Non-Contact Heart Rate Variability Monitoring with FMCW Radar via a Novel Signal Processing Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Traditional Methods
2.2. Machine Learning and Deep Learning
3. Overview of HRV Measurement Principles and Algorithms
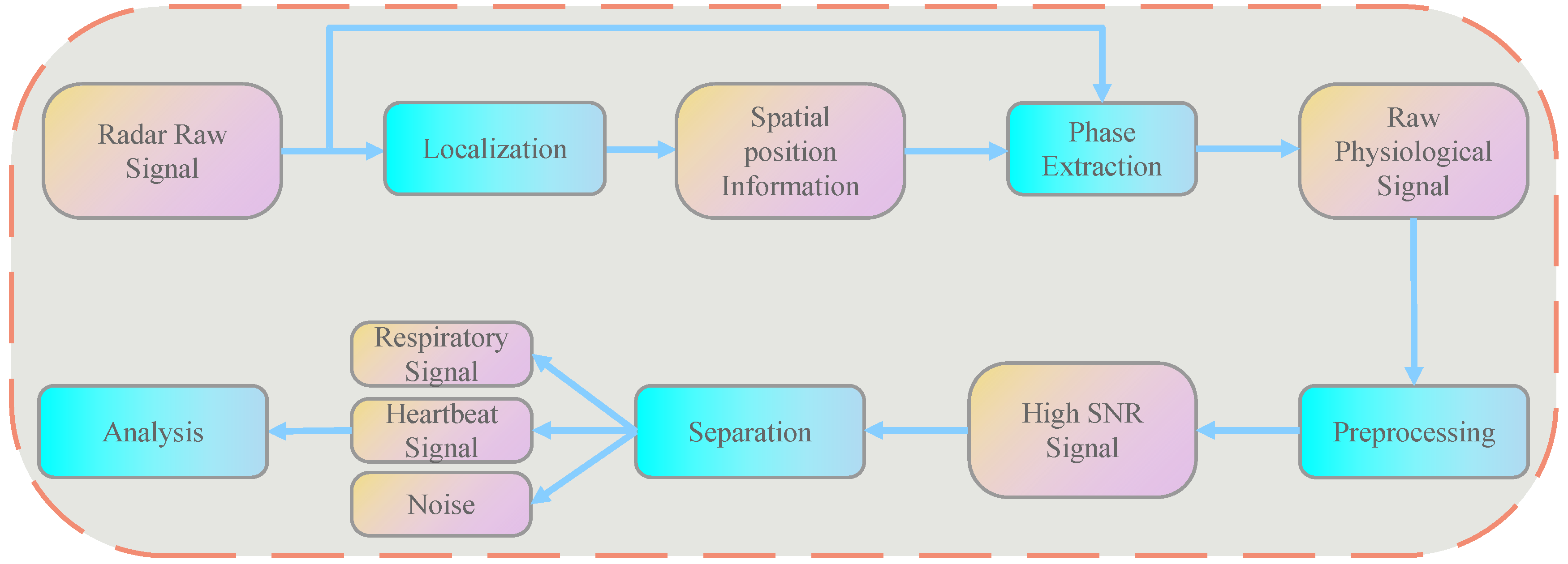
3.1. HRV Detection Principles and Algorithm Process
3.2. Target Localization Algorithm
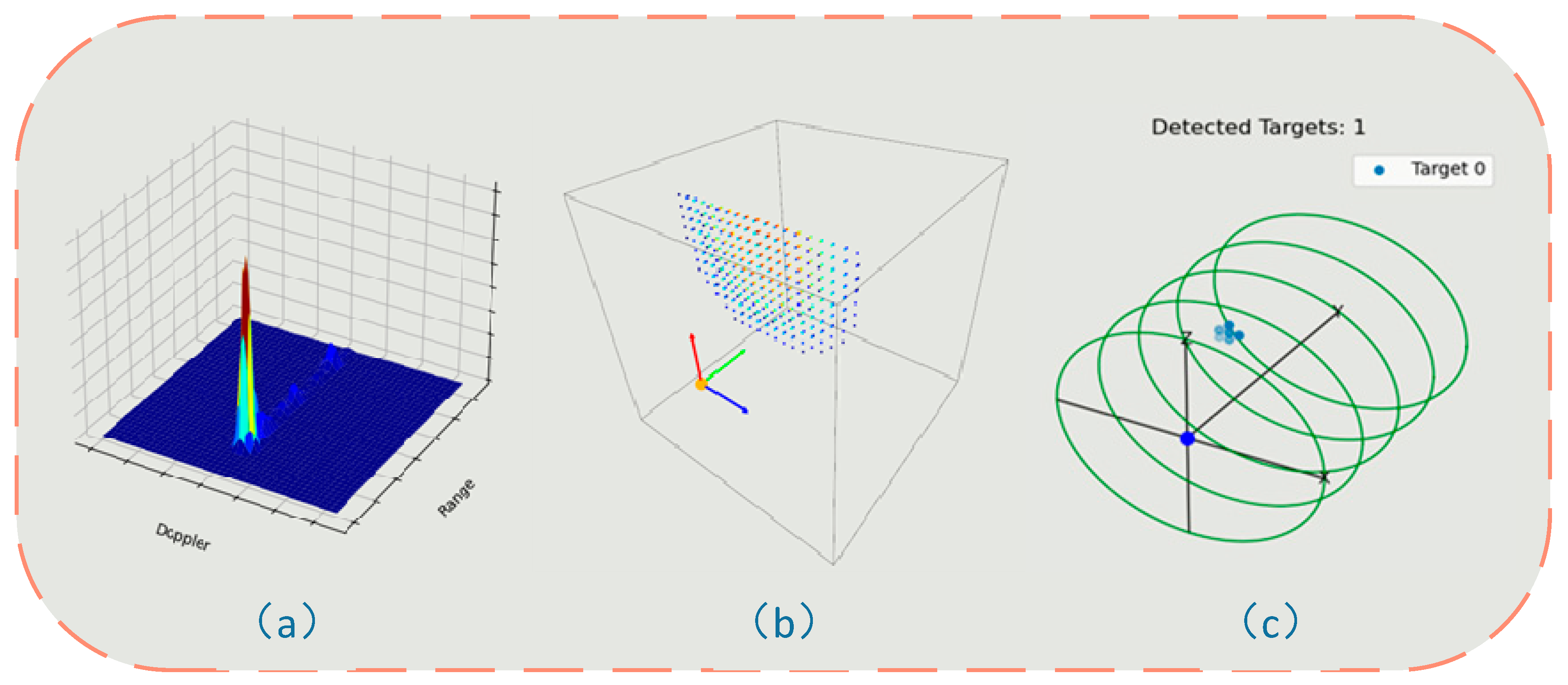
3.2.1. Signal Preprocessing and Spatial Spectral Analysis
3.2.2. Three-Dimensional Target Detection and Position Estimation
3.3. Second-Order Spectral Sparse Separation Algorithm Using Lagrangian Multipliers
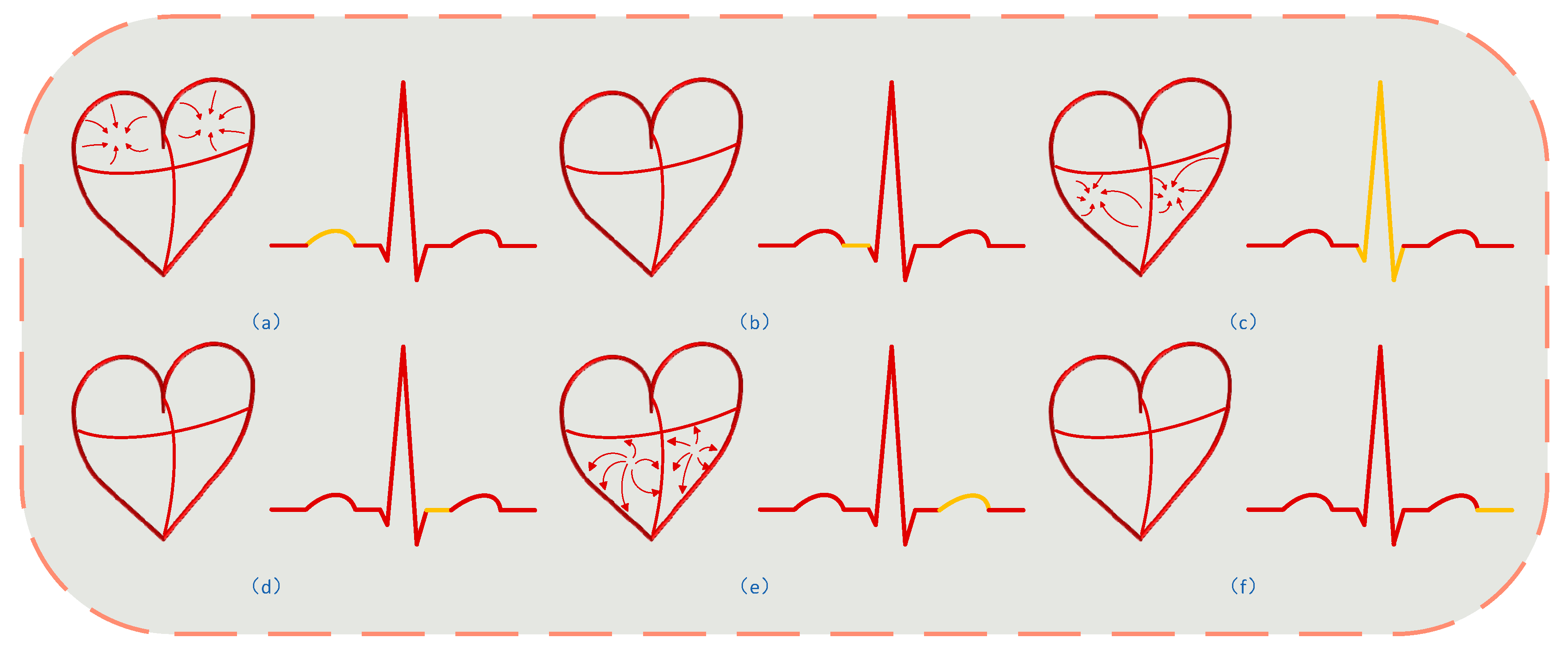
3.3.1. Establishing Respiratory and Heartbeat Models
3.3.2. Second-Order Spectral Sparse Separation Algorithm Using Lagrangian Multipliers for Separating Heartbeat Signals
3.4. HRV Estimation
4. Experimental Evaluation
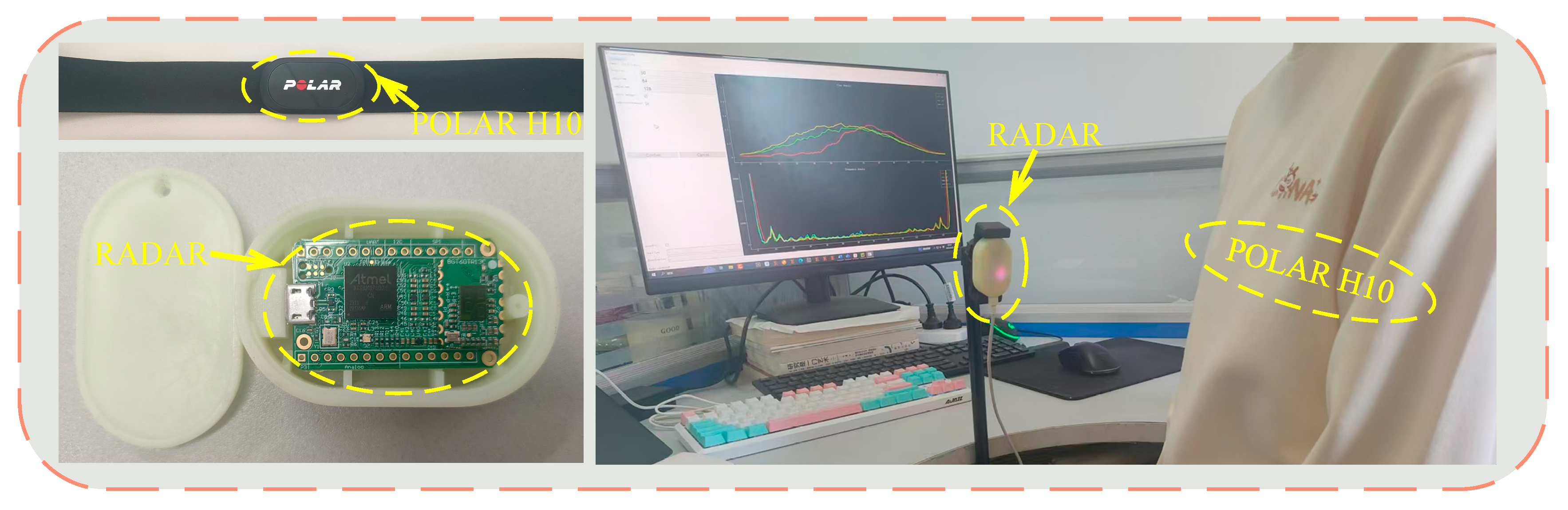
4.1. Methodology
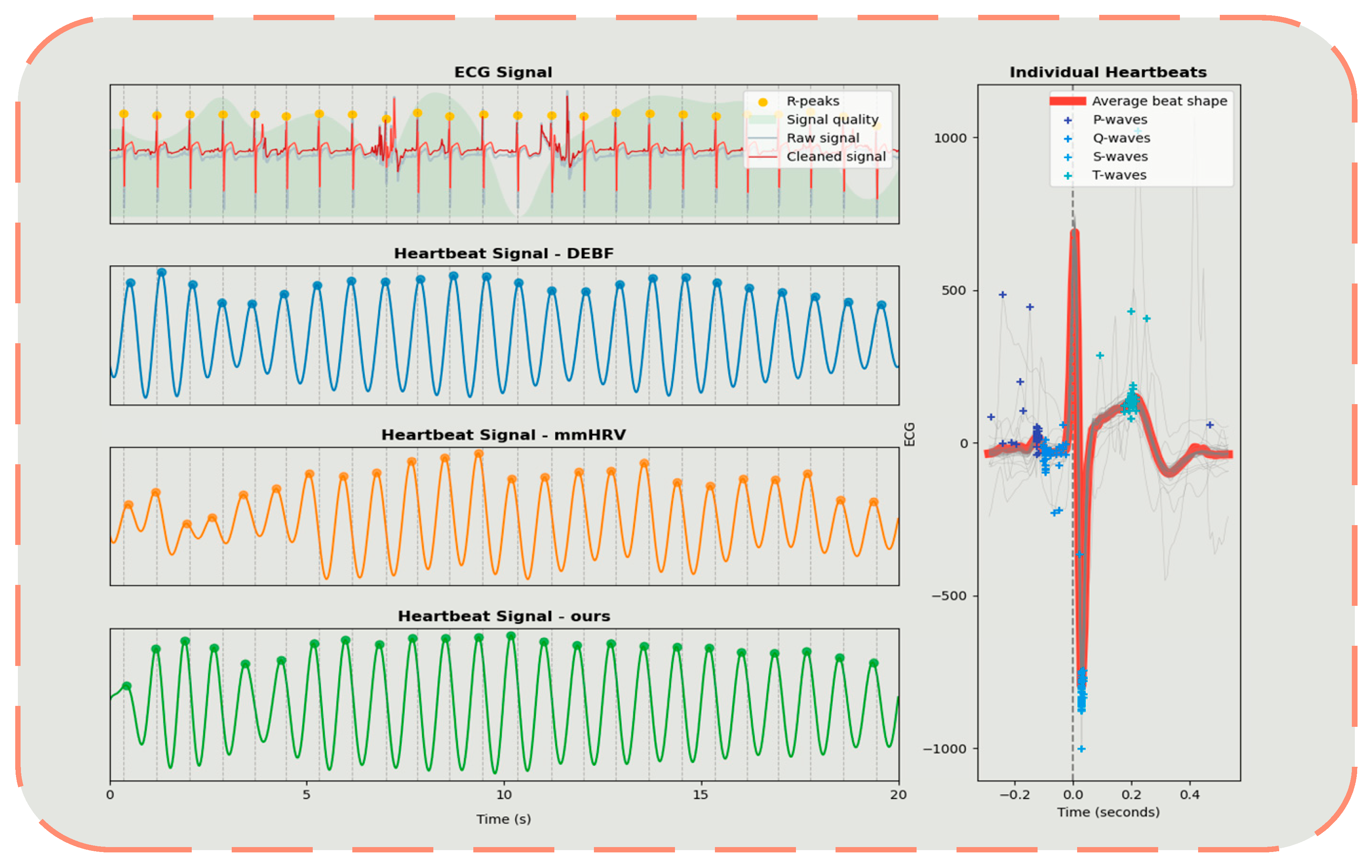
4.2. Overall Performance
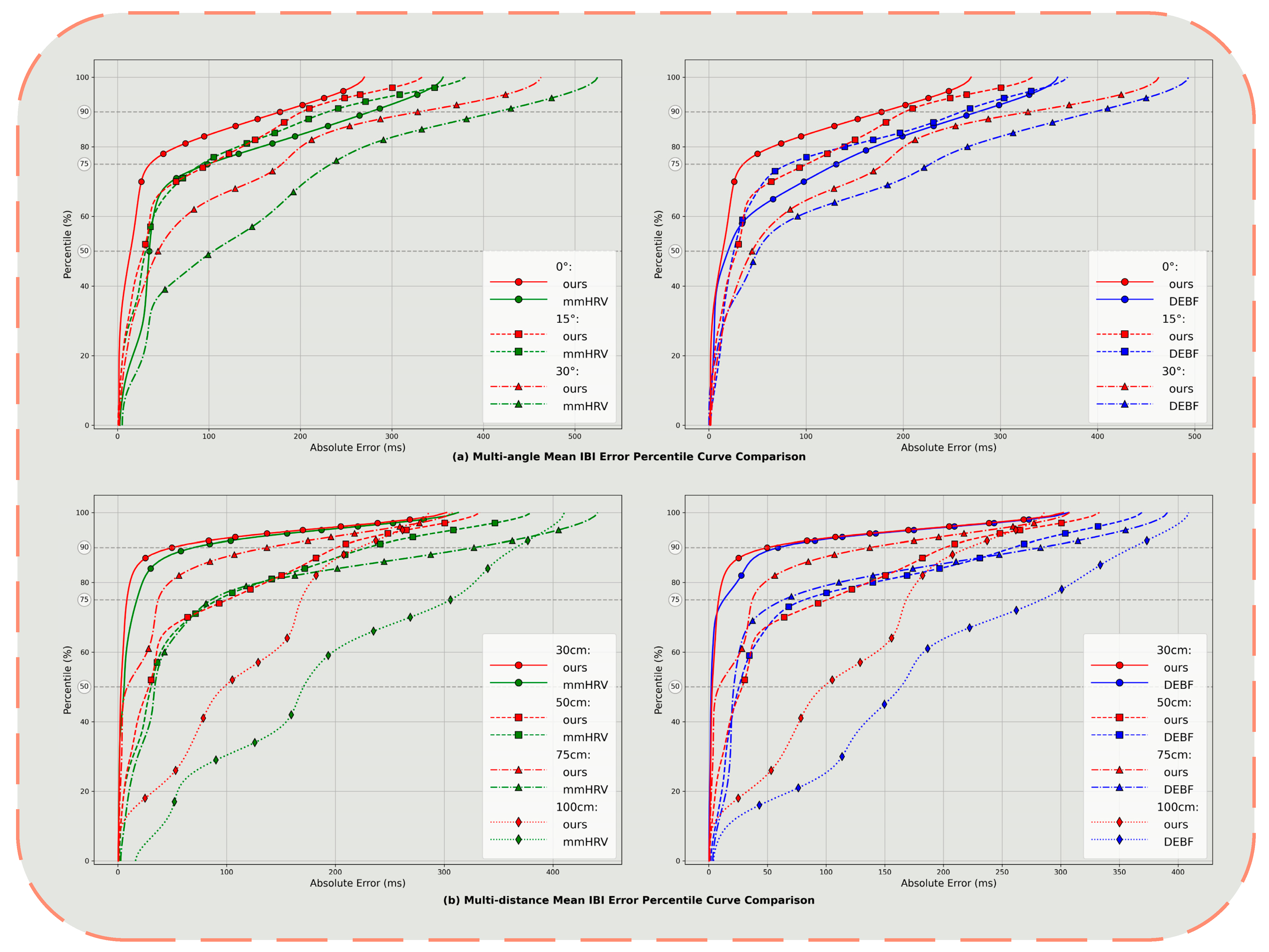
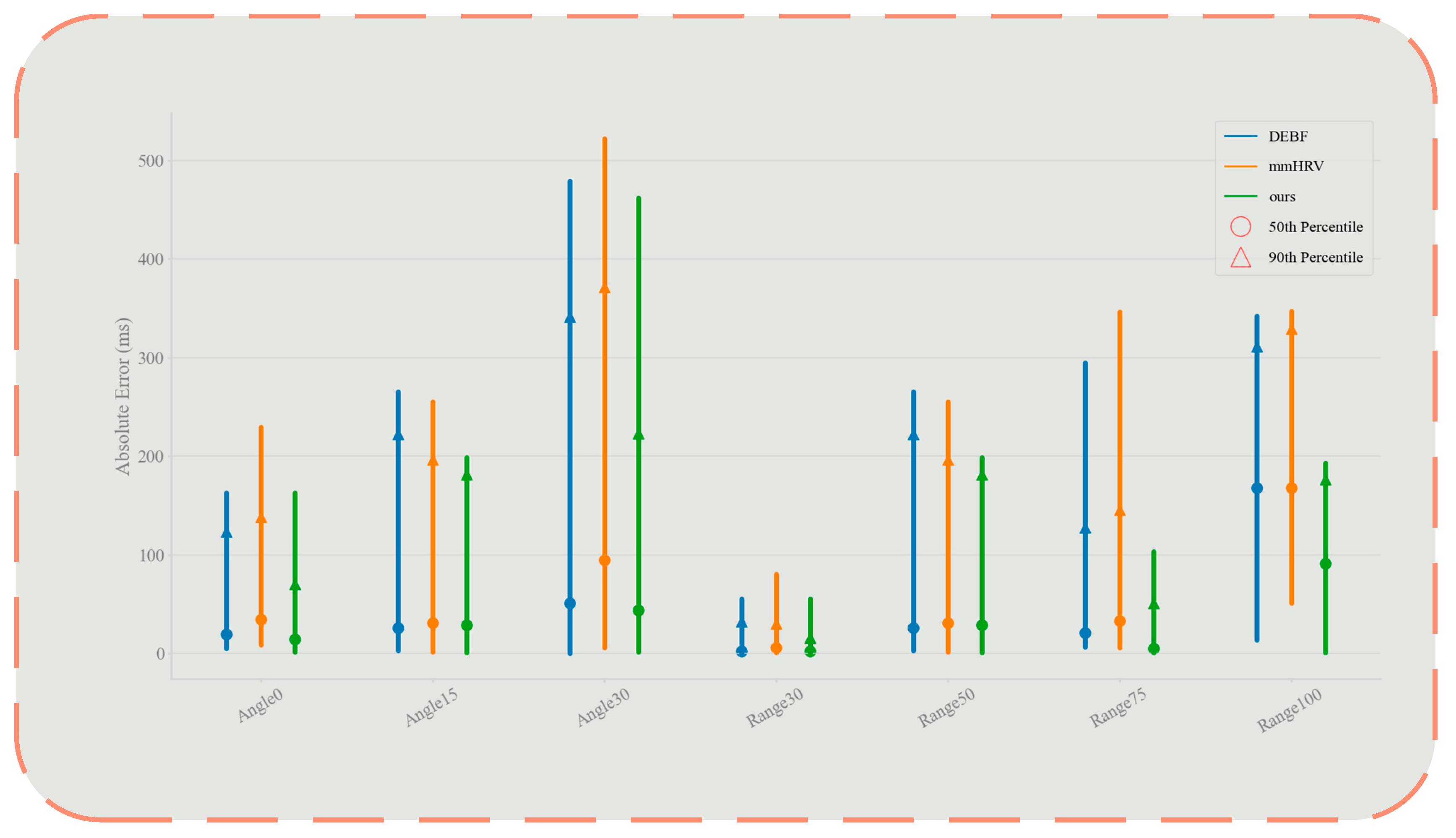
4.3. Impact of Distance and Angle
