Muscle Strength Estimation of Key Muscle–Tendon Units During Human Motion Using ICA-Enhanced sEMG Signals and BP Neural Network Modeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods for Predicting Muscle Strength of Key Muscle–Tendon Units in Human Movement
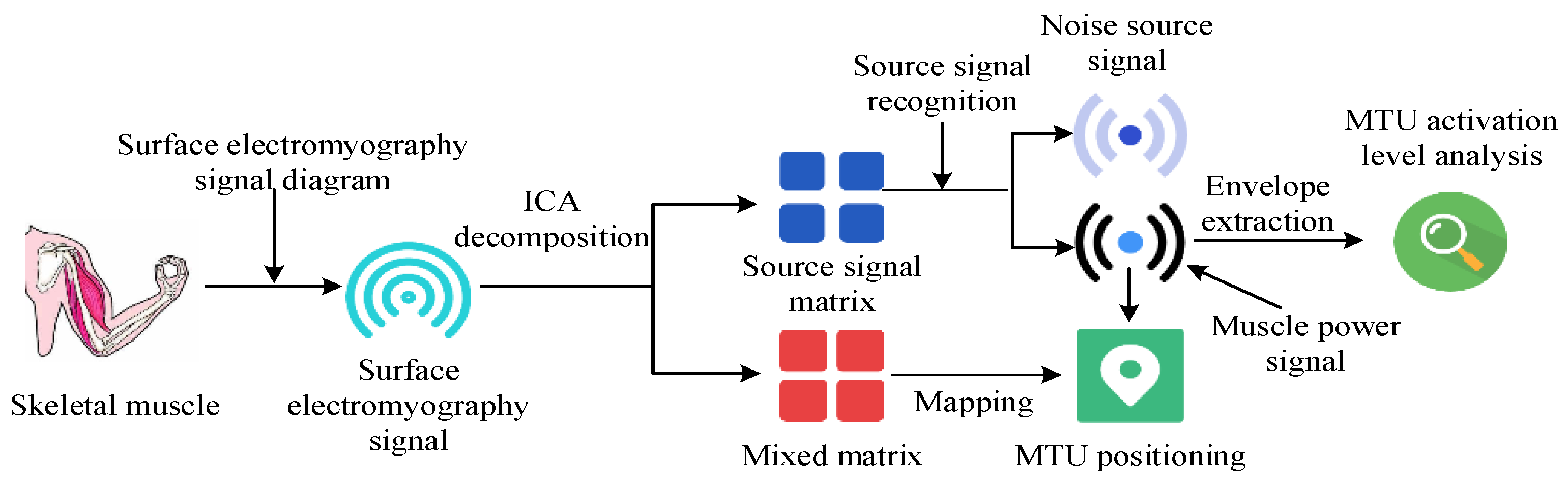
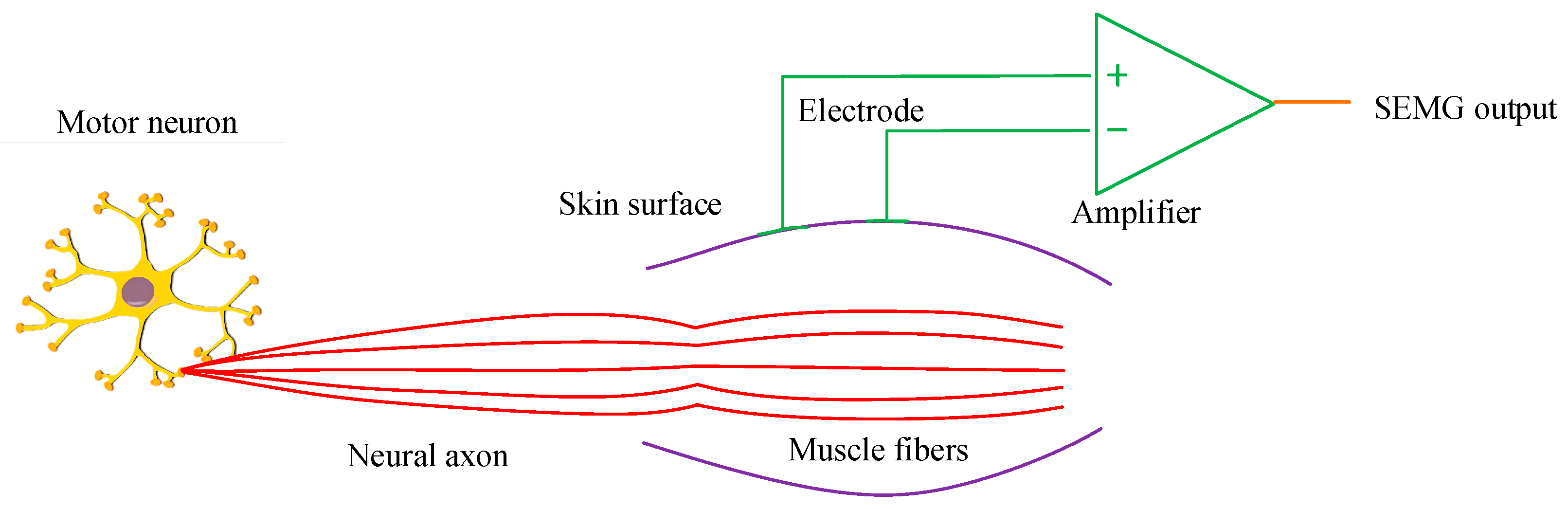
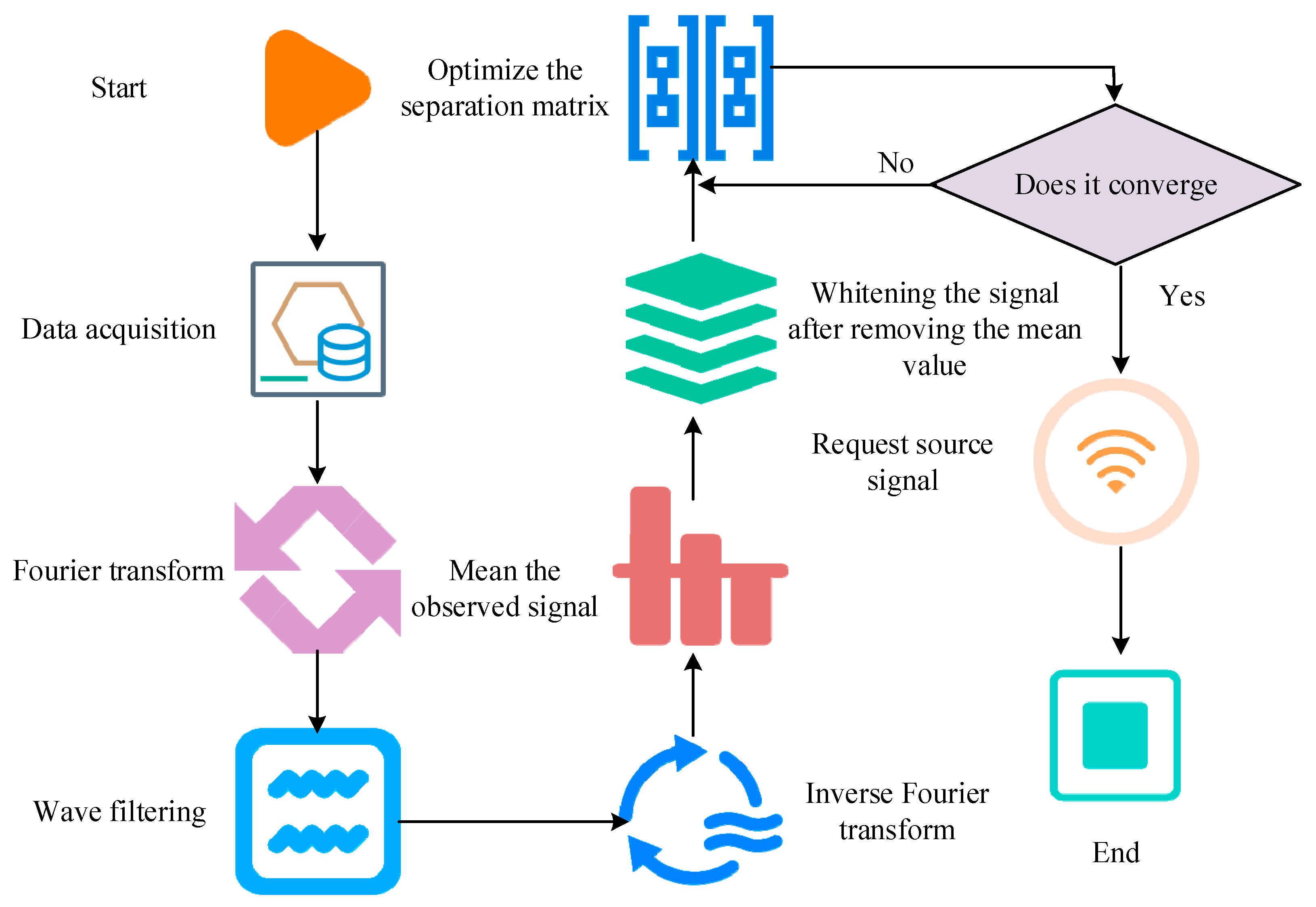
2.1. Key MTU Localization of Human Motion Based on Independent Component Analysis Algorithm
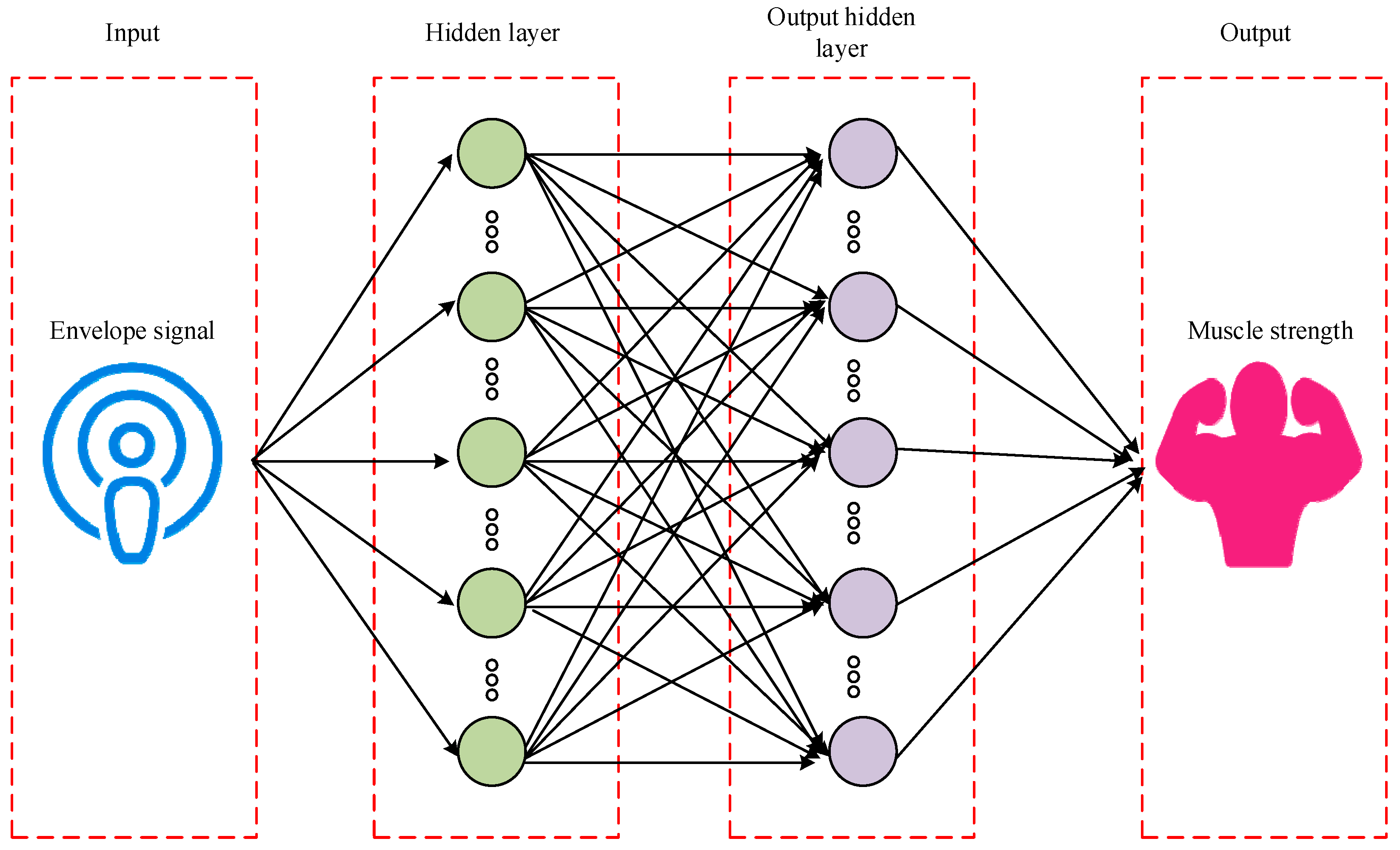
2.2. Muscle Strength Prediction and Evaluation of Key MTUs in Human Motion
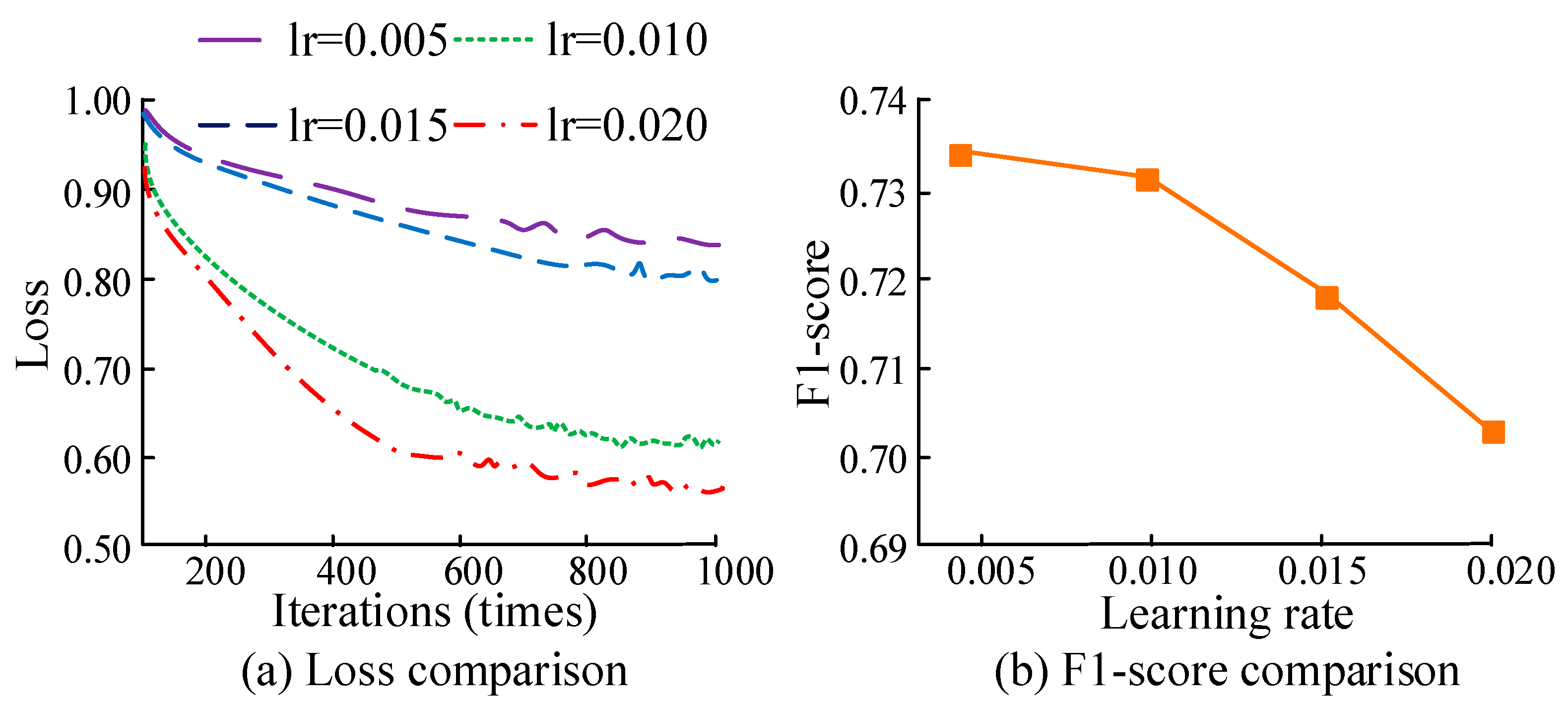
2.3. Experimental Parameter Settings
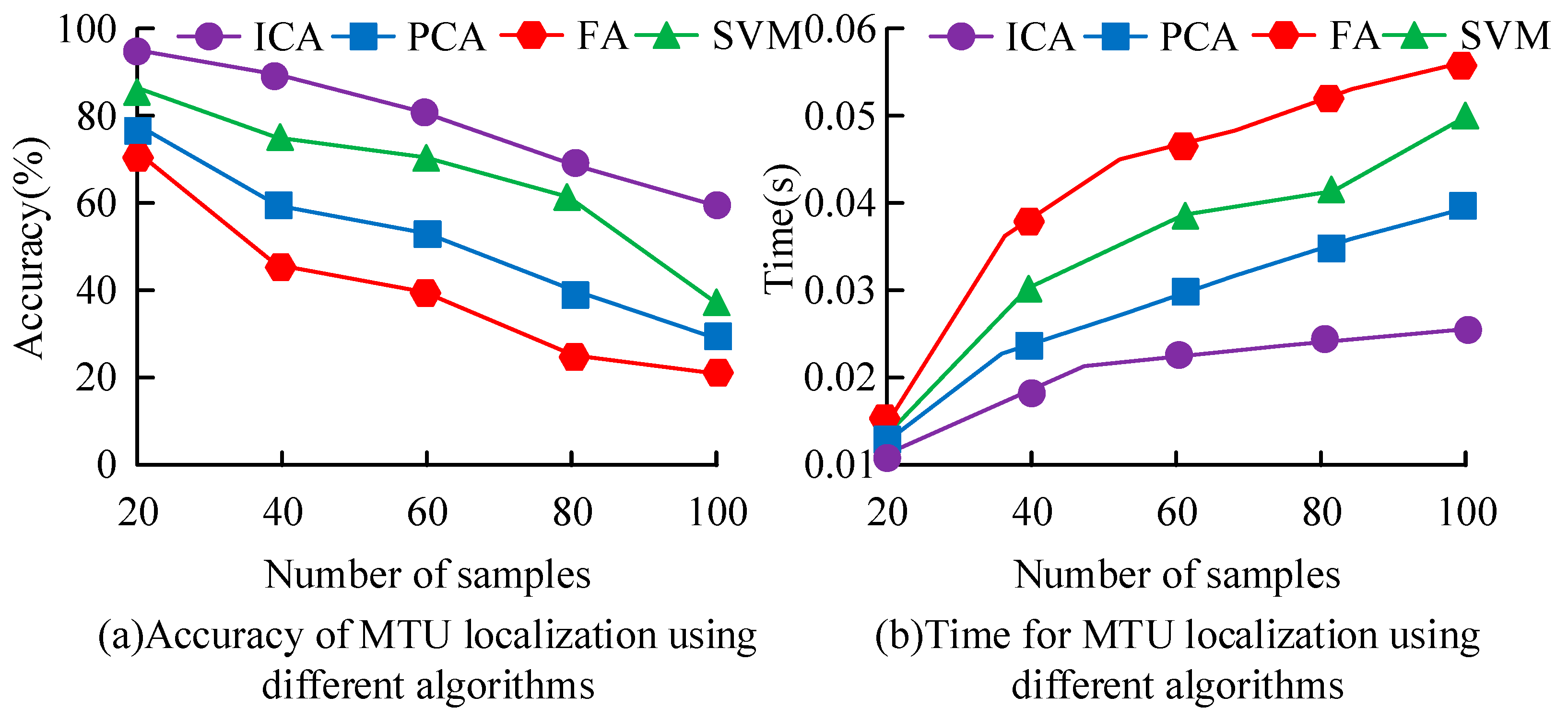
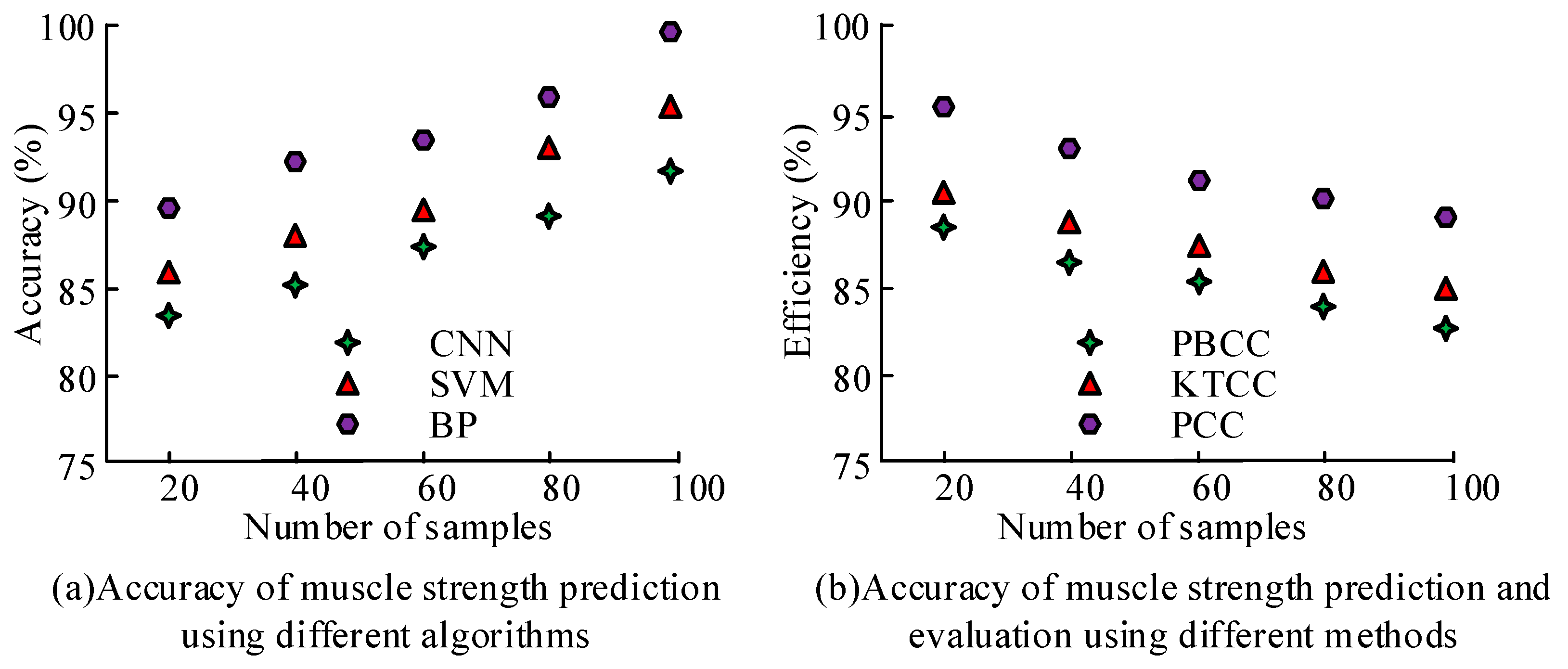
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Key MTU Localization in Human Motion Based on ICA Algorithm
3.2. The Effect of Muscle Strength Prediction and Evaluation of the Key MTUs in Human Motion
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, T.; Li, D.; Fan, B.; Tan, T.; Shull, P.B. Real-time ground reaction force and knee extension moment estimation during drop landings via modular LSTM modeling and wearable IMUs. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2023, 27, 3222–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Subramani, A.V.; Kote, V.; Baggaley, M.; Edwards, W.B.; Reifman, J. Effects of stature and load carriage on the running biomechanics of healthy men. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 70, 2445–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabulut, C.; Bilir, A.; Lacin, M.E.; Dumanli, S. 3D-engineered muscle tissue as a wireless sensor: Antenna live. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2023, 65, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lee, K.-M. Muscle-driven joint-torque estimation based on voltage-torque mapping of electrical impedance sensing. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 13966–13977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yu, Y.; Sheng, X.; Meng, J.; Zhu, X. Real-time hand gesture recognition by decoding motor unit discharges across multiple motor tasks from surface electromyography. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 70, 2058–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Wang, X.; Wu, M.; Gu, K.; Chen, X.; Geng, X. ICA-CNN: Gesture recognition using CNN with improved channel attention mechanism and multimodal signals. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 4052–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, S.; Liu, S.; Guo, G.; Cai, M.; Dai, Z. Leak location for urban elbowed water pipe based on complex-optimized FastICA blind deconvolution. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 4033–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midya, M.; Ganguly, P.; Datta, T.; Chattopadhyay, S. ICA-feature-extraction-based fault identification of vehicular starter motor. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2023, 7, 6001104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Ravelo-García, A.G.; Dias, F.M. A motion and illumination resistant non-contact method using undercomplete independent component analysis and Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 26, 4837–4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Zubair, M. Classification of alcoholic and non-alcoholic EEG signals based on sliding-SSA and independent component analysis. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 26198–26206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Geng, X. The real eigenpairs of symmetric tensors and its application to independent component analysis. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 52, 10137–10150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, C.; Shao, Z.; Liu, B. A non-intrusive identification method of harmonic source loads for industrial users. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2022, 37, 4358–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.F.; Foroughian, F.; Kvelashvili, T.; Liu, Q.; Kilic, O.; Fathy, E.A. Vital sign detection in any orientation using a distributed radar network via modified independent component analysis. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2021, 69, 4774–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaitheeshwari, R.; Yeh, S.-C.; Wu, E.H.