A Dual-Modality CNN Approach for RSS-Based Indoor Positioning Using Spatial and Frequency Fingerprints
Abstract
1. Introduction
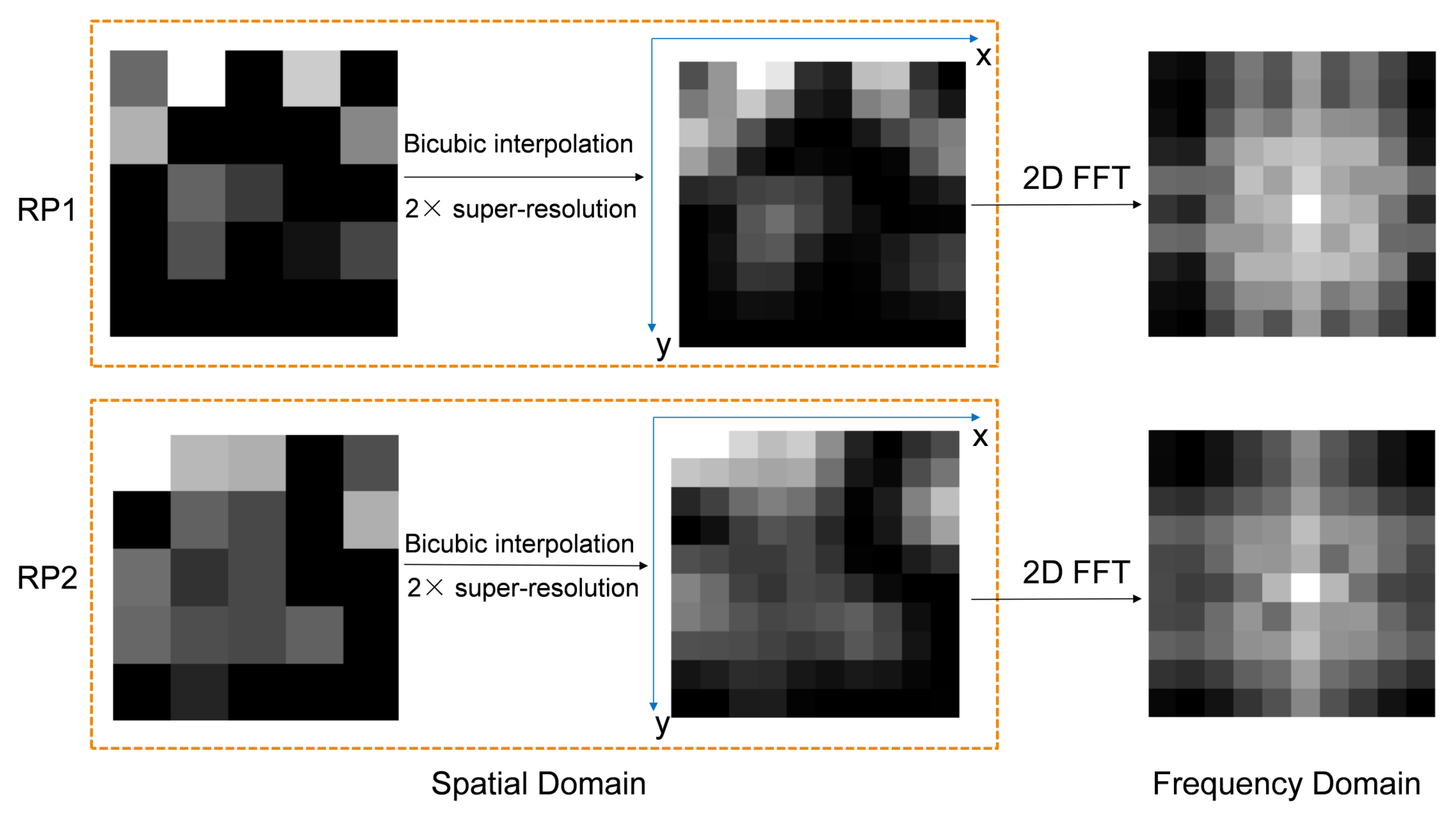
- The RSS sequence of each RP is converted into 2D spatial fingerprint images together with its frequency domain fingerprint images through the 2D FFT, thus creating two modalities’ fingerprint information of each RP.
- Bicubic interpolation is introduced to reconstruct higher-resolution fingerprint images with more detailed features through 2× super-resolution.
- An innovative cross-modality deep learning model for 3D indoor positioning is proposed. Our model utilizes spatial fingerprint and frequency domain fingerprint for cross-modality fusion and joint prediction and combines the advanced efficient multi-scale attention (EMA) module.
- Experimentation evaluations are performed in seven publicly available datasets. The results validate that our cross-modality deep learning method significantly enhances positioning accuracy and robustness.
