Pixel 5 Versus Pixel 9 Pro XL—Are Android Devices Evolving Towards Better GNSS Performance?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
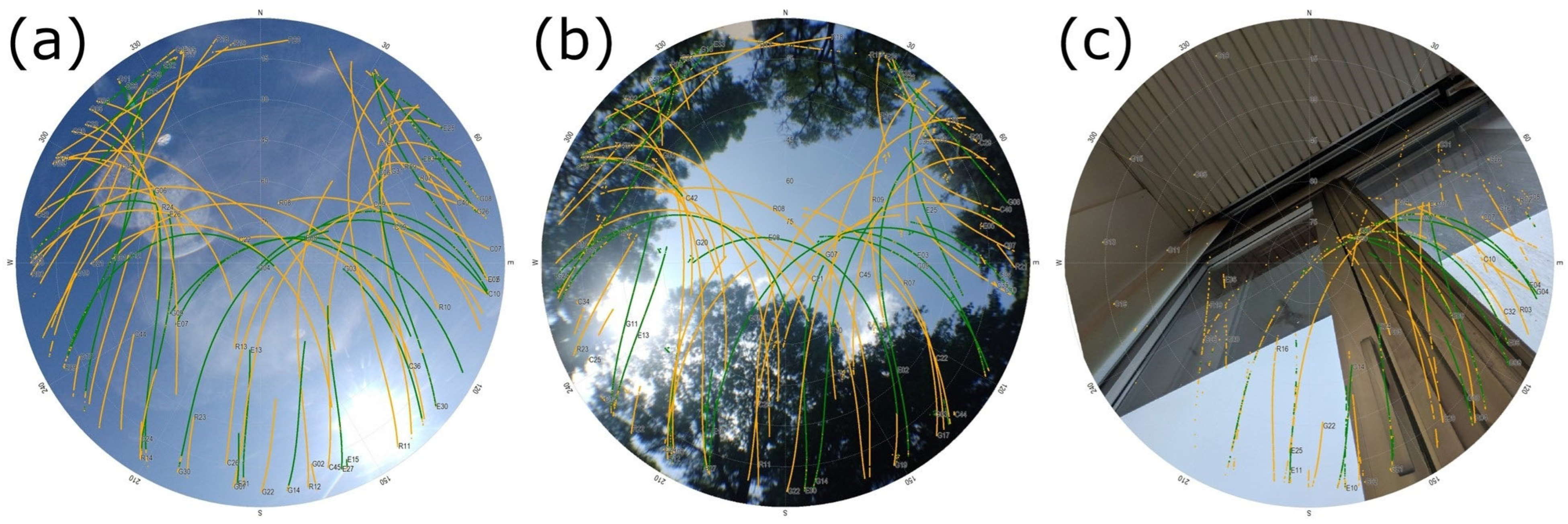
2.1. Data Acquisition
2.2. Quality Control (QC)
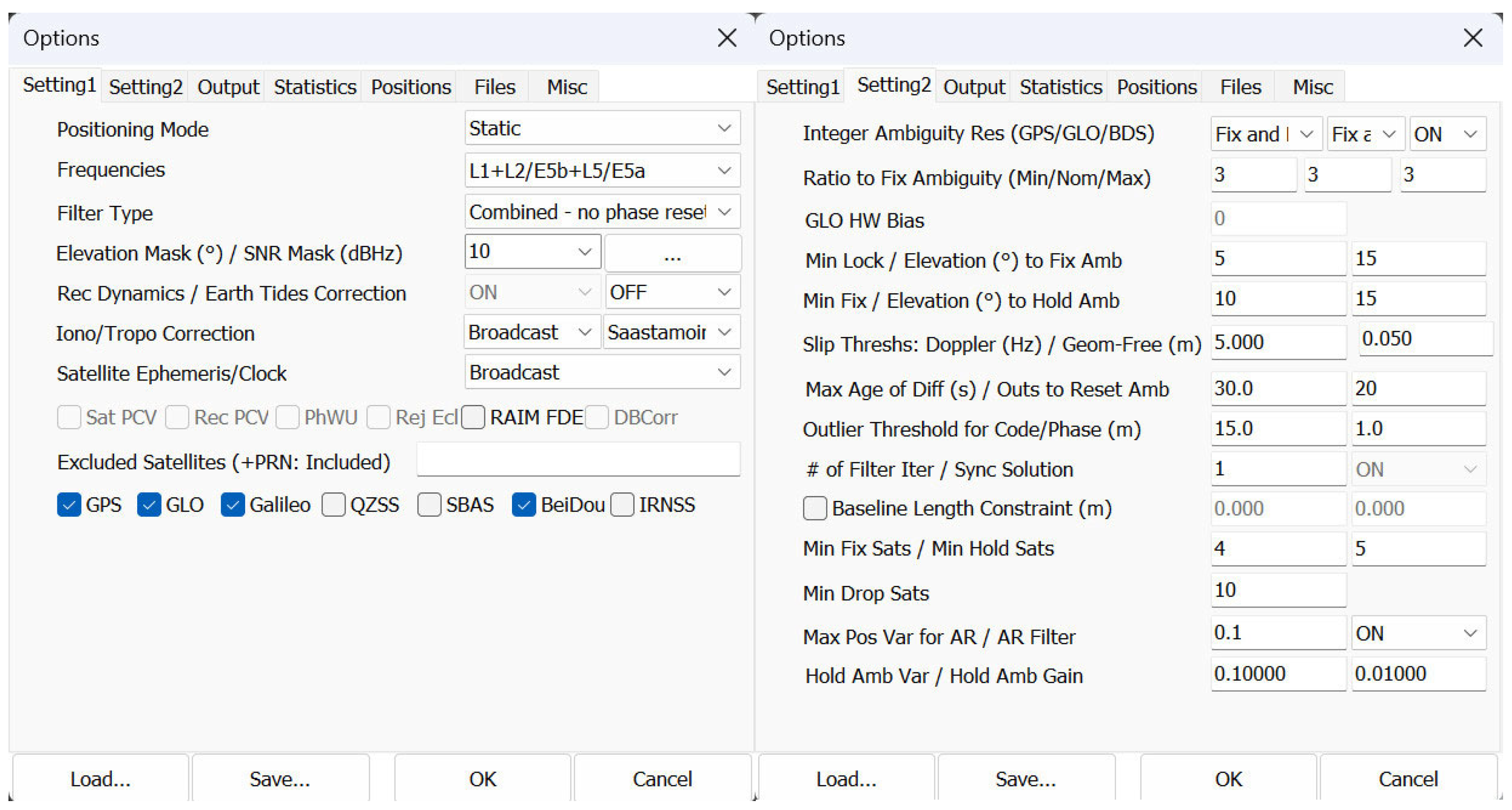
2.3. Positioning
3. Results
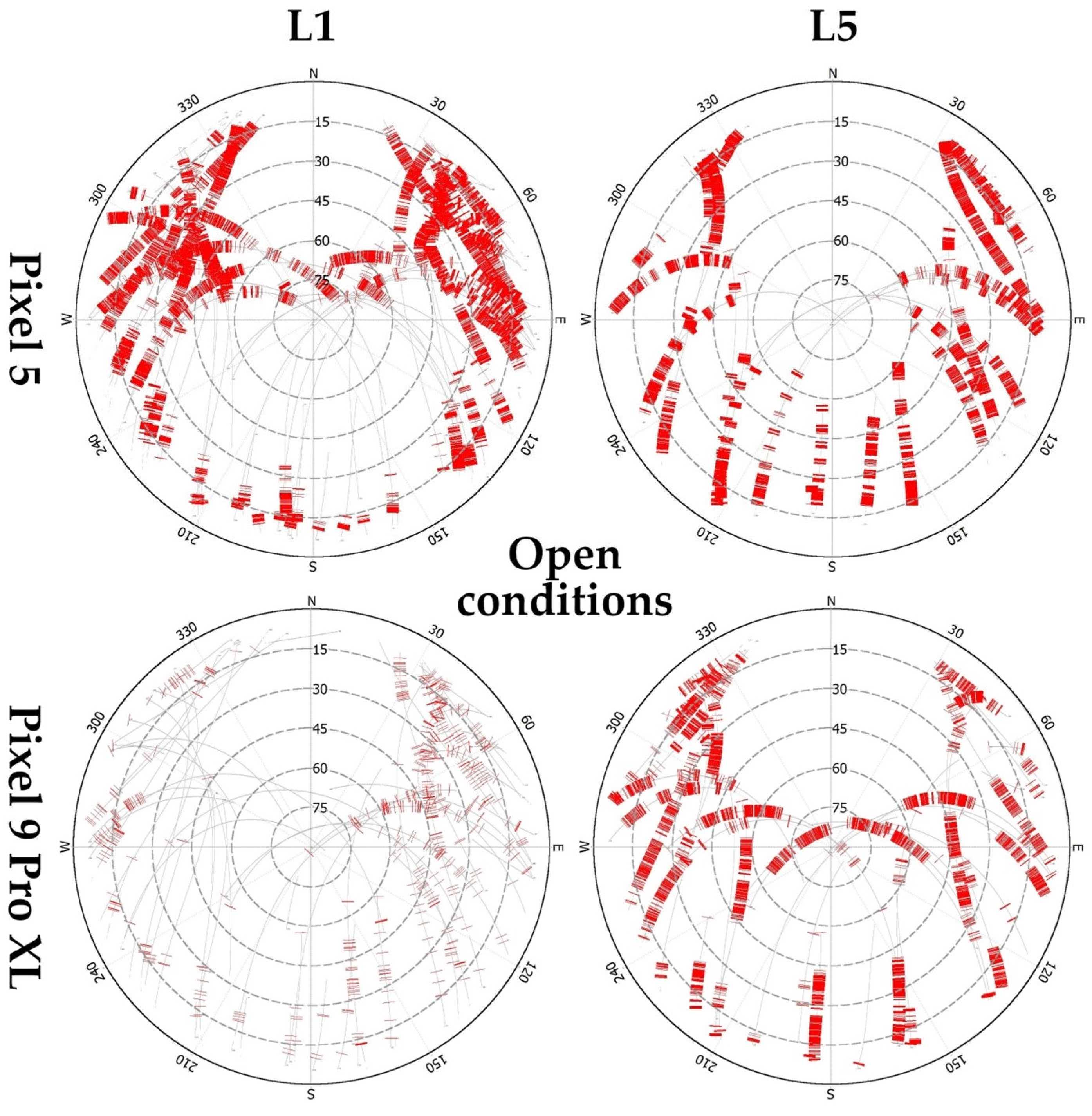
3.1. Quality Control
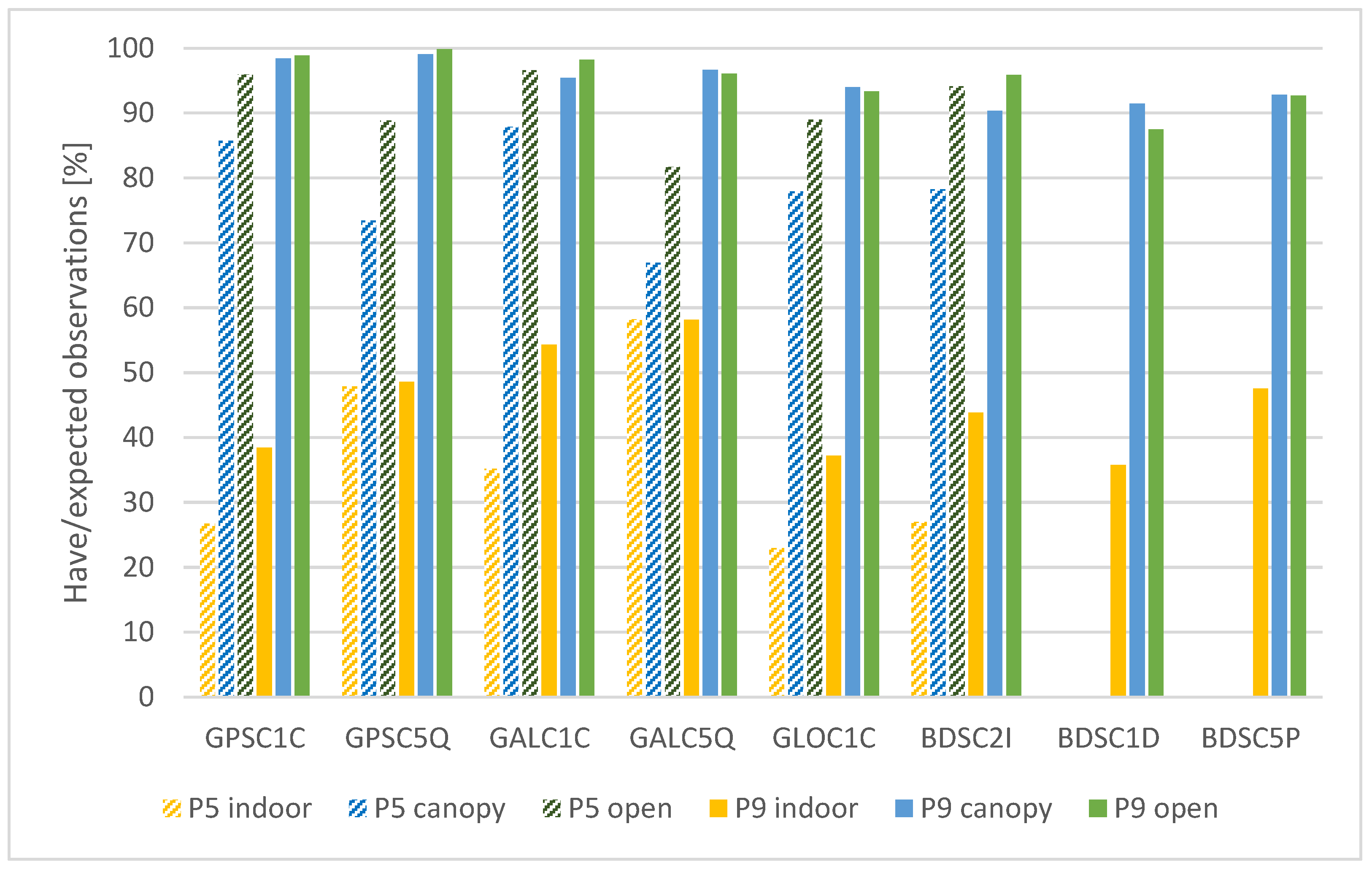
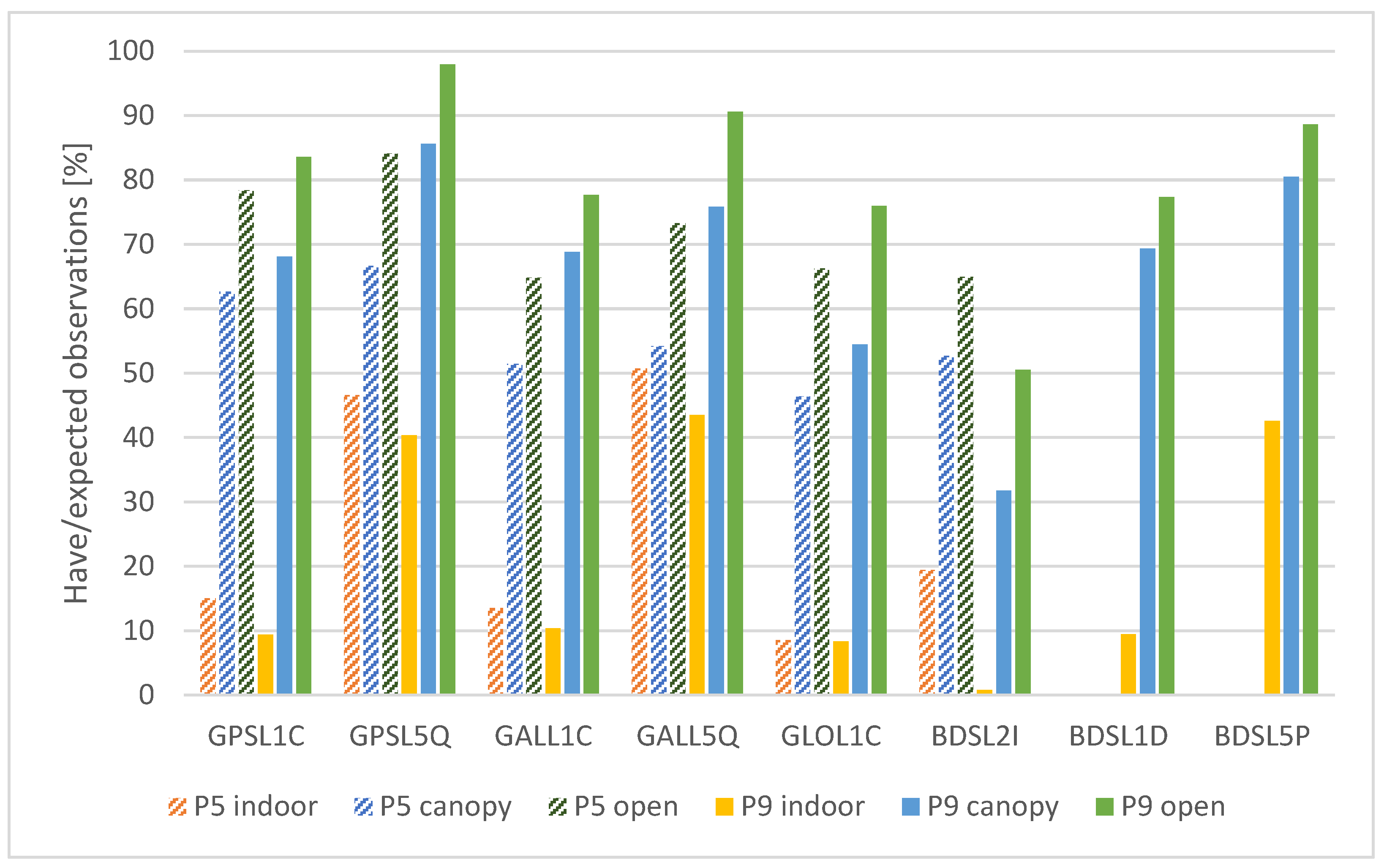
3.1.1. Have Versus Expected Observations
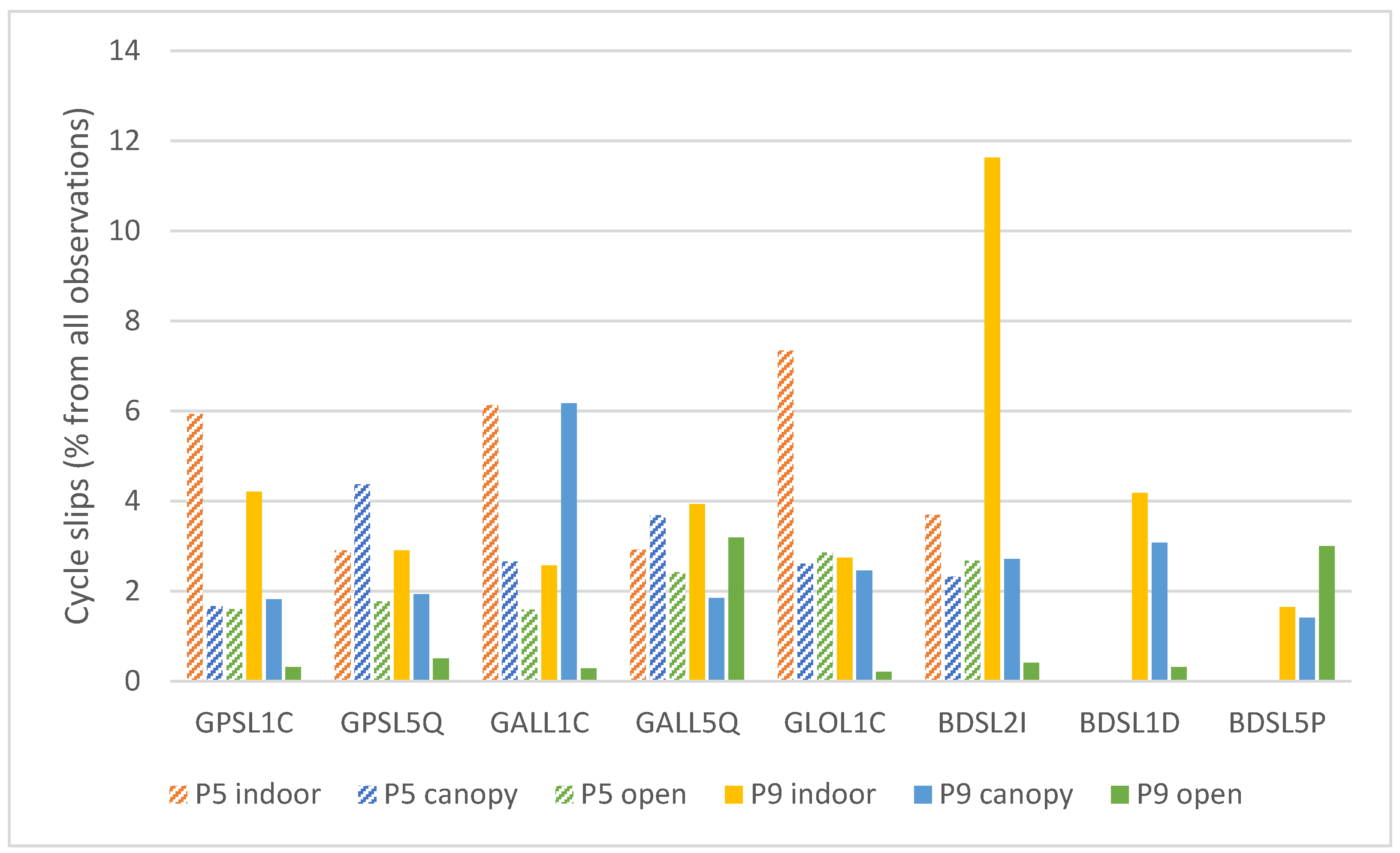
3.1.2. Cycle Slips
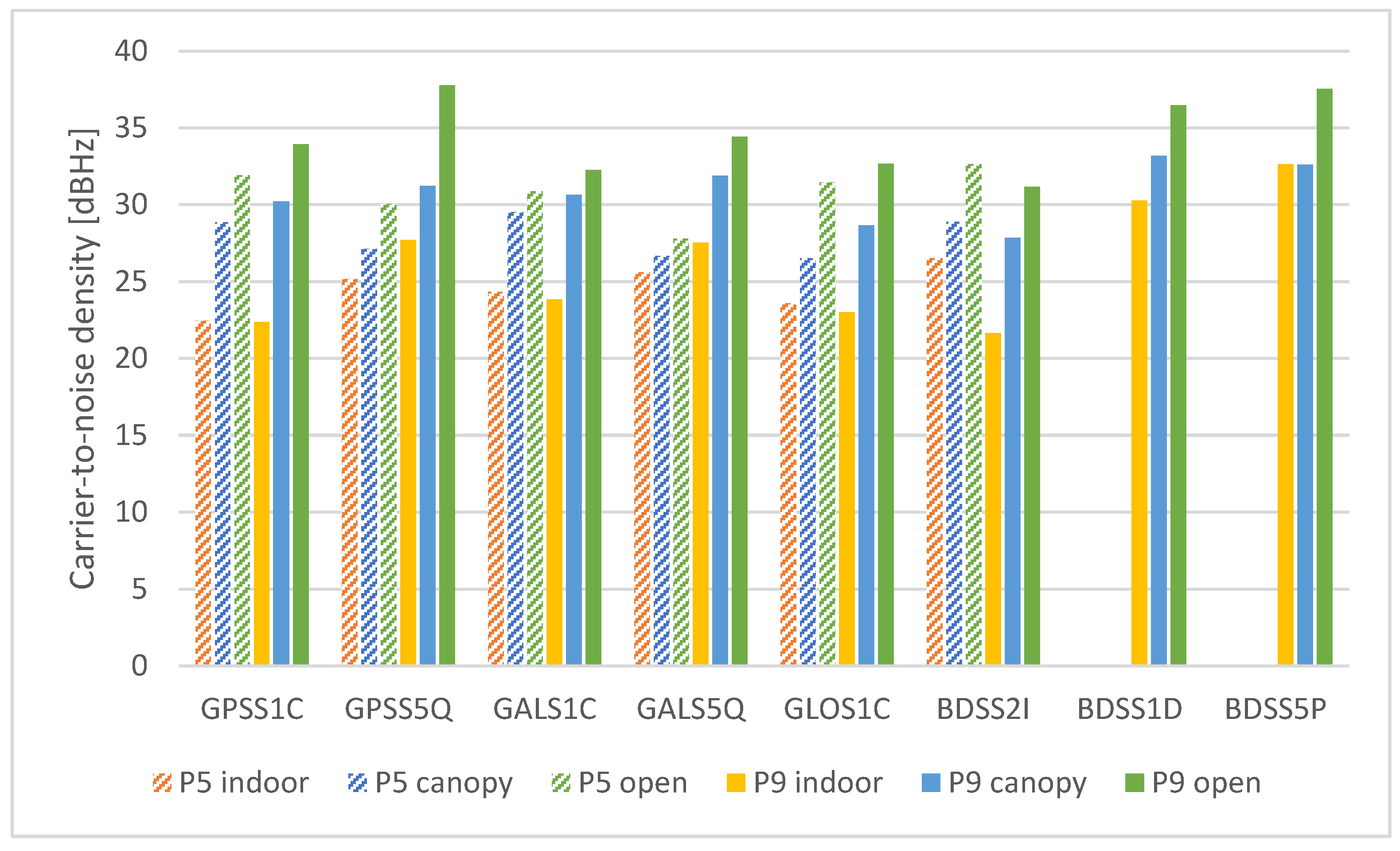
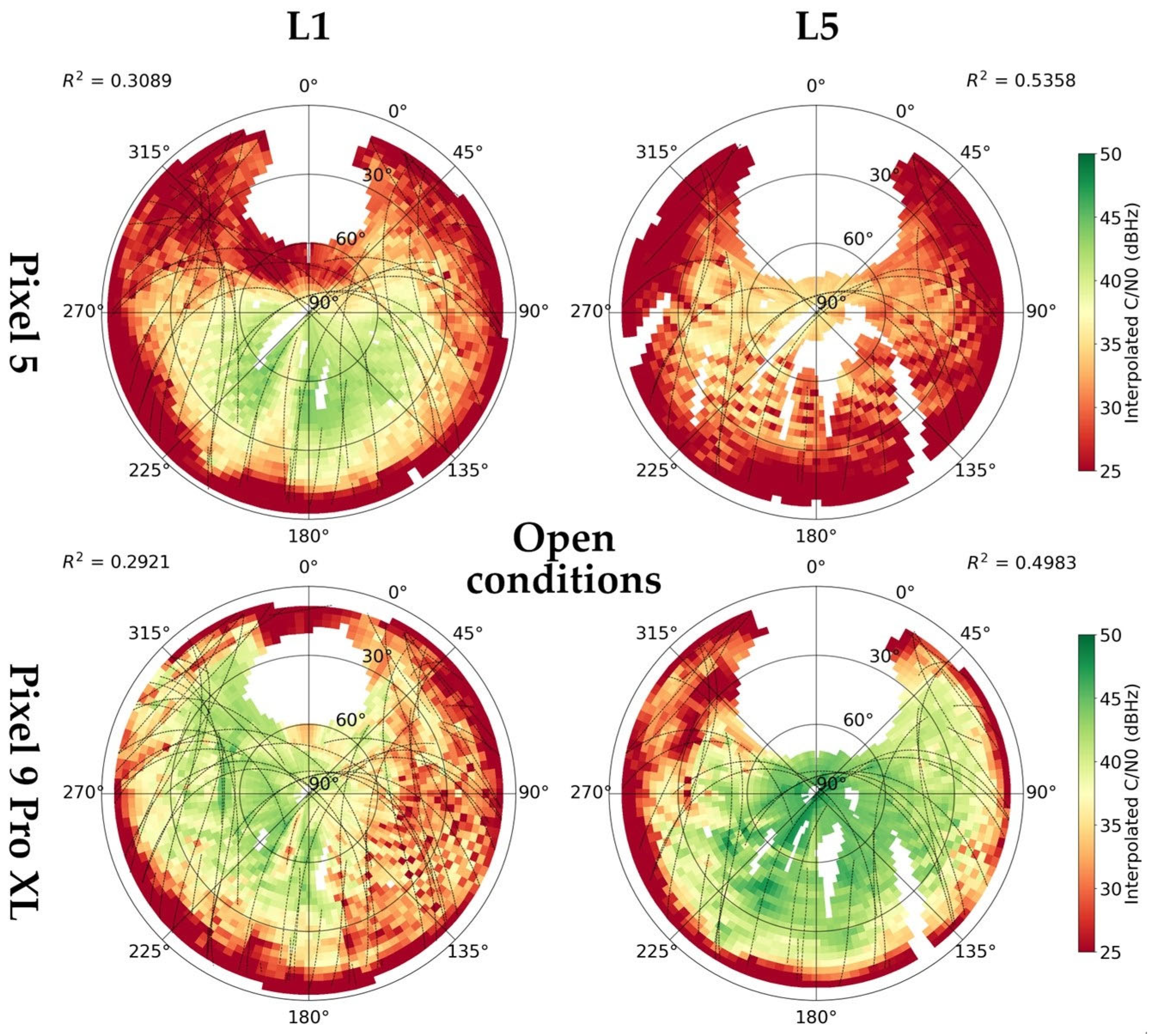
3.1.3. Carrie-to-Noise Density
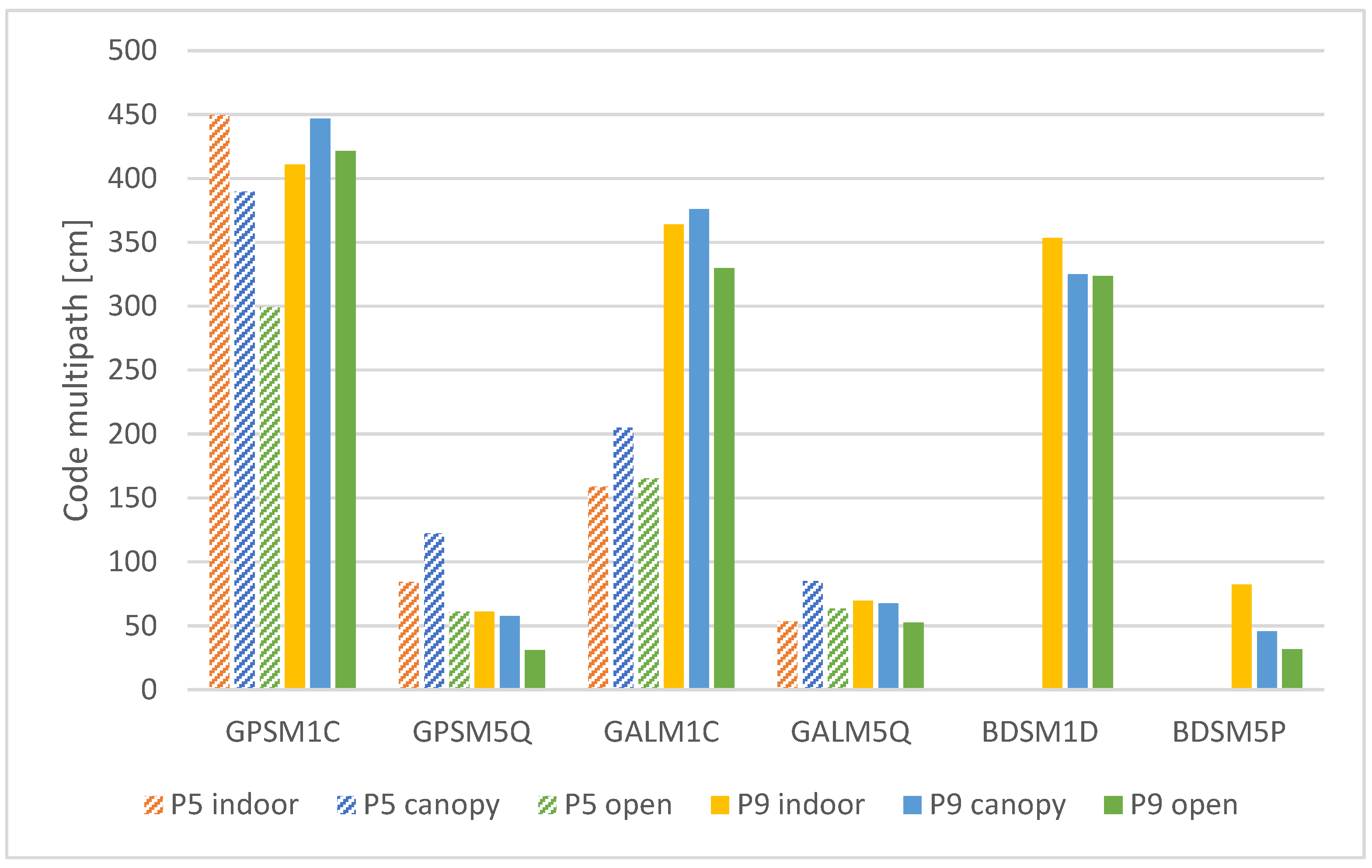
3.1.4. Code Multipath
3.2. Positioning
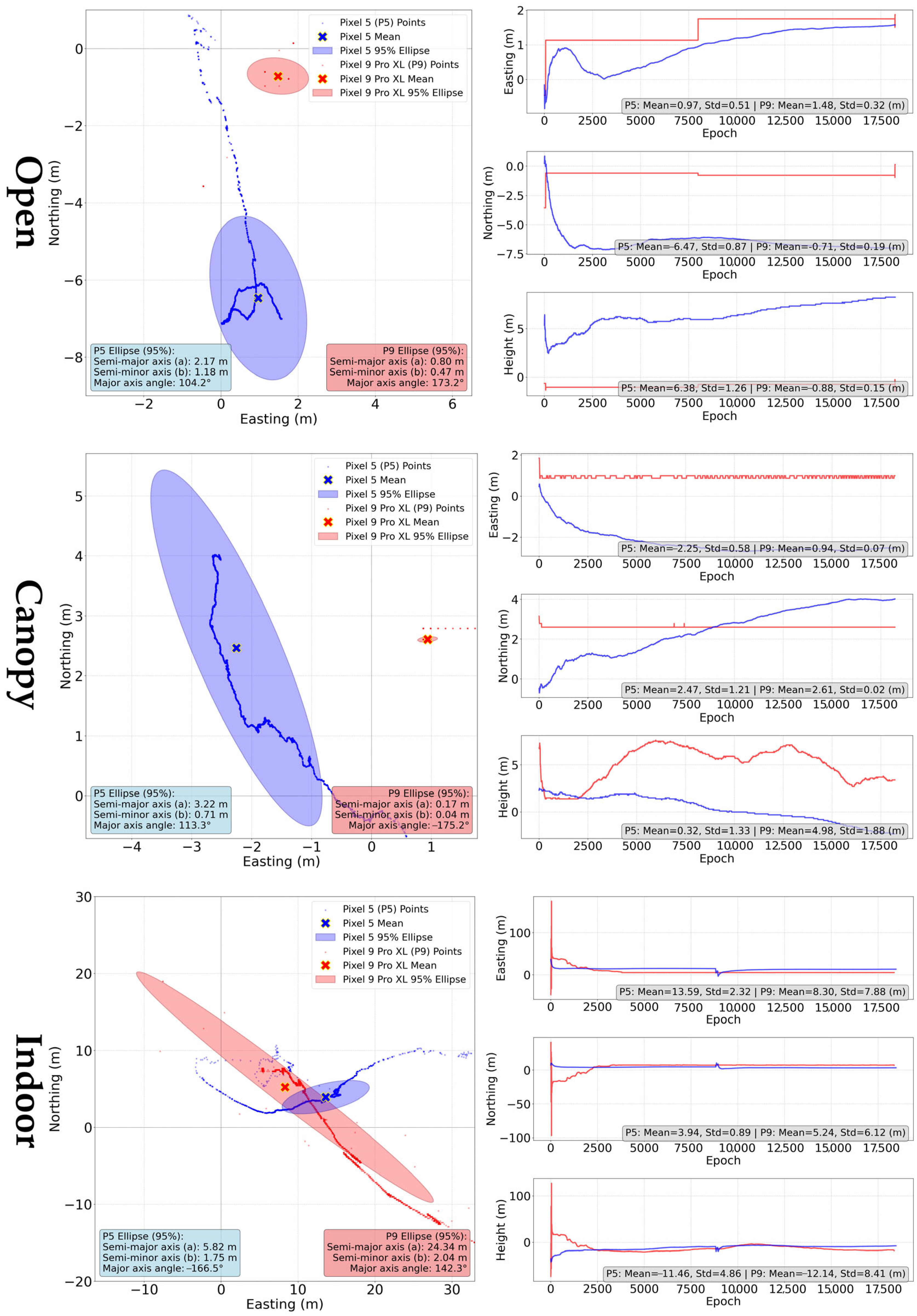
3.2.1. “Internal” Solution
3.2.2. “Single” Method
3.2.3. Precise Point Positioning
3.2.4. “Static” Method
3.2.5. Statistical Summary
4. Discussion
4.1. Quality Control
4.2. Positioning
4.3. Drawbacks, Limitations and Future Challenges
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite Systems |
| SPP | Single-Point Positioning |
| LBS | Location-Based Services |
| C/N0 | Signal-to-noise density |
| MP | Multipath |
| ETRS | European Terrestrial Reference System |
| ETRF | European Terrestrial Reference Frame |
| ITRF | International Terrestrial Reference Frame |
| QC | Quality Control |
| OS | Operating System |
| SBAS | Satellite-Based Augmentation Systems |
| CORS | Continuously Operating Reference Station |
| SKPOS | Slovak Real-Time Positioning Service |
| ADR | Accumulated Delta Range |
| DGNSS | Differential GNSS |
| RTK | Real-Time Kinematic |
| PPP | Precise Point Positioning |
Appendix A
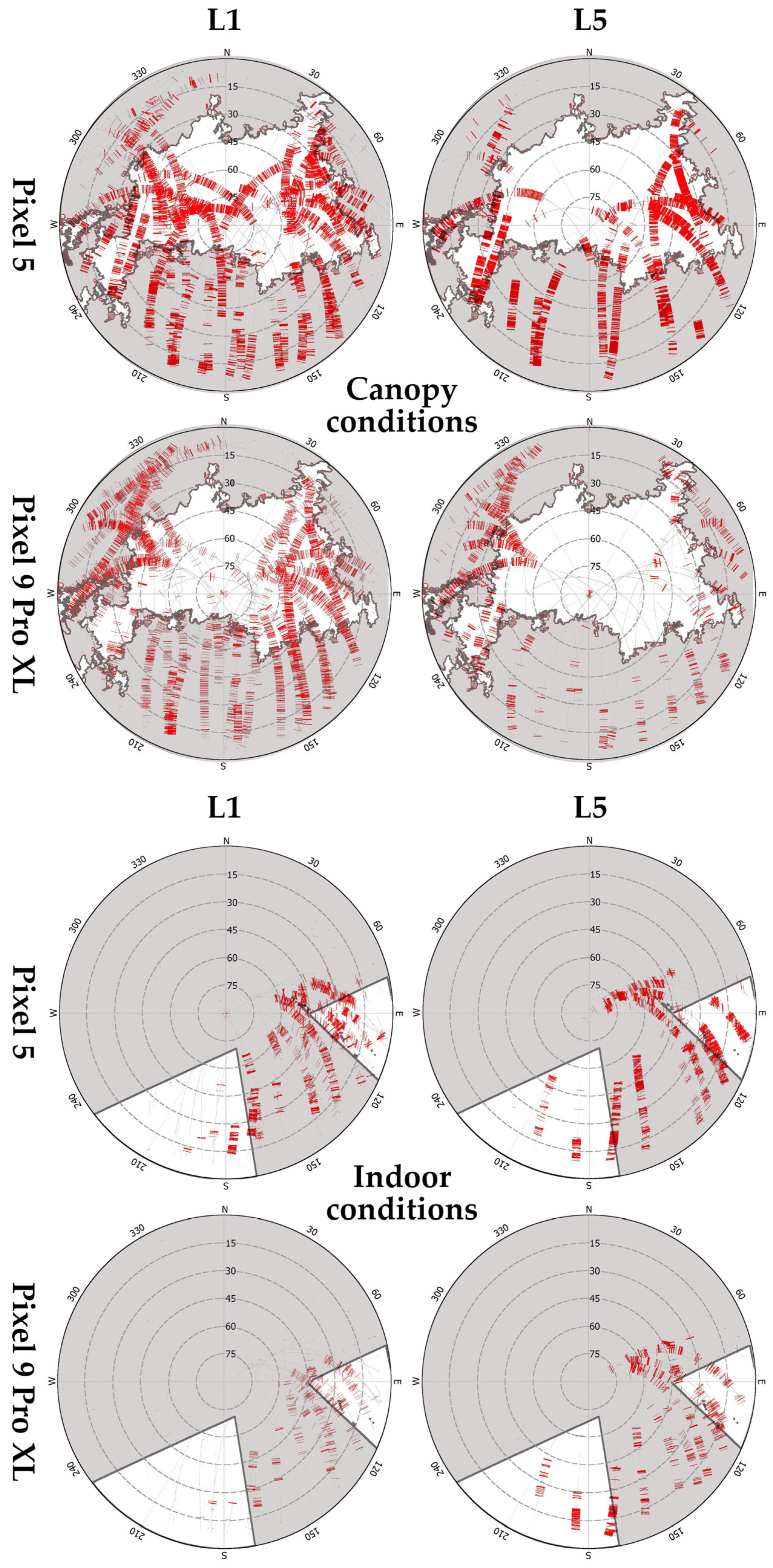
Appendix B
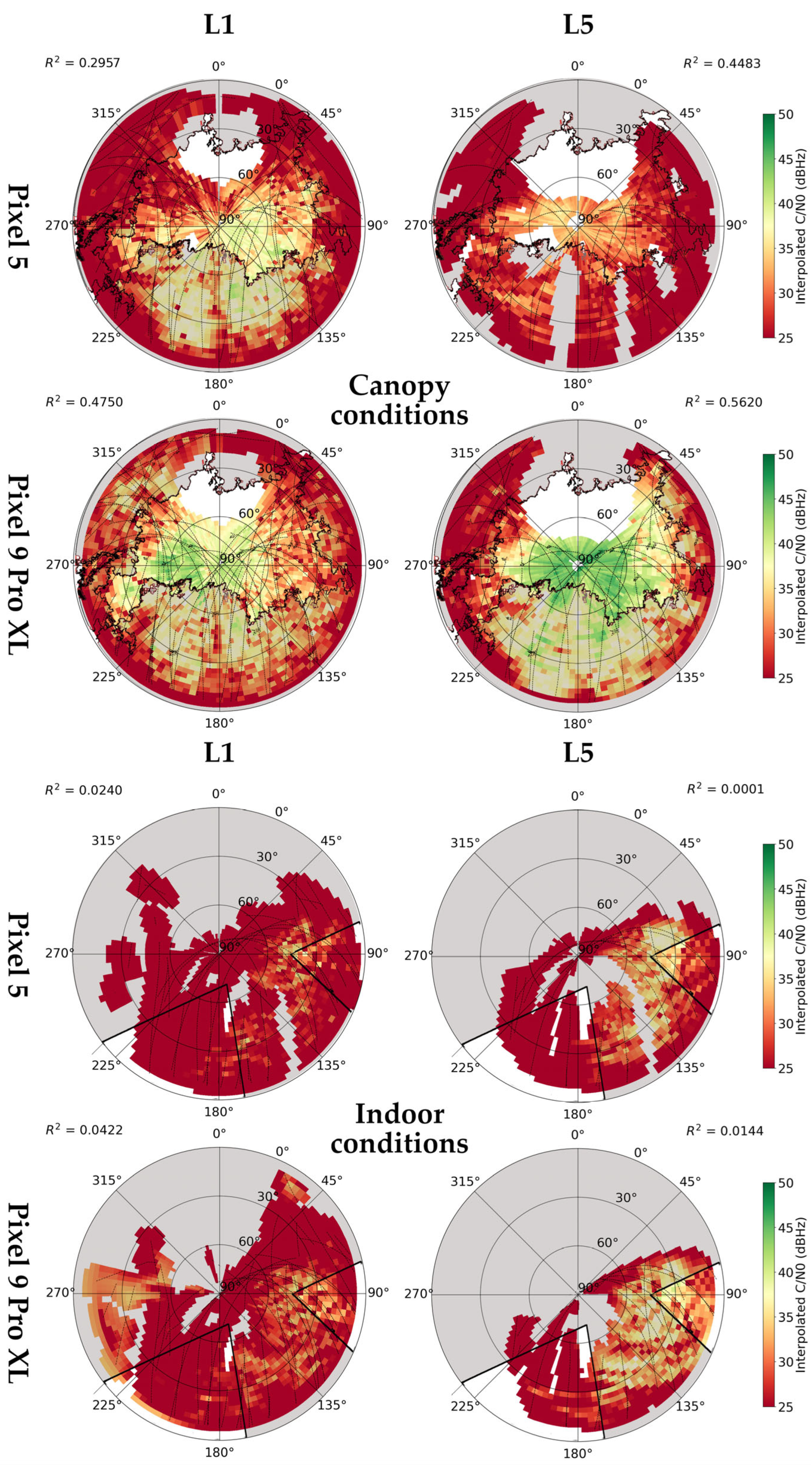
References
- Junglas, I.A.; Watson, R.T. Location-Based Services. Commun. ACM 2008, 51, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raw GNSS Measurements|Sensors and Location|Android Developers. Available online: https://developer.android.com/develop/sensors-and-location/sensors/gnss (accessed on 14 February 2025).
