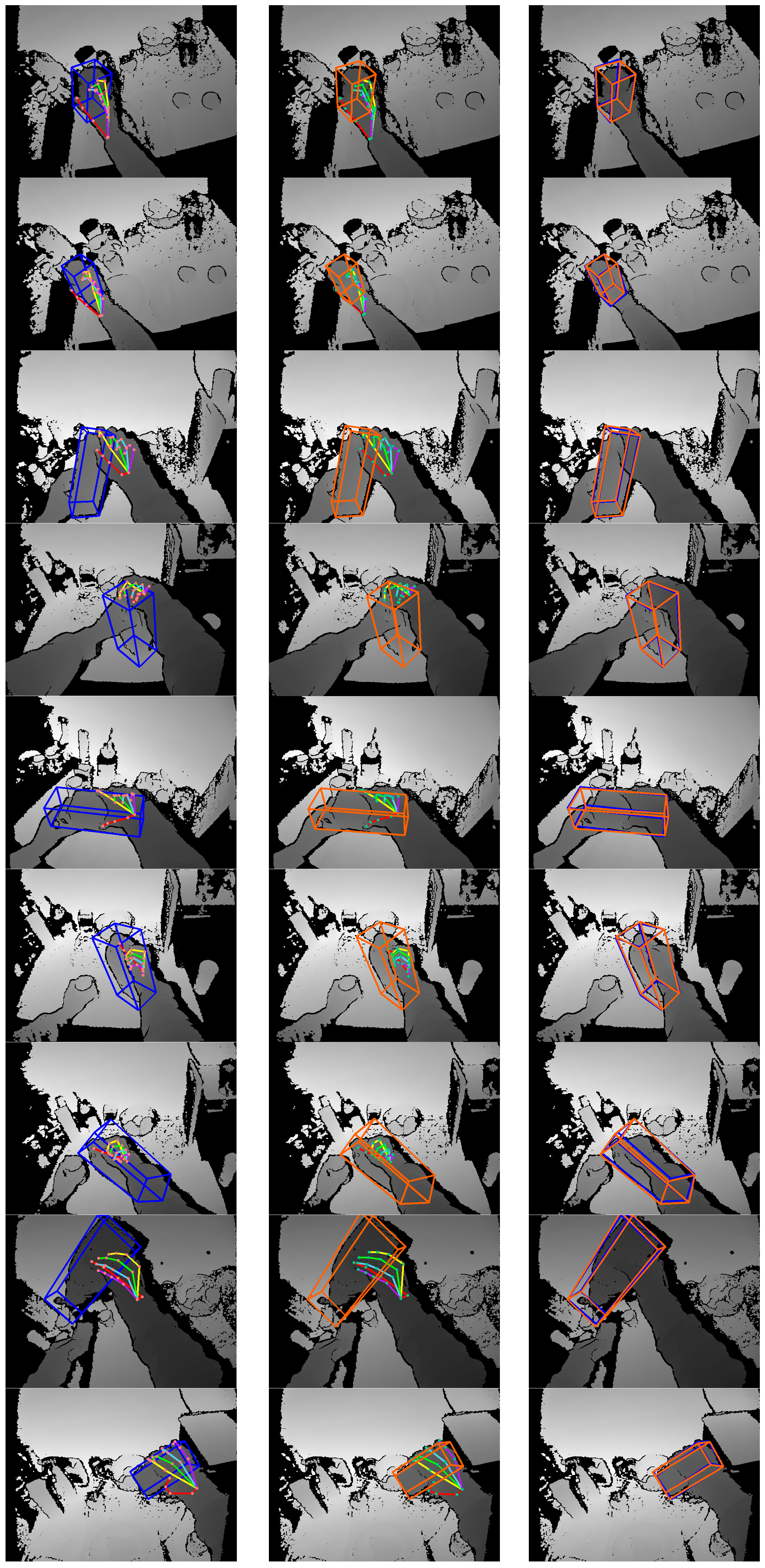
4.4. Experimental Results and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
| YOLO | You Only Look Once |
| ICA | Iterative Cropping Algorithm |
| FCL | Fully Connected Layer |
| SRN | Stacked Regression Network |
| AWR | Adaptive Weighted Regression |
| SSD | Single Shot Multibox Detector |
| BB8 | 8 Corners of the Bounding Box |
| GCN | Graph Convolution Network |
| FPN | Feature Pyramid Network |
| HOAR | Hand–Object Pose Estimation Module Based on Anchor Regression |
| FPHA | First-Person Hand Action |
| MKE | Mean Keypoint Error |
| PCK | Percentage of Correct Keypoint Estimation |
References
- Ge, L.; Liang, H.; Yuan, J.; Thalmann, D. Robust 3D hand pose estimation in single depth images: From single-view CNN to multi-view CNNs. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3593–3601. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Lee, D. Point-to-pose voting based hand pose estimation using residual permutation equivariant layer. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 11919–11928. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, H.; Yuan, J.; Lee, J.; Ge, L.; Thalmann, D. Hough forest with optimized leaves for global hand pose estimation with arbitrary postures. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 49, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Cai, Y.; Weng, J.; Yuan, J. Hand PointNet: 3D hand pose estimation using point sets. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8417–8426. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, S.; Garcia-Hernando, G.; Stenger, B.; Moon, G.; Chang, J.Y.; Lee, K.M.; Molchanov, P.; Kautz, J.; Honari, S.; Ge, L. Depth-based 3D hand pose estimation: From current achievements to future goals. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 2636–2645. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, L.; Liang, H.; Yuan, J.; Thalmann, D. 3D convolutional neural networks for efficient and robust hand pose estimation from single depth images. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5679–5688. [Google Scholar]
- Kanis, J.; Gruber, I.; Krňoul, Z.; Boháček, M.; Straka, J.; Hrúz, M. MuTr: Multi-stage transformer for hand pose estimation from full-scene depth image. Sensors 2023, 23, 5509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekin, B.; Sinha, S.N.; Fua, P. Real-time seamless single shot 6D object pose prediction. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 292–301. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Y.; Schmidt, T.; Narayanan, V.; Fox, D. PoseCNN: A convolutional neural network for 6D object pose estimation in cluttered scenes. arXiv 2017, arXiv:171100199. [Google Scholar]
- Costanzo, M.; De Simone, M.; Federico, S.; Natale, C. Non-prehensile manipulation actions and visual 6D pose estimation for fruit grasping based on tactile sensing. Robotics 2023, 12, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alterani, A.B.; Costanzo, M.; De Simone, M.; Federico, S.; Natale, C. Experimental comparison of two 6D pose estimation algorithms in robotic fruit-picking tasks. Robotics 2024, 13, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, H.; Lee, D. Hand pose estimation for hand-object interaction cases using augmented autoencoder. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 993–999. [Google Scholar]
- Sridhar, S.; Mueller, F.; Zollhöfer, M.; Casas, D.; Oulasvirta, A.; Theobalt, C. Real-time joint tracking of a hand manipulating an object from RGB-D input. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 294–310. [Google Scholar]
- Oikonomidis, I.; Kyriazis, N.; Argyros, A.A. Full DOF tracking of a hand interacting with an object by modeling occlusions and physical constraints. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 2088–2095. [Google Scholar]
- Ballan, L.; Taneja, A.; Gall, J.; Van Gool, L.; Pollefeys, M. Motion capture of hands in action using discriminative salient points. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Florence, Italy, 7–13 October 2012; pp. 640–653. [Google Scholar]
