Pulse–Glide Behavior in Emerging Mixed Traffic Flow Under Sensor Accuracy Variations: An Energy-Safety Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Methods
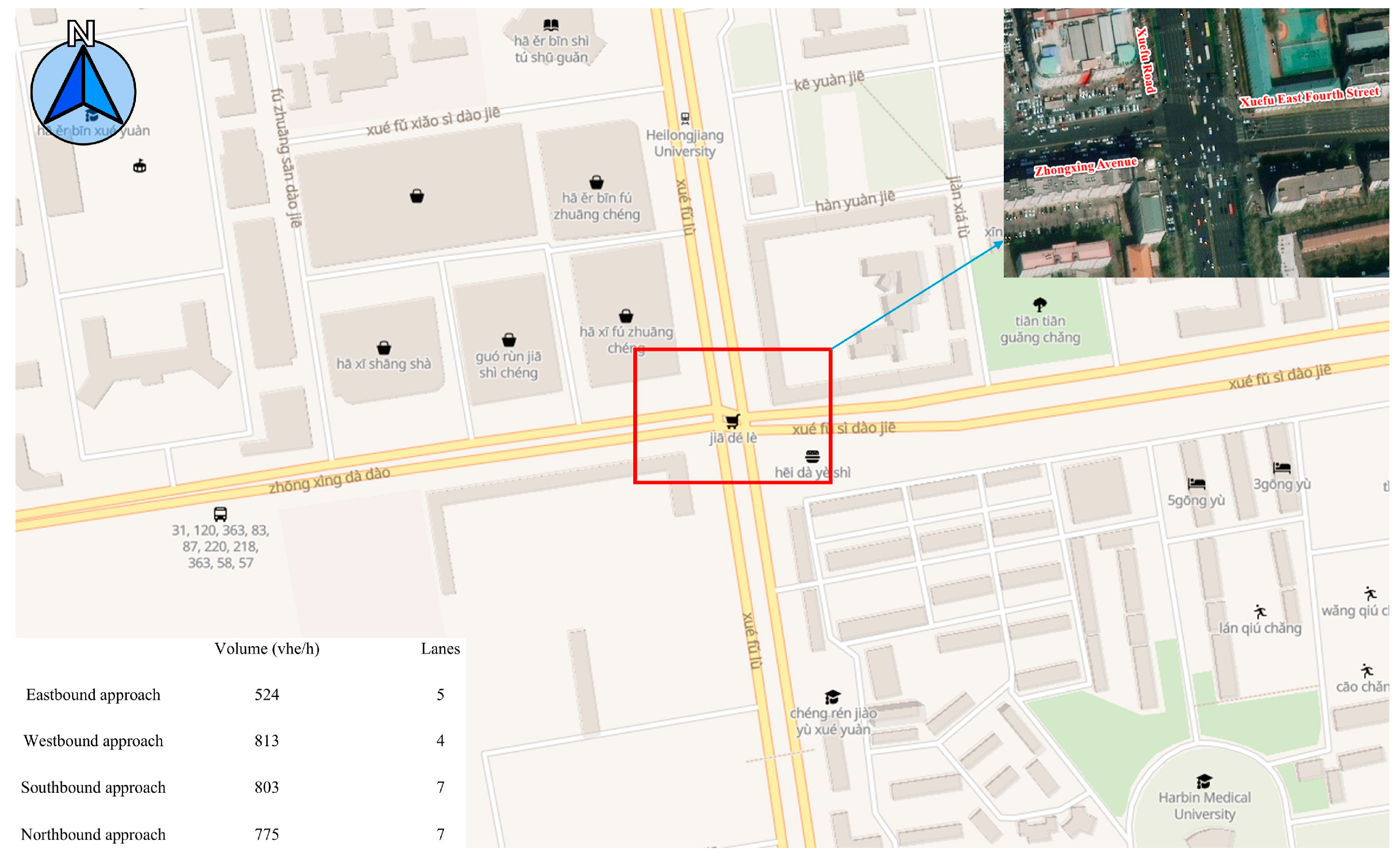
3.1. Construction of Road Model
3.2. Design of the Emerging Mixed Traffic Flow
3.3. Control Strategy for Vehicles
3.3.1. Car-Following Model
3.3.2. Planning for Speed
3.3.3. Measures for Fuel Consumption and Safety
4. Results
5. Discussion
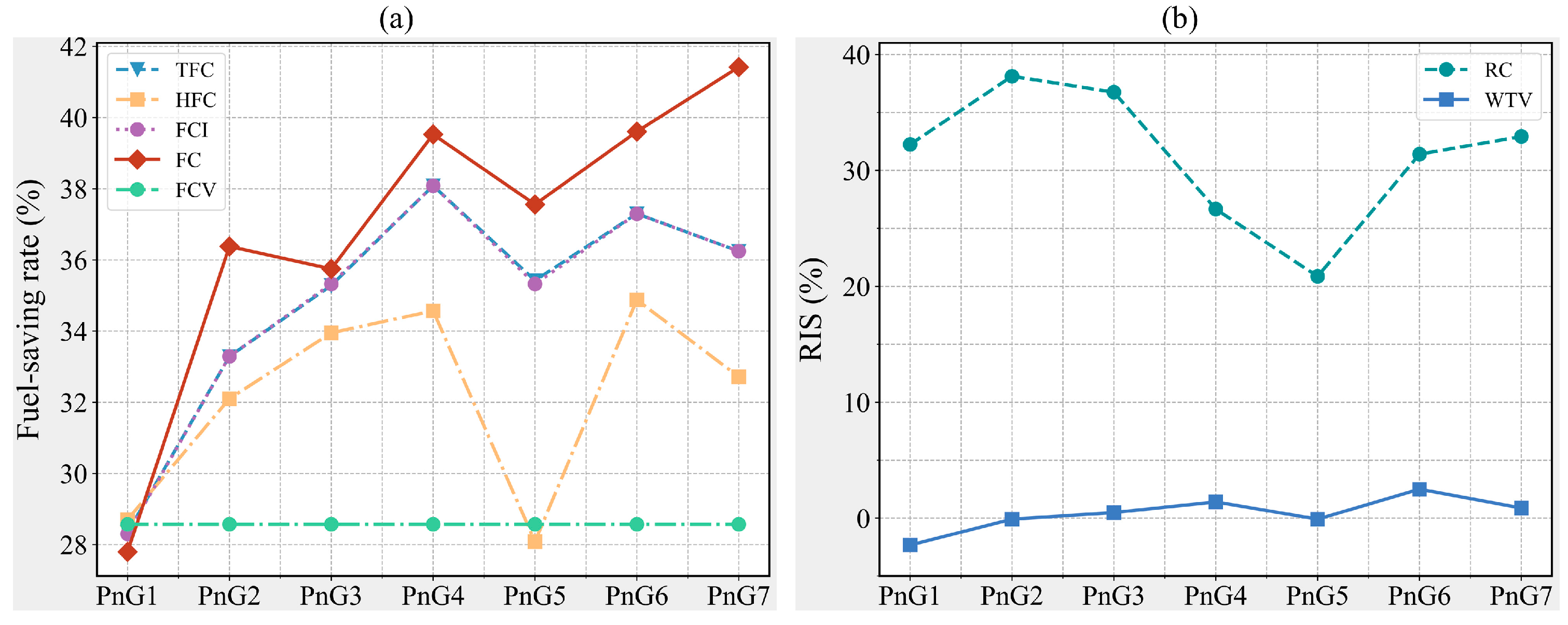
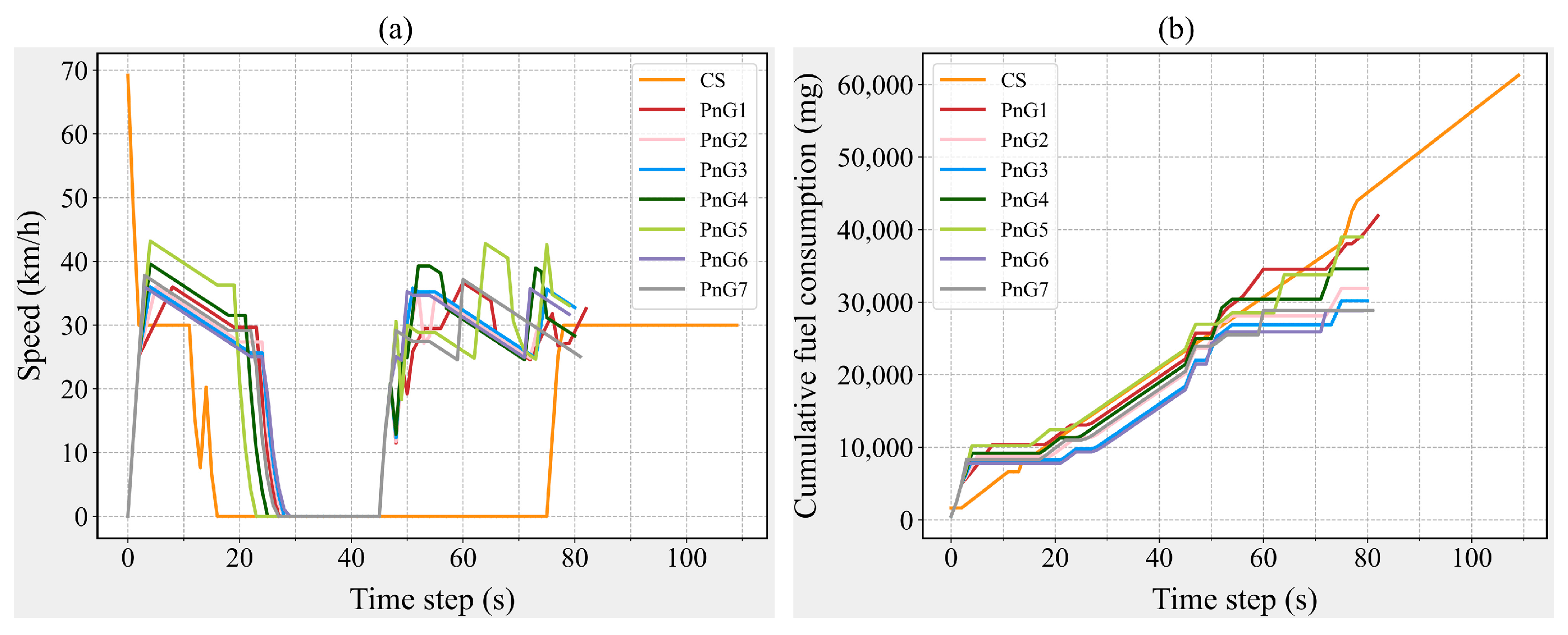
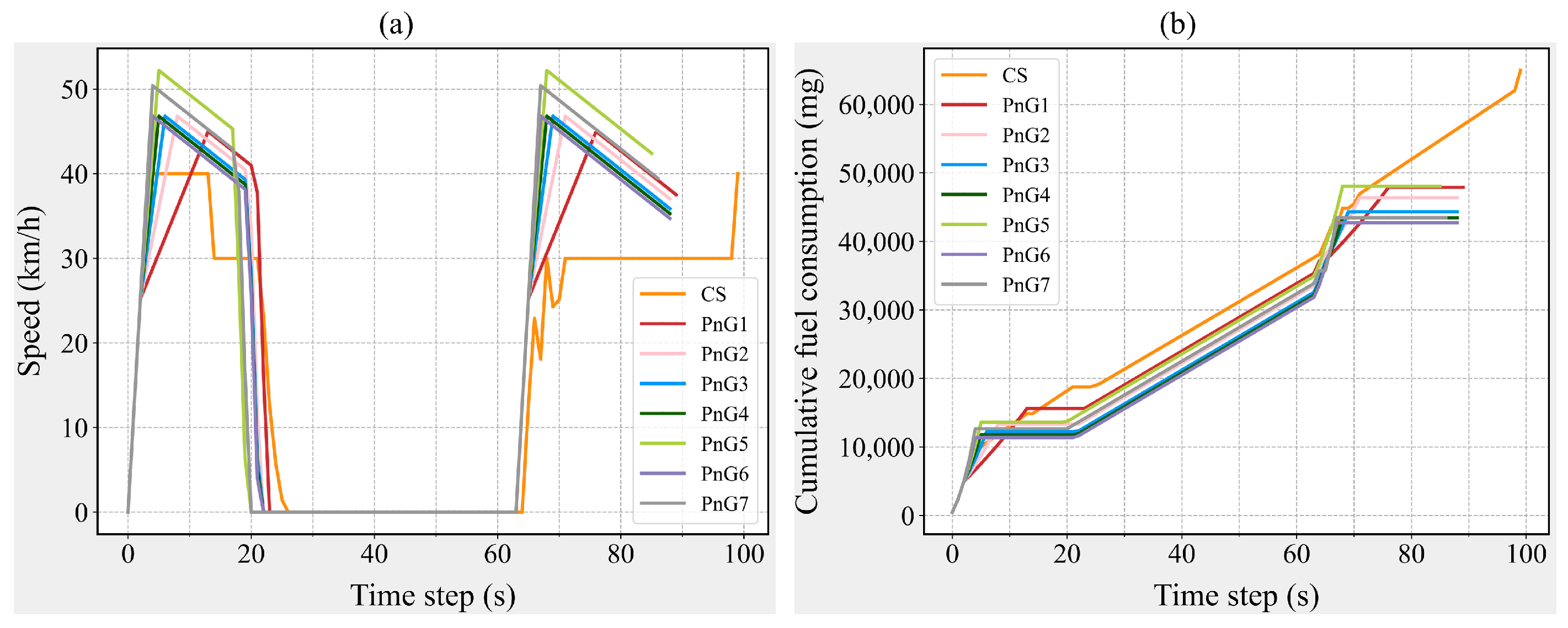
5.1. Fuel Consumption Under Different Driving Modes
5.2. Safety Under Different Driving Modes
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, Z.; He, J.; Yang, K.; Chen, H.H. Matching 5G connected vehicles to sensed vehicles for safe cooperative autonomous driving. IEEE Netw. 2024, 38, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousaridas, A.; Manjunath, R.P.; Perdomo, J.; Zhou, C.; Zielinski, E.; Schmitz, S. QoS prediction for 5G connected and automated driving. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2021, 59, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wei, H. CAV-enabled data analytics for enhancing adaptive signal control safety environment. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2023, 192, 107290. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Z.; Lee, E.E.; Nejad, M.; Lee, J. Influence of CAV clustering strategies on mixed traffic flow characteristics: An analysis of vehicle trajectory data. Transport. Res. Part C 2020, 115, 102611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhong, H.; Ma, W.; Abdel-Aty, M.; Park, J. How many crashes can connected vehicle and automated vehicle technologies prevent: A meta-analysis. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2020, 136, 105299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.Y.D.; Fisher, D.L. Safety impacts and benefits of connected and automated vehicles: How real are they? J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 25, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Topilin, I.; Feofilova, A.; Shao, M.; Wang, Y. Cooperative intelligent transport systems: The impact of C-V2X communication technologies on road safety and traffic efficiency. Sensors 2025, 25, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sun, H.; He, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.X.; Feng, S. Adaptive safety evaluation for connected and automated vehicles with sparse control variates. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 1761–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Jiang, H.; Fu, D.; Cai, P.; Cui, Z.; Li, A.; Yu, H. Hierarchical adaptive cross-coupled control of traffic signals and vehicle routes in large-scale road network. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Fan, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, K.; Gao, F.; Gao, Z. Constraint-guided behavior transformer for centralized coordination of connected and automated vehicles at intersections. Sensors 2024, 24, 5187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Masoud, N.; Liu, H.X. Anomaly detection and string stability analysis in connected automated vehicular platoons. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2023, 151, 104114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouadi, M.; Jiang, R.; Jia, B.; Zheng, S.T. String stability analysis of cooperative adaptive cruise control vehicles considering multi-anticipation and communication delay. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 11359–11369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folsom, T.C. Energy and autonomous urban land vehicles. IEEE Intell. Transp. Syst. Mag. 2012, 31, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenblatt, J.B.; Saxena, S. Autonomous taxis could greatly reduce greenhouse-gas emissions of US light-duty vehicles. Nat. Clim. Change 2015, 5, 860–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yu, C.; Liu, H.X. Spatiotemporal intersection control in a connected and automated vehicle environment. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2018, 89, 364–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mersky, A.C.; Samaras, C. Fuel economy testing of autonomous vehicles. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2016, 65, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiebat, M.; Brown, A.L.; Safford, H.R.; Qu, S.; Xu, M. A review on energy, environmental, and sustainability implications of connected and automated vehicles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 11449–11465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaras, G.; Samaras, Z. On the way to 130gCO2/km—Estimating the future characteristics of the average European passenger car. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 1826–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C. The state of the art of electric, hybrid, and fuel cell vehicles. Proc. IEEE 2007, 95, 704–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkenbus, J. Eco-driving: An overlooked climate change initiative. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Zhu, S.; Jiao, N.; Liu, B. Effects of peripheral transverse line markings on drivers’ speed and headway choice and crash risk in car-following: A naturalistic observation study. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2020, 146, 105701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, S.; Yang, L.; Wang, T.; Jing, S. Trajectory planning method for mixed vehicles considering traffic stability and fuel consumption at the signalized intersection. J. Adv. Transp. 2020, 2020, 1456207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Typaldos, P.; Papamichail, I.; Papageorgiou, M. Minimization of fuel consumption for vehicle trajectories. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 21, 1716–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Nelson, D.J.; Lohse-Busch, H. Vehicle Inertia Impact on Fuel Consumption of Conventional and Hybrid Electric Vehicles Using Acceleration and Coast Driving Strategy; SAE Paper 2009-01-1322; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Shieh, S.Y.; Ersal, T.; Peng, H. Pulse-and-glide operations for hybrid electric vehicles in the car-following scenario. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 9922–9937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.E.; Peng, H.; Li, K.; Wang, J. Minimum fuel control strategy in automated car-following scenarios. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2012, 61, 998–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgueiredo, C.F.; Orfila, O.; Pierre, G.S.; Doublet, P.; Glaser, S.; Doncieux, S.; Billat, V. Experimental testing and simulations of speed variations impact on fuel consumption of conventional gasoline passenger cars. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 57, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Lee, W.; Park, D.; Jung, J.; Kim, N. Energy-saving strategy for speed cruise control using pulse and glide driving. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 10, 1553–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.E.; Li, R.; Wang, J.; Hu, X.; Cheng, B.; Li, K. Stable periodic control of automated vehicle platoon with minimized fuel consumption. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2016, 8, 0180. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, F.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Jabari, S.E.; Lu, L. Analyzing the impact of automated vehicles on uncertainty and stability of the mixed traffic flow. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2020, 112, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Ban, X.; Aziz, H.M.A. Mixed traffic flow of human driven vehicles and automated vehicles on dynamic transportation networks. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2021, 128, 103159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Cen, Y.; Liu, B.; Song, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, J. A collaborative merging method for connected and automated vehicle platoons in a freeway merging area with considerations for safety and efficiency. Sensors 2023, 23, 4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.; Lu, Z.; Liu, H.; Wumaierjiang, A. Dynamic short-term crash risk prediction from traffic conflicts at signalized intersections with emerging mixed traffic flow: A novel conflict indicator. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2025, 217, 108065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, R.; Li, H.; Han, T.; Tian, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Proctor, R.W.; Chen, Y.; Feng, Y. Vehicle crash simulations for safety: Introduction of connected and automated vehicles on the roadways. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2023, 186, 107021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvin, R.; Khattak, A.J.; Kamrani, M.; Rio-Torres, J. Safety evaluation of connected and automated vehicles in mixed traffic with conventional vehicles at intersections. J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 25, 107–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, T.; Wang, Y.; Li, H. A cellular automaton model for mixed traffic flow considering the size of CAV platoon. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2024, 643, 129822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhu, F.; Wu, Y.; Yao, Z. A mixed capacity analysis and lane management model considering platoon size and intensity of CAVs. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2023, 615, 128557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, S.; Mekker, M. Public acceptance of connected vehicles: An extension of the technology acceptance model. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2022, 88, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, K.; Min, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Liu, P. What drives people to accept automated vehicles? Findings from a field experiment. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2018, 95, 320–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Zhao, F.; Zhu, G.; Liu, Z. Impacts of connected and autonomous vehicles with Level 2 automation on traffic efficiency and energy consumption. J. Adv. Transp. 2023, 2023, 6348778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stange, V.; Kühn, M.; Vollrath, M. Manual drivers’ experience and driving behavior in repeated interactions with automated Level 3 vehicles in mixed traffic on the highway. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2022, 87, 426–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Abdel-Aty, M.; Lee, J.; Rahman, M.H. Safety benefits of arterials’ crash risk under connected and automated vehicles. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2019, 100, 354–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, T.H.; Najmi, A.; Haider, A.; Wang, C.; Hosseinzadeh, F. What we know and do not know about connected and autonomous vehicles. Transp. A Transp. Sci. 2020, 16, 987–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Ren, Y.; Fang, J.; Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; Yu, H. SHIP: A state-aware hybrid incentive program for urban crowd sensing with for-hire vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 3041–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Meng, Z.; Han, X.; Li, H.; Tsukiji, T.; Xu, R.; Zheng, Z. An automated driving systems data acquisition and analytics platform. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2023, 151, 104120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Ren, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, Z.; Yu, H. Toward city-scale vehicular crowd sensing: A decentralized framework for online participant recruitment. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeong, D.J.; Velasco-Hernandez, G.; Barry, J.; Walsh, J. Sensor and sensor fusion technology in autonomous vehicles: A review. Sensors 2021, 21, 2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccari, S.; Hadded, M.; Ghazzai, H.; Touati, H.; Elhadef, M. Anomaly detection in connected and autonomous vehicles: A survey, analysis, and research challenges. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 19250–19276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahidi, A.; Sciarretta, A. Energy saving potentials of connected and automated vehicles. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2018, 95, 822–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhu, F.; Wu, J.; Wong, Y.D.; Chen, T. Managing mixed traffic at signalized intersections: An adaptive signal control and CAV coordination system based on deep reinforcement learning. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 238, 121959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensing, F.; Bideaux, E.; Trigui, R.; Tattegrain, H. Trajectory optimization for eco-driving taking into account traffic constraints. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2013, 18, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degraeuwe, B.; Beusen, B. Corrigendum on the paper “Using on-board data logging devices to study the longer-term impact of an eco-driving course”. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2013, 19, 48–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.E.; Deng, K.; Zheng, Y.; Peng, H. Effect of pulse-and-glide strategy on traffic flow for a platoon of mixed automated and manually driven vehicles. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2015, 30, 892–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Lu, Z.; Ding, N.; Bai, W. Distance headway-based safety evaluation of emerging mixed traffic flow under snowy weather. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2024, 642, 129792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatious, H.A.; Khan, M. An overview of sensors in Autonomous Vehicles. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 198, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimes, D.M.; Jones, T.O. Automotive radar: A brief review. Proc. IEEE 2005, 62, 804–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Wang, M.; Schakel, W.; van Arem, B. Unravelling effects of cooperative adaptive cruise control deactivation on traffic flow characteristics at merging bottlenecks. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2018, 96, 380–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanés, V.; Shladover, S.E.; Spring, J.; Nowakowski, C.; Kawazoe, H.; Nakamura, M. Cooperative adaptive cruise control in real traffic situations. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2014, 15, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Lu, Z.; Jiao, N.; Liu, Z.; Lu, L. Quantifying effects of reverse linear perspective as a visual cue on vehicle and platoon crash risk variations in car-following using path analysis. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2021, 159, 106215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tu, Y.; Fan, Q.; Dong, C.; Wang, W. Influence of cyber-attacks on longitudinal safety of connected and automated vehicles. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2018, 121, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virdi, N.; Grzybowska, H.; Waller, S.T.; Dixit, V. A safety assessment of mixed fleets with Connected and Autonomous Vehicles using the Surrogate Safety Assessment Module. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2019, 131, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, G.; Mohan, D.; Fazio, J. Conflict analysis for prediction of fatal crash locations in mixed traffic streams. Accid. Anal. Prev. 1998, 30, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
