1. Introduction
Against the backdrop of increasingly tight wireless spectrum resources, about 50 billion smart devices are expected to access IoT systems worldwide by 2030 [
1]. However, constrained by limited spectrum resources and increasingly complex heterogeneous communication scenarios, current fifth-generation (5G) mobile communication technologies (despite already having state-of-the-art performance) still struggle to meet future demands [
1,
2]. To enhance the efficiency of spectrum utilization, cognitive radio networks (CRNs) are considered a cutting-edge solution. In CRNs, primary users (
PUs) and secondary users (
SUs) belong to the primary network (PN) and secondary network (SN), respectively, and their behavioral modes include interweave mode (IM), underlay mode (UM), and overlay mode (OM) [
2,
3]. In IM mode,
SUs utilize the
PUs only when they are idle in the “spectrum hole” for transmission, and the strategy is dynamic spectrum access (DSA). In UM mode, the
SU coexists with the
PU and transmits using spectrum sharing (SS), which is required to keep the interference to the
PU within a threshold [
3]. In OM mode, the
SU helps the
PU to transmit through collaborative communication or precoding, thus gaining the transmission of its own information [
4].
Early optimization in CRNs predominantly relied on time division multiple access (TDMA) and frequency division multiple access (FDMA) resource allocation schemes; however, these methods have been shown to cause structural inefficiencies in time–frequency resource utilization in fourth-generation (4G) systems [
5,
6]. In recent years, CRNs’ resource optimization has been divided into three main classes of methods: The first is mathematical optimization, such as Karush–Kuhn–Tucker conditions (KKT) [
7], Lagrangian dyadic and convex optimization methods [
2], which transform the problem into an optimization or (pseudo) convex problem-solving process [
8]. The second category includes heuristic algorithms, such as the genetic algorithm (GA) [
9], particle swarm optimization (PSO) [
10], ant colony optimization (ACO) [
11,
12,
13], and the whale optimization algorithm (WOA) [
14]. The third category is reinforcement learning (RL)-based methods, such as Q-learning [
1], which utilize Markov Decision Processes (MDPs) for intelligence training [
15,
16,
17]. Recent works have further explored RL-based and joint optimization strategies for NOMA resource allocation, including multi-agent deep reinforcement learning with unsupervised learning for joint channel and power allocation [
18] and coalition game theory combined with Dinkelbach–SCA-based power optimization for uplink NOMA systems [
19]. However, mathematical optimization finds it difficult to address NP-hard problems, and convexity is hard to satisfy [
20]; while reinforcement learning, despite its potential, is still limited by computing power and practical adaptability in industrial deployments [
21,
22,
23,
24].
Hybrid user is a cutting-edge concept based on CRNs; such a user has the ability to selectively access PN and SN based on the channel situation [
3]. When this kind of user is in the PN, it has the same channel preference and usage rights as a normal
PU, and its priority is higher than that of a normal
SU; when it is in the SN, it has the same priority as an
SU and can exist as an
SU, and through such behavioral mode switching, the channel utilization is improved. Currently, research is underway to optimize user behavioral mode switching and linkage in CR networks. For example, in [
7], the joint perceived duration and subchannel power optimization algorithm for the same
SU in Overlay/Underlay dual-mode is investigated, but the scope of the discussion is only for single-
SU scenarios, and there is a lack of consideration of multi-user interference and fairness. The joint optimal allocation of bandwidth + power under OM/UM switching in CR networks has been studied in the literature [
8], but it lacks the consideration of IoT metrics, such as energy efficiency, and it is only for single-
PU scenarios, with a limited degree of expansion.
