Engineering Safety-Oriented Blasting-Induced Seismic Wave Signal Processing: An EMD Endpoint Suppression Method Based on Multi-Scale Feature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
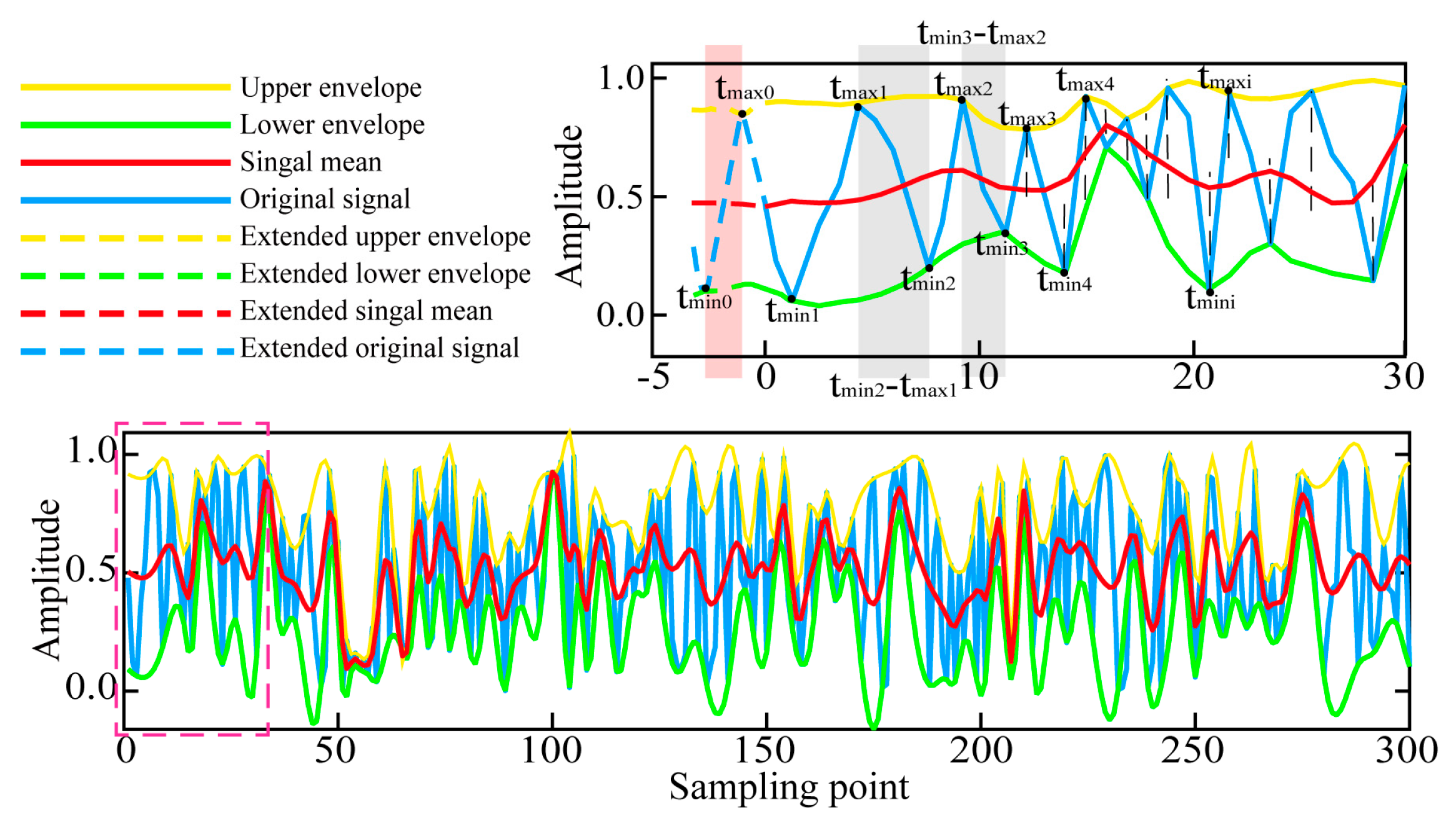
2.1. EMD Process and Endpoint Effect Mechanism
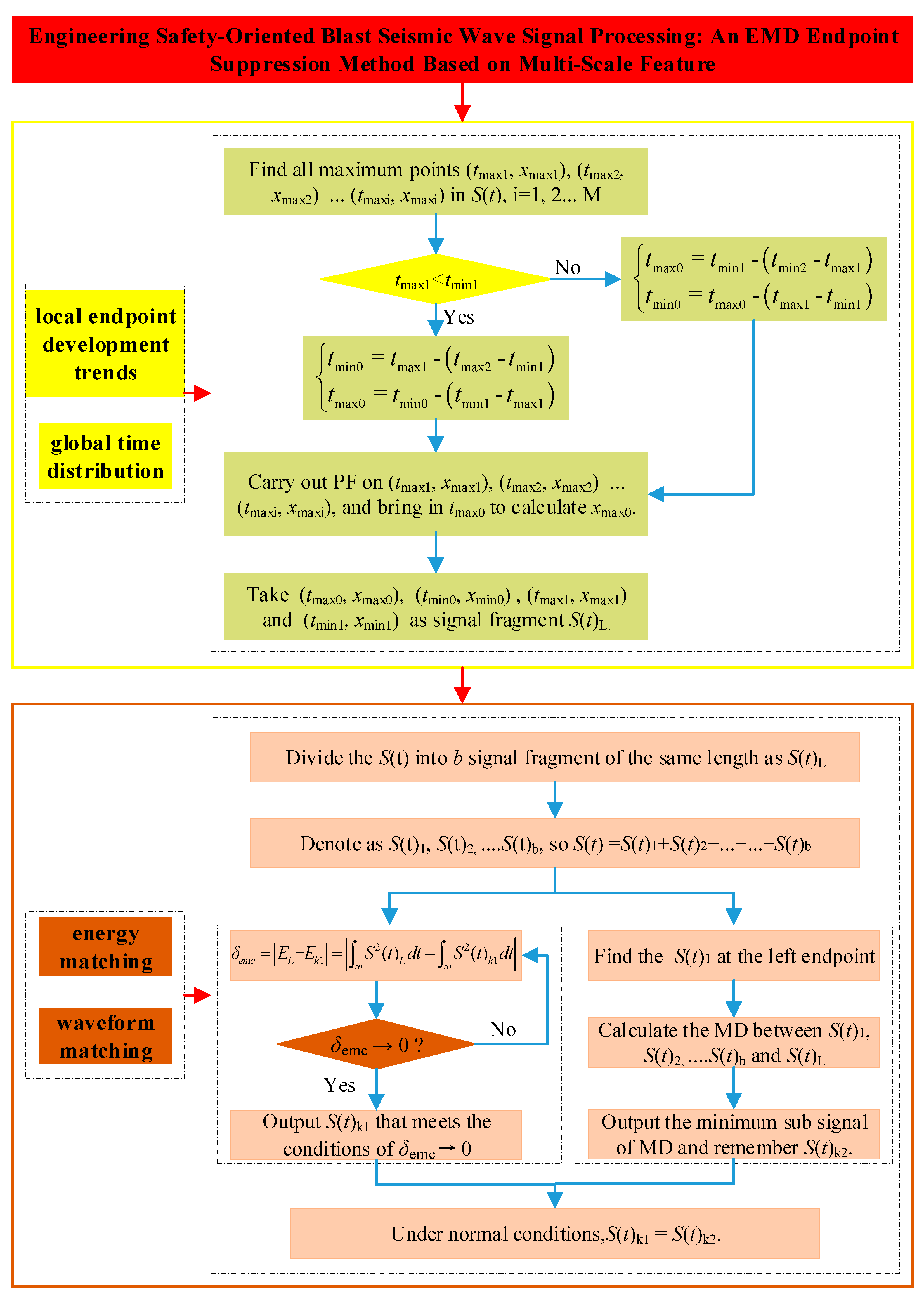
2.2. Proposed Endpoint Effect Suppression Algorithm
- (1)
- Local endpoint development trends
- (2)
- Global time distribution
- (3)
- Energy matching
- (4)