- Paziewski, J.; Pugliano, G.; Robustelli, U. Performance Assessment of GNSS Single Point Positioning with Recent Smartphones. In Proceedings of the MetroSea 2020—TC19 International Workshop on Metrology for the Sea, Naples, Italy, 5–7 October 2020; pp. 197–201. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, J.; Lim, C.; Park, B. Inherent Limitations of Smartphone GNSS Positioning and Effective Methods to Increase the Accuracy Utilizing Dual-Frequency Measurements. Sensors 2022, 22, 9879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakuła, M.; Uradziński, M.; Krasuski, K. Performance of DGPS Smartphone Positioning with the Use of P(L1) vs. P(L5) Pseudorange Measurements. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, T.; Taylor, T.; Lee, D.-K.; Akos, D.M. Optimizing the Use of RTKLIB for Smartphone-Based GNSS Measurements. Sensors 2022, 22, 3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabove, P.; Di Pietra, V. Single-Baseline RTK Positioning Using Dual-Frequency GNSS Receivers Inside Smartphones. Sensors 2019, 19, 4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggrey, J.; Bisnath, S.; Naciri, N.; Shinghal, G.; Yang, S. Use of PPP Processing for Next-Generation Smartphone GNSS Chips: Key Benefits and Challenges. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2019), Miami, FL, USA, 16–20 September 2019; pp. 3862–3878. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Sun, M.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, P. Precise Point Positioning Using Dual-Frequency GNSS Observations on Smartphone. Sensors 2019, 19, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, D.; Naciri, N.; Bisnath, S. Precise Positioning Utilizing Smartphone GNSS/IMU Integration with the Combination of Galileo High Accuracy Service (HAS) Corrections and Broadcast Ephemerides. GPS Solut. 