How Beyond-5G and 6G Makes IIoT and the Smart Grid Green—A Survey
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We provide a comprehensive review of the role of beyond-5G (B5G) and 6G wireless communication technologies in supporting sustainable Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and smart grid infrastructures.
- We identify and classify the main challenges in achieving energy efficiency, real-time responsiveness, and interoperability in smart energy systems powered by next-generation mobile networks.
- We examine major technological enablers for green IoT, including low-power wide-area networks (LPWAN), wake-up radios, energy harvesting methods, and edge computing architectures.
- We analyze energy-aware optimization strategies in 5G/6G networks and data centers, with a focus on AI-driven orchestration and resource management.
- We map critical smart grid applications to their communication requirements and discuss how emerging wireless capabilities—such as ultra-reliable low-latency communication and massive device connectivity—enable these use cases.
- We highlight existing research gaps, particularly in the areas of cross-layer energy optimization, empirical validation, and the integration of secure communication with energy efficiency.
- We propose future research directions to address the lack of unified standards and the need for interoperable, scalable, and testbed-validated communication platforms for sustainable cyber-physical infrastructures.
2. Green IoT in 5G and 6G Networks
2.1. LPWAN: Enabler for Ultra-Low-Energy 5G
2.2. Wake-Up Radio: Rethinking Sleep Cycles
2.3. Energy Harvesting
2.4. Device-to-Device Communication
2.5. MU-MIMO: Massive Antenna Arrays
2.6. Mobile Edge Computing
2.7. Further Support for Green IoT in 6G
2.8. Lessons Learned
3. Green Core and Telco Cloud
3.1. Making the Server’s Hardware Components Use Less Electricity
3.2. Making Data-Center Cooling More Power Efficient
3.3. Integrating Green Energy Sources into the Power Network of the Data Center
- Adding non-electric cooling [87]
- Pre-cooling [88]
- Usage of high-capacity batteries [89]
- Thermal storage to increase the capability to consume energy from renewable sources [87]
- Making better and fairer bargaining algorithms to further increase renewable sources [90]
- Making use of geo-distributed Data Centers to load-balance to those DCNs that have renewable energy at their disposal at a given moment [91]
- Usage of solar-power plant architecture that works well with DCNs [92]
3.4. Optimizing the Virtual-Hardware Resource Allocation
3.5. Optimization Beyond the Core Network
3.6. A Summary on Minimizing Power Consumption in 5G
3.7. Towards 6G
3.8. Challenges and Limitations of Green Technologies in 5G and Beyond Networks
3.9. Lessons Learned
4. Green Data Collection for the Smart Grid
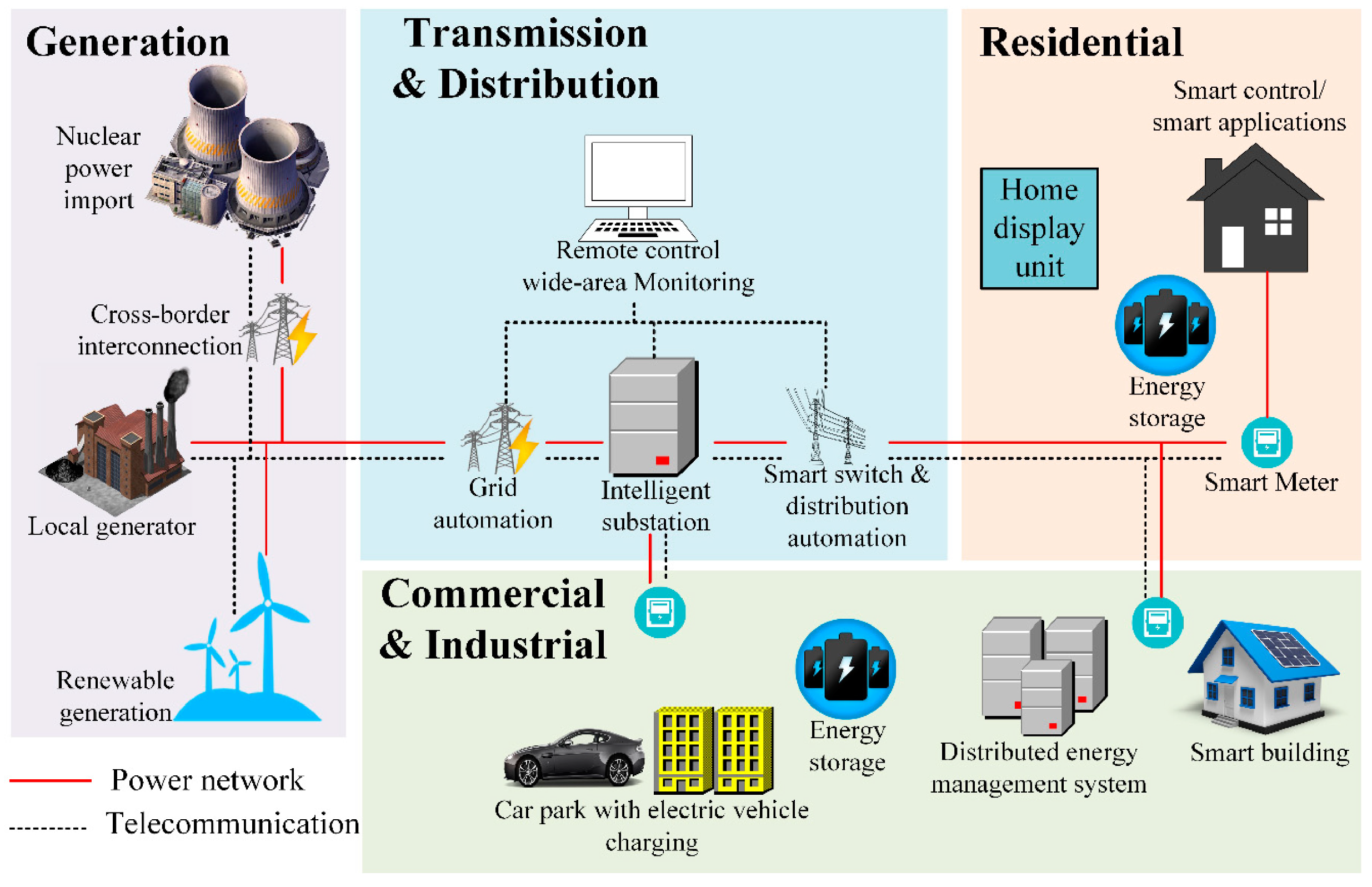
4.1. The Concept of the Smart Grid
- integration of renewable energy sources, resulting in bidirectional energy flows;
- a high level of observability, enabled by applying large numbers of sensors and processing large volumes of data with high data rates;
- a high level of controllability by deploying actuators and power flow control devices;
- a shift from centralized to decentralized and distributed intelligence in distribution system automation;
- the increased engagement of customers to interact in the production–consumption balancing process, which includes demand-side management programs, direct load/generation/storage control by system operators, or price signal-driven manual or automated actions.
4.2. Smart Grid Data Flows
4.2.1. Low-Voltage Distribution System Data Acquisition
4.2.2. Intelligent Distributed Feeder Automation
4.2.3. Millisecond-Level Precise Load Control
4.2.4. Distributed Generation
4.3. Data Communication Infrastructure in Smart Grid
- HANHAN facilitates two-way communications to provide demand response in the smart grid. It transmits energy data from home appliances such as charging stations, light dimmers, and water heater control to a smart meter as a gateway to the next network. This network is commonly deployed within a house or an office and utilizes a relatively lower data rate (100 kbps) than the other two, with up to 15 s latency [159,160]. Broadband internet connection is commonly used while its bandwidth resource is shared with the house occupants through a wired or wireless modem. Either way, it can also use power line communication (PLC), ZigBee, Bluetooth, or other narrowband technologies. Another importance of HAN is that it can also be used for home automation, such as heat scheduling and smart switching of either lighting, garage door, etc., so that it leads to efficient home energy management.
- NANNAN, which is located between HANs and WAN, is the main bridge between smart meter infrastructure devices and utility operators. It transfers data bi-directionally either from HAN to data concentrators in WAN, or vise-versa. A NAN is operated within dense residential areas spanning several kilometers, and accumulatively requires a data rate transmission up to 1 Gbps, as it ultimately carries thousands of HANs’ data traffic. Multiple technologies can be used to construct this network.Broadband PLC is commonly used, as it offers reasonably cheap installation. However, due to flexibility and other limitations mentioned previously, it is quite often extended or replaced by wireless technologies. Various wireless-based technologies operating on a license-free spectrum like LoRa are used in some cases. However, in most other cases, cellular networks such as a Universal Mobile Telecommunication System (UMTS) or Long-Term Evolution (LTE) are used due to the reliability and higher data rate requirement, although 802.15.4-based wireless technology such as ZigBee is sometimes used as well [161,162].