- Waveform matching
2.2.1. Stage 1: Generation of the Dual-Trend Characteristic Wave (DTCW)
- (1)
- DTCW time parameter
- (2)
- DTCW amplitude parameter
2.2.2. Stage 2: Dual-Criteria Matching Process
- (1)
- Adaptive energy matching
- (2)
- Adaptive waveform matching
3. Comparative Study on Various Suppression Methods of Endpoint Effects in Simulation Signals
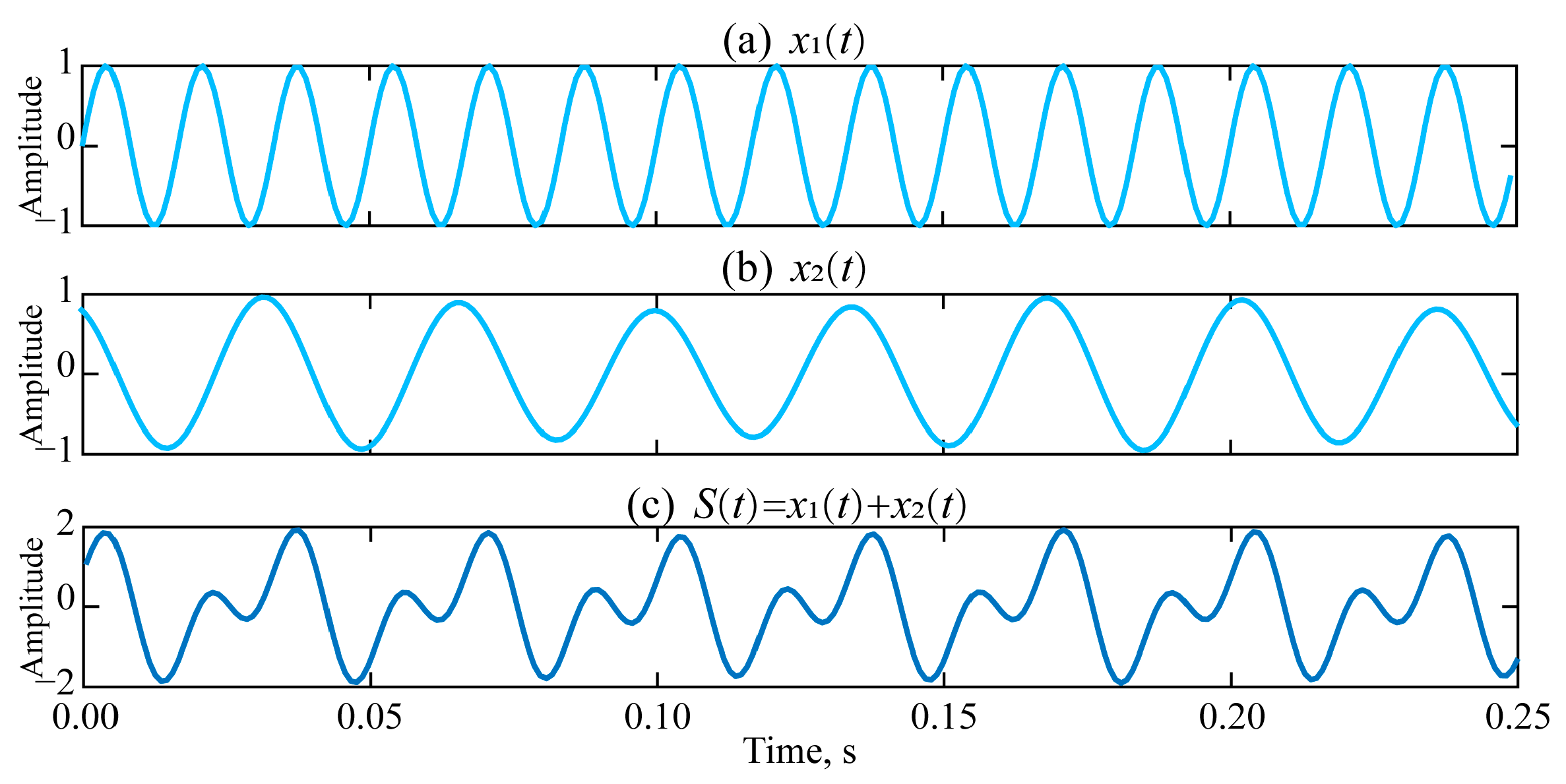
3.1. Generation of Simulated Vibration Signals
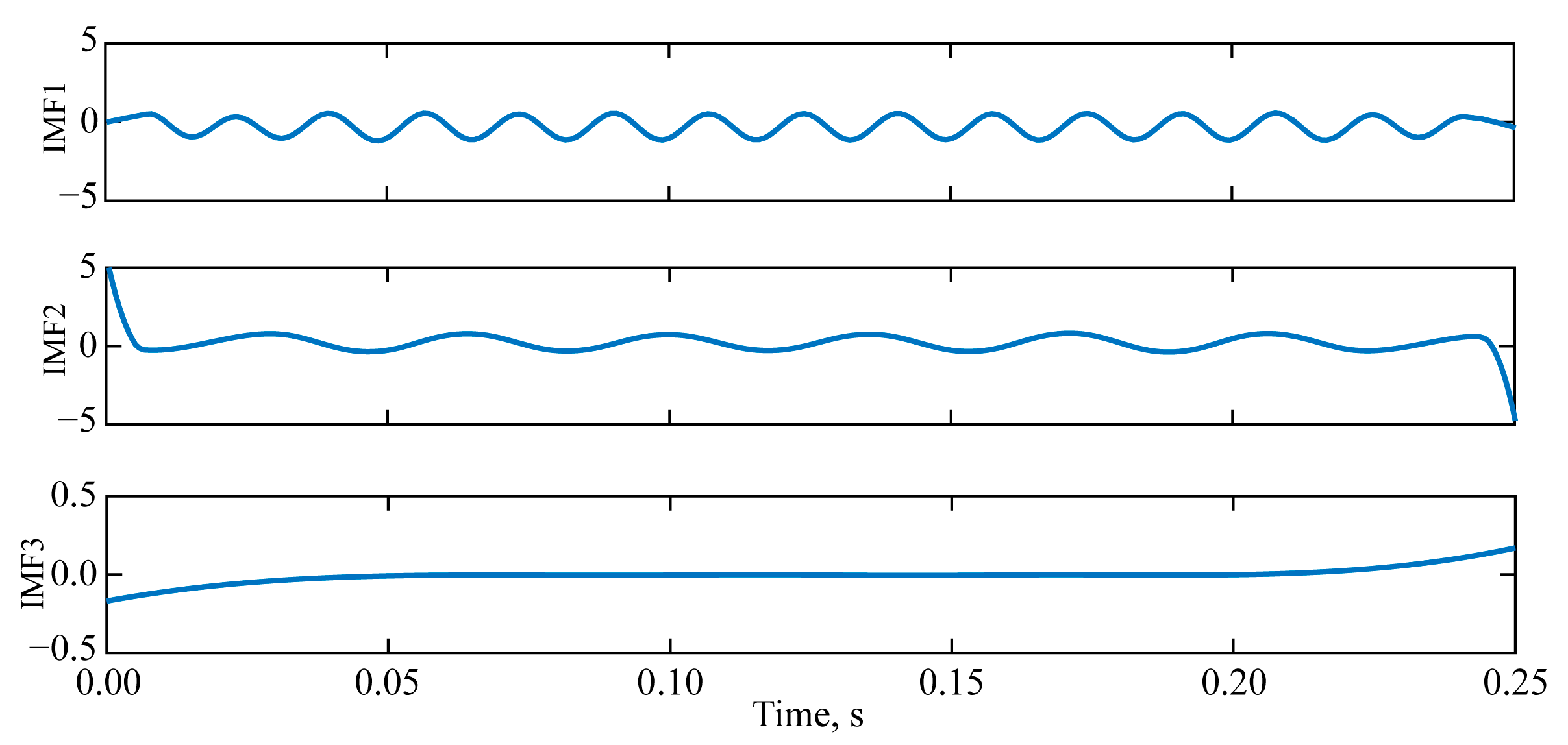