2024, 28, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández Olcina, J.; Anquela Julián, A.B.; Martín Furones, Á.E. Real-Time Cloud Computing of GNSS Measurements from Smartphones and Mobile Devices for Enhanced Positioning and Navigation. GPS Solut. 2024, 28, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochkati, M.; Sharma, H.; Lichtenberger, C.A.; Pany, T. Demonstration of Fused RTK (Fixed) + Inertial Positioning Using Android Smartphone Sensors Only; 2020 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS): Portland, OR, USA, 2020; pp. 1140–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Xia, L.; Li, Q.; Xia, J.; Cai, Y. IMU-Aided Precise Point Positioning Performance Assessment with Smartphones in GNSS-Degraded Urban Environments. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Bastos, L.; Magalhaes, A. Performance Assessment of the Android Smartphone’s IMU in a GNSS/INS Coupled Navigation Model. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 171073–171083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddakatte, R.; Broumandan, A.; Lachapelle, G. Performance Evaluation of Smartphone Gnss Measurements with Different Antenna Configurations. In Proceedings of the Royal Institute of Navigation International Navigation Conference, Brighton, UK, 8 May 2017; Volume 1, pp. 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Wanninger, L.; Heßelbarth, A. GNSS Code and Carrier Phase Observations of a Huawei P30 Smartphone: Quality Assessment and Centimeter-Accurate Positioning. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paziewski, J.; Sieradzki, R.; Baryla, R. Signal Characterization and Assessment of Code GNSS Positioning with Low-Power Consumption Smartphones. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purfürst, T. Evaluation of Static Autonomous GNSS Positioning Accuracy Using Single-, Dual-, and Tri-Frequency Smartphones in Forest Canopy Environments. Sensors 2022, 22, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angrisano, A.; Gaglione, S. Smartphone GNSS Performance in an Urban Scenario with RAIM Application. Sensors 2022, 22, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, L.