- WANWhile HANs and NAN cover smaller areas, WAN covers the whole interconnection among main power generations, power transmissions and distributions, operators and controls, and local data concentrators. It delivers real-time data for M2M control and measurements and integrates several NANs. Moreover, the communication of all smart grid components, including the operator control center, main and renewable energy generation, transmission, and distribution, are finally interconnected based on WAN. Therefore, WAN has a very high transmission data rate of up to a few Gbps [143,163].
4.4. Lessons Learned
- Sub-millisecond CommunicationAll CSG papers reviewed in this section indicate that, for the most part, the Smart Grid requires millisecond-level communication technology due to the time-critical controls, especially within substat xsion automation systems.
- Millimeter-Wave BandDiscussions on 5GISG in any technical development are dominated by the concerns of using mmWave to achieve 5G goals (ultra-low latency, more reliability, massive network capacity, increased availability, and a more uniform user experience with more users). Both 5G and 6G use mmWave frequencies that utilize sub-GHz and sub-THz bands. This spectrum will continue to be explored, as these bands offer far higher data rates with ultra-low latency than 4G, which is currently widespread. Semiconductor and antenna designs are the hot topics in this area.
- Energy Efficiency and ReliabilityIn SG itself, the most fundamental need of a smart grid, which is still under consideration even with the latest advancements, is the reliability and efficiency of energy generation, transmission, and distribution integrated via the electric power grid.
- Big Data AnalyticsLast but not least is BDSG. As the smart grid produces large volumes of data from IoT devices like smart meters and other sensor networks, it results in big data. Sensors installed in different areas of the smart grid, such as substations and consumer devices, rapidly produce petabytes of data, and it is humanly impossible to analyze this data without Smart Grid big data analytics. Data privacy is also one of the emerging issues intersecting this domain.
5. Underexplored Open Challenges and Future Directions
5.1. TeraHertz Integration Environmental Challenges
5.2. Behavioral Change and Human Factors in Green Communication Adoption
5.3. Human–Machine Communication Interfaces in 6G Systems
5.4. Circular Economy Implementation in 6G Infrastructure
5.5. Quantum-Resistant Security for Energy-Constrained Environments
5.6. Policy Frameworks for Sustainable 6G Deployment
5.7. Context-Aware Fallback Mechanisms for Smart Grid Resilience
5.8. Lessons Learned
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wild, T.; Braun, V.; Viswanathan, H. Joint design of communication and sensing for beyond 5G and 6G systems. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 30845–30857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustavsson, U.; Frenger, P.; Fager, C.; Eriksson, T.; Zirath, H.; Dielacher, F.; Studer, C.; Pärssinen, A.; Correia, R.; Matos, J.N.; et al. Implementation challenges and opportunities in beyond-5G and 6G communication. IEEE J. Microwaves 2021, 1, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelantado, F.; Vilajosana, X.; Tuset-Peiro, P.; Martinez, B.; Melia-Segui, J.; Watteyne, T. Understanding the Limits of LoRaWAN. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2017, 55, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, N.; Garg, R. Energy harvesting in IoT devices: A survey. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Intelligent Sustainable Systems (ICISS), Palladam, India, 7–8 December 2017; pp. 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y. Evolving Towards Artificial-Intelligence-Driven Sixth-Generation Mobile Networks: An End-to-End Framework, Key Technologies, and Opportunities. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froytlog, A.; Foss, T.; Bakker, O.; Jevne, G.; Haglund, M.A.; Li, F.Y.; Oller, J.; Li, G.Y. Ultra-low power wake-up radio for 5G IoT. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2019, 57, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavikia, Z.; Shabro, M. A comprehensive layered approach for implementing internet of things-enabled smart grid: A survey. Digit. Commun. Networks 2022, 8, 388–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekki, K.; Bajic, E.; Chaxel, F.; Meyer, F. A comparative study of LPWAN technologies for large-scale IoT deployment. ICT Express 2019, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, R.; Sarkar, N.I.; Mohaghegh, M.; Pervez, S. A Cross-Layer Secure and Energy-Efficient Framework for the Internet of Things: A Comprehensive Survey. Sensors 2024, 24, 7209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficzere, D.; Varga, P.; Wippelhauser, A.; Hejazi, H.; Csernyava, O.; Kovács, A.; Hegedűs, C. Large-Scale Cellular Vehicle-to-Everything Deployments Based on 5G—Critical Challenges, Solutions, and Vision towards 6G: A Survey. Sensors 2023, 23, 7031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohalete, N.C.; Aderibigbe, A.O.; Ani, E.C.; Ohenhen, P.E.; Daraojimba, D.O.; Odulaja, B.A. AI-driven solutions in renewable energy: A review of data science applications in solar and wind energy optimization. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2023, 20, 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, P.; Rashid, A.; Biswas, A.; Nasim, M.A.A.; Chakraborty, S.; Gupta, K.D.; George, R. AI-driven approaches for optimizing power consumption: A comprehensive survey. Discov. Artif. Intell. 2024, 4, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiwada, U.D.; Danyaro, K.U.; Sarlan, A.; Liew, M.; Taiwo, A.; Audi, U.I. Energy efficiency in 5G systems: A systematic literature review. Int. J. Knowl.-Based Intell. Eng. Syst. 2024, 28, 93–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzeddine, Z.; Khalil, A.; Zeddini, B.; Ouslimani, H.H. A Survey on Green Enablers: A Study on the Energy Efficiency of AI-Based 5G Networks. Sensors 2024, 24, 4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandiyan, P.; Saravanan, S.; Kannadasan, R.; Krishnaveni, S.; Alsharif, M.H.; Kim, M.K. A comprehensive review of advancements in green IoT for smart grids: Paving the path to sustainability. Energy Rep. 2024, 11, 5504–5531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, R.; Zahoor, S.; Shah, M.A.; Wahid, A.; Yu, H. Green IoT: An Investigation on Energy Saving Practices for 2020 and Beyond. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 15667–15681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statista. Number of Internet of Things (IoT) Connected Devices Worldwide from 2019 to 2023, with Forecasts from 2022 to 2030. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1183457/iot-connected-devices-worldwide/ (accessed on 4 December 2023).
- Kozma, D.; Soos, G.; Varga, P. Supporting Digital Production, Product Lifecycle and Supply Chain Management in Industry 4.0 by the Arrowhead Framework—A Survey. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN), Helsinki, Finland, 22–25 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrakopoulos, G.; Varga, P.; Gutt, T.; Schneider, G.; Ehm, H.; Hoess, A.; Tauber, M.; Karathanasopoulou, K.; Lackner, A.; Delsing, J. Industry 5.0: Research areas and challenges with artificial intelligence and human acceptance. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2024, 18, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.K.; Prasad, R. Impact of 5G Technologies on Industry 4.0. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2018, 100, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åkerman, M.; Lundgren, C.; Bärring, M.; Folkesson, M.; Berggren, V.; Stahre, J.; Engström, U.; Friis, M. Challenges Building a Data Value Chain to Enable Data-Driven Decisions: A Predictive Maintenance Case in 5G-Enabled Manufacturing. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 17, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahiliani, V.; Digalwar, M. Green IoT Systems: An Energy Efficient Perspective. In Proceedings of the 2018 Eleventh International Conference on Contemporary Computing (IC3), Noida, India, 2–4 August 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga-Lamas, P.; Lopes, S.I.; Fernández-Caramés, T.M. Green IoT and Edge AI as Key Technological Enablers for a Sustainable Digital Transition towards a Smart Circular Economy: An Industry 5.0 Use Case. Sensors 2021, 21, 5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericsson. 5G Network Coverage Outlook. Available online: https://www.ericsson.com/en/reports-and-papers/mobility-report/dataforecasts/network-coverage (accessed on 4 December 2023).
- Varga, P.; Peto, J.; Franko, A.; Balla, D.; Haja, D.; Janky, F.; Soos, G.; Ficzere, D.; Maliosz, M.; Toka, L. 5g support for industrial iot applications—challenges, solutions, and research gaps. Sensors 2020, 20, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Z.; Henna, S.; Akhunzada, A.; Raza, M.; Kim, S.W. Performance Evaluation of LoRaWAN for Green Internet of Things. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 164102–164112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruckebusch, P.; Giannoulis, S.; Moerman, I.; Hoebeke, J.; De Poorter, E. Modelling the energy consumption for over-the-air software updates in LPWAN networks: SigFox, LoRa and IEEE 802.15.4g. Internet Things 2018, 3–4, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Microchip Inc. ATmega328P Data Sheet. Available online: http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/DeviceDoc/ATmega48A-PA-88A-PA-168A-PA-328-P-DS-DS40002061A.pdf (accessed on 19 November 2020).
