The Social Side of Internet of Things: Introducing Trust-Augmented Social Strengths for IoT Service Composition
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Trust-Related Attacks: Malicious or misbehaving objects might execute various trust-related attacks, threatening to undermine the entire service provisioning process in an SIoT system [13].
- Dishonest Social Relationships: Malicious nodes could also exploit their close social ties with honest objects, forming deceptive or dishonest “friendship” relations within the network [14].
- Scalability and Resource Constraints: SIoT environments typically involve a vast number of heterogeneous smart objects, many of which have limited storage and computational resources. Existing trust management schemes often struggle to scale under these conditions, as they were not designed for networks of this size and device diversity.
- Dynamic Topology: Smart objects in SIoT are mobile; nodes may frequently join or leave the network [15]. A robust protocol must accommodate this dynamism by enabling an efficient exchange of trust information and allowing newly joined objects to rapidly establish trust relationships—all while maintaining a reasonable level of accuracy in trust estimation.
- Malicious Behavior and Resilience: Adversarial nodes might attempt to sabotage others’ reputations or fraudulently boost their own. Countering such behavior demands a trust management solution that is sustainable and resilient against various malicious attacks. In particular, the system should defend against reputation manipulation and ensure trust scores remain reliable [16,17].
- We formally define the terms social strength and trust in the context of SIoT, with their application in service composition.
- We develop a trust-augmented social strength computation algorithm which quantitatively measures the strengths of inter-object social relationships based on trust scores.
- The proposed TASS algorithm is scalable to large SIoT systems and can effectively handle the heterogeneity issue in SIoT.
- Our experimental results based on a real-world dataset show that the TASS algorithm can support accurate and efficient SIoT service composition, and provide resiliency against trust-related attacks.
2. Related Work
3. Malicious Behaviors in SIoT
4. Trust-Augmented Social Strength
4.1. Social Strength in SIoT
4.2. Trust in SIoT
5. TASS-Based Service Composition in SIoT
