Non-Invasive Position Measurement of a Spatial Pendulum Using Infrared Distance Sensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
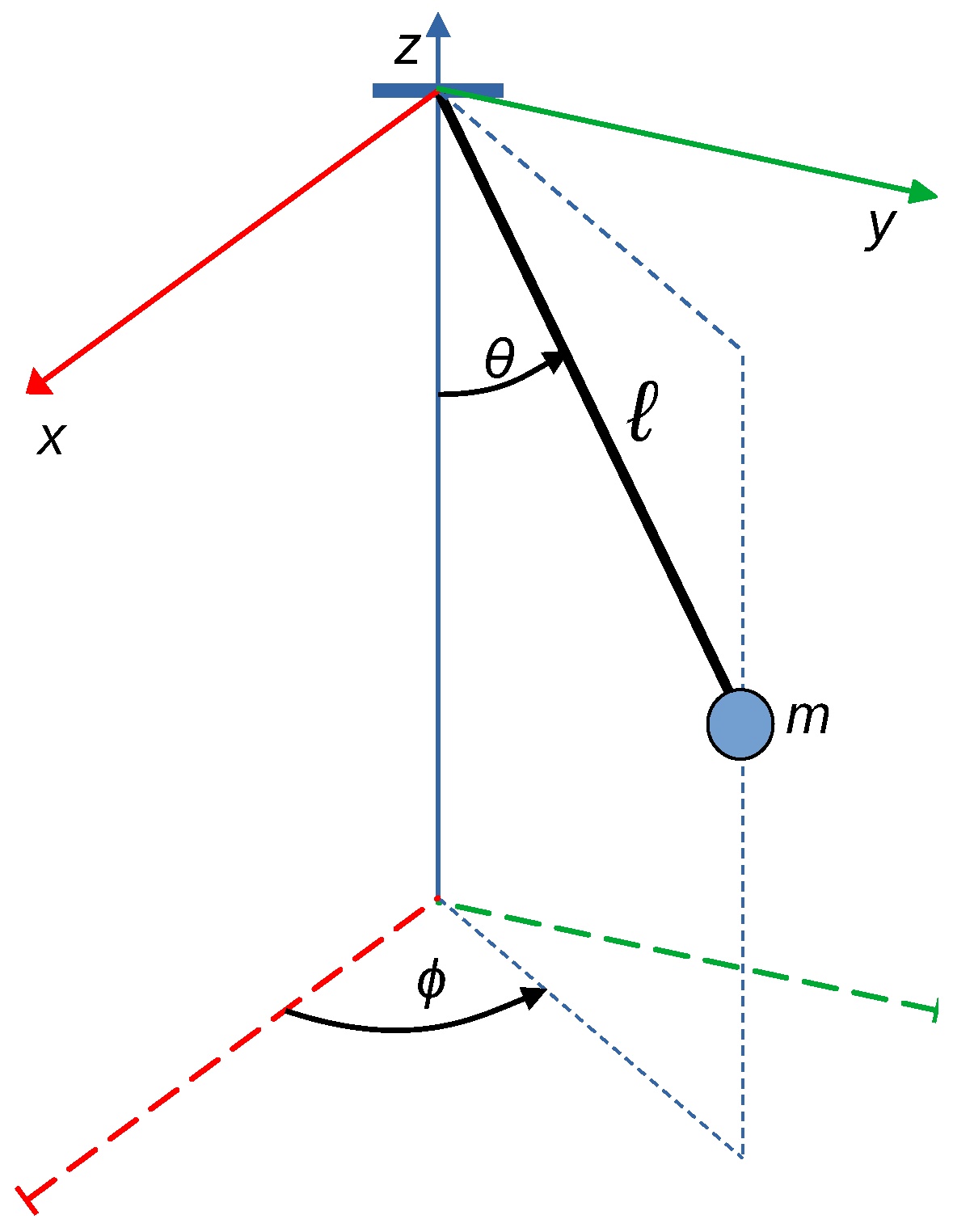
2. Mathematical Modeling of the Spatial Pendulum
- Kinetic energy
- Potential energy
3. Simulations
- , gravitational acceleration;
- m, pendulum length;
- kg, pendulum mass;
- , damping coefficient;
