Long-Lifetime Ag/AgCl Electrodes Prepared by Pulse Current Electrodeposition for Chloride Monitoring in the Concrete Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
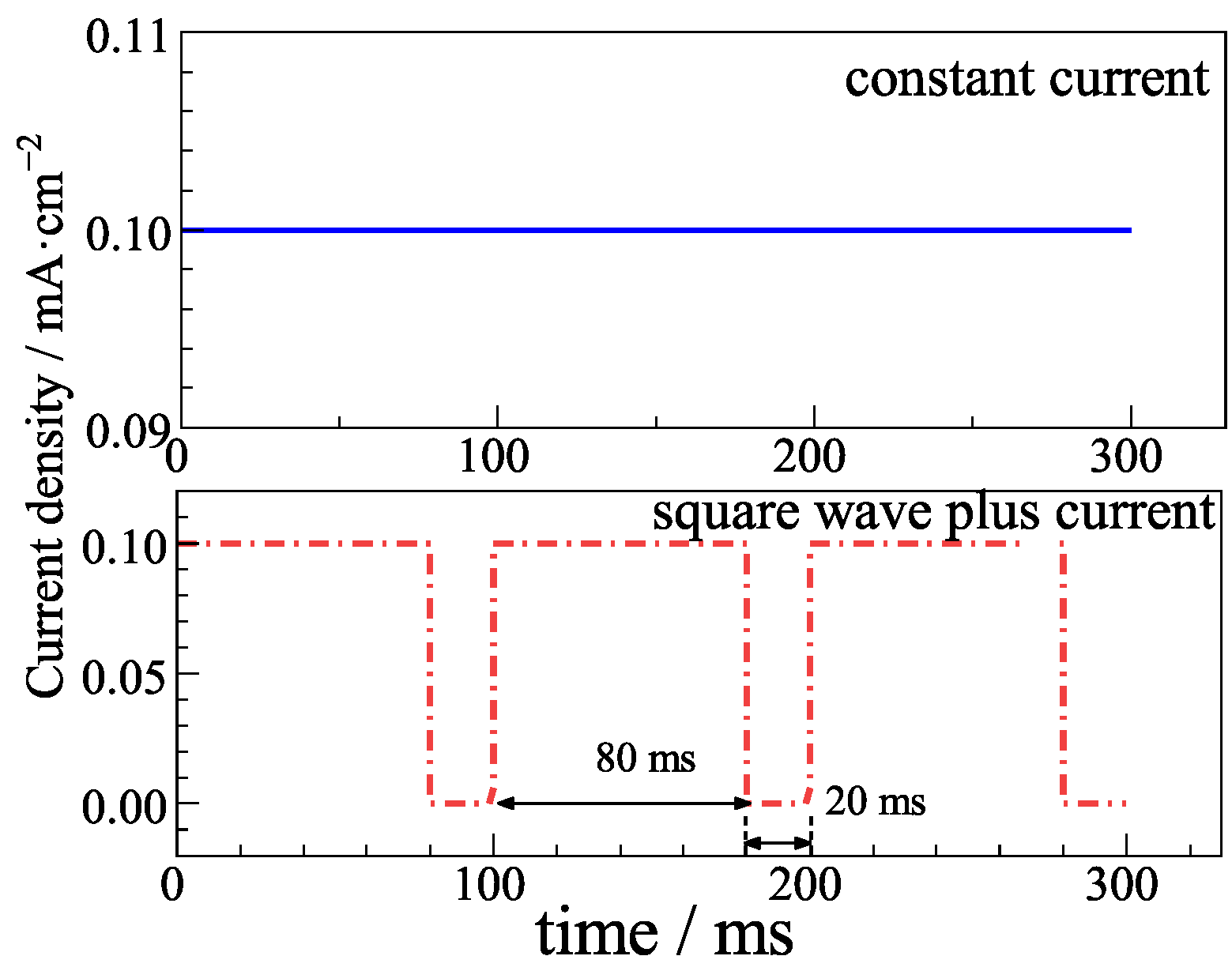
2.1. Preparation of Ag/AgCl Electrode
2.2. Electrochemical Measurements
2.3. Microstructure and Elemental Composition Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
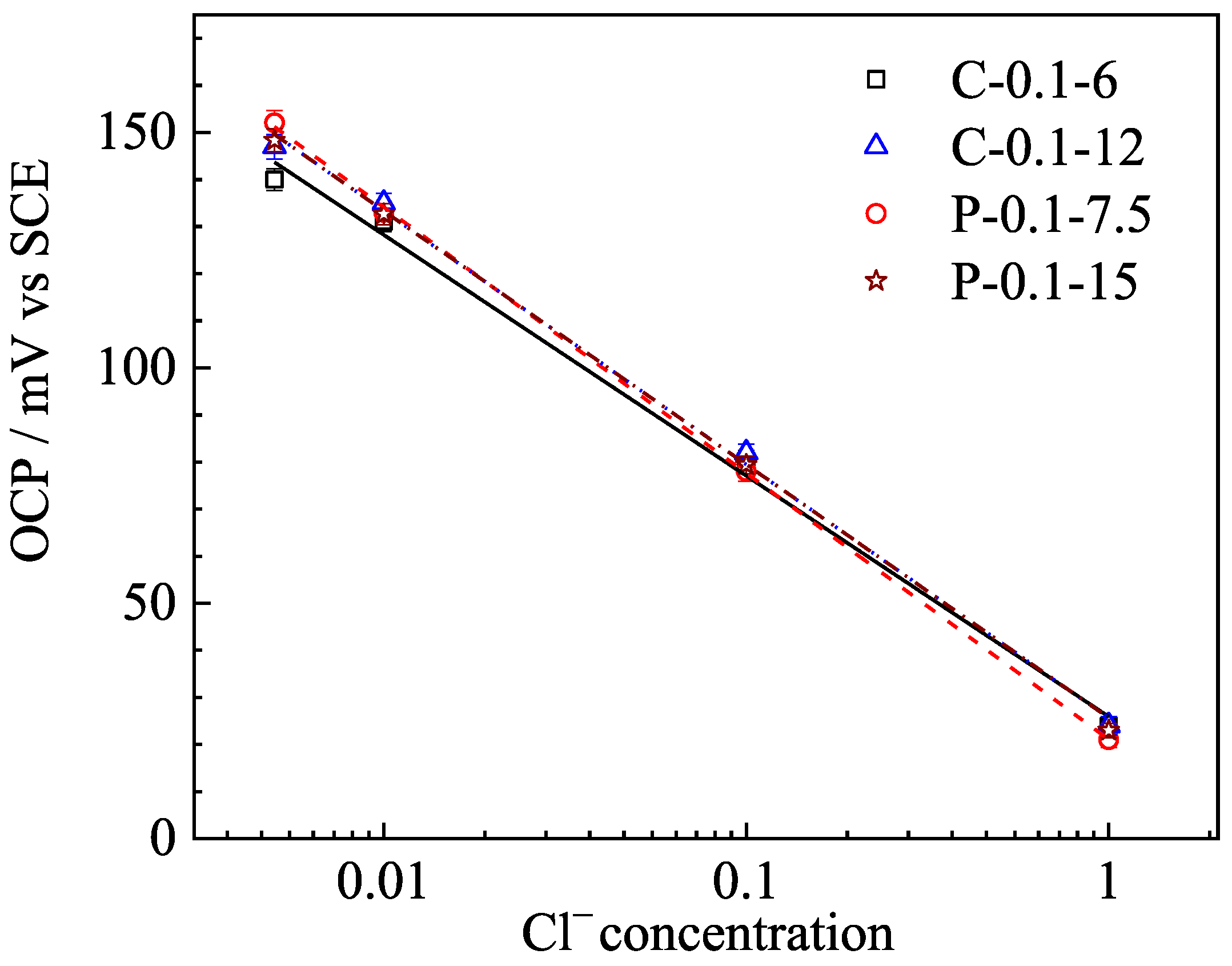
3.1. Sensitivity to Chloride Ion Concentration
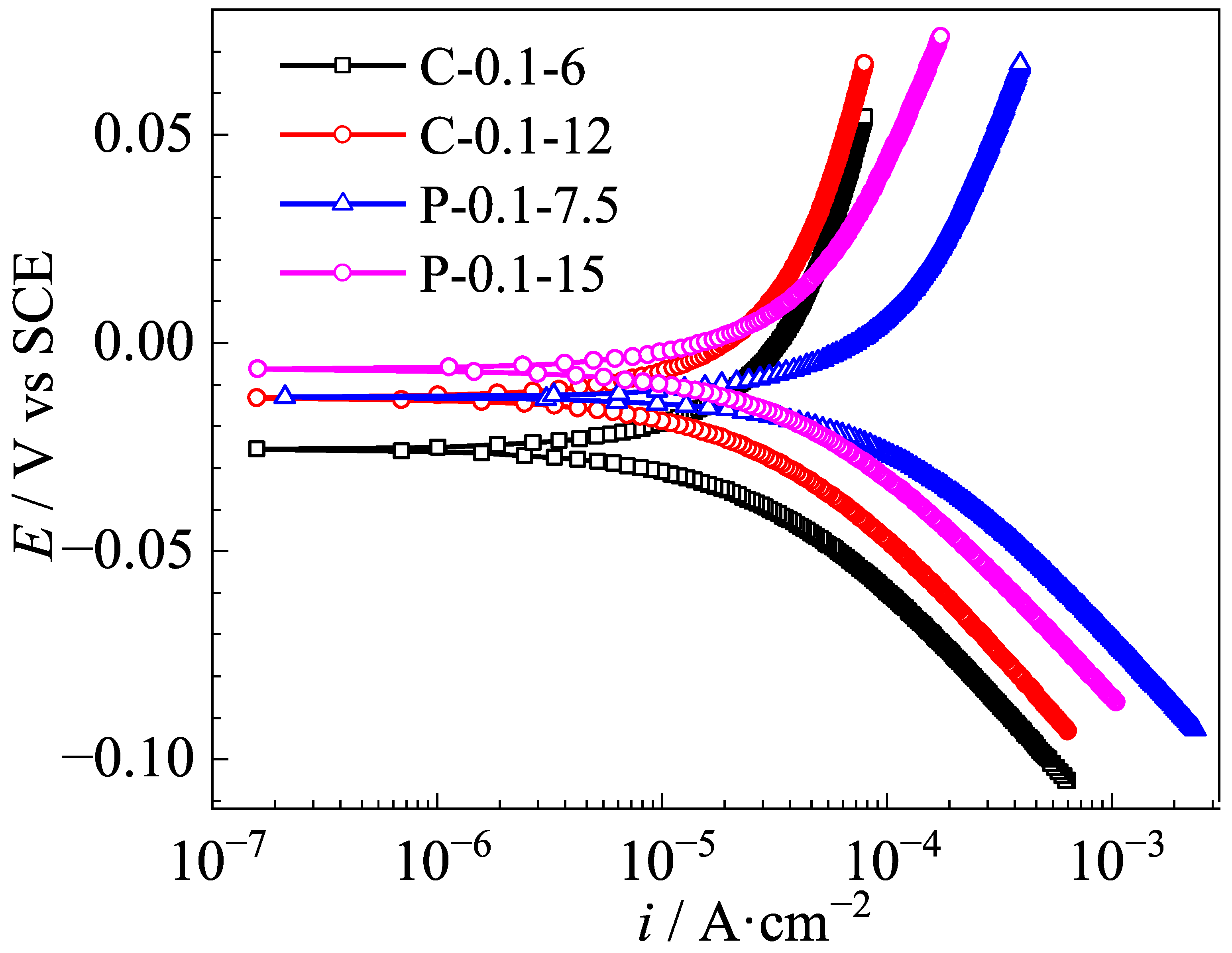
3.2. Polarization Curves of Ag/AgCl Electrodes
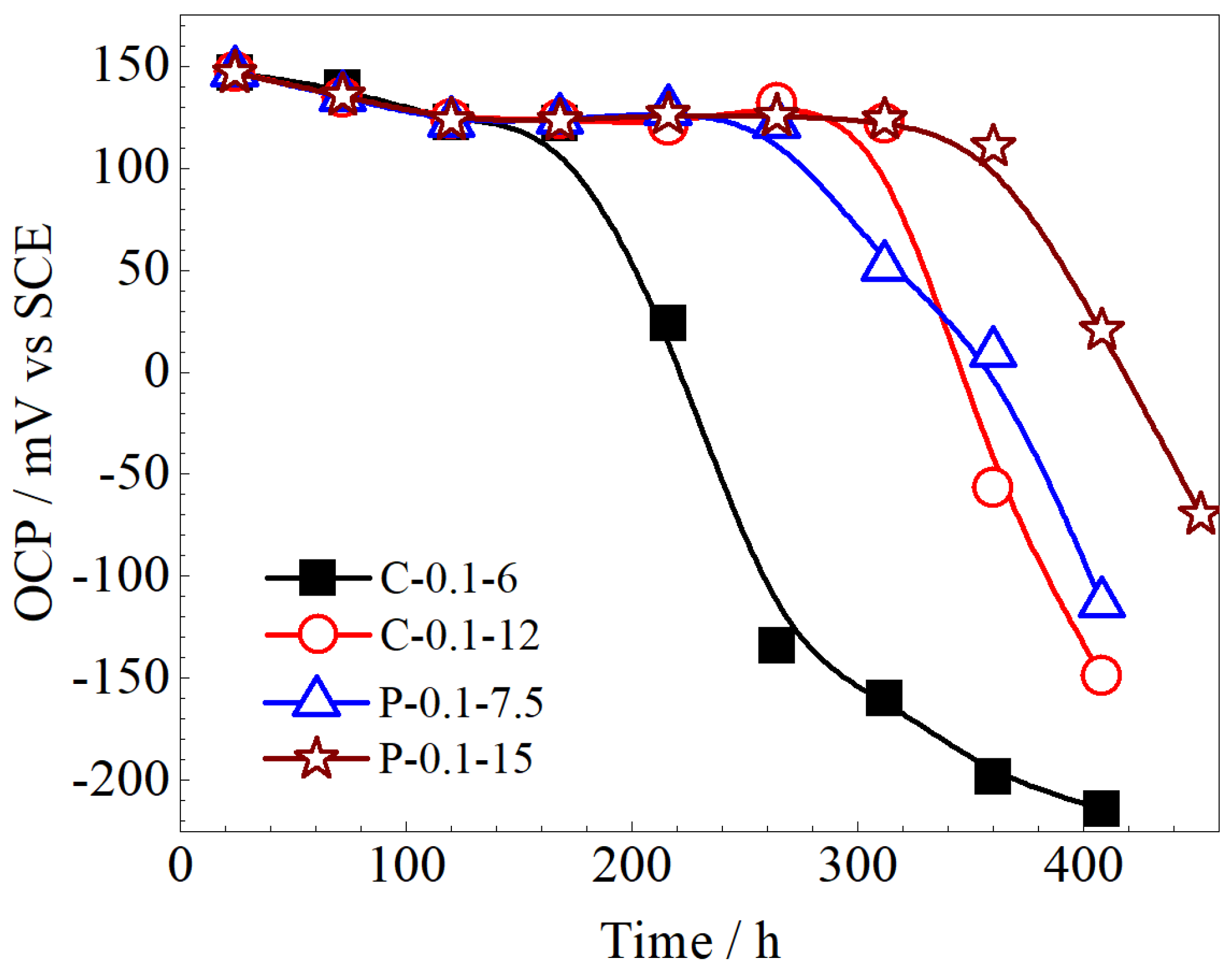
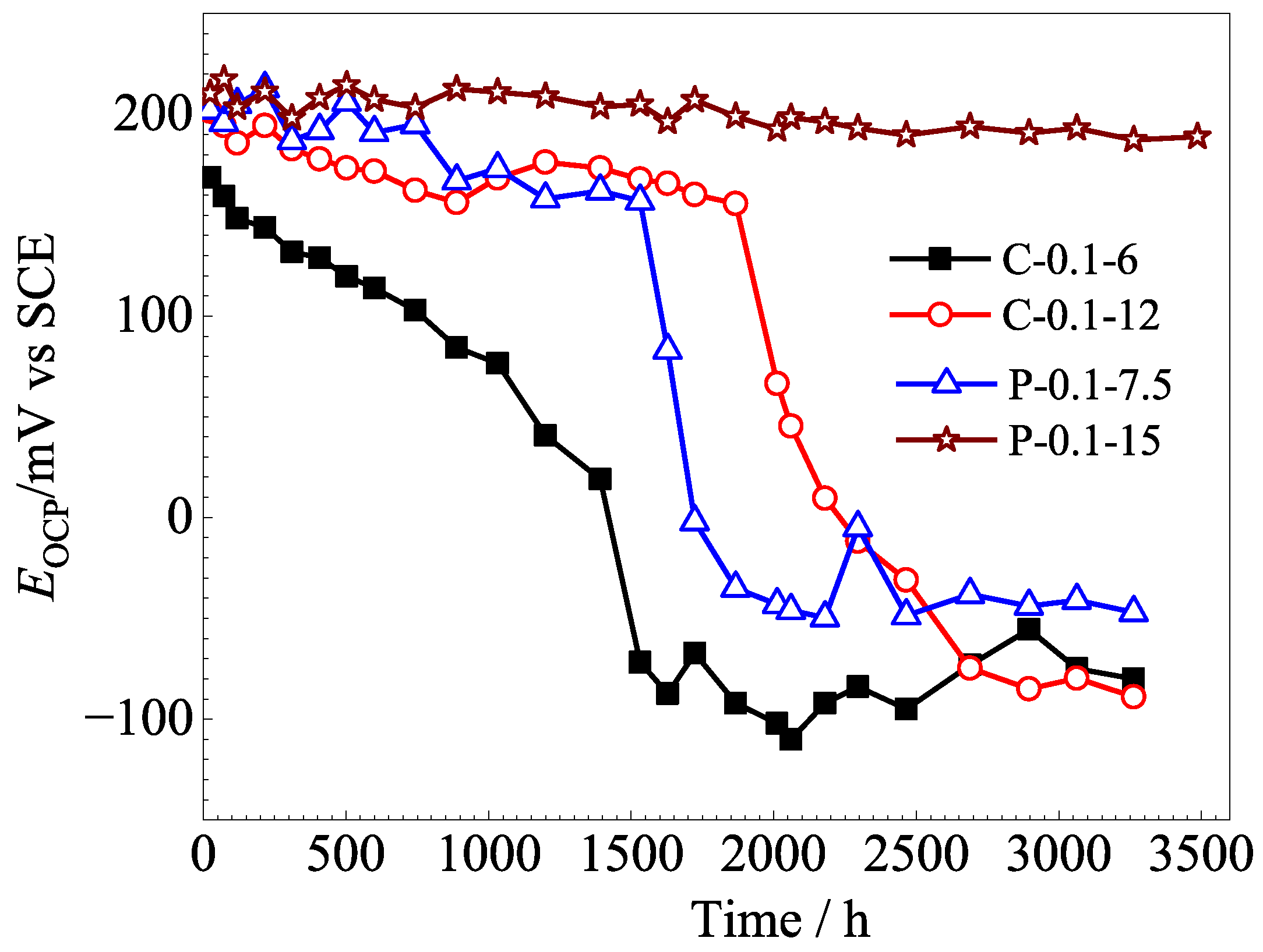
3.3. Stability of Ag/AgCl Electrodes
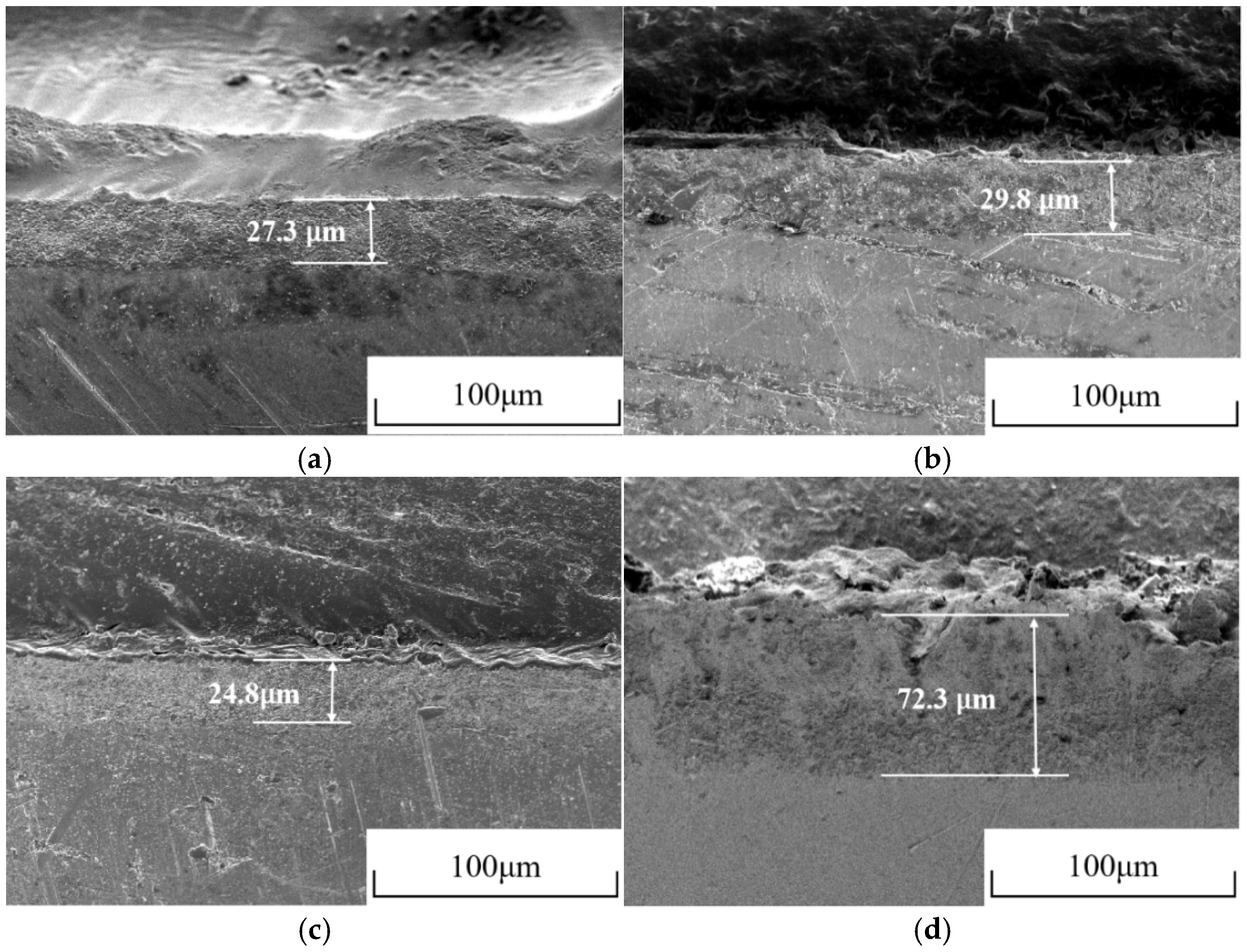
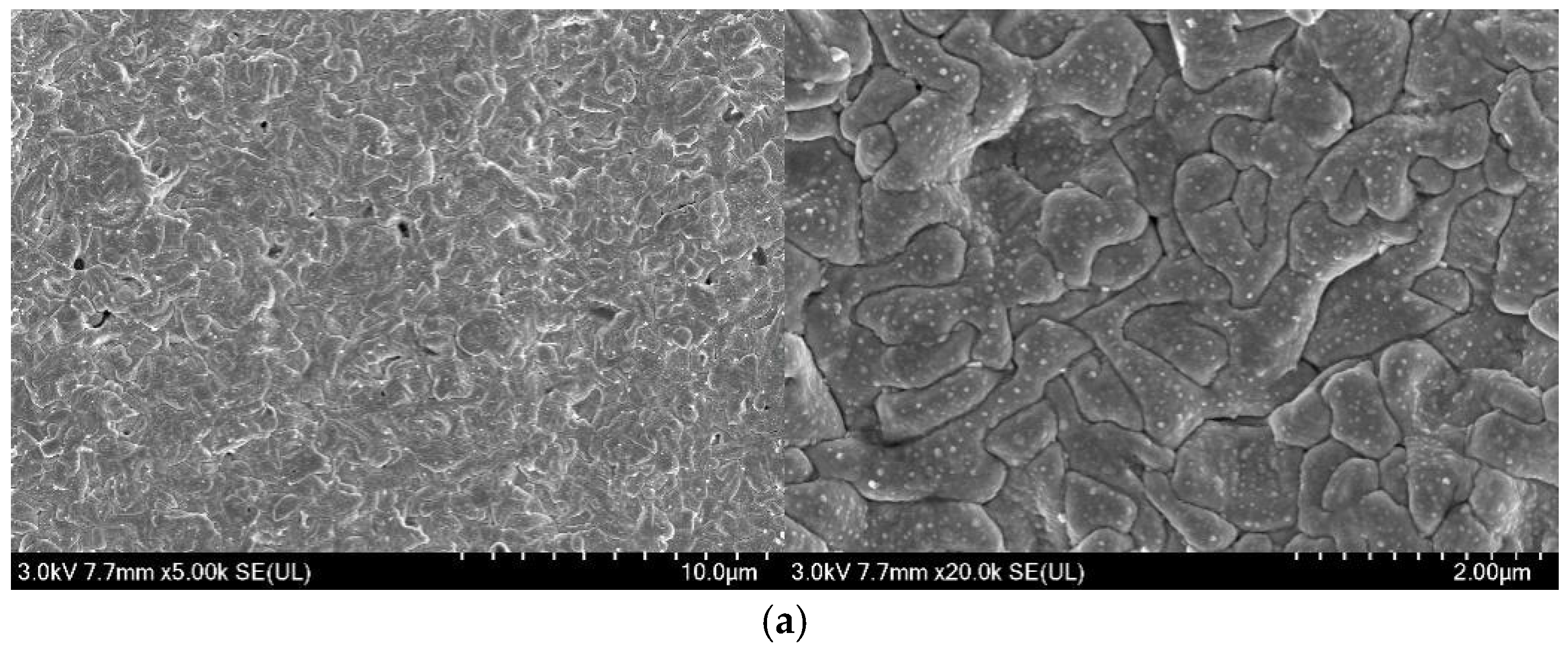
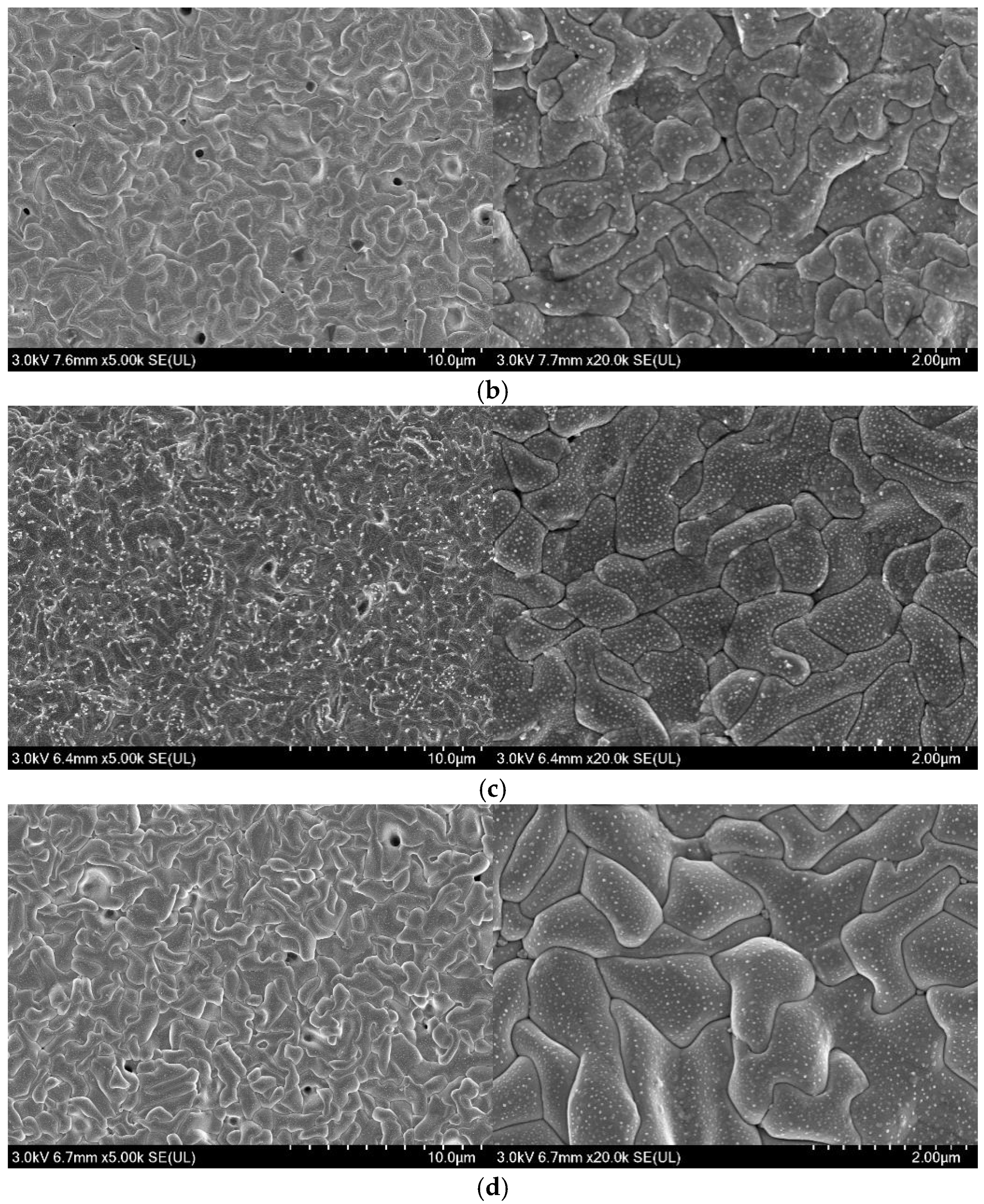
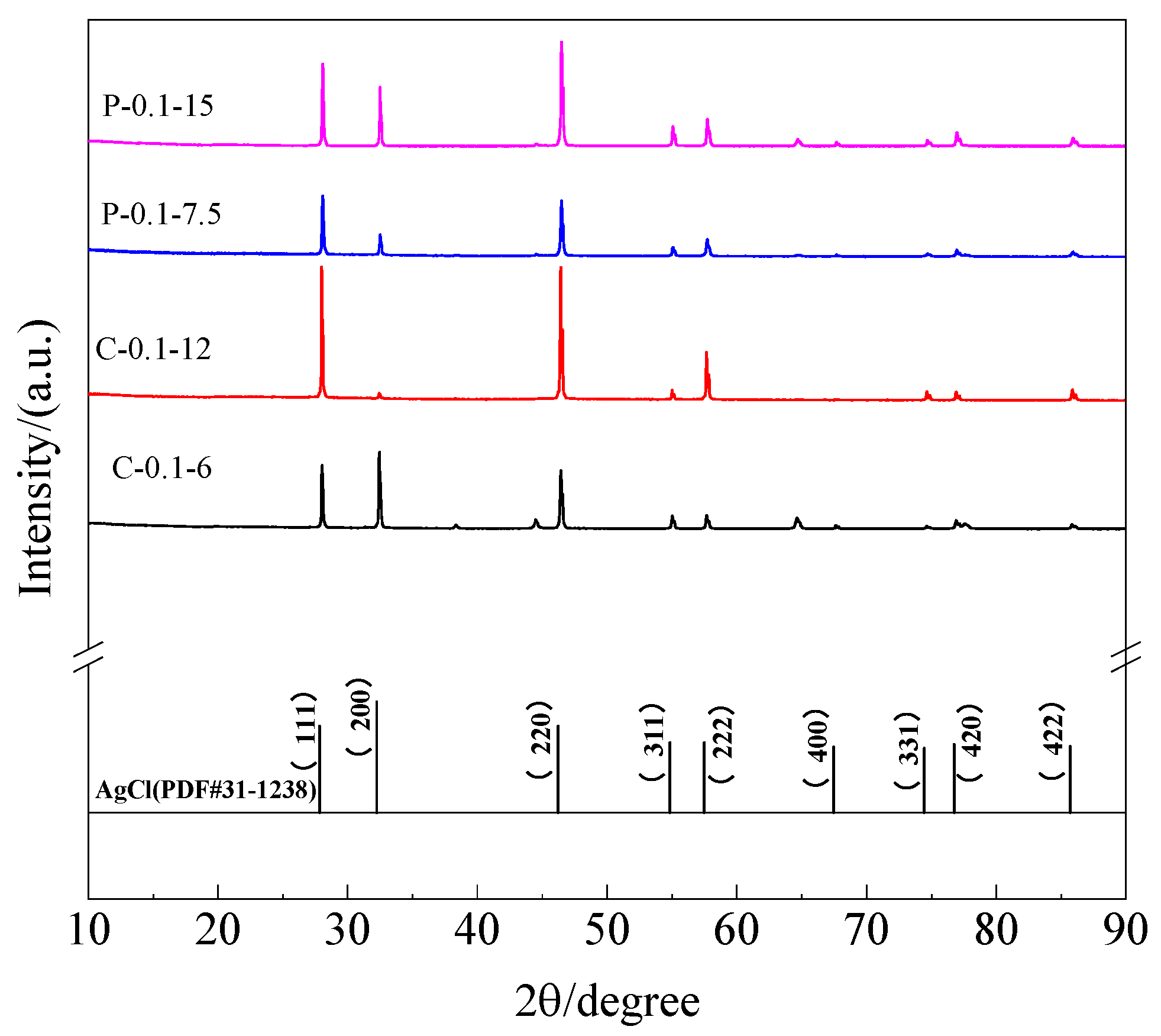
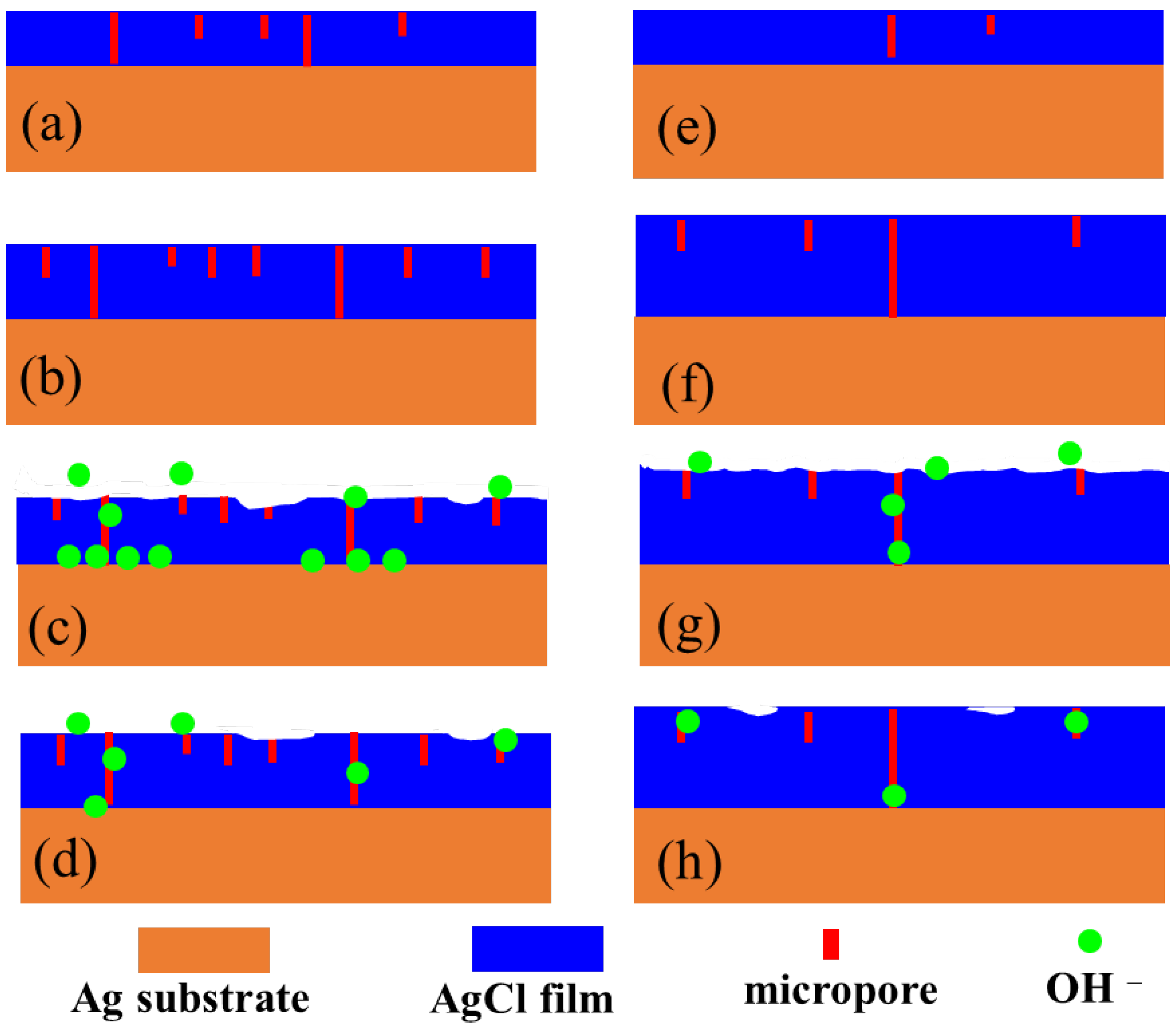
3.4. Microstructure Analysis of Ag/AgCl Electrodes
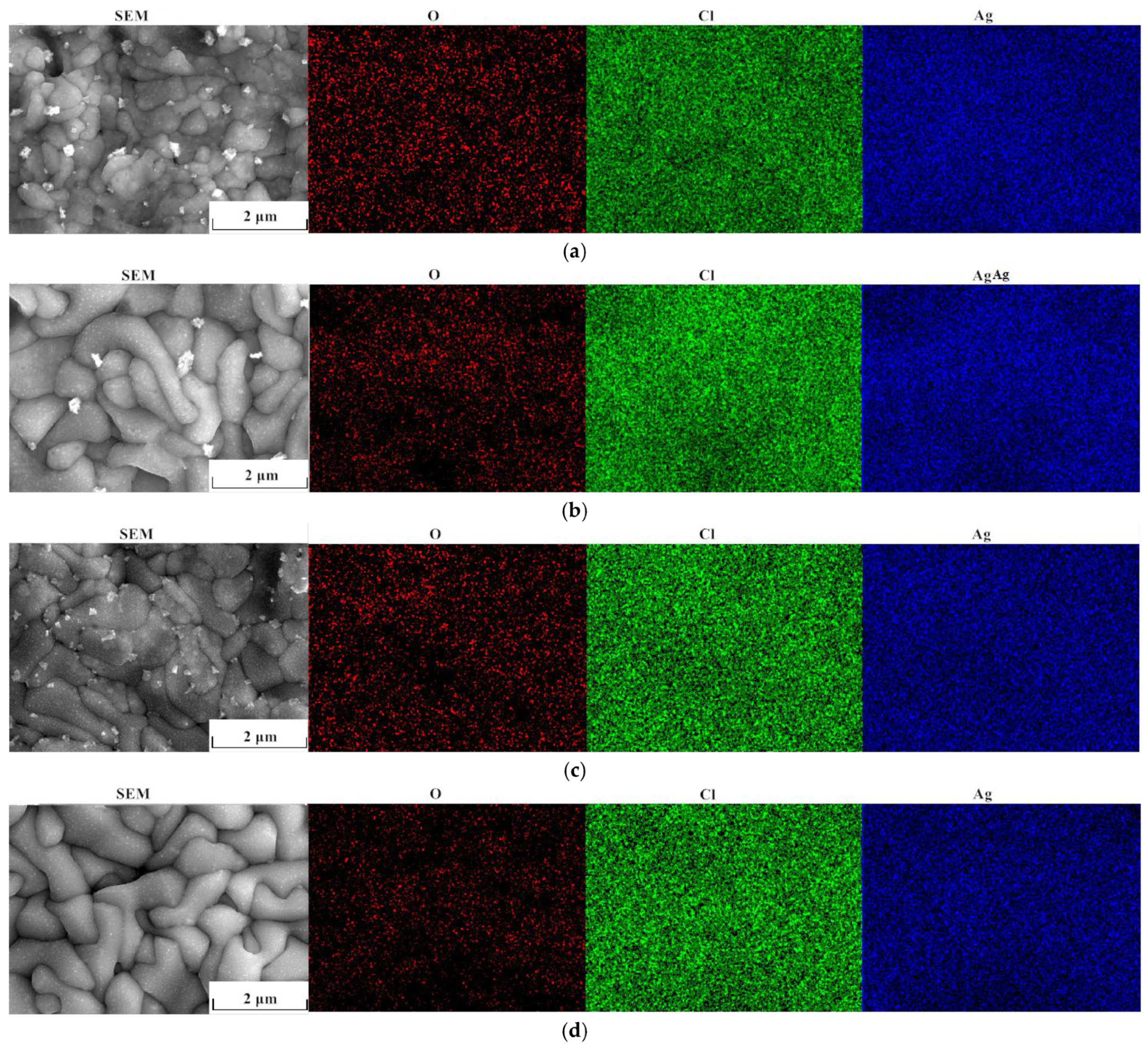
3.5. Composition Analysis of Ag/AgCl Electrodes
3.6. Ag/AgCl Electrode Prepared by Pulse Current Deposition and Its Performance
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Under the same equivalent charge transfer conditions, the Ag/AgCl electrodes prepared by applying the pulse current electrodeposition exhibit a wider potential response range and a higher exchange current density than those of the counterpart electrodeposited by the constant current in the identical Cl−-containing pore solution.
- (2)
