A Magnetoelectric Distance Estimation System for Relative Human Motion Tracking
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
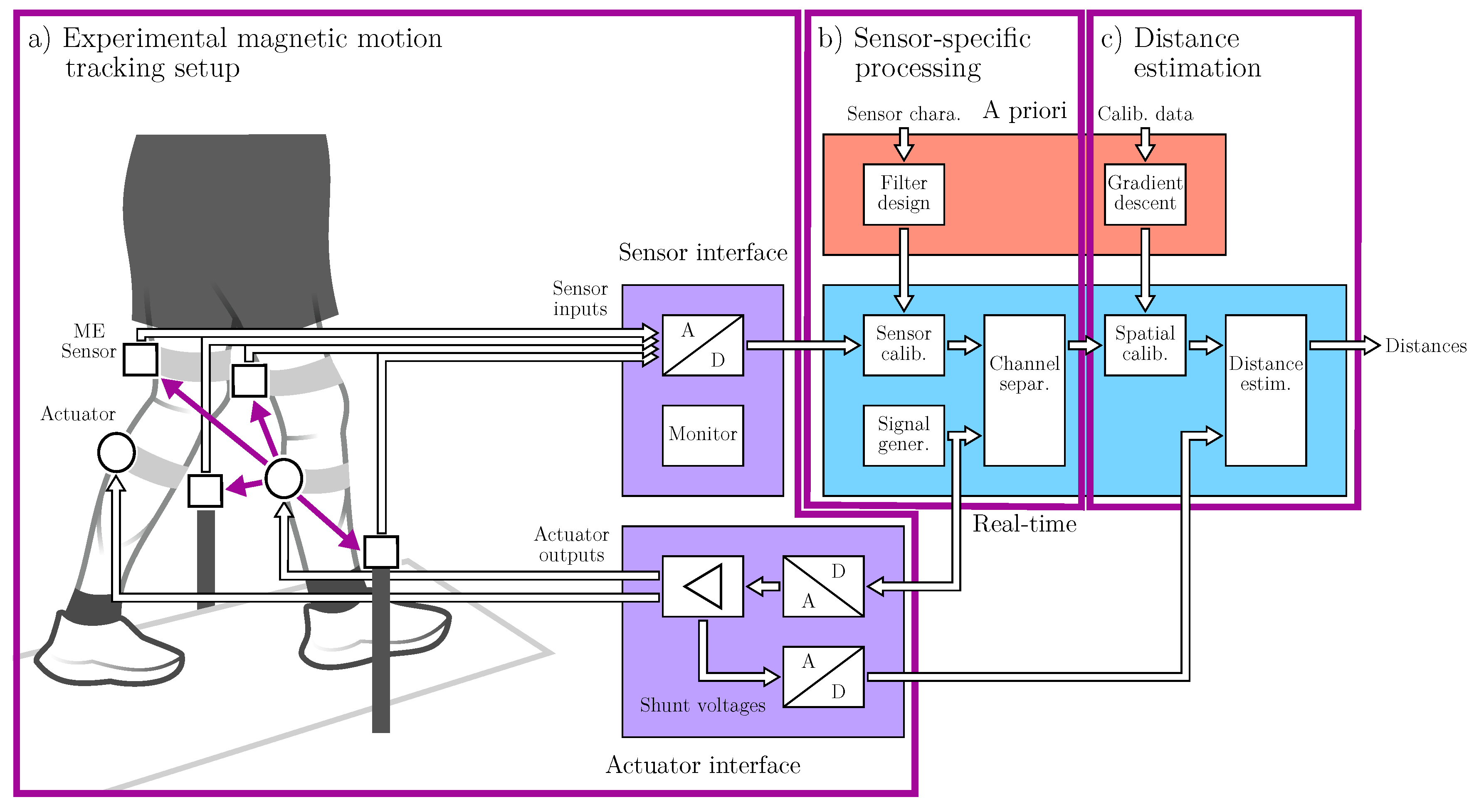
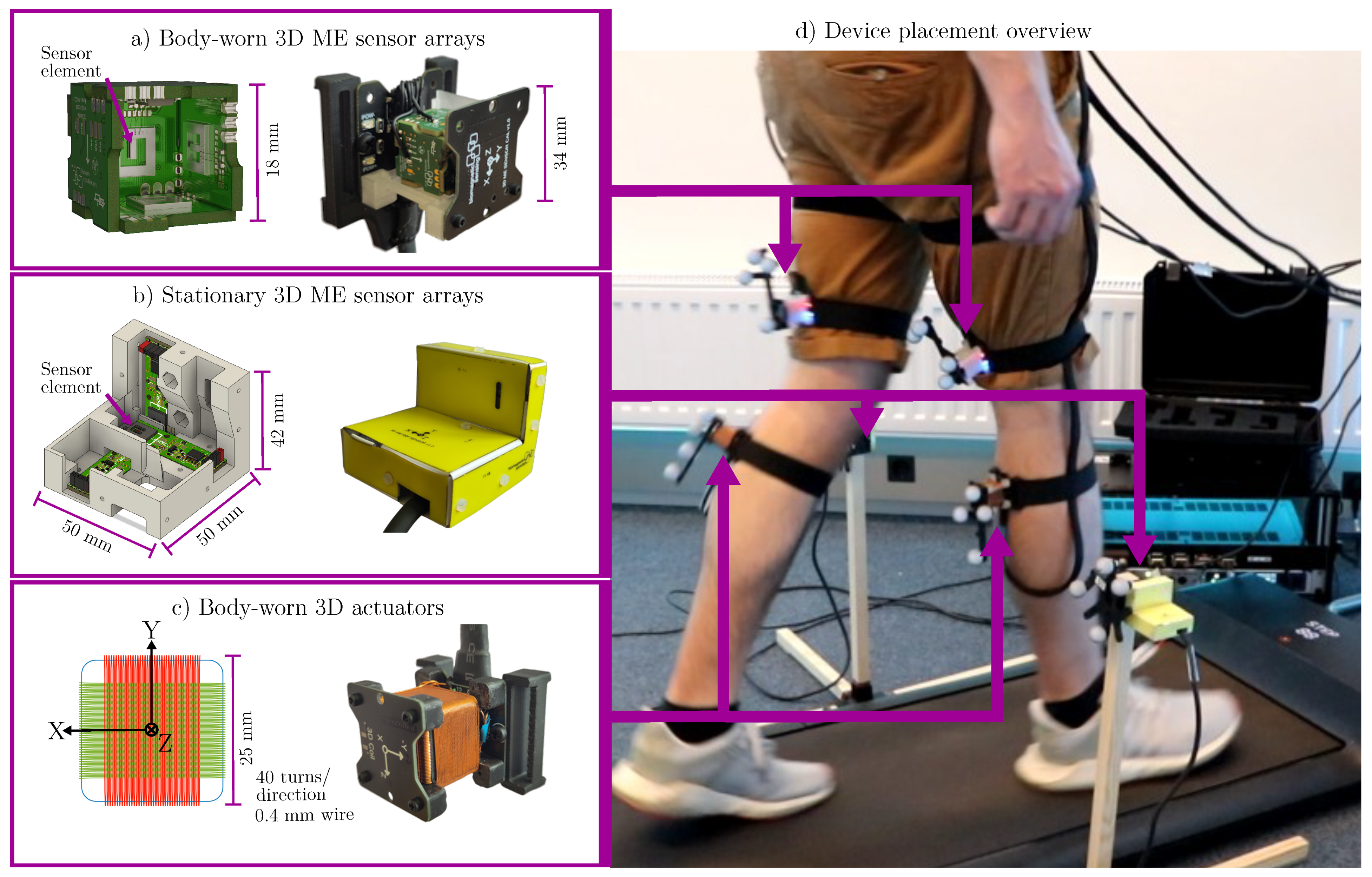
2.1. Experimental Motion Tracking Setup
2.1.1. Overview
2.1.2. Cube Sensor Arrays
2.1.3. L-Shaped Sensor Arrays
2.1.4. Actuators
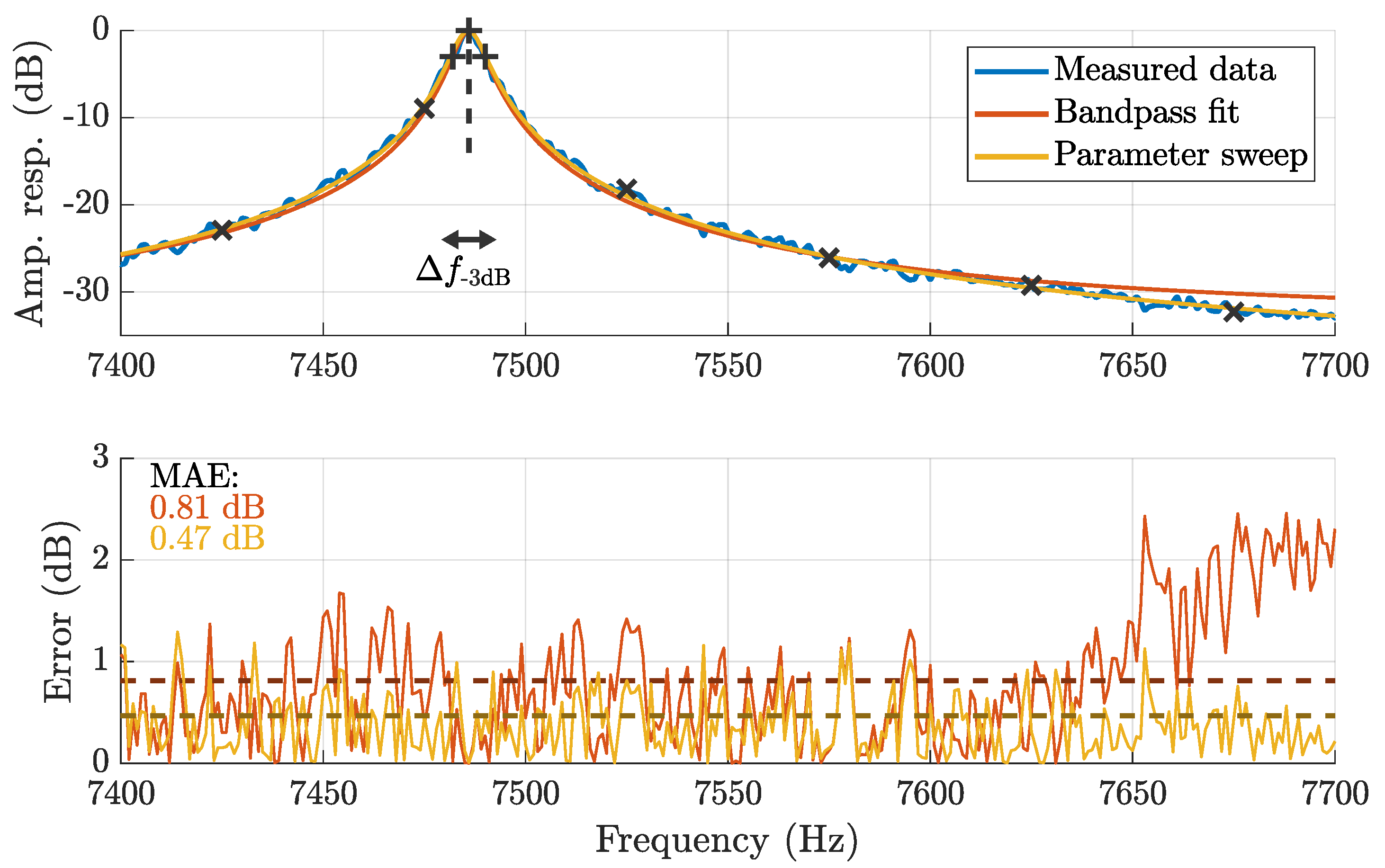
2.2. Sensor-Specific Signal Processing and Enhancement
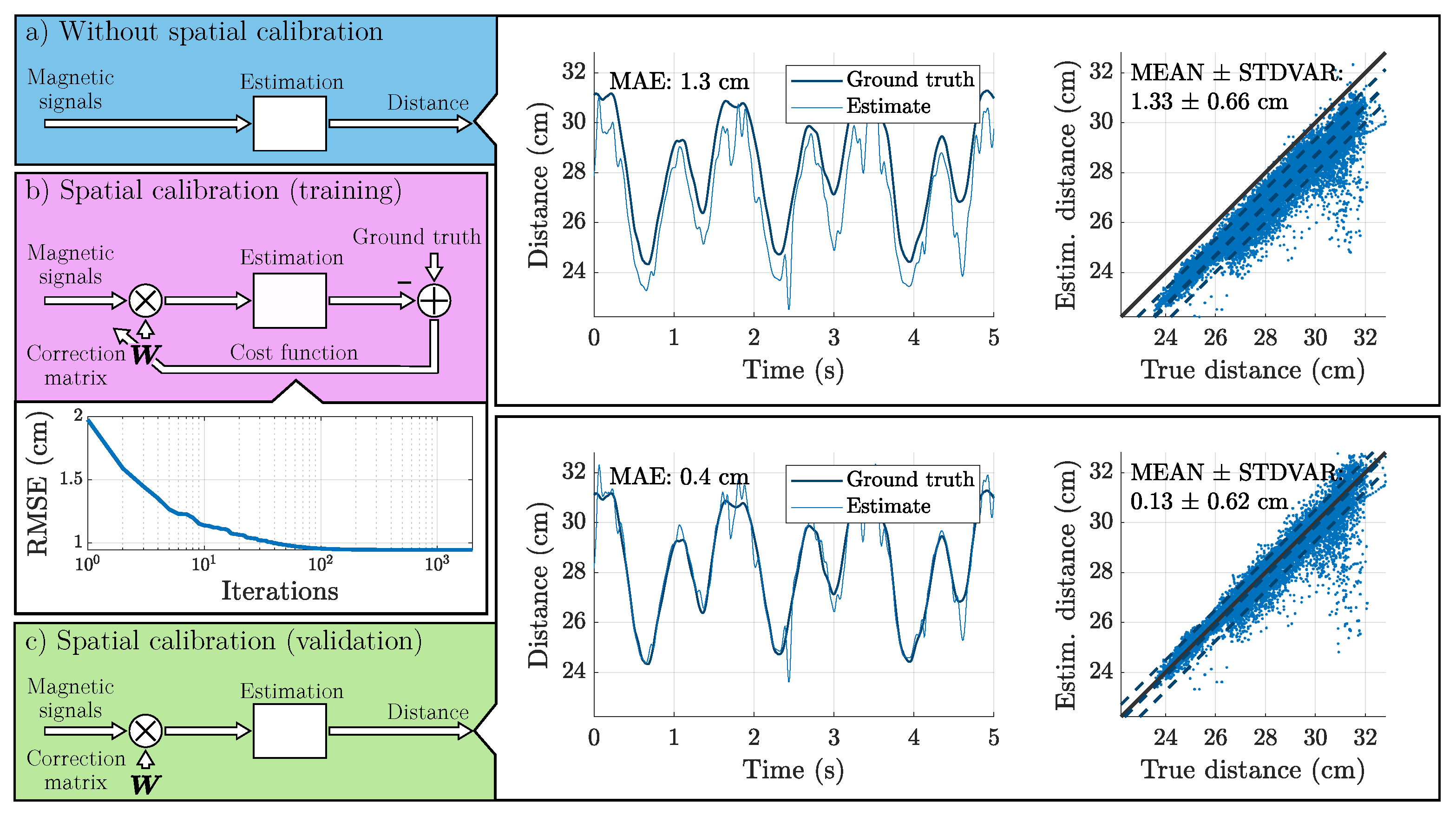
2.3. Distance Estimation and Spatial Calibration
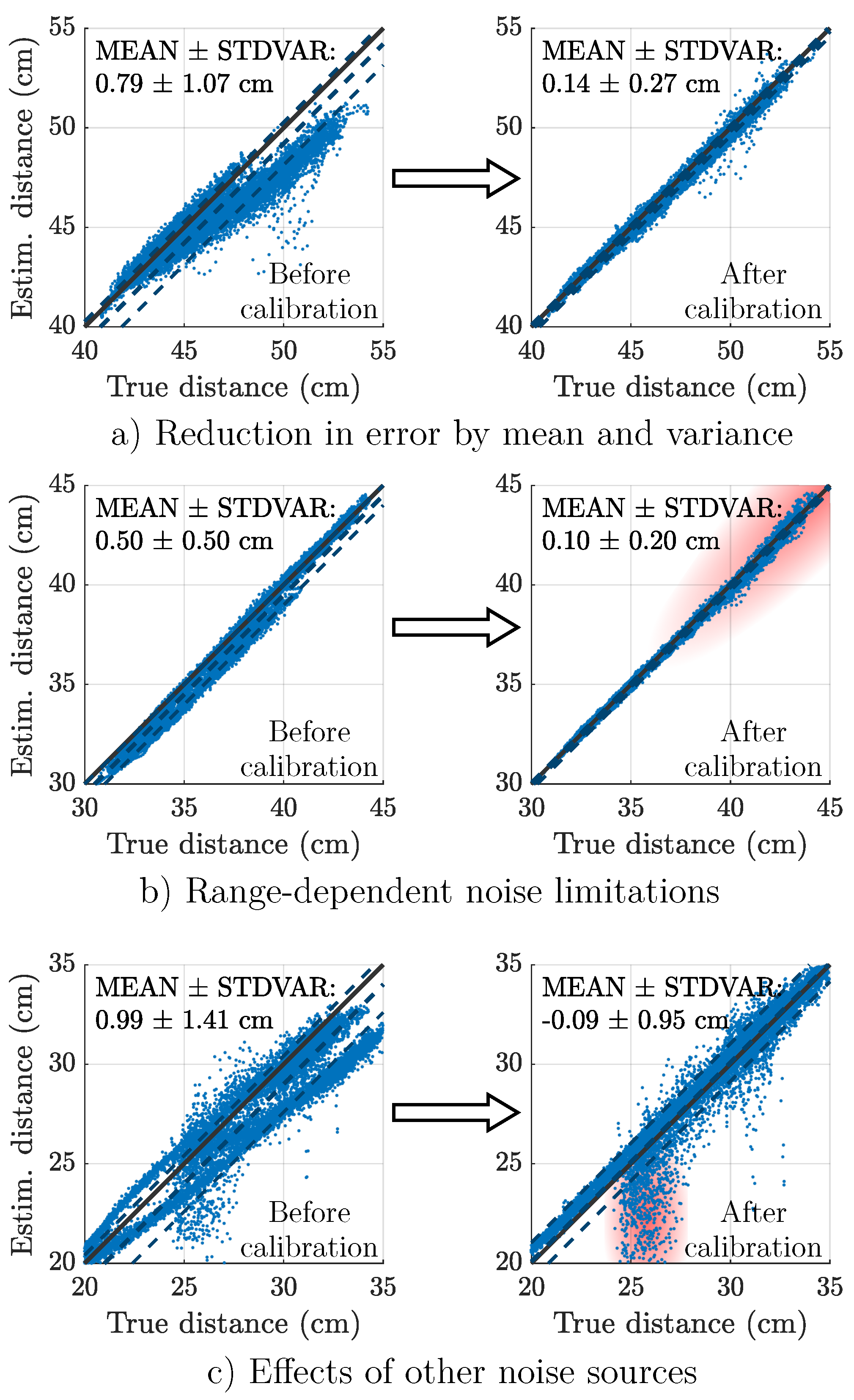
3. Results
3.1. Acquisition of Datasets
- Scenario A
- Scenario B
3.2. Qualitative Description of Exemplary Signals
3.3. Overview on System Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ME | Magnetoelectric |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| OMC | Optical motion capture |
| IMU | Inertial measurement unit |
| LiDAR | Light detection and ranging |
| UWB | Ultra-wideband |
| NLOS | Non-line of sight |
