Plantar Pressure Distribution in Charcot–Marie–Tooth Disease: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Study Selection and Data Extraction
- -
- Participants: number of patients and demographic characteristics (age and CMT subtype);
- -
- Intervention: measurement method (baropodometry, in-shoe sensors) and devices used;
- -
- Comparisons: comparison of the plantar pressure main findings between healthy controls and unaffected feet, idiopathic cavus vs. neurogenic foot, pre- and post-operative period;
- -
- Outcomes: plantar pressure parameters.
2.4. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Risk of Bias
3.2. Population
3.3. Plantar Pressure Systems and Outcomes
- -
- Peak pressure (PP) is the maximum pressure recorded under a defined plantar region during the stance phase, typically expressed in kilopascals (kPa). PP reflects the highest localized load experienced by the foot [34].
- -
- Pressure–time integral (PTI) is the area under the pressure–time curve for a given region, combining the magnitude and duration of loading (units kPa·s). PTI provides a cumulative measure of tissue stress throughout stance and may be more sensitive to overall load exposure than PP alone [35].
- -
- Center-of-pressure (CoP) trajectory is the path traced by the centroid of the resultant ground reaction force vector across the plantar surface during stance. CoP trajectory characterizes dynamic balance control and gait progression, with deviations indicating altered foot function or stability [36].
- -
- Contact time (CT) is the total duration for which the foot remains in contact with the support surface during a single gait cycle stance phase, usually measured in seconds. CT reflects temporal aspects of gait and is prolonged in conditions with muscle weakness or neuromuscular impairment [37].
- -
- Contact area (CA) is the surface area of the plantar foot in contact with the sensor or platform at any instant, reported in square centimeters (cm2). CA indicates the extent of load distribution under the foot and is altered in deformities that restrict or expand regional contact [38].
- -
- Peak force is the highest resultant force applied to a plantar region during stance, often normalized to body weight (N·%BW). Peak force quantifies the maximum load transmitted through the foot and, together with CA, underpins the calculation of PP [33].
- -
- Root mean square deviation (RMSD) is a statistical measure of the average deviation of an individual’s plantar pressure map from a normative reference pattern. RMSD captures global abnormalities in pressure distribution and is elevated in neuropathic or structural foot disorders [33].
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CMT | Charcot–Marie–Tooth |
| NOS | Newcastle–Ottawa Scale |
| HMSN | Hereditary Motor Sensory Neuropathies |
| PP | Peak Pressure |
| PTI | Pressure–time integral |
| CoP | Center-of-pressure |
| CA | Contact area |
| CT | Contact time |
| RMSD | Root mean square deviation |
References
- Faldini, C.; Traina, F.; Nanni, M.; Mazzotti, A.; Calamelli, C.; Fabbri, D.; Pungetti, C.; Giannini, S. Surgical Treatment of Cavus Foot in Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease: A Review of Twenty-Four Cases: AAOS Exhibit Selection. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2015, 97, e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Li, Y.; Dai, S.; Chu, M.; Sun, L.; Liu, L.; Zhou, J.-C. A Meta-Analysis on the Prevalence of Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease and Related Inherited Peripheral Neuropathies. J. Neurol. 2023, 270, 2468–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.H.; Choi, B.-O. Clinical and Genetic Aspects of Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Subtypes. Precis. Future Med. 2019, 3, 43–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, Y.; Takashima, H. Clinical Genetics of Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease. J. Hum. Genet. 2023, 68, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, A.; Yuan, J.-H.; Hashiguchi, A.; Ando, M.; Higuchi, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Okamoto, Y.; Nakagawa, M.; Takashima, H. Genetic Profile and Onset Features of 1005 Patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease in Japan. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemann, A.; Berger, P.; Suter, U. Pathomechanisms of Mutant Proteins in Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease. Neuromol. Med. 2006, 8, 217–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cardoso, J.; Rogean de Jesus Alves de Baptista, C.; Buzzetti, B.P.; Sartor, C.D.; Júnior, W.M.; de Sacco, I.C.N.; Mattiello-Sverzut, A.C. Vibration Perception among Children and Adolescents with Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease and Implications for Foot Posture. Clin. Biomech. 