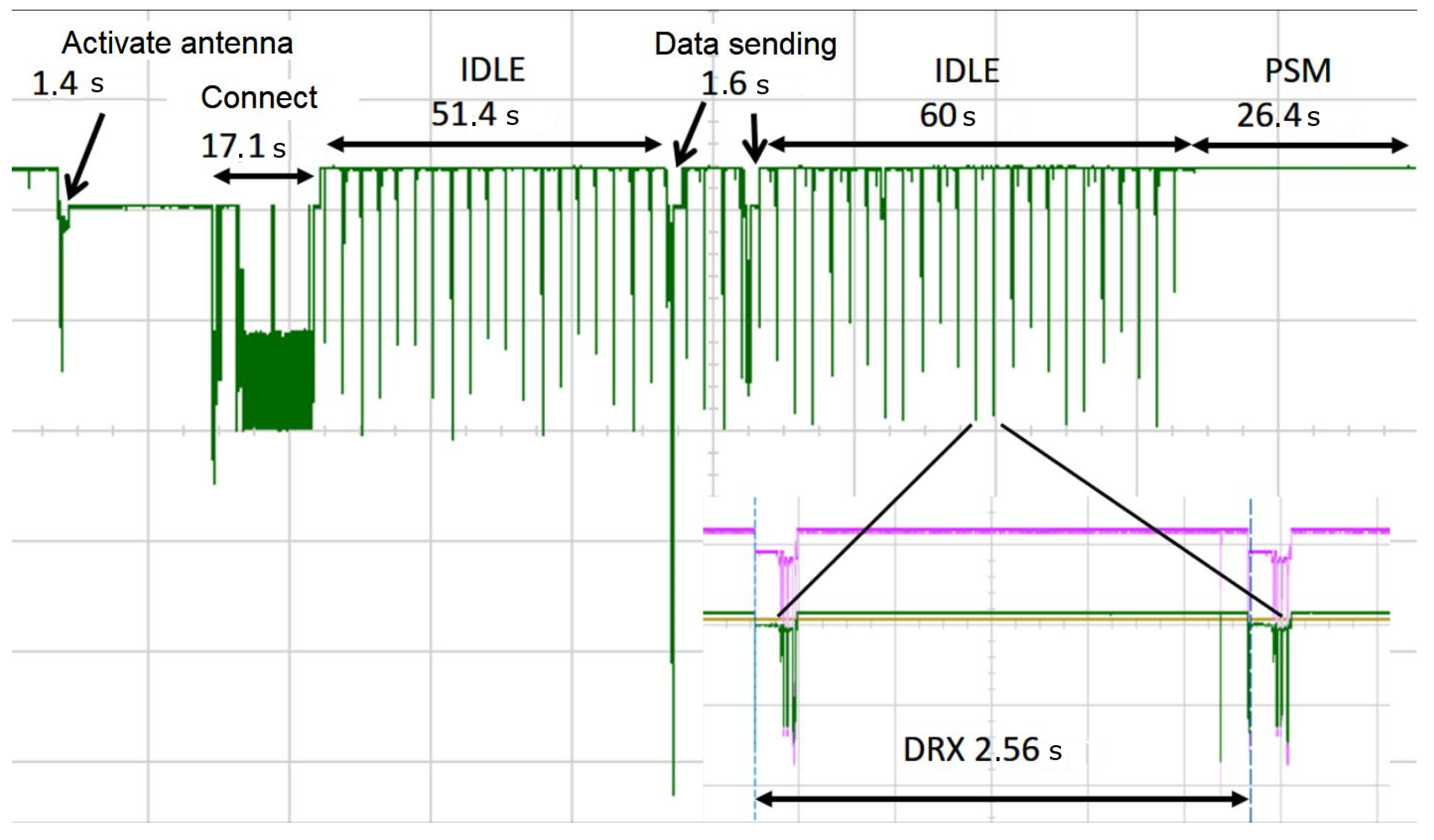
- Ficzere, D. IoT Eszközök Fogyasztásának és Adatátvitelének Vizsgálata NB-IoT és Cat-M1 Hálózaton. BME VIK TDK 2018 2018. p. 29. Available online: https://tdk.bme.hu/ConferenceFiles/VIK/2018/Paper/IoT-eszkozok-fogyasztasanak-es-adatatvitelenek1.pdf?paperId=8722 (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Ghose, D.; Frøytlog, A.; Li, F.Y. Enabling early sleeping and early data transmission in wake-up radio-enabled IoT networks. Comput. Netw. 2019, 153, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3GPP. Release 16. Available online: https://www.3gpp.org/release-16 (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- Wang, H.; Huang, M.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, M. Base Station Wake-Up Strategy in Cellular Networks With Hybrid Energy Supplies for 6G Networks in an IoT Environment. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 5230–5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, P.; Bhargava, L.; Singh, V.; Choudhary, M.; kumar Suhag, A. A survey—Energy harvesting sources and techniques for internet of things devices. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 30, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahi, H.; Munir, K.; Eugeni, M.; Atek, S.; Gaudenzi, P. Energy Harvesting towards Self-Powered IoT Devices. Energies 2020, 13, 5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Lan, G.; Hassan, M.; Hu, W.; Das, S.K. Sensing, Computing, and Communications for Energy Harvesting IoTs: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 2020, 22, 1222–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Shen, Q.; Liu, J.; Shen, X.S.; Xie, L. Optimizing Network Sustainability and Efficiency in Green Cellular Networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2014, 13, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.; Elsayed, H.; Abd El-Kader, S. Intensive Benchmarking of D2D communication over 5G cellular networks: Prototype, integrated features, challenges, and main applications. Wirel. Networks 2019, 26, 3183–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, M.; Giordano, S. Mobile ad hoc networking: Milestones, challenges, and new research directions. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.D.; Chung, Y.; Jo, M. Green data centers for cloud-assisted mobile ad hoc networks in 5G. IEEE Netw. 2015, 29, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Guo, H.; Qi, M.; Kato, N. Envisioning Device-to-Device Communications in 6G. IEEE Netw. 2020, 34, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, A.; Tetzner, J.; Sinha, K.; Matta, J. 5G device-to-device communication security and multipath routing solutions. Appl. Netw. Sci. 2019, 4, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, E.G.; Edfors, O.; Tufvesson, F.; Marzetta, T.L. Massive MIMO for next generation wireless systems. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, H.Q.; Larsson, E.G.; Marzetta, T.L. Energy and Spectral Efficiency of Very Large Multiuser MIMO Systems. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2013, 61, 1436–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Du, H.; Niyato, D.; Cui, S.; Ai, B.; Debbah, M.; Letaief, K.B.; Poor, H.V. A Tutorial on Extremely Large-Scale MIMO for 6G: Fundamentals, Signal Processing, and Applications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2024, 26, 1560–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dala Pegorara Souto, V.; Dester, P.S.; Soares Pereira Facina, M.; Gomes Silva, D.; de Figueiredo, F.A.P.; Rodrigues de Lima Tejerina, G.; Silveira Santos Filho, J.C.; Silveira Ferreira, J.; Mendes, L.L.; Souza, R.D.; et al. Emerging MIMO Technologies for 6G Networks. Sensors 2023, 23, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.N.R.S.V.; Hossain, E.; Bhargava, V.K. Energy Efficiency in Massive MIMO-Based 5G Networks: Opportunities and Challenges. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2017, 24, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; You, C.; Zhang, J.; Huang, K.; Letaief, K.B. A Survey on Mobile Edge Computing: The Communication Perspective. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 2017, 19, 2322–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, P.; Bácsi, S.; Sharma, R.; Fayad, A.; Mandeel, A.R.; Soos, G.; Franko, A.; Fegyo, T.; Ficzere, D. Converging telco-grade solutions 5g and beyond to support production in industry 4.0. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishtiaq, M.; Saeed, N.; Khan, M.A. Edge computing in IoT: A 6G perspective. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.08943. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, J.A.; Moreno, J.I.; Contreras, L.M.; Caamaño, M.B. Architecture and Methodology for Green MEC Services Using Programmable Data Planes in 5G and Beyond Networks. In Proceedings of the 2024 IFIP Networking Conference (IFIP Networking), Thessaloniki, Greece, 3–6 June 2024; pp. 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auer, G.; Giannini, V.; Desset, C.; Godor, I.; Skillermark, P.; Olsson, M.; Imran, M.A.; Sabella, D.; Gonzalez, M.J.; Blume, O.; et al. How much energy is needed to run a wireless network? IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2011, 18, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Mao, Y.; Leng, S.; Zhao, Q.; Li, L.; Peng, X.; Pan, L.; Maharjan, S.; Zhang, Y. Energy-Efficient Offloading for Mobile Edge Computing in 5G Heterogeneous Networks. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 5896–5907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basharat, S.; Hassan, S.A.; Pervaiz, H.; Mahmood, A.; Ding, Z.; Gidlund, M. Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces: Potentials, Applications, and Challenges for 6G Wireless Networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2021, 28, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Chen, M.Z.; Dai, J.Y.; Zeng, Y.; Zhao, X.; Jin, S.; Cheng, Q.; Cui, T.J. Wireless communications with programmable metasurface: New paradigms, opportunities, and challenges on transceiver design. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2020, 27, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jwair, M.H.; Elwi, T.A. Meta surface Antenna Circuitry for 5G Communication Networks. Infocommun. J. HTE 2023, 14, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Dai, L.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Yang, F.; Schober, R.; Poor, H.V. Active RIS vs. Passive RIS: Which Will Prevail in 6G? IEEE Trans. Commun. 2023, 71, 1707–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csathó, B.T.; Horváth, B.P. Physically Tenable Analysis and Control of Scattering from Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces. Infocommun. J. HTE 2025, 17, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Mu, X.; Ding, Z.; Schober, R.; Al-Dhahir, N.; Hossain, E.; Shen, X. Evolution of NOMA Toward Next Generation Multiple Access (NGMA) for 6G. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2022, 40, 1037–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belső, Z.; Pap, L. Effect of the Imperfect Channel Estimation on Achievable NOMA Rate. Infocommun. J. HTE 2025, 17, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parihar, A.S.; Singh, K.; Bhatia, V.; Li, C.P.; Duong, T.Q. Performance Analysis of NOMA-Enabled Active RIS-Aided MIMO Heterogeneous IoT Networks With Integrated Sensing and Communication. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 28137–28152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- I, C.; Rowell, C.; Han, S.; Xu, Z.; Li, G.; Pan, Z. Toward green and soft: A 5G perspective. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandotra, P. A Survey on Green Communication and Security Challenges in 5G Wireless Communication Networks. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2017, 96, 39–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Energy Institute. Statistical Review of World Energy; Technical Report; Energy Institute: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Our World In Data. Energy Consumption by Source, World. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/energy-consumption-by-source-and-country?stackMode=absolute&time=1993..latest&facet=none (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- International Energy Agency. Data Centres and Data Transmission Networks; Technical Report; International Energy Agency: Paris, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kelion, L. Record-Sized Data Centre Planned Inside Arctic Circle. Available online: https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/technology-40922048 (accessed on 4 November 2023).
