MSF-ACA: Low-Light Image Enhancement Network Based on Multi-Scale Feature Fusion and Adaptive Contrast Adjustment
Abstract
1. Introduction
- 1.
- A low-light image enhancing network based upon multi-scale feature fusion and contrast adaptive adjustment is proposed to achieve low-light image enhancement through a lightweight architecture synergizing multi-scale image feature fusion with dynamic optimization of image contrast.
- 2.
- A local–global image feature fusion module (LG-IFFB) is designed, which adopts a dual-path structure of local branching and global branching to simultaneously extract local and global information at different scales of the image, realizing a balance between detail preservation and global light optimization, and providing parameter mapping more suitable for complex low-light scenes for the subsequent luminance enhancement network.
- 3.
- An adaptive image contrast enhancement module (AICEB) is proposed, which consists of multiple iterative sub-modules, each of which dynamically generates contrast enhancement factors and luminance parameters through an adaptive attention normalization block (AANBlock). A confidence scoring mechanism is introduced in the module to realize the adaptive contrast enhancement, effectively balancing the contrast enhancement and computational efficiency.
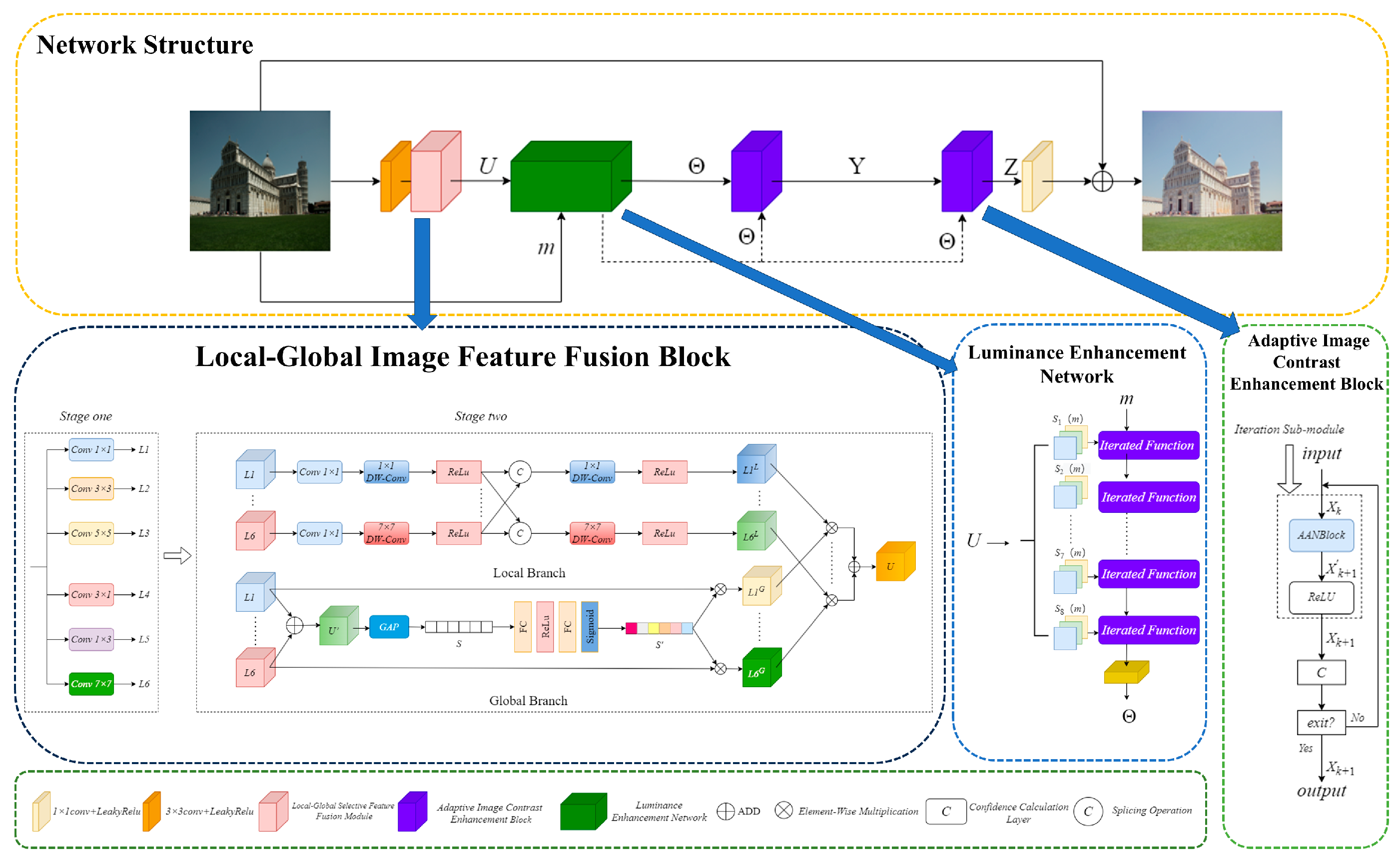
2. Methods
2.1. Local–Global Image Feature Fusion Block
2.2. Luminance Enhancement Network
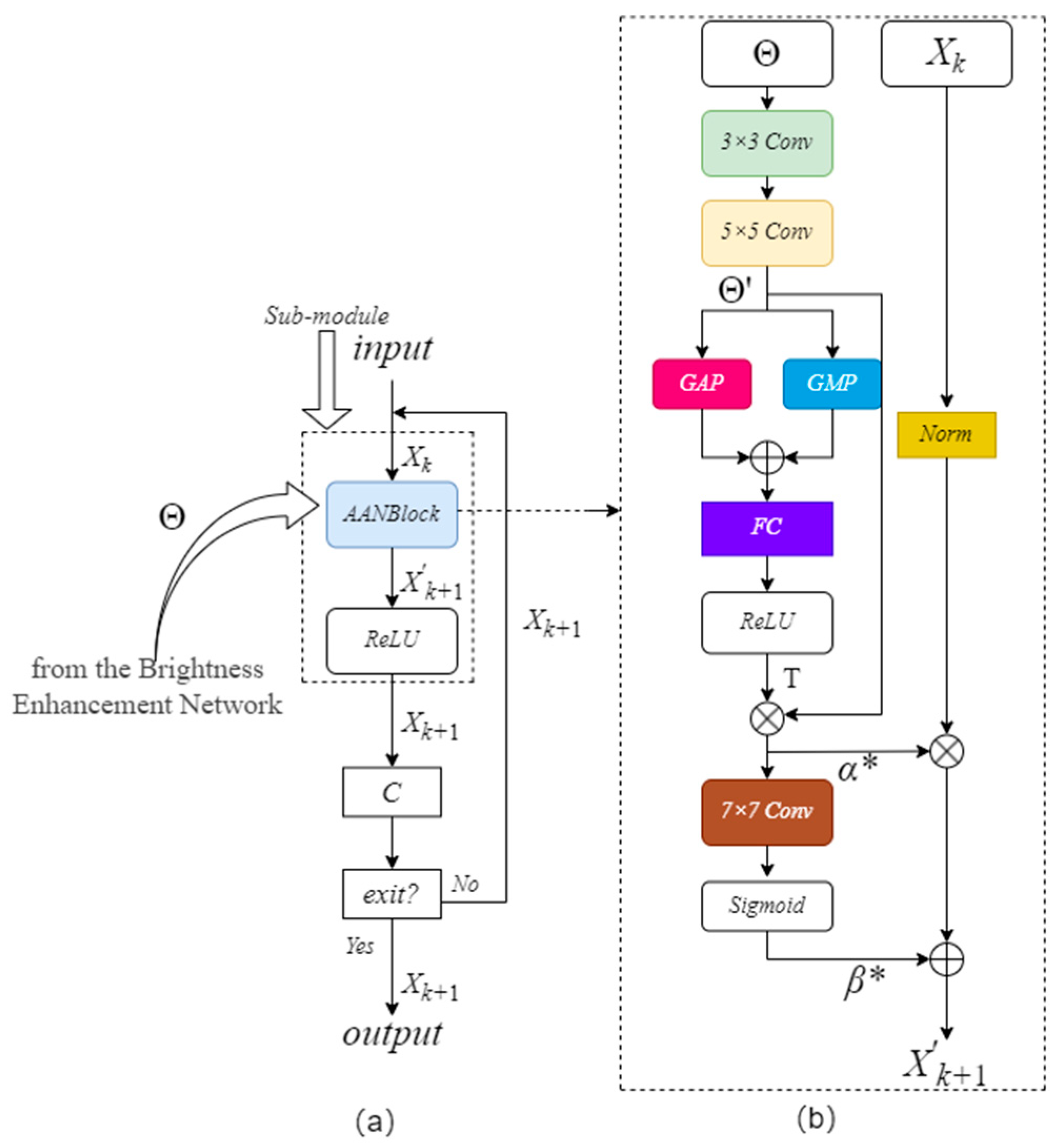
2.3. Adaptive Image Contrast Enhancement Block
2.4. Loss Function
3. Experiment
3.1. Implementation Details
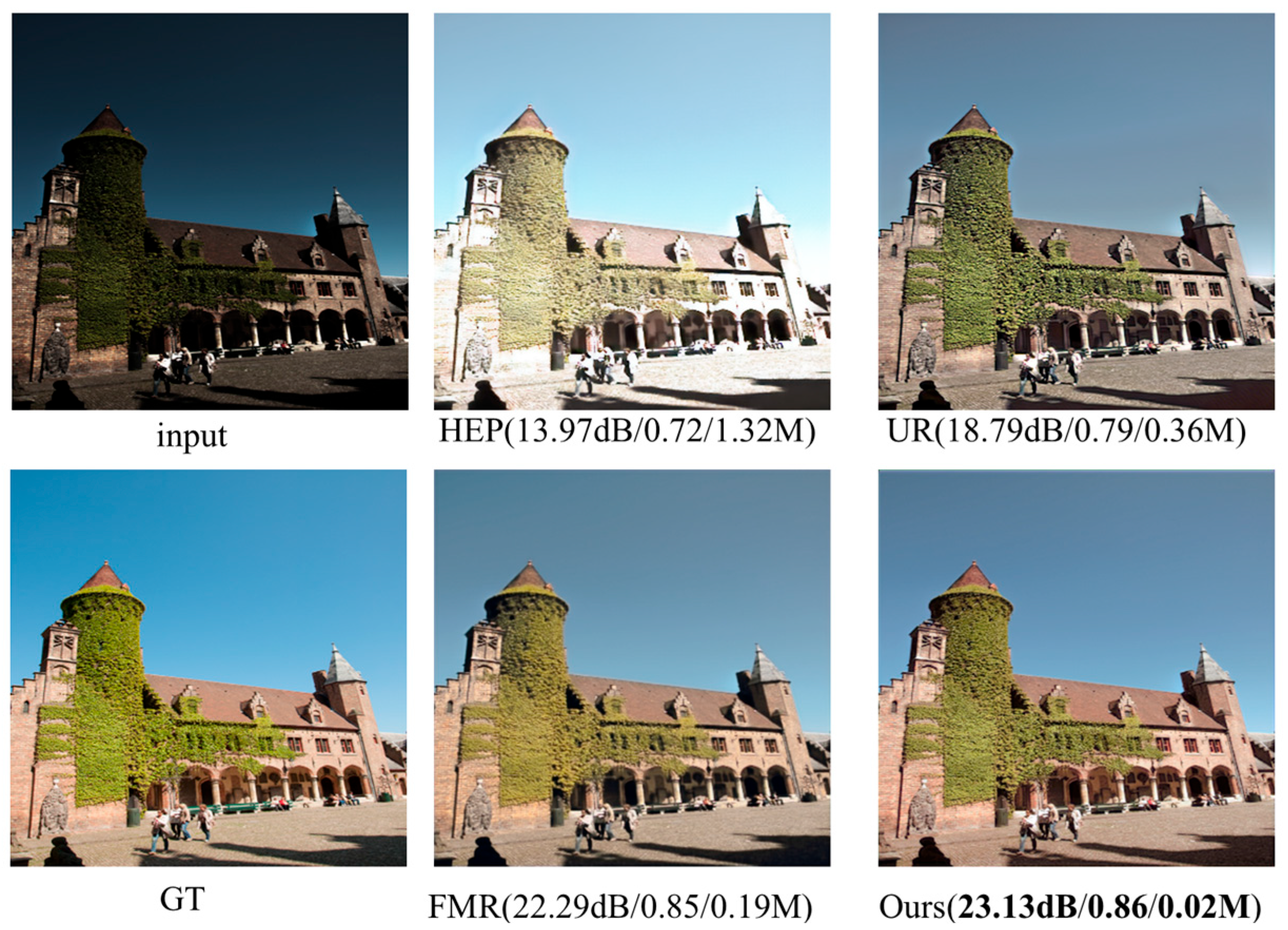
3.2. Comparison and Analysis of Paired Datasets
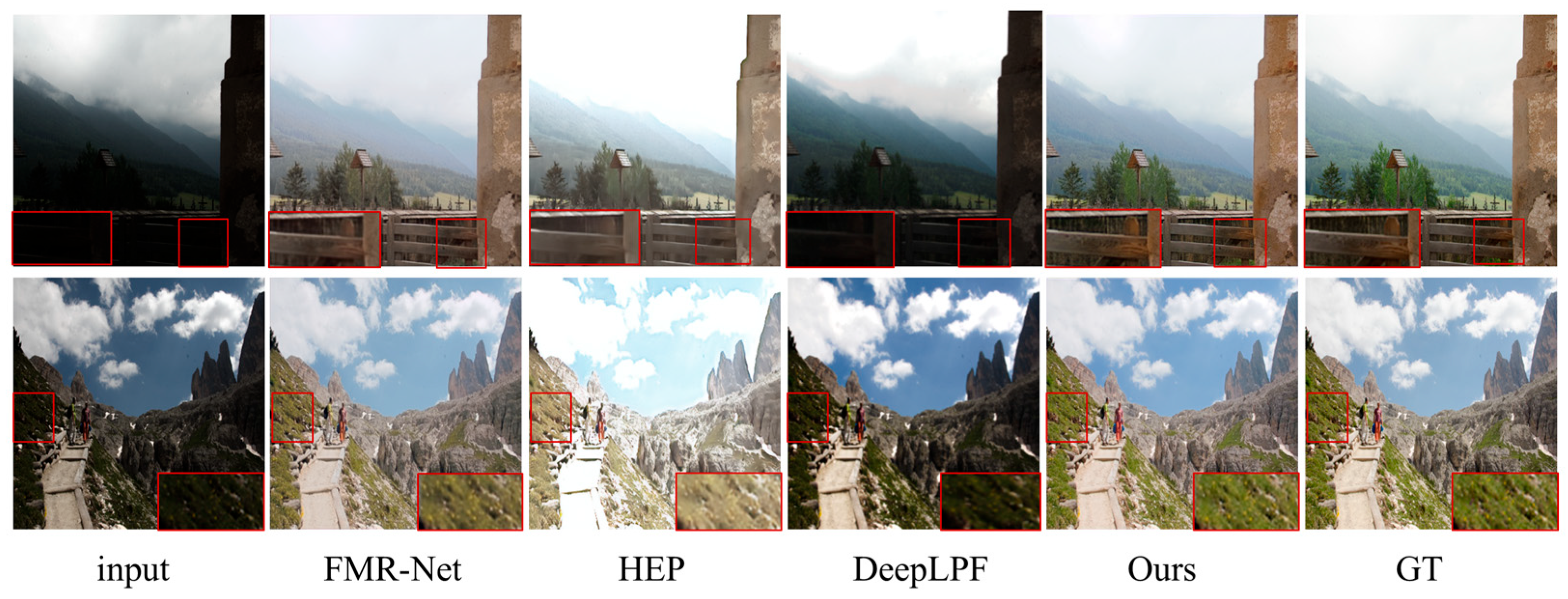
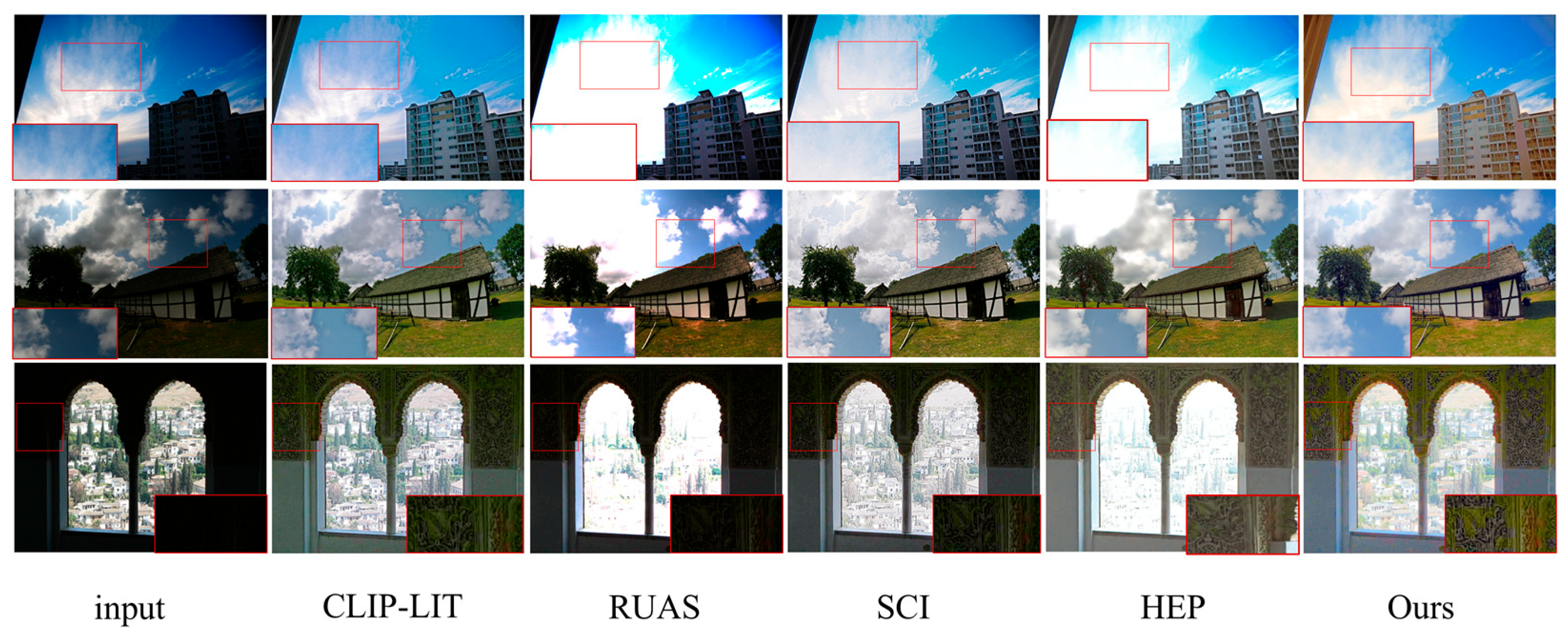
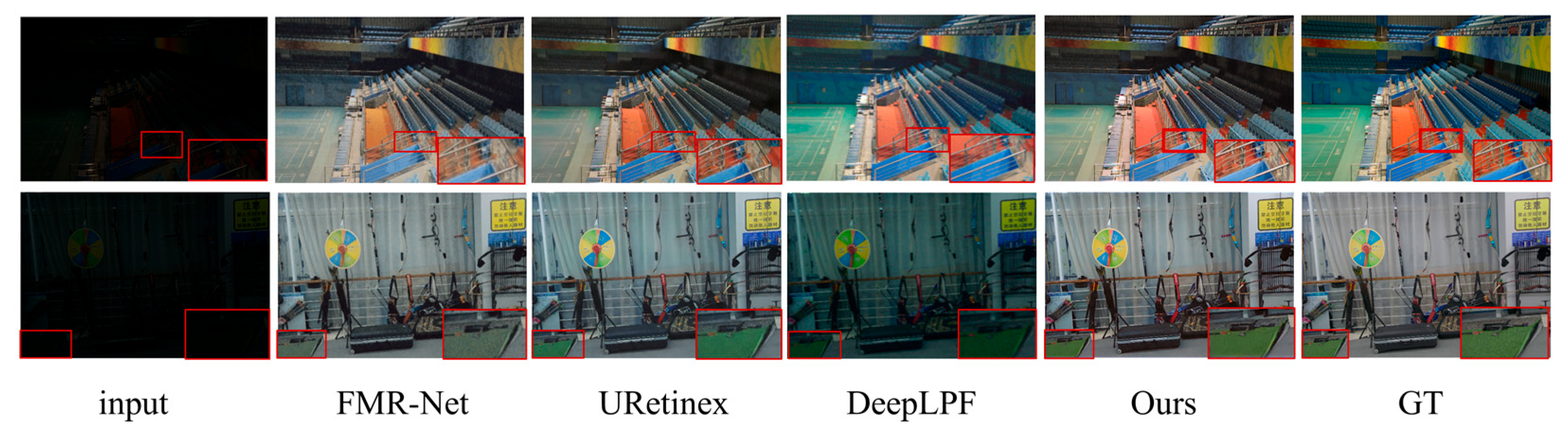



3.3. Comparison and Analysis of Unpaired Datasets
