ECG Biometrics via Dual-Level Features with Collaborative Embedding and Dimensional Attention Weight Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a novel framework to effectively learn the discriminative latent representation space for ECG biometrics. Our framework mainly has three parts: dual-level feature collaborative embedding, dimensional attention weight learning, and projection learning.
- To solve the overall objective loss, we propose an effective and efficient algorithm for optimization.
2. Related Works
3. Methodology
3.1. Problem Definition and Notation
3.2. Dual-Level Feature Collaborative Embedding
3.3. Dimensional Attention Weight Learning
3.4. Projection Matrix Learning
3.5. Overall Objective Loss
3.6. Optimization
| Algorithm 1 The proposed optimization algorithm |
| Input: dual-level features and ; ; parameters , , , , , and the total iteration number T. Output: projection matrices and . Main Algorithm: Randomly initialize variables. while not converged or not reaching the max iterations do Learn sub-problem with (6). Learn sub-problem with (8). Learn sub-problem with (10). Learn sub-problem with (12). Learn sub-problem with (14). Learn sub-problem with (18). end while |
3.7. Complexity Analysis
3.8. Matching Process
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Settings
Signal Preprocessing and Dual-Level Features Extraction
4.2. Comparisons with State-of-the-Art Methods
4.3. Ablation Experiments
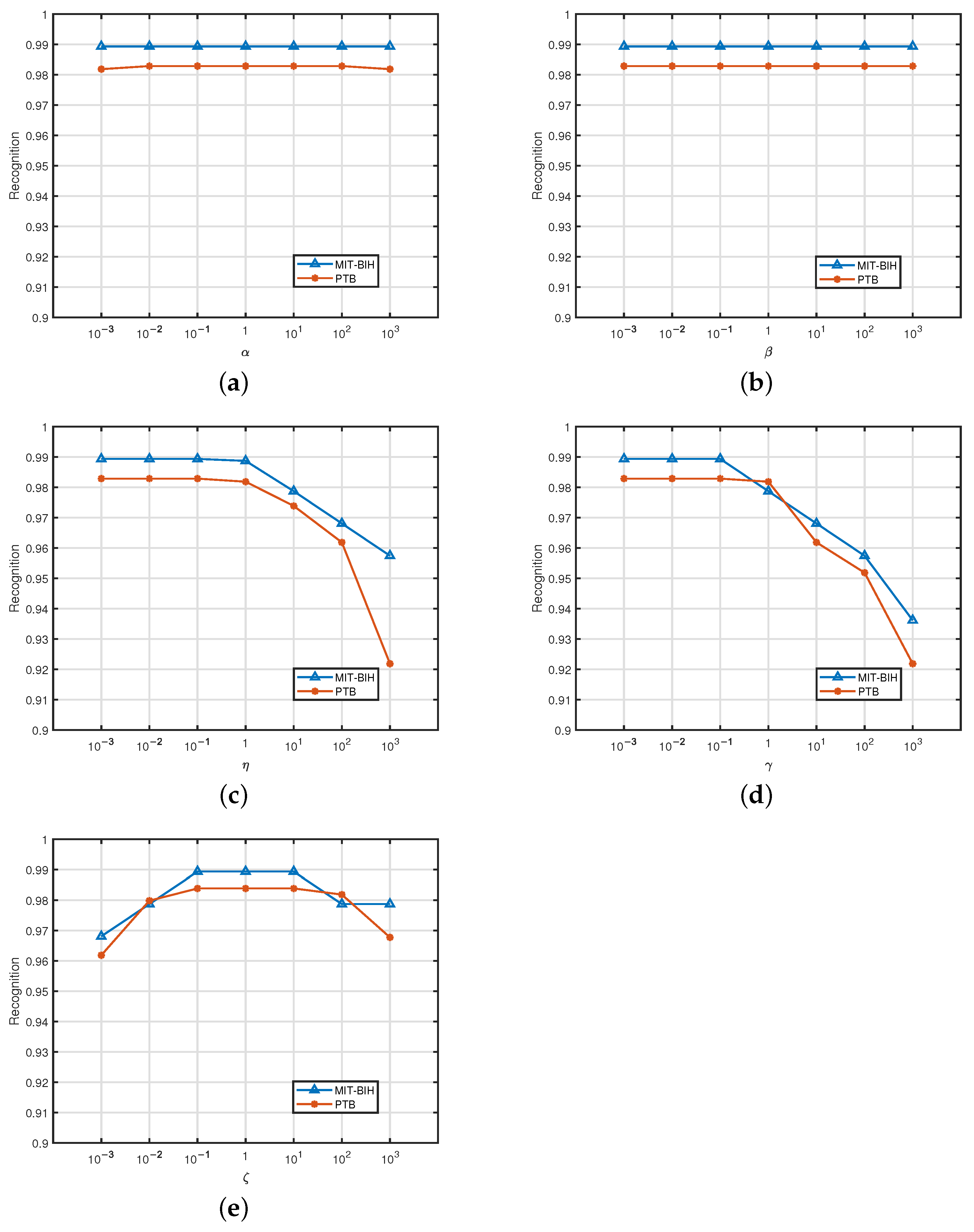
4.4. Parameter Sensitivity
4.5. Comparison with Multi-Feature Biometrics Methods
4.6. Convergence Analysis
4.7. Time–Cost Analysis
4.8. Further Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Biran, A.; Jeremic, A. ECG bio-identification using fréchet classifiers: A proposed methodology based on modeling the dynamic change of the ECG features. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 82, 104575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekhar, V.; Singh, P.; Paralkar, M.; Tonguz, O.K. Pulse ID: The case for robustness of ECG as a biometric identifier. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop on Machine Learning for Signal Processing, MLSP 2020, Espoo, Finland, 21–24 September 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Uwaechia, A.N.; Ramli, D.A. A comprehensive survey on ECG signals as new biometric modality for human authentication: Recent advances and future challenges. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 97760–97802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böck, C.; Kovács, P.; Laguna, P.; Meier, J.; Huemer, M. ECG beat representation and delineation by means of variable projection. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 68, 2997–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, T.M.C.; Conceição, R.C.; Sencadas, V.; Sebastixaxo, R. Biometric recognition: A systematic review on electrocardiogram data acquisition methods. Sensors 2023, 23, 1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorvillo, R.; Bacco, L.; Merone, M.; Zompanti, A.; Santonico, M.; Pennazza, G.; Iannello, G. Single beat ecg-based identification system: Development and robustness test in different working conditions. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Industry, Rome, Italy, 7–9 June 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 538–543. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, J.R.; Cardoso, J.S.; Lourenço, A.; Carreiras, C. Towards a continuous biometric system based on ECG signals acquired on the steering wheel. Sensors 2017, 17, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komeili, M.; Louis, W.; Armanfard, N.; Hatzinakos, D. Feature selection for nonstationary data: Application to human recognition using medical biometrics. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2018, 48, 1446–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alotaiby, T.N.; Alrshoud, S.R.; Alshebeili, S.A.; Aljafar, L.M. Ecg-based subject identification using statistical features and random forest. J. Sens. 2019, 2019, 6751932:1–6751932:13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Fang, B.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.-B.; Teng, Y.; Fortino, G. Emcnet: Ensemble multiscale convolutional neural network for single-lead ecg classification in wearable devices. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 8754–8762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byeon, Y.-H.; Pan, S.-B.; Kwak, K.-C. Intelligent deep models based on scalograms of electrocardiogram signals for biometrics. Sensors 2019, 19, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, K.; Yin, Y. Multi-view discriminant analysis with sample diversity for ECG biometric recognition. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2021, 145, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Patel, V.M.; Chellappa, R. Low-rank and joint sparse representations for multi-modal recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 4741–4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yang, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, F. Robust multi-view features fusion method based on cnmf. In Neural Information Processing: 25th International Conference, ICONIP 2018, Siem Reap, Cambodia, 13–16 December 2018, Proceedings, Part IV 25; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 27–39. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, K.; Liu, H.; Yin, Y. Learning joint and specific patterns: A unified sparse representation for off-the-person ECG biometric recognition. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2021, 16, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, K.; Liu, H.; Yin, Y. Robust multi-feature collective non-negative matrix factorization for ecg biometrics. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 123, 108376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türker, I.; Tan, S.O. Scientific impact of graph-based approaches in deep learning studies—A bibliometric comparison. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.07343. [Google Scholar]
- D’angelis, O.; Bacco, L.; Vollero, L.; Merone, M. Advancing ecg biometrics through vision transformers: A confidence-driven approach. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 140710–140721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga-Falconi, J.S.; Al Osman, H.; El Saddik, A. Ecg authentication for mobile devices. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas 2015, 65, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, A.; Rosário, D.; Resque, P.; Cerqueira, E. Heart of iot: ECG as biometric sign for authentication and identification. In Proceedings of the 2019 15th International Wireless Communications & Mobile Computing Conference (IWCMC), Tangier, Morocco, 24–28 June 2019; pp. 307–312. [Google Scholar]
- Fatimah, B.; Singh, P.; Singhal, A.; Pachori, R.B. Biometric identification from ecg signals using fourier decomposition and machine learning. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yang, G.; Huang, Y.; Yin, Y. Multi-scale differential feature for ECG biometrics with collective matrix factorization. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 102, 107211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yang, G.; Wang, K.; Huang, Y.; Yuan, F.; Yin, Y. Robust ECG biometrics using GNMF and sparse representation. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 129, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumbarov, O.; Velchev, Y.; Tonchev, K.; Paliy, I.; Chetty, G. Face and ecg based multi-modal biometric authentication. In Advanced Biometric Technologies; InTech: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hammad, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, K. Multimodal biometric authentication systems using convolution neural network based on different level fusion of ecg and fingerprint. IEEE Access 2018, 7, 26527–26542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashar, K. Ecg and eeg based multimodal biometrics for human identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Miyazaki, Japan, 7–10 October 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 4345–4350. [Google Scholar]
- El-Rahiem, B.A.; El-Samie, F.E.A.; Amin, M. Multimodal biometric authentication based on deep fusion of electrocardiogram (ecg) and finger vein. Multimed. Syst. 2022, 28, 1325–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.A.; Sprecher, E.; Levy, K.Y.; Lange, D.H. DE-PADA: Personalized augmentation and domain adaptation for ECG biometrics across physiological states. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.04973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, P.; Si, Y.; Fan, W.; Zhang, Y. ECG biometrics based on attention enhanced domain adaptive feature fusion network. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 1291–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammour, N.; Jomaa, R.M.; Islam, M.S.; Bazi, Y.; Alhichri, H.; Alajlan, N. Deep contrastive learning-based model for ecg biometrics. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Kanduri, A.; Aqajari, S.A.H.; Jafarlou, S.; Mousavi, S.R.; Liljeberg, P.; Malik, S.; Rahmani, A.M. ECG unveiled: Analysis of client re-identification risks in real-world ECG datasets. In Proceedings of the 20th IEEE International Conference on Body Sensor Networks, BSN 2024, Chicago, IL, USA, 15–17 October 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Abdeldayem, S.S.; Bourlai, T. A novel approach for ecg-based human identification using spectral correlation and deep learning. IEEE Trans. Biom. Behav. Identity Sci. 2020, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincon-Melchor, V.; Nakano-Miyatake, M.; Juarez-Sandoval, O.; Olivares-Mercado, J.; Saenz, J.M.; Benitez-Garcia, G. Deep learning algorithm for the people identification using their ECG signals as a biometric parameter. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing, TSP 2023, Prague, Czech Republic, 12–14 July 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 154–159. [Google Scholar]
- Hazratifard, M.; Agrawal, V.; Gebali, F.; Elmiligi, H.; Mamun, M. Ensemble siamese network (esn) using ecg signals for human authentication in smart healthcare system. Sensors 2023, 23, 4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehir, H.; Hafs, T.; Daas, S. Empirical mode decomposition-based biometric identification using gru and lstm deep neural networks on ecg signals. Evol. Syst. 2024, 15, 2193–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Mu, C.; Kumar, S.; Chang, S. Discrete graph hashing. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 27: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2014, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; Ghahramani, Z., Welling, M., Cortes, C., Lawrence, N.D., Weinberger, K.Q., Eds.; Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation, Inc. (NeurIPS): Montreal, QC, Canada, 2014; pp. 3419–3427. [Google Scholar]