- Masanet, E.; Shehabi, A.; Lei, N.; Smith, S.; Koomey, J. Recalibrating global data center energy-use estimates. Science 2020, 367, 984–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Technologies, E. Data Center Processors: State of the Industry and How to Keep Up to Date. Available online: https://exittechnologies.com/blog/cpu/data-center-processors/ (accessed on 5 November 2023).
- Editorial, H. HDD Remains Dominant Storage Technology. Available online: https://horizontechnology.com/news/hdd-remains-dominant-storage-technology-1219/ (accessed on 5 November 2023).
- Singh, T.; Rangarajan, S.; John, D.; Schreiber, R.; Oliver, S.; Seahra, R.; Schaefer, A. 2.1 Zen 2: The AMD 7nm Energy-Efficient High-Performance x86-64 Microprocessor Core. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Solid- State Circuits Conference—(ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 16–20 February 2020; pp. 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, J.; Hager, G.; Wellein, G.; Fey, D. An Analysis of Core- and Chip-Level Architectural Features in Four Generations of Intel Server Processors. In Proceedings of the High Performance Computing; Kunkel, J.M., Yokota, R., Balaji, P., Keyes, D., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 294–314. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, D. Japan 5G Network Tests Arm Chips, Claims Power Draw Down—Theregister.com. Available online: https://www.theregister.com/2022/09/30/in_japan_5g_networks_see/ (accessed on 6 April 2025).
- Haj-Yahya, J.; Volos, H.; Bartolini, D.; Antoniou, G.; Kim, J.; Wang, Z.; Kalaitzidis, K.; Rollet, T.; Chen, Z.; Geng, Y.; et al. AgileWatts: An Energy-Efficient CPU Core Idle-State Architecture for Latency-Sensitive Server Applications. In Proceedings of the 2022 55th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture (MICRO), Chicago, IL, USA, 1–5 October 2022; pp. 835–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomes, E.; Altiparmak, N. A Comparative Study of HDD and SSD RAIDs’ Impact on Server Energy Consumption. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Cluster Computing (CLUSTER), Honolulu, HI, USA, 5–8 September 2017; pp. 625–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G. Energy Efficiency in the Cloud Native 5G Core—Lightreading.com. Available online: https://www.lightreading.com/5g/energy-efficiency-in-the-cloud-native-5g-core (accessed on 6 April 2025).
- Singh, T.; Rangarajan, S.; John, D.; Henrion, C.; Southard, S.; McIntyre, H.; Novak, A.; Kosonocky, S.; Jotwani, R.; Schaefer, A.; et al. 3.2 Zen: A next-generation high-performance ×86 core. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 5–9 February 2017; pp. 52–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.; Schaefer, A.; Rangarajan, S.; John, D.; Henrion, C.; Schreiber, R.; Rodriguez, M.; Kosonocky, S.; Naffziger, S.; Novak, A. Zen: An Energy-Efficient High-Performance × 86 Core. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2018, 53, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intel Corporation. Improved Density and Power Efficiency for 5G Core Deployments. Available online: https://www.intel.com/content/dam/www/central-libraries/us/en/documents/2022-12/spr-upf-sb-final.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2023).
- Song, Z.; Zhang, X.; Eriksson, C. Data Center Energy and Cost Saving Evaluation. Energy Procedia 2015, 75, 1255–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Electronics, M. The Future of Data Center Cooling: AI Innovations and Advanced HVAC Motor Technologies—mckinsey-electronics.com. Available online: https://www.mckinsey-electronics.com/post/the-future-of-data-center-cooling-ai-innovations-and-advanced-hvac-motor-technologies (accessed on 6 April 2025).
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Dai, S.; Nie, B.; Ma, H.; Li, J.; Miao, Q.; Jin, Y.; Tan, L.; Ding, Y. Cooling technologies for data centres and telecommunication base stations—A comprehensive review. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 334, 130280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wen, Y.; Tao, D.; Guan, K. Transforming Cooling Optimization for Green Data Center via Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 50, 2002–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglioli, S.; Sakanova, A.; Persoons, T. Numerical Convective Heat Transfer Analysis of a Hybrid-Cooled Data Center Blade Server. In Proceedings of the 2019 18th IEEE Intersociety Conference on Thermal and Thermomechanical Phenomena in Electronic Systems (ITherm), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 28–31 May 2019; pp. 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shan, K.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Wang, S. Research and Technologies for next-generation high-temperature data centers—State-of-the-arts and future perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 171, 112991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antal, M.; Cioara, T.; Anghel, I.; Gorzenski, R.; Januszewski, R.; Oleksiak, A.; Piatek, W.; Pop, C.; Salomie, I.; Szeliga, W. Reuse of Data Center Waste Heat in Nearby Neighborhoods: A Neural Networks-Based Prediction Model. Energies 2019, 12, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manda, J.K. Green Data Center Innovations for Telecom: Exploring Innovative Technologies and Designs for Energy-Efficient and Sustainable Data Centers. SSRN 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioara, T.; Anghel, I.; Antal, M.; Crisan, S.; Salomie, I. Data center optimization methodology to maximize the usage of locally produced renewable energy. In Proceedings of the 2015 Sustainable Internet and ICT for Sustainability (SustainIT), Madrid, Spain, 14–15 April 2015; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madon, M.; Pierson, J.M. Integrating Pre-Cooling of Data Center operated with Renewable Energies. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conferences on Internet of Things (iThings) and IEEE Green Computing and Communications (GreenCom) and IEEE Cyber, Physical and Social Computing (CPSCom) and IEEE Smart Data (SmartData) and IEEE Congress on Cybermatics (Cybermatics), Rhodes Island, Greece, 2–6 November 2020; pp. 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Hou, Y.; Lee, Y.C.; Ji, H.; Zomaya, A.Y. Power Control Framework For Green Data Centers. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 2020, 10, 2876–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Zhang, J.; Poor, H.V. Data Center Demand Response With On-Site Renewable Generation: A Bargaining Approach. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2018, 26, 2707–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, K.; Li, P.; Xia, R.; Guo, S.; Guo, M. Renewable Energy-Aware Big Data Analytics in Geo-Distributed Data Centers with Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2020, 7, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith Pearlson, K.; Kaushik, V. Integrated solar power plant in Data Center. In Proceedings of the 2015 2nd International Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development (INDIACom), New Delhi, India, 11–13 March 2015; pp. 1670–1672. [Google Scholar]
- Skidmore, Z. Telecom Argentina Signs Ten-Year Solar Power Deal with MSU Green Energy—Datacenterdynamics.com. Available online: https://www.datacenterdynamics.com/en/news/telecom-argentina-signs-ten-year-solar-power-deal-with-msu-green-energy (accessed on 6 April 2025).
- Skidmore, Z. Orange Romania Inks 10-Year vPPA with Engie—Datacenterdynamics.com. Available online: https://www.datacenterdynamics.com/en/news/orange-romania-inks-10-year-vppa-with-engie/ (accessed on 6 April 2025).
- Walker, M. Telco Energy Use Flatlines in 2023; Green Energy’s Share of Total Creeps up to 20%. Available online: https://inform.tmforum.org/features-and-opinion/telco-energy-use-flatlines-in-2023-green-energys-share-of-total-creeps-up-to-20 (accessed on 6 April 2025).
