Land Subsidence in the Loess Plateau: SBAS-InSAR Analysis of Yan’an New District During 2017–2022
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sets
2.3. Methodology
- (1)
- High-resolution satellite imagery was used to identify areas without significant surface changes or construction activities during the study period;
- (2)
- Preliminary InSAR results were then used to select pixels within these areas that exhibited minimal deformation (cumulative displacement < 2 mm, standard deviation < 1 mm) and stable time series behavior.
3. Results
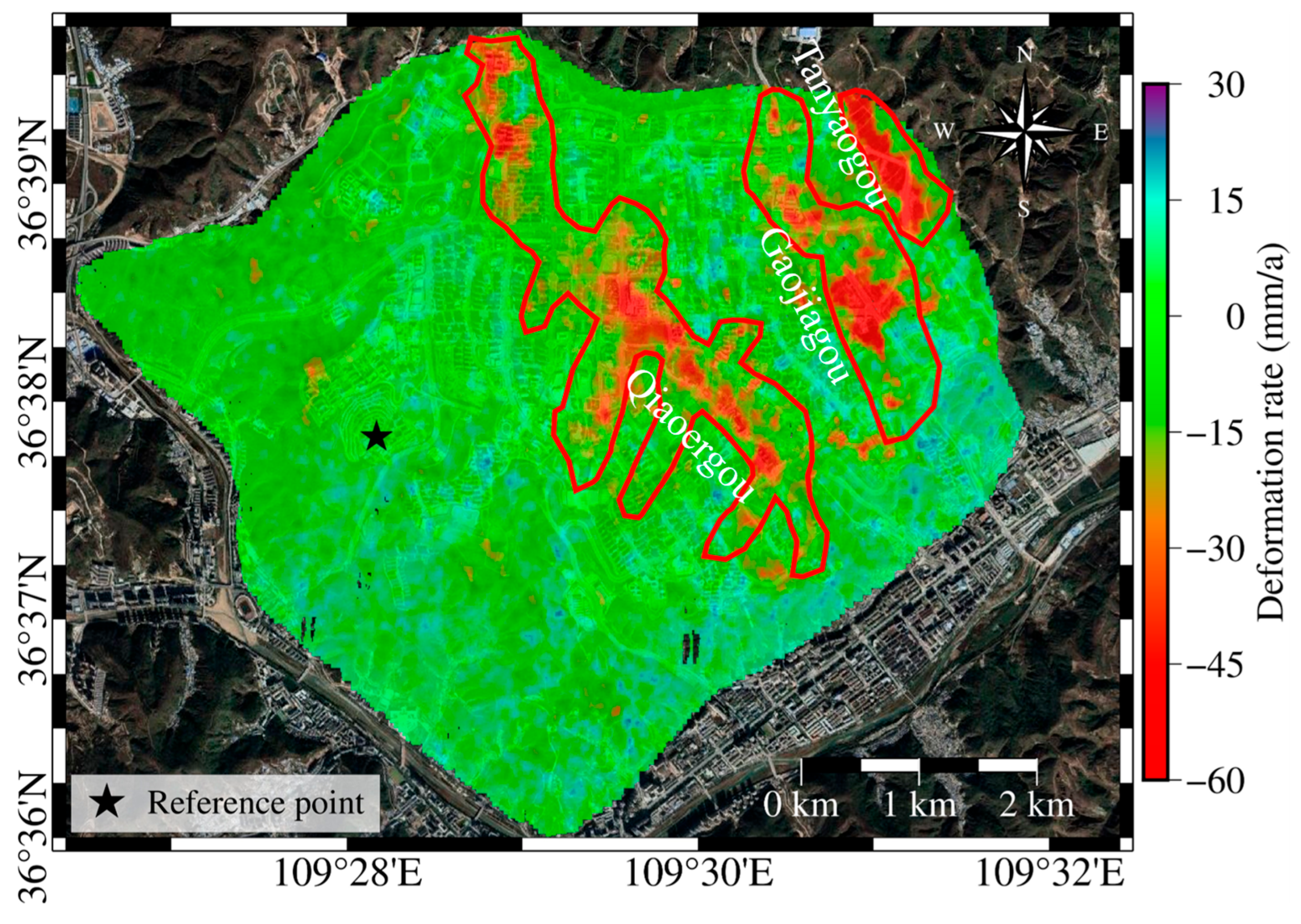
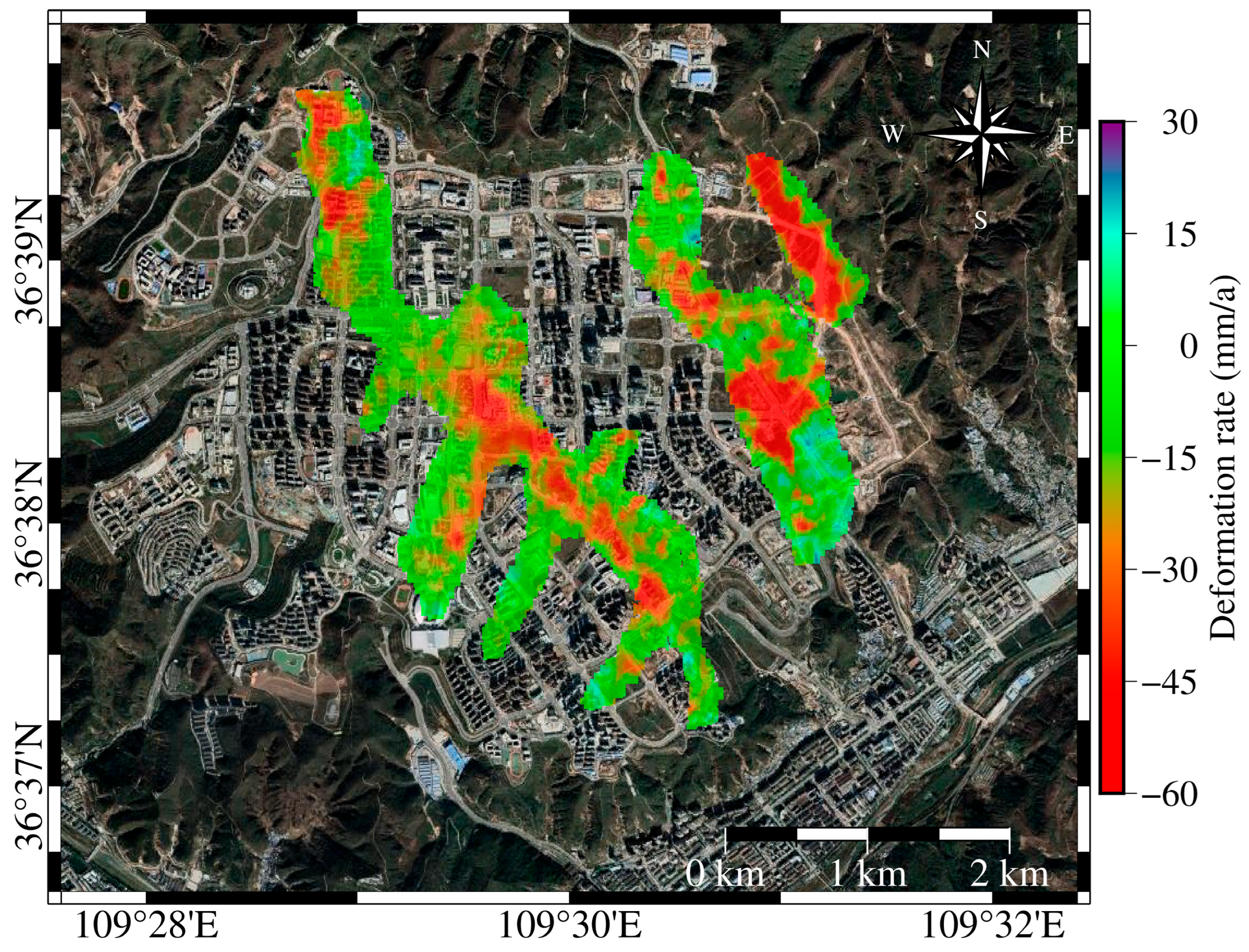
3.1. Ground Deformation Information Spatial Distribution
3.2. Subsidence Characteristics and Excavation-Filling Engineering Correlation Analysis
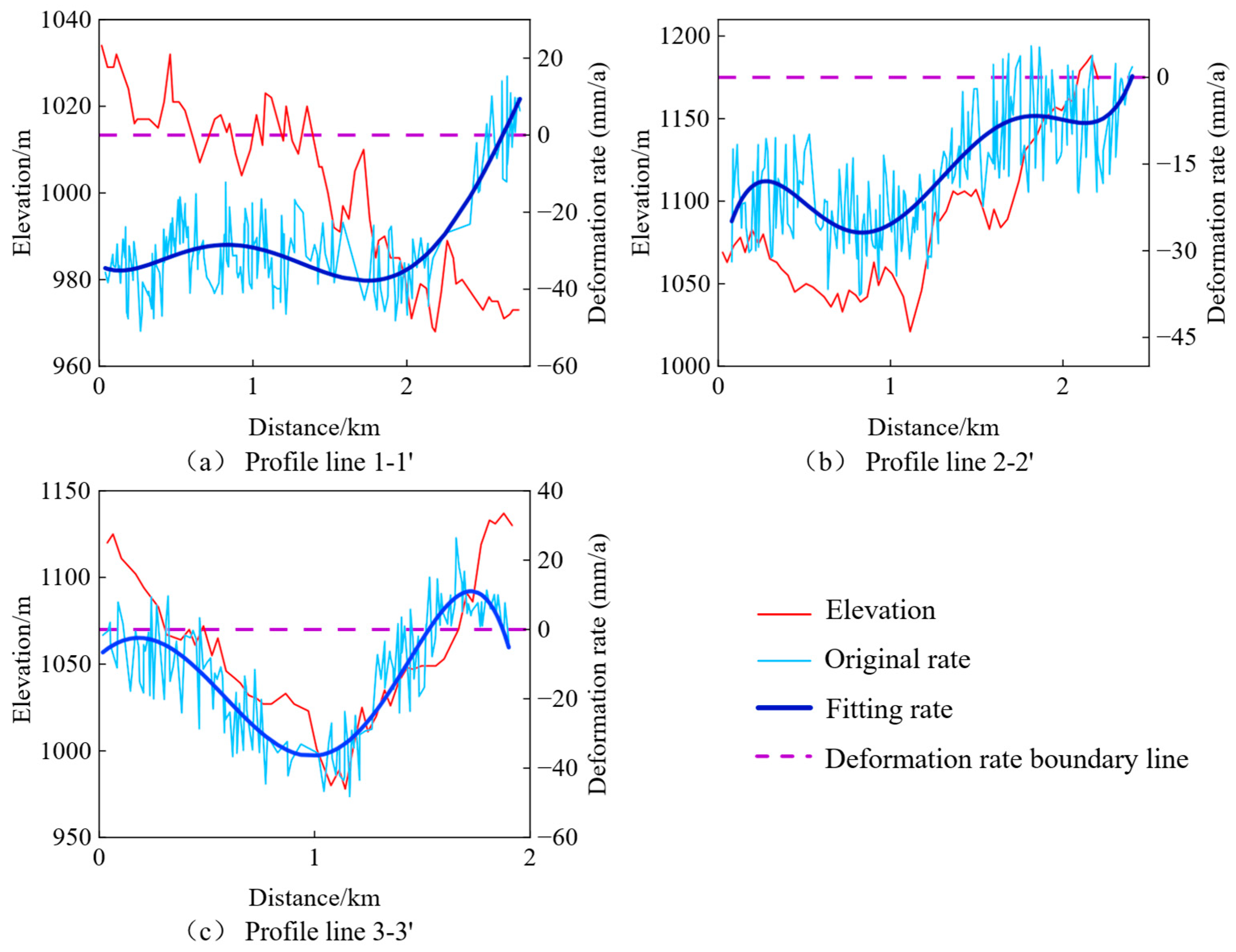
- Analysis of profile 1–1′: This area is situated in the valley region, with the terrain gradually descending to the south. As shown in Figure 6a, significant subsidence is evident in the fill area, while only the unconstructed section at the end demonstrates a stable condition.