In order to solve the problem of a single optimization index and low scenario expansion in the existing work in this field, this paper introduces the hybrid user concept to jointly model the system energy efficiency,
SU average SINR, and
SU fairness. The article adopts a heuristic optimization approach to solve the problem and proposes the Hybrid Mode-Aware Allocation with Coupled Power Control (HMAC) algorithm. The “Mode-Aware Allocation” principle refers to dynamically selecting the most suitable access mode (IM or UM) for each
SU based on real-time channel state information,
PU activity patterns, and interference constraints, ensuring that the allocation strategy adapts to both spectrum availability and network performance requirements. The core of HMAC is based on mode switching, an adaptive threshold, channel assignment based on the Hungarian algorithm, and a multi-stage power adjustment strategy. Among these, the Hungarian algorithm is widely used in user–subcarrier allocation and subchannel assignment. It has been proven to help reduce channel interference and improve network efficiency under different optimization conditions [
25,
26]. Power adjustment strategies are widely used in large-scale multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) communication systems, and have been proven to be closely related to user fairness and network energy efficiency [
27,
28]. HMAC extends the concept of hybrid users by scheduling system spectrum resources, transmitter power, user space resources, channel interference, etc., in terms of channels, and focuses on the behavioral logic of
PUs and
SUs in the channel, which weakens the concepts of PN and SN in the CRNs, and maximizes the performance metrics adopted. HMAC, from the basis of the generalized concept of
SUs, empowers the
SU to choose whether to co-exist with the same channel
PU or choose an empty channel for transmission. Interweave–Underlay Mode (I–UM) linkage is used to redefine the behavioral logic of such users. And a multi-objective optimization scheme is used to design the optimization algorithm for the system energy efficiency (EE), the Jain’s fairness index of
SUs and the average SINR of
SUs. In this paper, a large number of simulations are carried out to verify the advantages and robustness of the HMAC algorithm in terms of EE, Jain’s fairness index of
SUs and average SINR for a certain
PU fulfillment rate in terms of dimensions such as the number of
SU, the maximum power, and the diameter of the user-generated cell.
This paper is organized as follows:
Section 2 introduces the system model, including user node deployment and the channel fading model. In
Section 3, the optimization problem is formulated, and a complexity analysis of the problem is performed. In
Section 4, a hybrid user-based heuristic algorithm is proposed to solve the optimization problem.
Section 5 presents a variety of simulations and discusses them based on experimental results.
Section 6 concludes this paper and gives an outlook for future research.
2. System Model
As shown in
Figure 1, the system model of this study focuses on the channel allocation of
PUs and
SUs under a CR network, in which, due to the use of the concept of mixed users, the system model does not differentiate between PNs and SNs based on the traditional CR network, but uses the channel as the basic unit, and combines the
PUs and
SUs among a limited number of channels. The system model is defined based on the CRN model descriptions in [
1,
21]. Let the total number of channels be
, the number of
PUs be
, and the number of
SUs be
. Their quantitative relationships are satisfied as
In this network, the Base Station (BS) is aware of channels, and at most one PU and one SU exist simultaneously in the same channel. There is no situation where two or more PUs or SUs exist in a channel at the same time.
To emulate the channel environment and spatial layout of a cognitive radio network, this paper constructs a simplified system model on a two-dimensional plane, illustrated below.
Primary Users (
PUs): There are
N PUs in the system, each
PU occupies an independent channel, and the spatial locations of the
PUs are distributed in a two-dimensional real-numbered domain as
where
represents the coordinates of the ith
PU in that two-dimensional space, with a horizontal coordinate of
and a vertical coordinate of
.
Secondary Users (
SUs): The system generates up to
N SUs based on the experimental parameters. The location of the
SUs is restricted to a smaller area, which is a concentrated cluster as
where
represents the coordinates of the jth
SU in that two-dimensional space, with horizontal coordinates
and vertical coordinates
.
If , the corresponding SU is an unassigned user on the redundant channel. In addition, the system defines a center base station location that can be used in the path loss calculation.
In this paper, it is assumed that both
PUs and
SUs face random small-scale fading, and their channel gains are modeled as non-negative real numbers after taking the absolute value of the Gaussian distribution, i.e., the Rayleigh fading amplitude approximation is processed as
In order to characterize the interference of
SUs on
PUs, this paper uses the free-space propagation model to construct the power gain of the interference link. According to the description of the Friis transmission equation by Rappaport, T. S. in Wireless Communications—Principles and Practice, Second Edition [
29], the formula is determined as
where
denotes the transmitter antenna gain,
denotes the receiver antenna gain, is the wavelength,
the Euclidean distance between the nth
SU and the
PU, and
is the path loss index.
The received signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratios (SINRs) of
PUs and
SUs on the nth channel are defined as in Equation (6) following the formulation in [
1].
The overall system throughput is then obtained by summing the Shannon capacities of all channels allocated to the
PUs and
SUs, expressed in Equation (7) [
30] as
3. Problem Formulation
The aim of this paper is to develop a power allocation strategy for multiple SUs in a cognitive network that maximizes the overall system performance without interfering with the normal communication of PUs. To this end, the following four categories of core performance metrics are considered in this paper, namely PU Satisfiability, SU Average SINR, Energy Efficiency (EE), and Jain’s Fairness Index. The reason for choosing these four metrics is to comprehensively weigh the system’s ability to protect the communication quality of the PUs while achieving the communication performance improvement of the SUs, as well as to take into account the optimization of the energy efficiency of the resource use and the fairness among multiple users. Among them, PU satisfaction is used as one of the constraints of the objective function to measure the effectiveness of the protection of the PUs, the SU average SINR reflects the service quality of the SUs, the energy efficiency index evaluates the benefits gained by the system under the power consumption, and Jain’s fairness index quantifies the degree of balance of the resources obtained by each SU to ensure that the system does not over-optimize individual users at the expense of the overall fairness.