5. Discussion and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ChuDuc, H.; NguyenPhan, K.; NguyenViet, D. A Review of Heart Rate Variability and its Applications. APCBEE Procedia 2013, 7, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, J.L.; Alloy, L.B. Atypical reactivity of heart rate variability to stress and depression across development: Systematic review of the literature and directions for future research. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2016, 50, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shastri, A.; Valecha, N.; Bashirov, E.; Tataria, H.; Lentmaier, M.; Tufvesson, F.; Rossi, M.; Casari, P. A Review of Millimeter Wave Device-Based Localization and Device-Free Sensing Technologies and Applications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2022, 24, 1708–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranjec, J.; Beguš, S.; Geršak, G.; Šinkovec, M.; Drnovšek, J.; Hudoklin, D. Design and Clinical Evaluation of a Non-Contact Heart Rate Variability Measuring Device. Sensors 2017, 17, 2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic, V.L.; Jankovic, M.M.; Lupsic, A.V.; Mihajlovic, V.R.; Popovic-Bozovic, J.S. High-Accuracy Real-Time Monitoring of Heart Rate Variability Using 24 GHz Continuous-Wave Doppler Radar. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 74721–74733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Peng, Z.; Gu, C.; Li, S.; Wang, D.; Zhang, W. Differential Enhancement Method for Robust and Accurate Heart Rate Monitoring via Microwave Vital Sign Sensing. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 7108–7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antolinos, E.; García-Rial, F.; Hernández, C.; Montesano, D.; Godino-Llorente, J.I.; Grajal, J. Cardiopulmonary Activity Moni-toring Using Millimeter Wave Radars. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Jiang, X.; Jeong, M.-G.; Hong, H.; Fu, C.-H.; Yang, X.; Wang, E.; Zhu, X.; Liu, X. Multitarget Vital Signs Measurement With Chest Motion Imaging Based on MIMO Radar. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2021, 69, 4735–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuri, M.; Sacco, G.; Hornung, R.; Zhang, P.; Visser, H.J.; Hijdra, M.; Liu, Y.-H.; Pisa, S.; van Liempd, B.; Torfs, T. 2-D Localization, Angular Separation and Vital Signs Monitoring Using a SISO FMCW Radar for Smart Long-Term Health Monitoring Environments. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 11065–11077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuri, M.; Lu, Y.; Polito, S.; Wieringa, F.; Liu, Y.-H.; van der Veen, A.