3.2. Simulation Vibration Signal EMD Endpoint Effect Suppression Processing
3.3. Analysis of the Suppression Results of the EMD Endpoint Effect on Simulated Blasting Vibration Signals
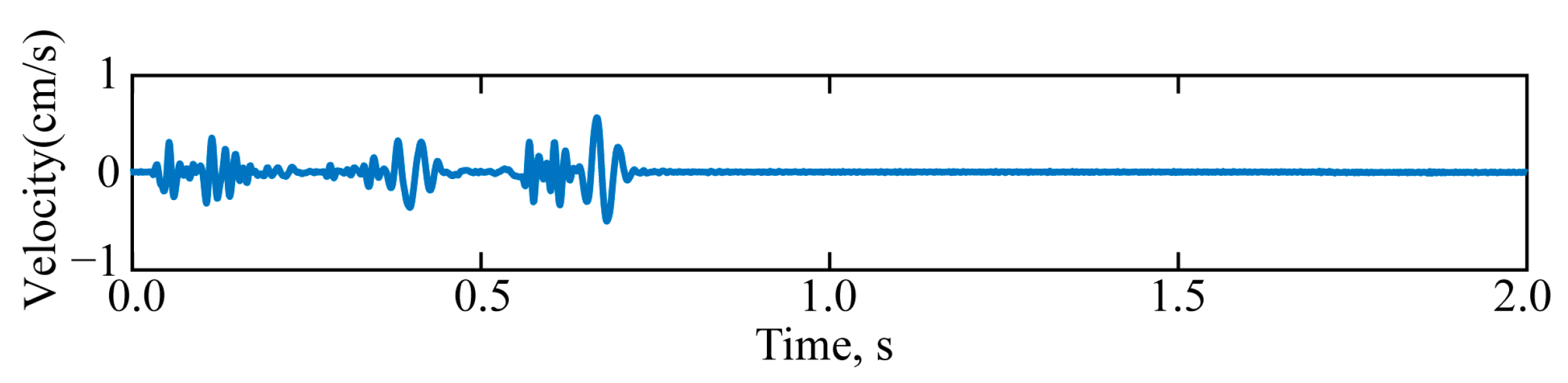
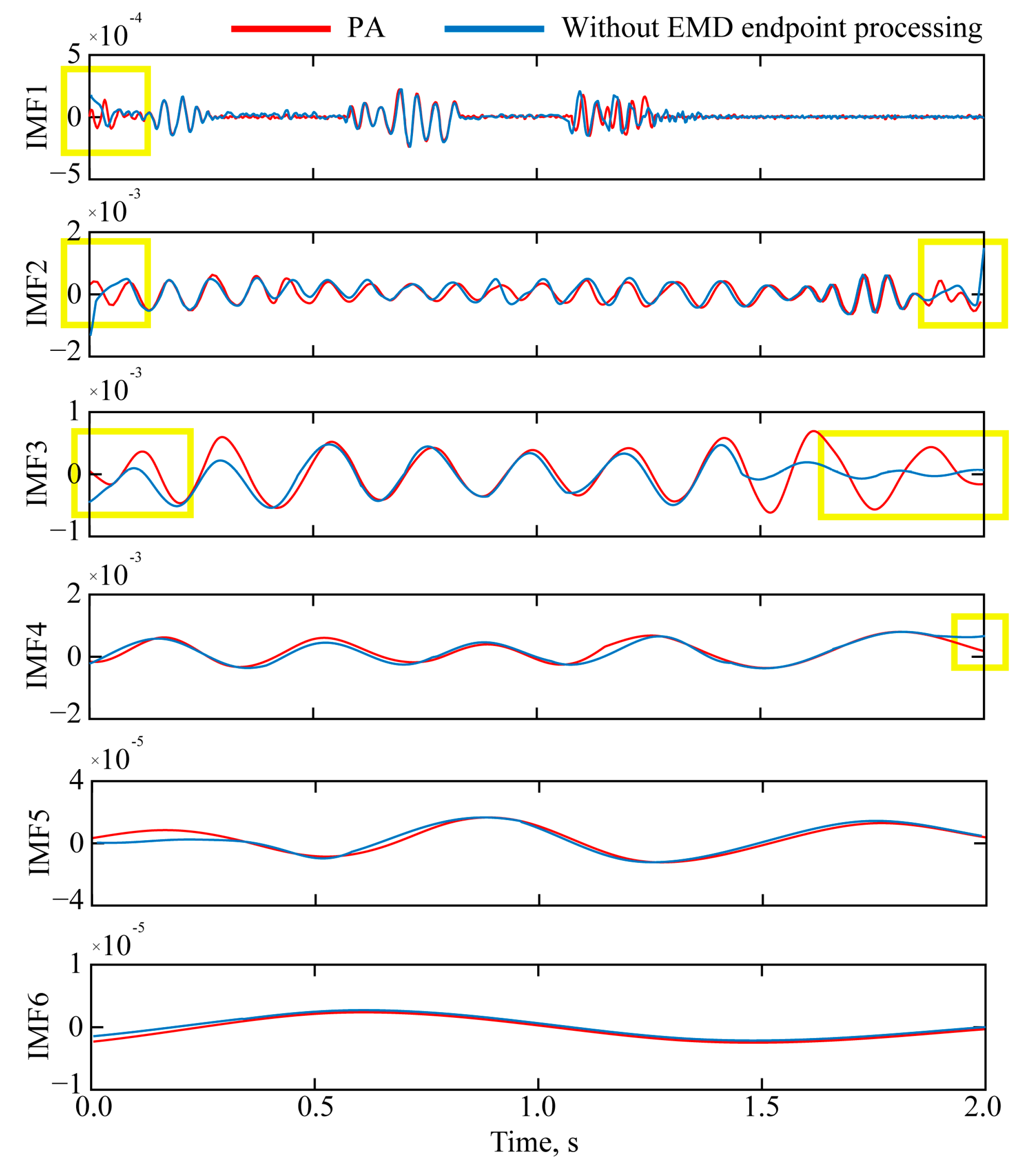
4. Application of the EMD Endpoint Suppression Method Based on Multi-Scale Feature in Blasting-Induced Seismic Wave Signal Processing
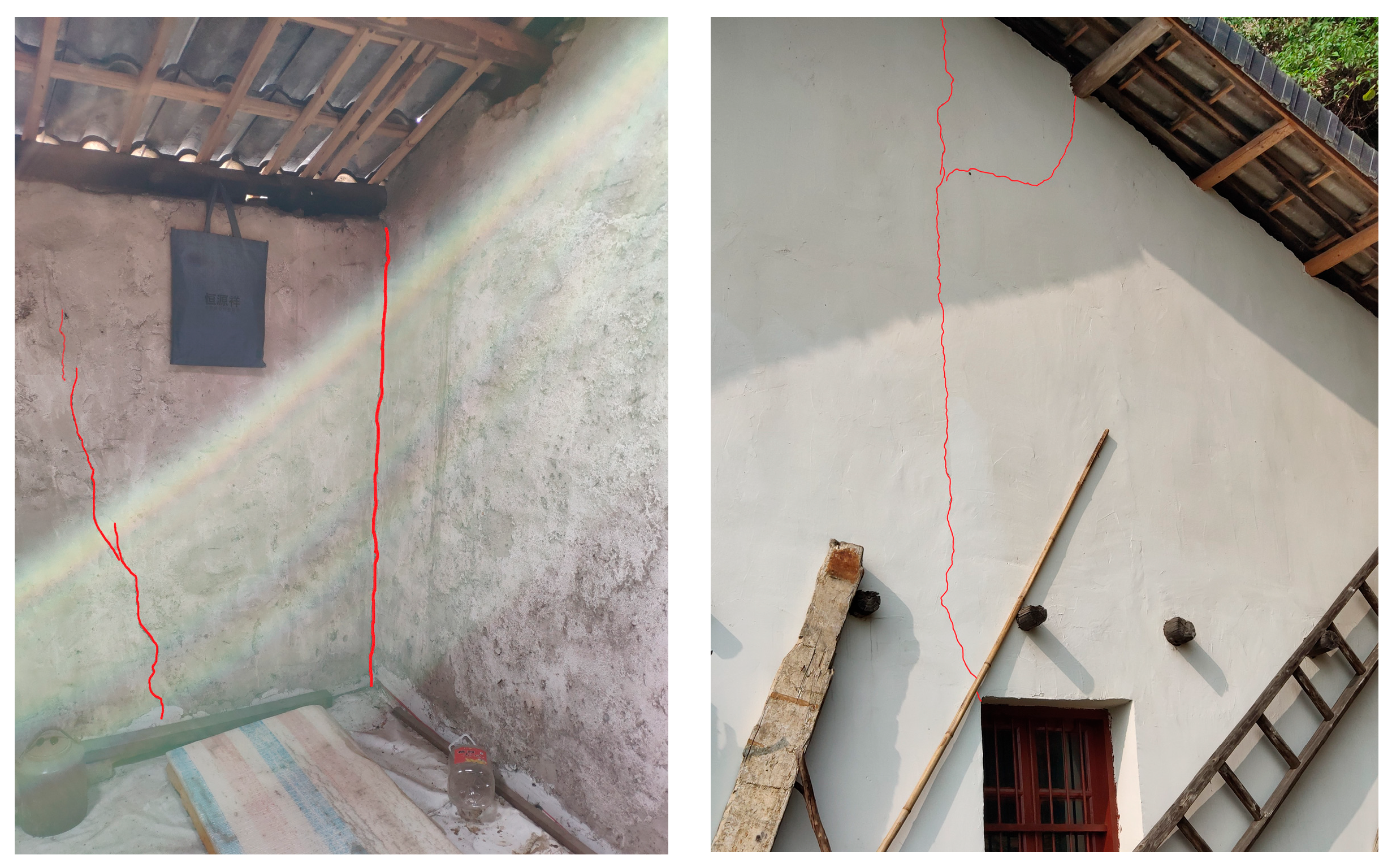
4.1. Engineering Background