The above four indicators are harmonized and integrated into an objective function
of the following form:
is subject to:
where
C1 and
C2 are the constraint conditions of the optimization problem. Specifically,
C1 requires that the
PU satisfaction ratio must exceed the threshold
and
C2 ensures that the
PU transmit power remains within the allowed range.
,
are the normalization factors taken from the maximum of all the current strategy outcomes.
,
,
are the weighting coefficients for each part of the objective function.
For EE, according to [
27], it is calculated as the ratio of the system throughput to the sum of the total power of the
PUs and
SUs in that channel. A higher EE value indicates better system energy efficiency. The equation for calculating EE is formed by Equation (7) and total power consumption, noted as:
The article uses the Jain fairness index to quantify the fairness of SINR allocation among active
SUs. According to the study of Jain et al. [
31] and Equation (6), the Jain fairness index is formed as
where
denotes the SINR of the ith active
SU and n denotes the number of sending
SUs. Values close to 1 indicate a high degree of equity, while values close to 1/
n indicate a high degree of inequality.
Secondly, it is observed that from Equation (8) to Equation (10), the original optimization problem
shares the same structure as the k-Knapsack decision problem. There exists a clear correspondence between their parameters. Specifically, the k-Knapsack can be viewed as a special case of
by treating each item as a
PU link, mapping the item’s weight to the minimum acceptable power, the total capacity to the upper power constraint, and the target number of selected items to the number of satisfied
PUs. Under this construction, the two problems are equivalent in the sense of determining whether a feasible solution exists. According to Kellerer et al.’s analysis of knapsack problem complexity, the k-Knapsack problem is at least NP-Complete [
32]. Therefore, the original optimization problem
is at least NP-Hard.
4. Optimization Algorithm Based on Hybrid User
In this section, this paper proposes a hybrid user-based heuristic algorithm, HMAC, specifically, the algorithm consists of three major parts, namely, a mode-switching adaptive threshold, channel allocation based on the Hungarian algorithm, and a multilevel power tuning strategy. Next, this paper will introduce these three parts of the algorithm in order and finally summarize the whole framework. The structure of the HMAC algorithm is illustrated in
Figure 2.
- A.
Mode-Switching Adaptive Threshold
First, the HMAC algorithm proposed in the paper involves switching between IM and UM. These modes involve the DSA model and the SS model, which aim to make the algorithm more inclined to use the opportunistic model when the number of
SUs is small, providing more channel resources to the
SUs. The algorithm tends to use the
PU–
SU coexistence model when the number of
SUs is large, which protects the
PU channel resources while allocating the additional channel resources to the
SUs for transmission as much as possible. The paper assumes that the CR network can be aware of the number of
SUs successfully accessed in the network at this moment, which is denoted as
. In addition, since this algorithm involves model switching, there exists a threshold variable
for deciding which model to use for transmission after the user assigns the channel and adjusts the power, see Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1 Mode-Switching Adaptive Threshold |
| Step/Description | Content |
| Input | |
| Output | |
| Initialization | |
| Step 1: SU counting rule | If
then
Else if
then
Else |
| Step 2: Convert to linear scale | |
| return | |
Here exists a threshold adjustment value
, which is represented by the congestion of
SUs in the network when
,
, and
satisfy the following relationship:
where
is used to determine the latest threshold, the old threshold is denoted by
, and the new threshold is denoted by
, which satisfies the following relation:
The new threshold judgment is determined by the threshold variable, which is indirectly determined by the SU congestion; when the number of SUs is very small, the threshold is lowered by to encourage more SUs to access to the network; and when the number of SUs is increased, the threshold is raised by to protect the channel resources of the PUs. With this simple channel sensing, the complexity of the model criterion can be reduced, and the computational power consumption is small.
- B.