- s, time step for numerical calculation.
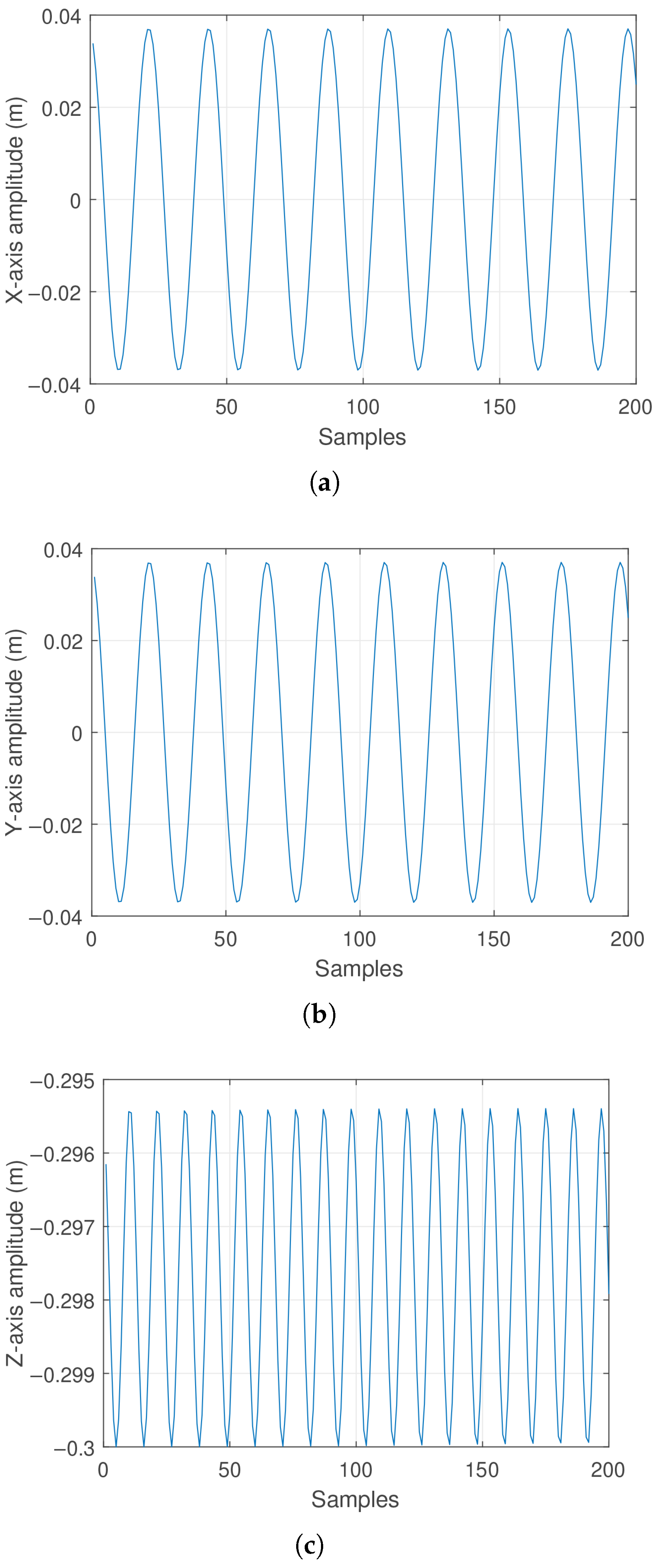
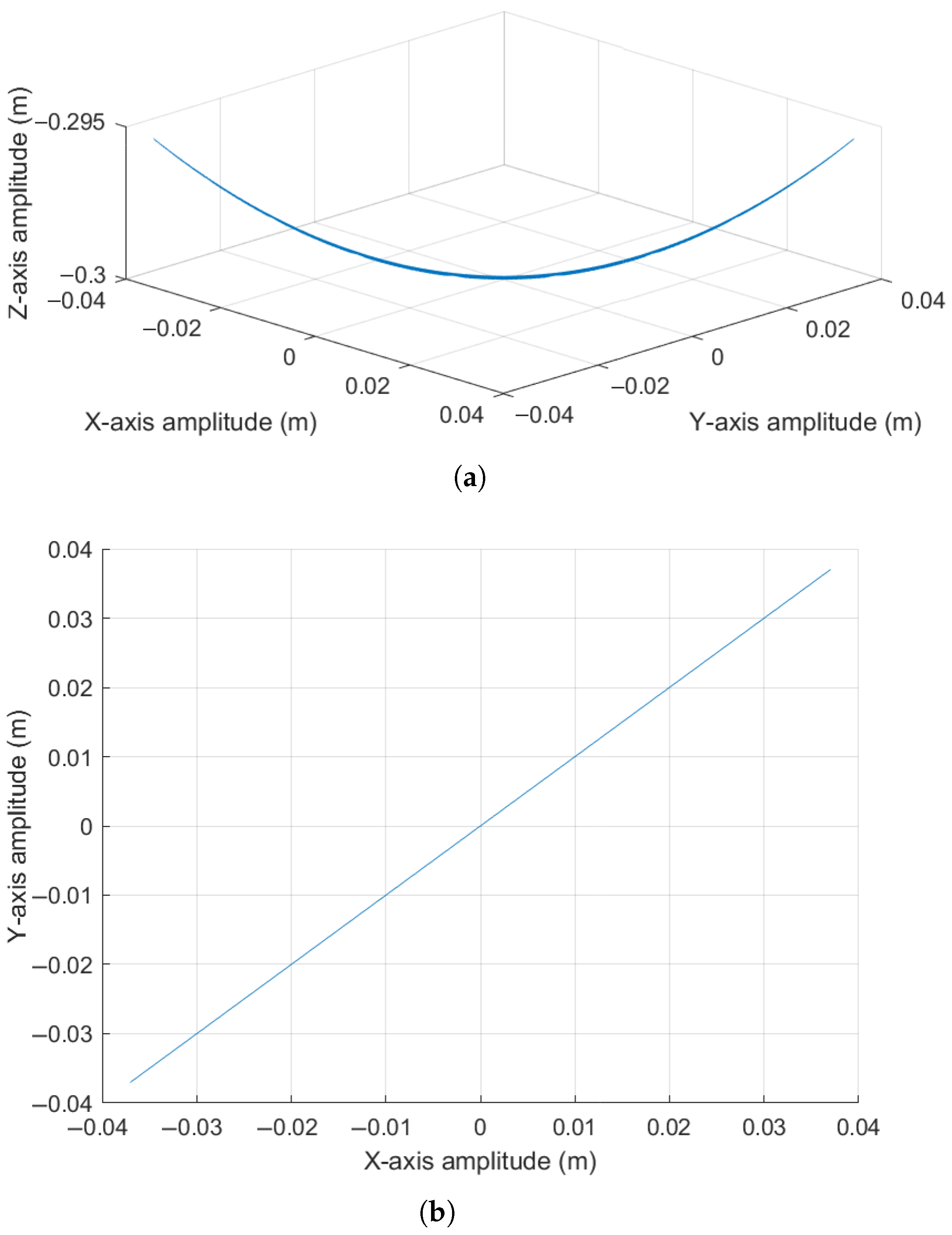
3.1. Case 1: Initial Angular Displacements Results
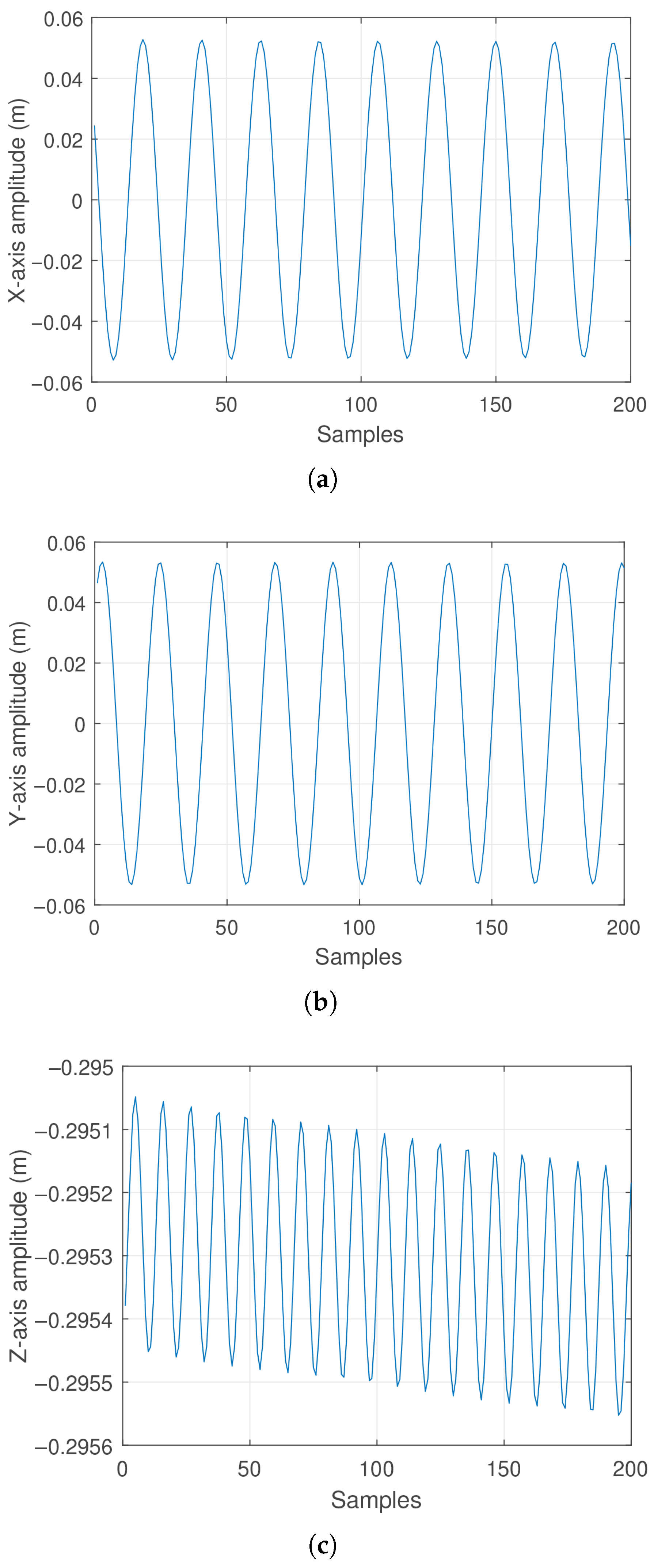
3.2. Case 2: Initial Angular and Velocity Displacements Results
4. Non-Invasive Sensing Using Infrared Sensors
4.1. Method of Sensing Justification
- Potentiometers introduce mechanical friction and wear.