| MEMS | Micro-electromechanical system |
| BIDS | Brain imaging data structure |
| OFDMA | Orthogonal frequency-division multiple access |
| PCB | Printed circuit board |
| LTI | Linear time-invariant |
| IIR | Infinite impulse response |
| MAE | Mean absolute error |
| (R)MSE | (Root) mean squared error |
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio |
Appendix A
| Sensor Element [Internal ID] | Center frequency (Hz) | Bandwidth (Hz) | Gain (dB) | Sensitivity (kV/T) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S0 - X [D4] | 7485.8 | 8.8 | −40 | 131.9 |
| S0 - Y [C1] | 7514.3 | 9.2 | −39 | 87.1 |
| S0 - Z [B7] | 7564.0 | 19 | −41 | 108.1 |
| S1 - X [G2] | 7669.1 | 9.2 | −44 | 192.8 |
| S1 - Y [C5] | 7666.0 | 10.4 | −44 | 161.1 |
| S1 - Z [G5] | 7685.4 | 9.9 | −45 | 98.6 |
| S2 - X [C1] | 7677.6 | 8.2 | −53 | 38.7 |
| S2 - Y [B1] | 7681.1 | 10.1 | −51 | 52.3 |
| S2 - Z [A4] | 7712.2 | 10.9 | −51 | 15.7 |
| S3 - X [C2] | 7687.0 | 13.6 | −48 | 20.7 |