- Analysis of profile 2–2′: The first half, representing the fill area, shows significant subsidence, while the latter half, the excavation area, exhibits a tendency toward stability.
- Analysis of profile 3–3′: This area exhibits topographical changes in a mountain-valley-mountain pattern. The excavation areas on the peaks demonstrate relatively stable conditions, while the fill area in the valley shows significant subsidence.
4. Analysis
4.1. Influence of Precipitation
4.2. Impact of Groundwater Storage
5. Discussion
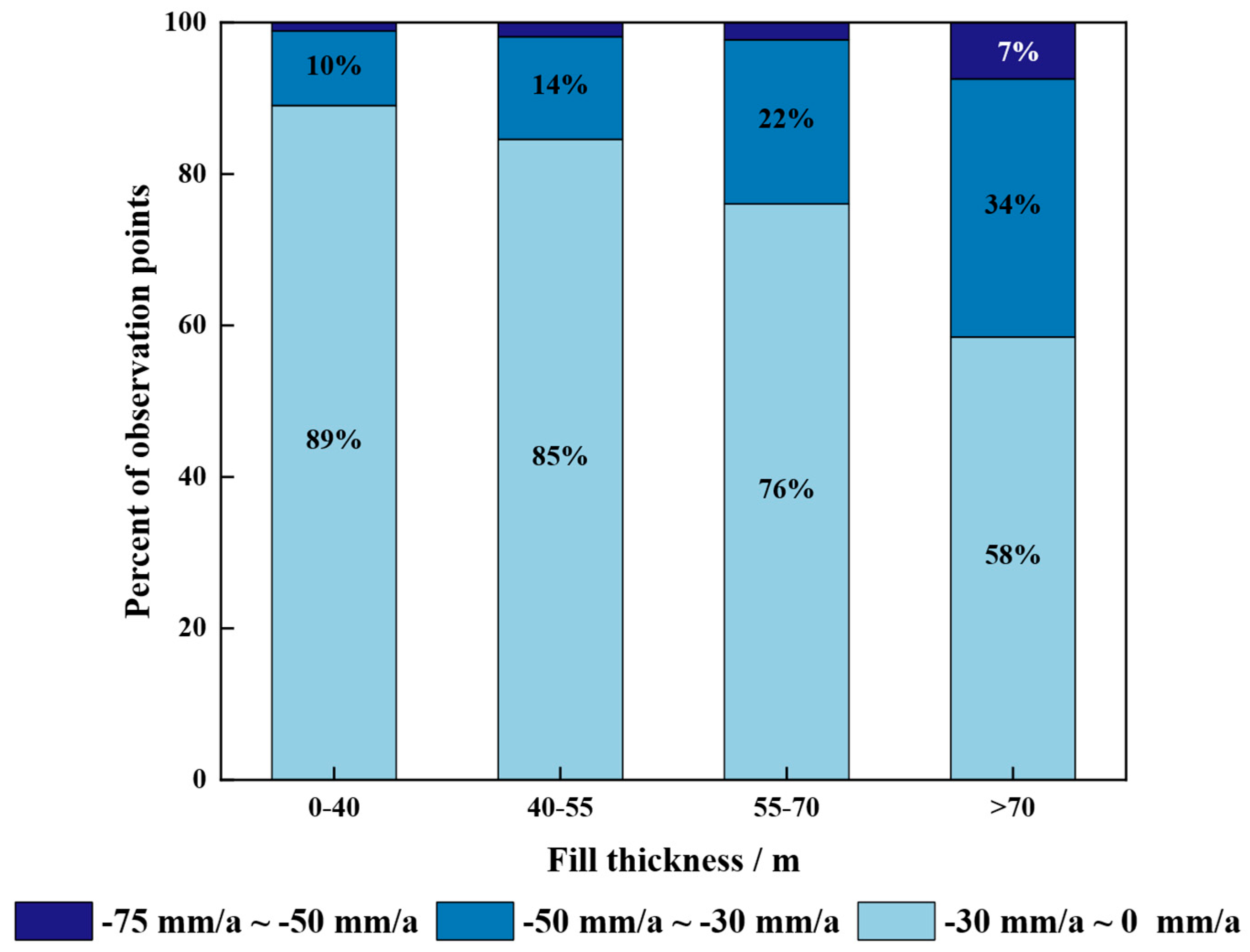
5.1. Relationship Between Fill Thickness and Settlement Rate
5.2. YND Post-Completion Urban Planning
6. Conclusions
- Based on Sentinel-1A imagery from 2017 to 2022, SBAS-InSAR monitoring revealed a clear subsidence trend in filled valley regions, with a maximum cumulative subsidence of 400 mm and a maximum subsidence rate of −89 mm/year. In contrast, excavation zones located on original mountain ridges exhibited only minor uplift, with a maximum deformation rate of 25 mm/year.
