Myoelectric and Inertial Data Fusion Through a Novel Attention-Based Spatiotemporal Feature Extraction for Transhumeral Prosthetic Control: An Offline Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
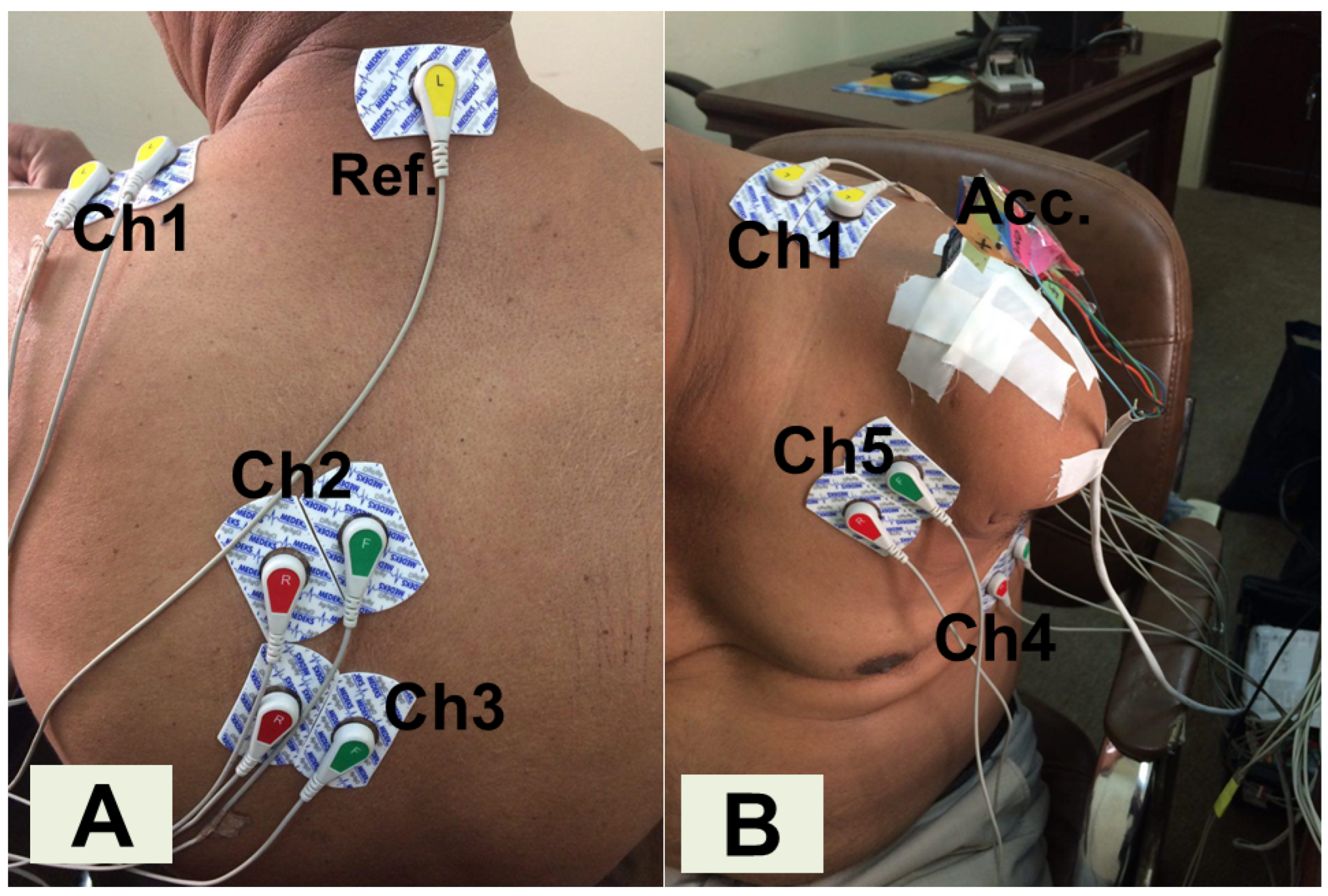
2.1. Experimental Protocol and Data Preprocessing
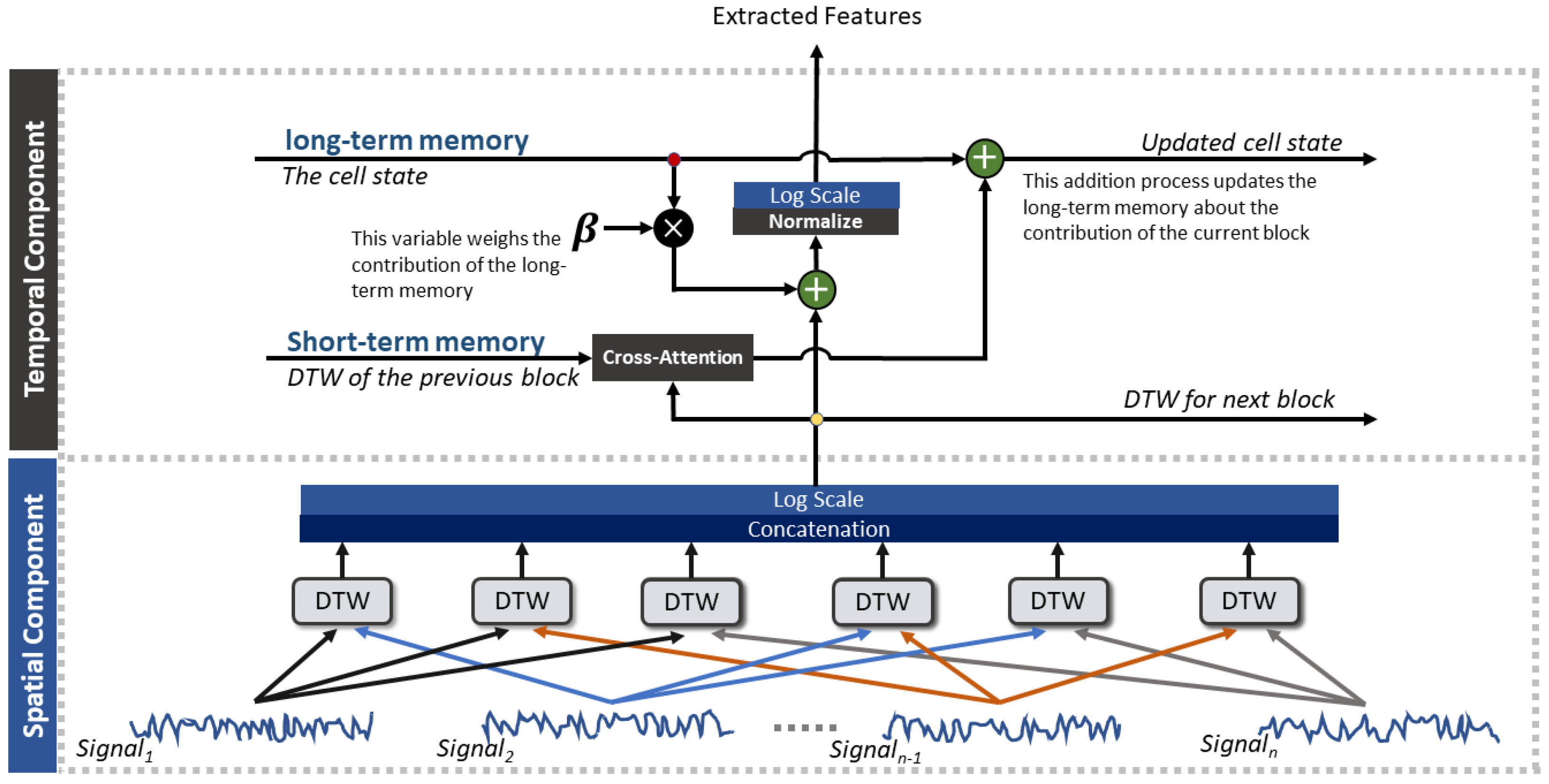
2.2. A-STW Feature Extraction Architecture
2.3. Clustering Properties Evaluation
2.4. Pattern Recognition Models
2.5. Ablation Study: A-STW Multi-Modal Feature Extraction vs. Multi-Modal Feature Concatenation
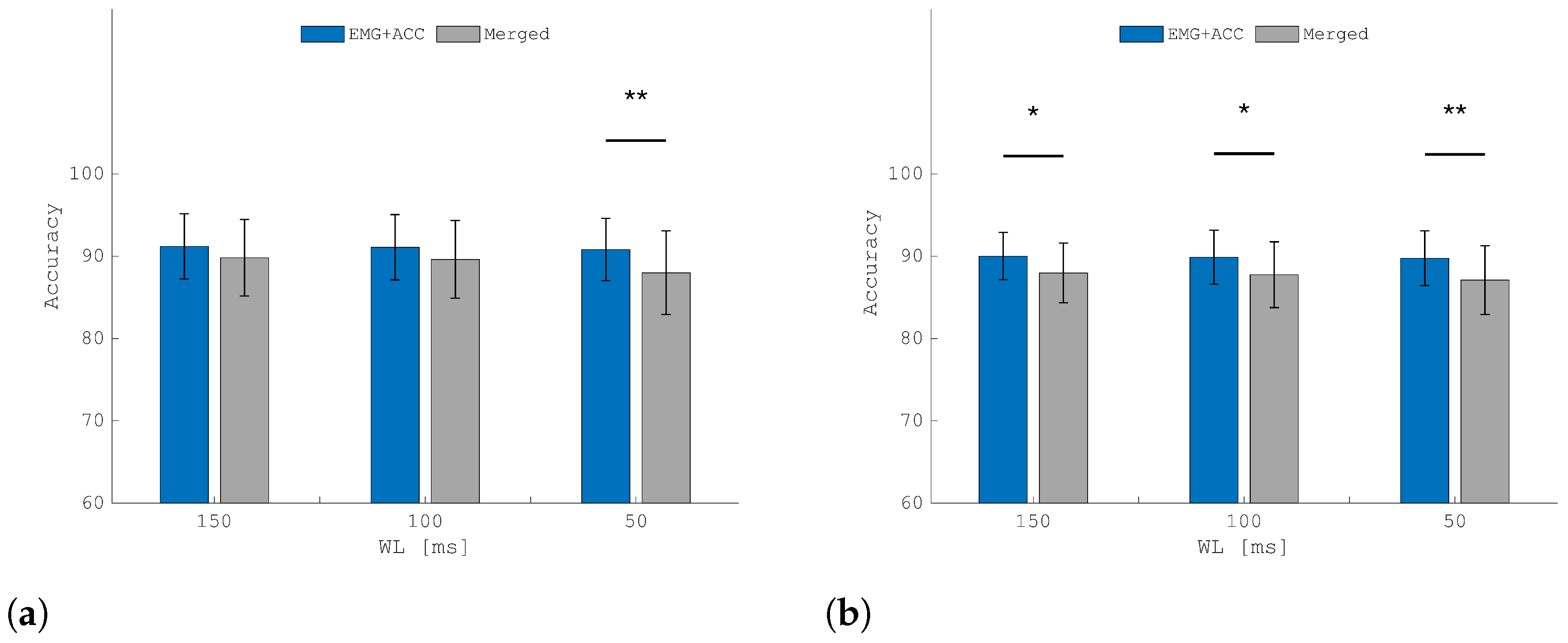
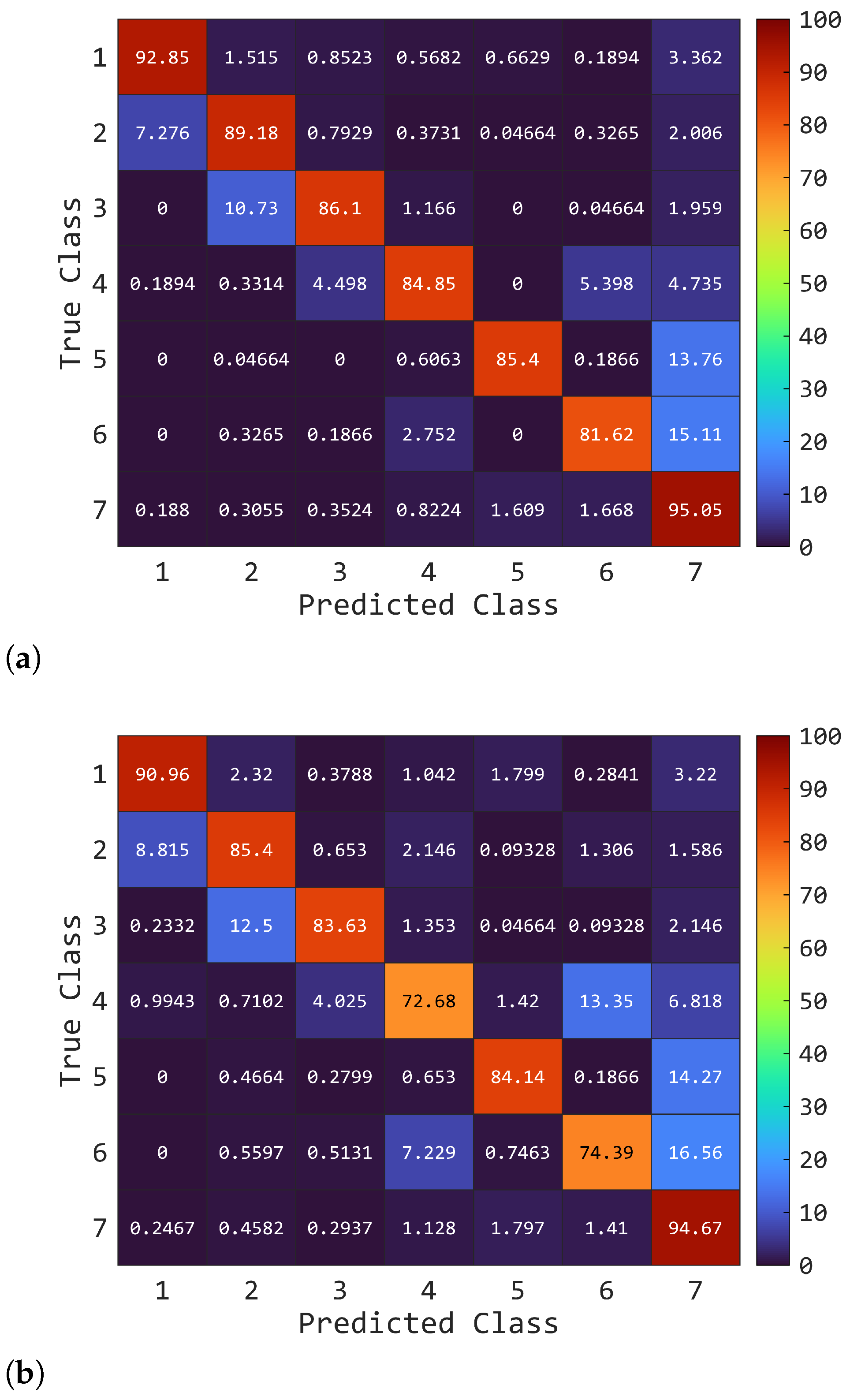
3. Results
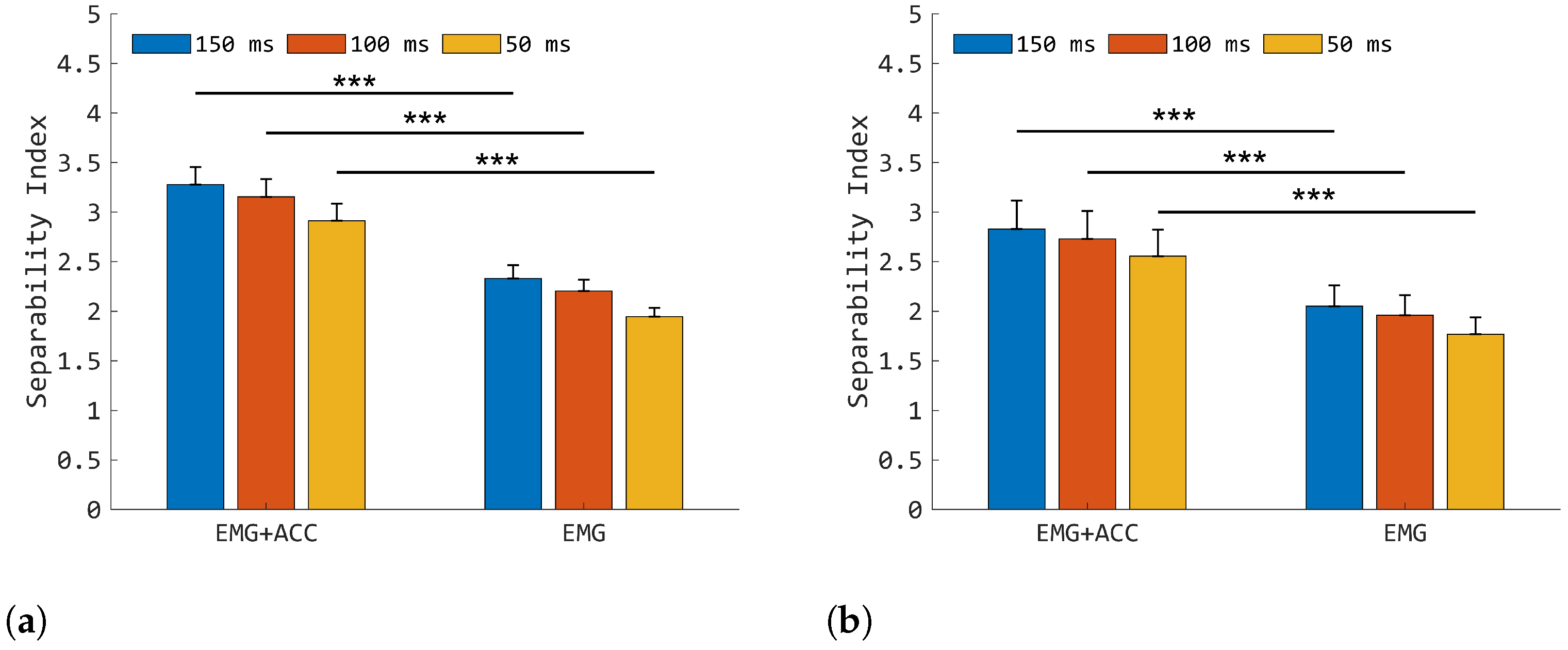
3.1. Class Separability Properties
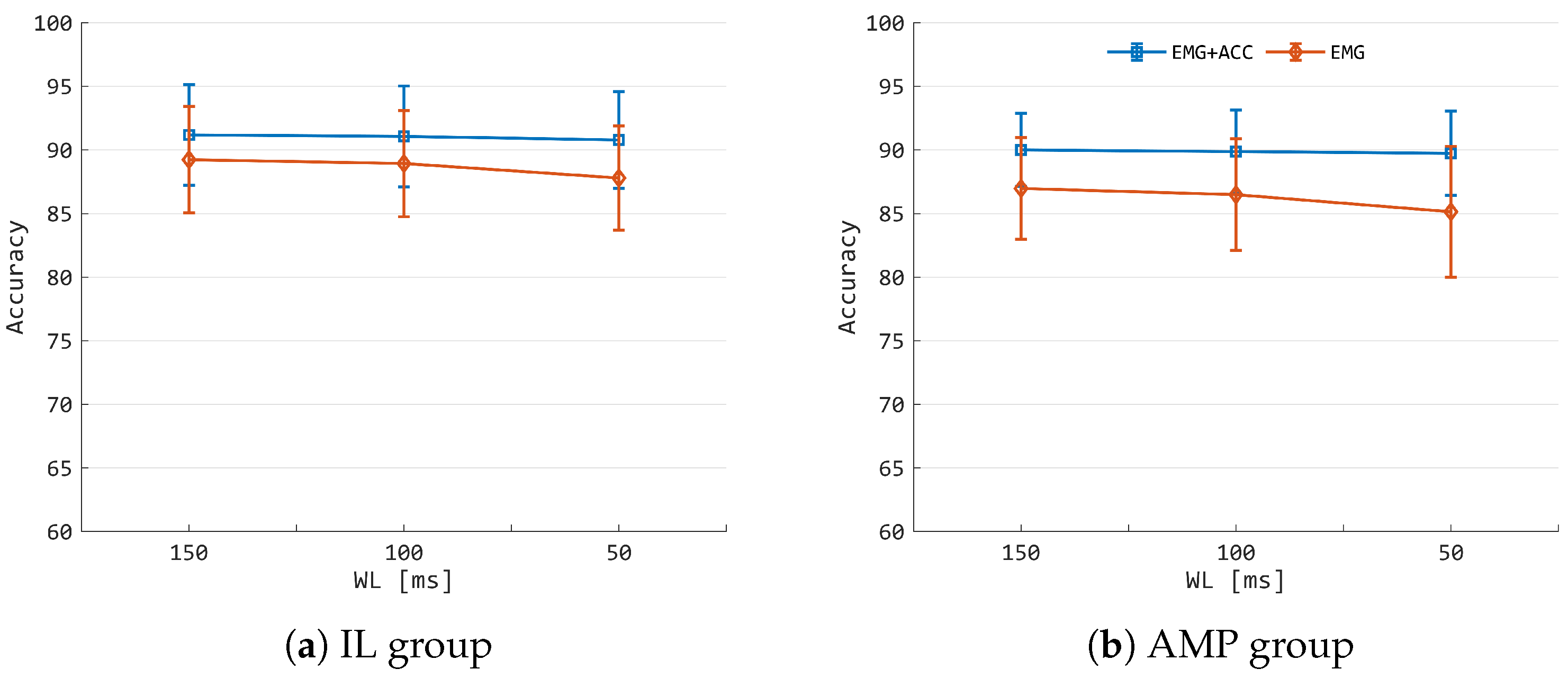
3.2. Classification Performances
3.3. Ablation Study: A-STW Multi-Modal Feature Extraction vs. Multi-Modal Feature Concatenation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farina, D.; Vujaklija, I.; Brånemark, R.; Bull, A.M.; Dietl, H.; Graimann, B.; Hargrove, L.J.; Hoffmann, K.P.; Huang, H.; Ingvarsson, T.; et al. Toward higher-performance bionic limbs for wider clinical use. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 7, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsugbe, E.; Al-Timemy, A.H. Shoulder girdle recognition using electrophysiological and low frequency anatomical contraction signals for prosthesis control. CAAI Trans. Intell. Technol. 2022, 7, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabban, L.; Dupan, S.; Zhang, D.; Ainsworth, B.; Nazarpour, K.; Metcalfe, B.W. Sensory feedback for upper-limb prostheses: Opportunities and barriers. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2022, 30, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordella, F.; Ciancio, A.L.; Sacchetti, R.; Davalli, A.; Cutti, A.G.; Guglielmelli, E.; Zollo, L. Literature review on needs of upper limb prosthesis users. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipriani, C.; Antfolk, C.; Controzzi, M.; Lundborg, G.; Rosén, B.; Carrozza, M.C.; Sebelius, F. Online myoelectric control of a dexterous hand prosthesis by transradial amputees. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2011, 19, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muceli, S.; Farina, D. Simultaneous and proportional estimation of hand kinematics from EMG during mirrored movements at multiple degrees-of-freedom. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2011, 20, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, A.; Rafiei, H.; Daliri, M.; Akbarzadeh-T, M.R.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Naddaf-Sh, A.M.; Naddaf-Sh, S. Clinical implementation of a bionic hand controlled with kineticomyographic signals. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buniya, A.; Al-Timemy, A.H.; Aldoori, A.; Khushaba, R.N. Analysis of Different Hand and Finger Grip Patterns using Surface Electromyography and Hand Dynamometry. Al-Khwarizmi Eng. J. 2020, 16, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Timemy, A.H.; Serrestou, Y.; Khushaba, R.N.; Yacoub, S.; Raoof, K. Hand gesture recognition with acoustic myography and wavelet scattering transform. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 107526–107535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, J.S.; Schoepp, K.R.; Stobbe, M.; Marasco, P.D.; Hebert, J.S. Fabrication and application of an adjustable myoelectric transhumeral prosthetic socket. Prosthetics Orthot. Int. 2019, 43, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, D.A.; Mitchell, J.E.; Truex, D.; Goldfarb, M. Design of a myoelectric transhumeral prosthesis. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2016, 21, 1868–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Lowery, M.M.; Englehart, K.B.; Huang, H.; Li, G.; Hargrove, L.; Dewald, J.P.; Kuiken, T.A. Decoding a new neural–machine interface for control of artificial limbs. J. Neurophysiol. 2007, 98, 2974–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargrove, L.J.; Miller, L.A.; Turner, K.; Kuiken, T.A. Myoelectric pattern recognition outperforms direct control for transhumeral amputees with targeted muscle reinnervation: A randomized clinical trial. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, M.; Marchand, C.; Richer, F.; Touillet, A.; Martinet, N.; Paysant, J.; Morel, G.; Jarrassé, N. Simultaneous control of 2DOF upper-limb prosthesis with body compensations-based control: A multiple cases study. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2022, 30, 1745–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, M.; Jarrassé, N.; de Montalivet, E.; Richer, F.; Morel, G. Closing the loop between body compensations and upper limb prosthetic movements: A feasibility study. IEEE Trans. Med. Robot. Bionics 2020, 3, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tigrini, A.; Al-Timemy, A.H.; Verdini, F.; Fioretti, S.; Morettini, M.; Burattini, L.; Mengarelli, A. Decoding transient sEMG data for intent motion recognition in transhumeral amputees. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 85, 104936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Zhou, P.; Li, G. Toward attenuating the impact of arm positions on electromyography pattern-recognition based motion classification in transradial amputees. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2012, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopke, J.V.; Ellis, M.D.; Hargrove, L.J. Determining user intent of partly dynamic shoulder tasks in individuals with chronic stroke using pattern recognition. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 28, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, E.; Phinyomark, A.; Scheme, E. Differences in perspective on inertial measurement unit sensor integration in myoelectric control. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.03424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khushaba, R.N.; Al-Timemy, A.H.; Samuel, O.W.; Scheme, E.J. Myoelectric Control With Fixed Convolution-Based Time-Domain Feature Extraction: Exploring the Spatio–Temporal Interaction. IEEE Trans. Hum.-Mach. Syst. 2022, 52, 1247–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbari, M.; Khushaba, R.; Nazarpour, K. Spatio-temporal warping for myoelectric control: An offline, feasibility study. J. Neural Eng. 2021, 18, 066028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khushaba, R.N.; Scheme, E.; Al-Timemy, A.H.; Phinyomark, A.; Al-Taee, A.; Al-Jumaily, A. A long short-term recurrent spatial-temporal fusion for myoelectric pattern recognition. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 178, 114977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tigrini, A.; Scattolini, M.; Mengarelli, A.; Fioretti, S.; Morettini, M.; Burattini, L.; Verdini, F. Role of the Window Length for Myoelectric Pattern Recognition in Detecting User Intent of Motion. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA), Messina, Italy, 22–24 June 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sharba, G.K.; Wali, M.K.; Al-Timemy, A.H. Wavelet-based feature extraction technique for classification of different shoulder girdle motions for high-level upper limb amputees. Int. J. Med. Eng. Inform. 