2023, 110, 106114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinci, P.; Perelli, S.L. Footdrop, Foot Rotation, and Plantarflexor Failure in Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2002, 83, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Joo, S.Y.; Choi, B.-O.; Kim, D.-H.; Park, J.B.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, D.Y. Gait Pattern in Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Type 1A According to Disease Severity. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, D.; Becker, H.-P. Plantar Pressure Distribution Measurements. Technical Background and Clinical Applications. Foot Ankle Surg. 1997, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brognara, L.; Mazzotti, A.; Zielli, S.O.; Arceri, A.; Artioli, E.; Traina, F.; Faldini, C. Wearable Technology Applications and Methods to Assess Clinical Outcomes in Foot and Ankle Disorders: Achievements and Perspectives. Sensors 2024, 24, 7059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzehgar, A.; Nia, R.G.N.N.; Hoseinkhani, M.; Masoumi, F.; Sayyed-Hosseinian, S.-H.; Eslami, S. An Overview of Plantar Pressure Distribution Measurements and Its Applications in Health and Medicine. Gait Posture 2025, 117, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzotti, A.; Arceri, A.; Artioli, E.; Langone, L.; Zielli, S.O.; Martini, B.; Traina, F.; Faldini, C.; Brognara, L. Hallux Valgus Plantar Pressure Distribution before and after a Distal Metatarsal Osteotomy. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzotti, A.; Arceri, A.; Martini, B.; Bonelli, S.; Zielli, S.; Artioli, E.; Brognara, L.; Faldini, C. Hallux Valgus Plantar Pressure Distribution Before and After Surgery. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2023, 113, 22–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.W.C.; Cheung, J.C.W.; Zhao, J.G.; Ni, M.; Yang, Z.Y. Forefoot Function After Hallux Valgus Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on Plantar Load Measurement. PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36835920/ (accessed on 5 June 2025).
- Zhai, J.N.; Wang, J.; Qiu, Y.S. Plantar Pressure Differences among Adults with Mild Flexible Flatfoot, Severe Flexible Flatfoot and Normal Foot When Walking on Level Surface, Walking Upstairs and Downstairs. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2017, 29, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Chevidikunnan, M.F.; BinMulayh, E.A.; Al-Lehidan, N.S. Plantar Pressure Distribution in the Evaluation and Differentiation of Flatfeet. Gait Posture 2023, 101, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veves, A.; Murray, H.J.; Young, M.J.; Boulton, A.J. The Risk of Foot Ulceration in Diabetic Patients with High Foot Pressure: A Prospective Study. Diabetologia 1992, 35, 660–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Torres, F.; Infanzón-Talango, H.; García-Ulloa, A.C.; Hernández-Jiménez, S.; Rodríguez-Reyes, G. Exploring Plantar Pressure Distribution in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Diabetes: Implications for Foot Ulcer Prevention in an Overweight Mexican Population. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. 2024, 71, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockhart, M.; Dinneen, S.F.; O’Keeffe, D.T. Plantar Pressure Measurement in Diabetic Foot Disease: A Scoping Review. J. Diabetes Investig. 2024, 15, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeheyawi, R.N.; Bricca, A.; Riskowski, J.L.; Barn, R.; Steultjens, M. Foot Characteristics and Mechanics in Individuals with Knee Osteoarthritis: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2021, 14, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigercioglu, N.B.; Bazancir-Apaydin, Z.; Apaydin, H.; Baltaci, G.; Guney-Deniz, H. Differences in Ankle and Knee Muscle Architecture and Plantar Pressure Distribution among Women with Knee Osteoarthritis. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2024, 17, e12028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panyarachun, P.; Angthong, C.; Jindasakchai, P.; Rajbhandari, P.; Rungrattanawilai, N. Abnormal Foot Pressure in Older Adults with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review. PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36111924/ (accessed on 5 June 2025).
- Lencioni, T.; Piscosquito, G.; Rabuffetti, M.; Sipio, E.D.; Diverio, M.; Moroni, I.; Padua, L.; Pagliano, E.; Schenone, A.; Pareyson, D.; et al. Electromyographic and Biomechanical Analysis of Step Negotiation in Charcot Marie Tooth Subjects Whose Level Walk Is Not Impaired. Gait Posture 2018, 62, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, G.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Peterson, je; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Non-Randomized Studies in Meta-Analysis. 2000. Available online: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 5 June 2025).