Channel Assignment Based on the Hungarian Algorithm
After determining the mode-switching threshold, the algorithm has to assign channels to the
PUs and
SUs for which spatial relationships have been determined so far. Here, it is assumed that the
PUs in the space have already occupied the channels separately, so for each
SU, a cost matrix
is set to determine which channel the
SU is assigned to, whether it chooses to coexist with the
PUs in a channel or to transmit in the idle channel, see Algorithm 2.
| Algorithm 2 Channel Assignment Based on the Hungarian Algorithm |
| Step/Description | Content |
| Input | |
| Output | |
| For each | |
|
For
to | |
|
For
to |
If
then set
Else compute distance
and set |
| Solve linear assignment | Minimize using Hungarian algorithm |
| Obtain mapping |
One-to-one mapping: |
| For to | If channel
is matched to some
, set
Else set |
For determining whether a channel exists with or without a
PU, whether it can serve an
SU alone as an idle channel is determined by the presence of
in that channel, for
satisfying
where
denotes the Euclidean distance between the
SU and the
PU discussed so far. It is denoted as
where the distance relation between all the
PUs and that
SU is traversed, and when the selected
PU has the maximum distance from the
SU, at that point of time, the channel interference between that
SU and the
PU is minimum. After all the
SUs have performed the computation of the cost matrix, the Hungarian algorithm [
25,
26] is performed to allocate the channel, and the Hungarian algorithm is denoted as:
where
indicates that the ith
SU is assigned to the jth channel, and
indicates that it is unassigned. Where
, denotes that
x is in the range of a two-dimensional constraint set.
With such an algorithm, after obtaining the spatial relationship between all the SUs and PUs, as well as the information about the empty channels currently in the network, the Matlab 24.2.0.2740171 (R2024b) simulation assigns a one-to-one correspondence to the SUs based on the cost matrix through the matchpairs function.
- C.
Multi-stage Power Adjustment Strategy
Following the mode-switching adaptive threshold and channel assignment based on the Hungarian algorithm, the proposed algorithm applies a multi-stage power adjustment strategy. This strategy is inspired by energy-efficient power control schemes in cell-free massive MIMO and heterogeneous networks, which demonstrate that adaptive power adjustment can improve energy efficiency while ensuring user fairness [
27,
28].
First, the model initializes the input system parameters to obtain the total number of channels, the number of
PUs, the number of
SUs, the maximum power, the bandwidth, the noise power, the main user SNR threshold, and the initial model-switching threshold. The maximum power is used to determine the subsequent power adjustment step, the power downward adjustment step is
and the power upward adjustment step is
, see Algorithm 3.
| Algorithm 3 Multi-stage Power Adjustment Strategy |
| Step/Description | Content |
| Input | |
| Output | |
| Constants | , |
| Step 1: SU counting |
Determine valid SUs
, set |
| Step 2: No–SU branch |
If :
on active-PU channels,
Compute and
Return |
| Step 3: Adaptive threshold | |
| Step 4: SU–PU assignment | |
| Step 5: Interference gain |
For to :
If or
Else |
| Step 6: Initial power | Set on PU-present channels
where SU assigned |
| Step 7: Per-channel iterative reduction | For to :
If PU absent:
Else if SU absent:
Else:
If , set and continue
Repeat until converged:
If :
Else if :
Else if and :
Else break |
| Step 8: Residual-power boost | Distribute surplus power on idle-PU channels using classic water-filling |
| Step 9: Coexistence-channel enhancement | Increase oncoexistence channels by , ensuring and |
| Step 10: Final metrics |
|
The process starts by counting the number of effective SUs within range and storing it in . If there are no SUs, the system calculates the PU throughput and SINR directly and ends the loop. If SUs are present, the mode-switching adaptive threshold is executed to update itself. Next, the channel assignment based on the Hungarian algorithm allocates channels to reduce interference. For each channel, if the PU is idle or no SU exists, the interference is set to zero. Otherwise, the SU-to-PU coupling is computed based on the path loss model. After parameter setup, power initialization begins. Each PU and SU is first assigned Pmax, and iterative tuning follows based on interference. In coexistence channels, if the PU SINR is below the threshold, the DSA algorithm shuts down the SU to protect the PU. If the SINR is acceptable, the SS strategy adjusts power: it reduces PU power when the SINR is too high, reduces SU power when the SINR is too low, and reuses the PU margin to help SUs if the PU SINR is stable. Finally, idle PU channels are reused by SUs using water-filling, and SU power is increased by step-by-step without breaking PU protection. After power adjustment, SINR and throughput are recalculated.
5. Simulations
In this section, the paper will simulate and discuss the objective function and weights identified in
Section 3, as well as the involved energy efficiency,
SU average SINR, and Jain’s fairness index.