3.4. Ablation Experiment
3.5. Selection of Iteration Thresholds
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X. Infrared image filtering and enhancement processing method based upon image processing technology. J. Electron. Imaging 2022, 31, 051408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Liu, S. DAFuse: A fusion for infrared and visible images based on generative adversarial network. J. Electron. Imaging 2022, 31, 043023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, G.; Li, Z.; Tao, Y.; Jin, T. Low-illumination traffic object detection using the saliency region of infrared image masking on infrared-visible fusion image. J. Electron. Imaging 2022, 31, 033029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Shen, L. Hopc: A novel similarity metric based on geometric structural properties for multi-modal remote sensing image matching. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2016, 3, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah-Al-Wadud, M.; Kabir, M.H.; Dewan, M.A.A.; Chae, O. A dynamic histogram equalization for image contrast enhancement. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2007, 53, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.; Kong, N.S.P. Brightness preserving dynamic histogram equalization for image contrast enhancement. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2007, 53, 1752–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Lee, C.; Kim, C.S. Contrast enhancement based on layered difference representation of 2D histograms. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 5372–5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, I.; Lee, C. An optimization-based approach to gamma correction parameter estimation for low-light image enhancement. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 18027–18042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Tang, S.; Yan, J.; Zhou, T. Low-light image enhancement via pair of complementary gamma functions by fusion. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 169887–169896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Xu, S.; Liu, S. Low-light image enhancement with illumination-aware gamma correction and complete image modelling network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 13128–13137. [Google Scholar]
- Land, E.H. The retinex theory of color vision. Sci. Am. 1977, 237, 108–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobson, D.J.; Rahman, Z.U.; Woodell, G.A. Properties and performance of a center/surround retinex. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1997, 6, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobson, D.J.; Rahman, Z.U.; Woodell, G.A. A multiscale retinex for bridging the gap between color images and the human observation of scenes. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1997, 6, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Zeng, D.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.P.; Ding, X. A weighted variational model for simultaneous reflectance and illumination estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2782–2790. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.; Wang, W.; Yang, W.; Liu, J. Deep retinex decomposition for low-light enhancement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1808.04560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bychkovsky, V.; Paris, S.; Chan, E.; Durand, F. Learning photographic global tonal adjustment with a database of input/output image pairs. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Ling, H. LIME: Low-light image enhancement via illumination map estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 26, 982–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X. Kindling the darkness: A practical low-light image enhancer. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Nice, France, 21–25 October 2019; pp. 1632–1640. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Weng, J.; Zhang, P.; Wang, X.; Yang, W.; Jiang, J. Uretinex-net: Retinex-based deep unfolding network for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 5901–5910. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, G.; Wang, X.; Shen, Y. FMR-Net: A fast multi-scale residual network for low-light image enhancement. Multimed. Syst. 2024, 30, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Gong, X.; Liu, D.; Cheng, Y.; Fang, C.; Shen, X.; Wang, Z. Enlightengan: Deep light enhancement without paired supervision. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 2340–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Guo, C.; Loy, C.C. Learning to enhance low-light image via zero-reference deep curve estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 4225–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Ma, T.; Liu, R.; Fan, X.; Luo, Z. Toward fast, flexible, and robust low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 5637–5646. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Shao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, K.; Gao, C.; Sang, N. Unsupervised low-light image enhancement via histogram equalization prior. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.01766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Yuan, H.; Deng, L.; Lu, Z. Reparameterized residual feature network for lightweight image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 1712–1721. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Cun, X.; Bao, J.; Zhou, W.; Liu, J.; Li, H. Uformer: A general u-shaped transformer for image restoration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 17683–17693. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Fu, X.; Liu, A.; Wu, F.; Zha, Z.J. Image de-raining transformer. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 12978–12995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamir, S.W.; Arora, A.; Khan, S.; Hayat, M.; Khan, F.S.; Yang, M.H. Restormer: Efficient transformer for high-resolution image restoration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 5728–5739. [Google Scholar]
- Zamir, S.W.; Arora, A.; Khan, S.; Hayat, M.; Khan, F.S.; Yang, M.H. Learning enriched features for fast image restoration and enhancement. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 1934–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulyanov, D.; Vedaldi, A.; Lempitsky, V. Improved texture networks: Maximizing quality and diversity in feed-forward stylization and texture synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6924–6932. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.H.; Yang, C.L.; Xie, S.L. Gradient-based structural similarity for image quality assessment. In Proceedings of the 2006 International Conference on Image Processing, Atlanta, GA, USA, 8–11 October 2006; pp. 2929–2932. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Wang, W.; Huang, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, J. Sparse gradient regularized deep retinex network for robust low-light image enhancement. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 2072–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Paszke, A. PyTorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.01703. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.; Li, C.; Zhou, S.; Feng, R.; Loy, C.C. Iterative Prompt Learning for Unsupervised Backlit Image Enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 8094–8103. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, S.; Kim, W. DSLR: Deep Stacked Laplacian Restorer for Low-Light Image Enhancement. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2020, 23, 4272–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Ma, L.; Zhang, J.; Fan, X.; Luo, Z. Retinex-inspired unrolling with cooperative prior architecture search for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 10561–10570. [Google Scholar]
- Moran, S.; Marza, P.; McDonagh, S.; Parisot, S.; Slabaugh, G. Deeplpf: Deep local parametric filters for image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 12826–12835. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, H. Retinexmamba: Retinex-based mamba for low-light image enhancement. In International Conference on Neural Information Processing, Proceedings of the 31st International Conference, ICONIP 2024, Auckland, New Zealand, 2–6 December 2024; Proceedings, Part VIII; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, J.; Hu, H.M.; Li, B. Naturalness preserved enhancement algorithm for non-uniform illumination images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 3538–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Zeng, K.; Wang, Z. Perceptual quality assessment for multi-exposure image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 3345–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blau, Y.; Mechrez, R.; Timofte, R.; Michaeli, T.; Zelnik-Manor, L. The 2018 PIRM challenge on perceptual image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) Workshops, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, A.; Moorthy, A.K.; Bovik, A.C. No-reference image quality assessment in the spatial domain. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 21, 4695–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talab, A.W.; Younis, N.K.; Ahmed, M.R. Analysis Equalization Images Contrast Enhancement and Performance Measurement. Open Access Libr. J. 2024, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Methods | Complexity | LOLV2-Real | LOLV2-Syn | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FLOPs (G) | Params (M) | PSNR ↑ | SSIM ↑ | PSNR ↑ | SSIM ↑ | |
| CLIP-LIT | 18.24 | 0.27 | 15.26 | 0.601 | 16.16 | 0.666 |
| DSLR | 5.88 | 14.93 | 17.00 | 0.596 | 13.67 | 0.623 |
| SCI | 0.06 | 0.0003 | 17.30 | 0.540 | 16.54 | 0.614 |
| RUAS | 0.83 | 0.003 | 18.37 | 0.723 | 16.55 | 0.652 |
| URetinex | 1.24 | 0.02 | 21.09 | 0.858 | 13.10 | 0.642 |
| HEP | 14.07 | 1.32 | 18.29 | 0.747 | 16.49 | 0.649 |
| DeepLPF | 5.86 | 1.77 | 14.10 | 0.480 | 16.02 | 0.587 |
| FMR-Net | 102.77 | 0.19 | 20.56 | 0.736 | 19.09 | 0.657 |
| Ours | 29.97 | 0.02 | 21.53 | 0.771 | 20.27 | 0.716 |
| Methods | DICM | LIME | MEF | NPE | VV | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRI ↓ | PI ↓ | BRI ↓ | PI ↓ | BRI ↓ | PI ↓ | BRI ↓ | PI ↓ | BRI ↓ | PI ↓ | |
| CLIP-LIT | 24.18 | 3.55 | 20.43 | 3.07 | 20.67 | 3.11 | 19.37 | 2.91 | 36.00 | 5.40 |
| DSLR | 25.67 | 4.07 | 22.68 | 6.01 | 22.49 | 6.74 | 33.69 | 5.07 | 28.35 | 6.64 |
| SCI | 27.92 | 3.70 | 25.17 | 3.37 | 26.71 | 3.28 | 28.88 | 3.53 | 22.80 | 3.64 |
| RUAS | 46.88 | 5.70 | 34.88 | 4.58 | 42.12 | 4.92 | 48.97 | 5.65 | 35.88 | 4.32 |
| URetinex | 24.54 | 3.56 | 29.02 | 3.71 | 34.72 | 3.66 | 26.09 | 3.15 | 22.45 | 2.89 |
| HEP | 25.74 | 3.01 | 31.86 | 5.74 | 30.38 | 3.28 | 29.73 | 2.36 | 39.86 | 2.98 |
| DeepLPF | 19.93 | 3.59 | 24.70 | 4.45 | 22.40 | 4.04 | 17.09 | 3.08 | 23.75 | 4.28 |
| FMR-Net | 19.63 | 2.91 | 28.96 | 3.77 | 21.67 | 3.25 | 18.01 | 2.70 | 17.56 | 2.64 |
| Ours | 14.45 | 2.36 | 16.61 | 2.76 | 18.31 | 2.70 | 25.44 | 1.78 | 28.02 | 2.32 |