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosbie, J.; Burns, J.; Ouvrier, R.A. Pressure Characteristics in Painful Pes Cavus Feet Resulting from Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease. Gait Posture 2008, 28, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.; Crosbie, J.; Hunt, A.; Ouvrier, R. The Effect of Pes Cavus on Foot Pain and Plantar Pressure. Clin. Biomech. 2005, 20, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, J.; de Baptista, C.R.J.A.; Sartor, C.D.; Nascimento Elias, A.H.; Júnior, W.M.; Martinez, E.Z.; Sacco, I.C.N.; Mattiello-Sverzut, A.C. Dynamic Plantar Pressure Patterns in Children and Adolescents with Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease. Gait Posture 2021, 86, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, G.; Sampath, J.; Miller, F.; Riddle, E.C.; Nagai, M.K.; Kumar, S.J. The Role of the Dynamic Pedobarograph in Assessing Treatment of Cavovarus Feet in Children with Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2007, 27, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, S.; Hosseinzadeh, P.; Iwinski, H.J.; Muchow, R.C.; Talwalkar, V.R.; Walker, J.L.; Milbrandt, T.A. Dynamic Pedobarography and Radiographic Evaluation of Surgically Treated Cavovarus Foot Deformity in Children with Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B 2015, 24, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloks, B.E.; Wilders, L.M.; Louwerens, J.W.K.; Geurts, A.C.; Nonnekes, J.; Keijsers, N.L.W. Quantitative Assessment of Plantar Pressure Patterns in Relation to Foot Deformities in People with Hereditary Motor and Sensory Neuropathies. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2023, 20, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melai, T.; IJzerman, T.H.; Schaper, N.C.; de Lange, T.L.H.; Willems, P.J.B.; Meijer, K.; Lieverse, A.G.; Savelberg, H.H.C.M. Calculation of Plantar Pressure Time Integral, an Alternative Approach. Gait Posture 2011, 34, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bus, S.A.; Waaijman, R. The Value of Reporting Pressure-Time Integral Data in Addition to Peak Pressure Data in Studies on the Diabetic Foot: A Systematic Review. Clin. Biomech. 2013, 28, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugade, V.; Kaufman, K. Center of Pressure Trajectory during Gait: A Comparison of Four Foot Positions. Gait Posture 2014, 40, 252–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusu, L.; Paun, E.; Marin, M.I.; Hemanth, J.; Rusu, M.R.; Calina, M.L.; Bacanoiu, M.V.; Danoiu, M.; Danciulescu, D. Plantar Pressure and Contact Area Measurement of Foot Abnormalities in Stroke Rehabilitation. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlin, M.N.; McPoil, T.G. Plantar Pressure Assessment. Phys. Ther. 2000, 80, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miniou, P.; Fontes, M. Therapeutic Development in Charcot Marie Tooth Type 1 Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambelli, C.; Mazzoli, D.; Galletti, M.; Basini, G.; Zerbinati, P.; Prati, P.; Mascioli, F.; Masiero, S.; Merlo, A. Foot Assessment Clinical Scales in Charcot-Marie-Tooth Patients: A Scoping Review. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 914340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCray, B.A.; Fridman, V. Clinical Outcome Assessments and Biomarkers in Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease. Neurology 2024, 103, e210120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassam, B.A. Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Variants-Classification, Clinical, and Genetic Features and Rational Diagnostic Evaluation. J. Clin. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2014, 15, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braathen, G.J. Genetic Epidemiology of Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease. Acta Neurol. Scand. Suppl. 2012, 126, iv-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abati, E.; Rizzuti, M.; Anastasia, A.; Comi, G.P.; Corti, S.; Rizzo, F. Charcot-Marie-Tooth Type 2A in Vivo Models: Current Updates. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e18293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagappa, M.; Sharma, S.; Taly, A.B. Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Pareyson, D.; Marchesi, C. Diagnosis, Natural History, and Management of Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 654–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zulkifli, S.S.; Loh, W.P. A State-of-the-Art Review of Foot Pressure. Foot Ankle Surg. 2020, 26, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, S.; Majumder, S.; Faisal, A.I.; Deen, M.J. Insole-Based Systems for Health Monitoring: Current Solutions and Research Challenges. PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35062398/ (accessed on 5 June 2025).