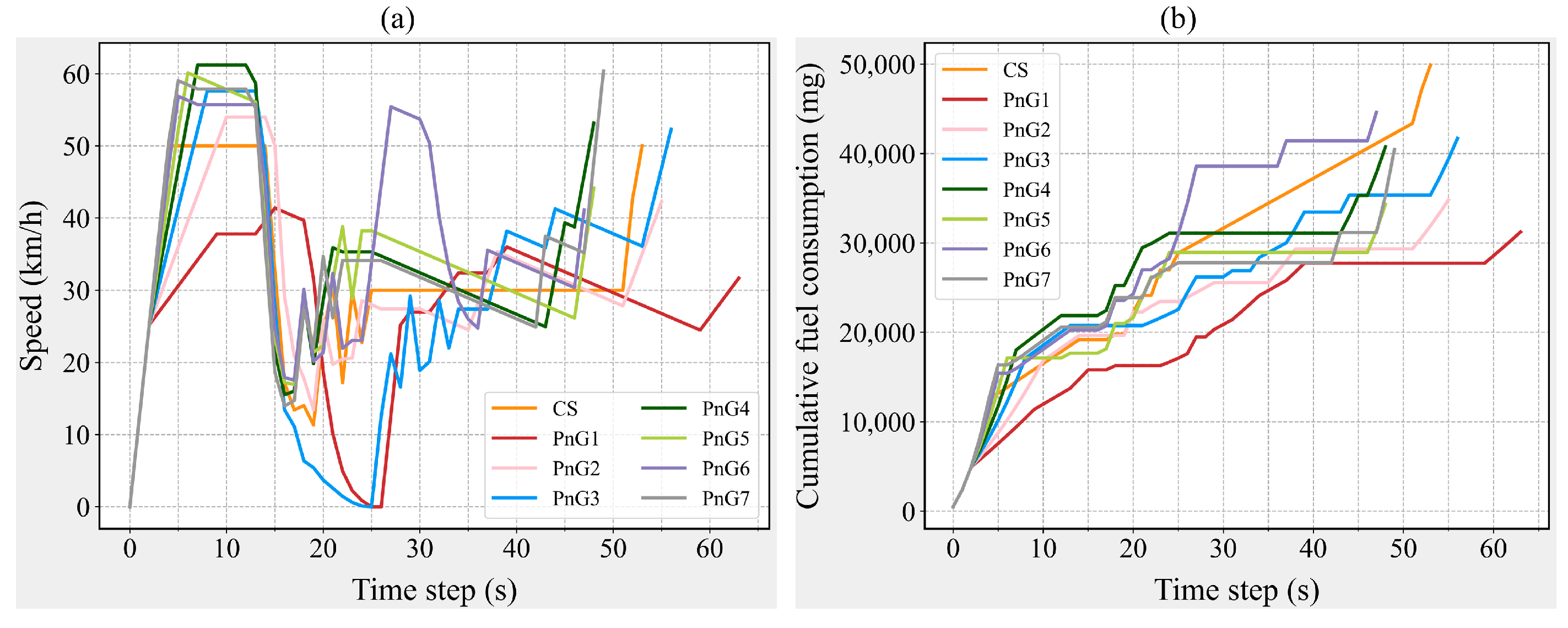
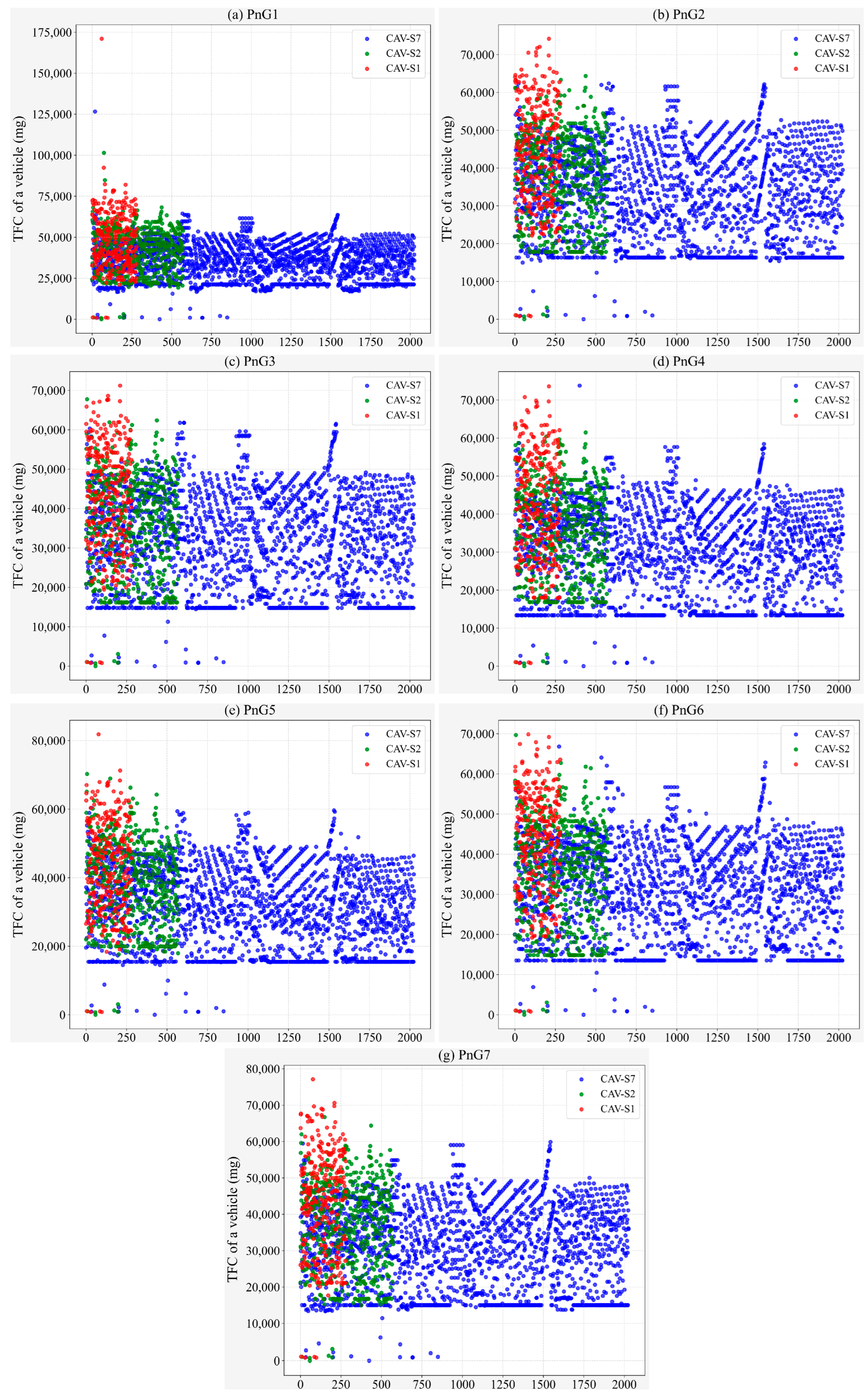
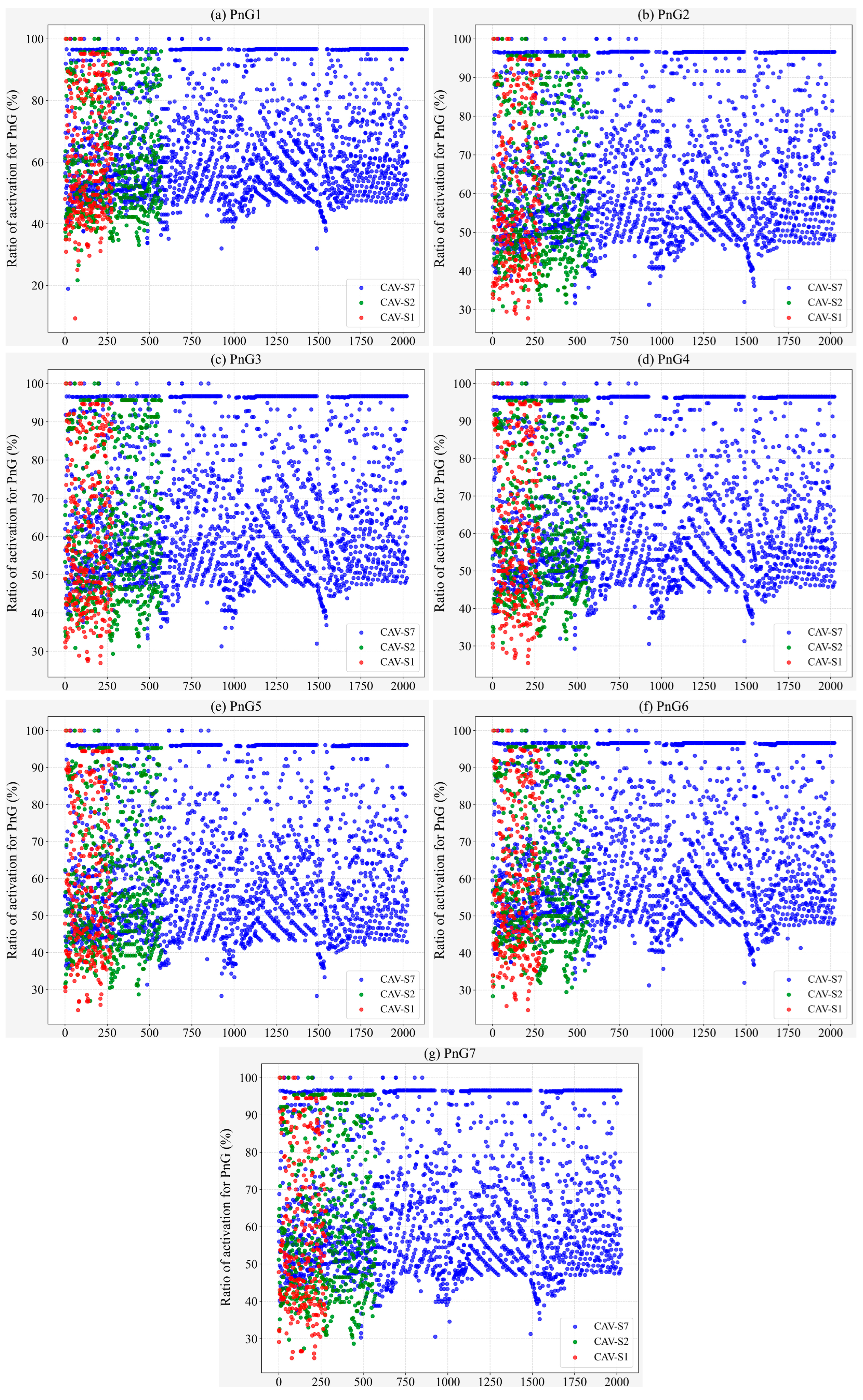

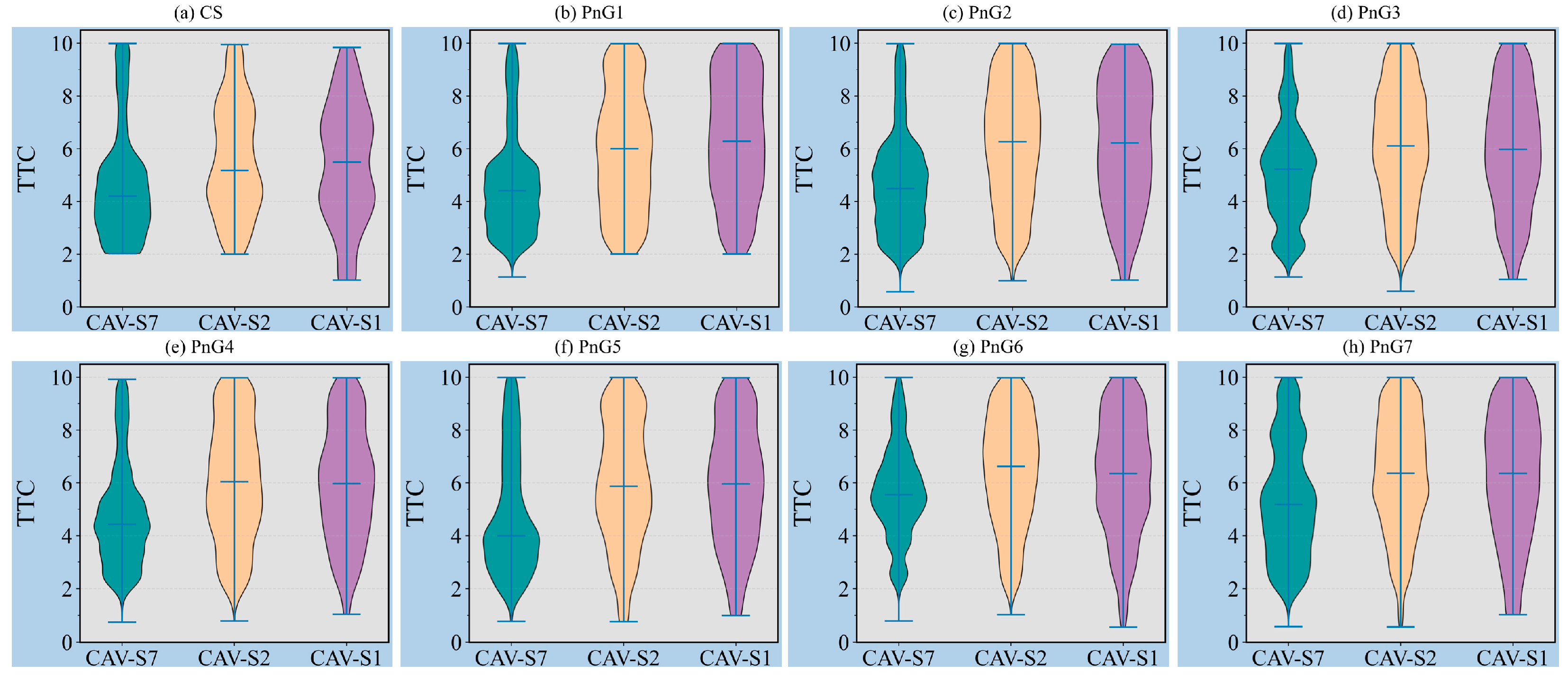
| Parameters | CS | PnG1 | PnG2 | PnG3 | PnG4 | PnG5 | PnG6 | PnG7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acceleration (m/s2) | 0 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 3.5 |
| Deceleration (m/s2) | 0 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 |
| Measures | CS | PnG1 | PnG2 | PnG3 | PnG4 | PnG5 | PnG6 | PnG7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TFC (L) | 210.16 | 150.60 | 140.20 | 136.01 | 130.12 | 135.72 | 131.77 | 133.99 |
| HFC (L/h) | 3.24 | 2.31 | 2.20 | 2.14 | 2.12 | 2.33 | 2.11 | 2.18 |
| FCV (L/veh) | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| FCI (L/100 km) | 15.23 | 10.92 | 10.16 | 9.85 | 9.43 | 9.85 | 9.55 | 9.71 |
| FC (L/100 km) | 12.70 | 9.17 | 8.08 | 8.16 | 7.68 | 7.93 | 7.67 | 7.44 |
| RC (%) | 13.09 | 8.87 | 8.10 | 8.28 | 9.60 | 10.36 | 8.98 | 8.78 |
| WTV (s) | 22.82 | 23.35 | 22.84 | 22.71 | 22.50 | 22.84 | 22.25 | 22.62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, M.; Sun, J.; Li, H.; Miao, Q. Pulse–Glide Behavior in Emerging Mixed Traffic Flow Under Sensor Accuracy Variations: An Energy-Safety Perspective. Sensors 2025, 25, 4189. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134189
Huang M, Sun J, Li H, Miao Q. Pulse–Glide Behavior in Emerging Mixed Traffic Flow Under Sensor Accuracy Variations: An Energy-Safety Perspective. Sensors. 2025; 25(13):4189. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134189
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Mengyuan, Jinjun Sun, Honggang Li, and Qiqi Miao. 2025. "Pulse–Glide Behavior in Emerging Mixed Traffic Flow Under Sensor Accuracy Variations: An Energy-Safety Perspective" Sensors 25, no. 13: 4189. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134189
APA StyleHuang, M., Sun, J., Li, H., & Miao, Q. (2025). Pulse–Glide Behavior in Emerging Mixed Traffic Flow Under Sensor Accuracy Variations: An Energy-Safety Perspective. Sensors, 25(13), 4189. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134189