- Optical encoders require direct contact with the pendulum shaft.
- Inertial sensors (IMUs) face challenges related to power supply or data transmission and are prone to cumulative errors or reference drifts during extended measurements [13].
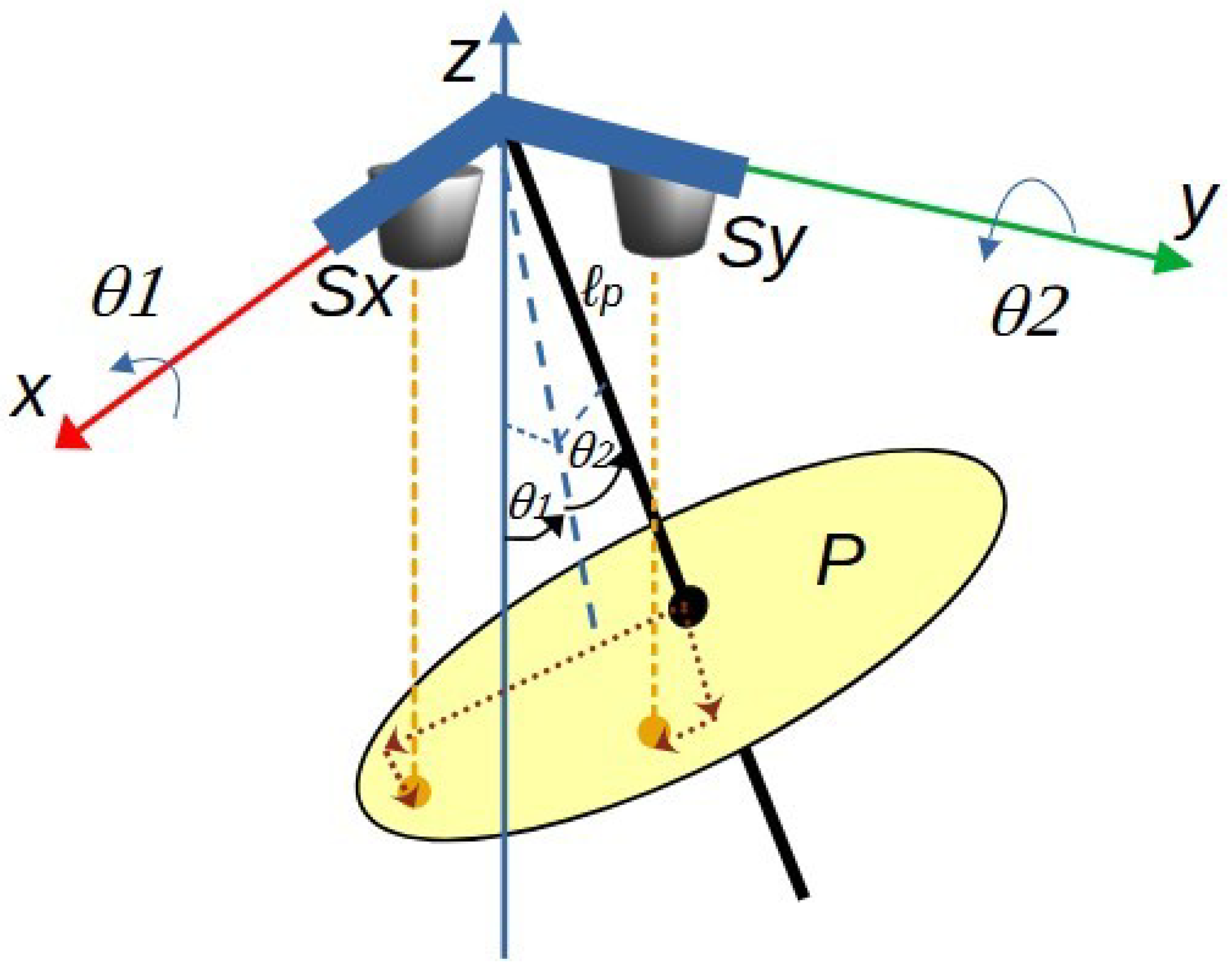
4.2. Sensing System Configuration
- Two infrared sensors are arranged in quadrature near the support point of the pendulum rod.
- Each sensor provides an analog output proportional to the intensity of light reflected from a flat surface mounted perpendicularly to the pendulum rod.
