Online Mapping from Weight Matching Odometry and Highly Dynamic Point Cloud Filtering via Pseudo-Occupancy Grid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Algorithm Framework
- (i)
- Data preprocessing: Raw point cloud data from LiDAR, IMU, and GNSS are processed to generate synchronized and fused multi-sensor measurements. This includes IMU pre-integration, ground point segmentation using the Progressive Morphological Filter (PMF), and motion compensation of LiDAR point clouds.
- (ii)
- Weight feature point matching: the weight coefficient of the Mahalanobis distance is determined by geometric and reflectance intensity similarities to obtain the optimized pose.
- (iii)
- Dynamic point filtering: Dynamic objects are removed from the point cloud, and the map is built in real time using a pseudo-occupancy grid filtering algorithm.
3. Data Fusion for Weight Matching LiDAR-IMU-GNSS Odometry
3.1. IMU Pre-Integration
3.2. Ground Point Segmentation
3.3. Motion Compensation of LiDAR Point Clouds
3.4. Weight Feature Point Matching Method Based on Geometric-Reflectance Intensity Similarity
4. Online Filtering Method for Highly Dynamic Point Clouds
5. Algorithm Validation
5.1. Accuracy of Proposed Odometry Systems
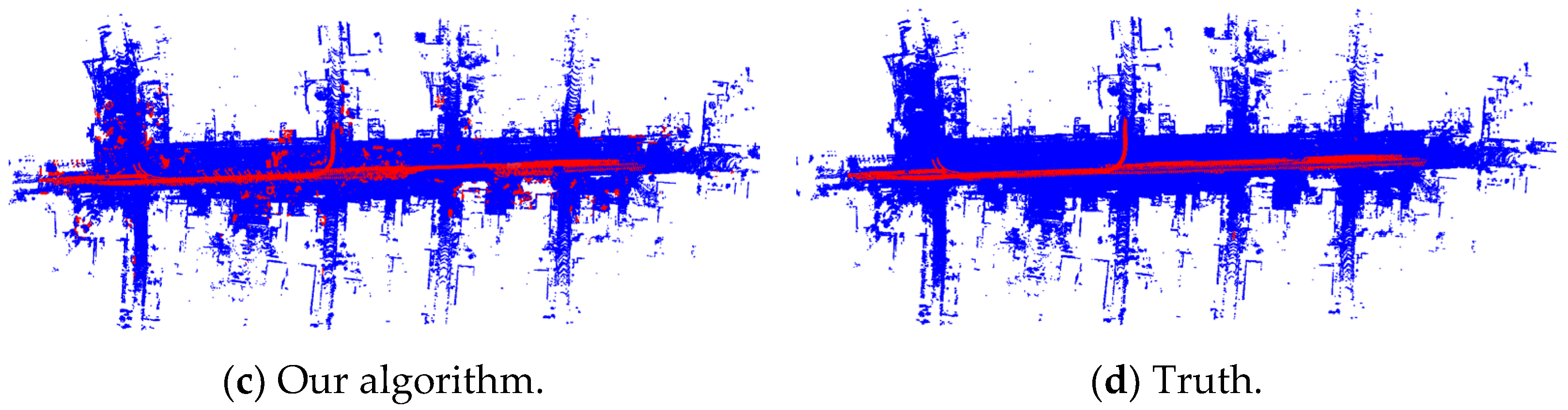
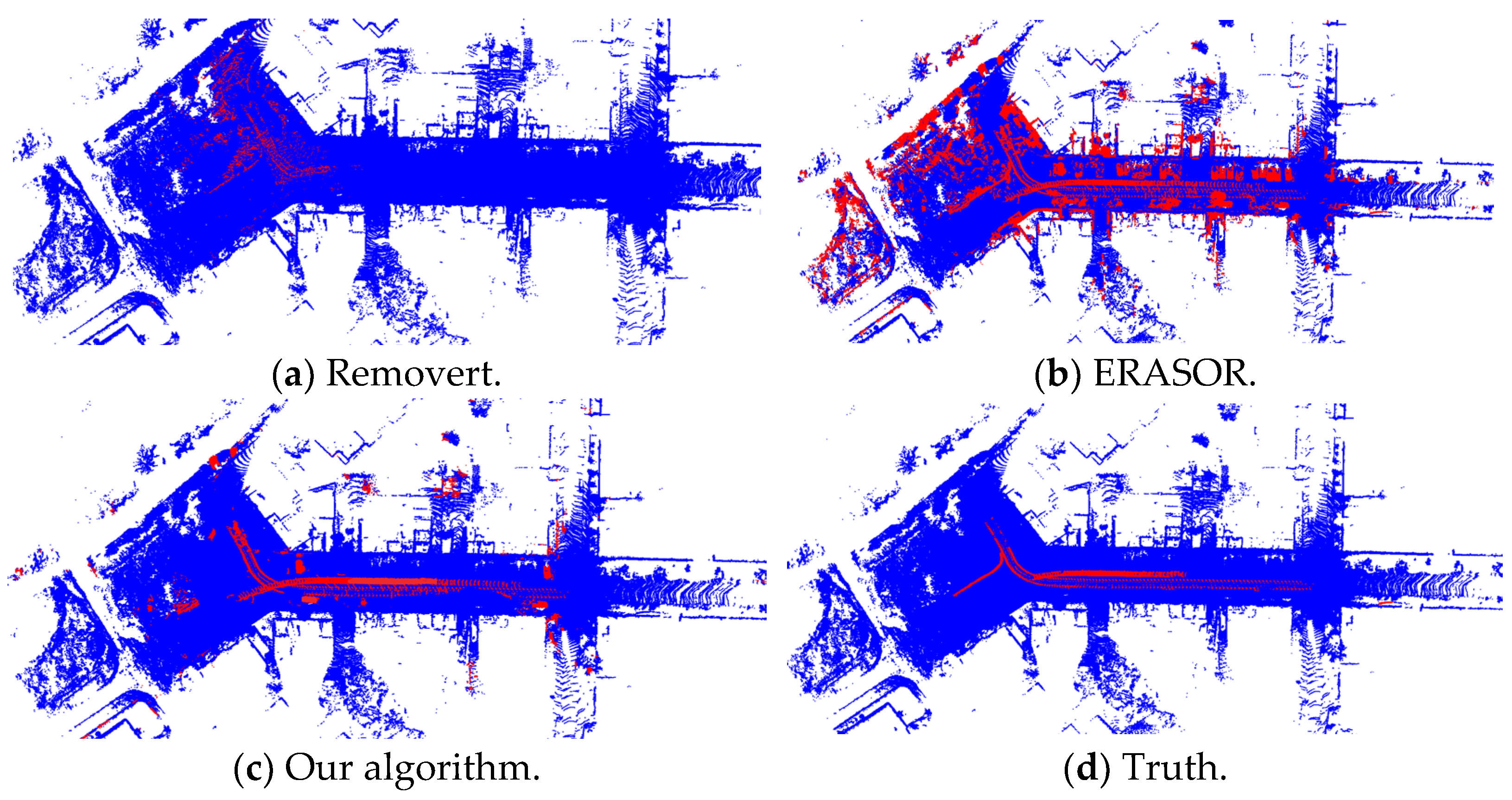
5.2. Comparison of Highly Dynamic Point Cloud Filtering Algorithm
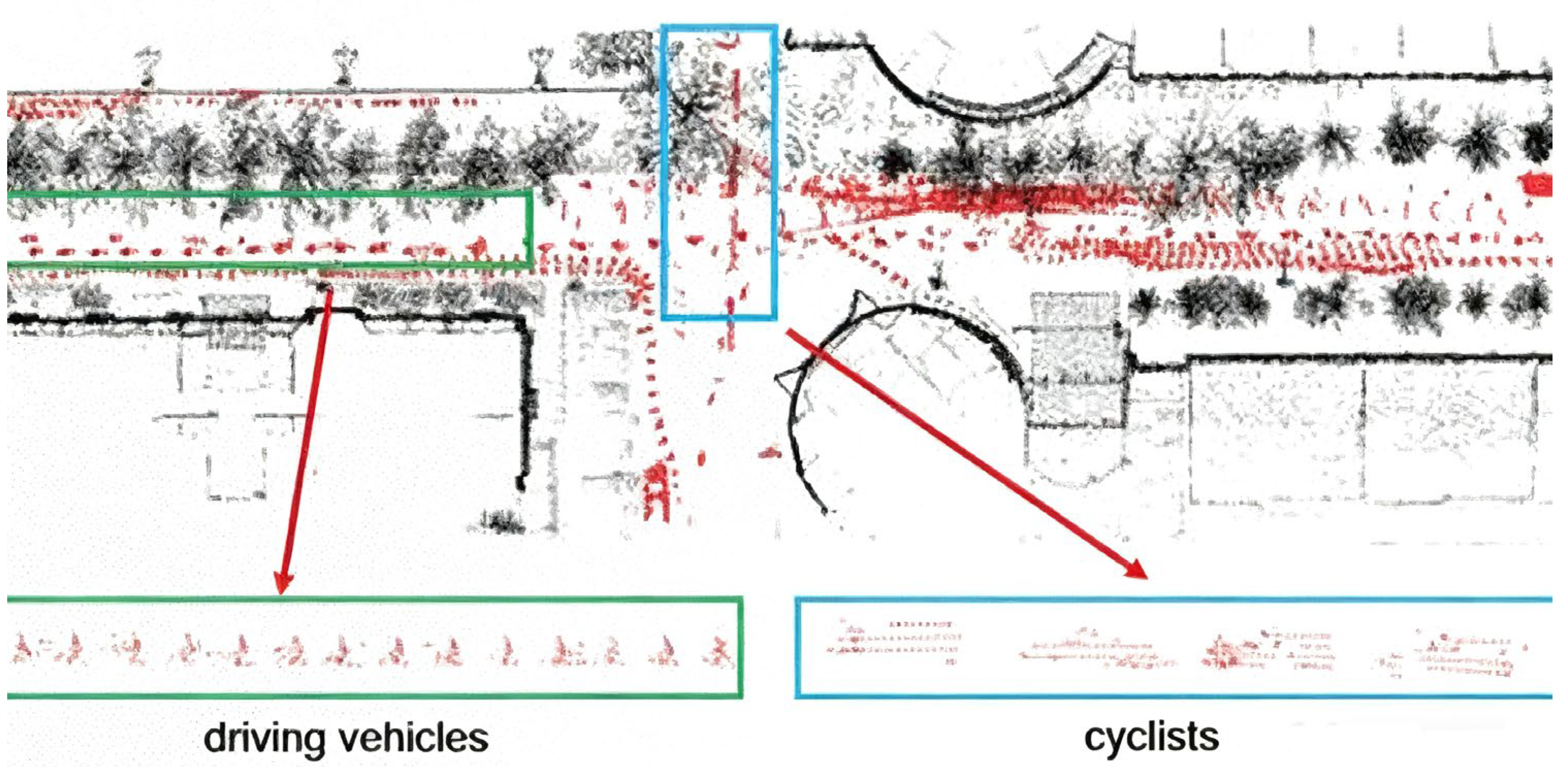
5.3. Online Filtering Experiment
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Faisal, A.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Currie, G. Understanding autonomous vehicles. J. Transp. Land Use 2019, 12, 45–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wei, C.; Hu, J.; Ding, M.; Zhang, M.; Kang, Z. RDP-LOAM: Remove-Dynamic-Points LiDAR Odometry and Mapping. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Unmanned Systems (ICUS), Hefei, China, 13–15 October 2023; pp. 211–216. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Chen, J.; Meng, S.; Wang, Y.; Chau, L.-P. A Survey on Occupancy Perception for Autonomous Driving: The Information Fusion Perspective. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.05173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Mao, M.; Bao, H.; Zhang, G.; Cui, Z. CP-SLAM: Collaborative Neural Point-based SLAM System. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 39429–39442. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Zhong, X.; Wiesmann, L.; Posewsky, T.; Behley, J.; Stachniss, C. PIN-SLAM: LiDAR SLAM Using a Point-Based Implicit Neural Representation for Achieving Global Map Consistency. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2024, 40, 4045–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerbl, B.; Kopanas, G.; Leimkuehler, T.; Drettakis, G. 3D Gaussian Splatting for Real-Time Radiance Field Rendering. ACM-Trans. Graph. 2023, 42, 139:1–139:14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Mou, L.; Li, D.; Ye, B.; Huang, R.; Zhao, H. VR-Robo: A Real-to-Sim-to-Real Framework for Visual Robot Navigation and Locomotion. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2025, 10, 7875–7882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Fu, M. Whole-body motion planning and tracking of a mobile robot with a gimbal RGB-D camera for outdoor 3D exploration. J. Field Robot. 2025, 41, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, A.; Chung, C.; Palieri, M.; Kim, S.-K.; Agha, A.; Guaragnella, C.; Khattak, S. Pixels-to-Graph: Real-time Integration of Building Information Models and Scene Graphs for Semantic-Geometric Human-Robot Understanding. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2506.22593. [Google Scholar]