4.2. Construction of the Model for Blasting-Induced Seismic Wave Signals
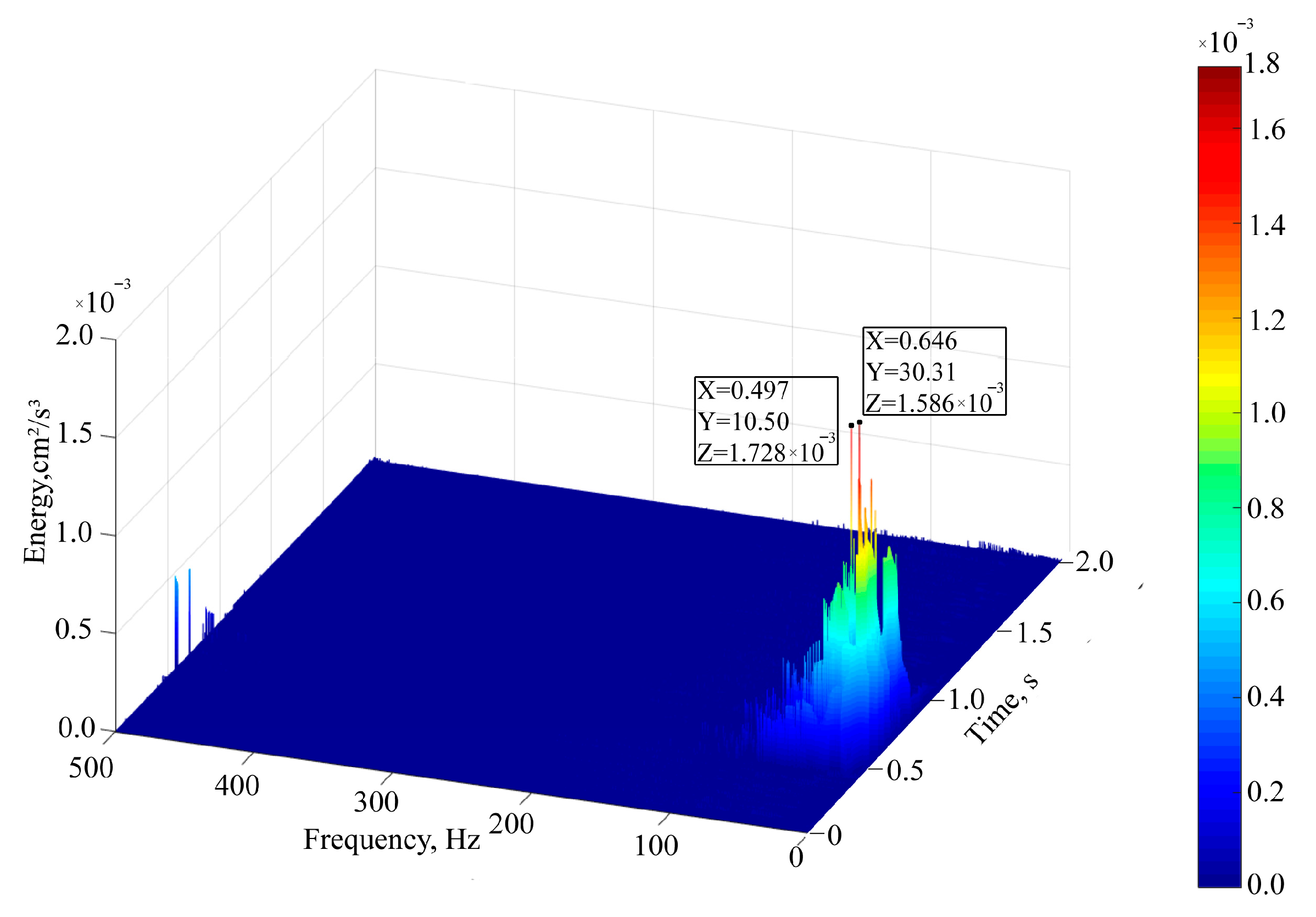
4.3. Analysis of Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The proposed method integrates four critical parameters—local endpoint development trends, global time distribution, energy matching, and waveform matching—to achieve comprehensive endpoint effect suppression. This multi-dimensional approach ensures superior preservation of signal characteristics while effectively eliminating boundary distortions, enabling more precise extraction of time–frequency features in blasting seismic analysis.
- (2)
- Systematic comparisons with conventional methods demonstrate the algorithm’s superior performance. Quantitative assessments reveal significant improvements, with correlation coefficients enhanced and error standard deviations reduced compared to existing techniques. The method’s effectiveness is consistently validated across both simulated and real-world blasting signals.