- Zhang, Z.; Dai, Y.; Xu, Z.; Grimaldi, N.; Wang, J.; Zhao, M.; Pang, R.; Sun, Y.; Gao, S.; Boyi, H. Insole Systems for Disease Diagnosis and Rehabilitation: A Review. Biosensors 2023, 13, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klöpfer-Krämer, I.; Brand, A.; Wackerle, H.; Müßig, J.; Kröger, I.; Augat, P. Gait Analysis—Available Platforms for Outcome Assessment. Injury 2020, 51, S90–S96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Razak, A.H.; Zayegh, A.; Begg, R.K.; Wahab, Y. Foot Plantar Pressure Measurement System: A Review. Sensors 2012, 12, 9884–9912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, R.A.; Missirian, J. Pathophysiology of Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1988, 234, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metaxiotis, D.; Accles, W.; Pappas, A.; Doederlein, L. Dynamic Pedobarography (DPB) in Operative Management of Cavovarus Foot Deformity. Foot Ankle Int. 2000, 21, 935–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, M.R.; Ricardo, D.; Teles, J.; Veloso, A.P.; João, F. Gait Analysis in Children with Cerebral Palsy: Are Plantar Pressure Insoles a Reliable Tool? Sensors 2022, 22, 5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basini, G.; Rambelli, C.; Galletti, M.; Zerbinati, P.; Prati, P.; Mascioli, F.; Masiero, S.; Mazzoli, D.; Merlo, A. Short-Term Effects of Foot Surgery on Walking-Related Pain, Function, and Satisfaction in Patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease: A Prospective Cohort Study. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1304258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, F.; Calafiore, D.; Curci, C.; Fortunato, F.; Carantini, I.; Genovese, F.; Lucchini, G.; Merlo, A.; Ammendolia, A.; de Sire, A. Effects of Intensive Rehabilitation on Functioning in Patients with Mild and Moderate Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease: A Real-Practice Retrospective Study. Neurol. Sci. 2024, 45, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, B.; Barnica, E.; Wrobel, J.S.; Burns, J. Dynamic Plantar Loading Index: Understanding the Benefit of Custom Foot Orthoses for Painful Pes Cavus. J. Biomech. 2012, 45, 1705–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.-K.; Cha, E.-J.; Kim, K.-A.; Won, Y.; Kim, J.-J. Effects of Custom-Made Insoles on Idiopathic Pes Cavus Foot during Walking. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 2015, 26, S705–S715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arceri, A.; Mazzotti, A.; Liosi, S.G.; Zielli, S.O.; Artioli, E.; Langone, L.; Traina, F.; Brognara, L.; Faldini, C. Safety Footwear Impact on Workers’ Gait and Foot Problems: A Comparative Study. Clin. Pract. 2024, 14, 1496–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caravaggi, P.; Rogati, G.; Zamagni, L.; Boriani, L.; Arceri, A.; Ortolani, M.; Lullini, G.; Berti, L.; Leardini, A. Functional Evaluation of a Novel Fibreglass-Reinforced Polyamide Custom Dynamic AFO for Foot Drop Patients: A Pilot Study. Gait Posture 2024, 109, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Ramos, M.; Orejana-García, Á.M.; García-Oreja, S.; del Mar Calvo-Wright, M.; Lázaro-Martínez, J.L.; Molines-Barroso, R.J. Effectiveness of Bespoke or Customised Orthotic Treatment in Plantar Pressure Reduction of the Central Metatarsals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39399760/ (accessed on 5 June 2025).