| Models | LG-IFFB | AICEB (Fixed Iteration) | AICEB | PSNR | SSIM | Number of Iterations ↓ | Time(s) ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 18.37 | 0.66 | - | - | |||
| A | √ | 19.11 | 0.67 | - | - | ||
| B | √ | √ | 19.50 | 0.67 | 20 | 0.22 | |
| C | √ | √ | 20.27 | 0.71 | 10.1 | 0.14 |
| Number of AICEB | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR/SSIM | 19.79/0.68 | 20.27 (+2.4%)/0.71 (+4.4%) | 20.20 (+2.0%)/0.71 (+4.4%) |
| Number of iterations | 7.3 | 10.1 (+38%) | 26.4 (+261%) |
| Average running time(s) | 0.11 | 0.14 (+27%) | 0.22 (+100%) |
| Threshold | 0.00001 | 0.00005 | 0.0001 | 0.0005 | 0.001 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of iterations | 20 | 19.5 | 19 (−3%) | 16.3 (−14%) | 15.1 (−20%) |
| PSNR | 7.6 | 9.9 | 9.4 (−5%) | 8.9 (−10%) | 8.4 (−15%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, Z.; Wu, Y.; Tian, F.; Feng, Z.; Li, Y. MSF-ACA: Low-Light Image Enhancement Network Based on Multi-Scale Feature Fusion and Adaptive Contrast Adjustment. Sensors 2025, 25, 4789. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154789
Cheng Z, Wu Y, Tian F, Feng Z, Li Y. MSF-ACA: Low-Light Image Enhancement Network Based on Multi-Scale Feature Fusion and Adaptive Contrast Adjustment. Sensors. 2025; 25(15):4789. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154789
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Zhesheng, Yingdan Wu, Fang Tian, Zaiwen Feng, and Yan Li. 2025. "MSF-ACA: Low-Light Image Enhancement Network Based on Multi-Scale Feature Fusion and Adaptive Contrast Adjustment" Sensors 25, no. 15: 4789. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154789
APA StyleCheng, Z., Wu, Y., Tian, F., Feng, Z., & Li, Y. (2025). MSF-ACA: Low-Light Image Enhancement Network Based on Multi-Scale Feature Fusion and Adaptive Contrast Adjustment. Sensors, 25(15), 4789. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154789






