Posture Estimation from Tactile Signals Using a Masked Forward Diffusion Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
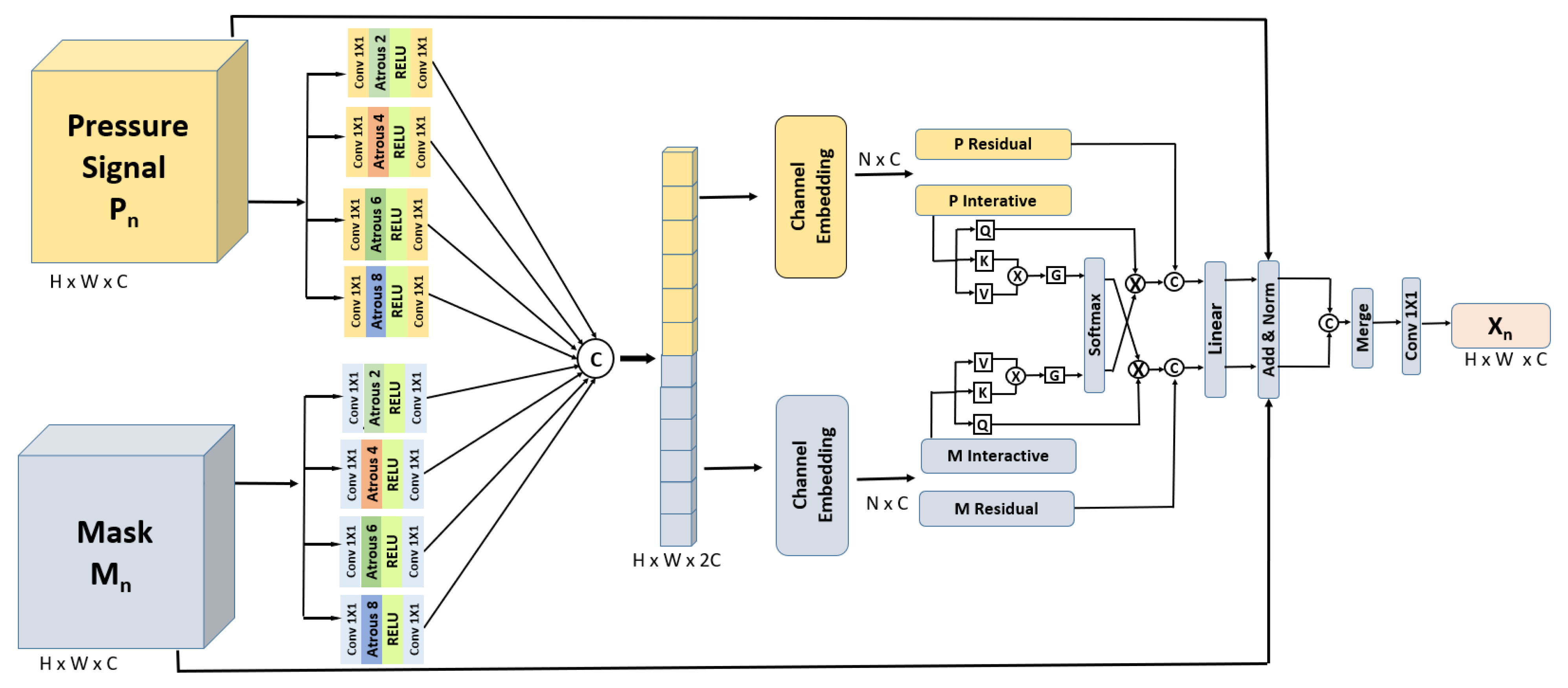
- A novel dual-diffusion signal enhancement (DDSE) architecture that adopts dual-forward diffusion processes. The noisy pressure signal and its associated morphological mask are each processed through their own forward diffusion pathways. At each step, features from both diffusion channels leverage a reverse diffusion process to denoise tactile information.
- A novel contour detection and alignment (CDA) layer, which integrates signals from dual-forward diffusion processes using spatial-pooling-based cross attention, significantly enhances spatial resolution by leveraging temporal information to enrich feature integration and refines contour detection from step-generated images.
- A pressure-to-posture inference technology (PPIT) dataset that combines tactile pressure maps with motion-captured data. This innovative motion-captured dataset addresses the challenges associated with image-based keypoint generation, thereby providing highly accurate ground truth for 3D keypoints.