- Buldt, A.K.; Allan, J.J.; Landorf, K.B.; Menz, H.B. The Relationship between Foot Posture and Plantar Pressure during Walking in Adults: A Systematic Review. Gait Posture 2018, 62, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauk, J.; Daunoraviciene, K.; Ihnatouski, M.; Griskevicius, J.; Raso, J.V. Analysis of the Plantar Pressure Distribution in Children with Foot Deformities. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2010, 12, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Seguín, L.M.; Diaz Mancha, J.A.; Sánchez Rodríguez, R.; Escamilla Martínez, E.; Gómez Martín, B.; Ramos Ortega, J. Comparison of Plantar Pressures and Contact Area between Normal and Cavus Foot. Gait Posture 2014, 39, 789–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurá, M.; Barnett, J.; Benfield, J.; Ramdharry, G.M.; Welck, M.J. Foot Surgery for Adults with Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease. Pract. Neurol. 2024, 24, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.M.; Balaganapathy, M. Normative Values of Static-Dynamic Plantar Pressure and Its Cutoff Values. Indian J. Med. Spec. 2024, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
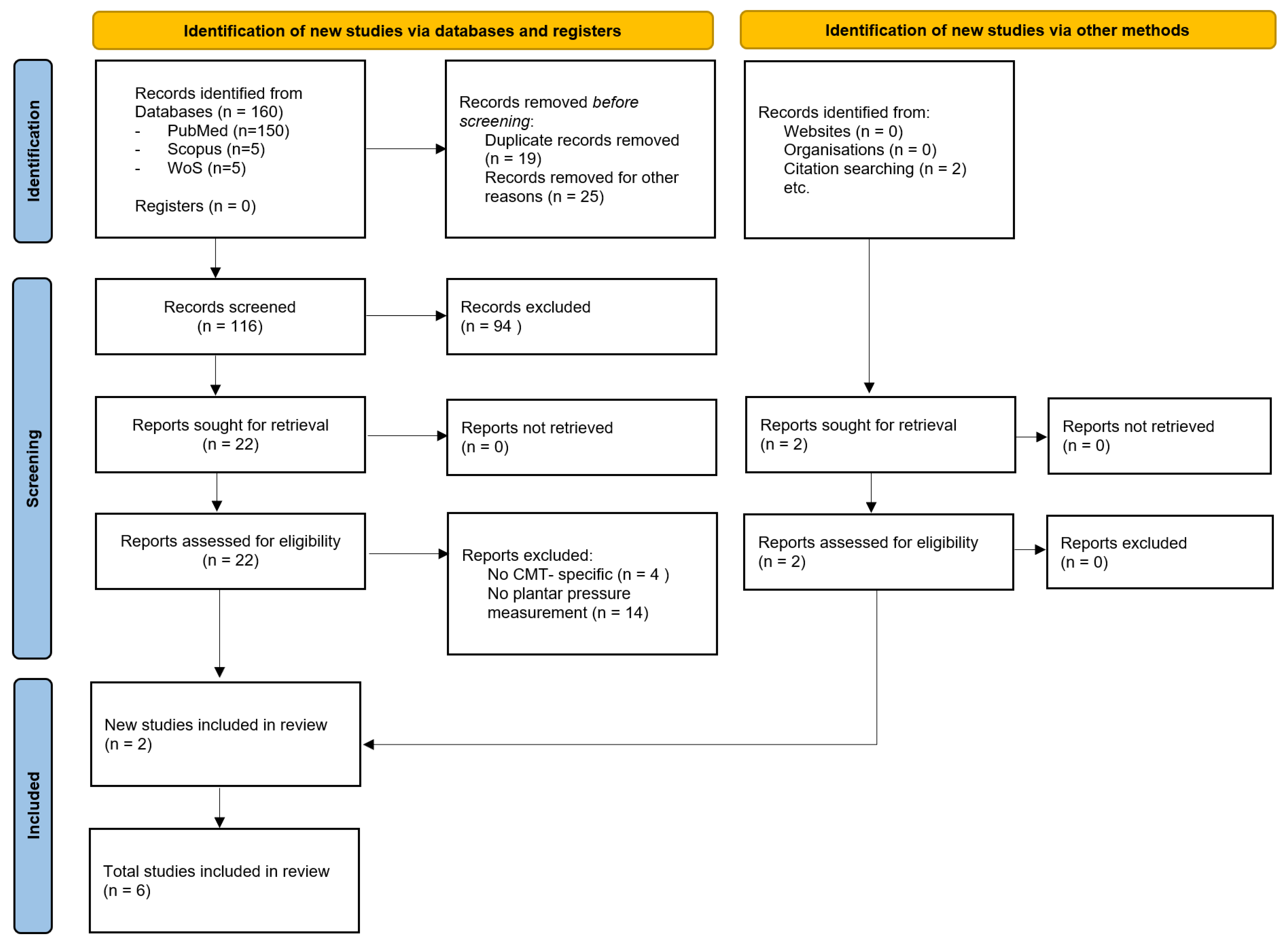
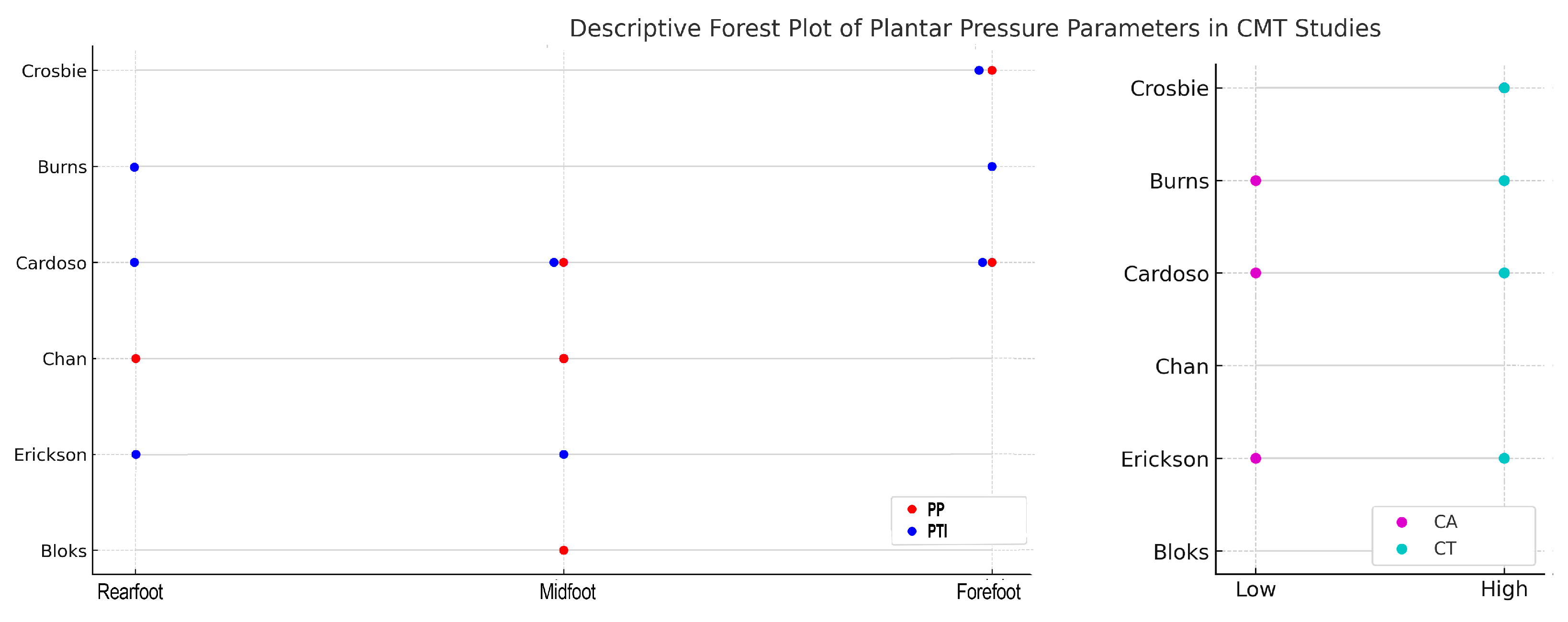
| Study (Year) | Study Design | Sample Size (Mean Age) | CMT Subtype | Method (Device) | Measured Parameters | Main Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crosbie et al. (2008) [28] | Cross-sectional | 16 (51.7 ± 16.2 y) | CMT1 (9), unknown (4), CMT2 (2), CMT X (1) | In-shoe sensors (Novel Pedar) | PP, PTI, CT | ↑ PP and PTI forefoot, prolonged CT |