- Tourani, A.; Bavle, H.; Sanchez-Lopez, J.L.; Voos, H. Visual SLAM: What are the Current Trends and What to Expect? Sensors 2022, 22, 9297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, K.; Dong, S.; Fan, Q.; Wang, H.; Yi, L.; Xia, F.; Wang, J.; Chen, B. Multi-Robot Active Mapping via Neural Bipartite Graph Matching. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.16319. [Google Scholar]
- Hester, G.; Smith, C.; Day, P.; Waldock, A. The next generation of unmanned ground vehicles. Meas. Control 2012, 45, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, S.; McDonald-Maier, K.; Hu, H. Towards autonomous localization and mapping of AUVs: A survey. Int. J. Intell. Unmanned Syst. 2013, 1, 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Yan, L.; Xie, H.; Dai, J.; Zhao, Y.; Su, S. A novel lidar inertial odometry with moving object detection for dynamic scenes. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Unmanned Systems (ICUS), Guangzhou, China, 28–30 October 2022; pp. 356–361. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Hu, Z.; Uchimura, K. SLAM estimation in dynamic outdoor environments: A review. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Robotics and Applications: Second International Conference, ICIRA 2009, Proceedings 2. Singapore, 16–18 December 2009; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 255–267. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Sun, W.; Liu, Y. Dloam: Real-time and robust lidar slam system based on cnn in dynamic urban environments. IEEE Open J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Xiang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Sun, H. Rf-lio: Removal-first tightly-coupled lidar inertial odometry in high dynamic environments. arXiv Preprint 2022, arXiv:2206.09463. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, T.; Englot, B.; Meyers, D.; Wang, W.; Ratti, C.; Rus, D. Lio-sam: Tightly-coupled lidar inertial odometry via smoothing and mapping. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24 October 2020–24 January 2021; pp. 5135–5142. [Google Scholar]
- Pfreundschuh, P.; Hendrikx, H.F.C.; Reijgwart, V.; Dube, R.; Siegwart, R.; Cramariuc, A. Dynamic object aware lidar slam based on automatic generation of training data. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 11641–11647. [Google Scholar]
- Schauer, J.; Nüchter, A. The peopleremover—Removing dynamic objects from 3-d point cloud data by traversing a voxel occupancy grid. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 1679–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Hwang, S.; Myung, H. ERASOR: Egocentric ratio of pseudo occupancy-based dynamic object removal for static 3D point cloud map building. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 2272–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Kim, A. Remove, then revert: Static point cloud map construction using multiresolution range images. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24 October 2020–24 January 2021; pp. 10758–10765. [Google Scholar]
- Behley, J.; Garbade, M.; Milioto, A.; Quenzel, J.; Behnke, S.; Stachniss, C.; Gall, J. Semantickitti: A dataset for semantic scene understanding of lidar sequences. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 9297–9307. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, G.; Fahandezh-Saadi, S.; Bai, X.; Zhan, W.; Tomizuka, M.; Hsu, L.-T. UrbanLoco: A full sensor suite dataset for mapping and localization in urban scenes. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 2310–2316. [Google Scholar]