2. Related Work
2.1. Human Pose Estimation Using Tactile Sensing
2.2. Human Pose Estimation Systems
2.3. Diffusion Models
2.4. Datasets for Tactile-Based HPE
3. Methodology
3.1. Pressure to Posture Estimation
3.2. Problem Definition
- 1.
- Stage 1: Denoise to reconstruct , thereby reducing noise and enhancing the input signal.
- 2.
- Stage 2: Use the denoised signal to estimate with high precision.
3.3. Stage 1: Dual-Diffusion Signal Enhancement (DDSE)
3.3.1. Sparse/Noisy Pressure Signal
3.3.2. Pressure Signal Forward Diffusion (PSFD)
3.3.3. Refined Mask Generation
3.3.4. Refined Soft Mask Forward Diffusion (RMFD)
3.3.5. Reverse Denoising Process
3.4. Stage 2: 3D Pose Prediction Transformer (3DPPT)
3.4.1. Transformer Encoder
3.4.2. Decoder Stage
4. Experimental Evaluation
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Experimental Protocol
4.3. Stage 1 Evaluation Metrics
4.3.1. Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR)
4.3.2. Structural Similarity (SSIM)
4.3.3. Learned Perceptual Image Patch Similarity (LPIPS)
4.4. Stage 2 Evaluation Metrics
4.4.1. Mean per Joint Position Error (MPJPE)
4.4.2. Average Keypoint Localization Error of Whole Body (AKLEB)
4.5. Evaluation of Pressure Signal Restoration
Computational Efficiency Comparison
4.6. Posture Prediction Evaluation
4.7. Ablation Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gong, J.; Foo, L.G.; Fan, Z.; Ke, Q.; Rahmani, H.; Liu, J. DiffPose: Toward More Reliable 3D Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 13041–13051. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; He, J.-Y.; Cheng, Z.-Q.; Xiang, W.; Yang, Q.; Chai, W.; Wang, G.; Bao, X.; Luo, B.; Geng, Y. Posynda: Multi-Hypothesis Pose Synthesis Domain Adaptation for Robust 3D Human Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia (ACMMM), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 29 October–3 November 2023; pp. 5542–5551. [Google Scholar]
- Clever, H.M.; Kapusta, A.; Park, D.; Erickson, Z.; Chitalia, Y.; Kemp, C.C. 3D Human Pose Estimation on a Configurable Bed from a Pressure Image. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; pp. 54–61. [Google Scholar]
- Marchand, E.; Uchiyama, H.; Spindler, F. Pose Estimation for Augmented Reality: A Hands-On Survey. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2016, 22, 2633–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachole, S.; Alkendi, Y.; Baghaei Naeini, F.; Makris, D.; Zweiri, Y. Asynchronous Events-Based Panoptic Segmentation Using Graph Mixer Neural Network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 4083–4092. [Google Scholar]
- Kachole, S.; Sajwani, H.; Baghaei Naeini, F.; Makris, D.; Zweiri, Y. Asynchronous Bioplausible Neuron for Spiking Neural Networks for Event-Based Vision. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; pp. 399–415. [Google Scholar]
- Kachole, S.; Mahakal, M.; Bhagwatkar, A. 3 Dimensional Welding SPM/Path Tracker. Int. J. Des. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 7, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Takalkar, M.; Kakarparthy, V.; Khan, I.R. Design & Development of TIG Welding—Special Purpose Machine. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. (IJRASET) 2017, 5, 1344–1351. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Shah, B.B.; Prakash, C. A Pilot Study on Human Pose Estimation for Sports Analysis. In Pattern Recognition and Data Analysis with Applications; Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering; Springer: Singapore, 2022; Volume 888, pp. 533–544. [Google Scholar]
- Seguin, G.; Alahari, K.; Sivic, J.; Laptev, I. Pose Estimation and Segmentation of Multiple People in Stereoscopic Movies. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1643–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, X.; Wang, C.; Xiao, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, B. A Portable Sitting Posture Monitoring System Based on a Pressure Sensor Array and Machine Learning. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 331, 112900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Joo, H.-T.; Chung, I.; Park, D.; Choi, Y.; Kim, K.-J. A Novel Approach for Virtual Locomotion Gesture Classification: Self-Teaching Vision Transformer for a Carpet-Type Tactile Sensor. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality Adjunct (ISMAR-Adjunct), Sydney, Australia, 16–20 October 2023; pp. 369–370. [Google Scholar]
- Clever, H.M.; Erickson, Z.; Kapusta, A.; Turk, G.; Liu, K.; Kemp, C.C. Bodies at Rest: 3D Human Pose and Shape Estimation from a Pressure Image Using Synthetic Data. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 6215–6224. [Google Scholar]