-J.; Van Hoof, C.; Torfs, T. Enabling Robust Radar-Based Localization and Vital Signs Monitoring in Multipath Propagation Environments. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 68, 3228–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zeng, X.; Wu, C.; Wang, B.; Liu, K.J.R. mmHRV: Contactless Heart Rate Variability Monitoring Using Millimeter-Wave Radio. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 16623–16636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Zou, Y.; Gu, M. A spectrum estimation approach for accurate heartbeat detection using Doppler radar based on combination of FTPR and TWV. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2022, 2022, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, B.; Gouveia, C.; Albuquerque, D.; Pinho, P. Impact and Classification of Body Stature and Physiological Variability in the Acquisition of Vital Signs Using Continuous Wave Radar. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Huang, R.; Qi, A.; Ma, M.; Qi, Y. Enhancing Road Safety: Fast and Accurate Noncontact Driver HRV Detection Based on Huber–Kalman and Autocorrelation Algorithms. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, M.; Han, K.; Hong, S. Multiple Human Heart Rate Variability Detection Using MIMO FMCW Radar With Differential Beam Techniques. IEEE Trans. Radar Syst. 2023, 1, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malešević, N.; Petrović, V.; Belić, M.; Antfolk, C.; Mihajlović, V.; Janković, M. Contactless Real-Time Heartbeat Detection via 24 GHz Continuous-Wave Doppler Radar Using Artificial Neural Networks. Sensors 2020, 20, 2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, S.; Zhao, L.; Mohan, M.P.; Jimeno, J.; Siyal, M.Y.; Alphones, A.; Karim, M.F. mm-Wave Radar-Based Vital Signs Monitoring and Arrhythmia Detection Using Machine Learning. Sensors 2022, 22, 3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Fan, S.; Deng, Z.; Pan, P. Heart Rate Variability Monitoring Based on Doppler Radar Using Deep Learning. Sensors 2024, 24, 2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lin, F. Noncontact Accurate Measurement of Cardiopulmonary Activity Using a Compact Quadrature Doppler Radar Sensor. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 61, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, G.; Singh, M. Three-dimensional reconstruction of cardiac displacement patterns on the chest wall during the P, QRS and T-segments of the ECG by laser speckle inteferometry. Med Biol. Eng. Comput. 