-T.; Gu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Kamijo, S. Urban Pedestrian Navigation Using Smartphone-Based Dead Reckoning and 3-D Map-Aided GNSS. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 1281–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IDC—Smartphone Market Insights—Home. Available online: https://www.idc.com/promo/smartphone-market-share (accessed on 19 February 2025).
- Zeng, S.; Kuang, C.; Yu, W. Evaluation of Real-Time Kinematic Positioning and Deformation Monitoring Using Xiaomi Mi 8 Smartphone. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massarweh, L.; Darugna, F.; Psychas, D.; Bruno, J. Statistical Investigation of Android GNSS Data: Case Study Using Xiaomi Mi 8 Dual-Frequency Raw Measurements. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2019), Miami, FL, USA, 16–20 September 2019; pp. 3847–3861. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Wang, F.; Sang, J.; Lin, X.; Gong, X.; Zhang, W. Characteristics Analysis of Raw Multi-GNSS Measurement from Xiaomi Mi 8 and Positioning Performance Improvement with L5/E5 Frequency in an Urban Environment. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szot, T.; Specht, C.; Specht, M.; Dabrowski, P.S. Comparative Analysis of Positioning Accuracy of Samsung Galaxy Smartphones in Stationary Measurements. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odolinski, R.; Yang, H.; Hsu, L.T.; Khider, M.; Fu, G.; Dusha, D. Evaluation of the Multi-GNSS, Dual-Frequency RTK Positioning Performance for Recent Android Smartphone Models in a Phone-to-Phone Setup. In Proceedings of the International Technical Meeting of The Institute of Navigation, Long Beach, CA, USA, 23–25 January 2024; pp. 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GPSTest—Aplikácie v Službe Google Play. Available online: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.android.gpstest (accessed on 17 January 2025).
