Integration of Physical Features and Machine Learning: CSF-RF Framework for Optimizing Ground Point Filtering in Vegetated Regions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology and Experimental Data
2.1. Experimental Data
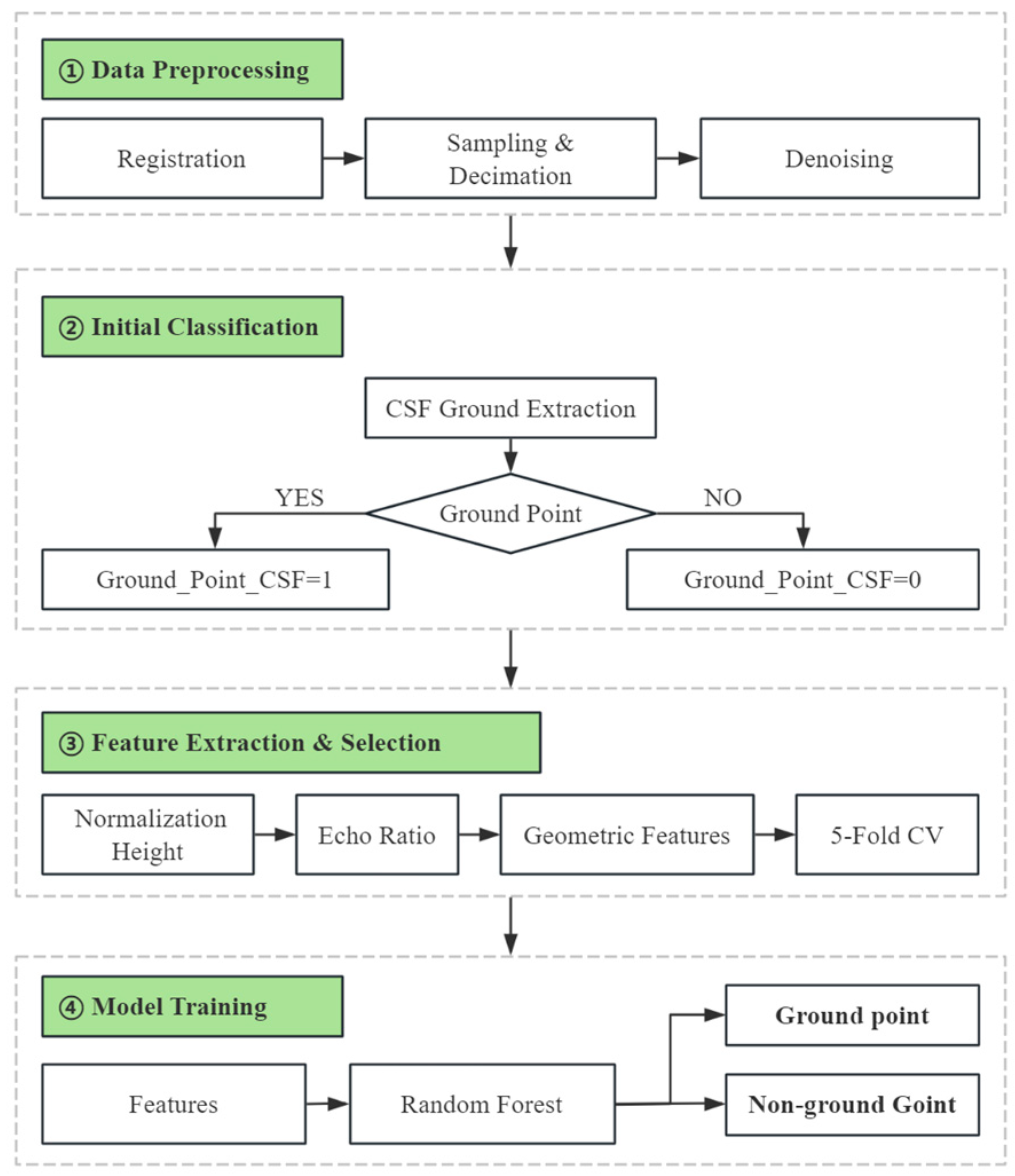
2.2. CSF-RF Framework
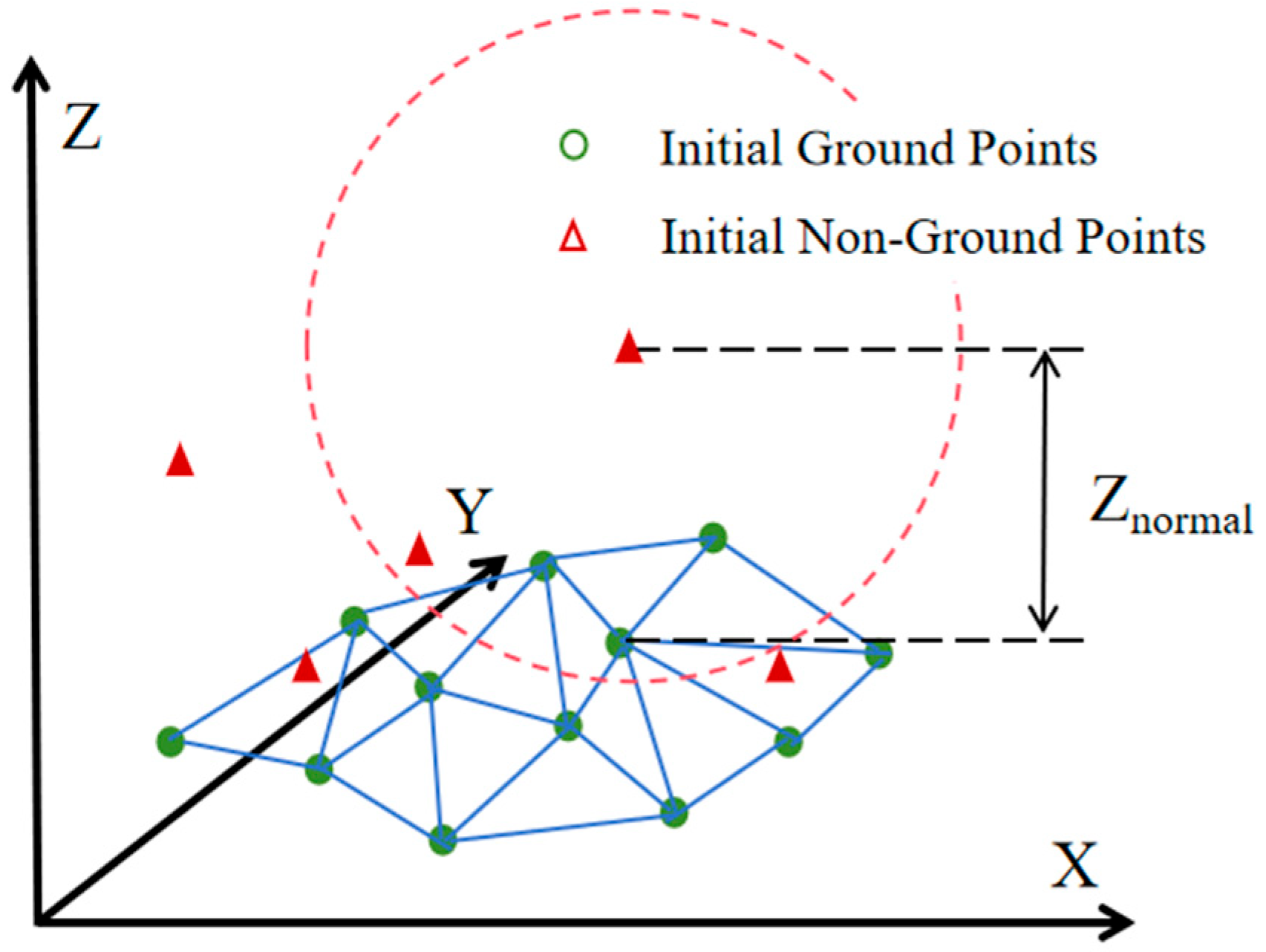
2.2.1. Point Cloud Data Preprocessing
2.2.2. Initial Classification of Point Cloud
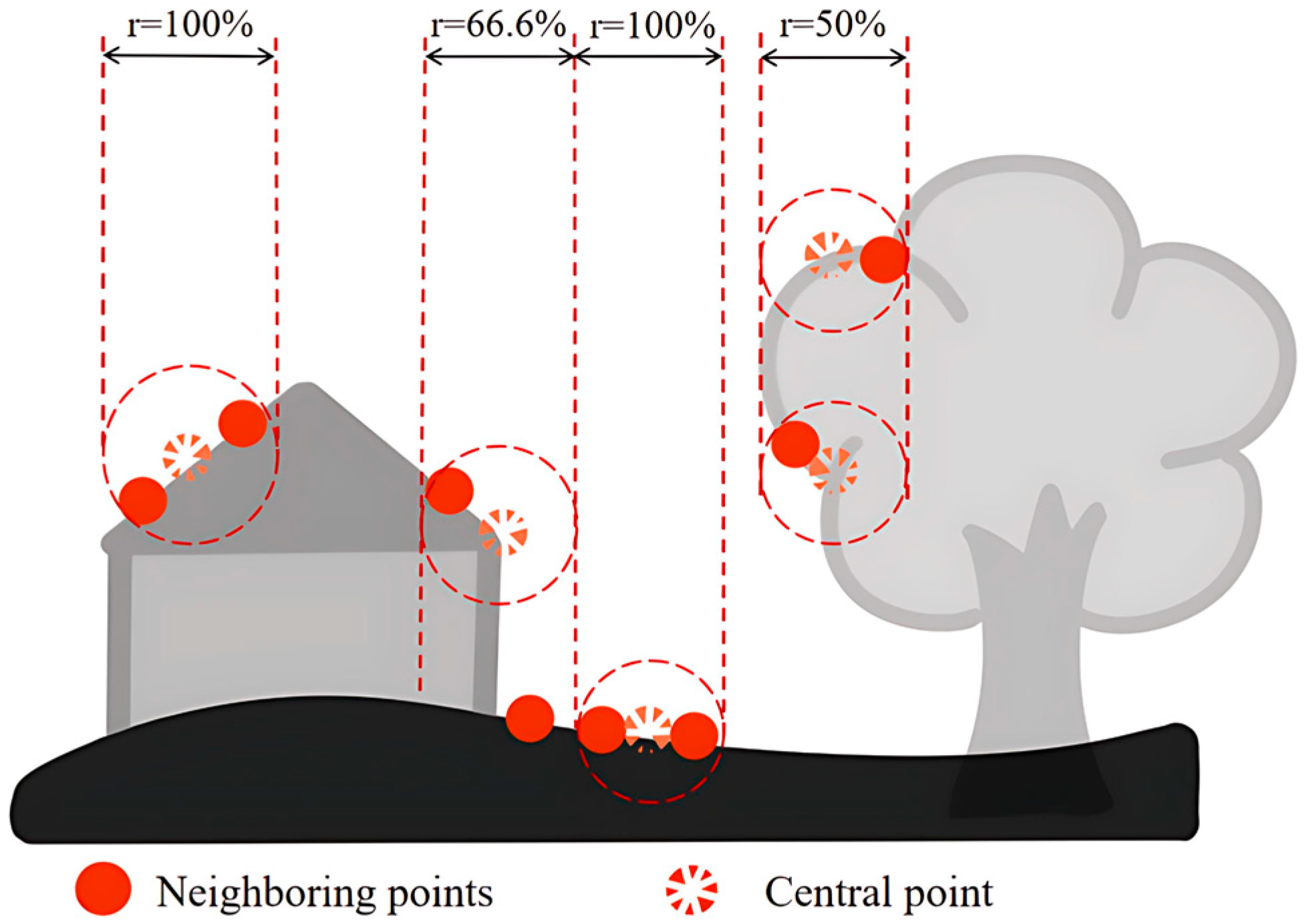
2.2.3. Feature Calculation
- (1)
- Normalized Height Calculation
- (2)
- Echo Ratio Calculation
2.2.4. Feature Selection
2.2.5. Model Validation and Analysis
3. Results and Analysis
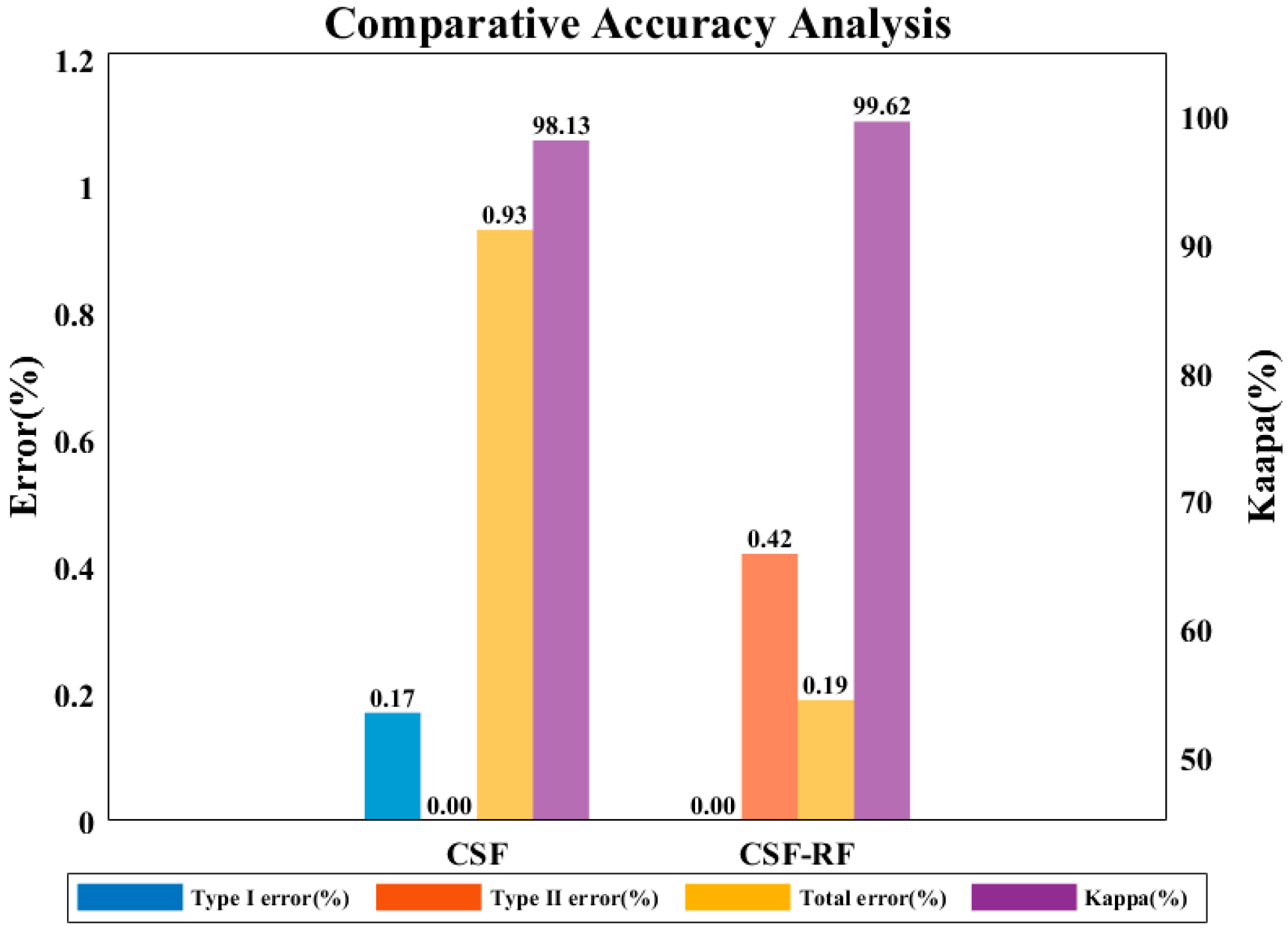
3.1. Effectiveness Analysis
- (1)
- Analysis of Feature Selection Effectiveness
- (2)
- Effectiveness Analysis of Normalized Height Index
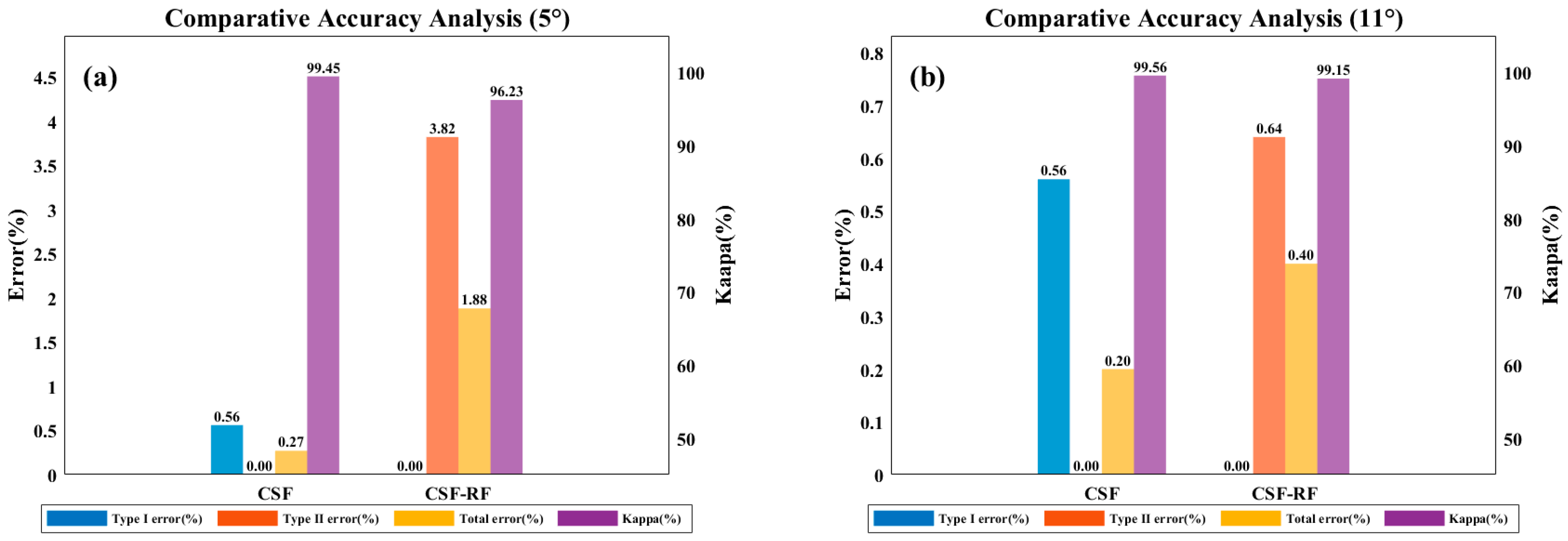
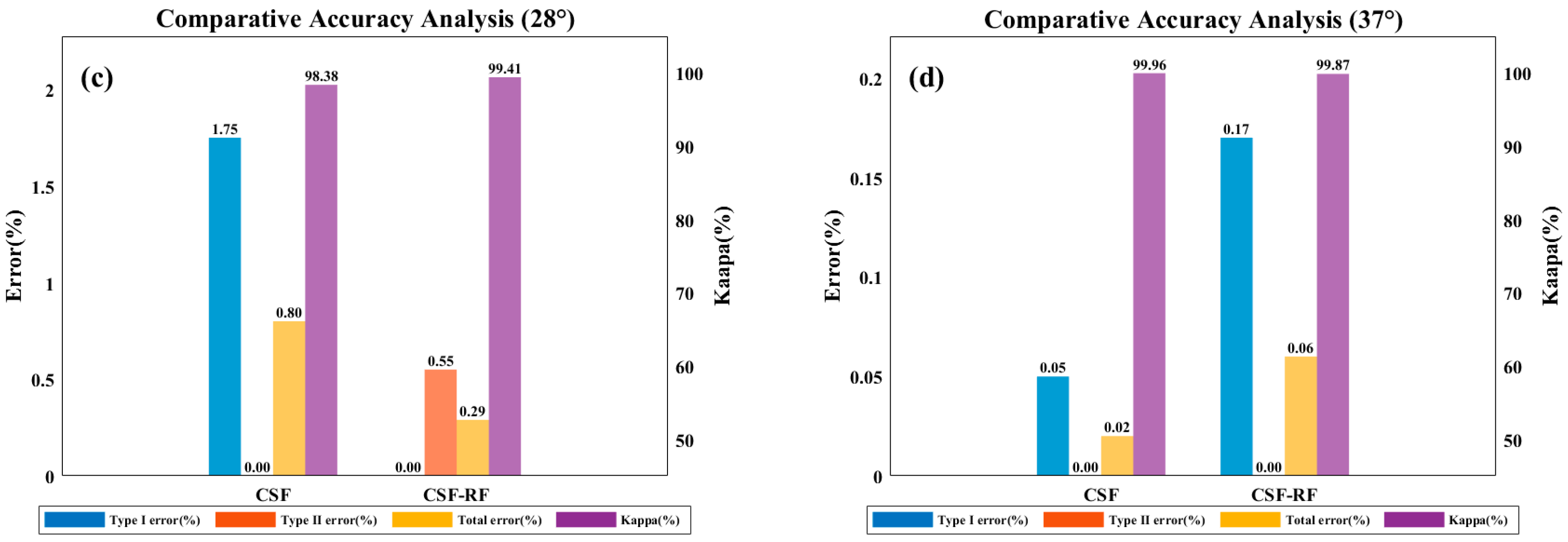
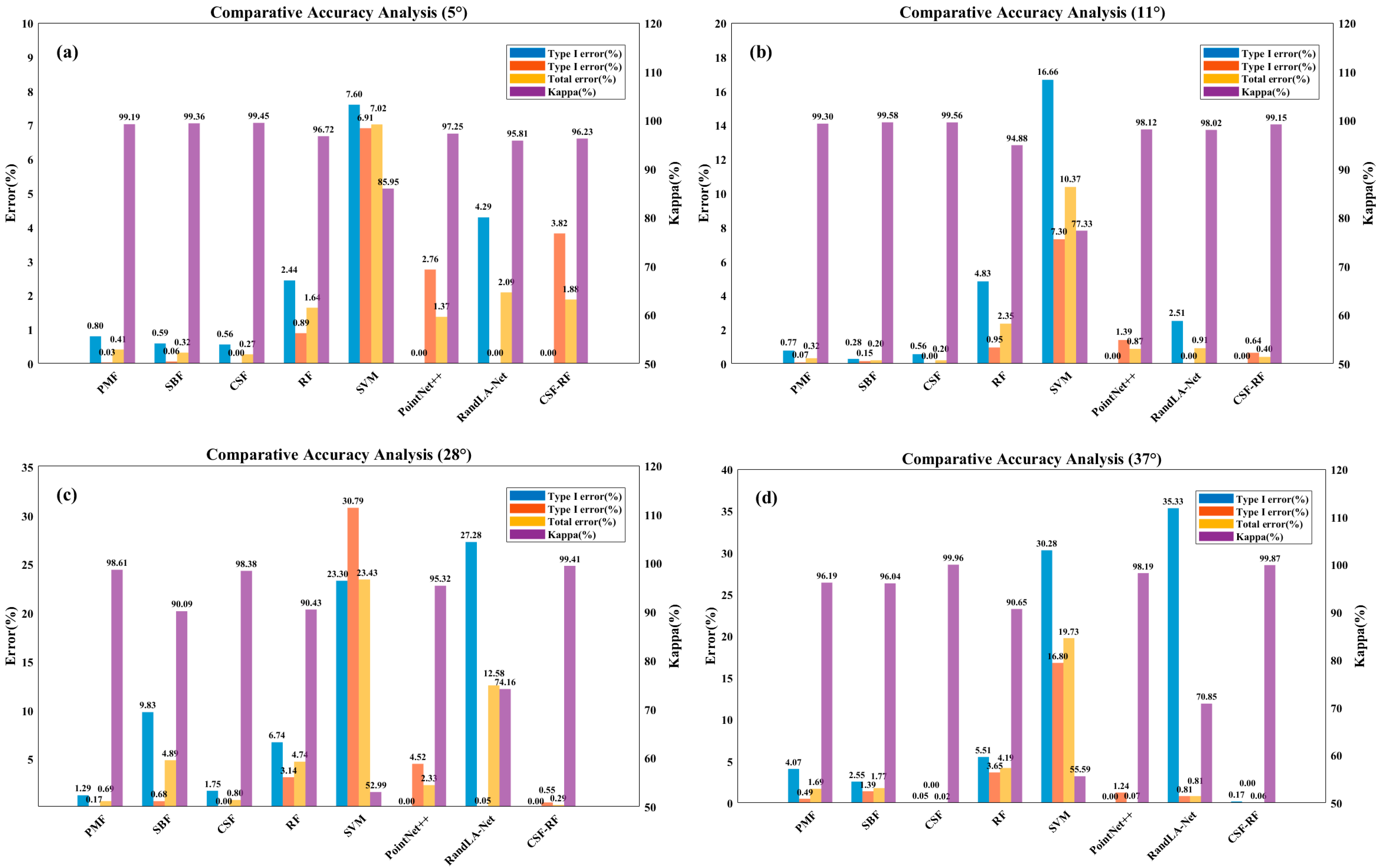
3.2. Results and Accuracy Validation Under Different Terrain Conditions
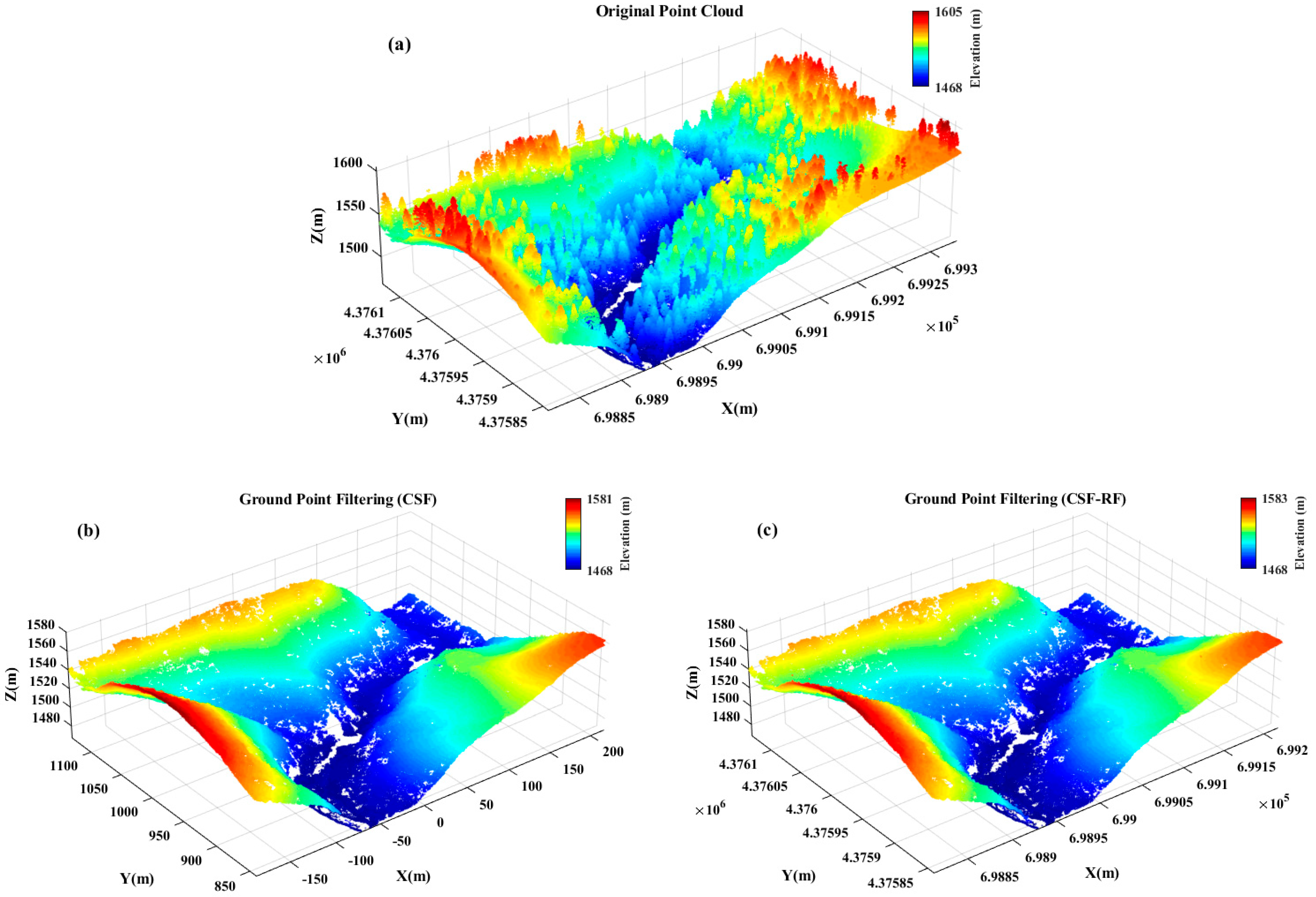
3.3. Results and Accuracy Validation in Dense Vegetation Scenes
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with Other Methods
4.2. Limitations of the Method