- Sequential: ;
- Selection: ;
- Parallel: .
6. Experiments
6.1. Experimental Setting
- A timestamp indicating the exact time of the interaction;
- A unique participant identifier (ID) to distinguish between different users;
- A unique object identifier (ID) representing the device involved in the interaction;
- A brief task description outlining the user’s intention or the context of the object usage (e.g., “preparing a meal”, “watching television”, etc.).
- Realistic and naturalistic environment, where participants carry out their daily routines without artificial constraints;
- Temporal and behavioral diversity, offering a wide range of object usage patterns across different individuals and time spans;
- Well-structured format that facilitates temporal, spatial, and behavioral modeling required by the TASS protocol.
6.2. Results
6.2.1. OPTIMAL
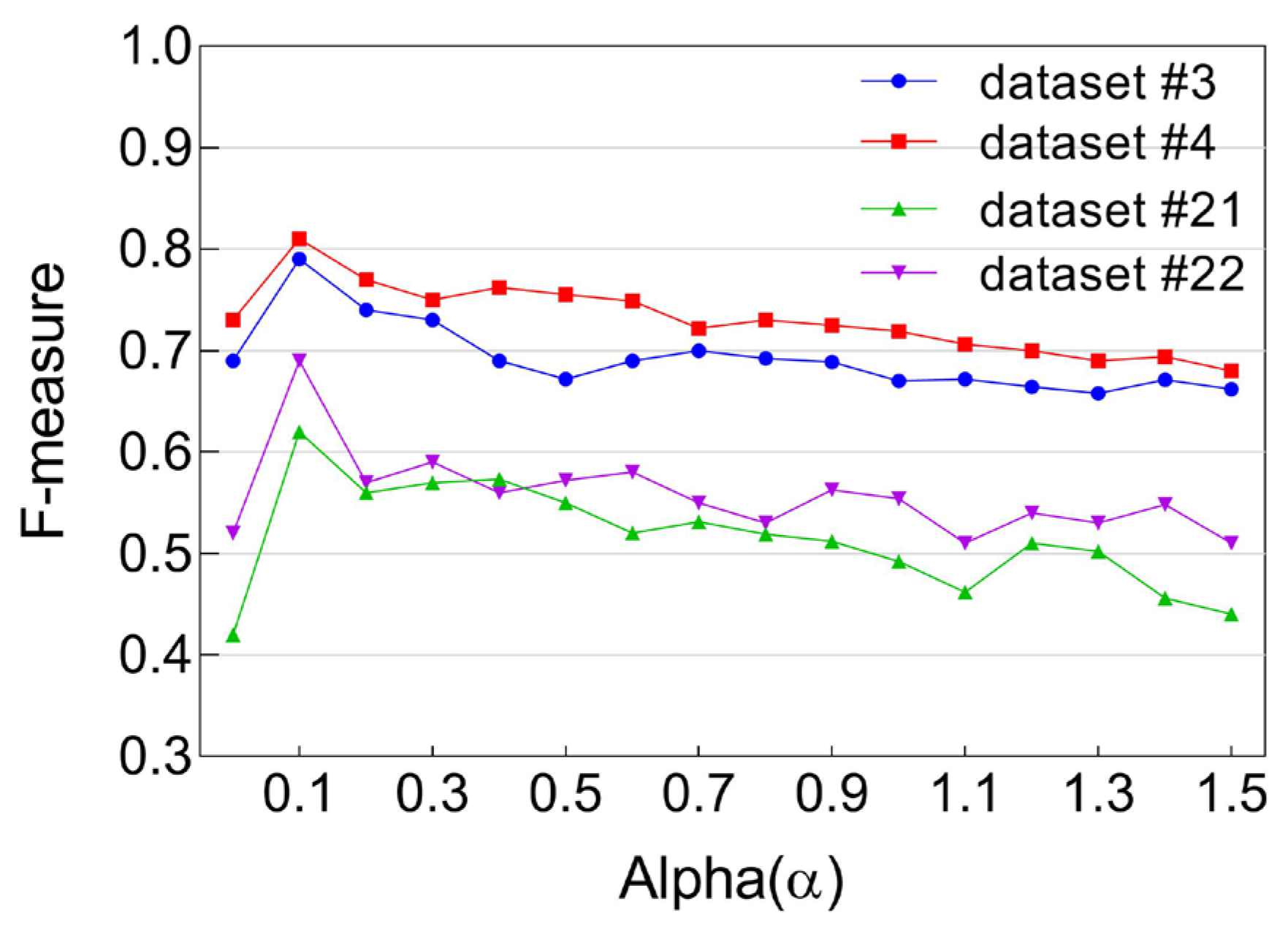
- Peak Performance at α = 0.1: All F-measure curves across the four datasets consistently peaked at α = 0.1, indicating that this value provides the most effective balance in moderating the influence of individual user co-usage frequencies on diversity. As such, α = 0.1 is identified as the optimal setting for controlling skewness caused by extreme co-usage behaviors.
- Degenerate Case at α = 0: When α is set to zero, the Renyi diversity measure reduces to a simple count of unique users, effectively ignoring repeated co-usage events by the same user. This oversimplification leads to underrepresentation of important behavioral patterns, and consequently, lower F-measure scores.
- Diminishing Returns for High α Values: As α increases beyond 0.1 toward 1.5, we observe a gradual decline in model performance. This decline stems from the increasing sensitivity of Renyi diversity to high-frequency outliers—instances where a small number of users exhibit disproportionately high co-usage. These outliers begin to dominate the diversity score, skewing social strength calculations and resulting in a rise in false positives.
- Over-Limiting at Very Low α Values: Conversely, decreasing α below 0.1 leads to over-suppression of frequency influence. While this helps reduce the effect of outliers, it also dampens the contribution of moderately frequent co-usage events, which are essential for robust diversity estimation. This over-limiting effect degrades model accuracy and illustrates the importance of selecting a balanced α.