- (3)
- The high-quality IMFs obtained enable more accurate time–frequency-energy spectrum analysis through Hilbert transform. The algorithm successfully extracts critical frequency–energy information from blasting vibrations, particularly facilitating the identification of potential resonance risks between blasting-induced vibrations and structural natural frequencies.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, N.E. New method for nonlinear and nonstationary time series analysis: Empirical mode decomposition and Hilbert spectral analysis. Proc. SPIE—Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2000, 4056, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, C.H.; Wu, T.C.; Huang, N.E. Application of the Empirical Mode Decomposition-Hilbert Spectrum Method to Identify Near-Fault Ground-Motion Characteristics and Structural Responses. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2001, 91, 1339–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Ran, X.; Xu, W.; Yan, W.; Li, T.; Dai, K.; Wan, J.; Lin, Y.; Tong, K. Fine Classification Method for Massive Microseismic Signals Based on Short-Time Fourier Transform and Deep Learning. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, W.; Gao, J.; He, Y. Empirical mode decomposition based instantaneous frequency and seismic thin-bed analysis. J. Seism. Explor. 2010, 19, 161–172. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Wen, J. Target location method for pipeline pre-warning system based on HHT and time difference of arrival. Measurement 2013, 46, 2716–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegah, A.; Bo, F.; Kahoo, A.R.; Huazhong, W. Introducing the modular approach for high-resolution time–frequency analysis of seismic signals: Application for low-frequency shadow detection. Acta Geophys. 2025, 73, 2353–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R. A new view of nonlinear water waves: The Hilbert spectrum. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1999, 31, 417–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. A study of the characteristics of white noise using the empirical mode decomposition method. Proc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2004, 460, 1597–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2011, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.Q. Data discussion of the EMD method in the practice. Signal Process. 2010, 26, 227–285. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, G.; Liu, D.; Lu, J.; Shen, T.; Wang, S. Analysis of rock microseismic signal based on blind source wavelet decomposition algorithm. AIP Adv. 2022, 12, 055131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Wu, Z. A review on Hilbert-Huang transform: Method and its applications to geophysical studies. Rev. Geophys. 2008, 46, RG2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlurmann, T. Spectral Analysis of Nonlinear Water Waves Based on the Hilbert-Huang Transformation. J. Offsho11re Mech. Arct. Eng. 2002, 124, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.F.; Fu, X.Y. Application of HHT Method in Identification of Blasting Millisecond Delay in Tunnel. DEStech Trans. Eng. Technol. Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dätig, M.; Schlurmann, T. Performance and limitations of the Hilbert–Huang transformation (HHT) with an application to irregular water waves. Ocean Eng. 2004, 31, 1783–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.R. Signatures of the Seismic Source in EMD-Based Characterization of the 1994 Northridge, California, Earthquake Recordings. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2003, 93, 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.X.; Liu, Y.S.; Zhang, C.; Wu, L. A novel denoising model of underwater drilling and blasting vibration signal based on CEEMDAN. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 46, 4857–4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.-J.; Cao, J.-X.; Wang, X.-J.; Li, Y.-X.; Du, J. Recent Developments in Local Wave Decomposition Methods for Understanding Seismic Data: Application to Seismic Interpretation. Surv. Geophys. 