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, G.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Y.; Chen, W.; Mao, H.; Zhang, X.; Ma, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; et al. First global XCO2 observations from spaceborne lidar: Methodology and initial result. Remote Sens. Environ. 2025, 330, 114954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, B.; Gong, W.; Ma, Y.; Jin, S.; Wang, W.; Fan, R.; Jiang, S. Influence of clouds on planetary boundary layer height: A comparative study and factors analysis. Atmos. Res. 2025, 314, 107784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, B.; Chen, B. Improved surface NO2 Retrieval: Double-layer machine learning model construction and spatio-temporal characterization analysis in China (2018–2023). J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 384, 125439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Chen, S.-C.; Whitman, D.; Shyu, M.-L.; Yan, J.; Zhang, C. A progressive morphological filter for removing nonground measurements from airborne LIDAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 872–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Gan, R.; Luo, B.; Wang, A.; Shi, S.; Du, L. An Improved Method for Individual Tree Segmentation in Complex Urban Scenes Based on Using Multispectral LiDAR by Deep Learning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 6561–6576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, K.; Pfeifer, N. Determination of terrain models in wooded areas with airborne laser scanner data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1998, 53, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosselman, G. Slope based filtering of laser altimetry data. IAPRS 2000, XXXIII, 935–942. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Qi, J.; Peng, W.; Wang, H.; Xie, D.; Wang, X.; Yan, G. An Easy-to-Use Airborne LiDAR Data Filtering Method Based on Cloth Simulation. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Feng, C.-C. Using multi-scale and hierarchical deep convolutional features for 3D semantic classification of TLS point clouds. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2018, 34, 661–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sithole, G.; Vosselman, G. Experimental comparison of filter algorithms for bare-Earth extraction from airborne laser scanning point clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2004, 59, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Yu, S. Filtering Airborne LiDAR Data in Forested Environments Based on Multi-Directional Narrow Window and Cloth Simulation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Zhong, L.; Li, Y.; Guan, H. A random forest based method for urban object classification