- More micropores can be observed in the electrodeposited AgCl films both by applying the constant current or the pulsed current when the electrodeposition duration was extended. The former AgCl film displayed a higher density of micropores than the latter films under the same equivalent charge transfer conditions. The thickness of the AgCl films were slightly and significantly increased by applying the constant current and the pulsed current when the electrodeposition duration was doubled.
- (3)
- No Ag2O can be detected in the AgCl films whether electrodeposition adopted the constant current or the pulsed current. The AgCl films prepared with the former current displayed a lower Cl/O ratio and a higher Ag/Cl ratio than those electrodeposited by applying the latter current.
- (4)
- The lifetimes of the Ag/AgCl electrodes prepared with the pulsed current were longer than those of the counterparts prepared by the constant current, with the same equivalent charge transfers, both in the pore solution and mortar. The lifetime of the Ag/AgCl electrode in the concrete environment was mainly determined by the thickness of the AgCl film.
- (5)
- In general, the Ag/AgCl electrodes prepared using 0.1 mA/cm2 pulse current for 15 h displayed the best comprehensive performance, and their lifetimes were about 420 in pore solution and more than 3500 h in mortar. In particular, the P-0.1-15 electrode did not show any significant decrease in OCPs after 3500 h in the mortar without Cl−. The lifetime of the Ag/AgCl electrode should be further confirmed in real concrete structures.