- Ramezani, M.; Wang, Y.; Camurri, M.; Wisth, D.; Mattamala, M.; Fallon, M. The newer college dataset: Handheld lidar, inertial and vision with ground truth. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24 October 2020–24 January 2021; pp. 4353–4360. [Google Scholar]
- Kullback, S.; Leibler, R.A. On information and sufciency. Ann. Math. Stat. 1951, 22, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Wang, S.; Lim, H.; Kang, U. Curved-voxel clustering for accurate segmentation of 3D LiDAR point clouds with real-time performance. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 3–8 November 2019; pp. 6459–6464. [Google Scholar]

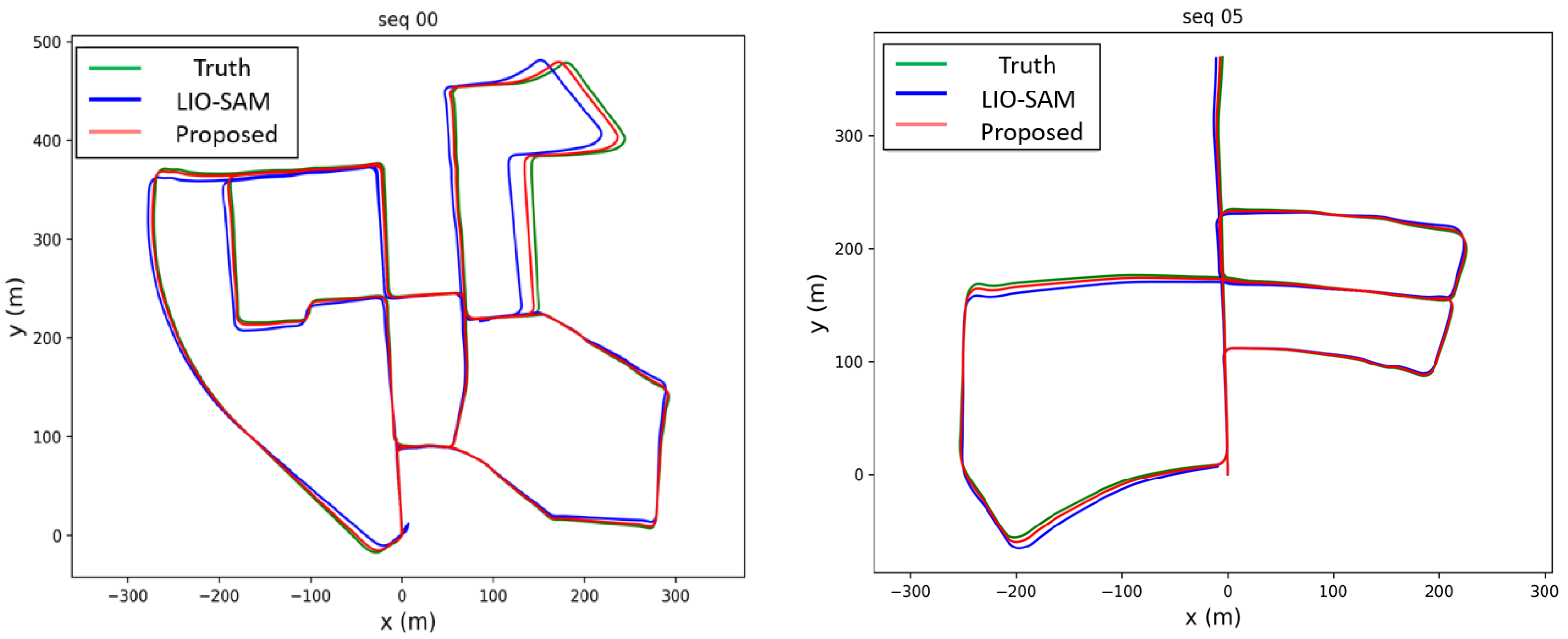


| Dataset | LIO-SAM | FAST-LIO2 | Our Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 00 | 5.8 | 3.7 | 1.1 |
| 01 | 11.3 | 10.8 | 10.9 |
| 02 | 11.8 | 13.2 | 12.9 |
| 03 | - | - | - |
| 04 | 1.2 | 1.0 | 0.9 |
| 05 | 3.0 | 2.8 | 2.5 |
| 06 | 1.0 | 1.3 | 1.1 |
| 07 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
| 08 | 4.4 | 3.9 | 3.9 |
| 09 | 4.3 | 4.8 | 2.1 |
| 10 UrbanLoCo-CA-1 UrbanLoCo-CA-2 UrbanLoCo-HK-1 UrbanLoCo-HK-2 NCD-long-13 | 2.4 5.295 11.635 1.342 1.782 0.187 | 1.7 10.943 7.901 1.196 1.802 0.194 | 1.5 4.615 7.189 1.159 1.768 0.163 |
| NCD-long-14 | 0.195 | 0.212 | 0.185 |
| NCD-long-15 | 0.162 | 0.173 | 0.169 |
| Dataset | Method | PR | RR | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00 | Removert | 86.8 | 90.6 | 0.88 |
| ERASOR | 93.9 | 97.0 | 0.95 | |
| Our Algorithm | 98.7 | 98.5 | 0.98 | |
| 01 | Removert | 95.8 | 57.0 | 0.71 |
| ERASOR | 91.8 | 94.3 | 0.93 | |
| Our Algorithm | 96.8 | 94.6 | 0.95 | |
| 05 | Removert | 86.9 | 87.8 | 0.87 |
| ERASOR | 88.7 | 98.2 | 0.93 | |