- Clever, H.M.; Grady, P.L.; Turk, G.; Kemp, C.C. Body Pressure-Inferring Body Pose and Contact Pressure from a Depth Image. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 137–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghaei Naeini, F.; Kachole, S.; Makris, D.; Zweiri, Y.H. Event Augmentation for Contact Force Measurements. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 123651–123660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, Y.; Foshey, M.; Shou, W.; Sharma, P.; Palacios, T.; Torralba, A.; Matusik, W. Intelligent Carpet: Inferring 3D Human Pose from Tactile Signals. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 11255–11265. [Google Scholar]
- Badiola-Bengoa, A.; Mendez-Zorrilla, A. A Systematic Review of the Application of Camera-Based Human Pose Estimation in the Field of Sport and Physical Exercise. Sensors 2021, 21, 5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-H.; Wu, T.-C.; Lin, W.-B. Exploration of Applying Pose Estimation Techniques in Table Tennis. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, T.; Klatt, S. Monocular 3D Human Pose Estimation for Sports Broadcasts Using Partial Sports Field Registration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 5108–5117. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, N.N.; Sameri, J.; Struye, J.; Vega, M.T.; Berkvens, R.; Famaey, J. Multi-Modal Pose Estimation in XR Applications Leveraging Integrated Sensing and Communication. In Proceedings of the 1st ACM Workshop on Mobile Immersive Computing, Networking, and Systems, New York, NY, USA, 8 October 2023; pp. 261–267. [Google Scholar]
- Ohri, A.; Agrawal, S.; Chaudhary, G.S. On-Device Realtime Pose Estimation & Correction. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Manag. (IJAEM) 2021, 3, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Boda, P.; Ramadevi, Y. Predicting Pedestrian Behavior at Zebra Crossings Using Bottom-Up Pose Estimation and Deep Learning. Int. J. Intell. Syst. Appl. Eng. 2024, 12, 527–544. [Google Scholar]
- Anvari, T.; Park, K.; Kim, G. Upper Body Pose Estimation Using Deep Learning for a Virtual Reality Avatar. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Guo, T. Xihe: A 3D Vision-Based Lighting Estimation Framework for Mobile Augmented Reality. In Proceedings of the 19th ACM International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications and Services (MobiSys), Virtual, 24–28 June 2021; pp. 28–40. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Wang, X.; Li, B.; Wang, H.; Chen, G.; Cai, M. YH-Pose: Human Pose Estimation in Complex Coal Mine Scenarios. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 127, 107338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskeliūnas, R.; Kulikajevas, A.; Damaševičius, R.; Griškevičius, J.; Adomavičienė, A. Biomac3D: 2D-to-3D Human Pose Analysis Model for Tele-Rehabilitation Based on Pareto Optimized Deep-Learning Architecture. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehraban, S.; Adeli, V.; Taati, B. MotionAGFormer: Enhancing 3D Human Pose Estimation with a Transformer-GCNFormer Network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 4–8 January 2024; pp. 6920–6930. [Google Scholar]
- Lupión, M.; Polo-Rodríguez, A.; Medina-Quero, J.; Sanjuan, J.F.; Ortigosa, P.M. 3D Human Pose Estimation from Multi-View Thermal Vision Sensors. Inf. Fusion 2024, 104, 102154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Sun, C.; Yuan, W.; Gu, W.; Cui, Z.; Chen, W. Smart Mat System with Pressure Sensor Array for Unobtrusive Sleep Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 11–15 July 2017; pp. 177–180. [Google Scholar]
- Ozioko, O.; Dahiya, R. Smart Tactile Gloves for Haptic Interaction, Communication, and Rehabilitation. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2022, 4, 2100091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Guo, S.; Xiao, S.; Zhao, X. Unconstrained Identification of the Positions of Chest and Abdomen and Detection of Respiratory Motions in Sleep by Using a Bed Size Tactile Sensor Sheet. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 16276–16286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagoli, A.; Chapelle, F.; Corrales-Ramon, J.-A.; Mezouar, Y.; Lapusta, Y. Large-Area and Low-Cost Force/Tactile Capacitive Sensor for Soft Robotic Applications. Sensors 2022, 22, 4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moro, F.; Hardy, E.; Fain, B.; Dalgaty, T.; Clémençon, P.; De Prà, A.; Esmanhotto, E.; Castellani, N.; Blard, F.; Gardien, F. Neuromorphic Object Localization Using Resistive Memories and Ultrasonic Transducers. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Xu, H.; Ke, Y.; Ming, X.; Jiang, H.; Li, M.; Wang, D. Accurate and Efficient Sitting Posture Recognition and Human-Machine Interaction Device Based on Fabric Pressure Sensor Array and Neural Network. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2024, 9, 2301579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; An, L.; Li, M.; Yu, T.; Liu, Y. Lightweight Multi-Person Total Motion Capture Using Sparse Multi-View Cameras. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 5560–5569. [Google Scholar]