1989, 27, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, A.E.; Welkenhuysen, L.; Montald j Wolf, L.; Geivers, H.; Minten, J.; Kesteloot, H.; Geest, H. Laser method for re-cording displacement of the heart and chest wall. J. Biomed. Eng. 1984, 6, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albanese, A.; Cheng, L.; Ursino, M.; Chbat, N.W. An integrated mathematical model of the human cardiopulmonary system: Model development. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2016, 310, H899–H921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwata, Y.; Thanh, H.T.; Sun, G.; Ishibashi, K. High Accuracy Heartbeat Detection from CW-Doppler Radar Using Singular Value Decomposition and Matched Filter. Sensors 2021, 21, 3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Vital Signal | Frequency | Amplitude |
|---|---|---|
| Breathing Rate (Adults) | 0.1–0.5 Hz | ~1–12 mm |
| Heart Rate (Adults) | 0.8–2.0 Hz | ~0.01–0.2 mm |
| Metrics | Methods | User ID | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |||
| Mean IBI | Value (ms) | ECG | 838.24 | 744.74 | 720.79 | 764.07 | 592.71 | 751.42 |
| DEBF | 846.25 | 760.11 | 711.89 | 857.55 | 591.30 | 754.49 | ||
| mmHRV | 850.09 | 774.11 | 737.20 | 856.58 | 599.05 | 754.29 | ||
| Ours | 842.56 | 744.31 | 711.56 | 812.39 | 592.01 | 753.20 | ||
| Error (ms) | DEBF | 8.01 | 15.37 | 8.90 | 93.49 | 1.41 | 3.07 | |