| Burns et al. (2005) [29] | Cross-sectional (idiopathic cavus vs. neurogenic foot vs. controls) | 10 CMT | Mixed | Dynamic baropodometry (EMED platform) | PP, PTI, CA, CT | ↑ PTI rearfoot and forefoot; ↓ CA; prolonged CT |
| Cardoso et al. (2021) [30] | Cross-sectional (children vs. adolescent vs. controls) | 40 (12.7 ± 0.6 y) | CMT1A (22), CMT2A (6), CMTX (1), unknown (11) | In-shoe sensors (Pedar-X) | PP, PTI, CA, CT | Children: ↓ CA, ↑ CT, ↑ PP medial forefoot and midfoot, ↑ PTI rearfoot, lateral midfoot and medial forefoot; Adolescents: ↓ CA, ↑ CT, no difference PP and PTI |
| Chan et al. (2007) [31] | Prospective interventional | 9 (13.3 ± 2.5) | Unspecified CMT | Dynamic pedobarograph (Tekscan High-Resolution Pressure Assessment System) | Segmental pressure–time profiles pre/post-surgery | Pre-op: ↑ lateral midfoot and rearfoot; ↓ medial midfoot and forefoot Post-op: ↓ lateral midfoot and medial midfoot, ↑ rearfoot |
| Erickson et al. (2015) [32] | Prospective interventional | 19 (11 ± 2 y) | CMT1A | Dynamic pedobarograph (EMED platform) | PP, PTI, peak force, CA, CT | Pre-op: ↑ PTI and CT lateral midfoot and rearfoot; ↓ CA and PP medial midfoot Post-op: ↓ peak force, ↑ CA |
| Bloks et al. (2023) [33] | Case–control | 52 (42.7 ± 17.1 y) | CMT1 (41), CMT2 (9), unknown (2) | Dynamic baropodometry (Footscan pressure plate) | RMSD, PP ratios, CoP trajectories | ↑ RMSD, ↑ CoP lateral deviation; ↑ PP ratios lateral midfoot |
| Study (Year) | Representativeness | Control Selection | Case Definition | No Outcome at Start | Comparability | Assessment Outcome | Follow-Up Long Enough | Outcome Adequacy | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crosbie et al. (2008) [28] | ★ | ★ | ★ | ★ | ★ | ★ | — | ★ | 7 ★ |