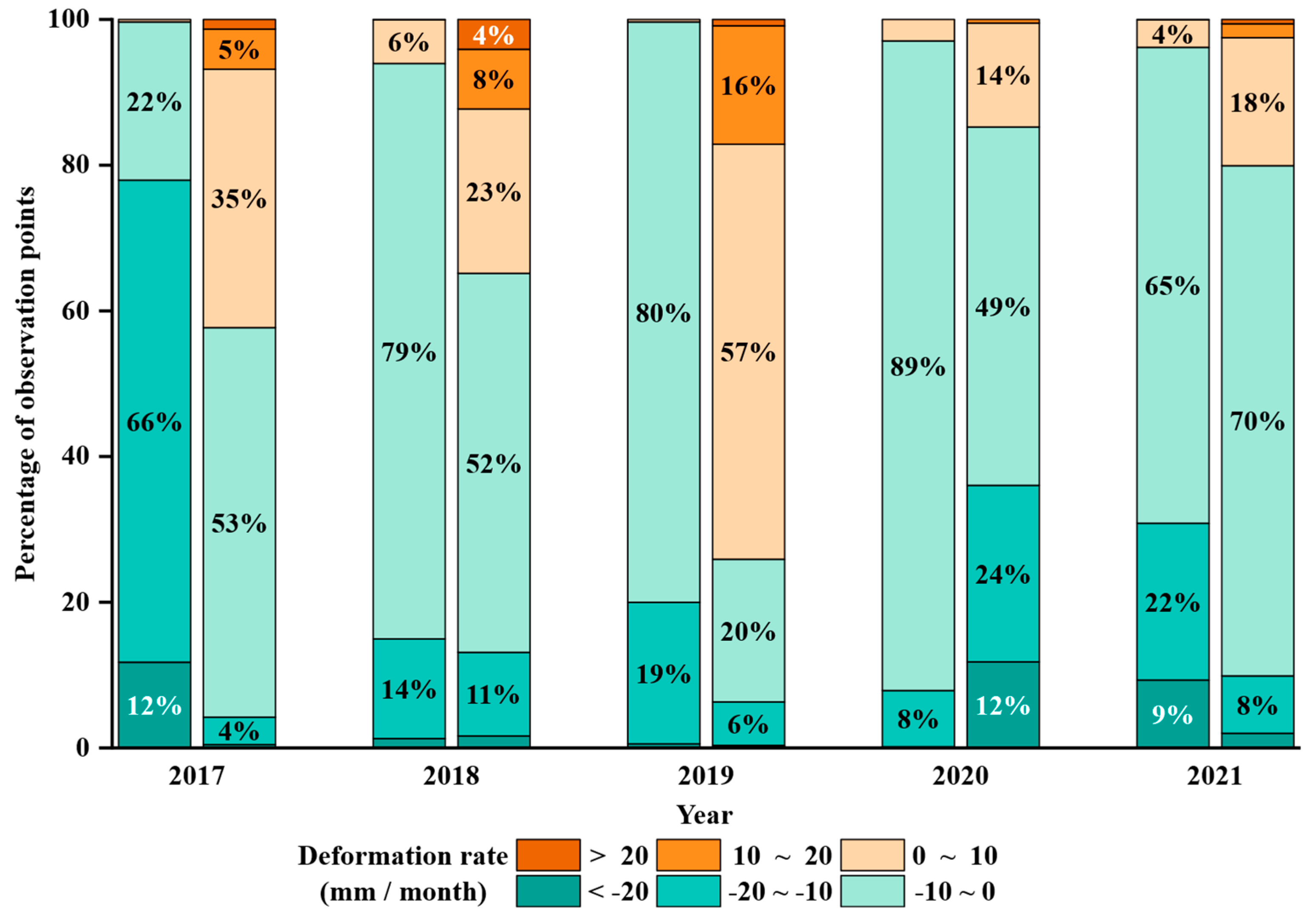
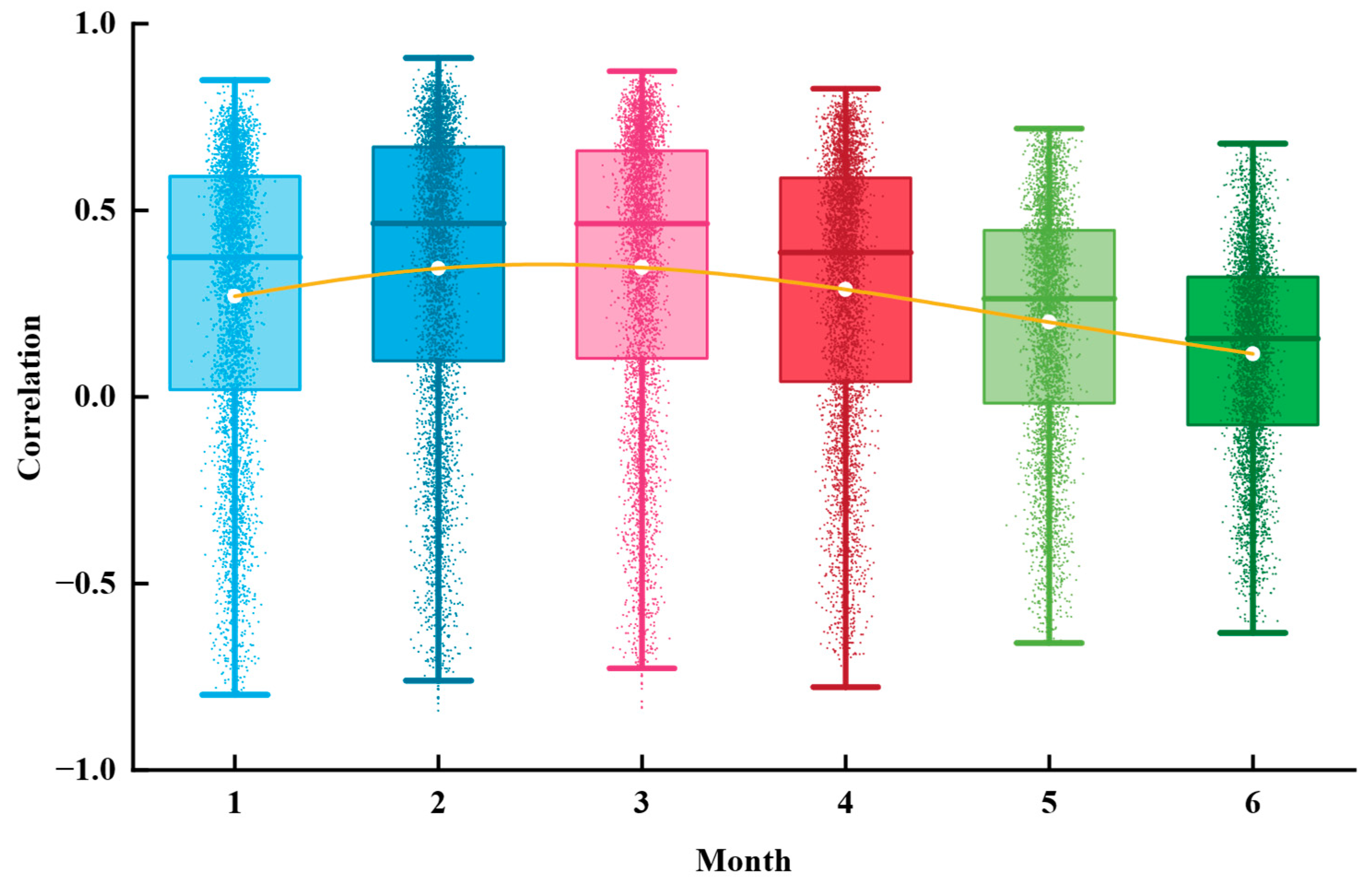
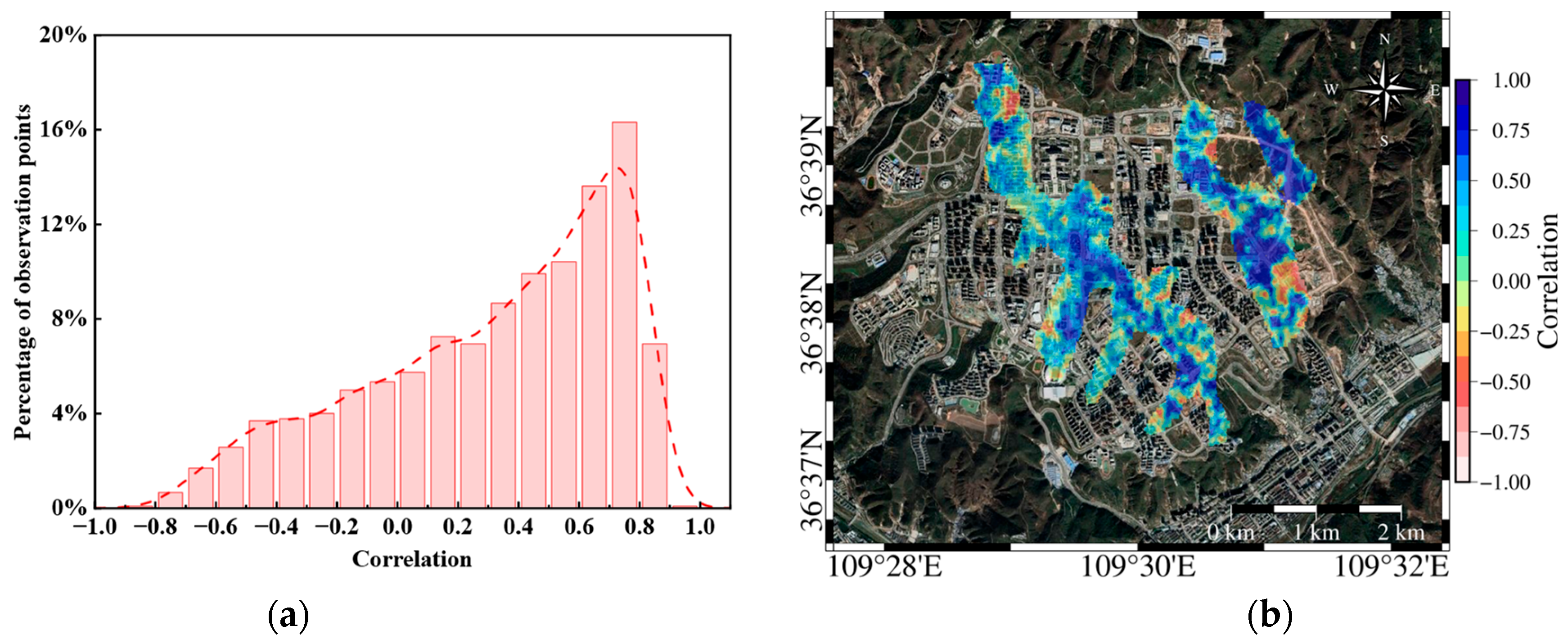
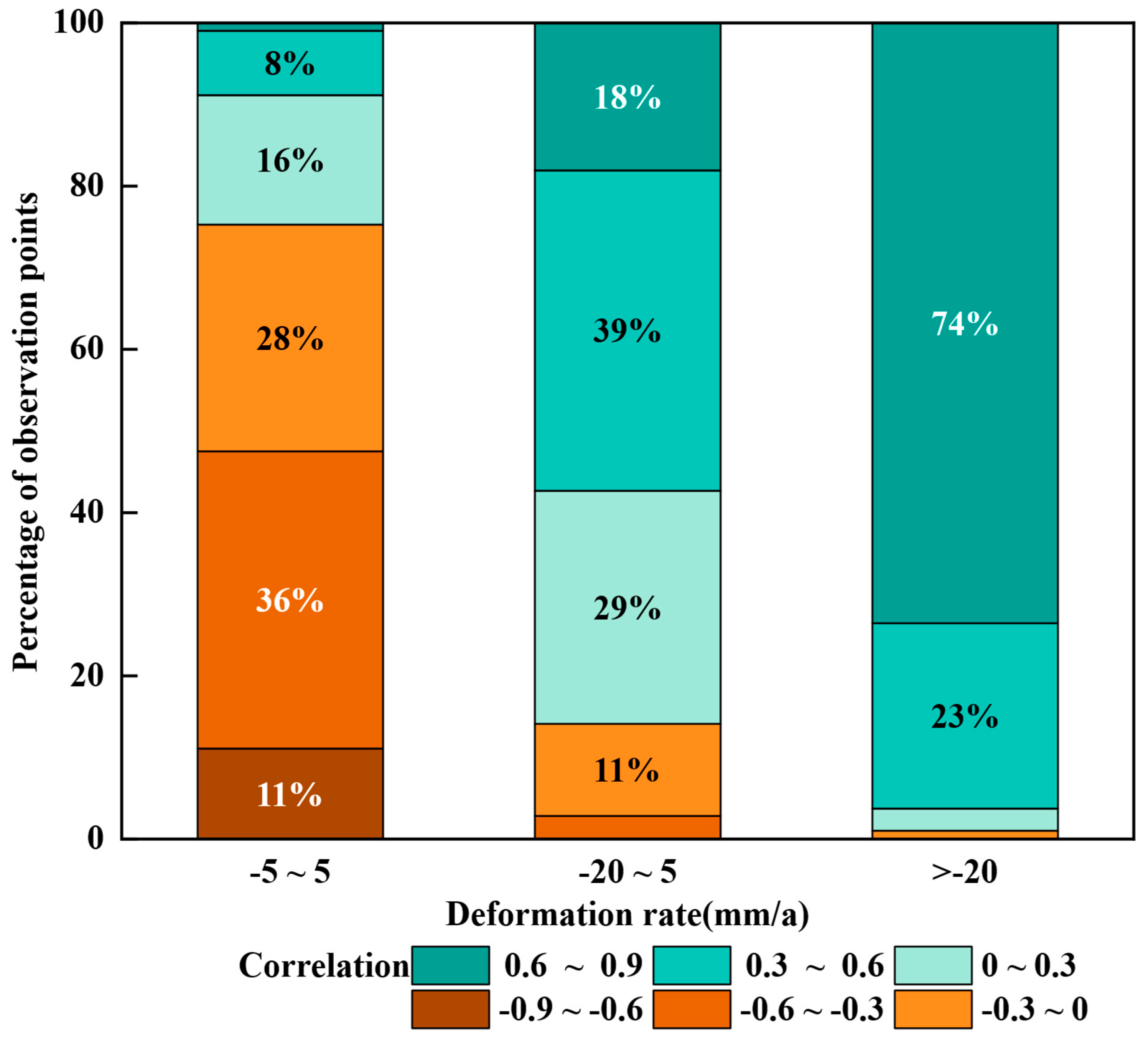
- Precipitation and groundwater storage are the primary natural factors contributing to subsidence. In areas with high precipitation (≥60 mm/month), the subsidence rate increases significantly. Precipitation alters surface water conditions, which then infiltrates the subsurface and affects groundwater storage, subsequently influencing ground deformation. A significant positive correlation was found between cumulative subsidence and groundwater storage with a two-month lag, with most correlation coefficients ranging between 0.4 and 0.8.