2020, 12, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criswell, E. Cram’s Introduction to Surface Electromyography; Jones & Bartlett Publishers: Burlington, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Trigili, E.; Grazi, L.; Crea, S.; Accogli, A.; Carpaneto, J.; Micera, S.; Vitiello, N.; Panarese, A. Detection of movement onset using EMG signals for upper-limb exoskeletons in reaching tasks. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2019, 16, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivela, D.; Scannella, A.; Pavan, E.E.; Frigo, C.A.; Belluco, P.; Gini, G. Analysis and comparison of features and algorithms to classify shoulder movements from sEMG signals. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 3714–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khushaba, R.N.; Al-Ani, A.; Al-Timemy, A.; Al-Jumaily, A. A fusion of time-domain descriptors for improved myoelectric hand control. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI), Athens, Greece, 6–9 December 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Timemy, A.H.; Khushaba, R.N.; Bugmann, G.; Escudero, J. Improving the performance against force variation of EMG controlled multifunctional upper-limb prostheses for transradial amputees. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2015, 24, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30 (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Franzke, A.W.; Kristoffersen, M.B.; Jayaram, V.; van der Sluis, C.K.; Murgia, A.; Bongers, R.M. Exploring the relationship between EMG feature space characteristics and control performance in machine learning myoelectric control. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2021, 29, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khushaba, R.N.; Takruri, M.; Miro, J.V.; Kodagoda, S. Towards limb position invariant myoelectric pattern recognition using time-dependent spectral features. Neural Netw. 2014, 55, 42–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelov, P.; Gu, X. Autonomous learning multi-model classifier of 0-order (ALMMo-0). In Proceedings of the 2017 Evolving and Adaptive Intelligent Systems (EAIS), Ljubljana, Slovenia, 31 May–2 June 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Angelov, P.P.; Gu, X. Empirical Approach to Machine Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tigrini, A.; Pettinari, L.A.; Verdini, F.; Fioretti, S.; Mengarelli, A. Shoulder motion intention detection through myoelectric pattern recognition. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2021, 5, 6001904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Lu, H.; Liu, H. Multi-modality deep forest for hand motion recognition via fusing sEMG and acceleration signals. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2022, 14, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khushaba, R.N.; Nazarpour, K. Decoding HD-EMG Signals for Myoelectric Control-How Small Can the Analysis Window Size be? IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 8569–8574. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, D.; He, X.; Han, J. Efficient kernel discriminant analysis via spectral regression. In Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM 2007), Omaha, NE, USA, 28–31 October 2007; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 427–432. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, L.H.; Hargrove, L.J.; Lock, B.A.; Kuiken, T.A. Determining the optimal window length for pattern recognition-based myoelectric control: Balancing the competing effects of classification error and controller delay. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2010, 19, 186–192. [Google Scholar]