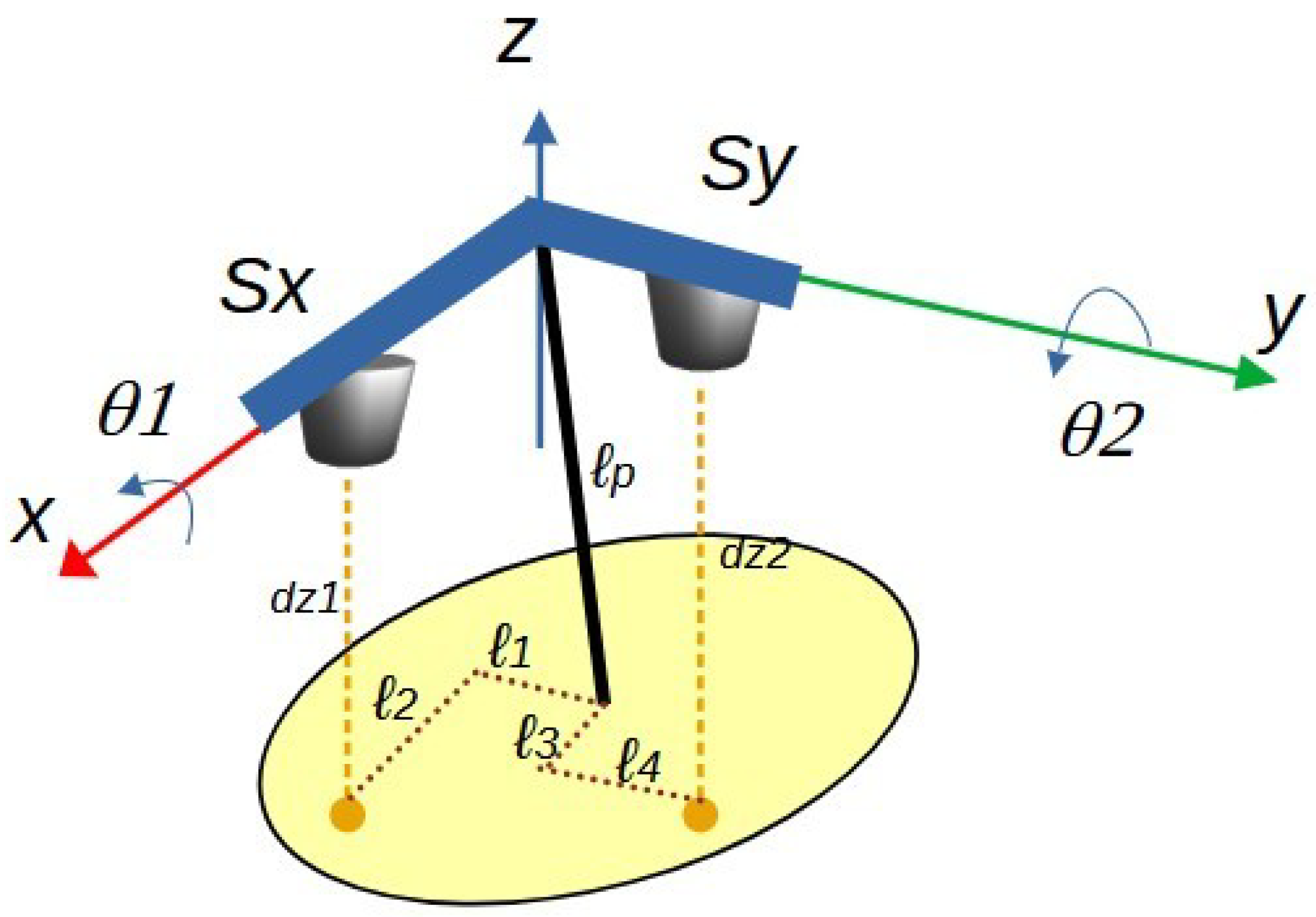
4.2.1. Generating the Distance Measured by Sensor
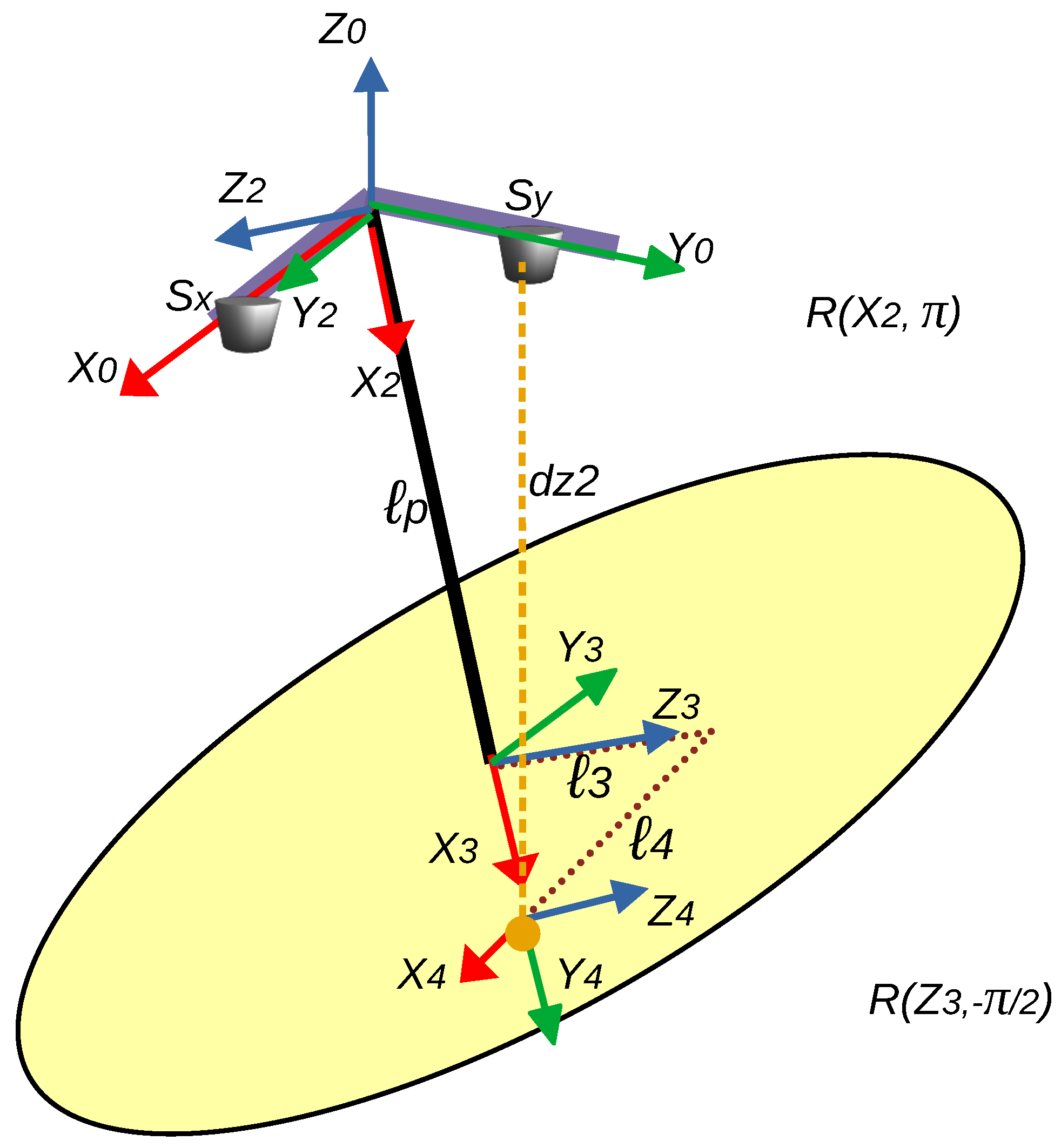
- The rotation from frame to frame involves a transformation , which corresponds to a rotation of radians about the axis.
