A Style Transfer-Based Fast Image Quality Assessment Method for Image Sensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We pioneer an FR-IQA framework inspired by style transfer principles and define a novel deep perceptual distance metric that integrates both content and style features. This dual-component metric comprehensively quantifies distortions across spatial and semantic hierarchies through multilevel feature comparisons.
- We formulate a well-designed convex optimization problem to determine the parameters of the proposed SCIQA model. This optimization approach allows the model to learn from subjective quality assessments while maintaining computational efficiency.
- The proposed SCIQA model exhibits strong interpretability, exceptional prediction accuracy, and low time complexity. These properties make it suitable for a wide range of applications in image processing and computer vision.
2. Related Work
2.1. Traditional FR-IQA Methods
2.2. Deep Learning-Based FR-IQA
2.3. Emerging Trends and Our Position
2.4. Research Gap and Our Contribution
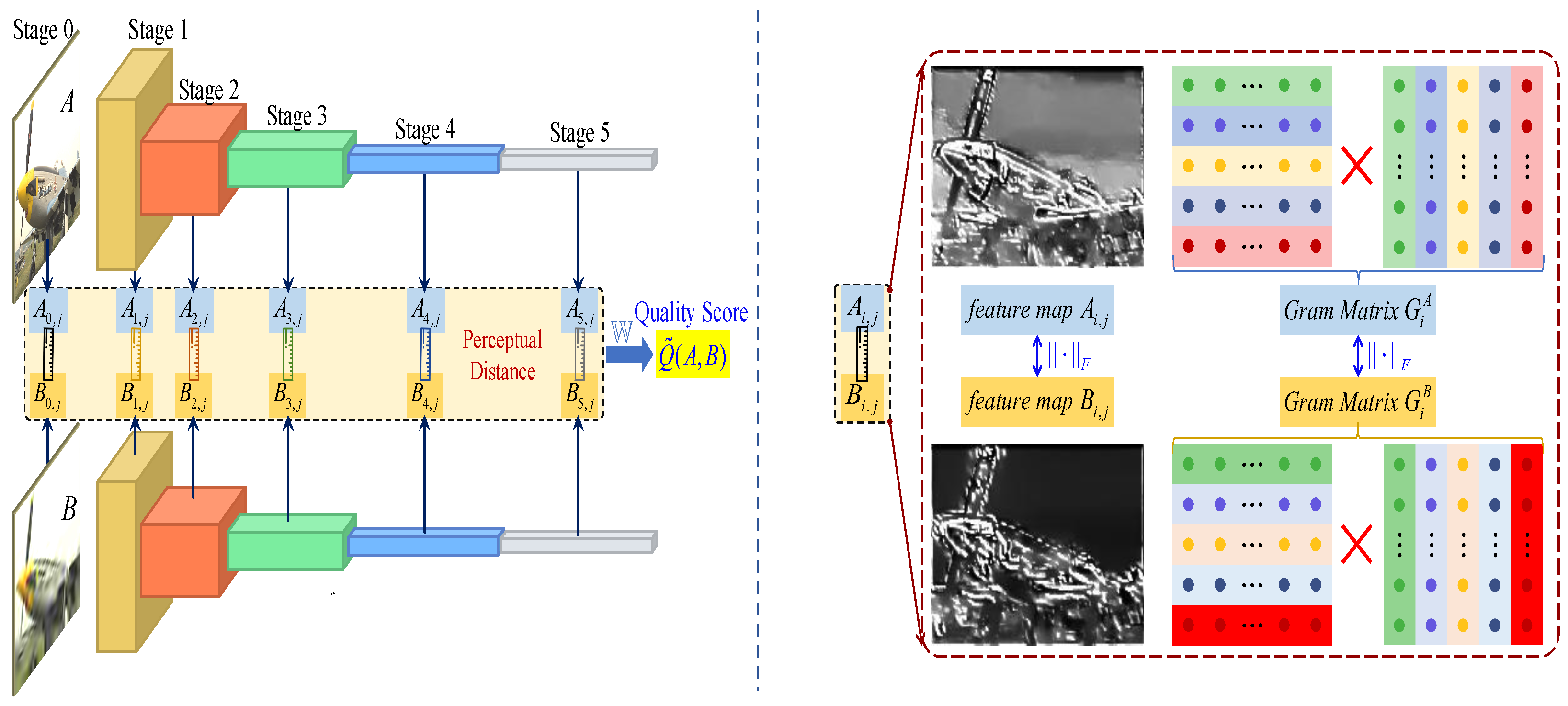
- Content Distance. Structural and semantic discrepancies are measured by computing the direct distance between feature maps.
- Style distance. Textural and stylistic differences are captured by calculating the distance between Gram matrices, which represent feature correlations.