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Sanchez, T.; Conciatori, D.; Laferriere, F.; Sorelli, L. Modelling capillary effects on the reactive transport of chloride ions in cementitious materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2020, 131, 106033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, X.; Cai, Y.; Li, Z. Atomic scale insight into the mechanisms of chloride induced steel corrosion in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 351, 128811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Shi, Z.; Zhu, R.; Feng, X. A comparison study of constant current and square wave current in the bidirectional electromigration rehabilitation on chloride-contaminated concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 409, 134216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, Q. Monitoring chloride ion penetration in concrete with different mineral admixtures based on embedded chloride ion selective electrodes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 143, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Feng, X.; Qu, Z.; Lu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, R.; Zhou, Q.; He, A.; Zhang, H.; Chen, S. An array sensor for monitoring the chloride concentration profile in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 478, 141419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Shi, X. Techniques of corrosion monitoring of steel rebar in reinforced concrete structures: A review. Struct. Health Monit. 2021, 21, 1879–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Xu, J.; Jiang, L.; Gao, G.; Chu, H.; Xiong, C.; Gao, H.; Jiang, P. Electrochemical characterization of a solid embeddable Ag/AgCl reference electrode for corrosion monitoring in reinforced concrete. Electrochemistry 2014, 82, 1040–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hu, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, J.; Yin, S.; Yu, Q. A state-of-the-art review on Ag/AgCl ion-selective electrode used for non-destructive chloride detection in concrete. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 200, 108289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yuan, H.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Bai, Y.; Wang, J.; Cao, F. A highly sensitive, long-time stable Ag/AgCl ultra-micro sensor for in situ monitoring chloride ions inside the crevice using SECM. Talanta 2024, 274, 126026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Jiang, L.; Tao, D.; Bai, S. Characterization of Ag/AgCl electrode manufactured by immersion in sodium hypochloride acid for monitoring chloride content in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 122, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Shi, R.; Ma, Y.; Huang, H.; Wang, H.; Wei, J.; Yu, Q. Relationship between microstructure of AgCl film and electrochemical behavior of Ag|AgCl electrode for chloride detection. Corros. Sci. 2021, 184, 109393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hu, J.; Xu, Z.; Huang, H.; Yin, S.; Ma, Y.; Wei, J.; Yu, Q. Degradation process of Ag/AgCl chloride-sensing electrode in cement extract with low chloride concentration. Corros. Sci. 2022, 198, 110107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Wang, H. Electrochemical investigation on the effect of chloride ion concentration on the corrosion of concrete reinforcement using in-situ nano-Ag/AgCl electrode. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 66, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hu, J.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Liu, S.; Guo, Y.; Huang, H.; Ma, Y.; Wei, J.; Yu, Q.; et al. Influence of AgCl film resistance on stability and potential response of Ag/AgCl chloride-sense electrode in simulated concrete pore solution. Electrochim. Acta 2024, 478, 143839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Femenias, Y.S.; Angst, U.; Caruso, F.; Elsener, B. Ag/AgCl ion-selective electrodes in neutral and alkaline environments containing interfering ions. Mater. Struct. 2015, 49, 2637–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, D.; Jiang, L.; Jin, M. A method of preparation of Ag/AgCl chloride celective electrode. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Sci. Ed. 2018, 33, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Song, Y.S.; Zhou, Y. Effect of sintering technology on Ag/AgCl electrode potential stability. Adv. Mater. Res. 2010, 152–153, 1900–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climent-Llorca, M.A.; Viqueira-Pérez, E.; López-Atalaya, M.M. Embeddable Ag/AgCl sensors for in-situ monitoring chloride contents in concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 1996, 26, 1157–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pargar, F.; Kolev, H.; Koleva, D.A.; van Breugel, K. Microstructure, surface chemistry and electrochemical response of Ag/AgCl sensors in alkaline media. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 7527–7550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pargar, F.; Kolev, H.; Koleva, D.A.; van Breugel, K. Potentiometric response of Ag/AgCl chloride sensors in model alkaline medium. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. Anal. 2018, 2018, 8135492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, P.J.; Leese, R.J.; Brown, R.J.C. An improved approach for fabricating Ag/AgCl reference electrodes. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018, 8135492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, P.J.; Minarro, M.D.; di Meane, E.A.; Brown, R.J.C. A high accuracy dilution system for generating low concentration reference standards of reactive gases. Measurement 2013, 47, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, P.J.; Leach, A.S.; Brown, R.J.C. The role of the electrolyte in the fabrication of Ag/AgCl reference electrodes for pH measurement. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 161, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.; Raj, V. A comparative study of DC and pulse gold electrodeposits. Trans. IMF 2005, 83, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanthi, C.; Barathan, S.; Jaiswal, R.; Arunachalam, R.M. Study of surface morphology in DC and pulse plating of silver alloy. Indian J. Eng. Mater. Sci. 2009, 16, 128–132. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y. Influence of double-pulse electrodeposition parameters on the performance of Ag/AgCl electrochemical electrode for marine electric field. Sensors 2024, 24, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.W.; Wang, P.G.; Zhao, T.J.; Ma, Z.M. Effect of current density and polarization time on morphology of Ag/AgCl electrode. Mater. Prot. 2016, 49, 22–25. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Du, R.G.; Huang, R.S.; Hu, R.G.; Zhao, B.; Lin, Y.H.; Tan, J.G.; Lin, C.J. Embeddable combination probe for in-situ measuring Cl- and pH at the reinforcing steel/concrete interface. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2005, 33, 29–32. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Du, Z.; Tian, L.; Wang, P.; Chen, Z.; Cui, D.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, H. All-solid-state chloride sensor for in-situ monitoring of chloride penetration in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 357, 129345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, U.; Elsener, B.; Larsen, K.C.; Vennesland, O. Potentiometric determination of the chloride ion activity in cement based materials. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2009, 40, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Krause, R.; Gogoi, E.; Reck, A.; Graf, A.; Wislicenus, M.; Hild, O.R.; Guhl, C. Multielectrode arrays at wafer-level for miniaturized sensors applications: Electrochemical growth of Ag/AgCl reference electrodes. Sensors 2023, 23, 6130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Specimen No. | Current Mode | Current Density/ (mA·cm−2) | Time/h |
|---|---|---|---|
| C-0.1-6 | Constant current Pulse current | 0.1 | 6 |
| C-0.1-12 P-0.1-7.5 | 0.1 0.1 | 12 7.5 | |
| P-0.1-15 | 0.1 | 15 |
| Specimen No. | Slope | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| C-0.1-6 | −51.131 | 0.9941 |
| C-0.1-12 | −53.846 | 0.9971 |
| P-0.1-7.5 | −56.540 | 0.9996 |
| P-0.1-15 | −54.431 | 0.9996 |
| Specimen No. | i0 (A/cm2) |
|---|---|
| C-0.1-6 | 3.735 × 10−5 |
| C-0.1-12 | 1.195 × 10−4 |
| P-0.1-7.5 | 4.658 × 10−5 |
| P-0.1-15 | 1.416 × 10−4 |