- Similarly, the rotation from frame to frame involves a transformation , indicating a rotation of radians about the axis.
4.2.2. Generating the Distance Measured by Sensor
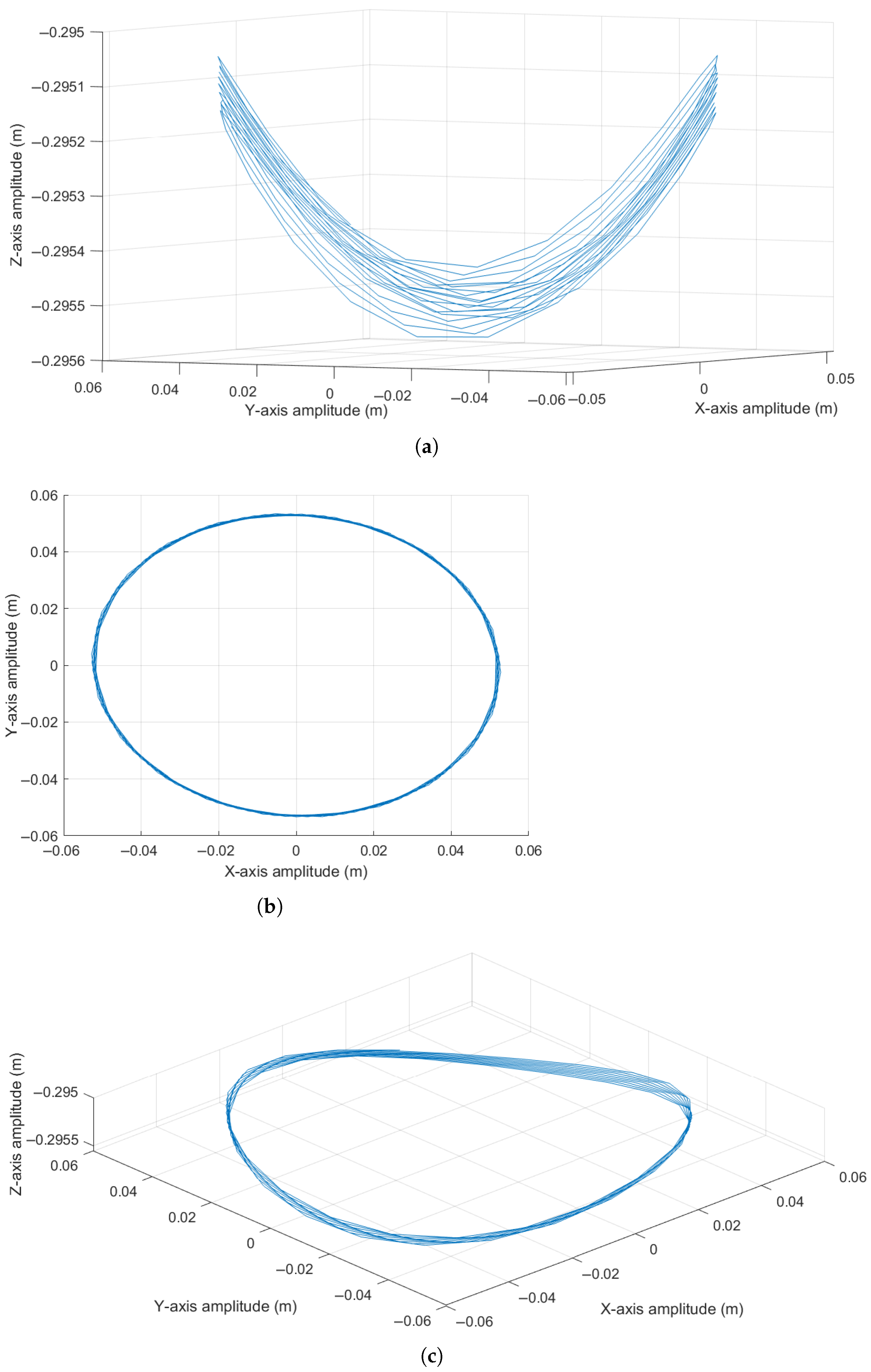
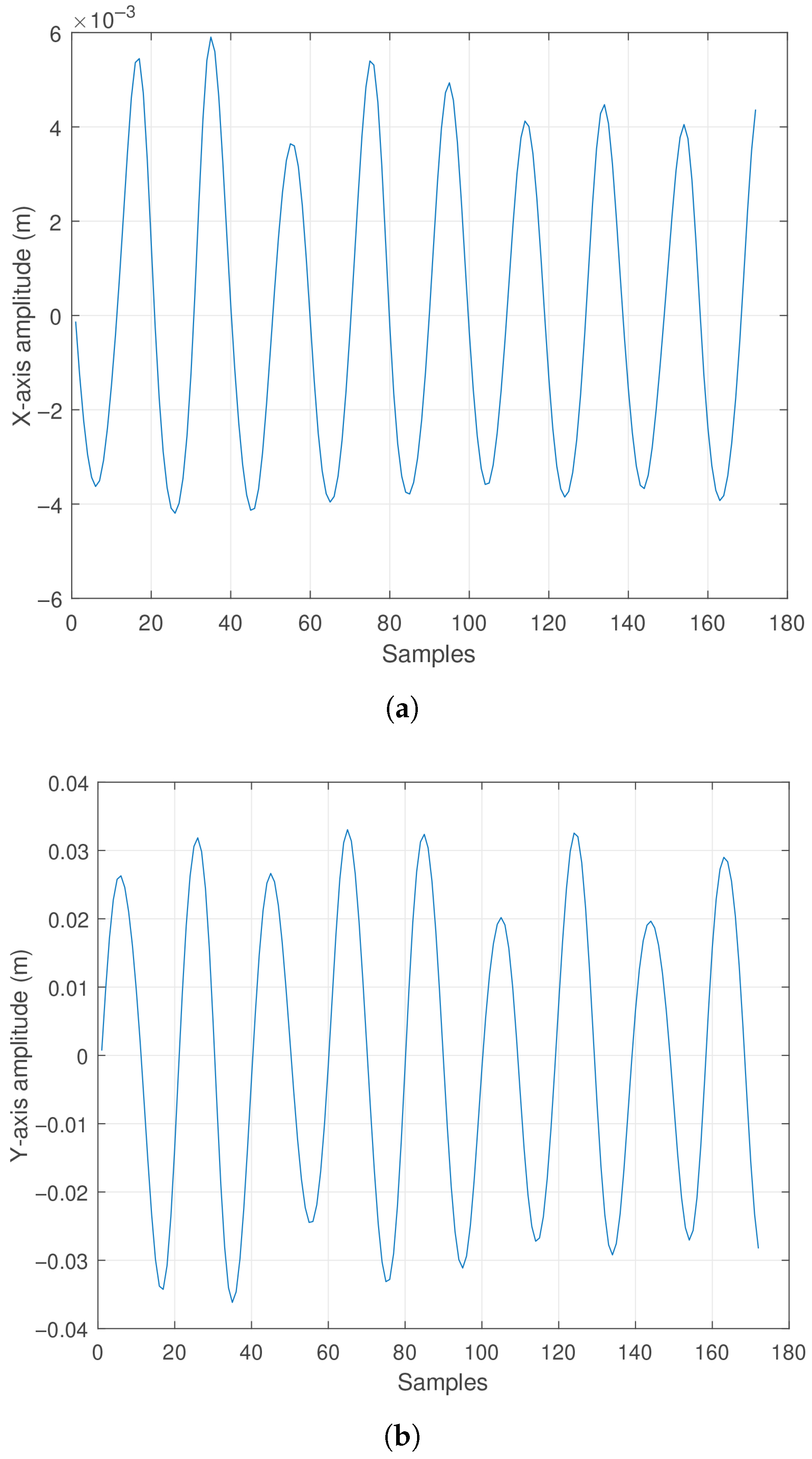
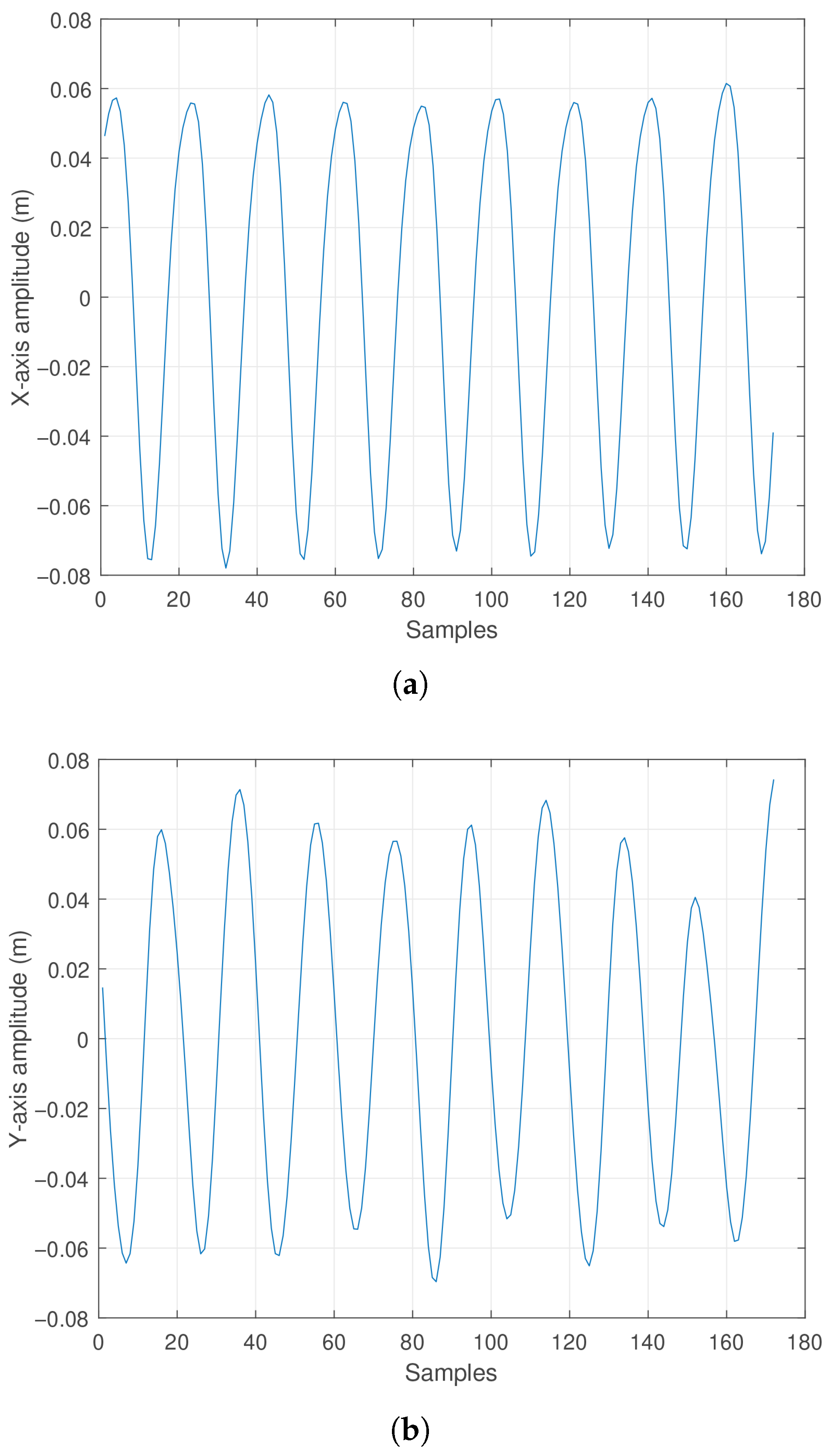
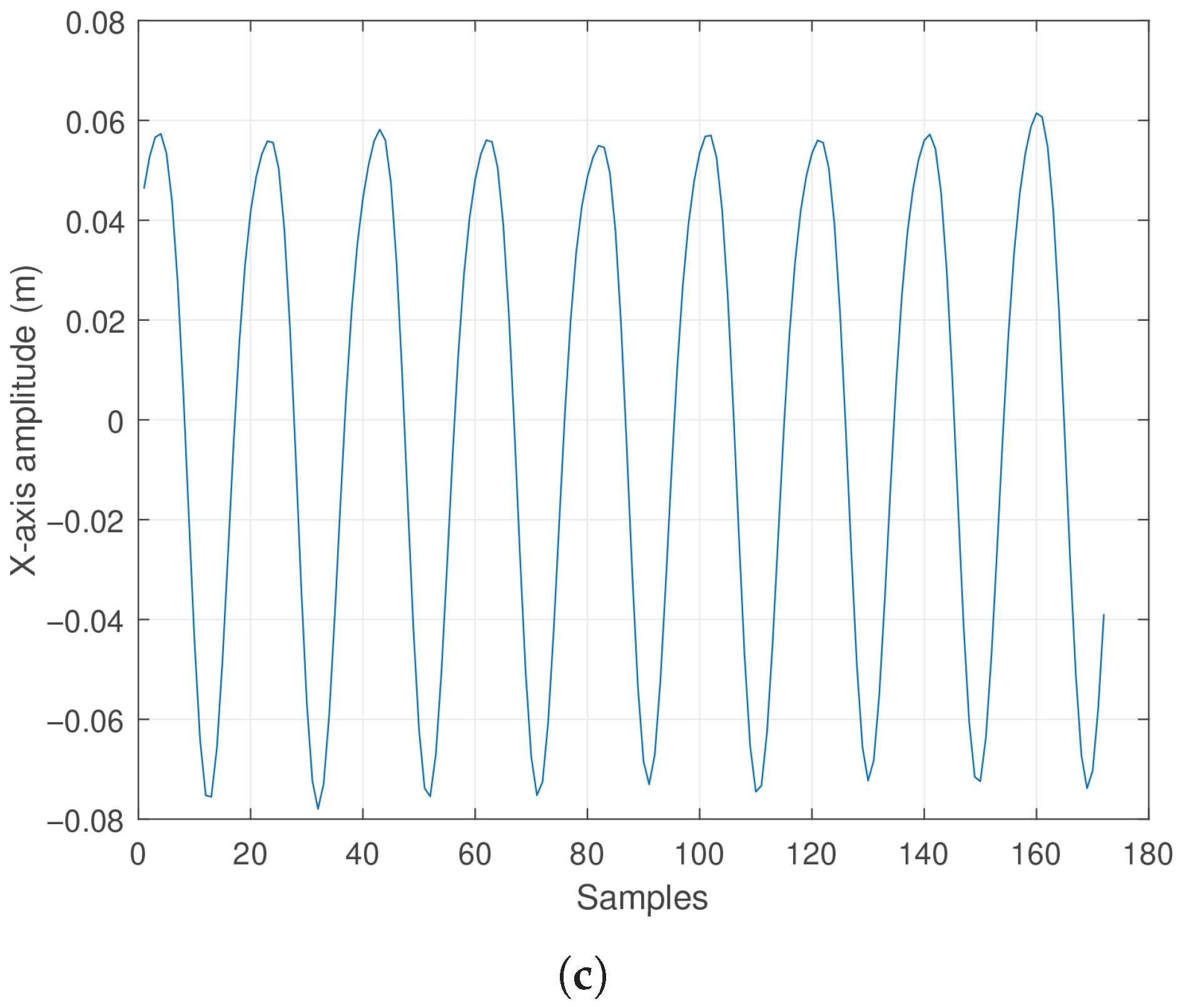
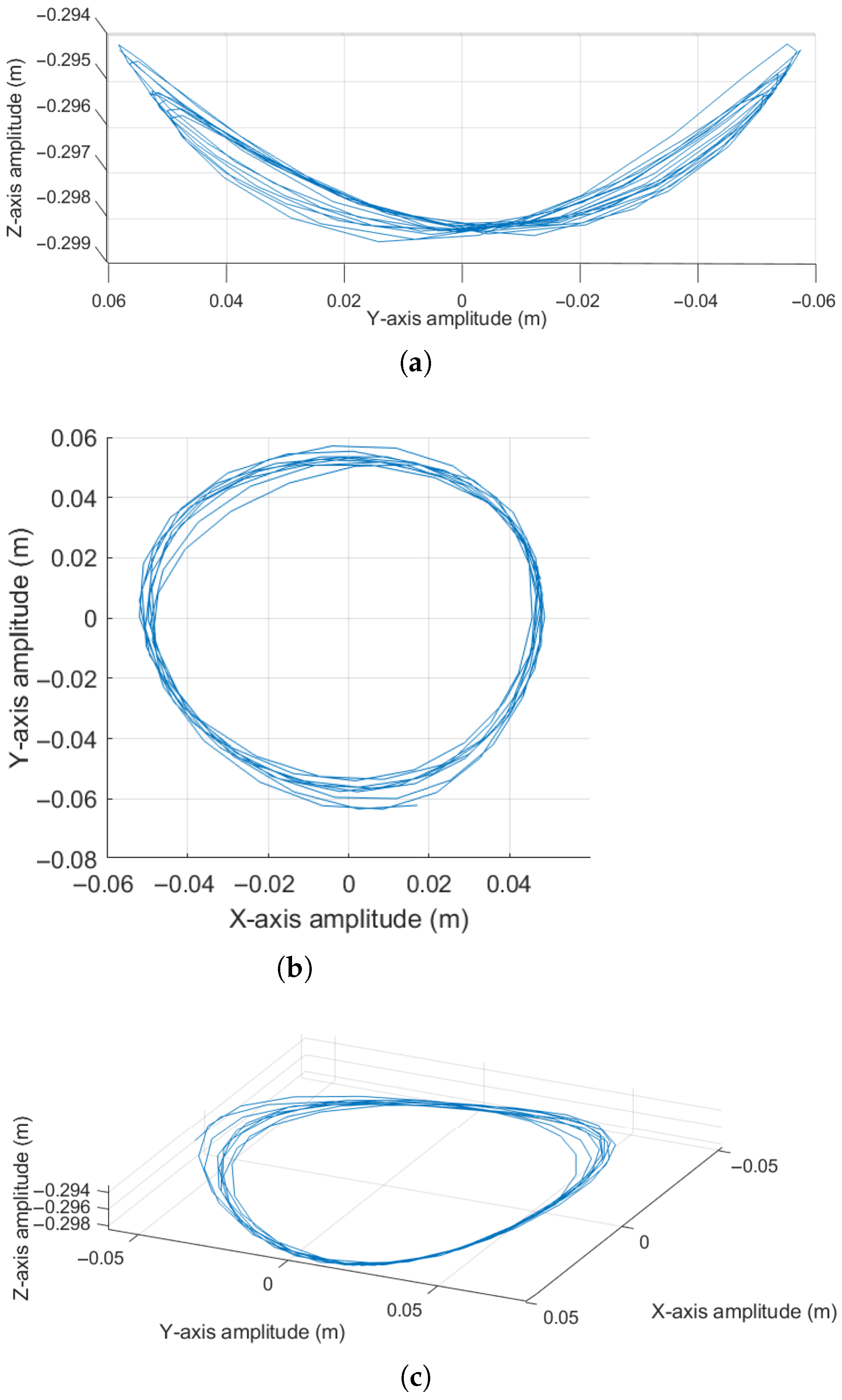
5. Experimental Results
5.1. Experimental Results Case 1
5.2. Experimental Results Case 2
6. Discussions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Hernandez-Maldonado, A.; Diaz-Martinez, J.G.; Kojima, H.; Gutierrez-Carmona, I.; Keshtkar, S. Experimental Platform for Modeling and Control of Articulated Bodies. Mech. Mach. Sci. 2020, 86, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Y. The Global Motion Control of First-order Rotary Parallel Double Inverted Pendulum. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), Harbin, China, 6–9 August 2023; pp. 1293–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Wang, X.; Fei, M. Research of parallel-type double inverted pendulum model based on lagrange equation and LQR controller. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Computing for Sustainable Energy and Environment, Wuxi, China, 17–21 September 2010; Lecture Notes in Computer Science (LNCS: Including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics). Volume 6328, pp. 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioaca, R.A.; Flutur, C. Reaction Wheel Control of an 3D Printed Inverted Pendulum. In Proceedings of the 2021 23rd International Conference on Control Systems and Computer Science (CSCS), Bucharest, Romania, 26–28 May 2021; pp. 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkinany, B.; Mohammed, A.; Krafes, S.; Chalh, Z. Backstepping controller design with a quadratic error for a double inverted pendulum. Int. J. Model. Identif. Control. 2020, 34, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shreedharan, S.; Ravikumar, V.; Mahadevan, S.K. Design and control of real-time inverted pendulum system with force-voltage parameter correlation. Int. J. Dyn. Control. 2021, 9, 1672–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S. A conceptual development of novel ultra-precision dimensional measurement technology. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2003, 33, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Mi, Y.; Glassmaker, N.; Shakouri, A.; Alam, M.A. In Situ Drift Monitoring and Calibration of Field-Deployed Potentiometric Sensors Using Temperature Supervision. ACS Sens. 2023, 8, 2799–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabros, M.; Amrhein, M.; Gujral, P.; Von Stockar, U. On-line recalibration of spectral measurements using metabolite injections and dynamic orthogonal projection. Appl. Spectrosc. 2007, 61, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolfe, P.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Scopesi, F.; Serra, G.; Yamakoshi, K.; Tanaka, S.; Yamakoshi, T.; Yamakoshi, Y.; Ogawa, M. Invasive and non-invasive measurement in medicine and biology: Calibration issues. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Precision Engineering Measurements and Instrumentation, Hangzhou, China, 8–10 August 2010; Volume 7544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, T.; Kang, Y.; Luo, Z. A quick-response and high-precision dynamic measurement method with application on small-angle measurement. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2022, 33, 045009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Fan, X.; Wang, C.; Lu, L. An improved intersection feedback micro-radian angle-measurement system based on the Laser self-mixing interferometry. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2020, 126, 105866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.S.A.; George, B.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C. Technologies and Applications of Angle Sensors: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 7195–7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Bai, Y.; Hu, M.; Li, H.; Qu, S.; Tang, M.; Wang, C.; Wu, S.; Xie, M.; Yang, X.; et al. Semiphysical Simulation of Space Inertial Sensor Utilizing Carrier Amplitude Modulation. IEEE Sens. J. 2025, 25, 8407–8416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wang, D.; Zhou, L.; Wu, S.; Xiang, R.; Zhang, W.; Lu, L.; Yu, B. A ultra-small-angle self-mixing sensor system with high detection resolution and wide measurement range. Opt. Laser Technol. 2017, 91, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.H.; Börger, M.; Thien, J.; Koß, H.J. The Good pH probe: Non-invasive pH in-line monitoring using Good buffers and Raman spectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2023, 415, 7247–7258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Fan, X.; Guo, Y.; Gui, H.