3. Methodology
3.1. Framework
3.2. Perceptual Dissimilarity Metric
3.2.1. Hierarchical Feature Representation
3.2.2. Structural Content Preservation
3.2.3. Style Consistency Measurement
3.3. SCIQA Model Formulation
| Algorithm 1 The proposed SCIQA Model |
|
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Implementation Details
4.2. Performance Comparison
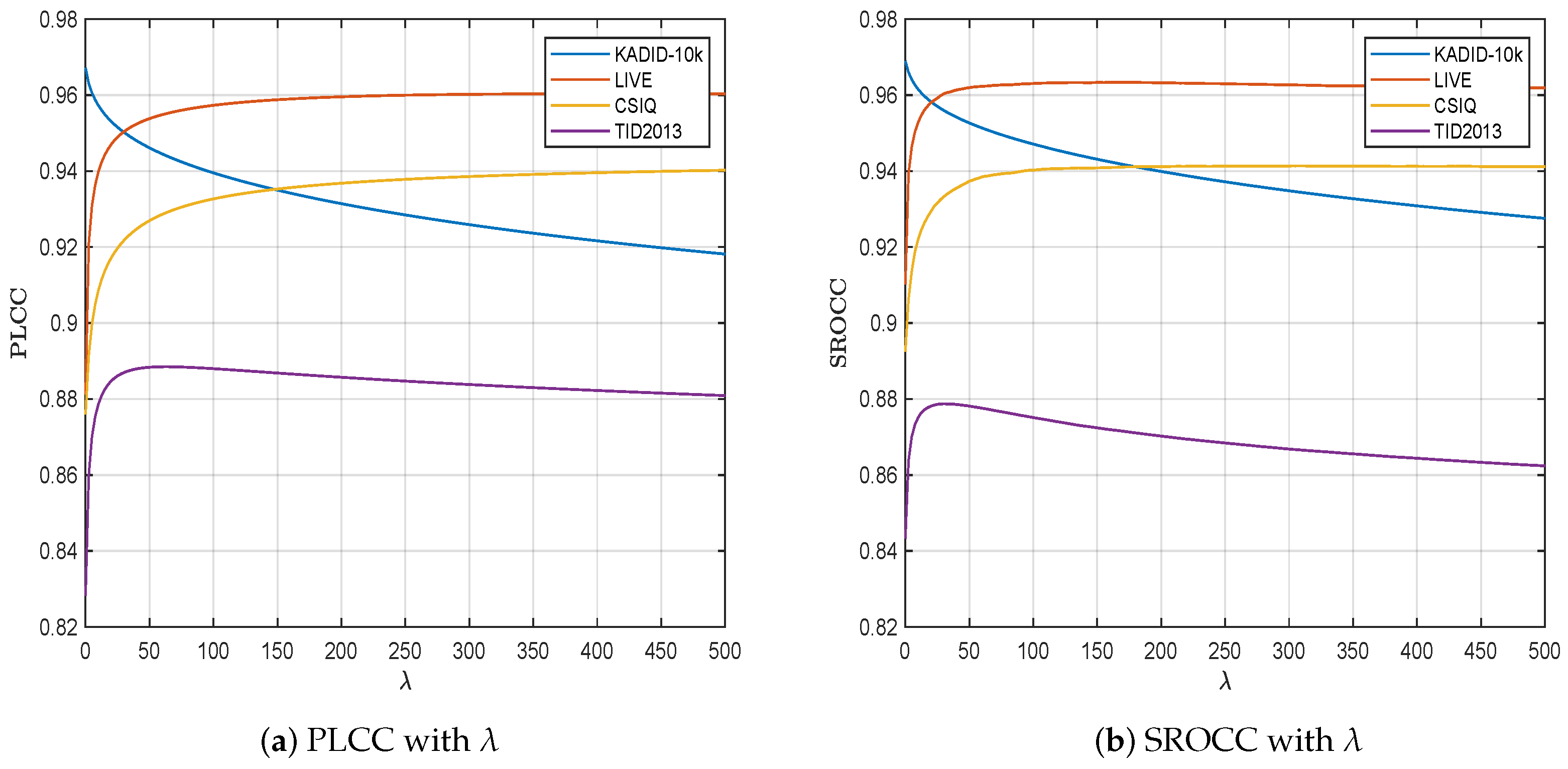
4.3. Parameter Sensitivity
4.4. Ablation Study
4.4.1. VGG-16 Network
4.4.2. Perceptual Distances
4.5. Time and Complexity Analysis
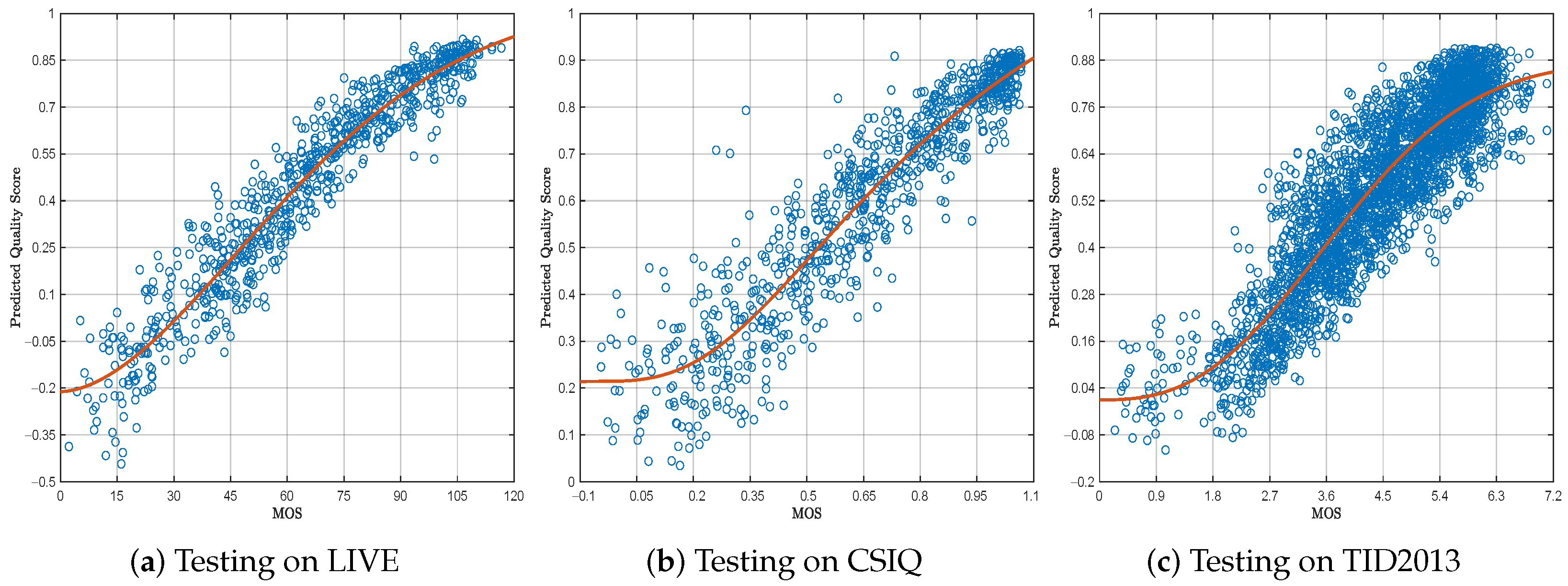
4.6. Subjective Consistency Experiments
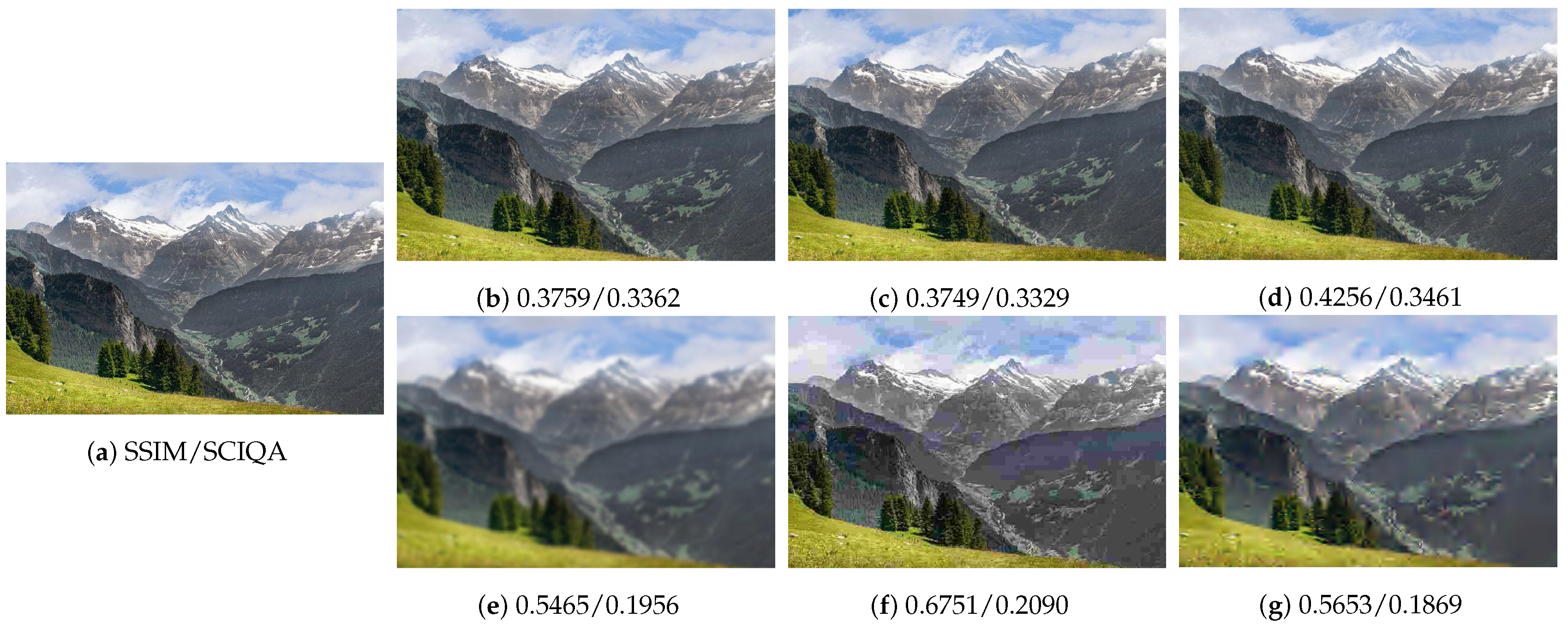
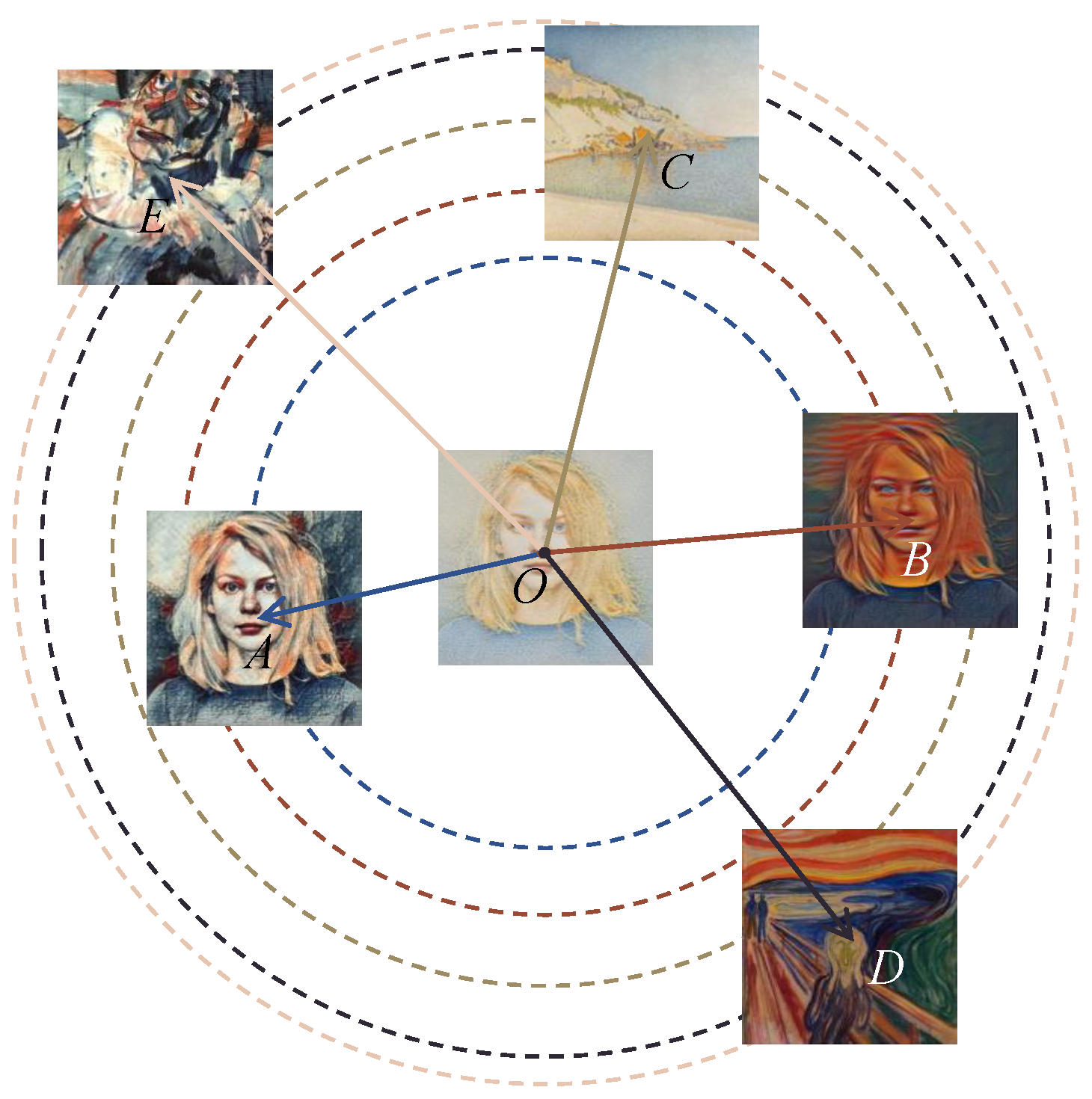
4.7. Interpretability Experiments
4.8. Discussion
4.8.1. Comparison Between SSHMPQA and SCIQA
4.8.2. Performance Comparison and Analysis
4.8.3. Limitations and Prospects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, C.; Kim, D.; Kim, D. Quality Assessment of High-Speed Motion Blur Images for Mobile Automated Tunnel Inspection. Sensors 2025, 25, 3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Du, J.; Li, J.; Lv, H. MDFN: Enhancing Power Grid Image Quality Assessment via Multi-Dimension Distortion Feature. Sensors 2025, 25, 3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotter, P.; Knapik, D.; Klemiato, M.; Rosół, M.; Putynkowski, G. Compensation of Speckle Noise in 2D Images from Triangulation Laser Profile Sensors Using Local Column Median Vectors with an Application in a Quality Control System. Sensors 2025, 25, 3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zeng, Q.; Guo, C.; Zhao, T.; Wen Chen, C. Target-Aware Camera Placement for Large-Scale Video Surveillance. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 34, 13338–13348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Wei, X.; Wang, S.; Kwong, S.; Fong, C.K.; Wong, P.H.W.; Yuen, W.Y.F. Global Rate-Distortion Optimization-Based Rate Control for HEVC HDR Coding. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2020, 30, 4648–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Lin, X. Complexity Correlation-Based CTU-Level Rate Control with Direction Selection for HEVC. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 2017, 13, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, M.; Ji, C.; Sui, X.; Bai, J. Cross-Frame Transformer-Based Spatio-Temporal Video Super-Resolution. IEEE Trans. Broadcast. 2022, 68, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Feng, Y.; Fang, B.; Zhou, M.; Kwong, S.; Qiang, B.H. DSRPH: Deep semantic-aware ranking preserving hashing for efficient multi-label image retrieval. Inf. Sci. 2020, 539, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Sheng, W.; Zhou, M.; Fang, B.; Luo, F.; Li, J. Method for Fault Diagnosis of Temperature-Related MEMS Inertial Sensors by Combining Hilbert–Huang Transform and Deep Learning. Sensors 2020, 20, 5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhou, M.; Wang, H.; Yang, H.; Chen, L.; Kwong, S. Recent Advances in Rate Control: From Optimization to Implementation and Beyond. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 34, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stępień, I.; Oszust, M. Three-branch neural network for No-Reference Quality assessment of Pan-Sharpened Images. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 139, 109594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolie, H.F.; Ren, J.; Chen, R.; Zhao, H.; Elyan, E. Blind sonar image quality assessment via machine learning: Leveraging micro- and macro-scale texture and contour features in the wavelet domain. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 141, 109730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jingnan, S.; Mingliang, Z.; Luo, J.; Pu, H.; Yong, F.; Wei, X.; Weijia, J. Boundary-Aware Feature Fusion with Dual-Stream Attention for Remote Sensing Small Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5600213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Song, J.; Zhou, M.; Wei, X.; Pu, H.; Luo, J.; Jia, W. EF-DETR: A Lightweight Transformer-Based Object Detector with an Encoder-Free Neck. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 12994–13002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zhao, X.; Luo, F.; Luo, J.; Pu, H.; Xiang, T. Robust RGB-T Tracking via Adaptive Modality Weight Correlation Filters and Cross-modality Learning. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 2023, 20, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Hechen, Z.; Zhou, M.; Li, Z.; Kwong, S. An Attention-Locating Algorithm for Eliminating Background Effects in Fine-Grained Visual Classification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2025, 35, 5993–6006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Wu, X.; Wei, X.; Xiang, T.; Fang, B.; Kwong, S. Low-Light Enhancement Method Based on a Retinex Model for Structure Preservation. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, M.; Yue, H.; Pu, H.; Luo, J. Image Defogging Based on Regional Gradient Constrained Prior. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 2023, 20, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zhou, M. Progressive Domain Translation Defogging Network for Real-World Fog Images. IEEE Trans. Broadcast. 2022, 68, 876–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingliang, Z.; Shen, W.; Wei, X.; Luo, J.; Jia, F.; Zhuang, X.; Weijia, J. Blind Image Quality Assessment: Exploring Content Fidelity Perceptibility via Quality Adversarial Learning. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2025, 133, 3242–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Zhou, M.; Wei, X.; Wang, H.; Fang, B.; Ji, C.; Zhuang, X.; Wang, J.; Luo, J.; Pu, H.; et al. A Blind Video Quality Assessment Method via Spatiotemporal Pyramid Attention. IEEE Trans. Broadcast. 2024, 70, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, W.; Zhou, M.; Fang, B.; Liao, X.; Ji, C.; Xiang, T.; Jia, W. Spatiotemporal Feature Hierarchy-Based Blind Prediction of Natural Video Quality via Transfer Learning. IEEE Trans. Broadcast. 2023, 69, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liang, J.; Fu, H.; Han, J. ROI-Based Deep Image Compression with Swin Transformers. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023—2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 4–10 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirer, T. Iteratively Preconditioned Guidance of Denoising (Diffusion) Models for Image Restoration. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2024—2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Seoul, Republic of Korean, 14–19 April 2024; pp. 2465–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.; Sheikh, H.; Simoncelli, E. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Simoncelli, E.; Bovik, A. Multiscale structural similarity for image quality assessment. In Proceedings of the Thrity-Seventh Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 9–12 November 2003; Volume 2, pp. 1398–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Bovik, A.C. Three-component weighted structural similarity index. In Proceedings of the Image Quality and System Performance VI, San Jose, CA, USA, 19–21 January 2009; Volume 7242, p. 72420Q. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Mou, X.; Zhang, D. FSIM: A Feature Similarity Index for Image Quality Assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 20, 2378–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, W.; Zhang, L.; Mou, X.; Bovik, A.C. Gradient Magnitude Similarity Deviation: A Highly Efficient Perceptual Image Quality Index. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 23, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shen, Y.; Li, H. VSI: A Visual Saliency-Induced Index for Perceptual Image Quality Assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 23, 4270–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narwaria, M.; Lin, W. Objective Image Quality Assessment Based on Support Vector Regression. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2010, 21, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosse, S.; Maniry, D.; Muller, K.R.; Wiegand, T.; Samek, W. Deep Neural Networks for No-Reference and Full-Reference Image Quality Assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, S. Deep Learning of Human Visual Sensitivity in Image Quality Assessment Framework. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1969–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prashnani, E.; Cai, H.; Mostofi, Y.; Sen, P. PieAPP: Perceptual Image-Error Assessment Through Pairwise Preference. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 1808–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, W.; Zhou, M.; Fang, B.; Kwong, S. A content-oriented no-reference perceptual video quality assessment method for computer graphics animation videos. Inf. Sci. 2022, 608, 1731–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, B.; Chen, R.; Zhou, M.; Pang, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Yang, M. Convolutional Neural Networks-Based Object Detection Algorithm by Jointing Semantic Segmentation for Images. Sensors 2020, 20, 5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, M.; Campbell-Valois, F.X.; Siu, S.W.I. A deep learning method for predicting the minimum inhibitory concentration of antimicrobial peptides against Escherichia coli using Multi-Branch-CNN and Attention. mSystems 2023, 8, e00345-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, M.; Kwok, H.F.; Siu, S.W. Multi-Branch-CNN: Classification of ion channel interacting peptides using multi-branch convolutional neural network. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 147, 105717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A.; Shechtman, E.; Wang, O. The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Deep Features as a Perceptual Metric. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Chen, B.; Zhu, H.; Wang, S.; Zhou, M.; Kwong, S. DeepWSD: Projecting Degradations in Perceptual Space to Wasserstein Distance in Deep Feature Space. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Lisbon, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022; pp. 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Wei, X.; Zhou, M.; Wong, H.S.; Kwong, S. Image Quality Assessment: Exploring Joint Degradation Effect of Deep Network Features Via Kernel Representation Similarity Analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2025, 1, 2799–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Lan, X.; Wei, X.; Liao, X.; Mao, Q.; Li, Y.; Wu, C.; Xiang, T.; Fang, B. An End-to-End Blind Image Quality Assessment Method Using a Recurrent Network and Self-Attention. IEEE Trans. Broadcast. 2023, 69, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Li, J.; Zhou, M.; Wang, X. Contrastive distortion-level learning-based no-reference image-quality assessment. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2022, 37, 8730–8746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Min, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhai, G.; Yang, X.; Le Callet, P. Confusing Image Quality Assessment: Toward Better Augmented Reality Experience. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 7206–7221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Cai, B.; Zheng, S.; Zhao, T.; Gu, K. Perception-and-Cognition-Inspired Quality Assessment for Sonar Image Super-Resolution. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 6398–6410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Leng, H.; Fang, B.; Xiang, T.; Wei, X.; Jia, W. Low-light Image Enhancement via a Frequency-based Model with Structure and Texture Decomposition. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 2023, 19, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, H.; Bovik, A. Image information and visual quality. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2006, 15, 430–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, D.M.; Hemami, S.S. VSNR: A Wavelet-Based Visual Signal-to-Noise Ratio for Natural Images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 2284–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.H.; Kim, M. DCT-QM: A DCT-Based Quality Degradation Metric for Image Quality Optimization Problems. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 4916–4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laparra, V.; Ballé, J.; Berardino, A.; Simoncelli, E.P. Perceptual image quality assessment using a normalized Laplacian pyramid. Electron. Imaging 2016, 2016, art00008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Tan, M.; Yu, J.; Zhu, Y. DeepSim: Deep similarity for image quality assessment. Neurocomputing 2017, 257, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Ma, K.; Wang, S.