using lidar data and aerial imagery. In Proceedings of the 2015 23rd International Conference on Geoinformatics, Wuhan, China, 19–21 June 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, B.; Wielgosz, M.; Kontogianni, T.; Peters, T.; Puliti, S.; Astrup, R.; Schindler, K. Automated forest inventory: Analysis of high-density airborne LiDAR point clouds with 3D deep learning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 305, 114078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, B.; Wielgosz, M.; Puliti, S.; Kr'al, K.; Krůček, M.; Missarov, A.; Astrup, R. ForestFormer3D: A Unified Framework for End-to-End Segmentation of Forest LiDAR 3D Point Clouds. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2506.16991. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Wang, H.; Song, D. A Filtering Method for LiDAR Point Cloud Based on Multi-Scale CNN with Attention Mechanism. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhong, Z.; Liu, F.; Chapman, M.A.; Cao, D.; Li, J. Deep Learning for LiDAR Point Clouds in Autonomous Driving: A Review. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 32, 3412–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulicki, M.; Cabo, C.; Trzciński, T.; Będkowski, J.; Stereńczak, K. Artificial Intelligence and Terrestrial Point Clouds for Forest Monitoring. Curr. For. Rep. 2024, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yue, D.; Wang, S.; Zhong, J. Airborne LiDAR Point Cloud Filtering Algorithm Based on Supervoxel Ground Saliency. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2024, X-2-2024, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.R.; Yi, L.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 5105–5114. [Google Scholar]
- Qi Charles, R.; Su, H.; Kaichun, M.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet: Deep Learning on Point Sets for 3D Classification and Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Yuan, Y. Deep-Learning-Based Classification for DTM Extraction from ALS Point Cloud. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Yang, B.; Xie, L.; Rosa, S.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Trigoni, N.; Markham, A. RandLA-Net: Efficient Semantic Segmentation of Large-Scale Point Clouds. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11105–11114. [Google Scholar]
- Cutler, A.; Cutler, D.; Stevens, J. Random Forests. In Ensemble Machine Learning; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Volume 45, pp. 157–176. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Qin, X. Point cloud classification algorithm based on IPTD and SVM. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2019, 56, 161002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodha, S.K.; Kreps, E.J.; Helmbold, D.P.; Fitzpatrick, D. Aerial LiDAR Data Classification Using Support Vector Machines (SVM). In Proceedings of the Third International Symposium on 3D Data Processing, Visualization, and Transmission (3DPVT'06), Chapel Hill, NC, USA, 14–16 June 2006; pp. 567–574. [Google Scholar]
- Ayazi, S.M.; Saadat Seresht, M. Comparison of Traditional and Machine Learning Base Methods for Ground Point Cloud Labeling. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, XLII-4/W18, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refaeilzadeh, P.; Tang, L.; Liu, H. Cross-validation. In Encyclopedia of Database Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 532–538. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, G.; Cui, X.; Yuan, D.; Zhang, L.; Yang, R. An Improved Point Cloud Filtering Algorithm Applies in Complex Urban Environments. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Sang, M.; Wang, W. A Novel Ground Filtering Method for Point Clouds in a Forestry Area Based on Local Minimum Value and Machine Learning. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
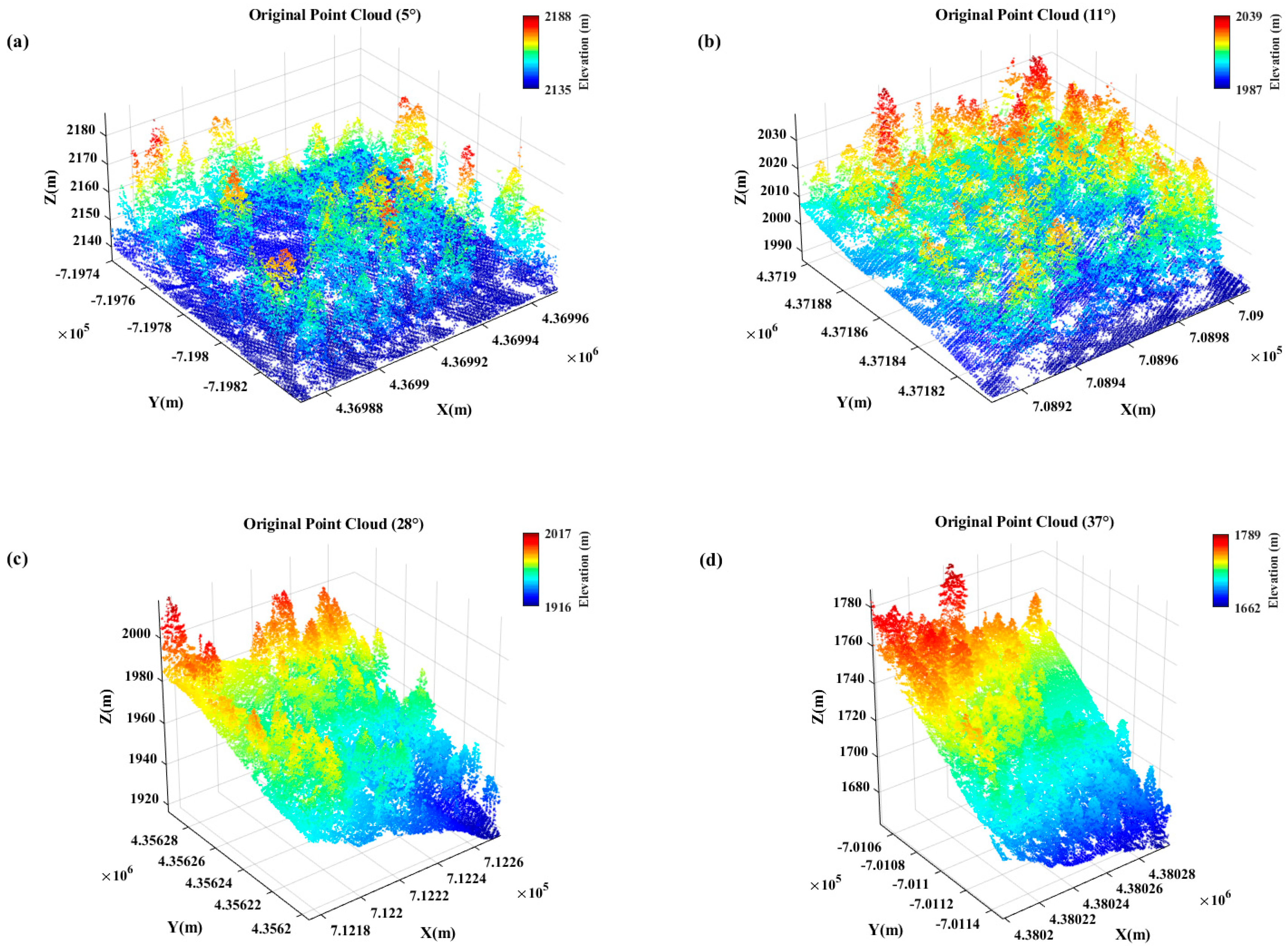
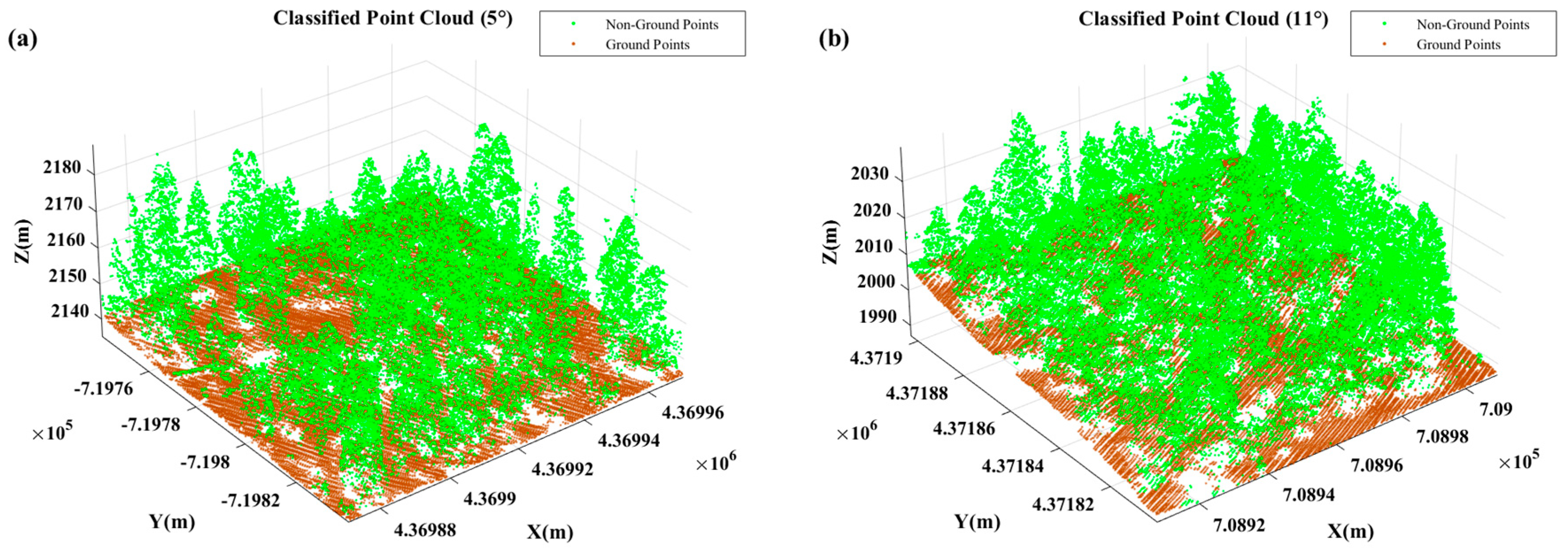
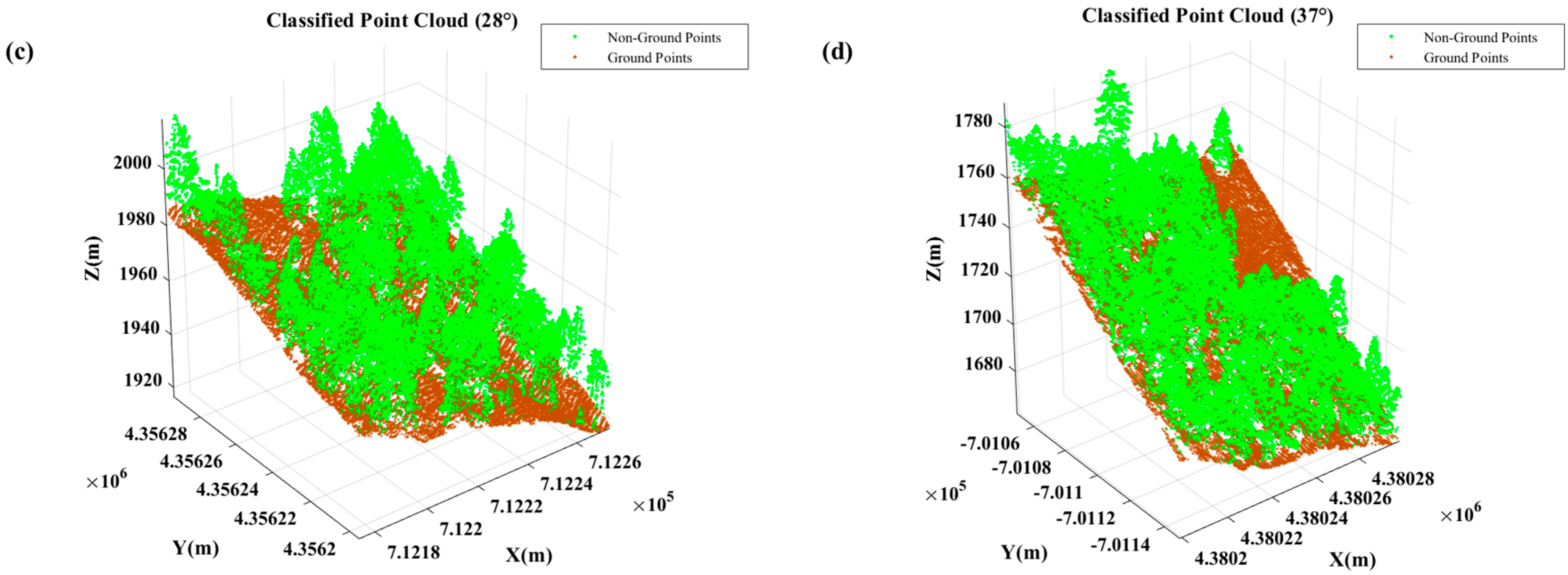