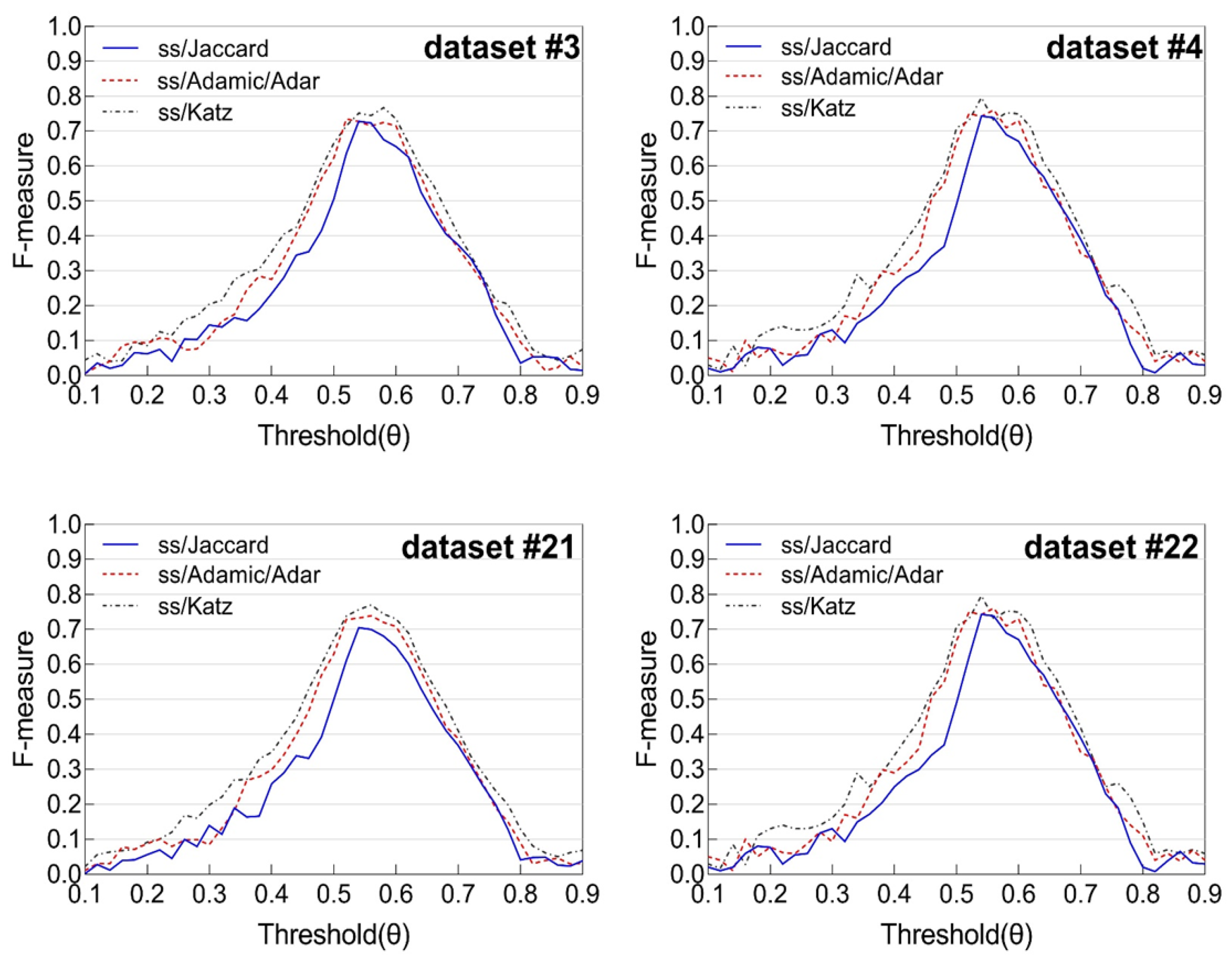
6.2.2. OPTIMAL Threshold and
- Jaccard Index: β = 0.424, 1 − β = 0.576;
- Adamic/Adar Similarity: β = 0.461, 1 − β = 0.539;
- Katz Score: β = 0.478, 1 − β = 0.522.
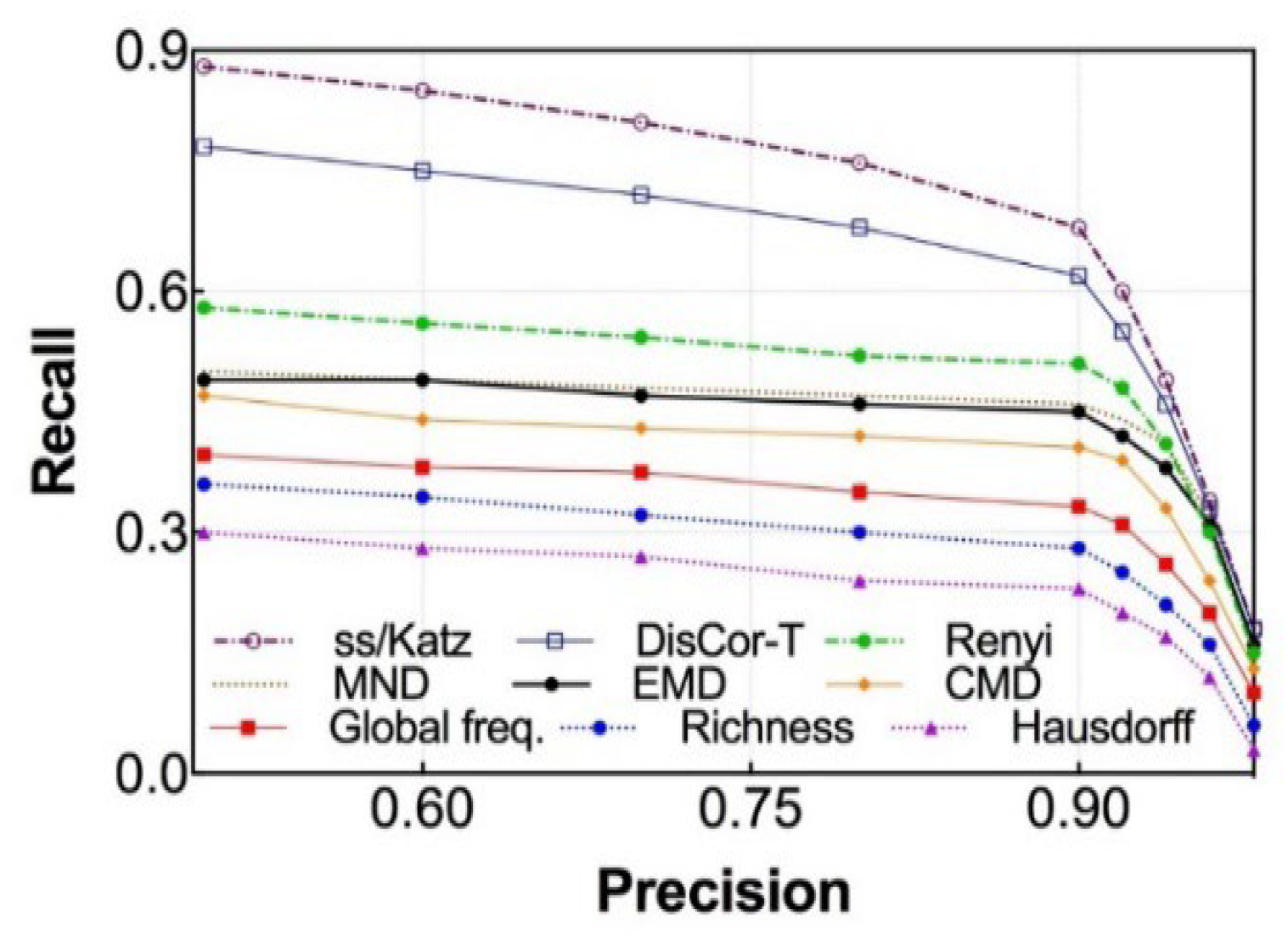
6.2.3. Precision vs. Recall
- User diversity, captured through Rényi entropy, which reflects the generalizability of co-usage patterns across different individuals;
- Spatial proximity, quantified via the Mutually Nearest Distance (MND), which captures the likelihood of physical co-occurrence of object usage;
- Temporal alignment, incorporated through co-usage vector construction within specific time intervals, which infers task-level coordination between objects.
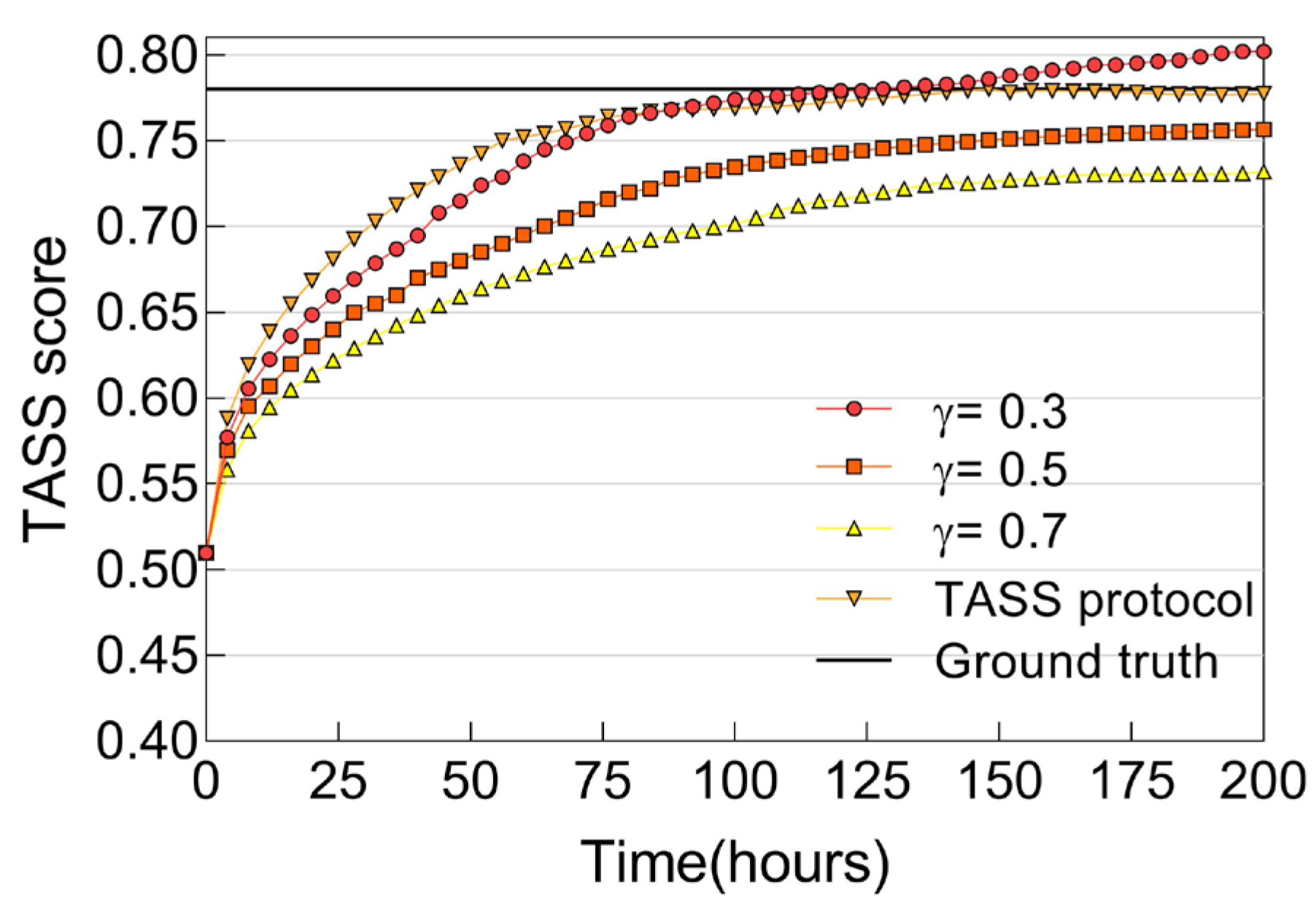
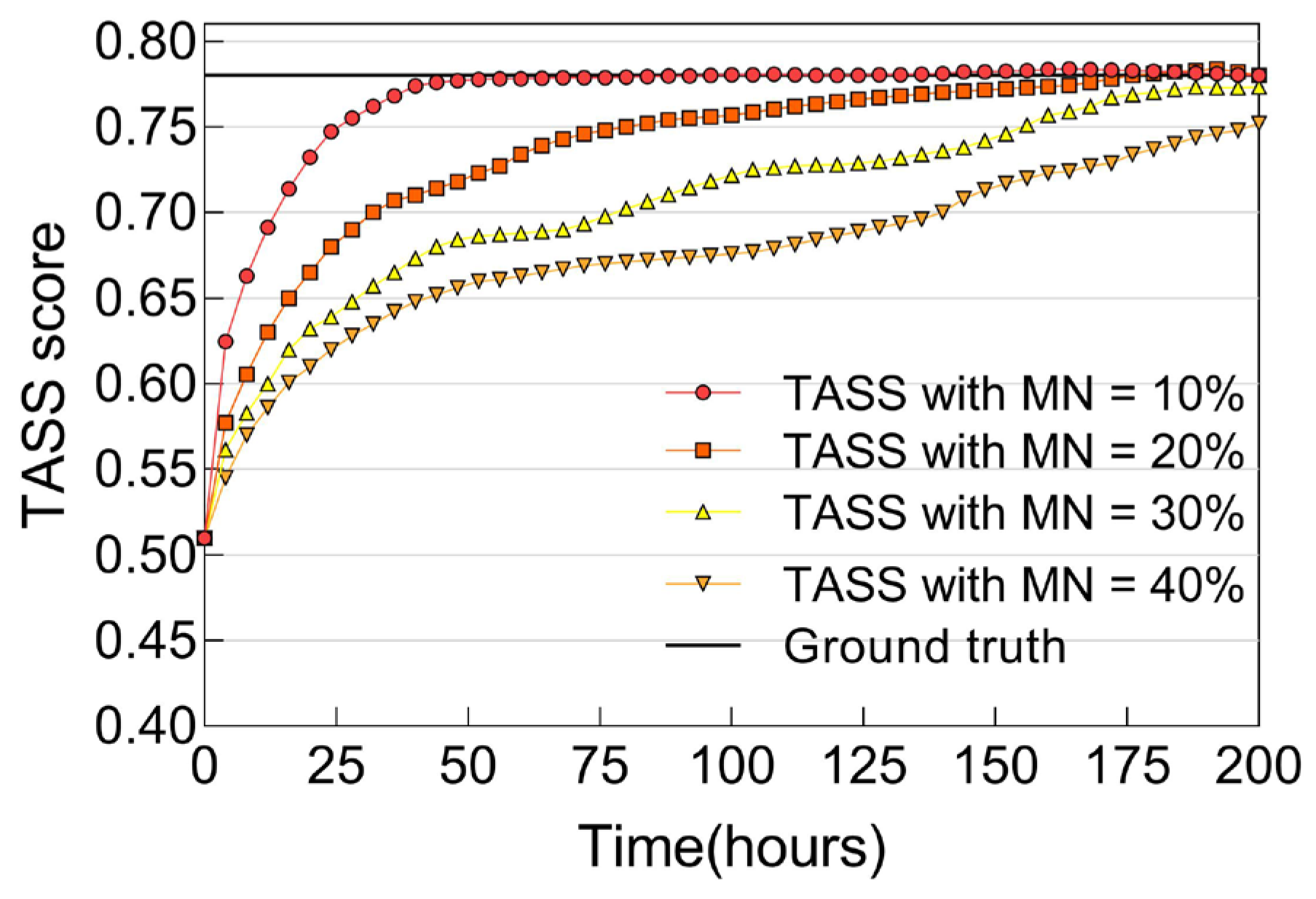
6.2.4. Trust Convergence, Accuracy, and Resiliency
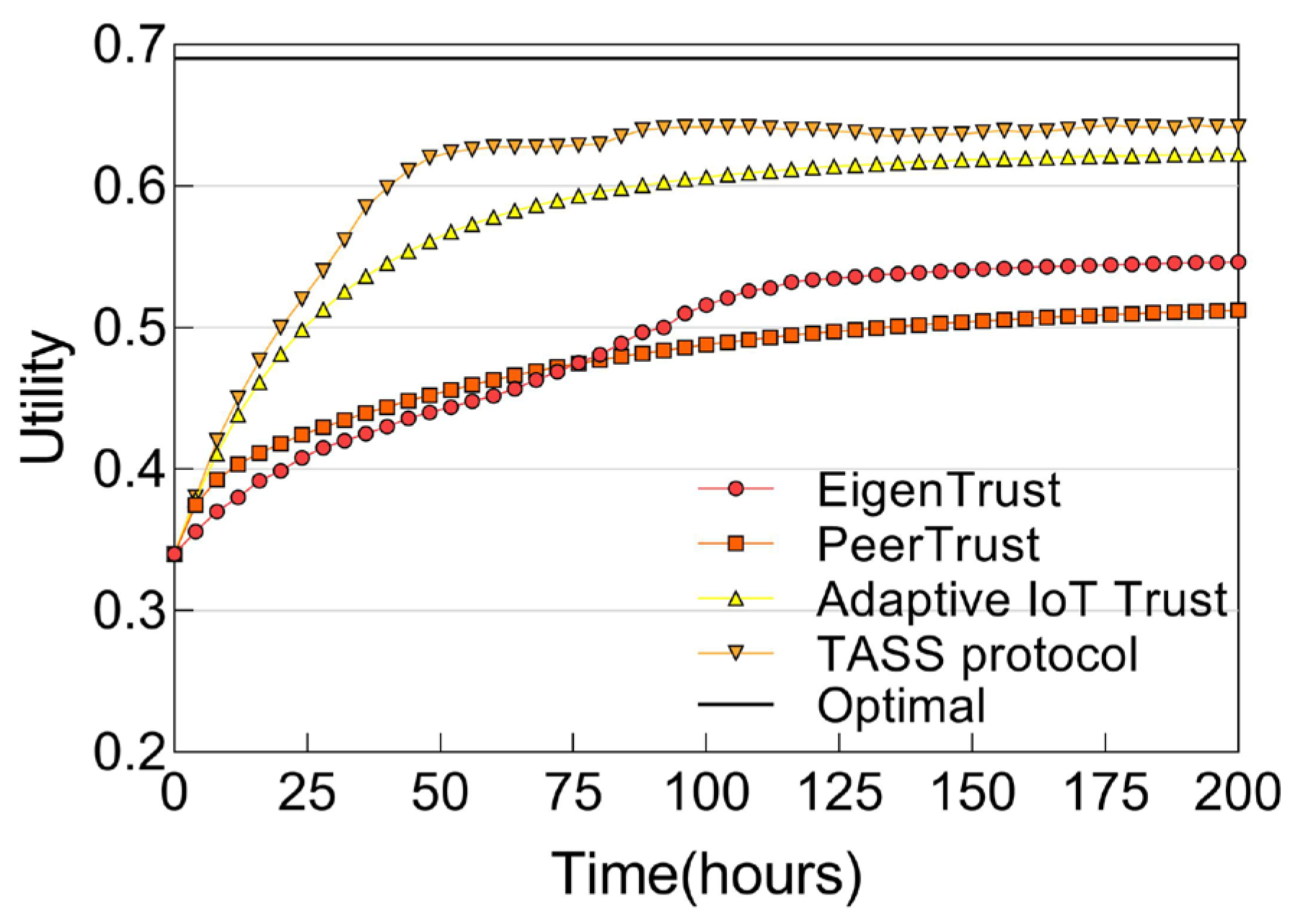
6.2.5. Utility Score of Service Composition
7. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Hamadi, H.; Chen, R. Trust-based decision making for health IoT systems. IEEE Internet Things J. 2017, 4, 1408–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Weon, I.; Cha, H. A Functional Model for Multi-Robot Control System. In Proceedings of the 2024 24th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 29 October–1 November 2024; pp. 1198–1199. [Google Scholar]
- Atzori, L.; Iera, A.; Morabito, G. SIoT: Giving a social structure to the internet of things. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2011, 15, 1193–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzori, L.; Iera, A.; Morabito, G.; Nitti, M. The social internet of things (SIoT)—When social networks meet the internet of things: Concept, architecture and network characterization. Comput. Netw. 2012, 56, 3594–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.C.; Tan, P.J.B. Understanding the dynamics of social interaction in SIoT: Human-machine engagement. Internet Things 2024, 28, 101337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzori, L.; Iera, A.; Morabito, G. From “smart objects” to “social objects”: The next evolutionary step of the internet of things. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqa, A.; Shah, M.A.; Khattak, H.A.; Akhunzada, A.; Ali, I.; Razak, Z.B.; Gani, A. Social internet of vehicles: Complexity, adaptivity, issues and beyond. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 62089–62106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zou, B.; Guo, G.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z. Optimal and effective web service composition with trust and user preference. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Web Services, New York, NY, USA, 27 June–2 July 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 329–336. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Wang, Y.; Orgun, M.A.; Zheng, X.; Liu, A.; Li, Z.; Zheng, K. Strong social component-aware trust sub-network ex-traction in contextual social networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Web Services, San Francisco, CA, USA, 27 June–2 July 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseinzadeh, M.; Mohammadi, V.; Lansky, J.; Nulicek, V. Advancing the Social Internet of Things (SIoT): Challenges, In-novations, and Future Perspectives. Mathematics 2024, 12, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Cai, C.; Li, Z.; Shen, Y.; Wu, G.; Yu, S. Deep Q-network-based heuristic intrusion detection against edge-based SIoT zero-day attacks. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 150, 111080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.C.; Tan, P.J.B. Artificial intelligence and internet of things to improve smart hospitality services. Internet Things 2025, 31, 101544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafey, S.E.A.; Abdel-Hamid, A.; El-Nasr, M.A. CBSTM-IoT: Context-based social trust model for the Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Selected Topics in Mobile & Wireless Networking, Cairo, Egypt, 11–13 April 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Orgun, M.A. Binet: Trust sub-network extraction using binary ant colony algorithm in contextual social networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Web Services, New York, NY, USA, 27 June–2 July 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 321–328. [Google Scholar]