| Burns et al. (2005) [29] | ★ | ★ | ★ | ★ | ★ | ★ | — | ★ | 7 ★ |
| Cardoso et al. (2021) [30] | ★ | ★ | ★ | ★ | ★ | ★ | — | ★ | 7 ★ |
| Chan et al. (2007) [31] | ★ | — | ★ | ★ | ★★ | ★ | — | ★ | 7 ★ |
| Erickson et al. (2015) [32] | ★ | — | ★ | ★ | ★★ | ★ | — | ★ | 7 ★ |
| Bloks et al. (2023) [33] | ★ | ★ | ★ | ★ | ★ | ★ | — | ★ | 7 ★ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arceri, A.; Mazzotti, A.; Sgubbi, F.; Zielli, S.O.; Langone, L.; Di Paola, G.; Brognara, L.; Faldini, C. Plantar Pressure Distribution in Charcot–Marie–Tooth Disease: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2025, 25, 4312. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144312
Arceri A, Mazzotti A, Sgubbi F, Zielli SO, Langone L, Di Paola G, Brognara L, Faldini C. Plantar Pressure Distribution in Charcot–Marie–Tooth Disease: A Systematic Review. Sensors. 2025; 25(14):4312. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144312
Chicago/Turabian StyleArceri, Alberto, Antonio Mazzotti, Federico Sgubbi, Simone Ottavio Zielli, Laura Langone, GianMarco Di Paola, Lorenzo Brognara, and Cesare Faldini. 2025. "Plantar Pressure Distribution in Charcot–Marie–Tooth Disease: A Systematic Review" Sensors 25, no. 14: 4312. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144312
APA StyleArceri, A., Mazzotti, A., Sgubbi, F., Zielli, S. O., Langone, L., Di Paola, G., Brognara, L., & Faldini, C. (2025). Plantar Pressure Distribution in Charcot–Marie–Tooth Disease: A Systematic Review. Sensors, 25(14), 4312. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144312