- Moody, G.; Mark, R. The impact of the mit-bih arrhythmia database. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2001, 20, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberger, A.L.; Amaral, L.A.; Glass, L.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Ivanov, P.C.; Mark, R.G.; Mietus, J.E.; Moody, G.B.; Peng, C.K.; Stanley, H.E. Physiobank, physiotoolkit, and physionet: Components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circulation 2000, 101, e215–e220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bousseljot, R.; Kreiseler, D.; Schnabel, A. Nutzung der ekg-signaldatenbank cardiodat der ptb über das internet. Biomed. Tech./Biomed. Eng. 1995, 40, 317–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Tompkins, W.J. A real-time qrs detection algorithm. T-BME 1985, 32, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassiouni, M.; Khaleefa, W.; El-Dahshan, E.; Salem, A.-B.M. A machine learning technique for person identification using ecg signals. Int. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 1, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Dar, M.N.; Akram, M.U.; Usman, A.; Khan, S.A. Ecg biometric identification for general population using multiresolution analysis of dwt based features. In Proceedings of the 2015 Second International Conference on Information Security and Cyber Forensics (InfoSec), Cape Town, South Africa, 15–17 November 2015; pp. 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, A.; Singh, Y.N. Ecg biometric recognition. In Mathematics and Computing; ICMC; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 61–73. [Google Scholar]
- Paiva, J.S.; Dias, D.; Cunha, J.P. Beat-id: Towards a computationally low-cost single heartbeat biometric identity check system based on electrocardiogram wave morphology. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Dataset | Method | Number of Subjects | Accuracy (%) | EER (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIT-BIH | [41] | 30 | 96.67 | 4.57 |
| [42] | 47 | 93.1 | 5.78 | |
| [22] | 47 | 94.68 | 2.73 | |
| [32] | 47 | 96.5 | 0.3 | |
| [35] | 47 | 98.57 | 0.73 | |
| ours | 47 | 98.94 | 0.87 |
| Dataset | Method | Number of Subjects | Accuracy (%) | EER (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTB | [43] | 100 | 97.1 | 2.88 |
| [44] | 10 | 97.5 | 4.58 | |
| [32] | 290 | 94.9 | 0.25 | |
| [34] | 290 | 96.8 | 1.69 | |
| [35] | 52 | 98.26 | 0.93 | |
| ours | 273 | 98.29 | 1.36 |
| Variant | MIT-BIH | PTB |
|---|---|---|
| CE-Ablation-1D | 89.36% | 86.08% |
| CE-Ablation-2D | 84.50% | 79.60% |
| DA-Ablation | 86.13% | 81.35% |
| PA-Ablation | 93.62% | 92.19% |
| Our method | 98.94% | 98.29% |
| Dataset | Method | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|
| MIT-BIH | [13] | 96.87 |
| [14] | 96.32 | |
| OURS | 98.94 | |
| PTB | [13] | 96.72 |
| [14] | 95.68 | |
| OURS | 98.29 |
| Method | Training | Preprocessing | Feature Extraction | Matching |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [16] | 0.143 | 0.001 | 0.009 | 0.004 |
| ours | 0.139 | 0.001 | 0.007 | 0.003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, K.; Wang, N. ECG Biometrics via Dual-Level Features with Collaborative Embedding and Dimensional Attention Weight Learning. Sensors 2025, 25, 5343. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175343
Wang K, Wang N. ECG Biometrics via Dual-Level Features with Collaborative Embedding and Dimensional Attention Weight Learning. Sensors. 2025; 25(17):5343. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175343
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Kuikui, and Na Wang. 2025. "ECG Biometrics via Dual-Level Features with Collaborative Embedding and Dimensional Attention Weight Learning" Sensors 25, no. 17: 5343. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175343
APA StyleWang, K., & Wang, N. (2025). ECG Biometrics via Dual-Level Features with Collaborative Embedding and Dimensional Attention Weight Learning. Sensors, 25(17), 5343. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175343