| S3 - Y [B1] | 7708.3 | 8.5 | −53 | 28.1 |
| S3 - Z [B2] | 7712.9 | 16.5 | −48 | 20.5 |
References
- Ebersbach, G.; Moreau, C.; Gandor, F.; Defebvre, L.; Devos, D. Clinical syndromes: Parkinsonian gait. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 1552–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creaby, M.W.; Cole, M.H. Gait characteristics and falls in Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Park. Relat. Disord. 2018, 57, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicirelli, G.; Impedovo, D.; Dentamaro, V.; Marani, R.; Pirlo, G.; D’Orazio, T.R. Human Gait Analysis in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Review. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 26, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maetzler, W.; Rochester, L.; Bhidayasiri, R.; Espay, A.J.; Sánchez-Ferro, A.; van Uem, J.M.T. Modernizing Daily Function Assessment in Parkinson’s Disease Using Capacity, Perception, and Performance Measures. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2021, 36, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brognara, L.; Palumbo, P.; Grimm, B.; Palmerini, L. Assessing Gait in Parkinson’s Disease Using Wearable Motion Sensors: A Systematic Review. Diseases 2019, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.L.; Dinesh, K.; Snyder, C.W.; Xiong, M.; Tarolli, C.G.; Sharma, S.; Dorsey, E.R.; Sharma, G. A real-world study of wearable sensors in Parkinson’s disease. Npj Park. Dis. 2021, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez, L.E.; Bahillo, A.; Otegui, J.; Otim, T. Step Length Estimation Methods Based on Inertial Sensors: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 6908–6926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluge, F.; Gaßner, H.; Hannink, J.; Pasluosta, C.; Klucken, J.; Eskofier, B.M. Towards Mobile Gait Analysis: Concurrent Validity and Test-Retest Reliability of an Inertial Measurement System for the Assessment of Spatio-Temporal Gait Parameters. Sensors 2017, 17, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riek, P.M.; Best, A.N.; Wu, A.R. Validation of Inertial Sensors to Evaluate Gait Stability. Sensors 2023, 23, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, H.T.; Suh, Y.S. A Human Gait Tracking System Using Dual Foot-Mounted IMU and Multiple 2D LiDARs. Sensors 2022, 22, 6368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alanazi, M.A.; Alhazmi, A.K.; Alsattam, O.; Gnau, K.; Brown, M.; Thiel, S.; Jackson, K.; Chodavarapu, V.P. Towards a Low-Cost Solution for Gait Analysis Using Millimeter Wave Sensor and Machine Learning. Sensors 2022, 22, 5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; He, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Duan, S. Towards Human Motion Tracking: Multi-Sensory IMU/TOA Fusion Method and Fundamental Limits. Electronics 2019, 8, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatini, A.M. Kalman-Filter-Based Orientation Determination Using Inertial/Magnetic Sensors: Observability Analysis and Performance Evaluation. Sensors 2011, 11, 9182–9206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Meng, M.Q.; Mandal, M. Efficient magnetic localization and orientation technique for capsule endoscopy. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2–6 August 2005; pp. 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roetenberg, D.; Slycke, P.; Veltink, P. Ambulatory Position and Orientation Tracking Fusing Magnetic and Inertial Sensing. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 54, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Liang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Ji, X. A robust indoor positioning system based on encoded magnetic field and low-cost IMU. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Savannah, GA, USA, 11–14 April 2016; pp. 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polhemus Liberty. Available online: https://polhemus.com/motion-tracking/all-trackers/liberty (accessed on 21 August 2024).