2. Methods
2.1. Data Preprocessing
2.2. Bicubic Interpolation
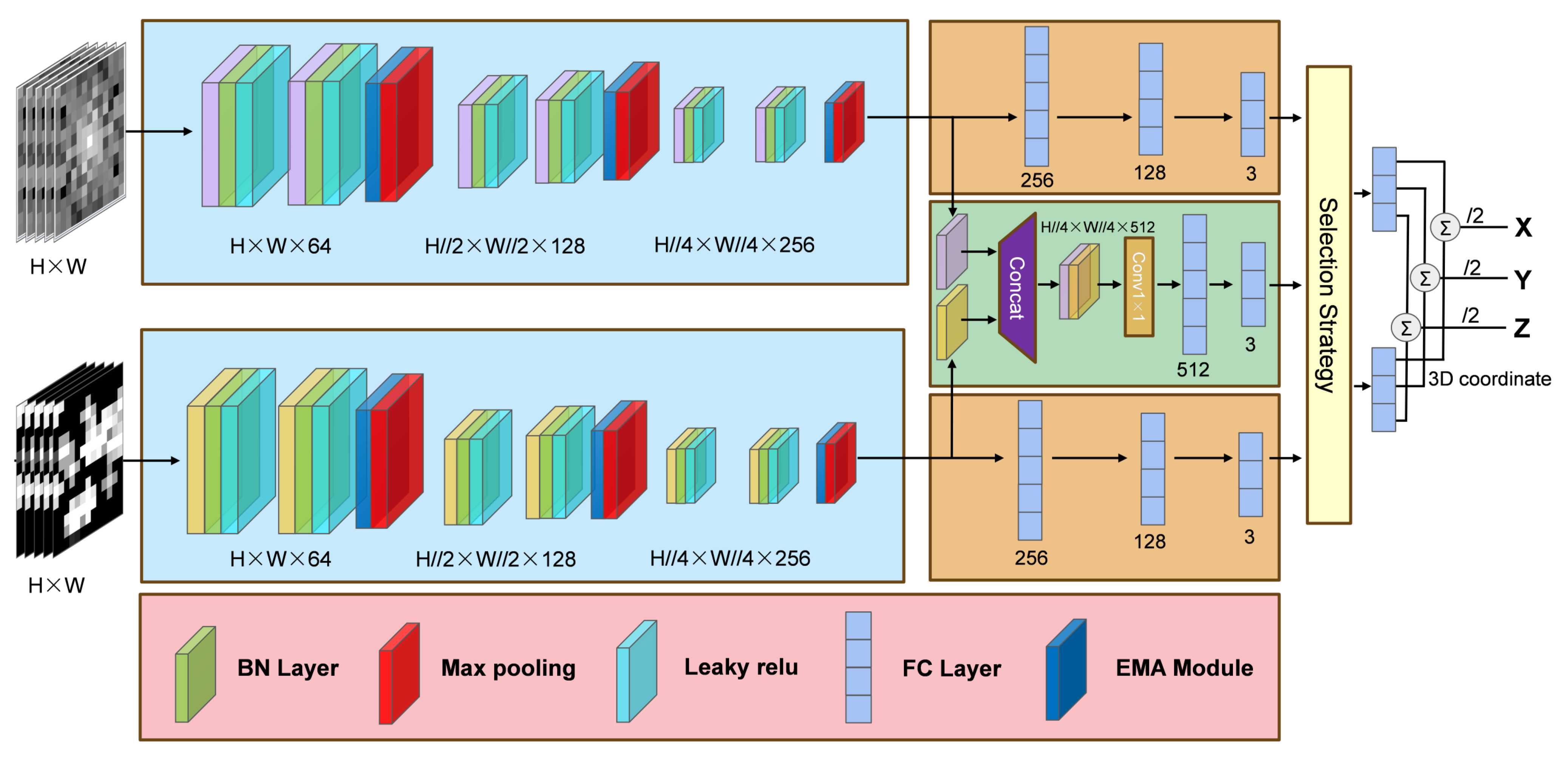
2.3. Deep Learning Model
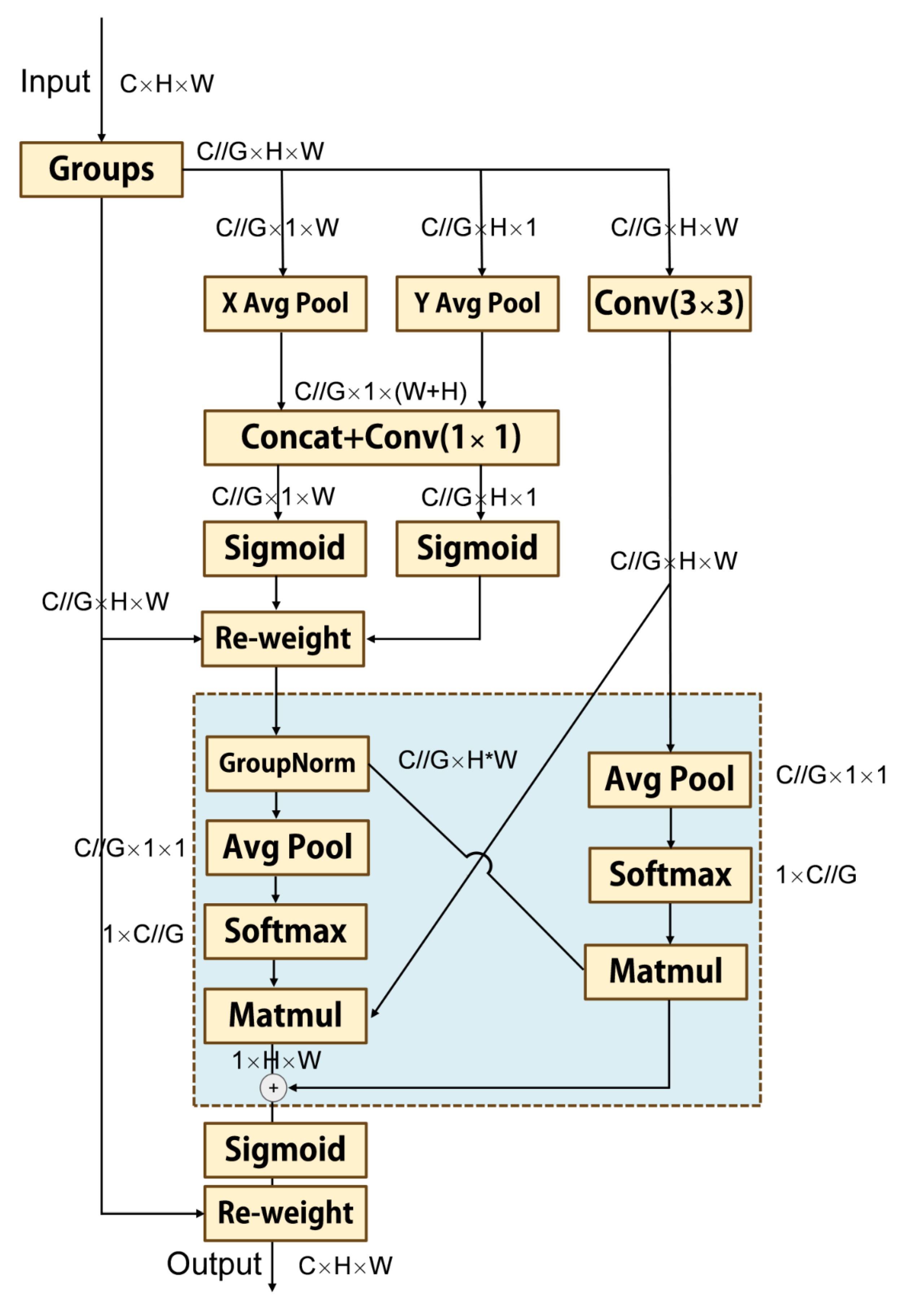
2.3.1. EMA Module
2.3.2. Proposed Cross-Modality Model
3. Experiment Setup
3.1. Datasets and Evaluation Metrics
3.2. Considered Benchmark Solutions
3.3. Implementation Details
4. Results and Discussion
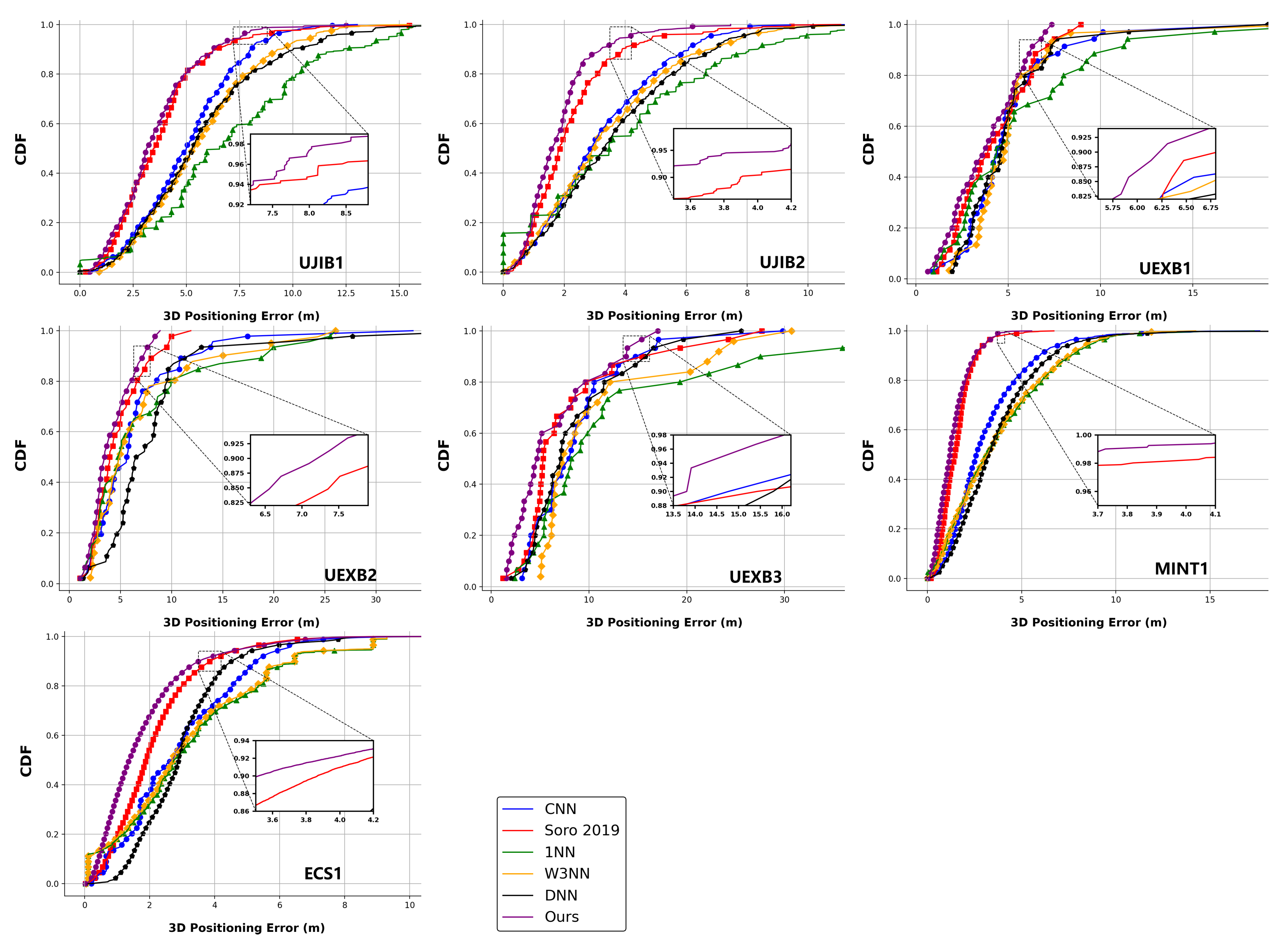
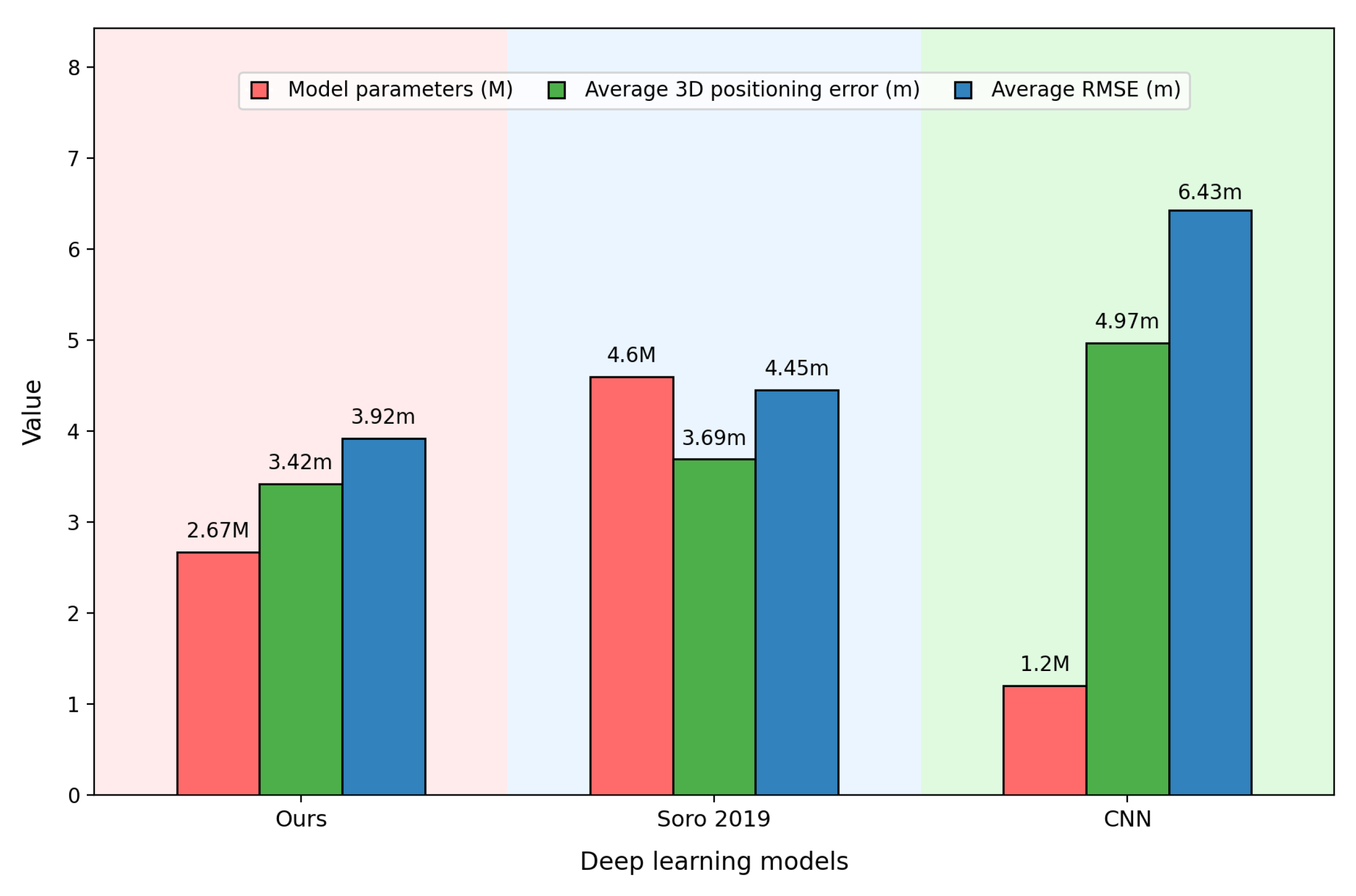
4.1. Models Performance
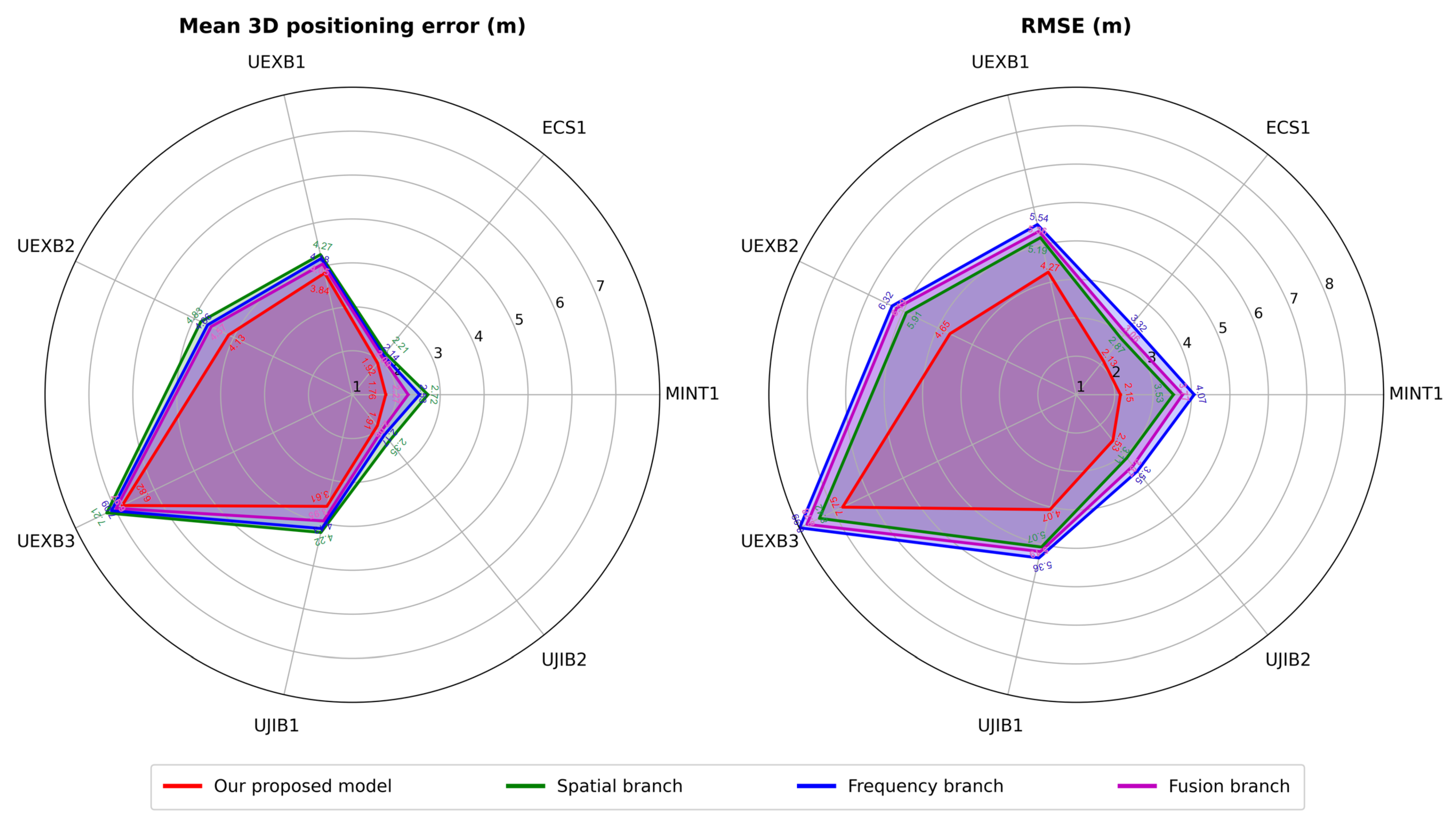
4.2. Modalities Performance
4.3. Ablation Experiment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gu, F.; Valaee, S.; Khoshelham, K.; Shang, J.; Zhang, R. Landmark Graph-Based Indoor Localization. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 8343–8355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J. Indoor Localization System Using Dual-Frequency Bands and Interpolation Algorithm. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 11183–11194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikonowicz, J.; Mahmood, A.; Ashraf, M.I.; Björnson, E.; Gidlund, M. Indoor Positioning in 5G-Advanced: Challenges and Solution Toward Centimeter-Level Accuracy with Carrier Phase Enhancements. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2024, 31, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, T.; Koo, I. A Comprehensive Review of Indoor Localization Techniques and Applications in Various Sectors. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitch, S.G.; Ahmed, Q.Z.; Abbas, W.B.; Hafeez, M.; Laziridis, P.I.; Sureephong, P.; Alade, T. On Indoor Localization Using WiFi, BLE, UWB, and IMU Technologies. Sensors 2023, 23, 8598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiglao, N.M.; Alipio, M.; Dela Cruz, R.; Bokhari, F.; Rauf, S.; Khan, S.A. Smartphone-based indoor localization techniques: State-of-the-art and classification. Measurement 2021, 179, 109349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahl, P.; Padmanabhan, V.N. RADAR: An in-building RF-based user location and tracking system. In Proceedings of the 19th Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications Societies, Tel Aviv, Israel, 26–30 March 2000; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2000; Volume 2, pp. 775–784. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Liu, J.; Yin, Y.; Wang, W.; Hu, D.; Chen, P.; Niu, Q. Survey on WiFi-Based Indoor Positioning Techniques. IET Commun. 2020, 14, 1372–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.; Kim, D.; Lee, J.; Moon, S.; Chu, M.; Bae, S.; You, C.; Liu, H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, D.J.; et al. Performance Analysis of 3D Localization for a Launch Vehicle Using TOA AOA and TDOA. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2018, 103, 1443–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, B.; Li, C. A Feature-Scaling-Based k-Nearest Neighbor Algorithm for Indoor Positioning Systems. IEEE Internet Things J. 2015, 3, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.A.; Boskany, N.W.; Ghafoor, K.Z.; Rawat, D.B. Wi-Fi Based Accurate Indoor Localization System Using SVM and LSTM Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 22nd International Conference on Information Reuse and Integration for Data Science (IRI), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 10–12 August 2021; pp. 416–422. [Google Scholar]
- Njima, W.; Bazzi, A.; Chafii, M. DNN-Based Indoor Localization Under Limited Dataset Using GANs and Semi-Supervised Learning. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 9812625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klus, R.; Talvitie, J.; Torres-Sospedra, J.; Quezada Gaibor, D.P.; Casteleyn, S.; Cabric, D.; Valkama, M. C2R: A Novel ANN Architecture for Boosting Indoor Positioning With Scarce Data. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 32868–32882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Engelmann, F.; Vysotska, O.; Pollefeys, M.; Baráth, D.B. SceneGraphLoc: Cross-Modality Coarse Visual Localization on 3D Scene Graphs. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2024; Leonardis, A., Ricci, E., Roth, S., Russakovsky, O., Varol, G., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 15066, pp. 127–150. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Lv, X. FSTNet: Learning spatial–temporal correlations from fingerprints for indoor positioning. Ad Hoc Netw. 2023, 149, 103244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alitaleshi, A.; Jazayeriy, H.; Kazemitabar, J. EA-CNN: A smart indoor 3D positioning scheme based on Wi-Fi fingerprinting and deep learning. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 117, 105509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Cheng, L.; Li, X.; Yuan, H. Neural-Network-Based Localization Method for Wi-Fi Fingerprint Indoor Localization. Sensors 2023, 23, 6992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.S.; Hwang, S.-H. Comparison of CNN Applications for RSSI-Based Fingerprint Indoor Localization. Electronics 2019, 8, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Wei, E.; Yang, L.; Xu, S. Improving Fingerprint Indoor Localization Using Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 193396–193411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.K.; Luo, B.Q. Hybrid Fingerprint Indoor Localization Method Based on ECA-CNN. J. Comput. Res. Dev. 2024, 61, 428–440. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Gao, L.; Mao, S. BiLoc: Bi-Modal Deep Learning for Indoor Localization With Commodity 5GHz WiFi. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 4209–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, U.M.; Umer, Z.; Hancke, G. Indoor Localization Using Wireless Fidelity (WiFi) and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) Signals. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 28th International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 12–14 June 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Monica, S.; Bergenti, F. Hybrid Indoor Localization Using WiFi and UWB Technologies. Electronics 2019, 8, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.H.; Tsaur, W.