- Ruan, X.; Chen, H.; Tian, Y.; Yin, S. Virtual machine allocation and migration based on performance-to-power ratio in energy-efficient clouds. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 100, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhwa, M.; Goel, A.; Choudhury, T.; Mishra, V.P. Green Cloud Computing—A Greener Approach To IT. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Knowledge Economy (ICCIKE), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 11–12 December 2019; pp. 760–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, A.S.; Alam, B.; Kaur, G. Observation of energy efficiency in Green cloud simulator. In Proceedings of the 2016 6th International Conference—Cloud System and Big Data Engineering (Confluence), Noida, India, 14–15 January 2016; pp. 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lago, D.G.; da Silva, R.A.; Madeira, E.R.; da Fonseca, N.L.; Medhi, D. SinergyCloud: A simulator for evaluation of energy consumption in data centers and hybrid clouds. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2021, 110, 102329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Tahir, M.; Sardaraz, M.; Alourani, A. A Resource Utilization Prediction Model for Cloud Data Centers Using Evolutionary Algorithms and Machine Learning Techniques. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Garg, S.; Aujla, G.S.S.; Alwasel, K.; Puthal, D.; Dustdar, S.; Zomaya, A.Y.; Rajan, R. Running Industrial Workflow Applications in a Software-defined Multi-Cloud Environment using Green Energy Aware Scheduling Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 17, 5645–5656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Liu, H.; Bi, J.; Zhou, M. Revenue and Energy Cost-Optimized Biobjective Task Scheduling for Green Cloud Data Centers. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2020, 18, 5645–5656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leif Johansson, Per Holmberg, Robert Skog Enhancing Infrastructure to Boost Energy Efficiency in 5G and 6G Core Networks. Available online: https://www.ericsson.com/en/reports-and-papers/ericsson-technology-review/articles/energy-efficient-core-networks (accessed on 6 April 2025).
- Nine, M.S.Z.; Kosar, T.; Bulut, M.F.; Hwang, J. GreenNFV: Energy-Efficient Network Function Virtualization with Service Level Agreement Constraints. In Proceedings of the International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis, Denver, CO, USA, 11–17 November 2023; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullaziz, O.I.; Capitani, M.; Casetti, C.E.; Chiasserini, C.F.; Chundrigar, S.B.; Landi, G.; Li, X.; Moscatelli, F.; Sakaguchi, K.; Talat, S.T. Energy monitoring and management in 5G integrated fronthaul and backhaul. In Proceedings of the 2017 European Conference on Networks and Communications (EuCNC), Oulu, Finland, 12–15 June 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolta, E.; Hatt, T.; Moore, S. Going Green: Benchmarking the Energy Efficiency of Mobile. Available online: https://data.gsmaintelligence.com/api-web/v2/research-file-download?id=60621137&file=300621-Going-Green-efficiency-mobile.pdf (accessed on 6 April 2025).
- Nokia. Intelligent RAN Operations: Go Beyond Automation with Machine Learning. Available online: https://www.nokia.com/mobile-networks/ran-operations/ (accessed on 7 April 2025).
- Dick, M.; Drangmeister, J.; Kern, E.; Naumann, S. Green software engineering with agile methods. In Proceedings of the 2013 2nd International Workshop on Green and Sustainable Software (GREENS), San Francisco, CA, USA, 20 May 2013; pp. 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calero, C.; Mancebo, J.; García, F.; Moraga, M.Á.; Berná, J.A.G.; Fernández-Alemán, J.L.; Toval, A. 5Ws of green and sustainable software. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2020, 25, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecker, A.; Bernardos, C.J.; Gavras, A.; Schörner, K.; Bou Rouphael, R.; AL-Naday, M.; Lombardo, C.; Ghoraishi, M. Sustainability of 6G: Ways to Reduce Energy Consumption. 2024. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/13986789 (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Kamran, R.; Kiran, S.; Jha, P.; Karandikar’T, A.; Chaporkar, P. Green 6G: Energy Awareness in Design. In Proceedings of the 2024 16th International Conference on COMmunication Systems & NETworkS (COMSNETS), Bengaluru, India, 3–7 January 2024; pp. 1122–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, B.; Tang, F.; Kawamoto, Y.; Kato, N. AI Models for Green Communications Towards 6G. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2022, 24, 210–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhussien, N.; Aaron Gulliver, T. Toward AI-Enabled Green 6G Networks: A Resource Management Perspective. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 132972–132995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. Research on future 6G green wireless networks. Green Technol. Sustain. 2025, 3, 100156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Tian, Z.; Du, X.; Guizani, M. An Energy-Efficient In-Network Computing Paradigm for 6G. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 2021, 5, 1722–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihsan, A.; Chen, W.; Asif, M.; Khan, W.U.; Wu, Q.; Li, J. Energy-Efficient IRS-Aided NOMA Beamforming for 6G Wireless Communications. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 2022, 6, 1945–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selva, E.; Gati, A.; Hamon, M.H.; Khorsandi, B.M.; Wunderer, S.; Bories, S.; Calochira, G.; Avino, G.; Wänstedt, S.; Bergmark, P.; et al. Towards a 6G Embedding Sustainability. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), Rome, Italy, 28 May–1 June 2023; pp. 1588–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Gupta, S.K.; Wang, H.C.; Kumari, C.S.; Korlam, S.S.V.P. From Efficiency to Sustainability: Exploring the Potential of 6G for a Greener Future. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, D.; Mewada, H.; Gondalia, V.; Almalki, F.A.; Patel, S.; Modi, H.; Kavaiya, S.; Trivedi, Y.; Mujlid, H.M. Balancing Technological Innovation and Environmental Sustainability: A Lifecycle Analysis of 6G Wireless Communication Technology. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, L.; Sovacool, B.K.; Foxon, T.J. The energy use implications of 5G: Reviewing whole network operational energy, embodied energy, and indirect effects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 157, 112033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myyara, M.; Lagnfdi, O.; Darif, A.; Farchane, A. Enhancing QoS for IoT Devices through Heuristics-based Computation Offloading in Multi-access Edge Computing. Infocommun. J. HTE 2024, 16, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Yu, Q.; Gu, G.; Gang, Q. Research on the architecture of electric power information communication network for smart grid. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Energy Internet and Energy System Integration (EI2), Beijing, China, 26–28 November 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, P.; Plosz, S.; Soos, G.; Hegedus, C. Security threats and issues in automation IoT. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 13th International Workshop on Factory Communication Systems (WFCS), Trondheim, Norway, 31 May–2 June 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ramezy, B.; Saadatmand, M.; Mozafari, B. Review of Communication Technologies for Smart Grid applications. In Proceedings of the National Conference on: New Approaches in Power Industry, Tehran, Iran, 11 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiasi, M.; Wang, Z.; Mehrandezh, M.; Jalilian, S.; Ghadimi, N. Evolution of smart grids towards the Internet of energy: Concept and essential components for deep decarbonisation. IET Smart Grid 2023, 6, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athari, H.; Raisz, D. Three-phase multi-frequency energy transfer system for realizing the energy internet. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 7th International Energy Conference (ENERGYCON), Riga, Latvia, 9–12 May 2022; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerihun, T.A.; Garau, M.; Helvik, B.E. Effect of Communication Failures on State Estimation of 5G-Enabled Smart Grid. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 112642–112658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhila, S.; Hemavathi. 5G Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication: Use Cases, Concepts and Challenges. In Proceedings of the 2023 10th International Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development (INDIACom), New Delhi, India, 15–17 March 2023; pp. 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher, J.C.; DeVine, M.E. Fifth-generation (5G) telecommunications technologies: Issues for congress. Congr. Res. Serv. 2019, 1, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, H.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Li, Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, C. IoT-G: A Low-Latency and High-Reliability Private Power Wireless Communication Architecture for Smart Grid. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Control, and Computing Technologies for Smart Grids (SmartGridComm), Beijing, China, 21–23 October 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmet Çinar, A.K. Self-Healing In Smart Grid: A Review. BEU J. Sci. 2018, 7, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Xiao, M.; Xiao, Y.; Pang, Z.; Poor, H.V.; Vucetic, B. High-Reliability and Low-Latency Wireless Communication for Internet of Things: Challenges, Fundamentals, and Enabling Technologies. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 7946–7970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Smart grid in america and europe: Similar desires, different approaches (part 1). Public Util. Fortn. 2011, 149, 1–5. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=1799705 (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Ghorbanian, M.; Dolatabadi, S.H.; Siano, P. Big Data Issues in Smart Grids: A Survey. IEEE Syst. J. 2019, 13, 4158–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Zhang, L.; Mei, C.; Li, J.; Zhu, X.; Liang, Y.; Song, J. A Survey on 5G Network Slicing Enabling the Smart Grid. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 25th International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems (ICPADS), Tianjin, China, 4–6 December 2019; pp. 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitì, A.; Verticale, G.; Rottondi, C.; Capone, A.; Schiavo, L.L. The Role of Smart Meters in Enabling Real-Time Energy Services for Households: The Italian Case. Energies 2017, 10, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Turjman, F.; Abujubbeh, M. IoT-enabled smart grid via SM: An overview. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 96, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, T. Big data analytics in smart grids: A review. Energy Inform. 2018, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, U.; Sharma, R. Data Analytics for Smart Grids and Applications—Present and Future Directions. In Data Analytics for Smart Grids Applications—A Key to Smart City Development; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Umapathy, K.; Sivakumar, M.; Kumar, T.D.; Omkumar, S.; Archana, M.; Amannah, C.; Alkhayyat, A.H. Big Data Analytics for Smart Grid: A Review on State-of-Art Techniques and Future Directions. In Data Analytics for Smart Grids Applications—A Key to Smart City Development; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Macmillan, M.; Wilson, K.; Baik, S.; Carvallo, J.P.; Dubey, A.; Holland, C.A. Shedding light on the economic costs of long-duration power outages: A review of resilience assessment methods and strategies. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2023, 99, 103055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalalas, C.; Vazquez-Gallego, F.; Alonso-Zarate, J. Handling mission-critical communication in smart grid distribution automation services through LTE. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications (SmartGridComm), Sydney, Australia, 6–9 November 2016; pp. 399–404. [Google Scholar]