- Yang, W.; Hu, C.; Meng, M.Q.H.; Song, S.; Dai, H. A Six-Dimensional Magnetic Localization Algorithm for a Rectangular Magnet Objective Based on a Particle Swarm Optimizer. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 3092–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Song, S.; Wang, X.; Meng, M.Q.H.; Li, B. A Novel Positioning and Orientation System Based on Three-Axis Magnetic Coils. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 2211–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paperno, E.; Keisar, P. Three-Dimensional Magnetic Tracking of Biaxial Sensors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2004, 40, 1530–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasku, V.; De Angelis, A.; De Angelis, G.; Arumugam, D.D.; Dionigi, M.; Carbone, P.; Moschitta, A.; Ricketts, D.S. Magnetic Field-Based Positioning Systems. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 2003–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachmann, G. Distortion correction of magnetic fields for position tracking. In Proceedings of the Computer Graphics International, Hasselt and Diepenbeek, Belgium, 23–27 June 1997; pp. 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.; Roldan-Vasco, S.; Krüger, K.; Niekiel, F.; Hansen, C.; Maetzler, W.; Orozco-Arroyave, J.R.; Schmidt, G. Pilot Study: Magnetic Motion Analysis for Swallowing Detection Using MEMS Cantilever Actuators. Sensors 2023, 23, 3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lage, E.; Woltering, F.; Quandt, E.; Meyners, D. Exchange biased magnetoelectric composites for vector field magnetometers. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 17C725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahns, R.; Knochel, R.; Greve, H.; Woltermann, E.; Lage, E.; Quandt, E. Magnetoelectric sensors for biomagnetic measurements. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications, Bari, Italy, 30–31 May 2011; pp. 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spetzler, E.; Spetzler, B.; McCord, J. A Magnetoelastic Twist on Magnetic Noise: The Connection with Intrinsic Nonlinearities. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2309867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilgaz, F.; Spetzler, E.; Wiegand, P.; Faupel, F.; Rieger, R.; McCord, J.; Spetzler, B. Miniaturized double-wing ΔE-effect magnetic field sensors. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spetzler, B.; Wiegand, P.; Durdaut, P.; Höft, M.; Bahr, A.; Rieger, R.; Faupel, F. Modeling and Parallel Operation of Exchange-Biased Delta-E Effect Magnetometers for Sensor Arrays. Sensors 2021, 21, 7594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzenheimer, E.; Hayes, P.; Thormählen, L.; Engelhardt, E.; Zaman, A.; Quandt, E.; Frey, N.; Höft, M.; Schmidt, G. Investigation of Converse Magnetoelectric Thin-Film Sensors for Magnetocardiography. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 5660–5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özden, M.; Barbieri, G.; Gerken, M. A Combined Magnetoelectric Sensor Array and MRI-Based Human Head Model for Biomagnetic FEM Simulation and Sensor Crosstalk Analysis. Sensors 2024, 24, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lage, E.; Kirchhof, C.; Hrkac, V.; Kienle, L.; Jahns, R.; Knöchel, R.; Quandt, E.; Meyners, D. Exchange biasing of magnetoelectric composites. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabel, S.; Kirchhof, C.; Yarar, E.; Meyners, D.; Quandt, E.; Faupel, F. Phase modulated magnetoelectric delta-E effect sensor for sub-nano tesla magnetic fields. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 152402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnetfeldsensor FL1-100 Stefan Mayer Instruments. Available online: https://stefan-mayer.com/de/produkte/magnetometer-und-sensoren/magnetfeldsensor-fl1-100.html (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- Type DJ Product Information MI Sensors Aichi Steel Corporation. Available online: https://www.aichi-steel.co.jp/ENGLISH/smart/mi/products/type-dj.html (accessed on 22 August 2024).
- Hoffmann, J.; Elzenheimer, E.; Bald, C.; Hansen, C.; Maetzler, W.; Schmidt, G. Active Magnetoelectric Motion Sensing: Examining Performance Metrics with an Experimental Setup. Sensors 2021, 21, 8000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.; Boueke, M.; Engelhardt, E.; Schmidt, T.; Hansen, C.; Welzel, J.; Maetzler, W.; Schmidt, G. Proof of Principle: Full 6D Point-to-Point Motion Tracking with Magnetoelectric Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Sensors, Kobe, Japan, 20–23 October 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reermann, J.; Schmidt, G.; Teliban, I.; Salzer, S.; Höft, M.; Knöchel, R.; Piorra, A.; Quandt, E. Adaptive Acoustic Noise Cancellation for Magnetoelectric Sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 5804–5812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiel Real-Time Application Tookit. Available online: https://dss-kiel.de/index.php/research/realtime-framework (accessed on 3 September 2024).