For user generation, the model simulates the principle of linear random distribution of
PUs in a large area and
SUs in a small area, by which the abstract model simulates a real scenario in a city such as a car or a bus passing by in a street or a residential area, and the whole is modeled after the rules for defining clusters of
SUs and the two-dimensional plane of Moayedian et al. in [
2]. Let the
PUs be generated in a two-dimensional plane of length a and width b. The generation rule is linear random. The base station is located at the orthocenter of this plane and serves as the coordinate origin. The
SU generation forms user clusters in a circular region of radius c with center coordinates (
d,
e), which also allows
PUs to be generated within its boundaries, and the circular region satisfies that all the coordinates of the points within the circle are within the two-dimensional plane in which the
PU is generated, and the center of the circle generation rule is
In order to reflect the advantages of this paper’s HMAC algorithm in terms of the research objectives, this paper adopts multiple baseline algorithms for simulation. The greedy model (Greedy) improves the total system throughput by randomly assigning a limited number of SUs to the channel and gradually decreasing the transmit power only for the SUs based on the initial full power configuration. In this process, the SINR thresholds for PUs and SUs are not considered, and no precise interference control is performed. The opportunistic model (Opportunistic) makes the SU transmit only in the channel where the PU is empty. The coexistence model (Coexistence) does not guarantee the minimum SINR of the PU, so that the SU and the PU transmit in the same channel. The Max-Power model, on the other hand, enables the SU and the PU to transmit at maximum power simultaneously, which belongs to a variant of the Coexistence model and does not consider channel interference between the two.
In terms of computational complexity, the Greedy, Opportunistic, Coexistence, and Max-Power models have relatively low complexity, typically , or lower, where denotes the number of available channels and denotes the number of users. These models do not require global matching. In contrast, the proposed HMAC algorithm employs the Hungarian algorithm for channel assignment, which has a complexity of , enabling more optimal SU–PU spatial matching at the cost of increased computation.
The simulation parameter settings are described below, see
Table 1:
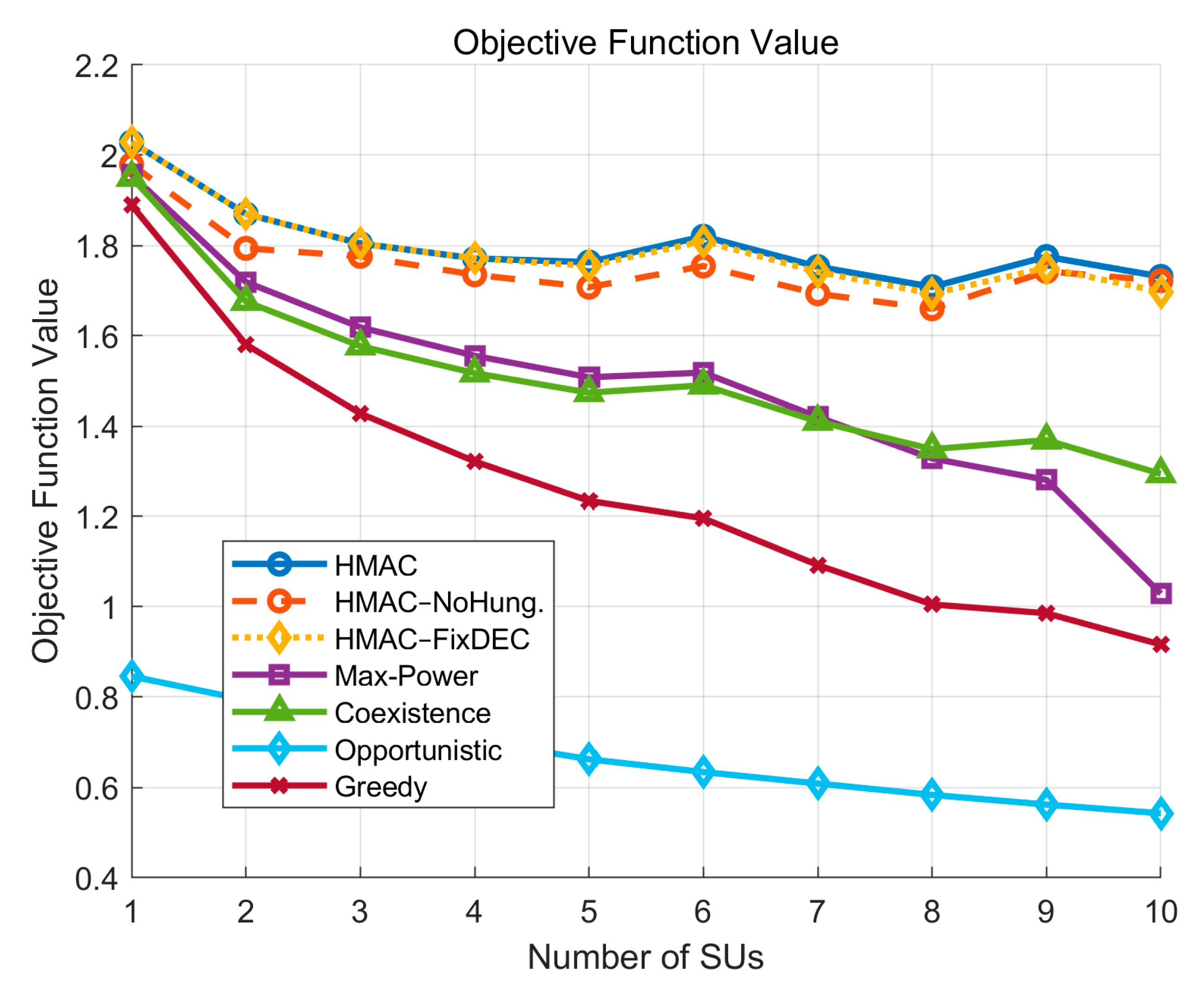
First, in accordance with the node allocation rules in
Section 2, the number of
SUs varies from 1 to 10 when there are 10
PUs in the network. As shown in