-J. FFK: Fourier-Transform Fuzzy-c-means Kalman-Filter Based RSSI Filtering Mechanism for Indoor Positioning. Sensors 2023, 23, 8274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soro, B.; Lee, C. A Wavelet Scattering Feature Extraction Approach for Deep Neural Network Based Indoor Fingerprinting Localization. Sensors 2019, 19, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soro, B.; Lee, C. Joint Time-Frequency RSSI Features for Convolutional Neural Network-Based Indoor Fingerprinting Localization. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 104892–104899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.; Lin, E.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J. An energy-efficient image filtering interpolation algorithm using domain-specific dynamic reconfigurable array processor. Integration 2024, 96, 102167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, T.; Xu, Y.; Jarhinbek, R. Detail texture detection based on Yolov4-tiny combined with attention mechanism and bicubic interpolation. IET Image Process. 2021, 15, 2736–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Xu, Z.H.; Lukasiewicz, T. A general survey on medical image super-resolution via deep learning. Comput. Biol. Med. 2025, 193, 110345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Silva, M.; Matey-Sanz, M.; Torres-Sospedra, J.; Huerta, J. BLE RSS measurements dataset for research on accurate indoor positioning. Data 2019, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, F.J.; Parralejo, F.; Álvarez, F.J.; Torres-Sospedra, J. Multi-slot BLE raw database for accurate positioning in mixed indoor/outdoor environments. Data 2020, 5, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.; Nicolau, M.J.; Silva, I.; Torres-Sospedra, J.; Pendão, C.; Meneses, F. Wi-Fi Fingerprinting Dataset with Multiple Simultaneous Interfaces (1.0) [Data Set]; Zenodo: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, B.; Bie, Y.; Cairns, D.; Harper, G.; Xu, J.; Chang, C.; Dong, X.; Lu, T. Wi-Fi and Bluetooth contact tracing without user intervention. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 91027–91044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, D.; He, S.; Zhang, G.; Luo, M.; Guo, H.; Zhan, J.; Huang, Z. Efficient Multi-Scale Attention Module with Cross-Spatial Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 4–10 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, I.; Kim, H.; Park, S.; Kim, H. Image retrieval using BIM and features from pretrained VGG network for indoor localization. Build. Environ. 2018, 140, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Le, D.V. Completely Automated CNN Architecture Design Based on VGG Blocks for Fingerprinting Localisation. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Lloret de Mar, Spain, 29 November–2 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Wang, N.; Chen, T.; Li, M. Empirical Evaluation of Rectified Activations in Convolution Network. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.00853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Sospedra, J.; Richter, P.; Moreira, A.; Mendoza-Silva, G.M.; Lohan, E.S.; Trilles, S.; Matey-Sanz, M.; Huerta, J. A Comprehensive and Reproducible Comparison of Clustering and Optimization Rules in Wi-Fi Fingerprinting. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2022, 21, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Yi, X.; Wang, W.; You, L.; Huang, Q.; Gao, X.; Liu, Q. Learning to Localize: A 3D CNN Approach to User Positioning in Massive MIMO-OFDM Systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 20, 4556–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Yang, F.; Cui, N.; Xiong, K.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y. A Federated Learning Framework for Fingerprinting-Based Indoor Localization in Multibuilding and Multifloor Environments. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 2615–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Dataset | Image Size (Before Interpolation) | Image Size (After Interpolation) |
|---|---|---|
| UJIB1 [30] | 5 × 5 | 10 × 10 |
| UJIB2 [30] | 5 × 5 | 10 × 10 |
| UEXB1 [31] | 6 × 6 | 12 × 12 |
| UEXB2 [31] | 6 × 6 | 12 × 12 |
| UEXB3 [31] | 6 × 6 | 12 × 12 |