- Altaf, A.; Abbas, H.; Iqbal, F.; Derhab, A. Trust models of internet of smart things: A survey, open issues, and future directions. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2019, 137, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Ye, X.; Ning, H. Thing relation modeling in the internet of things. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 17117–17125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Liu, X.; Gao, X.; Zhong, J.; Chen, G. iSim: An efficient integrated similarity based collaborative filtering approach for trust prediction in service-oriented social networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Service-Oriented Computing, Macau, China, 4–6 November 2016; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 501–516. [Google Scholar]
- Gamage, D.U.; Gallege, L.S.; Raje, R.R. A qos and trust prediction framework for context-aware composed distributed sys-tems. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Web Services, New York, NY, USA, 27 June–2 July 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Kanza, Y.; Kravi, E.; Safra, E.; Sagiv, Y. Location-based distance measures for geosocial similarity. ACM Trans. Web 2017, 11, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Xie, Y.; Wang, S.; Zheng, Y. Multi-level hyperedge distillation for social linking prediction on sparsely observed networks. In Proceedings of the Web Conference 2021 (WWW’21), Ljubljana, Slovenia, 19–23 April 2021; pp. 1939–1950. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Xie, Y.; Huang, X. Structure learning via meta-hyperedge for dynamic rumor detection. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2023, 35, 9128–9139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Bao, F.; Guo, J. Trust-based service management for social internet of things systems. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2016, 13, 684–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasinghe, U.; Lee, H.-W.; Lee, G.M. A computational model to evaluate honesty in social internet of things. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Applied Computing, Marrakech, Morocco, 4–6 April 2017; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1830–1835. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Xie, Y.; Huang, X. Self-supervised hypergraph representation learning for sociological analysis. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2023, 35, 11860–11871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokoris-Kogias, E.; Voutyras, O.; Varvarigou, T. TRM-SIoT: A scalable hybrid trust & reputation model for the social Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation, Berlin, Germany, 6–9 September 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kamvar, S.D.; Schlosser, M.T.; Garcia-Molina, H. The eigentrust algorithm for reputation management in p2p networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on World Wide Web, Budapest, Hungary, 20–24 May 2003; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 640–651. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, L.; Ling, L. Peertrust: Supporting reputation-based trust for peer-to-peer electronic communities. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2004, 16, 843–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Xu, M.; Zhu, C.; Han, W.; Zhang, W.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C. FETMS: Fast and efficient trust management scheme for information-centric networking in Internet of Things. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 13476–13485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guleng, S.; Wu, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Yoshinaga, T.; Ji, Y. Decentralized trust evaluation in vehicular Internet of Things. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 15980–15988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhu, L. Turing Instability Analysis of a Reaction–Diffusion System for Rumor Propagation in Continuous Space and Complex Networks. Inf. Process. Manag. 2024, 61, 103621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Kang, H.; Fan, J.; Li, Q.; Sandhu, R. IoT passport: A blockchain-based trust framework for collaborative inter-net-of-things. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Access Control Models and Technologies, Toronto, Canada, 3–6 June 2019; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Din, I.U.; Guizani, M.; Kim, B.