- Baimel, D.; Tapuchi, S.; Baimel, N. Smart grid communication technologies. J. Power Energy Eng. 2016, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Hai, X.; Du, S.; Zeng, L.; Bai, J.; Liu, J. Application of 5G network slicing technology in smart grid. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Big Data, Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things Engineering (ICBAIE), Nanchang, China, 26–28 March 2021; pp. 740–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, D.; Kalalas, C.; Raussi, P.; Michalopoulos, D.S.; Rodríguez, D.Z.; Kokkoniemi-Tarkkanen, H.; Ahola, K.; Nardelli, P.H.; Fraidenraich, G.; Popovski, P. Boosting 5G on Smart Grid Communication: A Smart RAN Slicing Approach. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2023, 30, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zho, Z.; Huang, B. URLLC Key Technologies and Standardization for 6G Power Internet of Things. IEEE Commun. Stand. Mag. 2021, 5, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvez, I.; Sundararajan, A.; Sarwat, A.I. Frequency band for HAN and NAN communication in Smart Grid. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence Applications in Smart Grid (CIASG), Orlando, FL, USA, 9–12 December 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabalci, Y. A survey on smart metering and smart grid communication. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 302–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansal, P.; Bose, A. Bandwidth and latency requirements for smart transmission grid applications. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2012, 3, 1344–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Meier, A.; Culler, D.; McEachern, A.; Arghandeh, R. Micro-synchrophasors for distribution systems. In Proceedings of the ISGT 2014, Washington, DC, USA, 19–22 February 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garau, M.; Anedda, M.; Desogus, C.; Ghiani, E.; Murroni, M.; Celli, G. A 5G cellular technology for distributed monitoring and control in smart grid. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Broadband Multimedia Systems and Broadcasting (BMSB), Cagliari, Italy, 7–9 June 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- BenRhouma, O.; Rebai, C.; Ben-Romdhane, M.; Di Cara, D.; Artale, G.; Panzavecchia, N. The Environmental Impacts of Radio Frequency and Power Line Communication for Advanced Metering Infrastructures in Smart Grids. Sensors 2023, 23, 9621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Pindoriya, N.M. Automated Demand Response in Smart Distribution Grid: A Review on Metering Infrastructure, Communication Technology and Optimization Models. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2022, 206, 107835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Azmi, K.H.; Mohamed Radzi, N.A.; Azhar, N.A.; Samidi, F.S.; Thaqifah Zulkifli, I.; Zainal, A.M. Active Electric Distribution Network: Applications, Challenges, and Opportunities. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 134655–134689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Rocha Albertini, A.; Yabe, V.T.; Di Santoz, S.G.; Juniorx, G.M. An Overview of Distributed Energy Resources Management System Guidelines and Functional Coverage. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Power Electronics, Smart Grid, and Renewable Energy (PESGRE), Trivandrum, India, 2–5 January 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, R.; Dai, Y.; Wang, D.; Cai, H.; Fan, J.; Li, Y. Research on Network Slicing for Smart Grid. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 10th International Conference on Electronics Information and Emergency Communication (ICEIEC), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 17–19 July 2020; pp. 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojkovic, Z.; Bakmaz, B. Smart grid communications architecture: A survey and challenges. In Proceedings of the 11th International coriference on Applied Computer and Applied Computational Science (ACACOS), Venice, Italy, 8 March 2012; pp. 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, A.; Tanwar, S.; Tyagi, S.; Kumar, N.; Obaidat, M.S.; Rodrigues, J.J. Fog computing for smart grid systems in the 5G environment: Challenges and solutions. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2019, 26, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyanka, C.N.; Ramachandran, N.; Kumar, C.K.; Mande, S. A Brief Analysis on Routing Models for Efficent Data Transmission in Smart Grid. In Proceedings of the 2022 OITS International Conference on Information Technology (OCIT), Bhubaneswar, India, 14–16 December 2022; pp. 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, B.; Shah, R.; Furqan, M. Neighborhood Area Networks Communication Model for Smart Grid: Design and Performance Evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2022 First International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Information and Communication Technologies (ICEEICT), Trichy, India, 16–18 February 2022; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopstein, A.; Nguyen, C.; O’Fallon, C.; Hastings, N.; Wollman, D. NIST Framework and Roadmap for Smart Grid Interoperability Standards, Release 4.0. Available online. Available online: https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/SpecialPublications/NIST.SP.1108r4.pdf (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Leligou, H.C.; Zahariadis, T.; Sarakis, L.; Tsampasis, E.; Voulkidis, A.; Velivassaki, T.E. Smart Grid: A demanding use case for 5G technologies. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops (PerCom Workshops), Athens, Greece, 19–23 March 2018; pp. 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.V.; Khursheed, A.; Alam, Z. Wired Communication Technologies and Networks for Smart Grid—A Review. In Cyber Security in Intelligent Computing and Communications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 183–195. [Google Scholar]
- Alomar, M.A. An IOT based smart grid system for advanced cooperative transmission and communication. Phys. Commun. 2023, 58, 102069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekki, K.; Bajic, E.; Chaxel, F.; Meyer, F. Overview of Cellular LPWAN Technologies for IoT Deployment: Sigfox, LoRaWAN, and NB-IoT. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops (PerCom Workshops), Athens, Greece, 19–23 March 2018; pp. 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberg, O.; Sundberg, M.; Wang, Y.P.E.; Bergman, J.; Sachs, J. Chapter 8—NB-IoT Performance. In Cellular Internet of Things; Liberg, O., Sundberg, M., Wang, Y.P.E., Bergman, J., Sachs, J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 297–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugroho, C.; Wibisono, G. NB-IoT Planning in Jakarta Area for Smart Meter Utilities. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Innovative Research and Development (ICIRD), Jakarta, Indonesia, 28–30 June 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoso, E.S.; Hidayati, A.; Suryanegara, M.; Nashiruddin, M.I. NB-IoT Network Planning for Smart Metering Services in Jakarta, Depok, Tangerang, and Bekasi. In Proceedings of the 2019 16th International Conference on Quality in Research (QIR): International Symposium on Electrical and Computer Engineering, Padang, Indonesia, 22–24 July 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogg, I. Benchmarking the Global 5G Experience—June 2023. Available online: https://www.opensignal.com/2023/06/30/benchmarking-the-global-5g-experience-june-2023 (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- GSA. 5G—GSA 5G Infographic December-2023. Available online: https://gsacom.com/paper/gsa-5g-infographic-december-2023/ (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- Qadir, J.; Cabus, J.E.U.; Butun, I.; Lagerström, R.; Gastaldo, P.; Caviglia, D.D. Analysis of LPWAN: Cyber-Security Vulnerabilities and Privacy Issues in LoRaWAN, Sigfox, and NB-IoT. In Low-Power Wide-Area Networks: Opportunities, Challenges, Risks and Threats; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 139–170. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, P.P.; Kumar, N.; Guizani, M. A Vision on 6G-Enabled NIB: Requirements, Technologies, Deployments, and Prospects. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2021, 28, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennanen, H.; Hänninen, T.; Tervo, O.; Tölli, A.; Latva-Aho, M. 6G: The Intelligent Network of Everything. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 1319–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehab, M.J.; Kassem, I.; Kutty, A.A.; Kucukvar, M.; Onat, N.; Khattab, T. 5G Networks Towards Smart and Sustainable Cities: A Review of Recent Developments, Applications and Future Perspectives. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 2987–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budhiraja, I.; Kumar, N.; Tyagi, S.; Tanwar, S.; Han, Z.; Piran, M.J.; Suh, D.Y. A Systematic Review on NOMA Variants for 5G and Beyond. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 85573–85644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manish Mandloi, Devendra Gurjar, P.P.H.N. 5G and Beyond Wireless Systems: PHY Layer Perspective. Available online: https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-981-15-6390-4 (accessed on 11 January 2024).