2019, 40, 1185–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley Stephen, D.; Atlas Les, E.; Chizeck Howard, J. Some Properties of an Empirical Mode Type Signal Decomposition Algorithm. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2010, 17, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; He, Z.; Huang, D. Reservoir detection based on EMD and correlation dimension. Appl. Geophys. 2009, 6, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.-C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yao, Y.; Luo, X.; Jiang, N.; Niu, S. Dynamic Response Evaluation for Single-Hole Bench Carbon Dioxide Blasting Based on the Novel SSA–VMD–PCC Method. Int. J. Geomech. 2023, 23, 04022248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.X.; Su, Y.; Wu, L.; Chen, C.; Vanali, M. Study on the Attenuation Characteristics of Seismic Wave Energy Induced by Underwater Drilling and Blasting. Shock Vib. 2019, 2019, 4367698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Zhou, C.B.; Jiang, N.; Meng, X.Z. A theoretical model to predict blast-induced vibration and its zoning characteristics in surrounding rock of a tunnel. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2025, 162, 106650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.-C.; Chen, Y.-H.; Wu, A.-Y. Low-complexity sinusoidal-assisted EMD (SAEMD) algorithms for solving mode-mixing problems in HHT. Digit. Signal Process. 2014, 24, 170–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.B.; Xu, M.Q.; Wei, Y.; Huang, W.H. An improvement EMD method based on the optimized rational Hermite interpolation approach and its application to gear fault diagnosis. Measurement 2015, 63, 330–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xu, W.; Zhang, D.; Feng, D.; Li, N. Improved Method and Application of EMD Endpoint Continuation Processing for Blasting Vibration Signals. J. Beijing Inst. Technol. 2019, 28, 428–436. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Luo, J.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, L. A novel method for diagnosis and de-noising of control rod drive mechanism within floating nuclear reactor. Ocean Eng. 2022, 244, 110398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Qu, L.; Yuan, L.P.; Wu, J.; Shen, Y.G. Time-frequency Analysis of Non-Stationary Vibration Signals based on EP-CEEMDAN Algorithm. Blasting 2024, 41, 150–155, 166. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hou, S.; Guo, W. Faulty Line Selection Based on Modified CEEMDAN Optimal Denoising Smooth Model and Duffing Oscillator for Un-Effectively Grounded System. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 5761642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.P.; Mo, J.L.; Gong, Y.J.; Zhao, F.W.; Du, M.H. Methods for Mitigation of End Effect in Empirical Mode Decomposition: A Quantitative Comparison. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2007, 29, 5. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qin, S.R.; Zhong, Y.M. A new envelope algorithm of Hilbert-Huang Transform. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2006, 20, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.M.; Wang, M.Z.; Xu, W.X.; Tan, M.T.; Zhang, M.Y.; Wang, S.K. Restriction of the end effect of EMD by utilizing slope and cubic spline based methods. J. Vib. Shock 2022, 41, 70–76. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.; Peng, S.P.; Zheng, J. LEMD endpoint extension method and its application in microseismic signals’ denoising. J. Vib. Shock 2014, 33, 155–160. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.X.; Liu, G.J.; Wu, L.; Zuo, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C. Comparative study on tunnel blast-induced vibration for the underground cavern group. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, F.Z.; Li, H.; Bu, J.; Duan, Y.; Song, Y. Fault location of transmission lines by wavelet packet decomposition based on SSSC and EMD. Electr. Eng. 2024, 106, 7853–7866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Sain, K. Empirical mode decomposition approach for delineating gas-hydrates and free gas in Mahanadi offshore, eastern Indian margin. Explor. Geophys. 