- GPSTest Database—Google Streadsheet. Available online: https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1jXtRCoEnnFNWj6_oFlVWflsf-b0jkfZpyhN-BXsv7uo/edit?gid=0#gid=0 (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Tomaštík, J.; Everett, T. Static Positioning under Tree Canopy Using Low-Cost GNSS Receivers and Adapted RTKLIB Software. Sensors 2023, 23, 3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GNSS, Interrupted: The Hidden Android Setting You Need to Know | by Sean Barbeau | Medium. Available online: https://barbeau.medium.com/gnss-interrupted-the-hidden-android-setting-you-need-to-know-d812d28a3821 (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Zhang, X.; Tao, X.; Zhu, F.; Shi, X.; Wang, F. Quality Assessment of GNSS Observations from an Android N Smartphone and Positioning Performance Analysis Using Time-Differenced Filtering Approach. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robustelli, U.; Baiocchi, V.; Pugliano, G. Assessment of Dual Frequency GNSS Observations from a Xiaomi Mi 8 Android Smartphone and Positioning Performance Analysis. Electronics 2019, 8, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darugna, F.; Wübbena, J.B.; Wübbena, G.; Schmitz, M.; Schön, S.; Warneke, A. Impact of Robot Antenna Calibration on Dual-Frequency Smartphone-Based High-Accuracy Positioning: A Case Study Using the Huawei Mate20X. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangenehnejad, F.; Gao, Y. GNSS Smartphones Positioning: Advances, Challenges, Opportunities, and Future Perspectives. Satell. Navig. 2021, 2, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomaštík, J.; Varga, M. Practical Applicability of Processing Static, Short-Observation-Time Raw GNSS Measurements Provided by a Smartphone under Vegetation Conditions. Measurement 2021, 178, 109397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruynix, C. ETRF/ITRF Coordinate Transformation Tool. Available online: https://www.epncb.oma.be/_productsservices/coord_trans/ (accessed on 14 February 2025).