Figure 3, for the objective function, the HMAC curve is the optimization algorithm proposed in this study. Overall, the performance is relatively outstanding, with a slightly downward trend with the increase in the number of Sus, but it is not much affected by the growth of the number of
SUs compared to other algorithms, which is due to the fact that under the framework of the HMAC algorithm, the energy efficiency of the system increases significantly with the increase in the number of
SUs. This growth weakens the negative impact of the decrease in the average SINR, and Jain’s fairness of the
SUs increases. Thus, the overall effect of the algorithm maintains a certain degree of robustness. For the other algorithms, compared to HMAC, they all decrease significantly with an increase in the number of
SUs, and the Max-Power curve and the Greedy curve decrease the most, which is due to the fact that all their related performance metrics exhibit a decreasing trend.
For the average SINR of
SUs, according to
Figure 4, the HMAC curve is at the top of the entire graph throughout the entire process. Moreover, compared with the maximum power model and the coexistence model, the robustness of the HMAC model is the highest. The difference between its maximum and minimum values is very low, and the curve changes smoothly. When the number of
SUSs is 5, the adaptive threshold of the HMAC mode-switching part is triggered. The weights of the coexistence strategy and the opportunistic strategy within the model change. The model is more inclined to protect the channel quality of the
PU, thereby forcing some
SUs to be silent within the channel. However, the
SUs that can trigger channel coexistence with the
PU naturally have richer channel resources. Because the
PU can tolerate its existence in the shared channel, it indicates that these
SUs are better in spatial position and have less interference, thereby achieving higher channel utilization efficiency. This dynamic handover mechanism, based on channel awareness and spatial topology, not only guarantees the communication quality of the
PU but also enables the remaining active
SUs to transmit data in a lower-interference environment, further raising the average SINR level of the
SUs. Therefore, the HMAC model still maintains good performance stability and channel fairness in multi-user congestion scenarios, demonstrating highly robust resource scheduling capabilities. This is why HMAC outperforms HMAC–FixDEC as the number of
SUs increases. However, the other curves all show a significant downward trend as a whole. Among them, the value of the Opportunisitic curve remained at 0 throughout because the channel was fully occupied by
PUs at this time and
SUs did not have the channel conditions for normal transmission.