| Specimen No. | O/% | Cl/% | Ag/% | Cl/O Ratio | Ag/Cl Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-0.1-6 | 3.055 | 36.588 | 60.387 | 11.976 | 5.042 |
| C-0.1-12 | 4.375 | 38.249 | 57.377 | 8.7426 | 6.563 |
| P-0.1-7.5 | 2.537 | 31.449 | 66.014 | 12.396 | 5.325 |
| P-0.1-15 | 2.040 | 38.517 | 59.444 | 18.881 | 3.148 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, X.; Hu, J.; Feng, X.; Zhou, Q.; Qu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, H.; Chen, S. Long-Lifetime Ag/AgCl Electrodes Prepared by Pulse Current Electrodeposition for Chloride Monitoring in the Concrete Environment. Sensors 2025, 25, 5032. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165032
Lu X, Hu J, Feng X, Zhou Q, Qu Z, Zhang J, Zhu R, Zhang H, Chen S. Long-Lifetime Ag/AgCl Electrodes Prepared by Pulse Current Electrodeposition for Chloride Monitoring in the Concrete Environment. Sensors. 2025; 25(16):5032. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165032
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Xiangyu, Jing Hu, Xingguo Feng, Qiyan Zhou, Zhanqing Qu, Jisheng Zhang, Ruihu Zhu, Huaqing Zhang, and Songgui Chen. 2025. "Long-Lifetime Ag/AgCl Electrodes Prepared by Pulse Current Electrodeposition for Chloride Monitoring in the Concrete Environment" Sensors 25, no. 16: 5032. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165032
APA StyleLu, X., Hu, J., Feng, X., Zhou, Q., Qu, Z., Zhang, J., Zhu, R., Zhang, H., & Chen, S. (2025). Long-Lifetime Ag/AgCl Electrodes Prepared by Pulse Current Electrodeposition for Chloride Monitoring in the Concrete Environment. Sensors, 25(16), 5032. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165032