- Orfanidis, S.J. Introduction to Signal Processing; Prentice-Hall, Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Wolframm, H.; Hoffmann, J.; Burgardt, R.; Elzenheimer, E.; Schmidt, G.; Höft, M. PCB Coil Enables In Situ Calibration of Magnetoelectric Sensor Systems. Curr. Dir. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 9, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zölzer, U. Digital Audio Signal Processing; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Horn, R.A.; Johnson, C.R. Matrix Analysis, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Spetzler, B.; Bald, C.; Durdaut, P.; Reermann, J.; Kirchhof, C.; Teplyuk, A.; Meyners, D.; Quandt, E.; Höft, M.; Schmidt, G.; et al. Exchange biased delta-E effect enables the detection of low frequency pT magnetic fields with simultaneous localization. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocedal, J.; Wright, S.J. Numerical Optimization, 2nd ed.; Springer Series in Operations Research; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Sui, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yan, Y.; Gu, Y. Line Search Methods—Cornell University Computational Optimization Open Textbook—Optimization Wiki. 2021. Available online: https://optimization.cbe.cornell.edu/index.php?title=Line_search_methods (accessed on 22 August 2024).
- Wang, H.; Ullah, Z.; Gazit, E.; Brozgol, M.; Tan, T.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Shull, P.B.; Ponger, P. Step Width Estimation in Individuals With and Without Neurodegenerative Disease Via a Novel Data-Augmentation Deep Learning Model and Minimal Wearable Inertial Sensors. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2024, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.; Welzel, J.; Hansen, C.; Maetzler, W.; Schmidt, G. Magnetic Distance Estimation Data from Gait Experiments with Magnetoelectric Sensors. 2024. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/13771428 (accessed on 17 September 2024).
- Jeung, S.; Cockx, H.; Appelhoff, S.; Berg, T.; Gramann, K.; Grothkopp, S.; Warmerdam, E.; Hansen, C.; Oostenveld, R.; Welzel, J. Motion-BIDS: An extension to the brain imaging data structure to organize motion data for reproducible research. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgolewski, K.J.; Auer, T.; Calhoun, V.D.; Craddock, R.C.; Das, S.; Duff, E.P.; Flandin, G.; Ghosh, S.S.; Glatard, T.; Halchenko, Y.O.; et al. The brain imaging data structure, a format for organizing and describing outputs of neuroimaging experiments. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Validation Datasets | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario A | Scenario B | ||||
| Mean MAE | Max. MAE | Mean MAE | Max. MAE | ||
| Training datasets | Without training | 1.4 cm | 2.4 cm | 1.0 cm | 1.8 cm |
| Scenario A | 1.2 cm | 1.9 cm | 1.0 cm | 2.9 cm | |
| Scenario B | 1.5 cm | 2.5 cm | 0.4 cm | 1.2 cm | |
| Scenarios A and B | 1.1 cm | 1.4 cm | 0.4 cm | 1.0 cm | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoffmann, J.; Wolframm, H.; Engelhardt, E.; Boueke, M.; Schmidt, T.; Welzel, J.; Höft, M.; Maetzler, W.; Schmidt, G. A Magnetoelectric Distance Estimation System for Relative Human Motion Tracking. Sensors 2025, 25, 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25020495
Hoffmann J, Wolframm H, Engelhardt E, Boueke M, Schmidt T, Welzel J, Höft M, Maetzler W, Schmidt G. A Magnetoelectric Distance Estimation System for Relative Human Motion Tracking. Sensors. 2025; 25(2):495. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25020495
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoffmann, Johannes, Henrik Wolframm, Erik Engelhardt, Moritz Boueke, Tobias Schmidt, Julius Welzel, Michael Höft, Walter Maetzler, and Gerhard Schmidt. 2025. "A Magnetoelectric Distance Estimation System for Relative Human Motion Tracking" Sensors 25, no. 2: 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25020495
APA StyleHoffmann, J., Wolframm, H., Engelhardt, E., Boueke, M., Schmidt, T., Welzel, J., Höft, M., Maetzler, W., & Schmidt, G. (2025). A Magnetoelectric Distance Estimation System for Relative Human Motion Tracking. Sensors, 25(2), 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25020495