- Cardarelli, S.; Mengarelli, A.; Tigrini, A.; Strazza, A.; Di Nardo, F.; Fioretti, S.; Verdini, F. Single IMU displacement and orientation estimation of human center of mass: A magnetometer-free approach. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 69, 5629–5639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardarelli, S.; di Florio, P.; Mengarelli, A.; Tigrini, A.; Fioretti, S.; Verdini, F. Magnetometer-free sensor fusion applied to pedestrian tracking: A feasibility study. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 23rd International Symposium on Consumer Technologies (ISCT), Ancona, Italy, 19–21 June 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 238–242. [Google Scholar]
- Chadwell, A.; Kenney, L.; Thies, S.; Head, J.; Galpin, A.; Baker, R. Addressing unpredictability may be the key to improving performance with current clinically prescribed myoelectric prostheses. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Ma, C.; Nazarpour, K. Plug-and-play myoelectric control via a self-calibrating random forest common model. J. Neural Eng. 2025, 22, 016029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulwa, F.; Tai, P.; Sarwatt, D.S.; Asogbon, M.G.; Khushaba, R.; Oyemakinde, T.T.; Aboyeji, S.T.; Li, G.; Samuel, O.W.; Li, Y. A NMF-based non-Euclidean Adaptive Feature Extraction Scheme for Limb Motion Pattern Decoding in Pattern Recognition System. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Participant | Age (years) | Sex | Amputated Side | Time Since Amputation (years) | Cause of Loss of Arm | Wearing a Prosthetic Limb | Dominant Limb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 65 | Male | Left | 32 | War | No | Right |
| A2 | 50 | Male | Left | 31 | War | No | Right |