- Marusic, A.; Nguyen, S.M.; Tapus, A. Evaluating Kinect, OpenPose, and BlazePose for Human Body Movement Analysis on a Low Back Pain Physical Rehabilitation Dataset. In Proceedings of the ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction (HRI), Stockholm, Sweden, 13–16 March 2023; pp. 587–591. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Yang, S.; Zhang, J.Z.; Manchester, Z.; Ramanan, D. PPR: Physically Plausible Reconstruction from Monocular Videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 3914–3924. [Google Scholar]
- Popescu, M.; Mronga, D.; Bergonzani, I.; Kumar, S.; Kirchner, F. Experimental Investigations into Using Motion Capture State Feedback for Real-Time Control of a Humanoid Robot. Sensors 2022, 22, 9853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agethen, P.; Otto, M.; Mengel, S.; Rukzio, E. Using Marker-Less Motion Capture Systems for Walk Path Analysis in Paced Assembly Flow Lines. Procedia CIRP 2016, 54, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michoud, B.; Guillou, E.; Bouakaz, S. Real-Time and Markerless Full-Body Human Motion Capture. In Actes du Groupe de Travail Animation et Simulation (GTAS’07); Association Française d’Informatique Graphique (AFIG): Lyon, France, 2007; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Sofianos, T.; Sampieri, A.; Franco, L.; Galasso, F. Space-Time-Separable Graph Convolutional Network for Pose Forecasting. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 11209–11218. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, J.; Jain, A.; Abbeel, P. Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. (NeurIPS) 2020, 33, 6840–6851. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2015, 9351, 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Nah, S.; Hyun Kim, T.; Mu Lee, K. Deep Multi-Scale Convolutional Neural Network for Dynamic Scene Deblurring. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3883–3891. [Google Scholar]
- Zamir, S.W.; Arora, A.; Khan, S.; Hayat, M.; Khan, F.S.; Yang, M.-H.; Shao, L. Multi-Stage Progressive Image Restoration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 14821–14831. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Lu, X.; Zhang, J.; Chu, X.; Chen, C. HiNet: Half Instance Normalization Network for Image Restoration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 182–192. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, F.-J.; Peng, Y.-T.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Tsai, C.-C.; Lin, C.-W. StripFormer: Strip Transformer for Fast Image Deblurring. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 146–162. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, D.; Xia, B.; Gu, J.; Kong, L.; Yuan, X. Hierarchical Integration Diffusion Model for Realistic Image Deblurring. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.12966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.M.; Chan, E.R.; Bergman, A.W.; Wetzstein, G. Diffusion in the Dark: A Diffusion Model for Low-Light Text Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 4–8 January 2024; pp. 4146–4157. [Google Scholar]
- Spetlik, R.; Rozumnyi, D.; Matas, J. Single-Image Deblurring, Trajectory, and Shape Recovery of Fast Moving Objects with Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 4–8 January 2024; pp. 6857–6866. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Liu, Y. Efficient Image Deblurring Networks Based on Diffusion Models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.05907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Hu, Y.; Song, W.; Liu, Y.; Torralba, A.; Matusik, W. CAvatar: Real-Time Human Activity Mesh Reconstruction via Tactile Carpets. In Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, Melbourne, Australia, 5–9 October 2024; Volume 7, pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Kachole, S.; Huang, X.; Baghaei Naeini, F.; Muthusamy, R.; Makris, D.; Zweiri, Y. Bimodal SegNet: Fused Instance Segmentation Using Events and RGB Frames. Pattern Recognit. 2024, 149, 110215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- TG0. Advanced Pressure Mat Demonstrator. Available online: https://www.tg0.co.uk/demonstrators/advanced-pressure-mat (accessed on 17 July 2025).