2023, 54, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Lu, X.M.; Quar, W.; Li, X.; Zhao, H.; Lin, G. An Effective Ionospheric TEC Predicting Approach Using EEMD-PE-Kmeans and Self-Attention LSTM. Neural Process. Lett. 2023, 55, 9225–9245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Pi, Y.C.; Tang, Z.Y.; Hua, H.; Wang, X. A Fusion Model for Predicting the Vibration Trends of Hydropower Units. Energies 2024, 17, 5847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.J.; Zhou, J.J.; Hou, F.Z.; Zhan, Q.B.; Shao, Y.; Ning, X.B. A method for extracting human gait series from accelerometer signals based on the ensemble empirical mode decomposition. Chin. Phys. B 2010, 19, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Zhang, Y.P.; Zhou, Q.Q.; Yang, X. A denoising method for blasting vibration signals based on improved EMD. J. Vib. Shock 2025, 44, 212–220. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ji, L.; Yao, Y.K.; Zhou, C.B.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, H.; Wu, T. Research on cumulative damage effects and safety criterion of surrounding rock in bench blasting of a large cross-section tunnel. Alex. Eng. J. 2024, 108, 626–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.P.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, C.T.; Wang, J.; Peng, Q.; Guo, J.; Zhu, J. Dynamic response of rock mass subjected to blasting disturbance during tunnel shaft excavation: A field study. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-Energy Geo-Resour. 2022, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civera, M.; Surace, C. A Comparative Analysis of Signal Decomposition Techniques for Structural Health Monitoring on an Experimental Benchmark. Sensors 2021, 21, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
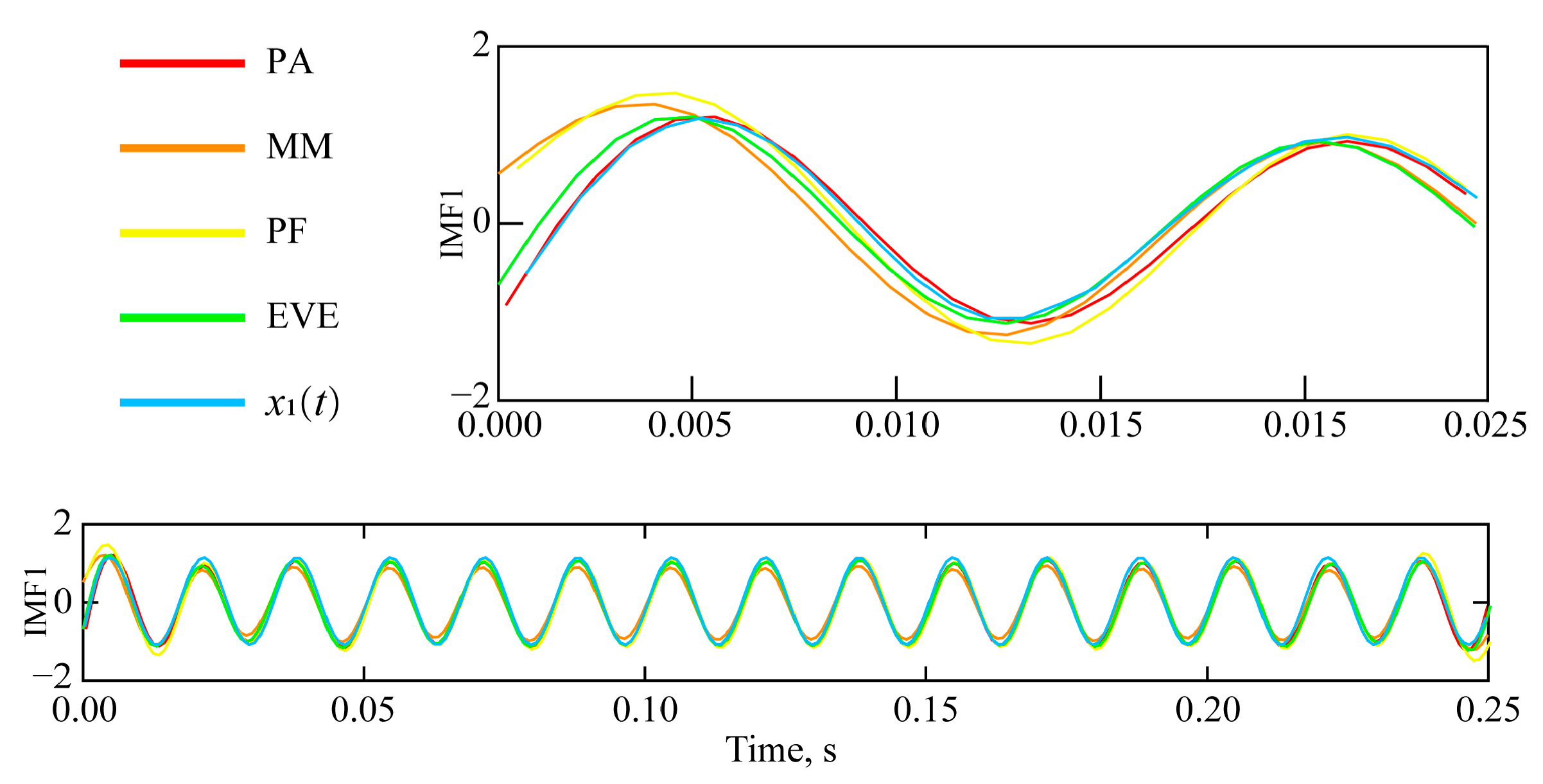
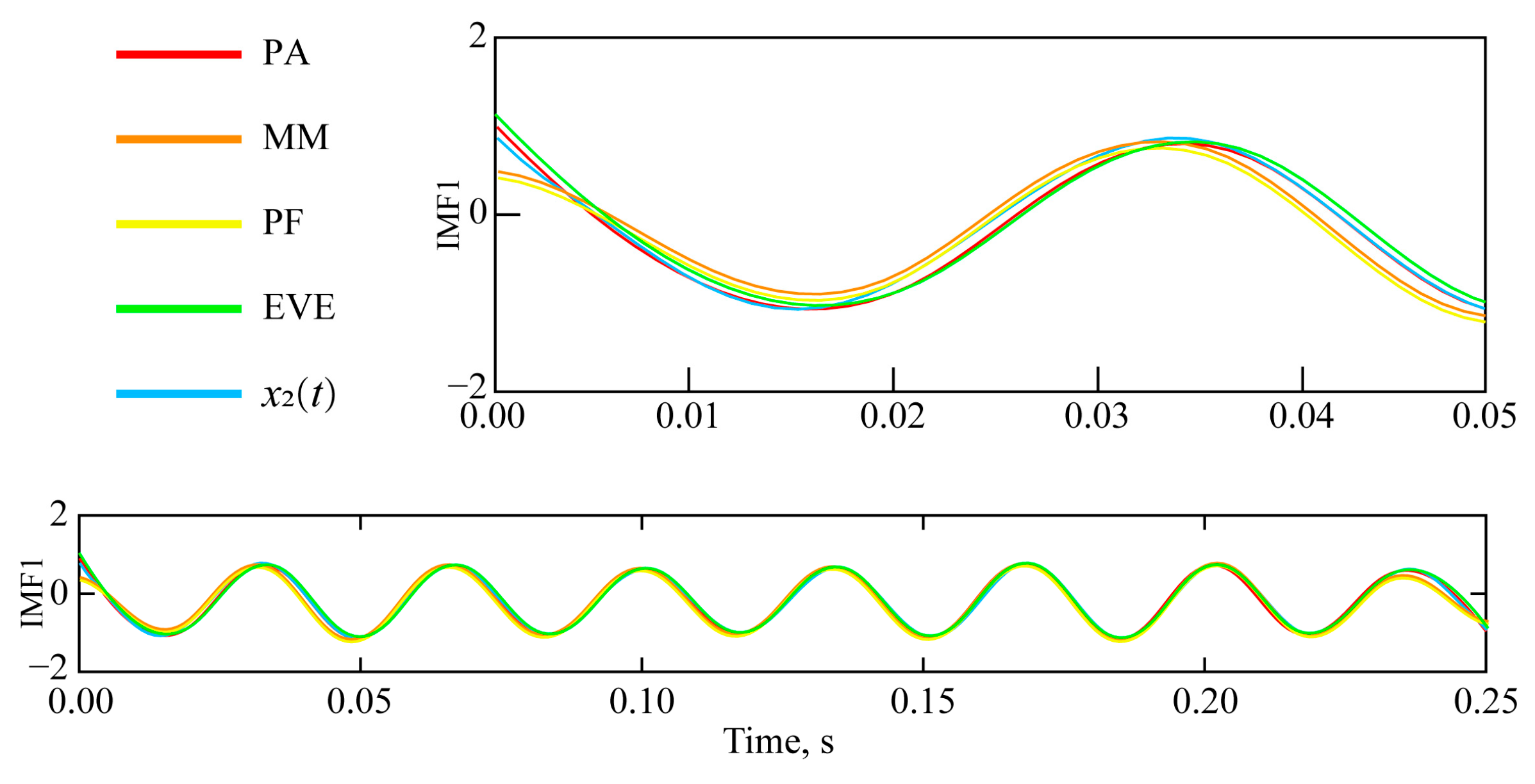


| Evaluation Index | PA | ME | PF | EVE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | IMF1 & x1(t) | 0.9682 | 0.8026 | 0.8141 | 0.8924 |
| IMF2 & x2(t) | 0.9517 | 0.8514 | 0.8465 | 0.8965 | |
| Dsde | IMF1 & x1(t) | 0.0324 | 0.2615 | 0.2525 | 0.1627 |
| IMF2 & x2(t) | 0.0857 | 0.2043 | 0.2144 | 0.1624 | |
| running time (s) | 0.1476 | 0.0173 | 0.0118 | 0.0169 | |
| Mode of Vibration | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural frequency (Hz) | 1.84 | 3.43 | 6.05 | 9.68 | 13.75 | 18.39 |
| Natural Frequency (Hz) | IMF Component | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMF1 (42.43) | IMF2 (30.65) | IMF3 (21.83) | IMF4 (10.45) | |
| 1 (1.84) | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.032 |
| 2 (3.43) | 0.006 | 0.013 | 0.025 | 0.121 |
| 3 (6.05) | 0.021 | 0.041 | 0.083 | 0.502 |
| 4 (9.68) | 0.055 | 0.111 | 0.244 | 5.062 |
| 5 (13.75) | 0.117 | 0.252 | 0.654 | 2.330 |
| 6 (18.39) | 0.231 | 0.560 | 2.347 | 1.472 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, M.; Wu, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, F.; Zhou, H. Engineering Safety-Oriented Blasting-Induced Seismic Wave Signal Processing: An EMD Endpoint Suppression Method Based on Multi-Scale Feature. Sensors 2025, 25, 4194. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134194
Sun M, Wu J, Lu Y, Yu F, Zhou H. Engineering Safety-Oriented Blasting-Induced Seismic Wave Signal Processing: An EMD Endpoint Suppression Method Based on Multi-Scale Feature. Sensors. 2025; 25(13):4194. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134194
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Miao, Jing Wu, Yani Lu, Fangda Yu, and Hang Zhou. 2025. "Engineering Safety-Oriented Blasting-Induced Seismic Wave Signal Processing: An EMD Endpoint Suppression Method Based on Multi-Scale Feature" Sensors 25, no. 13: 4194. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134194
APA StyleSun, M., Wu, J., Lu, Y., Yu, F., & Zhou, H. (2025). Engineering Safety-Oriented Blasting-Induced Seismic Wave Signal Processing: An EMD Endpoint Suppression Method Based on Multi-Scale Feature. Sensors, 25(13), 4194. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134194