-K.; Lin, F.-A. The swallowing intelligent assessment system based on tongue strength and surface EMG. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 17310–17318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, R.; Xiang, Y.; Rakshit, R.; Yang, J. Hybrid predictive model for lifting by integrating skeletal motion prediction with an OpenSim musculoskeletal model. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 69, 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Lee, J.; Xu, P.; Shin, I.; Park, J. Motor interaction control based on muscle force model and depth reinforcement strategy. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Keeffe, R.; Shirazi, S.Y.; Yang, J.; Mehrdad, S.; Rao, S.; Atashzar, S.F. Non-parametric functional muscle network as a robust biomarker of fatigue. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2023, 27, 2105–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Dong, M. Prediction of actively exerted torque from ankle joint complex based on muscle synergy. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 1729–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, B.; Wang, Q.; Lee, J.; Liu, L.; Xu, P.; Park, J. Mechanical modeling of the dynamic response of the knee joint angle in the evaluation of muscle nerve response and energy consumption. J. Biomech. 2025, 182, 112565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paggetti, F.; Gherardini, M.; Lucantonio, A.; Cipriani, C. To what extent implanting single vs pairs of magnets per muscle affect the localization accuracy of the myokinetic control interface? Evidence from a simulated environment. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 70, 2972–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q. A wearable co-located neural-mechanical signal sensing device for simultaneous bimodal muscular activity detection. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 70, 3401–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.-H.; Chang, T.-M.; Shen, C.-A.; Fouda, M.E.; Eltawil, A.M. High-throughput independent component analysis processor for full duplex systems. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2023, 41, 2821–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, J.; Sun, L.; Li, J.; Zhao, X. Research on sparse decomposition processing of ultrasonic signals of heat exchanger fouling. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 15795–15802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.; Park, S.; Kim, K. sEMG-based gesture recognition using temporal history. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 70, 2655–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Li, Q.; Li, Z.; Li, J. Multimodal fusion convolutional neural network based on sEMG and accelerometer signals for intersubject upper limb movement classification. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 12334–12345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Mou, J.; Banerjee, S.; Zhang, Y. Color-gray multi-image hybrid compression–encryption scheme based on BP neural network and knight tour. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2023, 53, 5037–5047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, B.; Cui, X.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, Y. Multi-source underwater DOA estimation using PSO-BP neural network based on high-order cumulant optimization. China Commun. 2023, 20, 212–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, N.; Yu, H.; You, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhou, T.; Han, N.; Liu, C.; Jiang, Z.; Qiao, S. Fuzzy logic and neural network-based risk assessment model for import and export enterprises: A review. J. Data Sci. Intell. Syst. 2023, 1, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Lu, X. Application of a stochastic gradient descent-based SVR online modeling method to time-varying forging processes. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 15444–15453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lin, K.-Y.; Li, L.; Hong, Y.; Chen, J. On faster convergence of scaled sign gradient descent. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 1732–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, M.; Hébert, L.J.; Perron, M.; Petitclerc, É.; Lake, S.-R.; Duchesne, E. Psychometric properties of a standardized protocol of muscle strength assessment by hand-held dynamometry in healthy adults: A reliability study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2023, 24, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.; Kwon, N.; Lee, D.; Kim, J.; Yang, S.; Youn, I.; Moon, H.-J.; Sung, J.-K.; Han, S. A Multimodal Fatigue Detection System Using sEMG and IMU Signals with a Hybrid CNN-LSTM-Attention Model. Sensors 2025, 25, 3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| MTU Localization | Muscle Strength Prediction | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
| Sampling rate | 1000 Hz | Hidden layers | 2 |
| Filter settings | 20–450 Hz | Number of neurons per layer | 5 |
| Window size | 0.5 s | Training set size | 80% |
| Step size | 0.2 s | Test set size | 20% |
| Number of components | 5 | Target error | 0.001 |
| Number of iterations | 1000 | Momentum | 0.9 |
| Convergence threshold | 0.0001 | Max epochs | 1000 |
| Number of Samples | Positioning Error Under N Posture | Positioning Error Under S Posture | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICA | PCA | FA | SVM | ICA | PCA | FA | SVM | |
| 20 | 1.24% | 2.98% | 1.99% | 1.64% | 2.33% | 3.45% | 2.89% | 2.59% |
| 40 | 1.46% | 3.12% | 2.18% | 1.87% | 2.56% | 3.67% | 3.01% | 2.73% |
| 60 | 1.78% | 3.44% | 2.45% | 2.03% | 2.79% | 3.89% | 3.22% | 2.95% |
| 80 | 2.63% | 2.76% | 3.06% | 2.58% | 3.06% | 4.05% | 3.50% | 3.31% |
| 100 | 2.55% | 3.58% | 3.87% | 3.12% | 3.42% | 4.24% | 3.67% | 3.56% |