- Qualisys. Qualisys-Advanced Motion Capture Systems. Available online: https://www.qualisys.com/ (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Kupyn, O.; Budzan, V.; Mykhailych, M.; Mishkin, D.; Matas, J. DeblurGAN: Blind Motion Deblurring Using Conditional Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 8183–8192. [Google Scholar]
- Loper, M.; Mahmood, N.; Romero, J.; Pons-Moll, G.; Black, M.J. SMPL: A Skinned Multi-Person Linear Model. In ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG); ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 34, pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Gao, T.; Dong, A.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, F. A Survey of the State of the Art in Monocular 3D Human Pose Estimation: Methods, Benchmarks, and Challenges. Sensors 2025, 25, 2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yu, C.; Liang, C.; Shi, Y. PoseAugment: Generative Human Pose Data Augmentation with Physical Plausibility for IMU-Based Motion Capture. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2409.14101. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, L.S.S.; Rey, V.F.; Zhou, B.; Suh, S.; Lukowicz, P. PressureTransferNet: Human Attribute Guided Dynamic Ground Pressure Profile Transfer Using 3D Simulated Pressure Maps. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.00538. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekaran, M.; Francik, J.; Makris, D. Enhancing Gait Recognition: Data Augmentation via Physics-Based Biomechanical Simulation. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2024 Workshops; Del Bue, A., Canton, C., Pont-Tuset, J., Tommasi, T., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; Volume 15635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
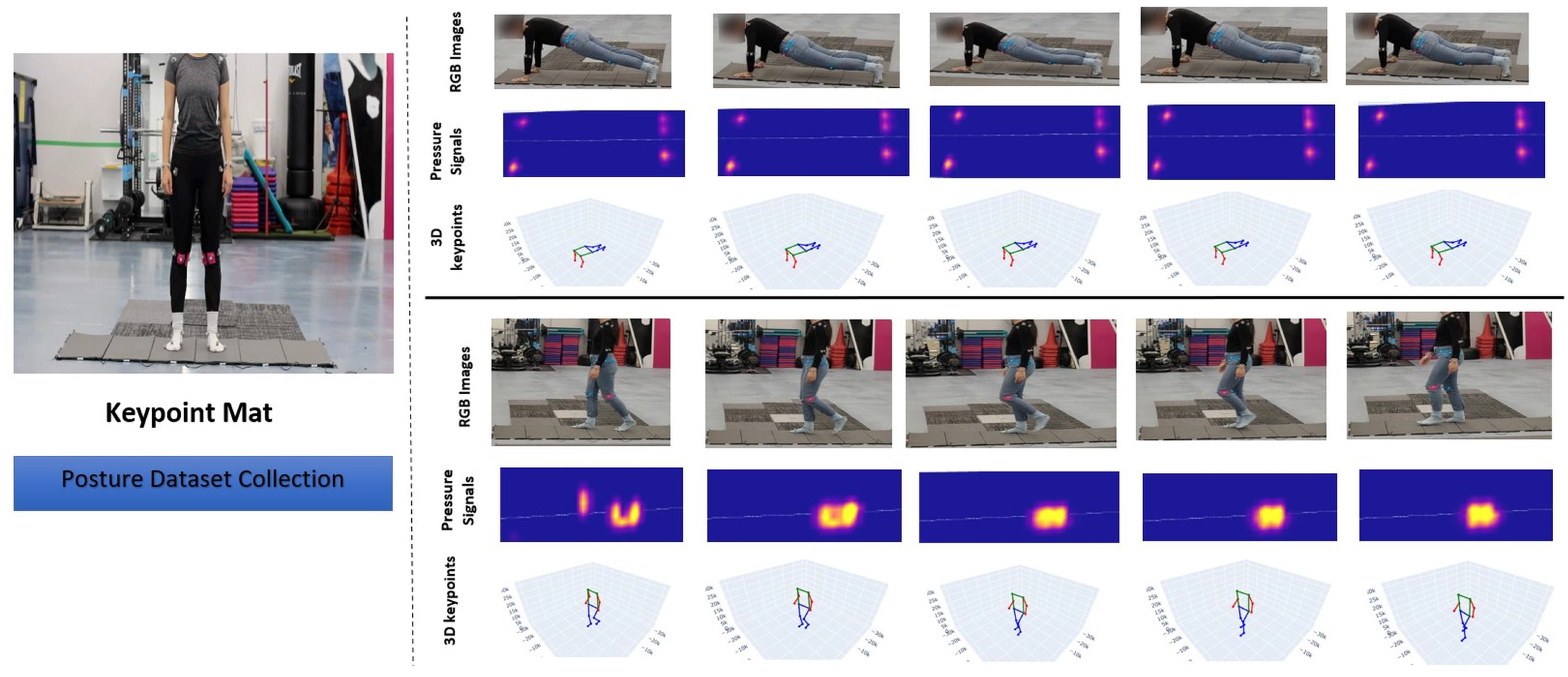

| Pose Title | Pose | Pressure Map | Motion Captured Skeleton |
|---|---|---|---|
| Squat |  |  |  |
| Stay in Goddess pose |  |  |  |
| Extend legs |  |  |  |
| Stay Standing |  |  |  |
| Bend upper body |  |  |  |
| Standing wide-legged and forward fold |  |  | 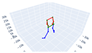 |
| Plank |  |  | 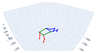 |
| Right Lunge |  |  | 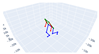 |
| Walking |  |  |  |
| Sit |  |  | 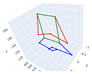 |
| Sit Up |  |  |  |
| Left Lunge |  |  |  |