- Fill thickness, as the dominant anthropogenic factor, shows a positive correlation with surface deformation. Greater fill thickness prolongs the primary consolidation stage, resulting in a longer period of rapid subsidence. After project completion, the Yan’an municipal government actively promoted greening efforts and avoided construction in high-risk areas (subsidence rate >−40 mm/year), instead developing public parks to reduce accident risks and improve the ecological environment of the new district.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, H.; Gong, H.; Chen, B.; Liu, K.; Gao, M. Analysis of the influence of groundwater on land subsidence in Beijing based on the geographical weighted regression (GWR) model. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 139405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Xue, L.; Yu, Y.; Guo, S.; Cui, Y.; Li, Y.; Qi, S. Remote sensing characterization of mountain excavation and city construction in Loess Plateau. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL095230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, F.; Tapete, D. Present-day land subsidence rates, surface faulting hazard and risk in Mexico City with 2014–2020 Sentinel-1 IW InSAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 253, 112161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbau, C.; Simeoni, U.; Zoccarato, C.; Mantovani, G.; Teatini, P. Coupling land use evolution and subsidence in the Po Delta, Italy: Revising the past occurrence and prospecting the future management challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 1196–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, H.Z.; Andreas, H.; Gamal, M.; Djaja, R.; Subarya, C.; Hirose, K.; Maruyama, Y.; Murdohardono, D.; Rajiyowiryono, H. Monitoring land subsidence of Jakarta (Indonesia) using leveling, GPS survey and InSAR techniques. In Proceedings of the A Window on the Future of Geodesy, Sapporo, Japan, 30 June–11 July 2005; pp. 561–566. [Google Scholar]
- Abidin, H.Z.; Andreas, H.; Gumilar, I.; Yuwono, B.D.; Murdohardono, D.; Supriyadi, S. On integration of geodetic observation results for assessment of land subsidence hazard risk in urban areas of Indonesia. In Proceedings of the IAG 150 Years, Postdam, Germany, 1–6 September 2016; pp. 435–442. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, M.; Dong, J.; Li, M.; Ao, M.; Zhang, L.; Shi, X. Identification of Landslide Hazards and Deformation Monitoring Using Radar Remote Sensing. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 25, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parizzi, A.; Brcic, R.; Zan, F.D. InSAR Performance for Large-Scale Deformation Measurement. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 8510–8520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zhou, Y. Optimization of InSAR based coseismic slip modeling for moderate earthquakes accounting for fore–aftershock sequence. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 305, 114065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.; Li, Y.; Gao, Z.; Hua, J.; Huang, X.; Gong, W.; Qu, C.; Zhao, D.; Chen, J.; Huang, C.; et al. Coseismic Deformation Characteristics and Surrounding Seismic Hazard Assessment of the 2022 Luding M_S6.8 Earthquake. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2023, 68, 944–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccarini, A.; Giacomelli, S.; Berti, P.S. Long term spatiotemporal evolution of land subsidence in the urban area of Bologna, Italy. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2024, 83, 35.31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manconi, A.; Jones, N.; Loew, S.; Strozzi, T.; Caduff, R.; Wegmueller, U. Monitoring surface deformation with spaceborne radar interferometry in landslide complexes: Insights from the Brienz/Brinzauls slope instability, Swiss Alps. Landslides 2024, 21, 2519–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wei, L.; Shouda, L.; Lianhuan, W. Landslide Deformation Monitoring Based on SBAS-InSAR Technology. J. Liaoning Univ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 44, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Jiang, L.; Gao, N.; Gao, S.; Li, J. Estimation and Analysis of Glacier Mass Balance in the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau Using TanDEM-X Bi-Static InSAR during 2000–2014. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wauthier, C.; Stephens, K.; Gervais, M.; Cervone, G.; La Femina, P.; Higgins, M. Automatic detection of volcanic surface deformation using deep learning. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2020, 125, e2020JB019840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisina, C.; Zucca, F.; Notti, D.; Colombo, A.; Cucchi, A.; Savio, G.; Giannico, C.; Bianchi, M. Geological interpretation of PSInSAR data at regional scale. Sensors 2008, 8, 7469–7492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponzo, F.C.; Auletta, G.; Ielpo, P.; Ditommaso, R. DInSAR–SBAS satellite monitoring of infrastructures: How temperature affects the “Ponte della Musica” case study. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2024, 14, 745–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizzani, P.; Berardino, P.; Casu, F.; Euillades, P.; Manzo, M.; Ricciardi, G.P.; Zeni, G.; Lanari, R. Surface deformation of Long Valley caldera and Mono Basin, California, investigated with the SBAS-InSAR approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Tan, X.; Dong, Y.; Sun, P.; Dong, P.; Lu, N. A Brief Analysis of Environmental Effects of Terracing Projects on the Loess Plateau—A Case Study of Yan’an New Area. Geol. Rev. 2019, 65, 1409–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Qian, H.; Wu, J. Environment: Accelerate research on land creation. Nature 2014, 510, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Jia, C.; Chen, S.; Li, H. SBAS-InSAR based deformation detection of urban land, created from mega-scale mountain excavating and valley filling in the Loess Plateau: The case study of Yan’an City. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z. The creation of farmland by gully filling on the Loess Plateau: A double-edged sword. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 883–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, C.H.; Dijkstra, T.; Wasowski, J.; Meng, X. Loess geohazards research in China: Advances and challenges for mega engineering projects. Eng. Geol. 2019, 251, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qi, S.; Ma, L.; Guo, S.; Li, Z.; Li, G.; Yang, J.; Zou, Y.; Li, T.; Hou, X. Three-dimensional pore characterization of intact loess and compacted loess with micron scale computed tomography and mercury intrusion porosimetry. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zeng, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Meng, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Meng, X.; Yang, Y. Subsidence monitoring and influencing factor analysis of mountain excavation and valley infilling on the Chinese Loess Plateau: A case study of Yan’an New District. Eng. Geol. 2022, 297, 106482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Pu, C.; Zhao, K.; He, P.