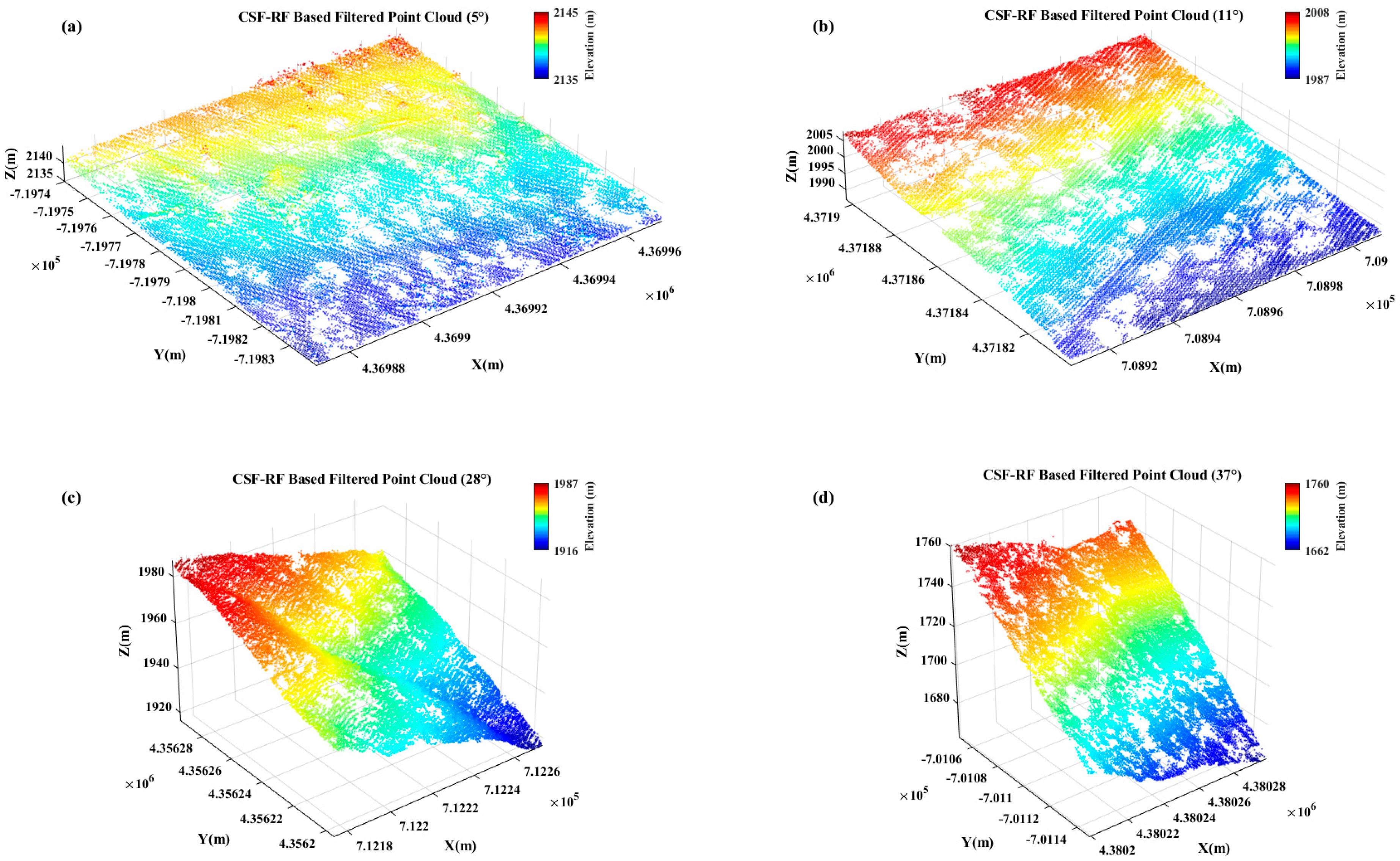
| Slope Grade | 0–5° | 6–25° | 25–35° | >35° |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ground Points (count) | 42,401 | 34,762 | 59,397 | 43,167 |
| Non-Ground Points (count) | 44,061 | 61,200 | 69,715 | 85,222 |
| Total Points (count) | 86,102 | 95,962 | 129,112 | 128,389 |
| Mean Importance Ranking | Feature | Mean Importance |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Normalized_z | 0.514202 |
| 2 | Scattering | 0.192790 |
| 3 | Echo_ratio | 0.101099 |
| 4 | Intensity | 0.071659 |
| 5 | Verticality | 0.047164 |
| 6 | EV_ratio | 0.034770 |
| 7 | Number_Of_Returns | 0.022380 |
| 8 | Return_Number | 0.015936 |
| Category | Ground Points | Non-Ground Points | Total Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ground points | TP | FN | TT = TP + FN |
| Non-ground points | FP | TN | FF = FP + TN |
| Total number | PP = TP + FP | NN = TN + FN | T = TP + TN + FP + FN |
| Category | Ground Points |
|---|---|
| Type I Error | FN/(TP + FN) |
| Type II Error | FP/(FP + TN) |
| Total Error | (FP + FN)/T |
| Po | (TP + TN)/T |
| Pe | ((TP + FN)(TP + FP) + (FP + TN)(FN + TN))/T2 |
| Kappa | (Po − Pe)/(1 − Pe) |
| Parameter | Without Feature Selection | After Feature Selection |
|---|---|---|
| OA (%) | 94.67 | 94.14 |
| Kappa (%) | 89.33 | 88.28 |
| Model runtime (s) | 263.42 | 68.43 |
| Parameter | With NEI | Without NEI |
|---|---|---|
| OA (%) | 94.28 | 88.19 |
| Kappa (%) | 88.56 | 76.38 |
| Total Time(s) | 22.43 | 23.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Qu, C.; Wu, Z.; Wang, W. Integration of Physical Features and Machine Learning: CSF-RF Framework for Optimizing Ground Point Filtering in Vegetated Regions. Sensors 2025, 25, 5950. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25195950
Zhang S, Qu C, Wu Z, Wang W. Integration of Physical Features and Machine Learning: CSF-RF Framework for Optimizing Ground Point Filtering in Vegetated Regions. Sensors. 2025; 25(19):5950. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25195950
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Sisi, Chenyao Qu, Zhimin Wu, and Wei Wang. 2025. "Integration of Physical Features and Machine Learning: CSF-RF Framework for Optimizing Ground Point Filtering in Vegetated Regions" Sensors 25, no. 19: 5950. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25195950
APA StyleZhang, S., Qu, C., Wu, Z., & Wang, W. (2025). Integration of Physical Features and Machine Learning: CSF-RF Framework for Optimizing Ground Point Filtering in Vegetated Regions. Sensors, 25(19), 5950. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25195950