| MINT1 [32] | 4 × 4 | 8 × 8 |
| ECS1 [33] | 4 × 4 | 8 × 8 |
| Dataset | Area [] | Technology | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UJIB1 [30] | 1680 | 420 | 24 | 151 | BLE |
| UJIB2 [30] | 2121 | 531 | 22 | 176 | BLE |
| UEXB1 [31] | 139 | 34 | 30 | 1000 | BLE |
| UEXB2 [31] | 184 | 46 | 30 | 1800 | BLE |
| UEXB3 [31] | 120 | 30 | 30 | 5800 | BLE |
| MINT1 [32] | 4973 | 810 | 11 | 1000 | WIFI |
| ECS1 [33] | 176,380 | 35,626 | 16 | 324 | WIFI |
| Mean 3D Error (m) | Ours | [26] | CNN | DNN | 1NN | W3NN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UJIB1 [30] | 3.61 | 3.79 | 5.04 | 5.71 | 6.97 | 5.59 |
| UJIB2 [30] | 1.91 | 2.24 | 3.21 | 3.63 | 3.90 | 3.45 |
| UEXB1 [31] | 3.84 | 4.19 | 5.07 | 5.03 | 5.87 | 4.70 |
| UEXB2 [31] | 4.13 | 4.62 | 6.55 | 8.39 | 7.46 | 6.51 |
| UEXB3 [31] | 6.82 | 6.93 | 8.76 | 8.86 | 12.89 | 10.33 |
| MINT1 [32] | 1.76 | 1.95 | 3.22 | 3.67 | 3.73 | 3.65 |
| ECS1 [33] | 1.92 | 2.08 | 2.95 | 3.12 | 3.33 | 3.23 |
| Average | 3.42 | 3.69 | 4.97 | 5.49 | 6.31 | 6.18 |
| RMSE (m) | Ours | [26] | CNN | DNN | 1NN | W3NN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UJIB1 [30] | 4.07 | 5.00 | 5.65 | 6.44 | 7.99 | 6.23 |
| UJIB2 [30] | 2.53 | 2.71 | 3.52 | 3.91 | 4.67 | 3.89 |
| UEXB1 [31] | 4.27 | 4.95 | 5.91 | 5.93 | 7.33 | 5.81 |
| UEXB2 [31] | 4.65 | 5.43 | 8.49 | 10.72 | 9.92 | 8.74 |
| UEXB3 [31] | 7.75 | 8.11 | 10.39 | 10.26 | 17.00 | 13.11 |
| MINT1 [32] | 2.15 | 2.38 | 3.73 | 4.07 | 4.63 | 4.50 |
| ECS1 [33] | 2.13 | 2.51 | 3.38 | 3.77 | 4.07 | 3.99 |
| Average | 3.92 | 4.45 | 6.43 | 6.44 | 7.94 | 7.53 |
| Dataset | Bicubic | EMA | Mean 3D Error (m) | Gain | RMSE (m) | Gain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MINT1 [32] | 2.66 | 3.39 | ||||
| ECS1 [33] | 2.49 | 2.81 | ||||
| UEXB1 [31] | 4.45 | 5.12 | ||||
| UEXB2 [31] | 5.65 | 6.57 | ||||
| UEXB3 [31] | 7.98 | 9.12 | ||||
| UJIB1 [30] | 4.42 | 4.96 | ||||
| UJIB2 [30] | 2.58 | 3.22 | ||||
| Average | 4.32 | 5.03 | ||||
| MINT1 [32] | ✓ | 2.57 | 3.4% | 3.32 | 2.1% | |
| ECS1 [33] | ✓ | 2.41 | 3.2% | 2.73 | 2.8% | |
| UEXB1 [31] | ✓ | 4.35 | 2.24% | 5.09 | 0.59% | |