- Tzionas, D.; Ballan, L.; Srikantha, A.; Aponte, P.; Pollefeys, M.; Gall, J. Capturing hands in action using discriminative salient points and physics simulation. Int. J. Comput. Vision 2016, 118, 172–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriazis, N.; Argyros, A. Physically plausible 3D scene tracking: The single actor hypothesis. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Chen, C. Tracking a hand in interaction with an object based on single depth images. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 6745–6762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepetit, V. Recent advances in 3D object and hand pose estimation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:200605927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, F.; Zhang, B.; Xiao, Y.; Cao, Z.; Yu, T.; Zhou, J.T.; Yuan, J. A2J: Anchor-to-joint regression network for 3D articulated pose estimation from a single depth image. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 793–802. [Google Scholar]
- Oberweger, M.; Wohlhart, P.; Lepetit, V. Generalized feedback loop for joint hand-object pose estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 1898–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekin, B.; Bogo, F.; Pollefeys, M. H+O: Unified egocentric recognition of 3D hand-object poses and interactions. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 4506–4515. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:180402767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberweger, M.; Wohlhart, P.; Lepetit, V. Hands deep in deep learning for hand pose estimation. arXiv 2015, arXiv:150206807. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W. 3D Hand Pose Estimation Using Depth Images. Ph.D. Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Shenzhen, China, July 2020. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Armagan, A.; Garcia-Hernando, G.; Baek, S.; Hampali, S.; Rad, M.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, S.; Chen, M.; Zhang, B.; Xiong, F. Measuring generalisation to unseen viewpoints, articulations, shapes and objects for 3D hand pose estimation under hand-object interaction. In Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 85–101. [Google Scholar]
- Paredes, E.J.; Manzano, E.A. Deep learning implementation for peruvian blueberry export standards: A YOLOv8n solution. Enfoque UTE 2025, 16, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, G.; Guo, H.; Zhang, C. Pose guided structured region ensemble network for cascaded hand pose estimation. Neurocomputing 2020, 395, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Park, J.H.; Ko, J.H. HandFoldingNet: A 3D hand pose estimation network using multiscale-feature guided folding of a 2D hand skeleton. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 11240–11249. [Google Scholar]
- Madadi, M.; Escalera, S.; Baró, X.; Gonzalez, J. End-to-end global to local CNN learning for hand pose recovery in depth data. arXiv 2017, arXiv:170509606. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, P.; Sun, H.; Huang, W.; Hao, J.; Cheng, D.; Qi, Q.; Wang, J.; Liao, J. Spatial-aware stacked regression network for real-time 3D hand pose estimation. Neurocomputing 2021, 437, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, R.Q.; Su, H.; Kaichun, M.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet: Deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Gao, Y.; Sang, N. Exploiting learnable joint groups for hand pose estimation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Online, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 3, pp. 1921–1929. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, G.; Lee, K.M. I2L-MeshNet: Image-to-lixel prediction network for accurate 3D human pose and mesh estimation from a single RGB image. In Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 752–768. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, P.; Sun, H.; Qi, Q.; Wang, J.; Huang, W. SRN: Stacked regression network for real-time 3D hand pose estimation. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), Cardiff, UK, 9–12 September 2019; p. 112. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Ren, P.; Wang, J.; Qi, Q.; Sun, H. AWR: Adaptive weighting regression for 3D hand pose estimation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 7, pp. 11061–11068. [Google Scholar]