In terms of EE comparison, according to
Figure 5, the HMAC model consistently maintains the highest energy efficiency value over the entire range of the number of
SUs. The energy efficiency increases steadily with the increase in the number of
SUs, showing good scalability. This shows that HMAC is able to effectively improve the overall EE of the system while guaranteeing the communication quality of the primary users (
PUs). Compared with the same series of HMAC–NoHung, HMAC further benefits from the Hungarian algorithm’s optimization of
SU–
PU spatial matching to achieve the optimal resource allocation in multiuser scenarios. The HMAC and HMAC–FixDEC curves almost coincide when the number of subusers is small, which is due to the fact that all
SUs preferentially take up the opportunistic channel in low-density scenarios with plenty of free
PU channels. Both algorithms are able to achieve optimal power utilization efficiency. This is because in low-density scenarios where there are plenty of free
PU channels, all
SUs preferentially occupy opportunistic channels, and the results of the two algorithms are basically the same in terms of power allocation and threshold setting. HMAC further benefits from the Hungarian algorithm’s optimization of the
SU–
PU spatial matching and the adaptive regulation mechanism of the dynamic judgment threshold, so that it still achieves the optimal resource allocation in multiuser scenarios. In contrast, the energy efficiency of the traditional models, such as Max-Power, Opportunistic, and Greedy, basically remains unchanged or slightly decreases, reflecting the lack of effective interference control and resource coordination mechanisms when the user density increases. Taken together, the HMAC model has a significant advantage in energy efficiency, reflecting its high resource sensitivity and scheduling robustness.
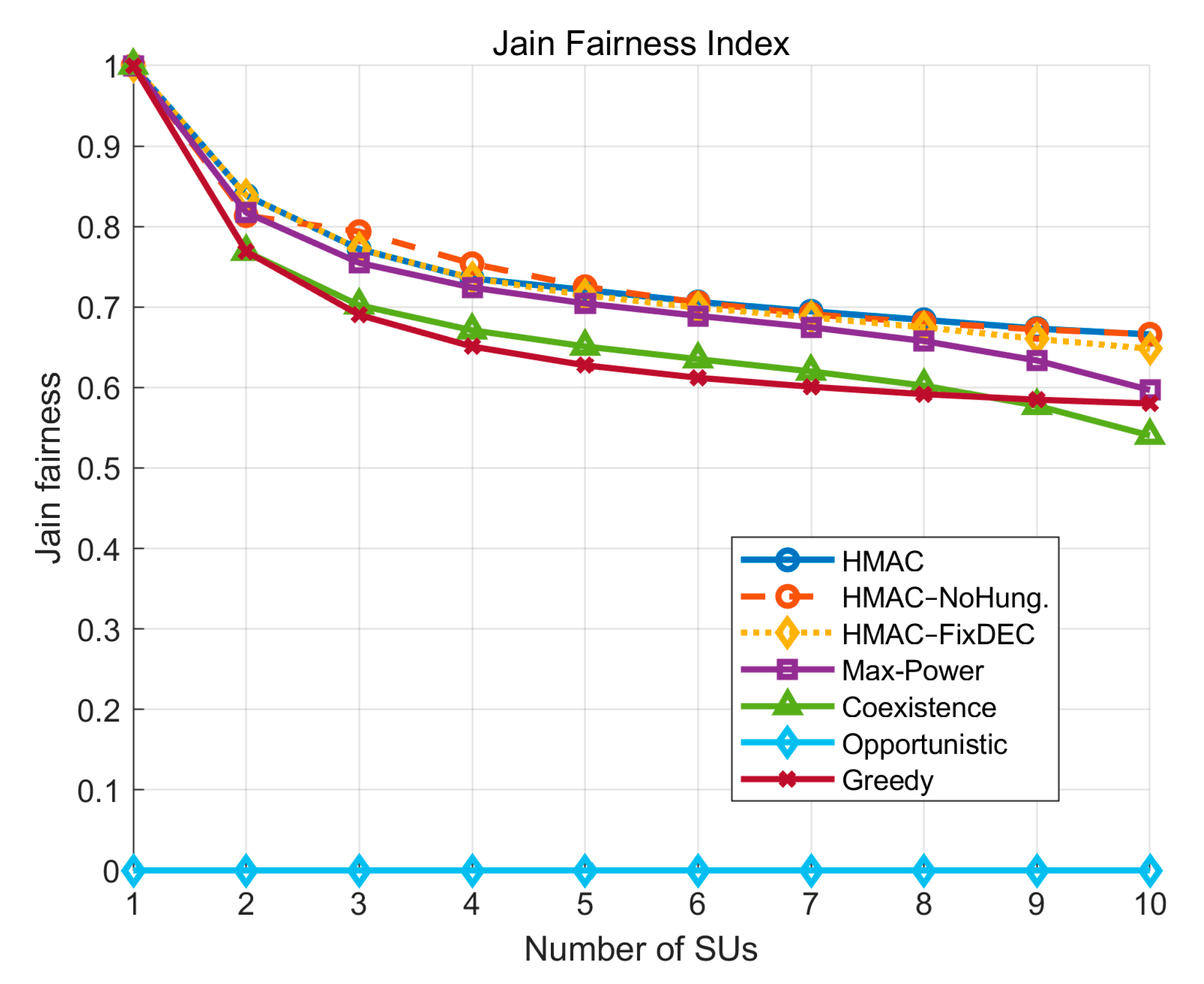
In the evaluation of Jain’s Fairness Index, according to
Figure 6, the performance of all the curves decreases gradually with the increase in the number of
SUs. Still, the three models of the HMAC series (HMAC, HMAC–NoHung, HMAC–FixDEC) have the highest values throughout the process and show higher fairness. Among them, HMAC–NoHung has even slightly higher fairness than the original HMAC model with Hungarian assignment when the number of
SUs is small (2 to 4). This is because, in low-density scenarios, the random channel assignment may, by chance, circumvent the strong interference paths between
SUs and
PUs, allowing some
SUs to access the channel at a lower cost and thus obtain a higher transmission efficiency. Since the Jain’s fairness index is calculated based on active
SUs only, and those
SUs that are forced to be silent are not counted in the fairness statistics, those
SUs that are not silenced and are randomly assigned better channels increase the overall fairness index. This localized advantage due to randomness is amplified in small-scale networks, which is reflected in the slightly better curve in the absence of the Hungarian mechanism. However, as the number of
SUs increases, HMAC gradually returns to its advantage in fairness performance by virtue of its interference-sensing and global matching capabilities.