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Yu, B.; Lu, L. Full-circle range and microradian resolution angle measurement using the orthogonal mirror self-mixing interferometry. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 10371–10381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, B.J.; Black, J.T.; Adams, C.S. Design and Calibration of a Torsion Pendulum for Micronewton-Class Spacecraft Thrusters. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2022, 35, 04022023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jonge, A.R. Discussion:“A Kinematic Notation for Lower-Pair Mechanisms Based on Matrices”(Denavit, J., and Hartenberg, RS, 1955, ASME J. Appl. Mech., 22, pp. 215–221). J. Appl. Mech. 1956, 23, 152–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpio, M.; Saltaren, R.; Cely, J.; Carpio, D.; Yupa, W. A Robotic System Based on a Universal Joint Actuated by Two Cables Applied to the Orientation of Photovoltaic Panels. In Proceedings of the 2024 7th Iberian Robotics Conference (ROBOT), Madrid, Spain, 6–8 November 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permadi, Y.; Darmawan, A.; Pitowarno, E. Application of Lagrange Method to Analyze Forces of Gyroscope Inverted Pendulum. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Electronics Symposium (IES), Surabaya, Indonesia, 27–28 September 2019; pp. 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Kar, I. Modeling, Control and Variational Integration for an inverted pendulum on S1. In Proceedings of the 2021 Seventh Indian Control Conference (ICC), Mumbai, India, 20–22 December 2021; pp. 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A. Treating the Solid Pendulum Motion by the Large Parameter Procedure. Int. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2020, 2020, 8853867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, R. The behaviour of a forced spherical pendulum operating in a weightless environment. Q. J. Mech. Appl. Math. 2023, 76, 349–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubanjo, A.A.; Oyetola, O.K. Dynamic mathematical modeling and control algorithms design of an inverted pendulum system. Turk. J. Eng. 2019, 3, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Zhao, X.; Sun, Q.; Yang, K.; Li, F. A new virtual-real gravity compensated inverted pendulum model and ADAMS simulation for biped robot with heterogeneous legs. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2020, 34, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokin, M.; Ceperkovic, V.; Prokin, D. Double Buffered Angular Speed Measurement Method for Self-Calibration of Magnetoresistive Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2023 12th Mediterranean Conference on Embedded Computing (MECO), Budva, Montenegro, 6–10 June 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandan, N.; Varma Muppala, A.; George, B. A Flexible, Planar-Coil-Based Sensor for Through-Shaft Angle Sensing. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 10217–10224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Mao, Z.; Ma, T.; Chen, S.; Ren, J.; Hu, Z.; Ju, M. Development of a Double-Resolver High-Sensitivity Torsion Spring-Type Torque Sensor via Iterative Error Self-Compensation Method. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 5618–5627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Matrix | d | a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | /2 + | |
| /2 + | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| /2 | 0 |
| Matrix | d | a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | /2 + | |
| /2 + | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0 | 0 | |||
| /2 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carpio, M.; Zambrano, J.; Saltaren, R.; Cely, J.; Carpio, D. Non-Invasive Position Measurement of a Spatial Pendulum Using Infrared Distance Sensors. Sensors 2025, 25, 4624. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154624
Carpio M, Zambrano J, Saltaren R, Cely J, Carpio D. Non-Invasive Position Measurement of a Spatial Pendulum Using Infrared Distance Sensors. Sensors. 2025; 25(15):4624. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154624
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarpio, Marco, Julio Zambrano, Roque Saltaren, Juan Cely, and David Carpio. 2025. "Non-Invasive Position Measurement of a Spatial Pendulum Using Infrared Distance Sensors" Sensors 25, no. 15: 4624. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154624
APA StyleCarpio, M., Zambrano, J., Saltaren, R., Cely, J., & Carpio, D. (2025). Non-Invasive Position Measurement of a Spatial Pendulum Using Infrared Distance Sensors. Sensors, 25(15), 4624. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154624