- Tomaštík, J.; Olcina, J.H.; Saloň, Š.; Tunák, D. Pixel 5 and Pixel 9 Pro XL Raw GNSS Data, 5 Hours, 3 Conditions. Mendeley Data. 2025. Available online: https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/b6rnphwxnv/1 (accessed on 14 February 2025).
- Geo++ RINEX Logger—Aplikácie v Službe Google Play. Available online: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=de.geopp.rinexlogger (accessed on 17 January 2025).
- Gnsslogger—Aplikácie Pre Android v Službe Google Play. Available online: https://play.google.com/store/search?q=gnsslogger&c=apps (accessed on 17 January 2025).
- Vaclavovic, P.; Dousa, J. G-Nut/Anubis: Open-Source Tool for Multi-GNSS Data Monitoring with a Multipath Detection for New Signals, Frequencies and Constellations. Int. Assoc. Geod. Symp. 2016, 143, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douša, J.; Václavovic, P. G-Nut/Anubis User Manual; G-Nut Software s.r.o.: Senohraby, The Czech Republic, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Takasu, T. RTKLIB Ver. 2.4.2 Manual; Tokyo University of Marine Science and Technology: Tokyo, Japan, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Everett, T. RTKLIB Manual: Demo5 Version. Available online: https://rtkexplorer.com/pdfs/manual_demo5.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Karaim, M.; Karamat, T.B.; Noureldin, A.; El-Shafie, A. GPS Cycle Slip Detection and Correction at Measurement Level. Curr. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 4239–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramanto, B.; Gumilar, I.; Kuswanti, I.A.N. Assessment of GNSS Observations and Positioning Performance from Non-Flagship Android Smartphones. J. Appl. Geod. 2024, 18, 189–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Geng, J. Characteristics of Raw Multi-GNSS Measurement Error from Google Android Smart Devices. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, A.; Bastos, L.; Maia, D.; Gonçalves, J.A. Relative Positioning in Remote Areas Using a Gnss Dual Frequency Smartphone. Sensors 2021, 21, 8354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, N.; Jiang, J.; Wang, G. Evaluation of Positioning Accuracy of Smartphones under Different Canopy Openness. Forests 2022, 13, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Špánik, P.; Hefty, J. Multipath Detection with the Combination of SNR Measurements—Example from Urban Environment. Geod. Cartogr. 2018, 66, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brach, M.; Stereńczak, K.; Bolibok, L.; Kwaśny, Ł.; Krok, G.; Laszkowski, M. Impacts of Forest Spatial Structure on Variation of the Multipath Phenomenon of Navigation Satellite Signals. Folia For. Pol. 2019, 61, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massarweh, L.; Fortunato, M.; Gioia, C. Assessment of Real-Time Multipath Detection with Android Raw GNSS Measurements by Using a Xiaomi Mi 8 Smartphone. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Portland, OR, USA, 20–23 April 2020; pp. 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zocca, S.; Dabove, P.; Dovis, F. Comparison of GNSS Multipath/NLoS Characterization Between Geodetic Receivers and Smartphones Across GPS L1 C/A and L5 Signals. In Proceedings of the 37th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2024), Baltimore, MD, USA, 16–20 September 2024; pp. 1428–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daponte, P.; De Vito, L.; Picariello, F.; Riccio, M. State of the Art and Future Developments of Measurement Applications on Smartphones. Measurement 2013, 46, 3291–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, M.; Woodyer, T. Assessing Absolute and Relative Accuracy of Recreation-Grade and Mobile Phone GNSS Devices: A Method for Informing Device Choice. Area 2015, 47, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaštík, J.; Chudá, J.; Tunák, D.; Chudý, F.; Kardoš, M. Advances in Smartphone Positioning in Forests: Dual-Frequency Receivers and Raw GNSS Data. Forestry 2021, 94, 292–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merry, K.; Bettinger, P. Smartphone GPS Accuracy Study in an Urban Environment. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psychas, D.; Bruno, J.; Massarweh, L.; Darugna, F. Towards Sub-Meter Positioning Using Android Raw GNSS Measurements. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation, ION GNSS+ 2019, Miami, FL, USA, 16–20 September 2019; Institute of Navigation: Manassas, VA, USA, 2019; pp. 3917–3931. [Google Scholar]