| mmHRV | 11.85 | 29.37 | 16.41 | 92.51 | 6.34 | 2.87 | ||
| Ours | 4.33 | 0.43 | 9.23 | 48.32 | 0.70 | 1.78 | ||
| SDRR | Value (ms) | ECG | 31.06 | 37.58 | 24.65 | 21.14 | 7.67 | 27.81 |
| DEBF | 62.64 | 62.81 | 51.02 | 103.76 | 33.22 | 38.73 | ||
| mmHRV | 49.22 | 84.10 | 69.81 | 72.56 | 46.19 | 32.11 | ||
| Ours | 26.60 | 10.36 | 34.01 | 84.82 | 26.43 | 25.41 | ||
| Error (ms) | DEBF | 31.58 | 25.22 | 26.37 | 82.62 | 25.54 | 10.92 | |
| mmHRV | 18.16 | 46.51 | 45.16 | 51.42 | 38.52 | 4.30 | ||
| Ours | 4.46 | 27.22 | 9.36 | 63.68 | 18.76 | 2.40 | ||
| RMSSD | Value (ms) | ECG | 30.79 | 22.19 | 12.46 | 21.25 | 7.26 | 25.89 |
| DEBF | 73.09 | 63.52 | 49.69 | 137.34 | 29.11 | 29.99 | ||
| mmHRV | 61.53 | 105.76 | 90.29 | 90.24 | 56.15 | 28.54 | ||
| Ours | 32.26 | 9.45 | 45.35 | 101.85 | 32.31 | 23.86 | ||
| Error (ms) | DEBF | 42.30 | 41.33 | 37.23 | 116.09 | 21.86 | 4.10 | |
| mmHRV | 30.74 | 83.57 | 77.83 | 69.00 | 48.90 | 2.65 | ||
| Ours | 1.47 | 12.74 | 32.89 | 80.60 | 25.05 | 2.03 | ||
| pNN50 | Value (ms) | ECG | 8.78 | 3.00 | 0.00 | 1.91 | 0.00 | 4.74 |
| DEBF | 12.38 | 13.72 | 16.42 | 29.29 | 6.12 | 5.83 | ||
| mmHRV | 18.24 | 13.50 | 16.91 | 24.22 | 8.83 | 4.49 | ||
| Ours | 8.70 | 0.00 | 7.31 | 23.24 | 1.52 | 5.77 | ||