- 5G/NR-NTN PHY Protocol. Available online: https://www.sharetechnote.com/html/5G/5G_NTN.html (accessed on 11 January 2024).
- Masini, G.; Reininger, P.; El Jaafari, M.; Vesely, A.; Chuberre, N.; Baudry, B.; Houssin, J.M. 5G Meets Satellite: Non-Terrestrial Network Architecture and 3GP. Int. J. Satell. Commun. Netw. 2023, 41, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbodo, E.U.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M.; Kurien, A.M. A Survey on 5G and LPWAN-IoT for Improved Smart Cities and Remote Area Applications: From the Aspect of Architecture and Security. Sensors 2022, 22, 6313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Völk, F.; Schlichter, T.; Kaltenberger, F.; Heyn, T.; Casati, G.; Schwarz, R.T.; Knopp, A. Field Trial of a 5G Non-Terrestrial Network Using OpenAirInterface. IEEE Open J. Veh. Technol. 2022, 3, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Alwis, C.; Kumar, P.; Pham, Q.V.; Dev, K.; Kalla, A.; Liyanage, M.; Hwang, W.J. Towards 6G: Key technological directions. ICT Express 2023, 9, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, T.; Chehri, A.; Fortier, P. Review of optical and wireless backhaul networks and emerging trends of next generation 5G and 6G technologies. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2021, 32, e4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimi, I.A.; Patel, R.K.; Muga, N.J.; Pinto, A.N.; Teixeira, A.L.; Monteiro, P.P. Towards Enhanced Mobile Broadband Communications: A Tutorial on Enabling Technologies, Design Considerations, and Prospects of 5G and beyond Fixed Wireless Access Networks. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porambage, P.; Gür, G.; Osorio, D.P.M.; Liyanage, M.; Gurtov, A.; Ylianttila, M. The Roadmap to 6G Security and Privacy. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2021, 2, 1094–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Salam, R.; Iqbal Ratyal, N.; Ahmed, U.; Aziz, I.; Sajid, M.; Mahmood, A. An Overview of Recent Wireless Technologies for IoT-Enabled Smart Grids. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2024, 2024, 2568751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chataut, R.; Nankya, M.; Akl, R. 6G networks and the AI revolution—Exploring technologies, applications, and emerging challenges. Sensors 2024, 24, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefati, S.S.; Halunga, S. Ultra-reliability and low-latency communications on the internet of things based on 5G network: Literature review, classification, and future research view. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2023, 34, e4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, J.; Firyaguna, F.; Sherazi, H.H.R.; Kushch, S.; Vijayan, A.; O’Connell, E.; Pesch, D.; O’Flynn, B.; O’Brien, W.; Hayes, M.; et al. Wireless communications for smart manufacturing and industrial IoT: Existing technologies, 5G and beyond. Sensors 2023, 23, 73. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, Y.; Guo, J.; Gao, N.; Zhu, Y.; Jin, S.; Li, X. A survey of blockchain and artificial intelligence for 6G wireless communications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 2023, 25, 2494–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, R.; Ricardo, M.; Pouttu, A.; Correia, L.M. Wireless technologies towards 6G. J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2023, 42, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Zografopoulos, I.; Hossain, M.T.; Badsha, S.; Konstantinou, C. A Resource Allocation Scheme for Energy Demand Management in 6G-enabled Smart Grid. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Power & Energy Society Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference (ISGT), Washington, DC, USA, 16–19 January 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rituraj, R.; Varkonyi, D.T.; Mosavi, A.; Koczy, A.V. 5G for Smart Grids: Review, Taxonomy, Bibliometrics, Applications and Future Trends. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 27th International Conference on Intelligent Engineering Systems (INES), Nairobi, Kenya, 26–28 July 2023; pp. 000275–000284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneria, S.; Pramanik, K.K. IoT Narrow Band for Smart Grid. In Proceedings of the 2023 3rd International Conference on Advance Computing and Innovative Technologies in Engineering (ICACITE), Greater Noida, India, 12–13 May 2023; pp. 2260–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansar, S.A.; Jaiswal, K.; Aggrarwal, S.; Srivastava, A.; Singh, V. NBIoT: Transitioning from IoT to an eco-friendly IoT approach. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2023; Volume 2954. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Wang, J.; Kumar, S.; Zheng, Y. Introduction to the Special Issue on Low Power Wide Area Networks. ACM Trans. Sen. Netw. 2023, 18, 58e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, B.; Vasa, J.; Patel, D. 5G-based LPWAN standard technologies, design characteristics, architectures, applications and open research challenges: A technical perspective. Int. J. Wirel. Mob. Comput. 2023, 25, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, K. Chapter 5—Devices and technology for monitoring transmission lines. In Inspection and Monitoring Technologies of Transmission Lines with Remote Sensing; Hu, Y., Liu, K., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 281–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios-Ulloa, A.; Cama-Pinto, D.; Arrabal-Campos, F.M.; Martínez-Lao, J.A.; Monsalvo-Amaris, J.; Hernández-López, A.; Cama-Pinto, A. Overview of Mobile Communications in Colombia and Introduction to 5G. Sensors 2023, 23, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedage, L.T.; Butler, B.; Balasubramaniam, S.; Koucheryavy, Y.; Jornet, J.M. Climate Change Sensing through Terahertz Communications: A Disruptive Application of 6G Networks. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.03074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidi Aman, A.; Hajasoa Malala, R. Terahertz Frequency Windows: Investigating Atmospheric Attenuation for Outdoor Communication. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2024, 13, IJERTV13IS030161. Available online: https://www.ijert.org/research/terahertz-frequency-windows-investigating-atmospheric-attenuation-for-outdoor-communication-IJERTV13IS030161.pdf (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Foltynowicz, R.J.; Wanke, M.C.; Mangan, M.A. Atmospheric Propagation of THz Radiation; Technical Report SAND2005-6389; Sandia National Laboratories: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 2005. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/923074-F7hnFq/ (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Neves, C.; Oliveira, T.; Santini, F. Extending the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology for sustainable technologies context. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2025, 80, 102838. Available online: https://novaresearch.unl.pt/en/publications/extending-the-unified-theory-of-acceptance-and-use-of-technology- (accessed on 29 June 2025). [CrossRef]
- Buba, A.K.; Ibrahim, O.; Shehzad, H.M.F. Behavioral intention model for green information technology adoption in Nigerian manufacturing industries. Aslib J. Inf. Manag. 2021. Available online: https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/AJIM-05-2021-0128/full/html (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- OECD. Mind Shift, Green Lift: Six Behavioural Science Trends for Environmental Policy. 2025. Available online: https://oecd-opsi.org/publications/mind-shift-green-lift-six-behavioural-science-trends-for-environmental-policy/ (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Han, B.; Schotten, H.D. Multi-Sensory HMI for Human-Centric Industrial Digital Twins: A 6G Vision of Future Industry. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications (ISCC), Rhodes, Greece, 30 June–3 July 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, N.; Shirokov, M.E.; Wilde, M.M. Energy-constrained two-way assisted private and quantum capacities of quantum channels. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.08102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banegas, G.; Zandberg, K.; Herrmann, A.; Baccelli, E.; Smith, B.A. Quantum-Resistant Security for Software Updates on Low-power Networked Embedded Devices. In Proceedings of the Conference Proceedings, June 2021. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/d615e8029910be3002976a9e1f33081ad34c5c41 (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Authors, V. Q-SECURE: A Quantum Resistant Security for Resource Constrained IoT Device Encryption. In Proceedings of the 2023 10th International Conference on Internet of Things: Systems, Management and Security (IOTSMS), San Antonio, TX, USA, 23–25 October 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veridify Security. Quantum-Resistant Security for IoT and M2M Devices. 2025. Available online: https://www.veridify.com/quantum-resistant-security-for-iot-and-m2m-devices/ (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Roma, C.A.; Tai, C.E.A.; Hasan, M.A. Energy Efficiency Analysis of Post-Quantum Cryptographic Algorithms. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 71295–71317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Carames, T.M.; Fraga-Lamas, P. From Pre-Quantum to Post-Quantum IoT Security: A Survey on Quantum-Resistant Cryptosystems for the Internet of Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 6457–6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Authors, V. Quantum-Resistant Homomorphic Encryption for IoT Security (QRHE). Al-Salam J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2024, 4, 36–51. Available online: https://journal.alsalam.edu.iq/index.php/ajest/article/view/349 (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- USTelecom. Beyond 5G—Towards a Policy Framework For 6G and The Future of Connectivity. 2021. Available online: https://www.ustelecom.org/beyond-5g-towards-a-policy-framework-for-6g-and-the-future-of-connectivity/ (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Consumer Unity & Trust Society Centre for Competition, Investment & Economic Regulation. In An Ethical Framework for 6G; Technical Report; CUTS CCIER: Jaipur, India, 2024; Available online: https://cuts-ccier.org/pdf/An-ethical-framework-for-6G.pdf (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- European Parliament. The Path to 6G; Technical Report EPRS_BRI(2024)757633_EN; European Parliament Research Service: Brussels, Belgium, 2024. Available online: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/RegData/etudes/BRIE/2024/757633/EPRS_BRI(2024)757633_EN.pdf (accessed on 29 June 2025).