| UEXB2 [31] | ✓ | 5.21 | 7.80% | 6.12 | 6.84% | |
| UEXB3 [31] | ✓ | 7.66 | 4.00% | 8.79 | 3.60% | |
| UJIB1 [30] | ✓ | 4.35 | 1.60% | 4.91 | 1.00% | |
| UJIB2 [30] | ✓ | 2.52 | 2.30% | 3.15 | 2.17% | |
| Average | 4.15 | 3.51% | 4.87 | 2.73% | ||
| MINT1 [32] | ✓ | 2.02 | 24.10% | 2.57 | 22.59% | |
| ECS1 [33] | ✓ | 2.17 | 12.85% | 2.45 | 12.81% | |
| UEXB1 [31] | ✓ | 4.05 | 8.98% | 4.65 | 9.11% | |
| UEXB2 [31] | ✓ | 4.86 | 13.98% | 5.69 | 13.39% | |
| UEXB3 [31] | ✓ | 7.19 | 9.89% | 8.23 | 9.75% | |
| UJIB1 [30] | ✓ | 3.97 | 10.18% | 4.42 | 10.88% | |
| UJIB2 [30] | ✓ | 2.23 | 13.56% | 2.89 | 10.25% | |
| Average | 3.75 | 13.36% | 4.42 | 12.68% | ||
| MINT1 [32] | ✓ | ✓ | 1.76 | 33.83% | 2.15 | 36.6% |
| ECS1 [33] | ✓ | ✓ | 1.92 | 22.90% | 2.13 | 22.00% |
| UEXB1 [31] | ✓ | ✓ | 3.84 | 13.70% | 4.27 | 16.60% |
| UEXB2 [31] | ✓ | ✓ | 4.13 | 26.90% | 4.65 | 29.20% |
| UEXB3 [31] | ✓ | ✓ | 6.82 | 14.50% | 7.75 | 14.40% |
| UJIB1 [30] | ✓ | ✓ | 3.61 | 18.30% | 4.07 | 17.90% |
| UJIB2 [30] | ✓ | ✓ | 1.91 | 30.00% | 2.53 | 21.39% |
| Average | 3.42 | 22.88% | 3.92 | 22.58% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, X.; Luo, Y.; Jia, Y. A Dual-Modality CNN Approach for RSS-Based Indoor Positioning Using Spatial and Frequency Fingerprints. Sensors 2025, 25, 5408. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175408
Lai X, Luo Y, Jia Y. A Dual-Modality CNN Approach for RSS-Based Indoor Positioning Using Spatial and Frequency Fingerprints. Sensors. 2025; 25(17):5408. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175408
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Xiangchen, Yunzhi Luo, and Yong Jia. 2025. "A Dual-Modality CNN Approach for RSS-Based Indoor Positioning Using Spatial and Frequency Fingerprints" Sensors 25, no. 17: 5408. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175408
APA StyleLai, X., Luo, Y., & Jia, Y. (2025). A Dual-Modality CNN Approach for RSS-Based Indoor Positioning Using Spatial and Frequency Fingerprints. Sensors, 25(17), 5408. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175408