| A3 | 35 | Male | Right | 23 | Terrorist bomb | No | Right |
| A4 | 16 | Male | Right | 11 | Terrorist bomb | No | Right |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tigrini, A.; Mengarelli, A.; Al-Timemy, A.H.; Khushaba, R.N.; Mobarak, R.; Scattolini, M.; Sharba, G.K.; Verdini, F.; Gambi, E.; Burattini, L. Myoelectric and Inertial Data Fusion Through a Novel Attention-Based Spatiotemporal Feature Extraction for Transhumeral Prosthetic Control: An Offline Analysis. Sensors 2025, 25, 5920. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185920
Tigrini A, Mengarelli A, Al-Timemy AH, Khushaba RN, Mobarak R, Scattolini M, Sharba GK, Verdini F, Gambi E, Burattini L. Myoelectric and Inertial Data Fusion Through a Novel Attention-Based Spatiotemporal Feature Extraction for Transhumeral Prosthetic Control: An Offline Analysis. Sensors. 2025; 25(18):5920. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185920
Chicago/Turabian StyleTigrini, Andrea, Alessandro Mengarelli, Ali H. Al-Timemy, Rami N. Khushaba, Rami Mobarak, Mara Scattolini, Gaith K. Sharba, Federica Verdini, Ennio Gambi, and Laura Burattini. 2025. "Myoelectric and Inertial Data Fusion Through a Novel Attention-Based Spatiotemporal Feature Extraction for Transhumeral Prosthetic Control: An Offline Analysis" Sensors 25, no. 18: 5920. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185920
APA StyleTigrini, A., Mengarelli, A., Al-Timemy, A. H., Khushaba, R. N., Mobarak, R., Scattolini, M., Sharba, G. K., Verdini, F., Gambi, E., & Burattini, L. (2025). Myoelectric and Inertial Data Fusion Through a Novel Attention-Based Spatiotemporal Feature Extraction for Transhumeral Prosthetic Control: An Offline Analysis. Sensors, 25(18), 5920. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185920