| Our Algorithm | 97.5 | 96.3 | 0.96 | |
| 07 | Removert | 80.6 | 98.8 | 0.88 |
| ERASOR | 90.6 | 99.2 | 0.948 | |
| Our Algorithm | 96.6 | 98.9 | 0.977 |
| Robosense Helio-32 | GW-NAV100B | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Values | Parameters | Values | |
| vertical field | range | +15°~−55° | frequency | 100 Hz |
| 2°(+15°~+7° and −8°~−55°) | (10 Hz for GNSS) | |||
| resolution | 1.5(+7°~+4°) | position resolution | 0.01 m in horizonal field | |
| 1.33(+4°~−8°) | 0.15 m in vertical field | |||
| horizontal field | range | 360° | velocity resolution | 0.03 m/s |
| resolution | 0.2° | 0.2° in roll | ||
| attitude resolution | 0.2° in pitch | |||
| 0.1° in yaw | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.; Cao, X.; Ding, M.; Jiang, D.; Wei, C. Online Mapping from Weight Matching Odometry and Highly Dynamic Point Cloud Filtering via Pseudo-Occupancy Grid. Sensors 2025, 25, 6872. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25226872
Zhao X, Cao X, Ding M, Jiang D, Wei C. Online Mapping from Weight Matching Odometry and Highly Dynamic Point Cloud Filtering via Pseudo-Occupancy Grid. Sensors. 2025; 25(22):6872. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25226872
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xin, Xingyu Cao, Meng Ding, Da Jiang, and Chao Wei. 2025. "Online Mapping from Weight Matching Odometry and Highly Dynamic Point Cloud Filtering via Pseudo-Occupancy Grid" Sensors 25, no. 22: 6872. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25226872
APA StyleZhao, X., Cao, X., Ding, M., Jiang, D., & Wei, C. (2025). Online Mapping from Weight Matching Odometry and Highly Dynamic Point Cloud Filtering via Pseudo-Occupancy Grid. Sensors, 25(22), 6872. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25226872