-S.; Hassan, S.; Khan, M.K. Trust management techniques for the internet of things: A survey. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 29763–29787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yekini, T.A.; Jaafar, F.; Zavarsky, P. Study of Trust at Device Level of the Internet of Things Architecture. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on High Assurance Systems Engineering, Hangzhou, China, 3–5 January 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 150–155. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, H.; Shahabi, C.; Liu, Y. Ebm: An entropy-based model to infer social strength from spatiotemporal data. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Management of Data, New York, NY, USA, 22–27 June 2013; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 265–276. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, H.; Shahabi, C.; Liu, Y. Inferring social strength from spatiotemporal data. ACM Trans. Database Syst. 2016, 41, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Guo, J.; Bao, F. Trust management for SOA-based IoT and its application to service composition. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2016, 9, 482–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamic, L.A.; Adar, E. Friends and Neighbors on the Web. Soc. Netw. 2003, 25, 211–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josang, A.; Ismail, R. The beta reputation system. In Proceedings of the 15th Bled Electronic Commerce Conference, Bled, Slovenia, 17–19 June 2002; Bled eCommerce Conference: Bled, Slovenia, 2002; pp. 2502–2511. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Wu, J. A novel framework for service set recommendation in mashup creation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Web Services, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 June 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, J.; Chun, S.; Jin, X.; Lee, K.H. Quantitative computation of social strength in social Internet of Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 4066–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, K.A.; Din, I.U.; Zareei, M.; Talha, M.; Guizani, M.; Jadoon, S.U. HoliTrust-a holistic cross-domain trust management mechanism for service-centric Internet of Things. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 52191–52201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Xiao, F.; Zhang, S.; Hu, C.; Cheng, X. Trustworthiness inference framework in the social Internet of Things: A con-text-aware approach. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM), Paris, France, 29 April–2 May 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 838–846. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Xie, Y.; Huang, X. Graph prompt learning: A comprehensive survey and beyond. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.11644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Xie, Y.; Huang, X. All in One: Multi-Task Prompting for Graph Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD’23), Long Beach, CA, USA, 6–10 August 2023; pp. 3781–3791. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Xie, Y.; Huang, X. When LLM meets hypergraph: A sociological analysis on personality via online social networks. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM’23), Birmingham, UK, 21–25 October 2023; pp. 4334–4338. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, J.; Weon, I. The Social Side of Internet of Things: Introducing Trust-Augmented Social Strengths for IoT Service Composition. Sensors 2025, 25, 4794. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154794
Jung J, Weon I. The Social Side of Internet of Things: Introducing Trust-Augmented Social Strengths for IoT Service Composition. Sensors. 2025; 25(15):4794. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154794
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Jooik, and Ihnsik Weon. 2025. "The Social Side of Internet of Things: Introducing Trust-Augmented Social Strengths for IoT Service Composition" Sensors 25, no. 15: 4794. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154794
APA StyleJung, J., & Weon, I. (2025). The Social Side of Internet of Things: Introducing Trust-Augmented Social Strengths for IoT Service Composition. Sensors, 25(15), 4794. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154794