| Pooling Strategy | Recall (%) | F1-Score | Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BP | 0.88 | 0.90 | 2.34 |
| SVM | 0.80 | 0.85 | 2.79 |
| RF | 0.75 | 0.80 | 3.98 |
| XGBoost | 0.85 | 0.92 | 2.45 |
| LSTM | 0.82 | 0.88 | 2.56 |
| CNN | 0.79 | 0.83 | 3.37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Park, J.; Lee, J.; Wang, D. Muscle Strength Estimation of Key Muscle–Tendon Units During Human Motion Using ICA-Enhanced sEMG Signals and BP Neural Network Modeling. Sensors 2025, 25, 6273. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206273
Liu H, Park J, Lee J, Wang D. Muscle Strength Estimation of Key Muscle–Tendon Units During Human Motion Using ICA-Enhanced sEMG Signals and BP Neural Network Modeling. Sensors. 2025; 25(20):6273. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206273
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hongyan, Jongchul Park, Junghee Lee, and Dandan Wang. 2025. "Muscle Strength Estimation of Key Muscle–Tendon Units During Human Motion Using ICA-Enhanced sEMG Signals and BP Neural Network Modeling" Sensors 25, no. 20: 6273. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206273
APA StyleLiu, H., Park, J., Lee, J., & Wang, D. (2025). Muscle Strength Estimation of Key Muscle–Tendon Units During Human Motion Using ICA-Enhanced sEMG Signals and BP Neural Network Modeling. Sensors, 25(20), 6273. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206273