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J. Monitoring and Analysis of Spatiotemporal Evolution Characteristics of Ground Subsidence in Yan’an New Area Using Time-Series InSAR. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2021, 46, 957–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, C.; Xu, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, K.; He, P.; Zhang, H.; Li, H. Time-Series InSAR Monitoring and Analysis of Ground Subsidence Distribution and Influencing Factors in Yan’an New Area. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2020, 45, 1728–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, C.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, K.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, J.; Kou, P. Monitoring and Analysis of Ground Uplift in Yan’an New Area Using Small Baseline Subset InSAR Technology. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2021, 46, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, C.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, K.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, P.; Du, P.; Yuan, S. Study on Ground Subsidence and Vegetation Restoration Characteristics of Pingshan Urban Construction Project in Yan’an New Area Based on Remote Sensing Analysis. J. Eng. Geol. 2020, 28, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Lan, H.; Bürgmann, R.; Warner, T.A.; Clague, J.J.; Li, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, J. Application of an improved multi-temporal InSAR method and forward geophysical model to document subsidence and rebound of the Chinese Loess Plateau following land reclamation in the Yan’an New District. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 279, 113102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Meng, R.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, L.; Lu, Z. Remote sensing characterizing and deformation predicting of Yan’an New District’s Mountain Excavation and City Construction with dual-polarization MT-InSAR method. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2025, 136, 104364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, S.; Wang, X.; Hao, J.; Zhi, B.; Zhang, H.; Deng, B. Experimental study on consolidation characteristics of compacted loess. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 6687858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Wen, X.; Rao, W.; Bradd, J.; Huang, J. Temporal variation of stable isotopes in a precipitation–groundwater system: Implications for determining the mechanism of groundwater recharge in high mountain–hills of the Loess Plateau, China. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 1491–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Li, N. Ranking of influence factors and control technologies for the post-construction settlement of loess high-filling embankments. Comput. Geotech. 2020, 118, 103320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Li, Z.; Penna, N.T.; Crippa, P. Generic atmospheric correction model for interferometric synthetic aperture radar observations. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 9202–9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Ding, Y.; Wen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Y.; Ren, J. Spatiotemporal change and trend analysis of potential evapotranspiration over the Loess Plateau of China during 2011–2100. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 233, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Rodell, M.; Kumar, S.; Beaudoing, H.K.; Getirana, A.; Zaitchik, B.F.; de Goncalves, L.G.; Cossetin, C.; Bhanja, S.; Mukherjee, A. Global GRACE data assimilation for groundwater and drought monitoring: Advances and challenges. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 7564–7586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Dong, Q.; Men, Y.; Chang, Y.; Ye, W.-J. Change of groundwater and water content of loess high fill in gully regions. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2018, 40, 1753–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Shi, P.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Z.; Guo, F. Deformation Monitoring and Analysis of Pingchuan Mining Area Based on SBAS-InSAR Technology. Geospat. Inf. 2024, 22, 53–56+60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.W.; Ding, X.L.; Huang, C.; Zhu, J.J.; Chen, Y.L. Improved filtering parameter determination for the Goldstein radar interferogram filter. Isprs J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2008, 63, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Penna, N.T.; Li, Z. Generation of real-time mode high-resolution water vapor fields from GPS observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 2008–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M. A novel phase unwrapping method based on network programming. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 36, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunjun, Z.; Fattahi, H.; Amelung, F. Small baseline InSAR time series analysis: Unwrapping error correction and noise reduction. Comput. Geosci. 2019, 133, 104331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Yang, G.; Liu, T.; Shao, M.; Ma, Z. Research on groundwater change and land subsidence hysteresis based on InSAR and GRACE data. Remote Sens. Nat. Resour. 2024, 37, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, R.; Yang, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhao, F.; Meng, X. Detection of land subsidence associated with land creation and rapid urbanization in the chinese loess plateau using time series insar: A case study of Lanzhou new district. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wang, W. Analysis of the Relationship Between Groundwater Level Changes and Precipitation. Groundwater 2009, 31, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Aliya, B. Mathematical fitting of influencing factors and measured groundwater level: Take Keriya River Basin in Hetian area as an example. Prog. Geogr. 2018, 37, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Jing, Z. Land Subsidence Monitoring and Building Risk Assessment Using InSAR and Machine Learning in a Loess Plateau City—A Case Study of Lanzhou, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, Y.; Chen, P.; Yao, Y.; Qiu, L.; Liu, H.; Zhu, C.; Lu, J. Land Subsidence in the Loess Plateau: SBAS-InSAR Analysis of Yan’an New District During 2017–2022. Sensors 2025, 25, 6298. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206298
Hong Y, Chen P, Yao Y, Qiu L, Liu H, Zhu C, Lu J. Land Subsidence in the Loess Plateau: SBAS-InSAR Analysis of Yan’an New District During 2017–2022. Sensors. 2025; 25(20):6298. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206298
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Yang, Peng Chen, Yibin Yao, Liangcai Qiu, Hang Liu, Chengchang Zhu, and Jierui Lu. 2025. "Land Subsidence in the Loess Plateau: SBAS-InSAR Analysis of Yan’an New District During 2017–2022" Sensors 25, no. 20: 6298. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206298
APA StyleHong, Y., Chen, P., Yao, Y., Qiu, L., Liu, H., Zhu, C., & Lu, J. (2025). Land Subsidence in the Loess Plateau: SBAS-InSAR Analysis of Yan’an New District During 2017–2022. Sensors, 25(20), 6298. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206298