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image Quality Assessment: Unifying Structure and Texture Similarity. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 2567–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Cai, H.; Chen, H.; Ye, X.; Ren, J.; Dong, C. Image quality assessment for perceptual image restoration: A new dataset, benchmark and metric. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.15002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, S.; Gong, Y.; Shi, S.; Yang, S.; Wu, T.; Wang, J.; Xia, W.; Yang, Y. Attentions Help CNNs See Better: Attention-based Hybrid Image Quality Assessment Network. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–20 June 2022; pp. 1139–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Yang, W.; Liao, Q. Robust Content-Variant Reference Image Quality Assessment Via Similar Patch Matching. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023—2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greec, 4–9 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Mo, J.; Hou, J.; Wu, H.; Liao, L.; Sun, W.; Yan, Q.; Lin, W. TOPIQ: A Top-Down Approach From Semantics to Distortions for Image Quality Assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2024, 33, 2404–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Zhou, M.; Luo, J.; Li, Z.; Kwong, S. Graph-Represented Distribution Similarity Index for Full-Reference Image Quality Assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2024, 33, 3075–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, W.; Zhou, M.; Fang, B.; Xiang, T.; Jia, W.; Chen, B. Perceptual Quality Analysis in Deep Domains Using Structure Separation and High-Order Moments. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 2219–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Zhou, M.; Chen, Y.; Wei, X.; Luo, J.; Pu, H.; Jia, W. Image Quality Assessment: Investigating Causal Perceptual Effects with Abductive Counterfactual Inference. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (Accepted), Nashville, TN, USA, 11–15 June 2025; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, K.; Ma, K.; Wang, S.; Simoncelli, E.P. Comparison of Full-Reference Image Quality Models for Optimization of Image Processing Systems. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 1258–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Ma, K.; Liang, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L. A Comprehensive Study of Multimodal Large Language Models for Image Quality Assessment. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Milan, Italy, 29 September—4 October 2024; pp. 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Z.; Li, Z.; Gu, J.; Yin, Z.; Xue, T.; Dong, C. Depicting Beyond Scores: Advancing Image Quality Assessment Through Multi-modal Language Models. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Milan, Italy, 29 September—4 October 2024; pp. 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirshahi, S.A.; Pedersen, M.; Stella, X.Y. Image Quality Assessment by Comparing CNN Features between Images. Electron. Imaging 2017, 29, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Wei, X.; Zhou, M.; Yan, J.; Pu, H.; Luo, J.; Li, Z. A Semantic-Aware Detail Adaptive Network for Image Enhancement. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2025, 35, 1787–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatys, L.A.; Ecker, A.S.; Bethge, M. Image Style Transfer Using Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2414–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.; Alahi, A.; Fei-Fei, L. Perceptual Losses for Real-Time Style Transfer and Super-Resolution. In Proceedings of the the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 694–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, H.; Sabir, M.; Bovik, A. A Statistical Evaluation of Recent Full Reference Image Quality Assessment Algorithms. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2006, 15, 3440–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, E.C.; Chandler, D.M. Most apparent distortion: Full-reference image quality assessment and the role of strategy. J. Electron. Imaging 2010, 19, 011006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomarenko, N.; Jin, L.; Ieremeiev, O.; Lukin, V.; Egiazarian, K.; Astola, J.; Vozel, B.; Chehdi, K.; Carli, M.; Battisti, F.; et al. Image database TID2013: Peculiarities, results and perspectives. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2015, 30, 57–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Hosu, V.; Saupe, D. KADID-10k: A Large-scale Artificially Distorted IQA Database. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Quality of Multimedia Experience (QoMEX), Berlin, Germany, 5–7 June 2019; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Cai, H.; Chen, H.; Ye, X.; Ren, J.S.; Dong, C. PIPAL: A Large-Scale Image Quality Assessment Dataset for Perceptual Image Restoration. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part XI. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 633–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, P.G.; Dunn, J.R. The five-parameter logistic: A characterization and comparison with the four-parameter logistic. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 343, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Feature | LIVE | CSIQ | TID2013 | KADID-10k | PIPAL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference Images | 29 | 30 | 25 | 81 | 250 |
| Distorted Images | 779 | 866 | 3000 | 10,125 | 25,850 |
| Distortion Types | 5 | 6 | 24 | 25 | 40 |
| Evaluation Method | DMOS | DMOS | MOS | MOS | Elo |
| Primary Focus | Traditional | Traditional | Multitype | Multilevel | Multitype |
| Method | Dataset | LIVE | CSIQ | TID2013 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Criterion | PLCC | ROCC | KROCC | PLCC | SROCC | KROCC | PLCC | SROCC | KROCC |
| Traditional Methods | PSNR | 0.781 | 0.801 | 0.677 | 0.792 | 0.807 | 0.603 | 0.664 | 0.687 | 0.496 |
| SSIM | 0.847 | 0.851 | 0.789 | 0.852 | 0.865 | 0.680 | 0.665 | 0.627 | 0.545 | |
| MS-SSIM | 0.886 | 0.903 | 0.805 | 0.875 | 0.879 | 0.730 | 0.830 | 0.786 | 0.605 | |
| VIF | 0.949 | 0.953 | 0.817 | 0.899 | 0.879 | 0.743 | 0.771 | 0.677 | 0.518 | |
| FSIM | 0.910 | 0.920 | 0.806 | 0.875 | 0.884 | 0.769 | 0.877 | 0.851 | 0.667 | |
| VSI | 0.877 | 0.899 | 0.806 | 0.902 | 0.915 | 0.786 | 0.898 | 0.895 | 0.718 | |
| GMSD | 0.909 | 0.910 | 0.787 | 0.938 | 0.939 | 0.804 | 0.855 | 0.804 | 0.634 | |