In order to observe the relationship between the user’s maximum power, according to
Figure 7, the number of
SUs, and the optimization target, this paper presents a joint plot of these parameters. In this 3D plot, the
x-axis represents the maximum power value, the
y-axis represents the number of
SUs, and the
z-axis represents the objective function. The higher value of the target indicates better performance of the algorithm. From this figure, it can be seen that the HMAC scheme has the best performance across the range of variation of the Pmax value and the number of
SUs. The plane formed by HMAC is more horizontal, which indicates the robustness of the scheme compared to other schemes.
For the cell size, this experiment simplifies the 2D plane generation rule by making L = W = a = b so that the surfacegenerated by the
PU is a square plane. From the simulation results, according to
Figure 8, it can be seen that the HMAC model still resides in the uppermost part of the map, and the performance advantage is obvious. In the HMAC series of curves, the smaller the cell diameter, the more obvious the advantage of the algorithm proposed in this paper. When the cell diameter becomes larger, the performance of the three curves tends to be consistent. This is because the cell range becomes larger, the channel interference between
SUs and
PUs is reduced, and the advantage of the channel allocation algorithm and adaptive threshold is no longer obvious. However, the HMAC series algorithms have an overall trend of better performance with a larger cell range.
In the Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF) curve of the objective function, according to
Figure 9, the HMAC curve is always on the rightmost side of all the compared algorithms, which indicates that, under the same level of probability accumulation, the Target Value achieved by the HMAC model is significantly higher than that of other algorithms. This not only verifies that the HMAC model has stronger convergence stability in the optimal solution space, but also reflects its superior global performance distribution in large-scale simulations.
In addition, the two variants of HMAC (HMAC–NoHung and HMAC–FixDEC) also follow and significantly outperform the traditional strategies (e.g., Greedy and Opportunistic), with the distribution of the Greedy strategy shifted to the left, which indicates that its probability of generating high-quality objective values is much lower than that of HMAC. This right-skewed distribution indicates that the HMAC model is not only more stable on average but also has a better global performance distribution in large-scale simulations. This right-skewed distribution property suggests that the HMAC model is not only superior on average but also more robust and guarantees upper-bound performance, which maintains high objective function values even under unfavorable network states.
Table 2 and
Figure 3,
Figure 4,
Figure 5,
Figure 6,
Figure 7,
Figure 8 and
Figure 9 show that the proposed HMAC algorithm achieves the best overall performance, with the highest average objective function value (1.81),
SU SINR (3.72), energy efficiency (8.01 bit/Joule), and fairness (0.75). These results demonstrate that HMAC can effectively balance throughput, interference control, and resource allocation, ensuring both
PU protection and
SU performance. The HMAC–NoHung and HMAC–FixDEC variants perform slightly worse, confirming the benefit of Hungarian-based allocation and adaptive DEC threshold switching. In contrast, Max-Power and Coexistence suffer from lower SINR and objective values due to either excessive interference or inefficient spectrum utilization, while Opportunistic yields the lowest overall performance because of its overly conservative access strategy. Across varying
SU numbers and cell sizes, HMAC consistently maintains a clear advantage, and its CDF curve indicates greater stability, reliability, and robustness than all baselines.