| Comparison Criteria | Current Paper | Maiwada et al. (2024) [13] | Ezzeddine et al. (2024) [14] | Pandiyan et al. (2024) [15] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scope | 5G/6G, smart grid, IIoT | 5G, Digital twins | AI-based 5G networks | Green IoT and smart grids |
| Key Focus | Green communications and smart grids | Energy efficiency, DT, and QoS in 5G | Energy efficiency using AI techniques | Sustainable IoT and energy-aware solutions |
| Reviewed Technologies | LPWAN, MEC, energy harvesting, IoT | Digital twins, DDoS detection, QoS mechanisms | Massive MIMO, NOMA, SDN, NFV, MEC | RFID, Zigbee, BLE, LoRa, MEC, energy-aware protocols |
| Energy Efficiency Strategies | Integrated cross-layer optimizations | Intrusion detection, QoS-based techniques | ML-driven optimization at multiple network layers | HW-SW co-optimization, harvesting, sleep scheduling |
| Empirical Validation | Identified gap, recommends empirical studies | Primarily theoretical analysis | Simulation and analytical approaches | High-level review; empirical studies mentioned as future need |
| Interoperability | Highlighted need, emphasizes cross-domain integration | Not extensively covered | Limited discussion, implied via technology integration | Discussed as critical for 5G-IoT integration |
| Coverage of Standards | Calls for unified standards | Minimal coverage | Minimal explicit discussion | Explicit discussion of standards |
| Highlighted Challenges | Fragmentation, security-energy balance, interoperability | DDoS attacks, handover efficiency, QoS consistency | Co-channel interference, network capacity constraints | Heterogeneity, scalability, energy-security trade-off, infrastructure cost |
| SigFox | LoRa | |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency band | Unlicensed | Unlicensed |
| Urban range | 3–10 km | 2–5 km |
| Rural range | 30–50 km | 15–20 km |
| Bandwidth | 100 Hz | 125 kHz |
| Maximum data rate | 100 bps | 50 kbps |
| Topology | Star | Star |
| Maximum devices per access point | 1 M | 100 k |
| End device cost | <USD 2 | USD 3–10 |
| Deployment cost | Subscription-based USD 2–5/year | >USD 100/gateway >USD 1000/base station |
| Technique | Description and Benefits |
|---|---|
| Low-Power Wide-Area Networks (LPWAN) | Enables long-range, low-power communication suitable for IoT applications, significantly reducing the power consumption of end devices. |
| Wake-Up radios | Special radios are activated only upon receiving specific signals, drastically reducing idle power consumption in IoT devices and sensors. |
| Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) | Offloading computation-intensive tasks to edge servers close to users, minimizing latency and reducing energy consumption at end devices. |
| Massive MIMO | Employs large antenna arrays to optimize signal transmission, enhancing spectral efficiency and reducing transmission power per user. |
| Device-to-Device (D2D) Communication | Enables direct communication between nearby devices, decreasing base station load and energy consumption. |
| Network Function Virtualization (NFV) | Virtualizing network functions to optimize resource utilization and dynamically allocate resources, thereby reducing overall energy use. |
| Software-Defined Networking (SDN) | Centralized control allows efficient traffic management and resource allocation, significantly reducing redundant energy consumption. |
| Heterogeneous Networks (HetNets) | Utilize macro, micro, and pico base stations strategically to manage traffic loads, optimizing energy usage across varying cell sizes. |
| Dynamic Power Management | Intelligent algorithms dynamically adjust the transmission power of network elements based on real-time demand, saving energy during low-traffic periods. |
| Energy Harvesting | Integrating renewable sources such as solar panels and RF harvesting to power network equipment, reducing dependence on grid power. |
| AI-Driven Optimization | Employing AI techniques (ML, DL) for predictive analytics, resource allocation, and dynamic management, enhancing network energy efficiency. |
| Base Station Sleep Modes | Turning off or putting base stations into low-power states during low usage periods substantially reduces operational energy consumption. |
| Green Core and Telco Cloud | Optimizing data center components, cooling systems, and employing efficient processors (e.g., ARM-based), significantly lowering core network energy usage. |
| Cross-layer Optimization | Integrating energy-efficient solutions across multiple network layers (physical, MAC, network), enhancing overall network energy efficiency. |
| Energy-Efficient Hardware | Deployment of advanced hardware components designed for minimal energy consumption, including power amplifiers, antennas, and processors. |
| Approach | Main Papers | Core Ideas |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware development | [70,73,78] | Reduction of processor consumption; AgileWatts |
| Cooling optimization | [82,83,84] | Technological optimization; control policy optimization; high-temperature DC concept |
| Green energy integration | [87,88,91] | Pre-cooling; thermal storage; geo-distributed load-balancing |
| Hardware resource optimization | [96,100] | Load-balancing; prediction-based resource allocation |
| Future possibilities | [115,116] | In-network computing; NOMA and IRS |
| Metric | Use Case | Pre-5G | 5G | 6G (Emerging) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latency | IIoT | 10 ms–1 s | 1–10 ms | <1 ms (THz, RIS) |
| Smart Grid | 10 ms–1 s | <5 ms | Sub-ms (AI control) | |
| Bandwidth | IIoT | 0.3–250 kbps | 1–100 Mbps, to 10 Gbps | 10+ Gbps |
| Smart Grid | <50 kbps | 10–100 Mbps | 10+ Gbps | |
| Device Density | IIoT | 1 k–10 k/km2 | 1 M/km2 | 10 M+/km2 |
| Smart Grid | Limited mesh | 100 k/km2 | 1 M+/km2 | |
| Energy Efficiency | IIoT | Ultra-low (10+ yr battery) | Moderate (NB-IoT) | AI-optimized |
| Smart Grid | Low-power (LoRa) | Medium (5G PMUs) | RF harvesting | |
| Reliability | IIoT | Low (best-effort) | 99.999% (URLLC) | 99.99999% (det’istic) |
| Smart Grid | Moderate mesh | 99.9999% | Self-optimizing | |
| Use Cases | IIoT | Remote monitoring | Predictive maintenance | Autonomous factory |
| Smart Grid | AMI, outage alerts | PMUs, pricing | AI grids, DTwins | |
| AI/Edge Support | General | Minimal (centralized) | Basic edge (MEC) | Native AI, RIS |
| Wireless Technology | Use | Data Rate | Latency | Device Number | Range/ Device | Security | Frequency License |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LoRa [136] | NAN | ∼50 kbps | 400 ms | 1.5 k | <20 km | built-in | ISM 422, 868, 923 MHz |
| ZigBee [197] | NAN | ∼250 kbps | 18 ms | 65 k | 100 m–1 km | built-in | ISM 2.4 GHz |
| SigFox [165] | WAN | ∼100 bps | >400 ms | 50 k | 10–40 km | none | ISM 433, 868, 915 MHz |
| 5G NB-IoT [165,166] | NAN, WAN | 200 kbps | 0.6–1 s | 100 k | 1–10 km | built-in | Cellular 5G Standard |
| 5G NB2-IoT [198] | NAN, WAN | ∼700 kbps | 0.6–1 s | 1000 k | 10 km | built-in | Cellular 5G Standard |
| 5G NTN [177,178,180] | WAN | varied | long | multitude | wide | built-in | 5G NTN Standard |
| 5G NR [181,182] | HAN, NAN, WAN | ∼20 Gbps | <1 ms | 1 M/km2 | <1 km | known entities | Cellular 5G Standard |
| 6G [183,184] | HAN, NAN, WAN | ∼1 Tbps | 10–100 µs | 10 M/km2 | <1 km | unknown entities | Cellular 6G Standard |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Varga, P.; Jászberényi, Á.I.; Pásztor, D.; Nagy, B.; Nasar, M.; Raisz, D. How Beyond-5G and 6G Makes IIoT and the Smart Grid Green—A Survey. Sensors 2025, 25, 4222. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134222
Varga P, Jászberényi ÁI, Pásztor D, Nagy B, Nasar M, Raisz D. How Beyond-5G and 6G Makes IIoT and the Smart Grid Green—A Survey. Sensors. 2025; 25(13):4222. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134222
Chicago/Turabian StyleVarga, Pal, Áron István Jászberényi, Dániel Pásztor, Balazs Nagy, Muhammad Nasar, and David Raisz. 2025. "How Beyond-5G and 6G Makes IIoT and the Smart Grid Green—A Survey" Sensors 25, no. 13: 4222. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134222
APA StyleVarga, P., Jászberényi, Á. I., Pásztor, D., Nagy, B., Nasar, M., & Raisz, D. (2025). How Beyond-5G and 6G Makes IIoT and the Smart Grid Green—A Survey. Sensors, 25(13), 4222. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134222