- Banville, S.; Hassen, E.; Lamothe, P.; Farinaccio, J.; Donahue, B.; Mireault, Y.; Goudarzi, M.A.; Collins, P.; Ghoddousi-Fard, R.; Kamali, O. Enabling Ambiguity Resolution in CSRS-PPP. Navig. J. Inst. Navig. 2021, 68, 433–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, N.; Li, R.; Liu, A. Real-Time GNSS Precise Point Positioning with Smartphones for Vehicle Navigation. Satell. Navig. 2022, 3, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Huang, T.; Li, W.; Zhao, Q.; Jiang, K. Precise Point Positioning with Mixed Single- and Dual-Frequency GNSS Observations from Android Smartphones Considering Code-Carrier Inconsistency. Adv. Space Res. 2024, 74, 2664–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paziewski, J.; Fortunato, M.; Mazzoni, A.; Odolinski, R. An Analysis of Multi-GNSS Observations Tracked by Recent Android Smartphones and Smartphone-Only Relative Positioning Results. Measurement 2021, 175, 109162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandbergen, P.A.; Barbeau, S.J. Positional Accuracy of Assisted GPS Data from High-Sensitivity GPS-Enabled Mobile Phones. J. Navig. 2011, 64, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Han, J.H.; Kim, O.J.; Kim, J.; Kee, C. One-Way Deep Indoor Positioning System for Conventional GNSS Receiver Using Paired Transmitters. Navig. J. Inst. Navig. 2021, 68, 601–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Chen, W.; Xu, Y.; Ji, S.; Liu, J. Improved GNSS-Based Indoor Positioning Algorithm for Mobile Devices. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 1721–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, H.; Zhang, S.; Tang, K.; Li, N.; Huang, W.; Wang, Y. Robust Low-Latency Indoor Localization Using Bluetooth Low Energy. In Proceedings of the Institute of Navigation Pacific Positioning, Navigation and Timing Meeting, Pacific PNT 2019, Oahu, HI, USA, 15–18 April 2019; pp. 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Chu, X.; Lu, Z. Enhancing Indoor Positioning with GNSS-Aided In-Building Wireless Systems. Electronics 2025, 14, 2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabove, P.; Di Pietra, V. Towards High Accuracy GNSS Real-Time Positioning with Smartphones. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 63, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, M.; Ravanelli, M.; Mazzoni, A. Real-Time Geophysical Applications with Android GNSS Raw Measurements. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachapelle, G.; Gratton, P.; Horrelt, J.; Lemieux, E.; Broumandan, A. Evaluation of a Low Cost Hand Held Unit with GNSS Raw Data Capability and Comparison with an Android Smartphone. Sensors 2018, 18, 4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, J.; Li, G. On the Feasibility of Resolving Android GNSS Carrier-Phase Ambiguities. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 2621–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.; Geng, J.; Li, G.; Guo, J. Precise Point Positioning with Ambiguity Resolution Using an External Survey-Grade Antenna Enhanced Dual-Frequency Android GNSS Data. Measurement 2020, 157, 107634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stopar, B.; Sterle, O.; Pavlovčič-Prešeren, P.; Hamza, V. Observations and Positioning Quality of Low-Cost GNSS Receivers: A Review. GPS Solut. 2024, 28, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Device | Pixel 5 | Pixel 9 Pro XL |