| Method | PSNR (db) ↑ | SSIM ↑ | MAE (mm) ↓ | LPIPS ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeblurGAN [58] | 23.95 | 0.614 | 0.057 | 0.315 |
| DeepDeblur [44] | 24.06 | 0.621 | 0.055 | 0.347 |
| MPRNet [45] | 26.48 | 0.758 | 0.054 | 0.348 |
| HINET [46] | 29.61 | 0.745 | 0.053 | 0.231 |
| Stripformer [47] | 30.34 | 0.734 | 0.052 | 0.214 |
| Hi Diff [48] | 34.71 | 0.714 | 0.05 | 0.271 |
| DID [49] | 35.5 | 0.842 | 0.051 | 0.201 |
| SI-DDPM-FMO [50] | 35.66 | 0.862 | 0.048 | 0.116 |
| Swintormer [51] | 35.68 | 0.821 | 0.049 | 0.013 |
| Ours | 36.24 | 0.873 | 0.045 | 0.109 |
| Method | Param (M) | MACs (G) | PSNR (dB) ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stripformer [47] | 36.13 | 18.7 | 30.34 |
| Hi Diff [48] | 85.17 | 130.35 | 34.71 |
| DID [49] | 128.23 | 6.52 | 35.5 |
| SI-DDPM-FMO [50] | 131.53 | 15.43 | 35.68 |
| Swintormer [51] | 154.89 | 8.02 | 35.66 |
| Ours | 135.41 | 7.05 | 36.24 |
| Method | MPJPE (mm) | AKLEB (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y | Z | ||
| Weibing et al. [34] | 78.25 | 92.71 | 83.52 | 81.23 |
| Luo et al. [16] | 61.82 | 81.52 | 68.38 | 61.79 |
| Wenqiang et al. [52] | 65.21 | 74.62 | 65.15 | 59.65 |
| Ours (Stage 1+ 2) | 48.41 | 73.75 | 63.8 | 56.93 |
| Novel Elements of Architecture | MPJPE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSFD | 16.7904 | |||
| PSFD | RMFD | CA | - | 6.7812 |
| PSFD | RMFD | CA | PP | 4.4382 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kachole, S.; Nayak, B.; Brouner, J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, L.; Makris, D. Posture Estimation from Tactile Signals Using a Masked Forward Diffusion Model. Sensors 2025, 25, 4926. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25164926
Kachole S, Nayak B, Brouner J, Liu Y, Guo L, Makris D. Posture Estimation from Tactile Signals Using a Masked Forward Diffusion Model. Sensors. 2025; 25(16):4926. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25164926
Chicago/Turabian StyleKachole, Sanket, Bhagyashri Nayak, James Brouner, Ying Liu, Liucheng Guo, and Dimitrios Makris. 2025. "Posture Estimation from Tactile Signals Using a Masked Forward Diffusion Model" Sensors 25, no. 16: 4926. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25164926
APA StyleKachole, S., Nayak, B., Brouner, J., Liu, Y., Guo, L., & Makris, D. (2025). Posture Estimation from Tactile Signals Using a Masked Forward Diffusion Model. Sensors, 25(16), 4926. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25164926