| NLPD | 0.882 | 0.889 | 0.758 | 0.913 | 0.926 | 0.749 | 0.839 | 0.800 | 0.625 | |
| Deep Learning- Based Methods | WaDIQaM | 0.940 | 0.947 | 0.791 | 0.901 | 0.909 | 0.732 | 0.834 | 0.831 | 0.631 |
| PieAPP | 0.866 | 0.865 | 0.740 | 0.864 | 0.883 | 0.712 | 0.859 | 0.876 | 0.683 | |
| LPIPS | 0.934 | 0.932 | 0.765 | 0.896 | 0.876 | 0.689 | 0.749 | 0.670 | 0.497 | |
| DeepWSD | 0.904 | 0.925 | 0.813 | 0.941 | 0.950 | 0.812 | 0.894 | 0.874 | 0.783 | |
| DISTS | 0.924 | 0.925 | 0.807 | 0.919 | 0.920 | 0.746 | 0.855 | 0.830 | 0.639 | |
| CVRIQA | 0.944 | 0.954 | 0.811 | 0.903 | 0.869 | 0.689 | 0.734 | 0.732 | 0.546 | |
| TOPIQ | 0.882 | 0.887 | 0.775 | 0.894 | 0.893 | 0.789 | 0.854 | 0.820 | 0.664 | |
| SSHMPQA | 0.959 | 0.963 | 0.828 | 0.945 | 0.945 | 0.795 | 0.897 | 0.879 | 0.694 | |
| 2cSCIQA (ours) | 0.956 | 0.964 | 0.828 | 0.941 | 0.940 | 0.798 | 0.895 | 0.877 | 0.690 | |
| Category | Method | PLCC | SROCC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Methods | PSNR | 0.398 | 0.392 |
| SSIM | 0.489 | 0.486 | |
| MS-SSIM | 0.571 | 0.545 | |
| VIF | 0.572 | 0.545 | |
| MAD | 0.614 | 0.591 | |
| FSIM | 0.597 | 0.573 | |
| VSI | 0.548 | 0.526 | |
| GMSD | 0.614 | 0.569 | |
| NLPD | 0.489 | 0.464 | |
| Deep Learning- Based Methods | PieAPP | 0.597 | 0.607 |
| LPIPS | 0.633 | 0.595 | |
| SWDN | 0.634 | 0.624 | |
| DISTS | 0.687 | 0.655 | |
| SSHMPQA | 0.709 | 0.692 | |
| ICIQA | 0.694 | 0.656 | |
| SCIQA (ours) | 0.705 | 0.702 | |
| Criterion | PLCC | SROCC | KROCC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pretrained VGG-16 | 0.956 | 0.964 | 0.828 |
| Self-trained VGG-16 | 0.795 | 0.789 | 0.624 |
| Dataset | LIVE | CSIQ | TID2013 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Criterion | PLCC | SROCC | KROCC | PLCC | SROCC | KROCC | PLCC | SROCC | KROCC |
| original SCIQA | 0.956 | 0.964 | 0.828 | 0.941 | 0.940 | 0.798 | 0.895 | 0.877 | 0.690 |
| W/O | 0.827 | 0.816 | 0.691 | 0.811 | 0.803 | 0.655 | 0.793 | 0.788 | 0.546 |
| W/O | 0.917 | 0.928 | 0.779 | 0.924 | 0.916 | 0.776 | 0.836 | 0.825 | 0.624 |
| Method | Inference Speed (FPS) |
|---|---|
| SSHMPQA | 0.76 |
| DISTS | 12.3 |
| LPIPS | 18.5 |
| SCIQA (ours) | 23.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xian, W.; Chen, B.; Yan, J.; Wei, X.; Guo, K.; Fang, B.; Zhou, M. A Style Transfer-Based Fast Image Quality Assessment Method for Image Sensors. Sensors 2025, 25, 5121. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165121
Xian W, Chen B, Yan J, Wei X, Guo K, Fang B, Zhou M. A Style Transfer-Based Fast Image Quality Assessment Method for Image Sensors. Sensors. 2025; 25(16):5121. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165121
Chicago/Turabian StyleXian, Weizhi, Bin Chen, Jielu Yan, Xuekai Wei, Kunyin Guo, Bin Fang, and Mingliang Zhou. 2025. "A Style Transfer-Based Fast Image Quality Assessment Method for Image Sensors" Sensors 25, no. 16: 5121. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165121
APA StyleXian, W., Chen, B., Yan, J., Wei, X., Guo, K., Fang, B., & Zhou, M. (2025). A Style Transfer-Based Fast Image Quality Assessment Method for Image Sensors. Sensors, 25(16), 5121. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165121