|---|---|---|
| GNSS hardware name | redfin;MPSS.HI.2.0.c8-00264-SAIPAN_GEN_PACK-1.34428.9 (Qualcomm Snapdragon 765G) | S.LSI,K042,SPOTNAV_4.15.1_18_240628_R1_225564 (Samsung Exynos 5400) |
| Hardware year | 2018 | 2023 |
| Supported GNSS constellations and frequencies | GPS (L1, L5) GLONASS (L1) Galileo (E1, E5a) BeiDou (B1I) | GPS (L1, L5) GLONASS (L1) Galileo (E1, E5a) BeiDou (B1I, B1C, B2a) |
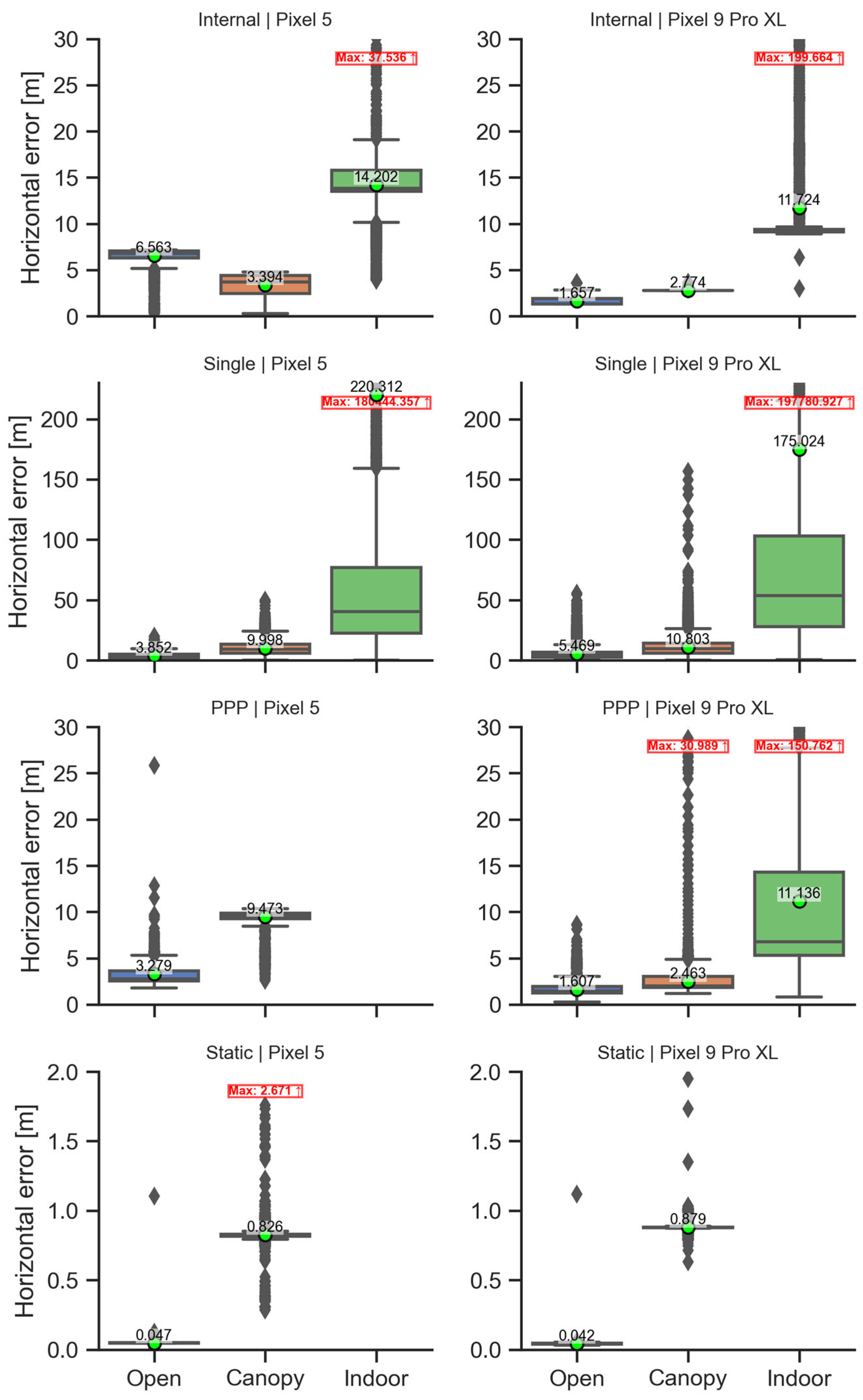
| Pixel 5 | Pixel 9 Pro XL | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Condition | HE (m) | AP (m) | VE (m) | HE (m) | AP (m) | VE (m) |
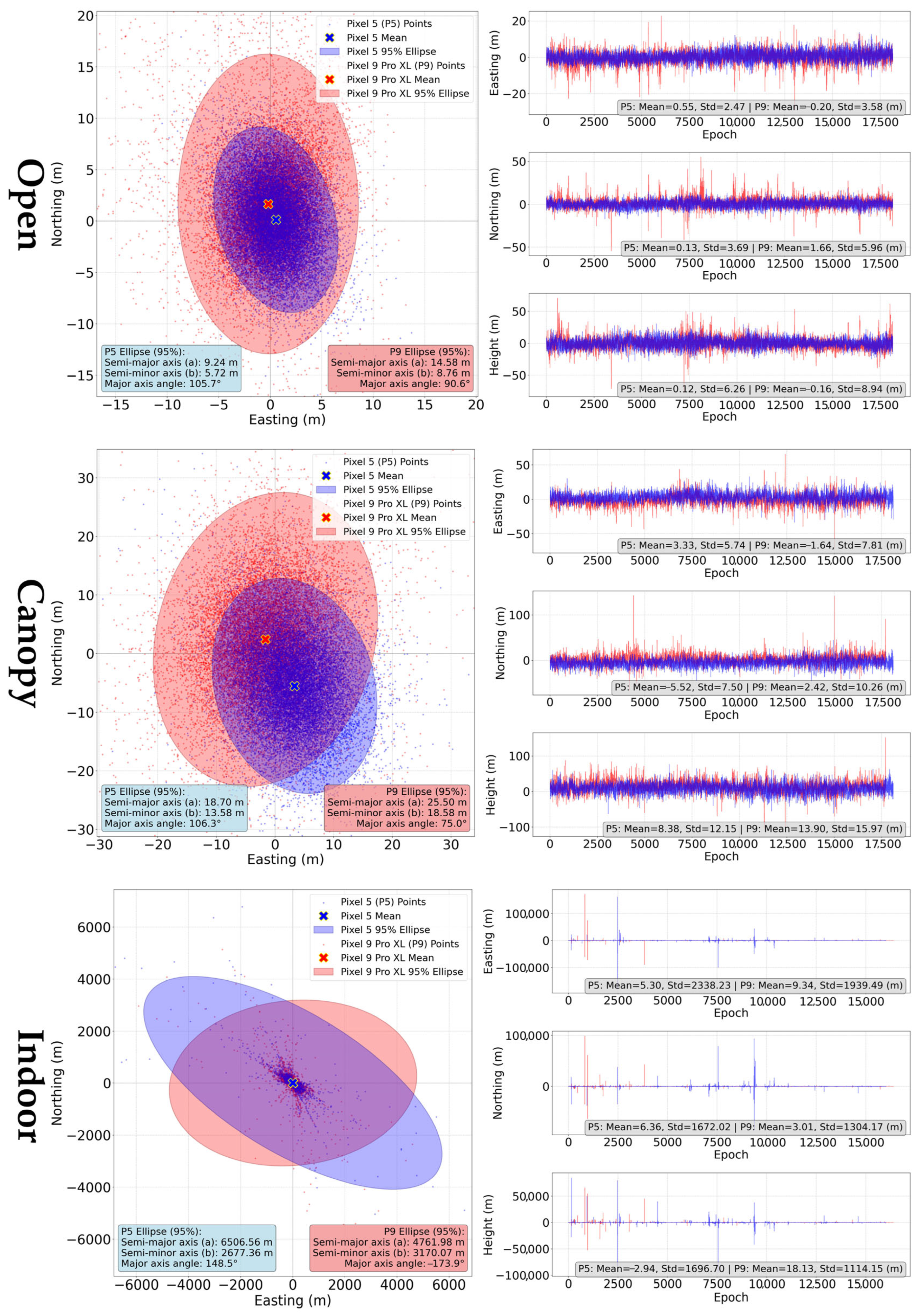
| Open | 6.56 | 6.54 | 6.38 | 1.66 | 1.64 | −0.88 |
| Canopy | 3.39 | 3.34 | 0.32 | 2.77 | 2.77 | 4.98 |
| Indoor | 14.20 | 14.15 | −11.46 | 11.69 | 9.81 | −12.14 |
| Pixel 5 | Pixel 9 Pro XL | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Condition | HE (m) | AP (m) | VE (m) | HE (m) | AP (m) | VE (m) |
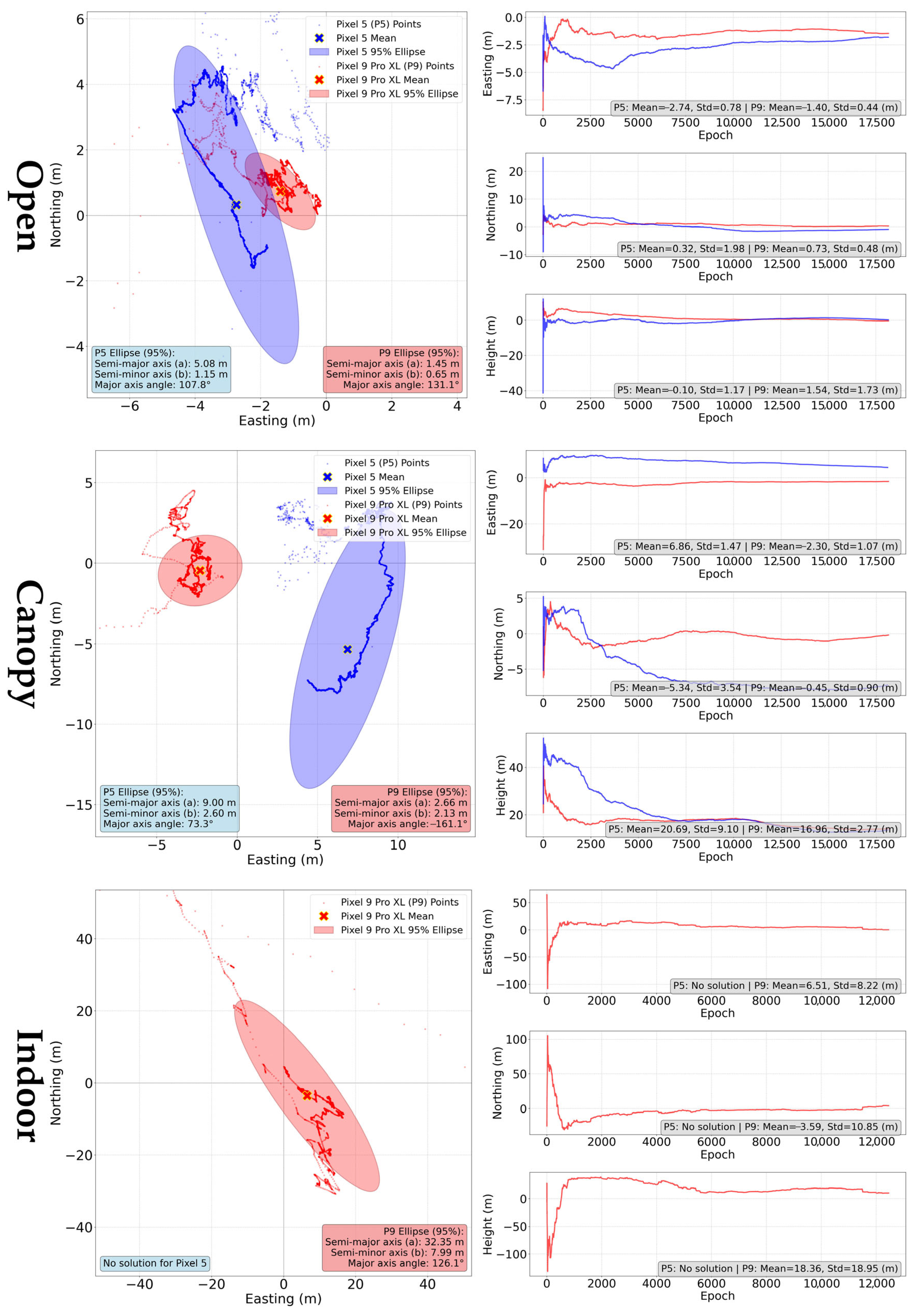
| Open | 3.85 | 0.56 | 0.12 | 5.47 | 1.68 | −0.17 |
| Canopy | 10.00 | 6.44 | 8.38 | 10.80 | 2.93 | 13.90 |
| Indoor | 220.31 | 8.28 | 6.44 | 175.02 | 9.81 | −2.94 |
| Pixel 5 | Pixel 9 Pro XL | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Condition | HE (m) | AP (m) | VE (m) | HE (m) | AP (m) | VE (m) |
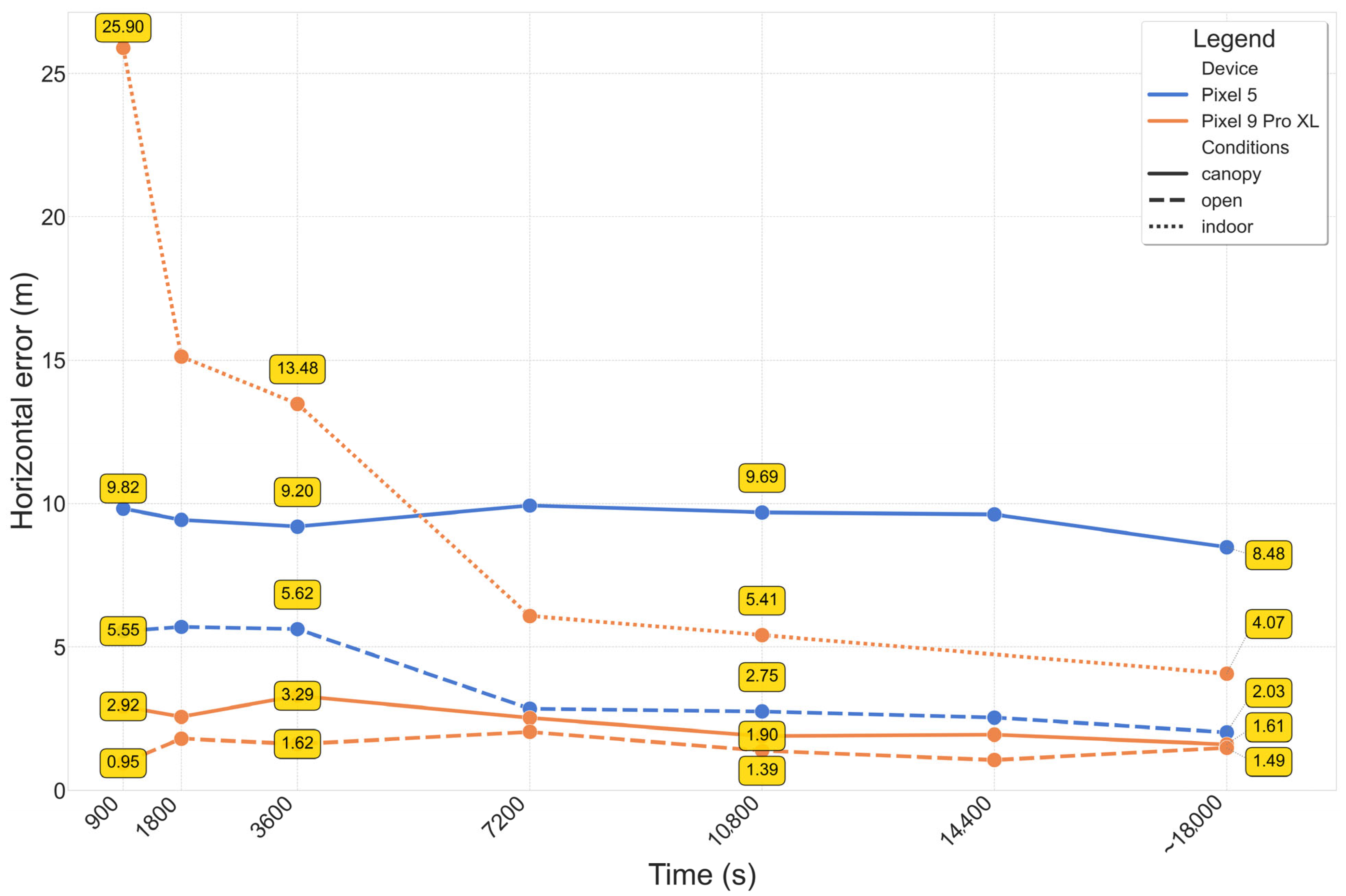
| Open | 3.28 | 2.76 | −0.10 | 1.61 | 1.58 | 1.55 |
| Canopy | 9.47 | 8.70 | 20.70 | 2.46 | 2.34 | 16.96 |
| Indoor | - | - | - | 11.14 | 7.44 | 18.36 |
| Device | HE (m) | AP (m) | VE (m) | Fix/Float Ratio (%) | Std (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
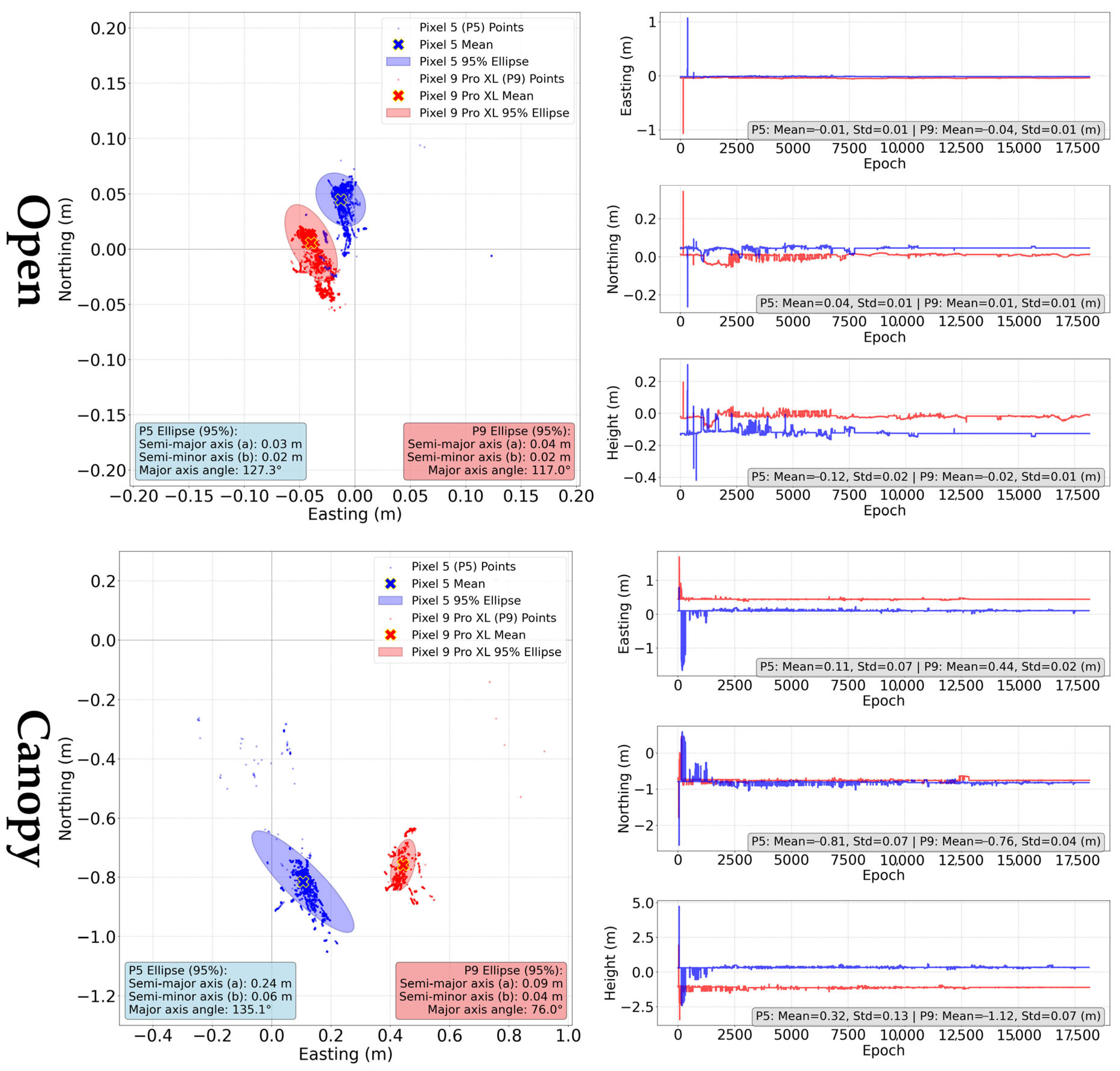
| Pixel 5 | 0.047 | 0.050 | −0.120 | 37.5/62.5 | 0.011 |
| Pixel 9 Pro XL | 0.042 | 0.050 | −0.019 | 82.1/17.9 | 0.009 |
| Device | HE (m) | AP (m) | VE (m) | Fix/Float/DGNSS Ratio (%) | Std (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pixel 5 | 0.826 | 0.820 | 0.323 | 24.8/71.5/3.7 | 0.054 |
| Pixel 9 Pro XL | 0.879 | 0.873 | −1.119 | 13.4/84.8/1.8 | 0.025 |
| df | sum_sq | mean_sq | F | PR(>F) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C(method) | 3.0 | 2.894590 × 108 | 9.648632 × 107 | 162.501442 | 2.855157 × 10−105 * |
| C(device) | 1.0 | 1.939542 × 106 | 1.939542 × 106 | 3.266561 | 7.070651 × 10−2 |
| C(conditions) | 2.0 | 3.671323 × 108 | 1.835661 × 108 | 309.160531 | 6.994686 × 10−135 * |
| C(method):C(device) | 3.0 | 6.761830 × 106 | 2.253943 × 106 | 3.796072 | 9.802334 × 10−3 * |
| C(method):C(conditions) | 6.0 | 4.398505 × 108 | 7.330842 × 107 | 123.465419 | 1.367281 × 10−156 * |
| C(device):C(conditions) | 2.0 | 5.706611 × 106 | 2.853305 × 106 | 4.805513 | 8.185011 × 10−3 * |
| C(method):C(device):C(conditions) | 6.0 | 6.609575 × 106 | 1.101596 × 106 | 1.855298 | 8.439085 × 10−2 |
| Residual | 371,938.0 | 2.208407 × 1011 | 5.937567 × 105 | NaN | NaN |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomaštík, J.; Hernández Olcina, J.; Saloň, Š.; Tunák, D. Pixel 5 Versus Pixel 9 Pro XL—Are Android Devices Evolving Towards Better GNSS Performance? Sensors 2025, 25, 4452. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144452
Tomaštík J, Hernández Olcina J, Saloň Š, Tunák D. Pixel 5 Versus Pixel 9 Pro XL—Are Android Devices Evolving Towards Better GNSS Performance? Sensors. 2025; 25(14):4452. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144452
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomaštík, Julián, Jorge Hernández Olcina, Šimon Saloň, and Daniel Tunák. 2025. "Pixel 5 Versus Pixel 9 Pro XL—Are Android Devices Evolving Towards Better GNSS Performance?" Sensors 25, no. 14: 4452. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144452
APA StyleTomaštík, J., Hernández Olcina, J., Saloň, Š., & Tunák, D. (2025). Pixel 5 Versus Pixel 9 Pro XL—Are Android Devices Evolving Towards Better GNSS Performance? Sensors, 25(14), 4452. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144452