| Error (ms) | DEBF | 3.61 | 10.72 | 16.42 | 27.39 | 6.12 | 1.09 | |
| mmHRV | 9.47 | 10.50 | 16.91 | 22.32 | 8.83 | 0.25 | ||
| Ours | 0.08 | 3.00 | 7.31 | 21.34 | 1.52 | 1.03 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q. Non-Contact Heart Rate Variability Monitoring with FMCW Radar via a Novel Signal Processing Algorithm. Sensors 2025, 25, 5607. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175607
Cui G, Wang Y, Zhang X, Li J, Liu X, Li B, Wang J, Zhang Q. Non-Contact Heart Rate Variability Monitoring with FMCW Radar via a Novel Signal Processing Algorithm. Sensors. 2025; 25(17):5607. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175607
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Guangyu, Yujie Wang, Xinyi Zhang, Jiale Li, Xinfeng Liu, Bijie Li, Jiayi Wang, and Quan Zhang. 2025. "Non-Contact Heart Rate Variability Monitoring with FMCW Radar via a Novel Signal Processing Algorithm" Sensors 25, no. 17: 5607. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175607
APA StyleCui, G., Wang, Y., Zhang, X., Li, J., Liu, X., Li, B., Wang, J., & Zhang, Q. (2025). Non-Contact Heart Rate Variability Monitoring with FMCW Radar via a Novel Signal Processing Algorithm. Sensors, 25(17), 5607. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175607