- Kehl, W.; Manhardt, F.; Tombari, F.; Ilic, S.; Navab, N. SSD-6D: Making RGB-based 3D detection and 6D pose estimation great again. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1530–1538. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.-Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single shot multibox detector. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Rad, M.; Lepetit, V. BB8: A scalable, accurate, robust to partial occlusion method for predicting the 3D poses of challenging objects without using depth. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 3848–3856. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Bao, H. PVNet: Pixel-wise voting network for 6DOF pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 4556–4565. [Google Scholar]
- Fischler, M.A.; Bolles, R.C. Random sample consensus: A paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Commun. ACM 1981, 24, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Song, J.; Huang, Q. HybridPose: 6D object pose estimation under hybrid representations. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 428–437. [Google Scholar]
- Hasson, Y.; Varol, G.; Tzionas, D.; Kalevatykh, I.; Black, M.J.; Laptev, I.; Schmid, C. Learning joint reconstruction of hands and manipulated objects. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 11799–11808. [Google Scholar]
- Doosti, B.; Naha, S.; Mirbagheri, M.; Crandall, D.J. Hope-Net: A graph-based model for hand-object pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 6607–6616. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Sun, W.; Liu, J.; Zheng, J.; Xiao, J.; Mian, A. Occlusion-aware 3D hand-object pose estimation with masked autoencoders. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2506.10816. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, P.; Shkodrani, S.; Moulon, P.; Hampali, S.; Han, S.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, L.; Fountain, J.; Miller, E.; Basol, S.; et al. HOT3D: Hand and object tracking in 3D from egocentric multi-view videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 10–17 June 2025; pp. 7061–7071. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Chao, Y.-W.; Wen, B.; Guo, X.; Xiang, Y. HO-Cap: A capture system and dataset for 3D reconstruction and pose tracking of hand-object interaction. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.06843. [Google Scholar]
- Hampali, S.; Rad, M.; Oberweger, M.; Lepetit, V. HOnnotate: A method for 3D annotation of hand and object poses. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 3193–3203. [Google Scholar]
- Brahmbhatt, S.; Tang, C.; Twigg, C.D.; Kemp, C.C.; Hays, J. ContactPose: A dataset of grasps with object contact and hand pose. In Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 361–378. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, Y.-W.; Yang, W.; Xiang, Y.; Molchanov, P.; Handa, A.; Tremblay, J.; Narang, Y.S.; Van Wyk, K.; Iqbal, U.; Birchfield, S.; et al. DexYCB: A benchmark for capturing hand grasping of objects. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 9040–9049. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Hernando, G.; Yuan, S.; Baek, S.; Kim, T.-K. First-person hand action benchmark with RGB-D videos and 3D hand pose annotations. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 409–419. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, A.; Zisserman, A.; Torr, P.H. Hand detection using multiple proposals. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), Dundee, UK, 29 August–2 September 2011; Volume 3, p. 5. [Google Scholar]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, J.; Li, D.; Chen, C.; Zhao, Z. Hand–Object Pose Estimation Based on Anchor Regression from a Single Egocentric Depth Image. Sensors 2025, 25, 6881. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25226881
Lin J, Li D, Chen C, Zhao Z. Hand–Object Pose Estimation Based on Anchor Regression from a Single Egocentric Depth Image. Sensors. 2025; 25(22):6881. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25226881
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Jingang, Dongnian Li, Chengjun Chen, and Zhengxu Zhao. 2025. "Hand–Object Pose Estimation Based on Anchor Regression from a Single Egocentric Depth Image" Sensors 25, no. 22: 6881. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25226881
APA StyleLin, J., Li, D., Chen, C., & Zhao, Z. (2025). Hand–Object Pose Estimation Based on Anchor Regression from a Single Egocentric Depth Image. Sensors, 25(22), 6881. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25226881







